YAP Inhibition by Nuciferine via AMPK-Mediated Downregulation of HMGCR Sensitizes Pancreatic Cancer Cells to Gemcitabine
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Antibodies and Reagents
2.2. Cell Lines and Cell Culture
2.3. MTT Assay
2.4. Colony Formation Assay
2.5. Western Blot Assay
2.6. Real-Time PCR Analysis
- β-actin- Forward (5′-TCCTTCCTGGGCATGGAGTC-3′),
- β-actin- Reverse (5′-TTCTGCATCCTGTCGGCAATG-3′);
- CYR61- Forward (5′-AGCCTCGCATCCTATACAACC-3′),
- CYR61- Reverse (5′-GAGTGCCGCCTTGTGAAAGAA-3′);
- CTGF- Forward (5′-CCAATGACAACGCCTCCTG-3′),
- CTGF- Reverse (5′-GAGCTTTCTGGCTGCACCA-3′).
2.7. ATP and ADP Quantification Assays
2.8. Immunoprecipitation
2.9. Immunofluorescent (IF) Staining
2.10. Small Interfering RNA (siRNA) Transient Transfection
2.11. Plasmid Extraction and Transfection
2.12. Animal Tumor Model and Treatments
2.13. Histological Analysis
2.14. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
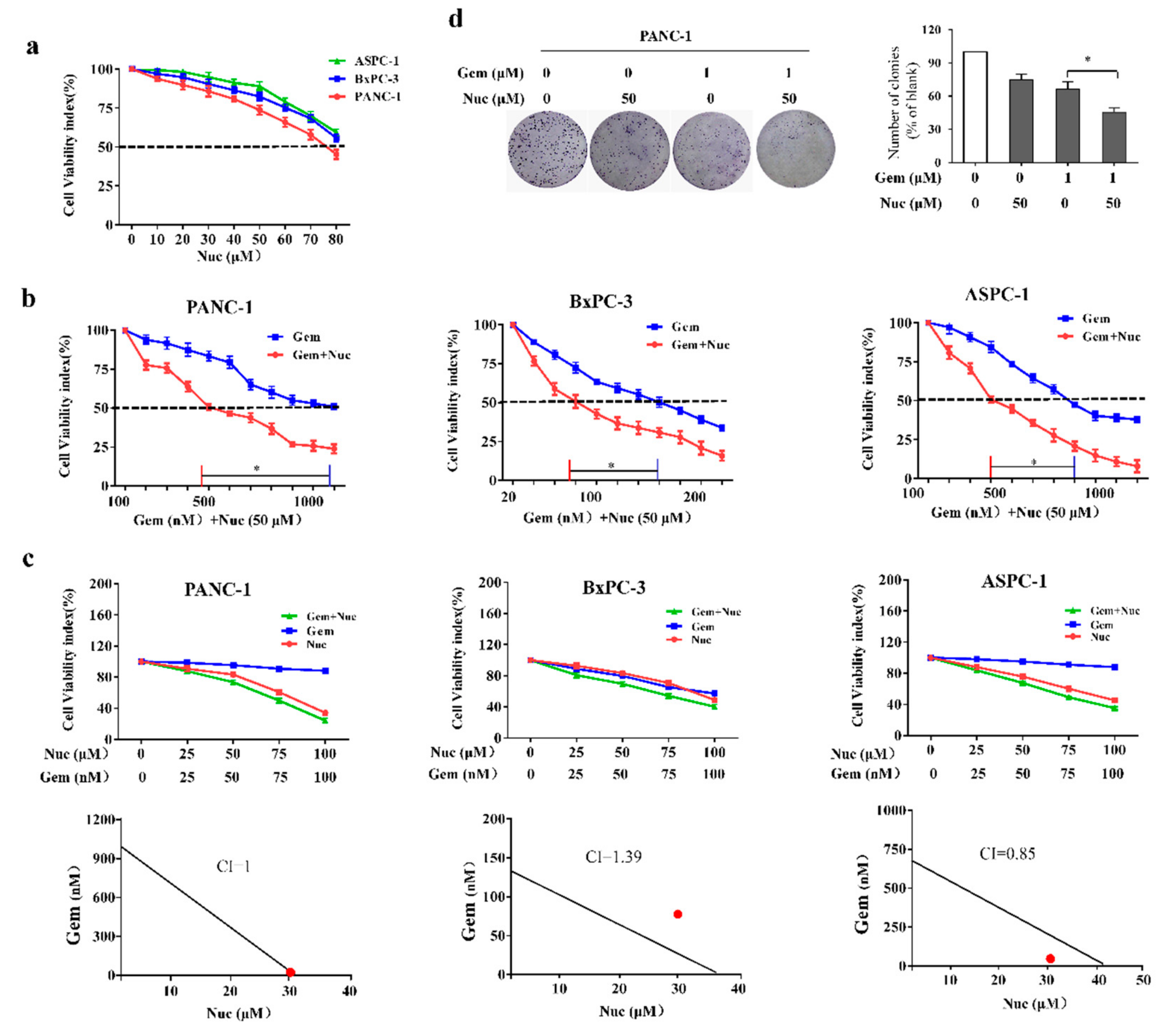
3.1. Nuciferine Attenuates Gemcitabine Resistance of Pancreatic Cancer Cells
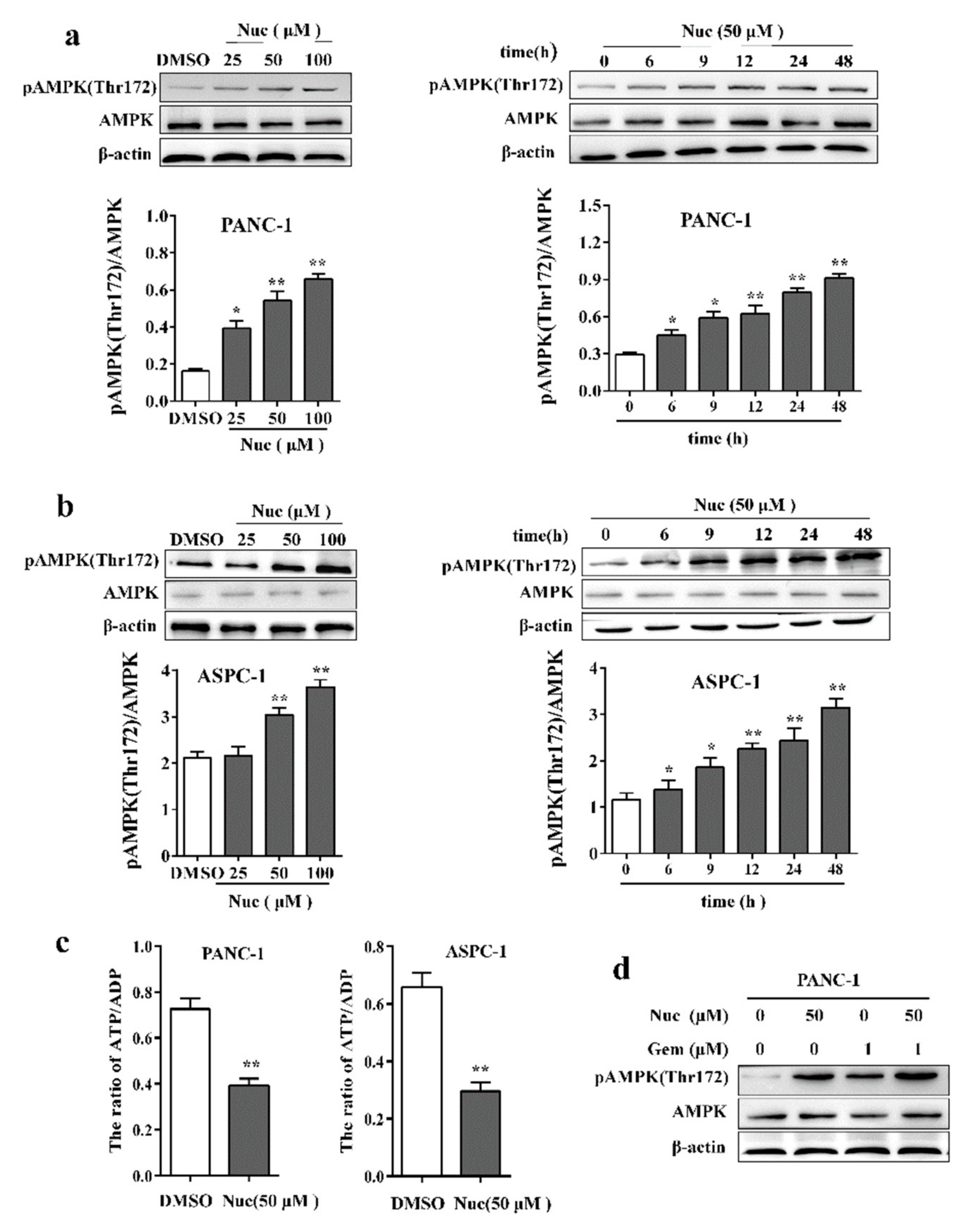
3.2. Nuciferine Activates AMPK in Pancreatic Cancer Cells
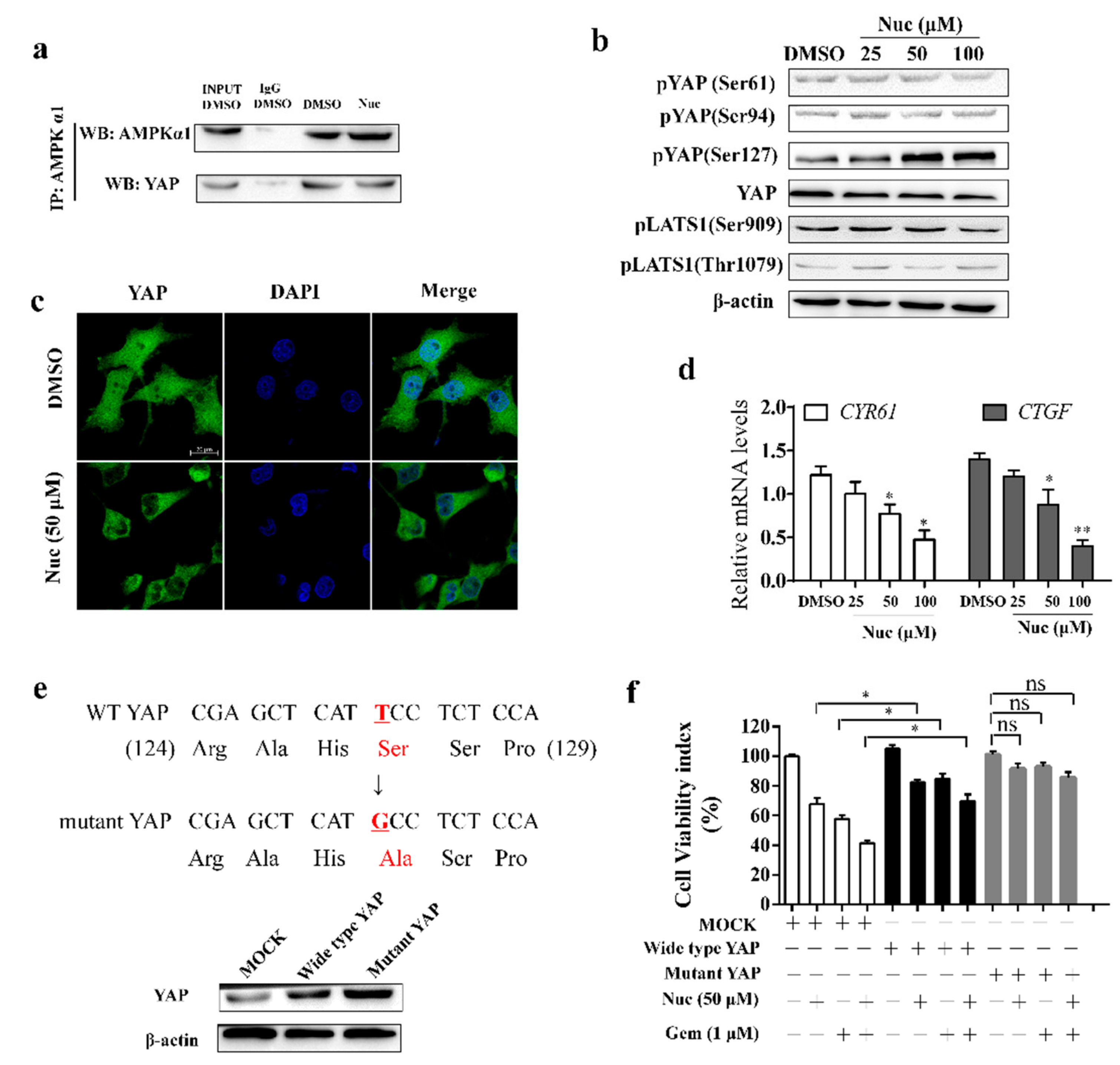
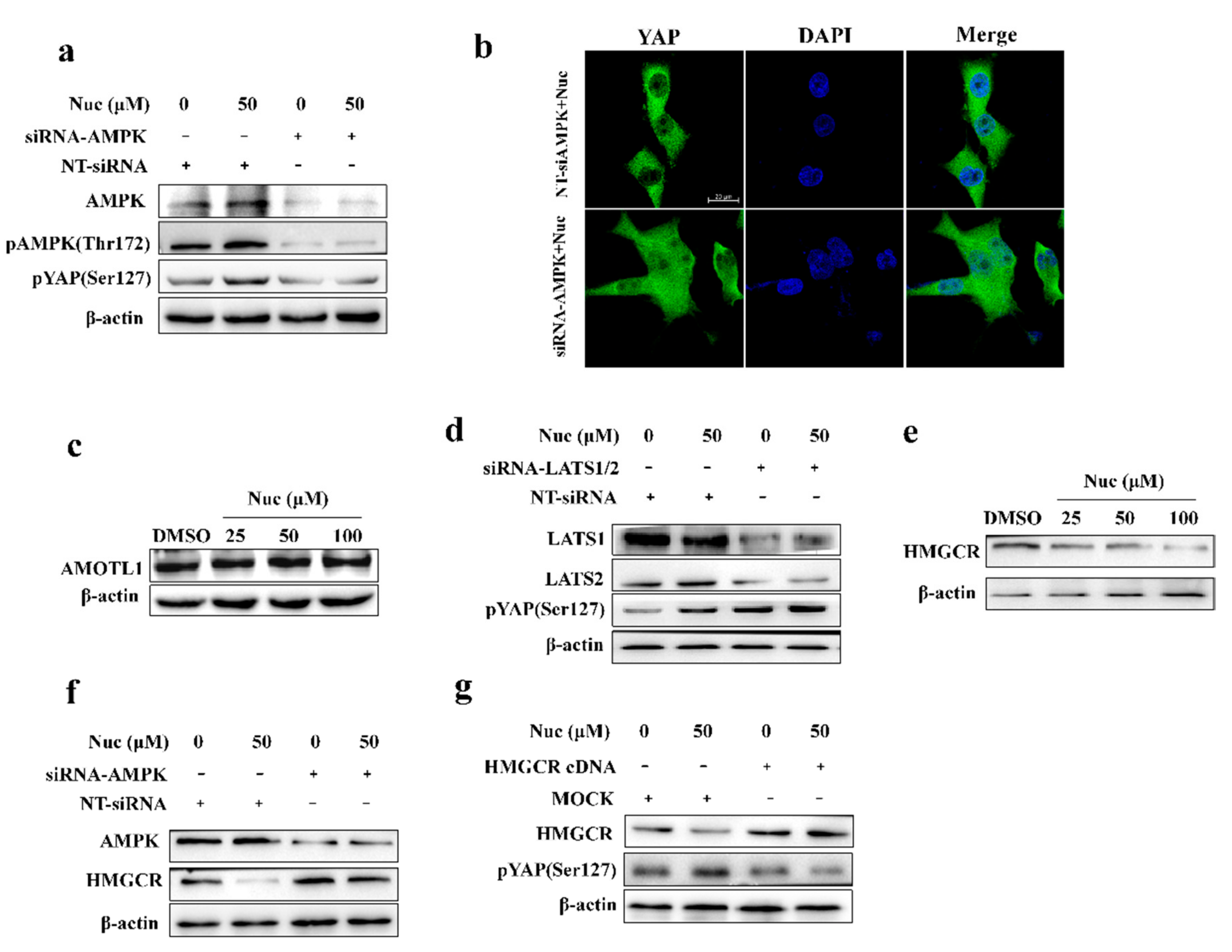
3.3. Nuciferine Induces YAP Ser127 Phosphorylation and Cytoplasmic Retention
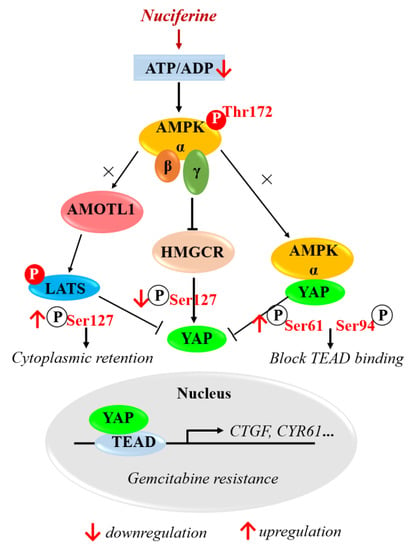
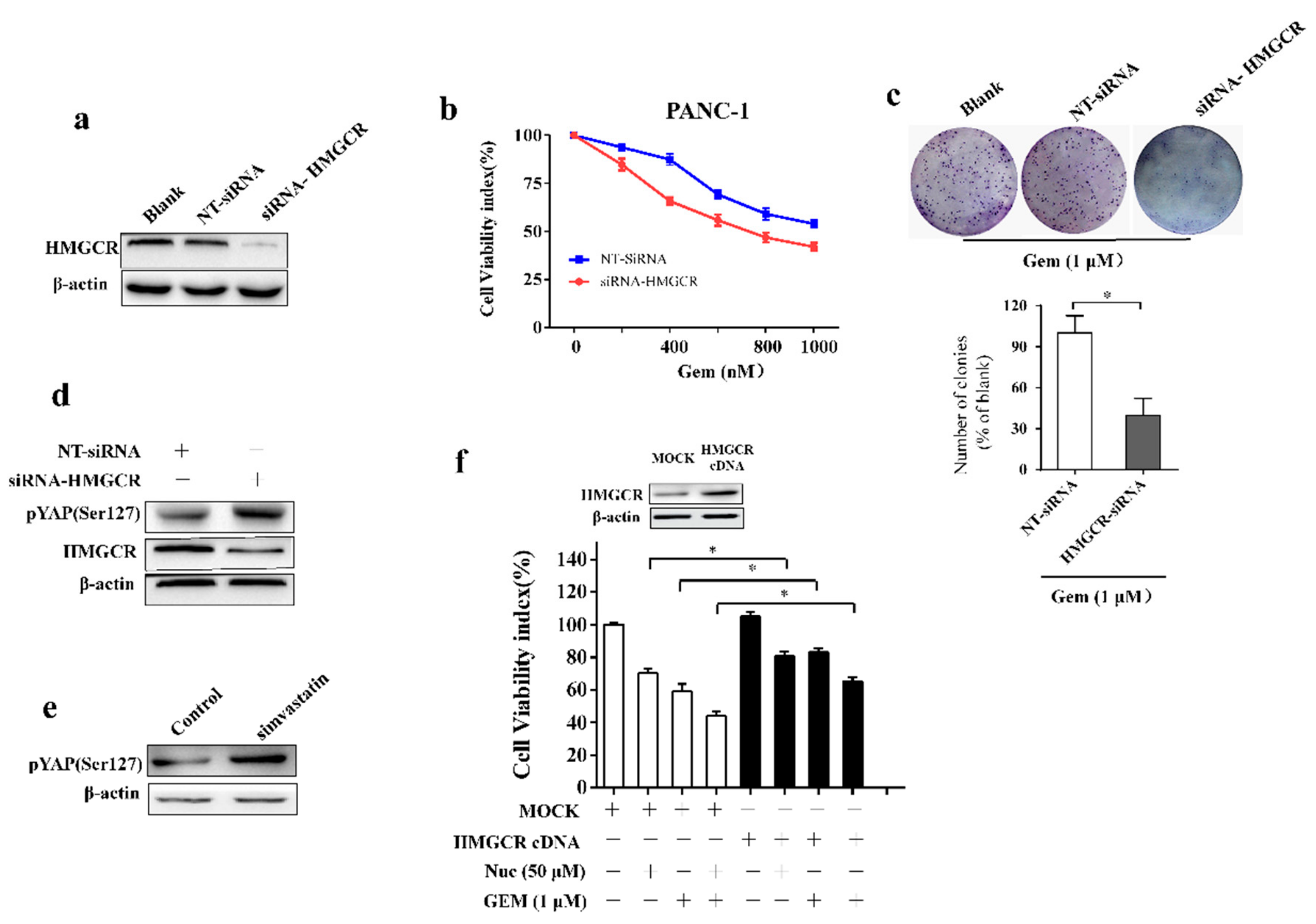
3.4. Nuciferine Inhibits YAP Involving AMPK-Mediated Downregulation of HMGCR
3.5. Nuciferine Sensitizes Pancreatic Cancer Cells to Gemcitabine by Down-Regulating HMGCR
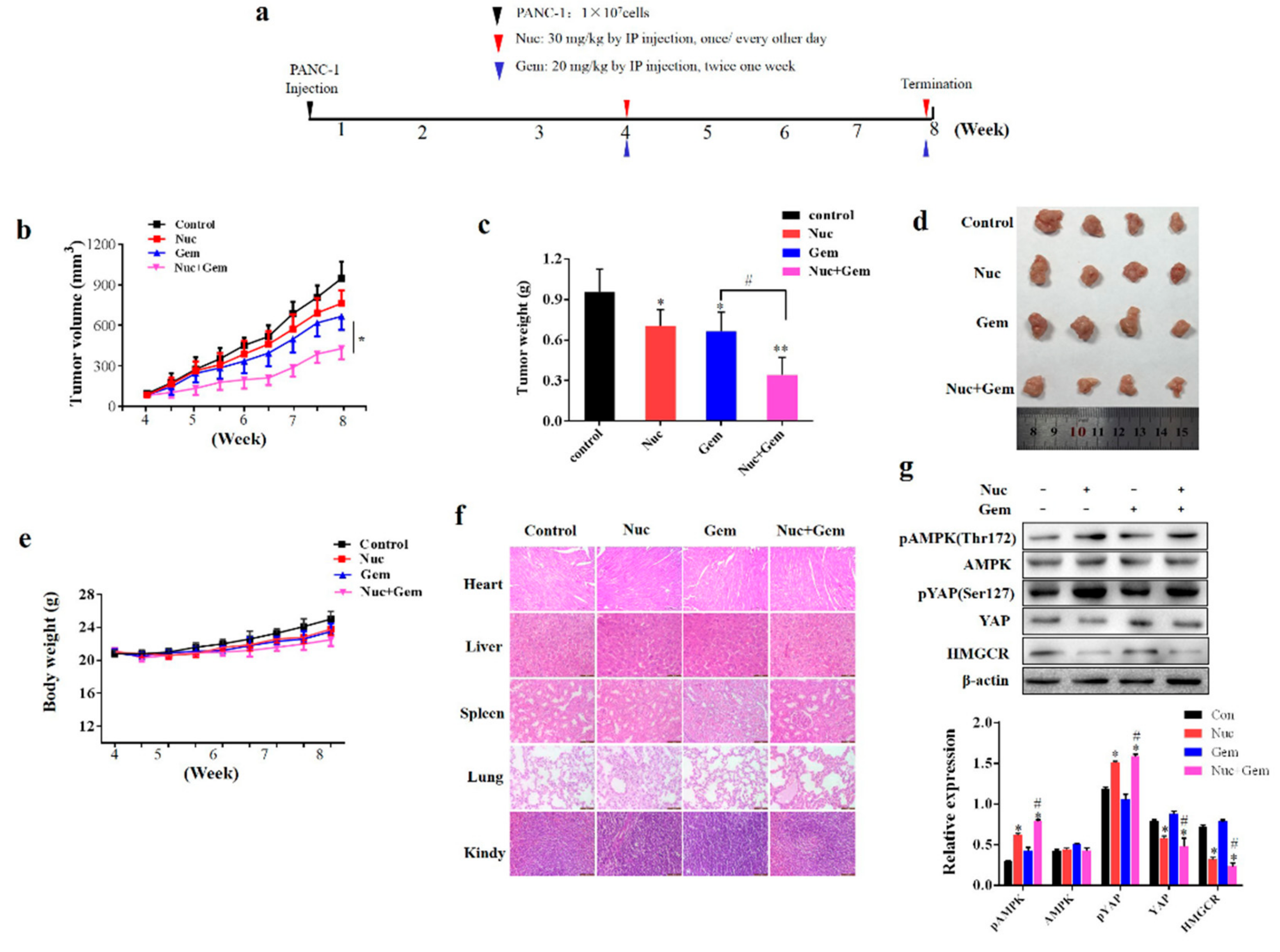
3.6. Nuciferine Enhances PANC-1 Cells Sensitivity to Gemcitabine in Vivo
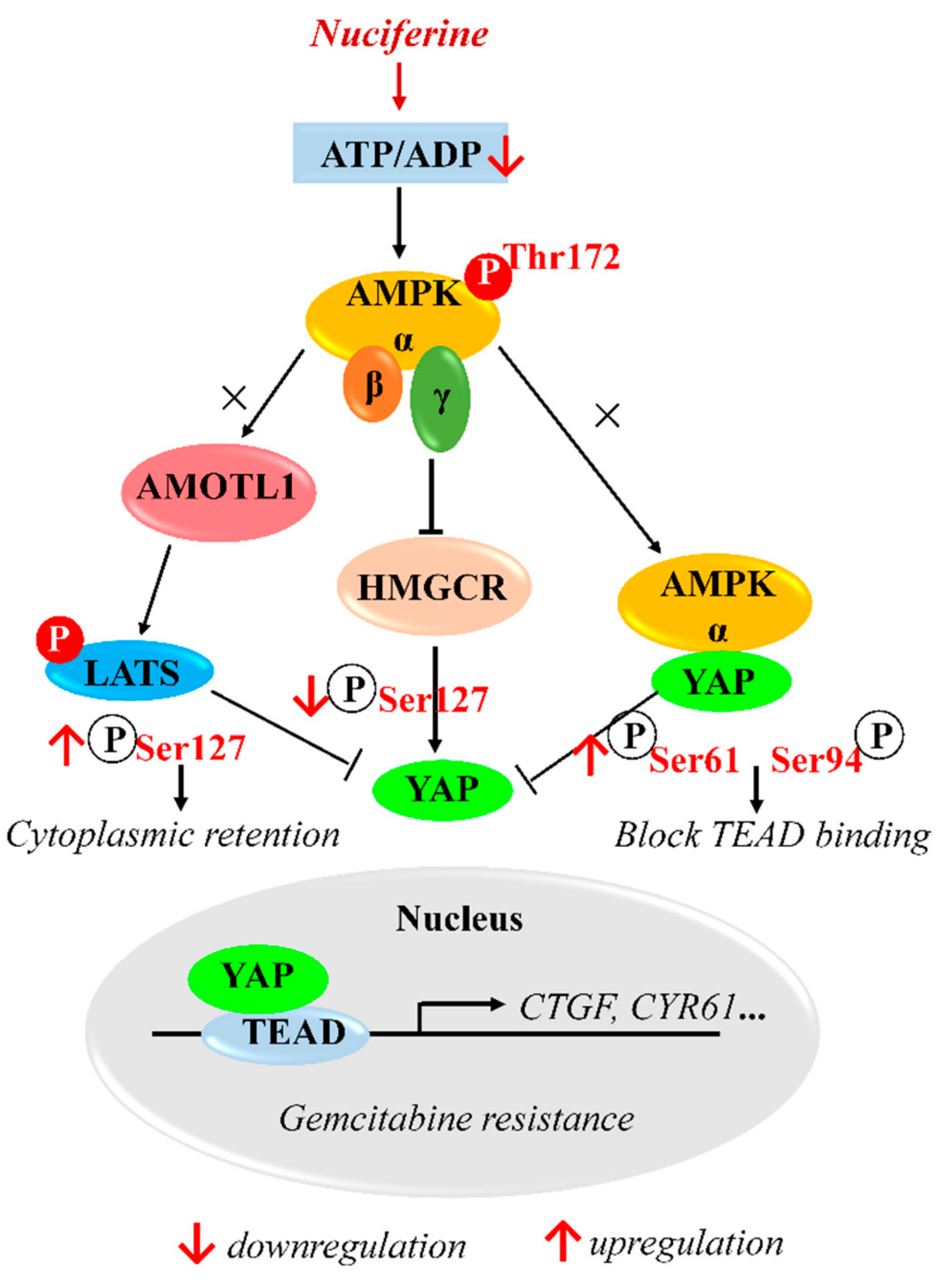
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rawla, P.; Sunkara, T.; Gaduputi, V. Epidemiology of pancreatic cancer: Global trends, etiology and risk factors. World J. Oncol. 2019, 10, 10–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, Y.; Sekine, I.; Hanazono, M.; Morinaga, T.; Fan, M.; Takiguchi, Y.; Tada, Y.; Shingyoji, M.; Yamaguchi, N.; Tagawa, M. AMPK activation induced in pemetrexed-treated cells is associated with development of drug resistance independently of target enzyme expression. Mol. Oncol. 2019, 13, 1419–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, C.; Yao, X.; Jiang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, D.; Chen, X.; Fan, X.; Xie, C.; Cheng, J.; Fu, J.; et al. Cordycepin inhibits drug-resistance non-small cell lung cancer progression by activating AMPK signaling pathway. Pharmacol. Res. 2019, 144, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, P.; Chen, Q.; Deng, S.; Liu, X.; Situ, H.; Zhong, S.; Hann, S.; Lin, Y. Targeting AMPK signaling pathway to overcome drug resistance for cancer therapy. Curr. Drug Targets 2016, 17, 853–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, W.; Zhong, Z.; Carney, R.P.; Men, Y.; Li, J.; Pan, T.; Wang, Y. Deciphering the metabolic role of AMPK in cancer multi-drug resistance. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2019, 56, 56–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.D.; Hu, Z.M.; Shang, M.J.; Zhao, D.J.; Zhang, C.W.; Hong, D.F.; Huang, D.S. Cordycepin down-regulates multiple drug resistant (MDR)/HIF-1alpha through regulating AMPK/mTORC1 signaling in GBC-SD gallbladder cancer cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 12778–12790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, Y.; Li, H.; Yi, D.; Sun, Y.; Bai, Y.; Zhong, S.; Song, Y.; Zhao, G.; Chen, Y. Cordycepin augments the chemosensitivity of human Glioma cells to Temozolomide by activating AMPK and inhibiting the AKT signaling pathway. Mol. Pharm. 2018, 15, 4912–4925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.F.; Xie, C.W.; Yang, S.X.; Xiong, J.P. AMPK activators suppress breast cancer cell growth by inhibiting DVL3-facilitated Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway activity. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 15, 899–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Duan, W.; Chen, K.; Jiang, Z.; Chen, X.; Sun, L.; Li, J.; Lei, J.; Xu, Q.; Ma, J.; Li, X.; et al. Desmoplasia suppression by metformin-mediated AMPK activation inhibits pancreatic cancer progression. Cancer Lett. 2017, 385, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitburn, J.; Edwards, C.M.; Sooriakumaran, P. Metformin and prostate cancer: A new role for an old drug. Curr. Urol. Rep. 2017, 18, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, D.; Ohlsson, H.; Althini, C.; Bauden, M.; Zhou, Q.; Hu, D.; Andersson, R. The Hippo signaling pathway in pancreatic cancer. Anticancer Res. 2019, 39, 3317–3321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rozengurt, E.; Eibl, G. Central role of Yes-associated protein and WW-domain-containing transcriptional co-activator with PDZ-binding motif in pancreatic cancer development. World J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 25, 1797–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Z.; Zhou, C.; Cheng, L.; Yan, B.; Chen, K.; Chen, X.; Zong, L.; Lei, J.; Duan, W.; Xu, Q.; et al. Inhibiting YAP expression suppresses pancreatic cancer progression by disrupting tumor-stromal interactions. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer. Res. 2018, 37, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Xiao, Z.D.; Li, X.; Aziz, K.E.; Gan, B.; Johnson, R.L.; Chen, J. AMPK modulates Hippo pathway activity to regulate energy homeostasis. Nat. Cell Biol. 2015, 17, 490–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeRan, M.; Yang, J.; Shen, C.H.; Peters, E.C.; Fitamant, J.; Chan, P.; Hsieh, M.; Zhu, S.; Asara, J.M.; Zheng, B.; et al. Energy stress regulates hippo-YAP signaling involving AMPK-mediated regulation of angiomotin-like 1 protein. Cell Rep. 2014, 9, 495–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorrentino, G.; Ruggeri, N.; Specchia, V.; Cordenonsi, M.; Mano, M.; Dupont, S.; Manfrin, A.; Ingallina, E.; Sommaggio, R.; Piazza, S.; et al. Metabolic control of YAP and TAZ by the mevalonate pathway. Nat. Cell Biol. 2014, 16, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mijatovic, S.; Bramanti, A.; Nicoletti, F.; Fagone, P.; Kaluderovic, G.N.; Maksimovic-Ivanic, D. Naturally occurring compounds in differentiation based therapy of cancer. Biotechnol. Adv. 2018, 36, 1622–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buyel, J.F. Plants as sources of natural and recombinant anti-cancer agents. Biotechnol. Adv. 2018, 36, 506–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avgerinos, K.I.; Spyrou, N.; Mantzoros, C.S.; Dalamaga, M. Obesity and cancer risk: Emerging biological mechanisms and perspectives. Metabolism 2019, 92, 121–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eibl, G.; Rozengurt, E. KRAS, YAP, and obesity in pancreatic cancer: A signaling network with multiple loops. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2019, 54, 50–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Wu, L.; Tu, J.; Zhao, Z.; Fan, X.; Mao, J.; Weng, Q.; Wu, X.; Huang, L.; Xu, M.; et al. miR-590-5p suppresses hepatocellular carcinoma chemoresistance by targeting YAP1 expression. EBioMedicine 2018, 35, 142–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Z.; Zhao, T.T.; Jin, F.; Li, J.G.; Xu, Y.Y.; Dong, H.T.; Liu, Q.; Xing, P.; Zhu, G.L.; Xu, H.; et al. Downregulation of RASSF6 promotes breast cancer growth and chemoresistance through regulation of Hippo signaling. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 503, 2340–2347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Y.; Li, D.; Li, H.; Wang, L.; Tian, G.; Dong, Y. YAP overexpression promotes the epithelial-mesenchymal transition and chemoresistance in pancreatic cancer cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 2016, 13, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, T.C. Drug combination studies and their synergy quantification using the Chou-Talalay method. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 440–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Qi, L.; Jiang, L.; Zhou, P.; Ma, J.; Xu, X.; Li, P. Antitumor activity of gemcitabine can be potentiated in pancreatic cancer through modulation of TLR4/NF-kappaB signaling by 6-shogaol. AAPS J. 2014, 16, 246–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Yi, Y.; Yuan, Q.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, P.; Xu, M.; Xie, S. VAOS, a novel vanadyl complexes of alginate saccharides, inducing apoptosis via activation of AKT-dependent ROS production in NSCLC. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2018, 129, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.B.; Lee, J.S.; Lee, M.S.; Cha, E.Y.; Kim, S.; Sul, J.Y. Corosolic acid reduces 5FU chemoresistance in human gastric cancer cells by activating AMPK. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 18, 2880–2888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, D.H.; Choi, Y.J.; Park, J.W. SIRT1 and AMPK mediate hypoxia-induced resistance of non-small cell lung cancers to cisplatin and doxorubicin. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 298–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, E.H.; Nousiainen, M.; Chalamalasetty, R.B.; Schafer, A.; Nigg, E.A.; Sillje, H.H. The Ste20-like kinase Mst2 activates the human large tumor suppressor kinase Lats1. Oncogene 2005, 24, 2076–2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praskova, M.; Xia, F.; Avruch, J. MOBKL1A/MOBKL1B phosphorylation by MST1 and MST2 inhibits cell proliferation. Curr. Biol. 2008, 18, 311–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wu, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Mei, L.; Fang, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, F.; Chen, H.; Liu, Y.; et al. Interplay of mevalonate and Hippo pathways regulates RHAMM transcription via YAP to modulate breast cancer cell motility. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, E89–E98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gujral, T.S.; Kirschner, M.W. Hippo pathway mediates resistance to cytotoxic drugs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E3729–E3738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, C.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Liao, Q.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, X.; Guo, Q.; Shen, P.; Zhen, B.; Qian, X.; et al. Regulation of the Hippo-YAP pathway by Glucose sensor O-GlcNAcylation. Mol. Cell 2017, 68, 591–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.S.; Sung, J.H.; Lee, S.K. Inhibition of Cholesterol synthesis in HepG2 cells by GINST-decreasing HMG-CoA reductase expression Via AMP-activated Protein Kinase. J. Food Sci. 2017, 82, 2700–2705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishihara, E.; Nishina, H. Role of Hippo-YAP/TAZ signaling pathway in mechanotransduction. Clin. Calcium 2016, 26, 1751–1756. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, B.; Li, L.; Wang, L.; Wang, C.Y.; Yu, J.; Guan, K.L. Cell detachment activates the Hippo pathway via cytoskeleton reorganization to induce anoikis. Genes Dev. 2012, 26, 54–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, K.; Osada, H.; Murakami-Tonami, Y.; Horio, Y.; Hida, T.; Sekido, Y. Statin suppresses Hippo pathway-inactivated malignant mesothelioma cells and blocks the YAP/CD44 growth stimulatory axis. Cancer Lett. 2017, 385, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, A.J.; Cortes, E.; Lachowski, D.; Cheung, B.C.H.; Karim, S.A.; Morton, J.P.; Del Rio Hernandez, A. Matrix stiffness induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition and promotes chemoresistance in pancreatic cancer cells. Oncogenesis 2017, 6, e352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xian, G.; Zhao, J.; Qin, C.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, Y.; Su, Z. Simvastatin attenuates macrophage-mediated gemcitabine resistance of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma by regulating the TGF-beta1/Gfi-1 axis. Cancer Lett. 2017, 385, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, L.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, H.; Li, Y.; Xie, S.; Xu, M. YAP Inhibition by Nuciferine via AMPK-Mediated Downregulation of HMGCR Sensitizes Pancreatic Cancer Cells to Gemcitabine. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 620. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom9100620
Zhou L, Wang Q, Zhang H, Li Y, Xie S, Xu M. YAP Inhibition by Nuciferine via AMPK-Mediated Downregulation of HMGCR Sensitizes Pancreatic Cancer Cells to Gemcitabine. Biomolecules. 2019; 9(10):620. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom9100620
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Ling, Qiaoyun Wang, Han Zhang, Youjie Li, Shuyang Xie, and Maolei Xu. 2019. "YAP Inhibition by Nuciferine via AMPK-Mediated Downregulation of HMGCR Sensitizes Pancreatic Cancer Cells to Gemcitabine" Biomolecules 9, no. 10: 620. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom9100620
APA StyleZhou, L., Wang, Q., Zhang, H., Li, Y., Xie, S., & Xu, M. (2019). YAP Inhibition by Nuciferine via AMPK-Mediated Downregulation of HMGCR Sensitizes Pancreatic Cancer Cells to Gemcitabine. Biomolecules, 9(10), 620. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom9100620