Emerging Roles of Lysyl Oxidases in the Cardiovascular System: New Concepts and Therapeutic Challenges
Abstract
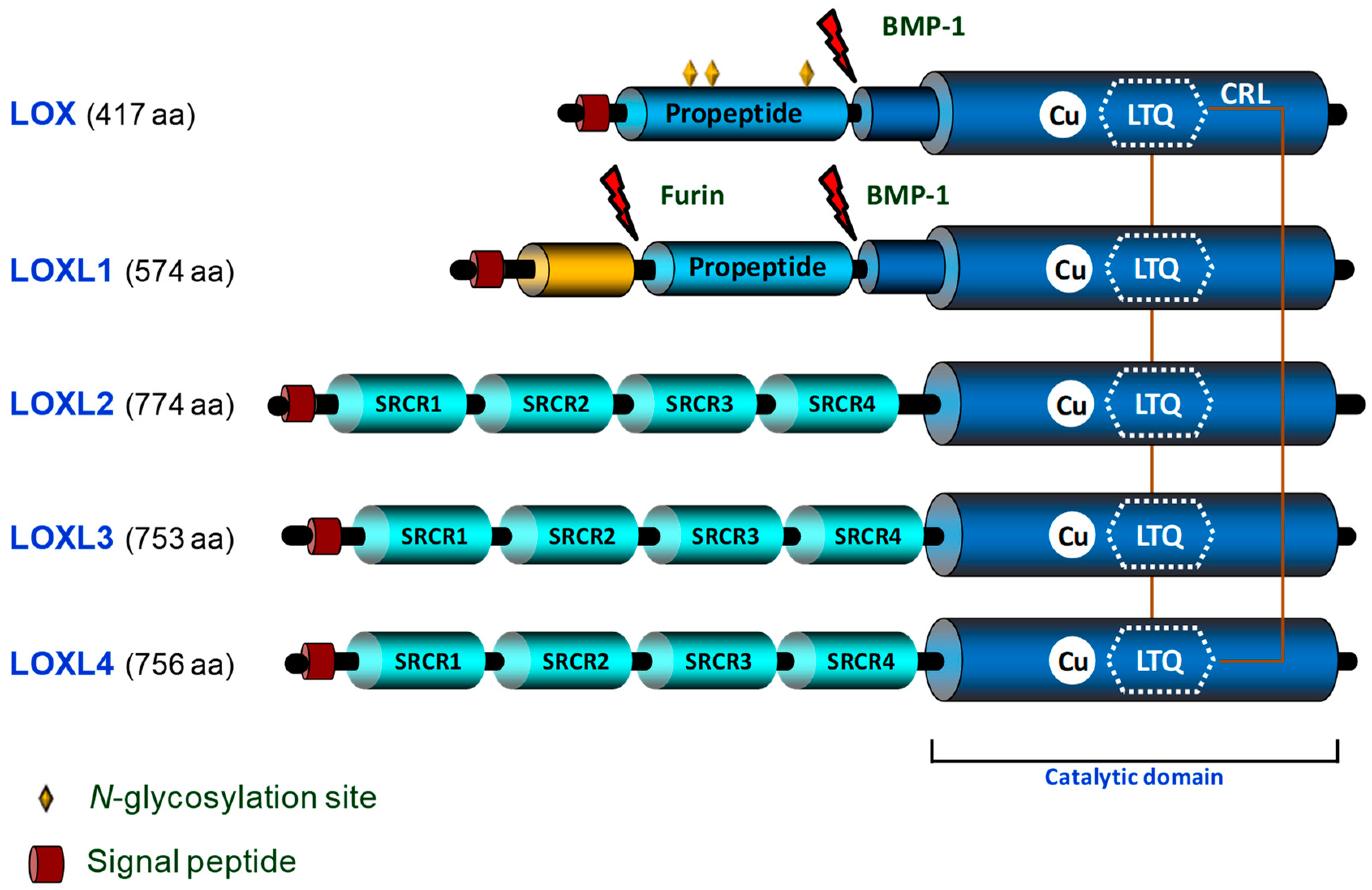
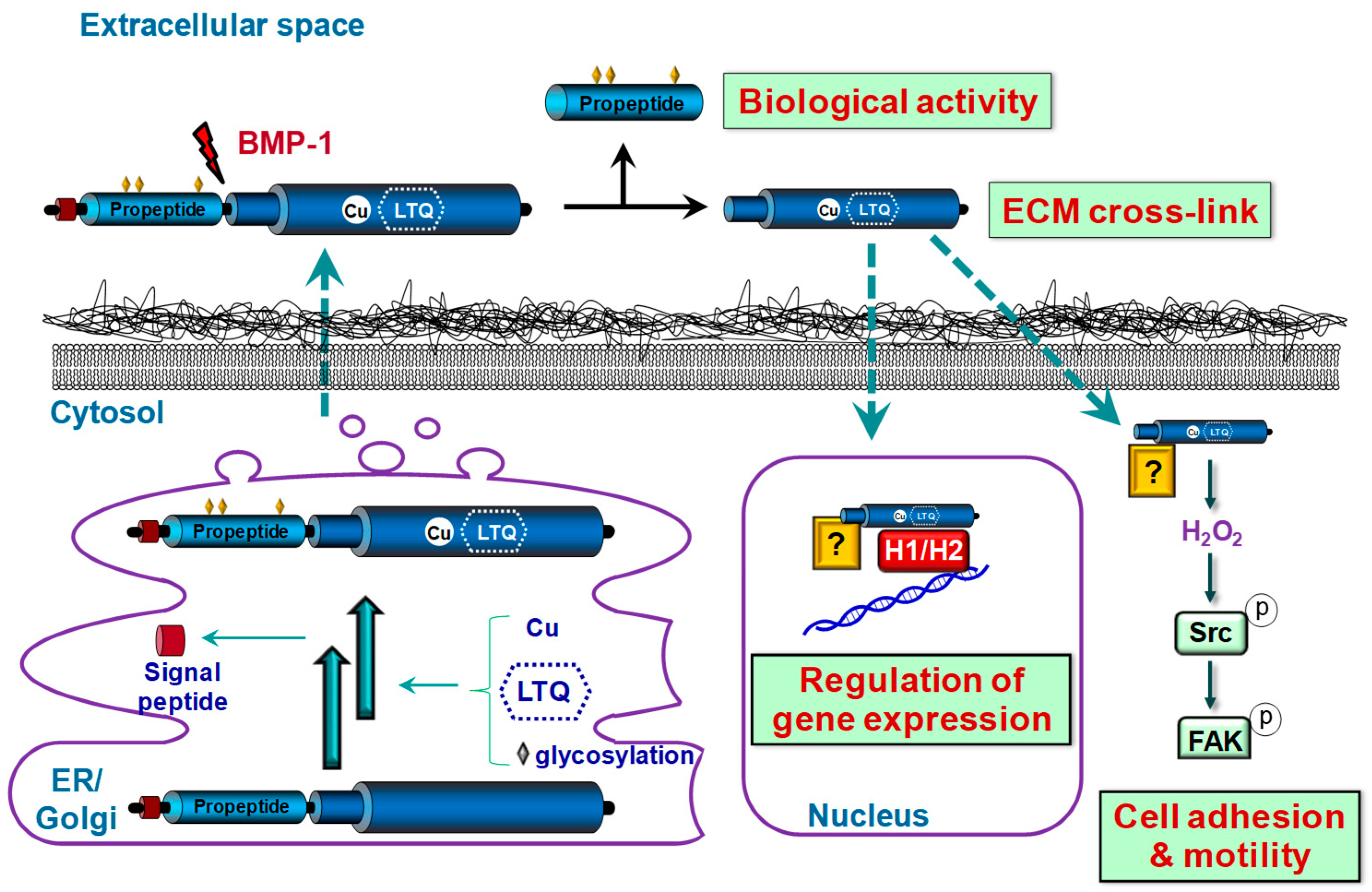
1. Introduction
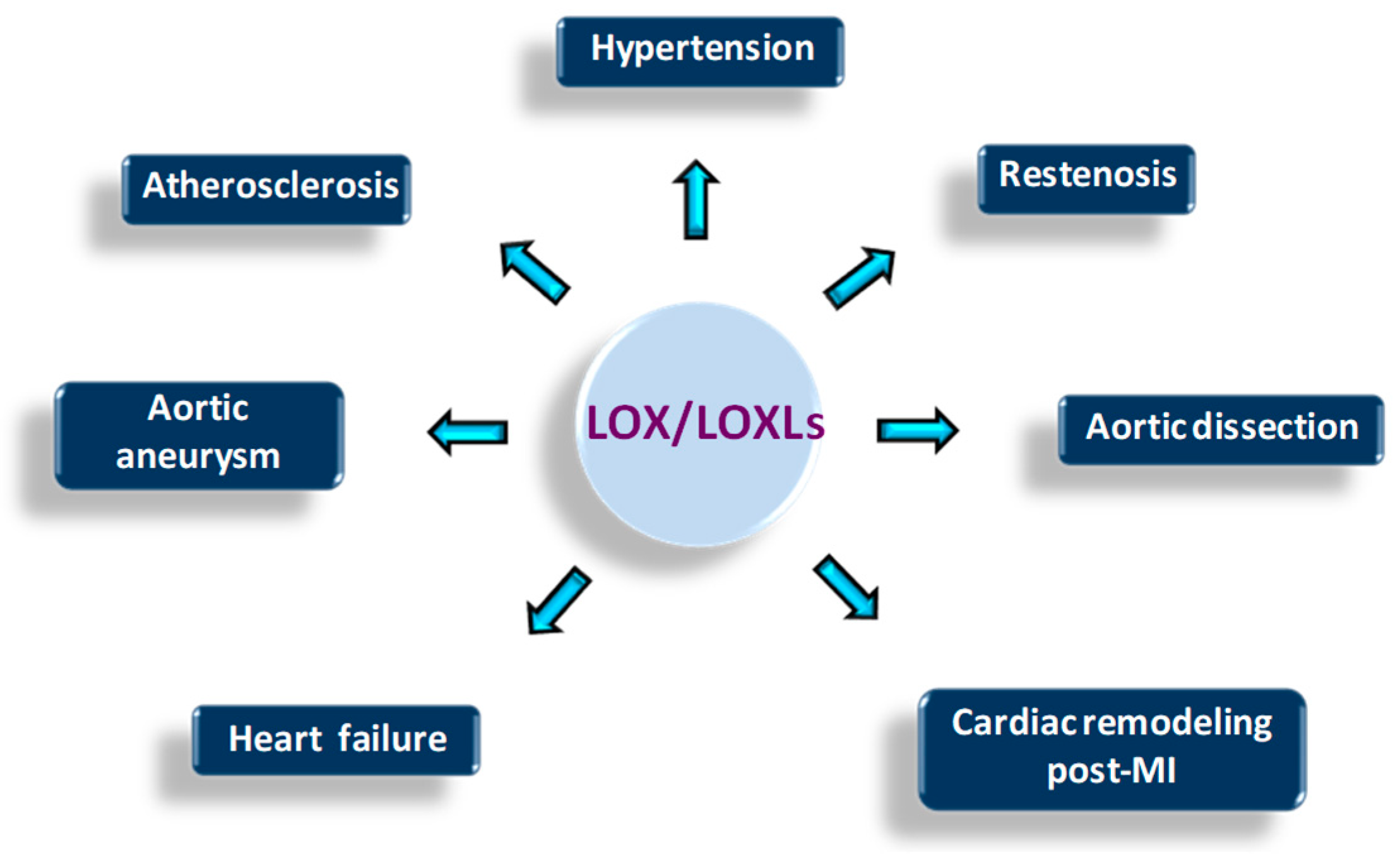
2. Regulation of Vascular Homeostasis by LOX/LOXLs: Pathophysiological Impact
2.1. Contribution to Arterial Aneurysms and Aortic Dissections
2.2. LOX in Endothelial Dysfunction
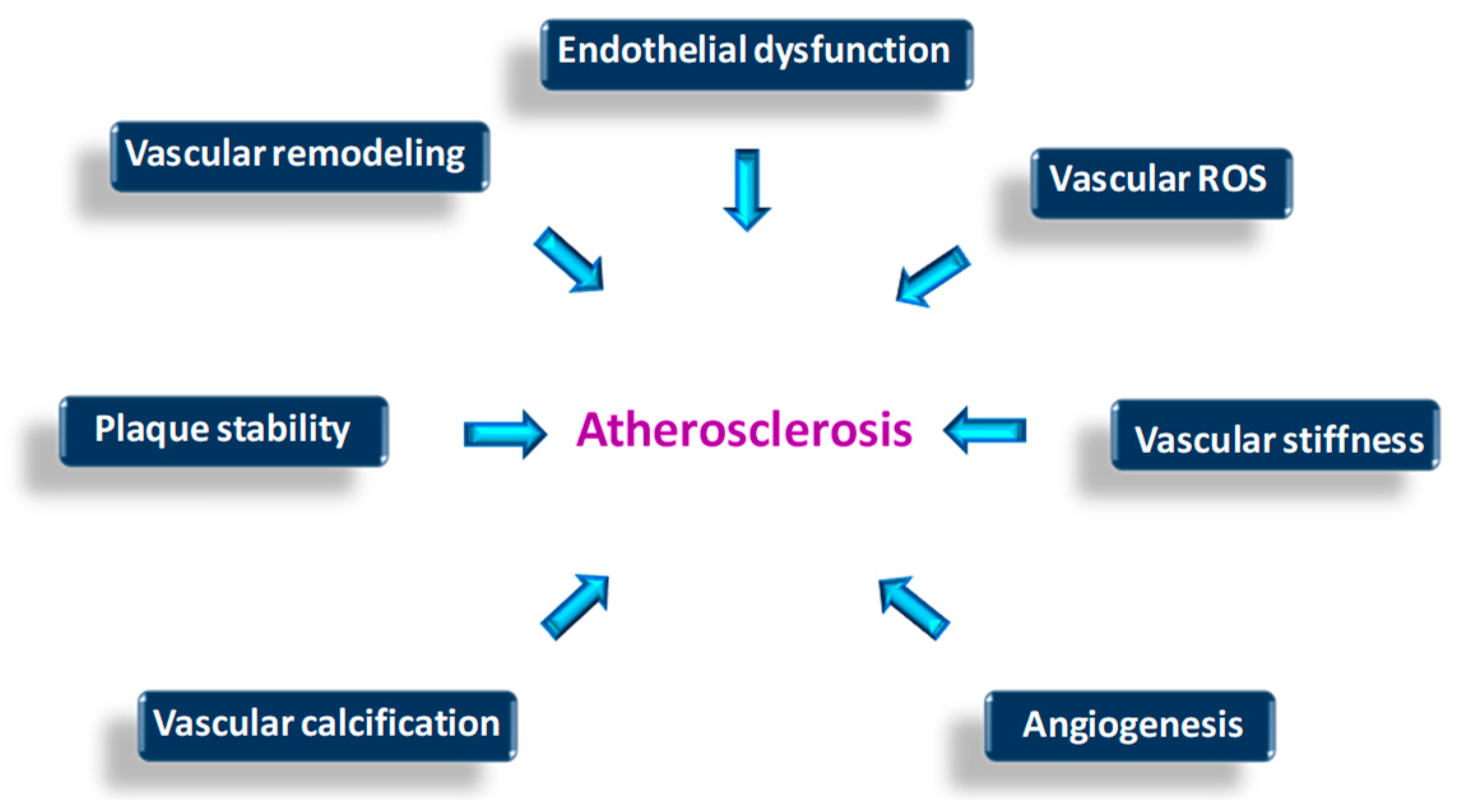
2.3. LOX in Atherosclerosis Progression and Plaque Instability
2.4. LOX in VSMC, Vascular Remodeling, and Restenosis
2.5. LOX in Vascular Calcification
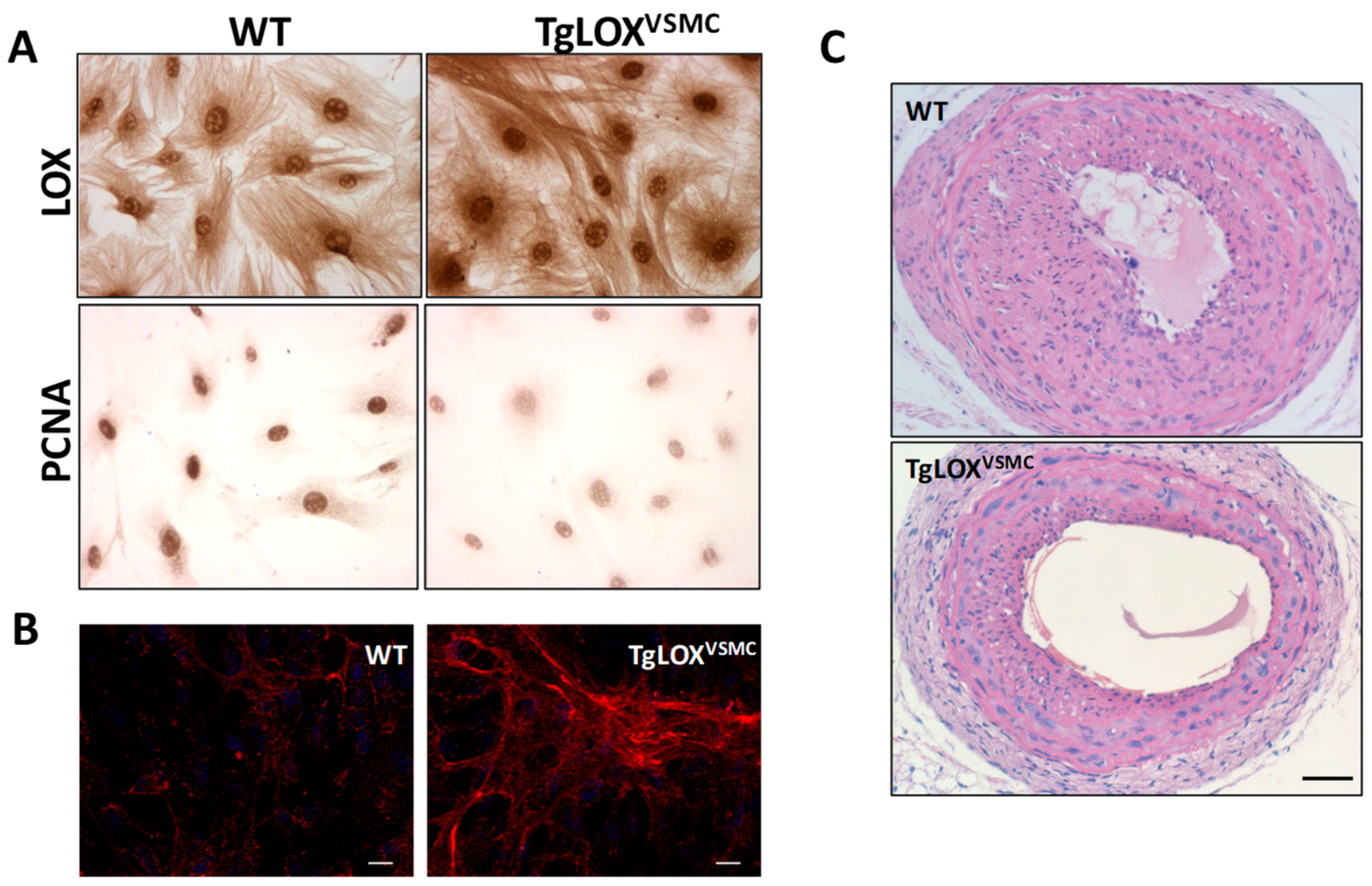
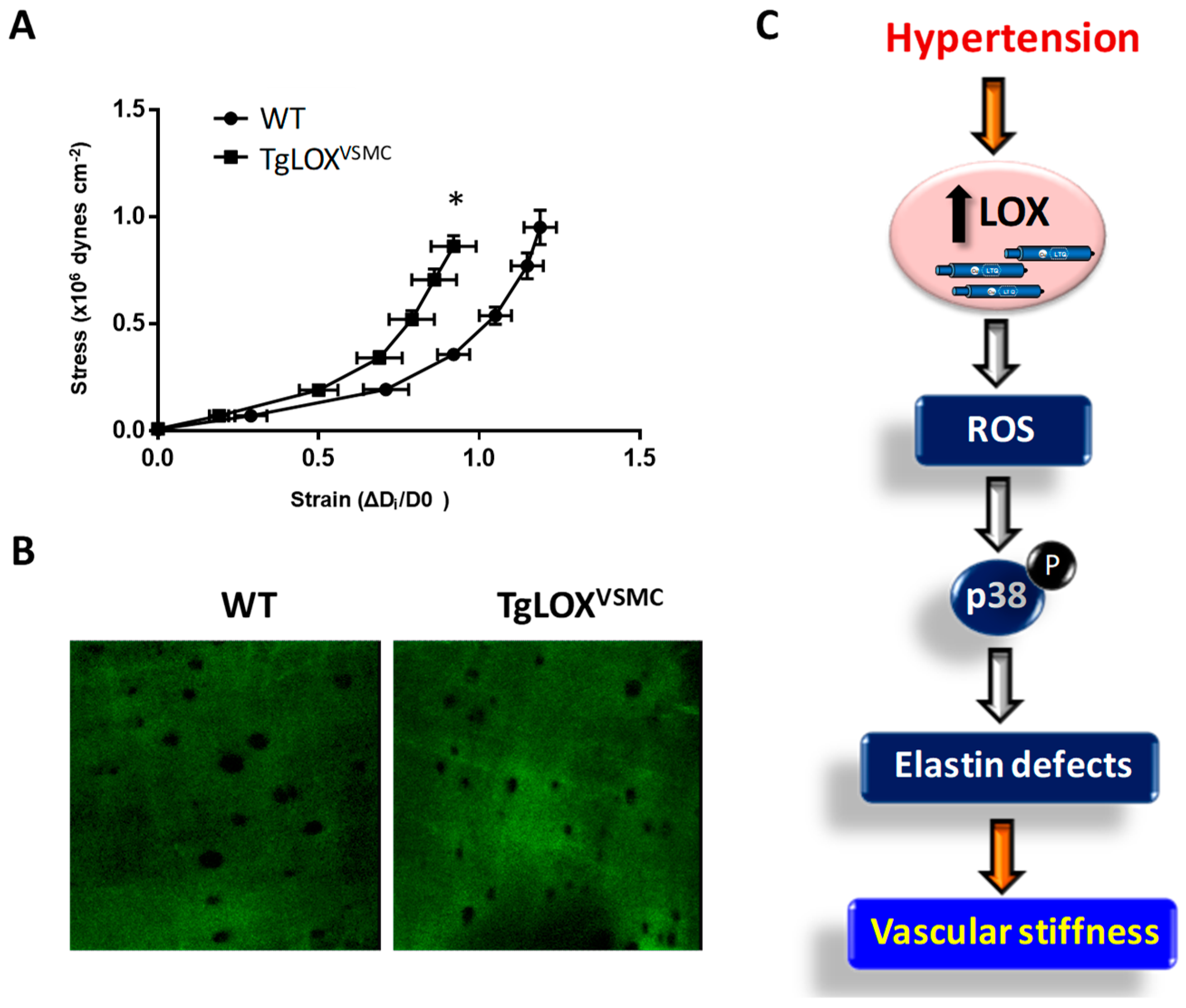
2.6. LOXs, Vascular Stiffness, and Oxidative Stress: Impact on Hypertension
2.7. LOX and LOXLs in Neovascularization
3. LOX and Heart Disease
4. LOXs as Pharmacological Targets for Cardiovascular Diseases
5. Conclusions and Future Challenges
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rodríguez, C.; Martínez-González, J.; Raposo, B.; Alcudia, J.F.; Guadall, A.; Badimon, L. Regulation of lysyl oxidase in vascular cells: Lysyl oxidase as a new player in cardiovascular diseases. Cardiovasc. Res. 2008, 79, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kagan, H.M.; Li, W. Lysyl oxidase: Properties, specificity, and biological roles inside and outside of the Cell. J. Cell Biochem. 2003, 88, 660–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molnar, J.; Fong, K.S.; He, Q.P.; Hayashi, K.; Kim, Y.; Fong, S.F.; Fogelgren, B.; Szauter, K.M.; Mink, M.; Csiszar, K. Structural and functional diversity of lysyl oxidase and the LOX-like proteins. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2003, 1647, 220–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, C.; Rodríguez-Sinovas, A.; Martínez-González, J. Lysyl oxidase as a potential therapeutic target. Drug News Perspect. 2008, 21, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fogelgren, B.; Polgár, N.; Szauter, K.M.; Ujfaludi, Z.; Laczkó, R.; Fong, K.S.; Csiszar, K. Cellular fibronectin binds to lysyl oxidase with high affinity and is critical for its proteolytic activation. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 24690–24697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Zhao, Y.; Gao, J.; Pawlyk, B.; Starcher, B.; Spencer, J.A.; Yanagisawa, H.; Zuo, J.; Li, T. Elastic fiber homeostasis requires lysyl oxidase-like 1 protein. Nat. Genet. 2004, 36, 178–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, A.; Salvador, F.; Moreno-Bueno, G.; Floristán, A.; Ruiz-Herguido, C.; Cuevas, E.P.; Morales, S.; Santos, V.; Csiszar, K.; Dubus, P.; et al. Lysyl oxidase-like 2 represses notch1 expression in the skin to promote squamous cell carcinoma progression. EMBO J. 2015, 34, 1090–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yang, R.; Liu, Z.; Hou, C.; Zong, W.; Zhang, A.; Sun, X.; Gao, J. Loss of lysyl oxidase-like 3 causes cleft palate and spinal deformity in mice. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2015, 24, 6174–6185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busnadiego, O.; González-Santamaría, J.; Lagares, D.; Guinea-Viniegra, J.; Pichol-Thievend, C.; Muller, L.; Rodríguez-Pascual, F. LOXL4 is induced by transforming growth factor β1 through Smad and JunB/Fra2 and contributes to vascular matrix remodeling. Mol. Cell Biol. 2013, 33, 2388–2401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nave, A.H.; Mižíková, I.; Niess, G.; Steenbock, H.; Reichenberger, F.; Talavera, M.L.; Veit, F.; Herold, S.; Mayer, K.; Vadász, I.; et al. Lysyl oxidases play a causal role in vascular remodeling in clinical and experimental pulmonary arterial hypertension. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2014, 34, 1446–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordon, I.M.; Hinchliffe, R.J.; Loftus, I.M.; Thompson, M.M. Pathophysiology and epidemiology of abdominal aortic aneurysms. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2011, 8, 92–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brüel, A.; Ortoft, G.; Oxlund, H. Inhibition of cross-links in collagen is associated with reduced stiffness of the aorta in young rats. Atherosclerosis 1998, 140, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huffman, M.D.; Curci, J.A.; Moore, G.; Kerns, D.B.; Starcher, B.C.; Thompson, R.W. Functional importance of connective tissue repair during the development of experimental abdominal aortic aneurysms. Surgery 2000, 128, 429–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshimura, K.; Aoki, H.; Ikeda, Y.; Fujii, K.; Akiyama, N.; Furutani, A.; Hoshii, Y.; Tanaka, N.; Ricci, R.; Ishihara, T.; et al. Regression of abdominal aortic aneurysm by inhibition of c-Jun N-terminal kinase. Nat. Med. 2005, 11, 1330–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Remus, E.W.; O’Donnell, R.E.; Rafferty, K.; Weiss, D.; Joseph, G.; Csiszar, K.; Fong, S.F.; Taylor, W.R. The role of lysyl oxidase family members in the stabilization of abdominal aortic aneurysms. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2012, 303, H1067–H1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onoda, M.; Yoshimura, K.; Aoki, H.; Ikeda, Y.; Morikage, N.; Furutani, A.; Matsuzaki, M.; Hamano, K. Lysyl oxidase resolves inflammation by reducing monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 in abdominal aortic aneurysm. Atherosclerosis 2010, 208, 366–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mäki, J.M.; Räsänen, J.; Tikkanen, H.; Sormunen, R.; Mäkikallio, K.; Kivirikko, K.I.; Soininen, R. Inactivation of the lysyl oxidase gene Lox leads to aortic aneurysms, cardiovascular dysfunction, and perinatal death in mice. Circulation 2002, 106, 2503–2509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hornstra, I.K.; Birge, S.; Starcher, B.; Bailey, A.J.; Mecham, R.P.; Shapiro, S.D. Lysyl oxidase is required for vascular and diaphragmatic development in mice. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 14387–14393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonesson, B.; Hansen, F.; Länne, T. Abdominal aortic aneurysm: A general defect in the vasculature with focal manifestations in the abdominal aorta? J. Vasc. Surg. 1997, 26, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidholm, C.L.; Beck, H.C.; Madsen, J.B.; Palstrøm, N.B.; Lindholt, J.S.; Rasmussen, L.M. Preliminary analysis of proteome alterations in non-aneurysmal, internal mammary artery tissue from patients with abdominal aortic aneurysms. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0192957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, V.S.; Halabi, C.M.; Hoffman, E.P.; Carmichael, N.; Leshchiner, I.; Lian, C.G.; Bierhals, A.J.; Vuzman, D.; Brigham Genomic Medicine; Mecham, R.P.; et al. Loss of function mutation in LOX causes thoracic aortic aneurysm and dissection in humans. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 8759–8764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, D.C.; Regalado, E.S.; Gong, L.; Duan, X.; Santos-Cortez, R.L.; Arnaud, P.; Ren, Z.; Cai, B.; Hostetler, E.M.; Moran, R.; et al. LOX mutations predispose to thoracic aortic aneurysms and dissections. Circ. Res. 2016, 118, 928–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Shi, E.; Gu, T.; Tang, R.; Gao, S.; Wang, Y.; Liu, H. Overexpression of microRNA-30a contributes to the development of aortic dissection by targeting lysyl oxidase. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2017, 154, 1862–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sibon, I.; Sommer, P.; Lamaziere, J.M.; Bonnet, J. Lysyl oxidase deficiency: A new cause of human arterial dissection. Heart 2005, 91, e33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Busnadiego, O.; Gorbenko Del Blanco, D.; González-Santamaría, J.; Habashi, J.P.; Calderon, J.F.; Sandoval, P.; Bedja, D.; Guinea-Viniegra, J.; Lopez-Cabrera, M.; Rosell-Garcia, T.; et al. Elevated expression levels of lysyl oxidases protect against aortic aneurysm progression in Marfan syndrome. J. Mol. Cell Cardiol. 2015, 85, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki, T.; Kataoka, H.; Ishibashi, R.; Nozaki, K.; Morishita, R.; Hashimoto, N. Reduced collagen biosynthesis is the hallmark of cerebral aneurysm: Contribution of interleukin-1beta and nuclear factor-kappaB. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2009, 29, 1080–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akagawa, H.; Narita, A.; Yamada, H.; Tajima, A.; Krischek, B.; Kasuya, H.; Hori, T.; Kubota, M.; Saeki, N.; Hata, A.; et al. Systematic screening of lysyl oxidase-like (LOXL) family genes demonstrates that LOXL2 is a susceptibility gene to intracranial aneurysms. Hum. Genet. 2007, 121, 377–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, C.; Raposo, B.; Martínez-González, J.; Alcudia, J.F.; Guadall, A.; Badimon, L. Lysyl oxidase (LOX) expression in the vascular wall: Mechanisms involved in LOX regulation by low density lipoproteins. Clin. Invest. Arterioscler. 2007, 19, 113–121. [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez, C.; Raposo, B.; Martinez-Gonzalez, J.; Casani, L.; Badimon, L. Low density lipoproteins down-regulates lysyl oxidase in vascular endothelial cells and the arterial wall. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2002, 22, 1409–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raposo, B.; Rodriguez, C.; Martinez-Gonzalez, J.; Badimon, L. High levels of homocysteine inhibit lysyl oxidase (LOX) and down-regulates LOX expression in vascular endothelial cells. Atherosclerosis 2004, 177, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, C.; Alcudia, J.F.; Martínez-González, J.; Raposo, B.; Navarro, M.A.; Badimon, L. Lysyl oxidase (LOX) down-regulation by TNFalpha: A new mechanism underlying TNFalpha-induced endothelial dysfunction. Atherosclerosis 2008, 196, 558–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coral, K.; Angayarkanni, N.; Gomathy, N.; Bharathselvi, M.; Pukhraj, R.; Rupak, R. Homocysteine levels in the vitreous of proliferative diabetic retinopathy and rhegmatogenous retinal detachment: Its modulating role on lysyl oxidase. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2009, 50, 3607–3612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thaler, R.; Agsten, M.; Spitzer, S.; Paschalis, E.P.; Karlic, H.; Klaushofer, K.; Varga, F. Homocysteine suppresses the expression of the collagen cross-linker lysyl oxidase involving IL-6, Fli1, and epigenetic DNA methylation. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 5578–5588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez, C.; Alcudia, J.F.; Martínez-González, J.; Guadall, A.; Raposo, B.; Sánchez-Gómez, S.; Badimon, L. Statins normalize vascular lysyl oxidase down-regulation induced by proatherogenic risk factors. Cardiovasc. Res. 2009, 83, 595–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamopoulos, C.; Piperi, C.; Gargalionis, A.N.; Dalagiorgou, G.; Spilioti, E.; Korkolopoulou, P.; Diamanti-Kandarakis, E.; Papavassiliou, A.G. Advanced glycation end products upregulate lysyl oxidase and endothelin-1 in human aortic endothelial cells via parallel activation of ERK1/2-NF-κB and JNK-AP-1 signaling pathways. Cell Mol. Life. Sci. 2016, 73, 1685–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chvapil, M.; Stith, P.L.; Tillema, L.M.; Carlson, E.C.; Campbell, J.B.; Eskelson, C.D. Early changes in the arterial wall of chickens fed a cholesterol diet. Atherosclerosis 1976, 24, 393–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kagan, H.M.; Raghavan, J.; Hollander, W. Changes in aortic lysyl oxidase activity in diet-induced atherosclerosis in the rabbit. Arteriosclerosis 1981, 1, 287–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kothapalli, D.; Liu, S.L.; Bae, Y.H.; Monslow, J.; Xu, T.; Hawthorne, E.A.; Byfield, F.J.; Castagnino, P.; Rao, S.; Rader, D.J.; et al. Cardiovascular protection by ApoE and ApoE-HDL linked to suppression of ECM gene expression and arterial stiffening. Cell Rep. 2012, 2, 1259–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jover, E.; Silvente, A.; Marín, F.; Martínez-González, J.; Orriols, M.; Martinez, C.M.; Puche, C.M.; Valdés, M.; Rodriguez, C.; Hernández-Romero, D. Inhibition of enzymes involved in collagen cross-linking reduces vascular smooth muscle cell calcification. FASEB J. 2018, 32, 4459–4469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamauchi, M.; Sricholpech, M. Lysine post-translational modifications of collagen. Essays Biochem. 2012, 52, 113–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ovchinnikova, O.A.; Folkersen, L.; Persson, J.; Lindeman, J.H.; Ueland, T.; Aukrust, P.; Gavrisheva, N.; Shlyakhto, E.; Paulsson-Berne, G.; Hedin, U.; et al. The collagen cross-linking enzyme lysyl oxidase is associated with the healing of human atherosclerotic lesions. J. Intern. Med. 2014, 276, 525–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butticè, G.; Miller, J.; Wang, L.; Smith, B.D. Interferon-gamma induces major histocompatibility class II transactivator (CIITA), which mediates collagen repression and major histocompatibility class II activation by human aortic smooth muscle cells. Circ. Res. 2006, 98, 472–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.L.; Ford, J.W.; Gordon, D.; Shanley, C.J. Regulation of lysyl oxidase by interferon-gamma in rat aortic smooth muscle cells. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2000, 20, 982–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ovchinnikova, O.; Robertson, A.K.; Wågsäter, D.; Folco, E.J.; Hyry, M.; Myllyharju, J.; Eriksson, P.; Libby, P.; Hansson, G.K. T-cell activation leads to reduced collagen maturation in atherosclerotic plaques of Apoe(-/-) mice. Am. J. Pathol. 2009, 174, 693–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ovchinnikova, O.; Gylfe, A.; Bailey, L.; Nordström, A.; Rudling, M.; Jung, C.; Bergström, S.; Waldenström, A.; Hansson, G.K.; Nordström, P. Osteoprotegerin promotes fibrous cap formation in atherosclerotic lesions of ApoE-deficient mice—Brief report. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2009, 29, 1478–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guadall, A.; Orriols, M.; Alcudia, J.F.; Cachofeiro, V.; Martinez-Gonzalez, J.; Rodriguez, C. Hypoxia-induced ROS signaling is required for LOX up-regulation in endothelial cells. Front. Biosci. 2011, 3, 955–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuura, S.; Mi, R.; Koupenova, M.; Eliades, A.; Patterson, S.; Toselli, P.; Thon, J.; Italiano, J.E., Jr.; Trackman, P.C.; Papadantonakis, N.; et al. Lysyl oxidase is associated with increased thrombosis and platelet reactivity. Blood 2016, 127, 1493–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mäki, J.M.; Sormunen, R.; Lippo, S.; Kaarteenaho-Wiik, R.; Soininen, R.; Myllyharju, J. Lysyl oxidase is essential for normal development and function of the respiratory system and for the integrity of elastic and collagen fibers in various tissues. Am. J. Pathol. 2005, 167, 927–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gacheru, S.N.; Thomas, K.M.; Murray, S.A.; Csiszar, K.; Smith-Mungo, L.I.; Kagan, H.M. Transcriptional and post-transcriptional control of lysyl oxidase expression in vascular smooth muscle cells: Effects of TGF-beta 1 and serum deprivation. J. Cell Biochem. 1997, 65, 395–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, R.S.; Lieb, M.E.; Weintraub, A.S.; Gacheru, S.N.; Rosenfield, C.L.; Shah, S.; Kagan, H.M.; Taubman, M.B. Identification of lysyl oxidase and other platelet-derived growth factor-inducible genes in vascular smooth muscle cells by differential screening. Lab. Invest. 1995, 73, 476–482. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, Y.X.; Jiang, J.; Jiang, X.H.; Wang, X.D.; Ji, S.Y.; Han, Y.; Long, D.K.; Shen, B.R.; Yan, Z.Q.; Chien, S.; et al. PDGF-BB and TGF-{beta}1 on cross-talk between endothelial and smooth muscle cells in vascular remodeling induced by low shear stress. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 1908–1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez, E.; Rodríguez, C.; Miana, M.; Jurado-López, R.; Bartolomé, M.V.; Luaces, M.; Islas, F.; Martínez-González, J.; López-Andrés, N.; Cachofiero, V. The lysyl oxidase inhibitor β-aminopropionitrile reduces leptin profibrotic effects and ameliorates cardiovascular remodeling in diet-induced obesity in rats. J. Mol. Cell Cardiol. 2016, 92, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atsawasuwan, P.; Mochida, Y.; Katafuchi, M.; Kaku, M.; Fong, K.S.; Csiszar, K.; Yamauchi, M. Lysyl oxidase binds transforming growth factor-beta and regulates its signaling via amine oxidase activity. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 34229–34240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weissen-Plenz, G.; Eschert, H.; Volker, W.; Sindermann, J.R.; Beissert, S.; Robenek, H.; Scheld, H.H.; Breithardt, G. Granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor deficiency affects vascular elastin production and integrity of elastic lamellae. J. Vasc. Res. 2008, 45, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucero, H.A.; Kagan, H.M. Lysyl oxidase: An oxidative enzyme and effector of cell function. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2006, 63, 2304–2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Liu, G.; Chou, I.N.; Kagan, H.M. Hydrogen peroxide-mediated, lysyl oxidase-dependent chemotaxis of vascular smooth muscle cells. J. Cell Biochem. 2000, 78, 550–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucero, H.A.; Ravid, K.; Grimsby, J.L.; Rich, C.B.; DiCamillo, S.J.; Mäki, J.M.; Myllyharju, J.; Kagan, H.M. Lysyl oxidase oxidizes cell membrane proteins and enhances the chemotactic response of vascular smooth muscle cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 24103–24117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, C.D.; Balagurunathan, Y.; Dougherty, E.R.; Afshari, C.A.; He, Q.; Ramos, K.S. Insight into redox-regulated gene networks in vascular cells. Bioinformation 2007, 1, 379–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Nuthakki, V.K.; Fleser, P.S.; Malinzak, L.E.; Seymour, M.L.; Callahan, R.E.; Bendick, P.J.; Zelenock, G.B.; Shanley, C.J. Lysyl oxidase expression in a rat model of arterial balloon injury. J. Vasc. Surg. 2004, 40, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brasselet, C.; Durand, E.; Addad, F.; Al Haj Zen, A.; Smeets, M.B.; Laurent-Maquin, D.; Bouthors, S.; Bellon, G.; de Kleijn, D.; Godeau, G.; et al. Collagen and elastin cross-linking: A mechanism of constrictive remodeling after arterial injury. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2005, 289, H2228–H2233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurtado, P.A.; Vora, S.; Sume, S.S.; Yang, D.; St Hilaire, C.; Guo, Y.; Palamakumbura, A.H.; Schreiber, B.M.; Ravid, K.; Trackman, P.C. Lysyl oxidase propeptide inhibits smooth muscle cell signaling and proliferation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2008, 366, 156–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orriols, M.; Guadall, A.; Galán, M.; Martí-Pàmies, I.; Varona, S.; Rodríguez-Calvo, R.; Briones, A.M.; Navarro, M.A.; de Diego, A.; Osada, J.; et al. Lysyl oxidase (LOX) in vascular remodelling. Insight from a new animal model. Thromb. Haemost. 2014, 112, 812–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varona, S.; Orriols, M.; Galan, M.; Cañes, L.; Aguilo, S.; Sirvent, M.; Martínez-González, J.; Rodríguez, C. Lysyl oxidase (LOX) limits VSMC proliferation and neointimal thickening through its extracellular enzymatic activity. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 13258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Nellaiappan, K.; Strassmaier, T.; Graham, L.; Thomas, K.M.; Kagan, H.M. Localization and activity of lysyl oxidase within nuclei of fibrogenic cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 12817–12822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nellaiappan, K.; Risitano, A.; Liu, G.; Nicklas, G.; Kagan, H.M. Fully processed lysyl oxidase catalyst translocates from the extracellular space into nuclei of aortic smooth-muscle cells. J. Cell Biochem. 2000, 79, 576–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giampuzzi, M.; Botti, G.; Di Duca, M.; Arata, L.; Ghiggeri, G.; Gusmano, R.; Ravazzolo, R.; Di Donato, A. Lysyl oxidase activates the transcription activity of human collagene III promoter. Possible involvement of Ku antigen. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 36341–36349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giampuzzi, M.; Oleggini, R.; Di Donato, A. Demonstration of in vitro interaction between tumor suppressor lysyl oxidase and histones H1 and H2: Definition of the regions involved. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2003, 1647, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oleggini, R.; Gastaldo, N.; Di Donato, A. Regulation of elastin promoter by lysyl oxidase and growth factors: Cross control of lysyl oxidase on TGF-beta1 effects. Matrix Biol. 2007, 26, 494–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saad, F.A.; Torres, M.; Wang, H.; Graham, L. Intracellular lysyl oxidase: Effect of a specific inhibitor on nuclear mass in proliferating cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010, 396, 944–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Detrano, R.; Guerci, A.D.; Carr, J.J.; Bild, D.E.; Burke, G.; Folsom, A.R.; Liu, K.; Shea, S.; Szklo, M.; Bluemke, D.A.; et al. Coronary calcium as a predictor of coronary events in four racial or ethnic groups. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 358, 1336–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, S.A.; Bakker, M.; den Ruijter, H.M.; Bots, M.L. Added value of CAC in risk stratification for cardiovascular events: A systematic review. Eur. J. Clin. Invest. 2012, 42, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenland, P.; LaBree, L.; Azen, S.P.; Doherty, T.M.; Detrano, R.C. Coronary artery calcium score combined with Framingham score for risk prediction in asymptomatic individuals. JAMA 2004, 291, 210–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugitani, H.; Wachi, H.; Mecham, R.P.; Seyama, Y. Accelerated calcification represses the expression of elastic fiber components and lysyl oxidase in cultured bovine aortic smooth muscle cells. J. Atheroscler. Thromb. 2002, 9, 292–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Hutson, H.N.; Marohl, T.; Anderson, M.; Eliceiri, K.; Campagnola, P.; Masters, K.S. Calcific aortic valve disease is associated with layer-specific alterations in collagen architecture. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0163858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willum-Hansen, T.; Staessen, J.A.; Torp-Pedersen, C.; Rasmussen, S.; Thijs, L.; Ibsen, H.; Jeppesen, J. Prognostic value of aortic pulse wave velocity as index of arterial stiffness in the general population. Circulation 2006, 113, 664–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laurent, S.; Cockcroft, J.; Van Bortel, L.; Boutouyrie, P.; Giannattasio, C.; Hayoz, D.; Pannier, B.; Vlachopoulos, C.; Wilkinson, I.; Struijker-Boudier, H. European Network for Non-invasive Investigation of Large Arteries. Expert consensus document on arterial stiffness: Methodological issues and clinical applications. Eur. Heart J. 2006, 27, 2588–2605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, G.F. Arterial stiffness and hypertension: Chicken or egg? Hypertension 2014, 64, 210–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Revelles, S.; García-Redondo, A.B.; Avendaño, M.S.; Varona, S.; Palao, T.; Orriols, M.; Roque, F.R.; Fortuño, A.; Touyz, R.M.; Martínez-González, J.; et al. Lysyl oxidase induces vascular oxidative stress and contributes to arterial stiffness and abnormal elastin structure in hypertension: Role of p38MAPK. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2017, 27, 379–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, J.M.; Briones, A.M.; Starcher, B.; Conde, M.V.; Somoza, B.; Daly, C.; Vila, E.; McGrath, I.; González, M.C.; Arribas, S.M. Influence of elastin on rat small artery mechanical properties. Exp. Physiol. 2005, 90, 463–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eberson, L.S.; Sanchez, P.A.; Majeed, B.A.; Tawinwung, S.; Secomb, T.W.; Larson, D.F. Effect of lysyl oxidase inhibition on angiotensin II-induced arterial hypertension, remodeling, and stiffness. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0124013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staiculescu, M.C.; Kim, J.; Mecham, R.P.; Wagenseil, J.E. Mechanical behavior and matrisome gene expression in the aneurysm-prone thoracic aorta of newborn lysyl oxidase knockout mice. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2017, 313, H446–H456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levy, D.; Larson, M.G.; Benjamin, E.J.; Newton-Cheh, C.; Wang, T.J.; Hwang, S.J.; Vasan, R.S.; Mitchell, G.F. Framingham heart study 100K project: Genome-Wide associations for blood pressure and arterial stiffness. BMC Med. Genet. 2007, 8, S3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steppan, J.; Wang, H.; Bergman, Y.; Rauer, M.J.; Tan, S.; Jandu, S.; Nandakumar, K.; Barreto-Ortiz, S.; Cole, R.N.; Boronina, T.N.; et al. Lysyl oxidase-like 2 depletion is protective in age-associated vascular stiffening. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2019, 317, H49–H59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, H.; Zhu, Y.; Sun, Z.; Trzeciakowski, J.P.; Gansner, M.; Depre, C.; Resuello, R.R.; Natividad, F.F.; Hunter, W.C.; Genin, G.M.; et al. Short communication: Vascular smooth muscle cell stiffness as a mechanism for increased aortic stiffness with aging. Circ. Res. 2010, 107, 615–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bignon, M.; Pichol-Thievend, C.; Hardouin, J.; Malbouyres, M.; Bréchot, N.; Nasciutti, L.; Barret, A.; Teillon, J.; Guillon, E.; Etienne, E.; et al. Lysyl oxidase-like protein-2 regulates sprouting angiogenesis and type IV collagen assembly in the endothelial basement membrane. Blood 2011, 118, 3979–3989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Toro, R.; Prahst, C.; Mathivet, T.; Siegfried, G.; Kaminker, J.S.; Larrivee, B.; Breant, C.; Duarte, A.; Takakura, N.; Fukamizu, A.; et al. Identification and functional analysis of endothelial tip cell-enriched genes. Blood 2010, 116, 4025–4033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Jong, O.G.; van der Waals, L.M.; Kools, F.R.W.; Verhaar, M.C.; van Balkom, B.W.M. Lysyl oxidase-like 2 is a regulator of angiogenesis through modulation of endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition. J. Cell Physiol. 2019, 234, 10260–10269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaffryar-Eilot, S.; Marshall, D.; Voloshin, T.; Bar-Zion, A.; Spangler, R.; Kessler, O.; Ghermazien, H.; Brekhman, V.; Suss-Toby, E.; Adam, D.; et al. Lysyl oxidase-like-2 promotes tumour angiogenesis and is a potential therapeutic target in angiogenic tumours. Carcinogenesis 2013, 34, 2370–2379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Barry-Hamilton, V.; Spangler, R.; Marshall, D.; McCauley, S.; Rodriguez, H.M.; Oyasu, M.; Mikels, A.; Vaysberg, M.; Ghermazien, H.; Wai, C.; et al. Allosteric inhibition of lysyl oxidase-like-2 impedes the development of a pathologic microenvironment. Nat. Med. 2010, 16, 1009–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.; Lucas, M.C.; Leonte, L.E.; Garcia-Montolio, M.; Singh, L.B.; Findlay, A.D.; Deodhar, M.; Foot, J.S.; Jarolimek, W.; Timpson, P.; et al. Pre-clinical evaluation of small molecule LOXL2 inhibitors in breast cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 26066–26078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, A.M.; Bird, D.; Welti, J.C.; Gourlaouen, M.; Lang, G.; Murray, G.I.; Reynolds, A.R.; Cox, T.R.; Erler, J.T. Lysyl oxidase plays a critical role in endothelial cell stimulation to drive tumor angiogenesis. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 583–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osawa, T.; Ohga, N.; Akiyama, K.; Hida, Y.; Kitayama, K.; Kawamoto, T.; Yamamoto, K.; Maishi, N.; Kondoh, M.; Onodera, Y.; et al. Lysyl oxidase secreted by tumour endothelial cells promotes angiogenesis and metastasis. Br. J. Cancer. 2013, 109, 2237–2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossow, L.; Veitl, S.; Vorlová, S.; Wax, J.K.; Kuhn, A.E.; Maltzahn, V.; Upcin, B.; Karl, F.; Hoffmann, H.; Gätzner, S.; et al. LOX-catalyzed collagen stabilization is a proximal cause for intrinsic resistance to chemotherapy. Oncogene 2018, 37, 4921–4940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nareshkumar, R.N.; Sulochana, K.N.; Coral, K. Inhibition of angiogenesis in endothelial cells by human lysyl oxidase propeptide. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 10426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Feng, M.; Ma, J.; Li, J.; Yang, X.; Fang, F.; Xia, Q.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Exosome-mediated secretion of LOXL4 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma cell invasion and metastasis. Mol. Cancer. 2019, 18, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucharzewska, P.; Christianson, H.C.; Welch, J.E.; Svensson, K.J.; Fredlund, E.; Ringnér, M.; Mörgelin, M.; Bourseau-Guilmain, E.; Bengzon, J.; Belting, M. Exosomes reflect the hypoxic status of glioma cells and mediate hypoxia-dependent activation of vascular cells during tumor development. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 7312–7317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kore, R.A.; Edmondson, J.L.; Jenkins, S.V.; Jamshidi-Parsian, A.; Dings, R.P.M.; Reyna, N.S.; Griffin, R.J. Hypoxia-derived exosomes induce putative altered pathways in biosynthesis and ion regulatory channels in glioblastoma cells. Biochem. Biophys. Rep. 2018, 14, 104–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Santamaría, J.; Villalba, M.; Busnadiego, O.; López-Olañeta, M.M.; Sandoval, P.; Snabel, J.; López-Cabrera, M.; Erler, J.T.; Hanemaaijer, R.; Lara-Pezzi, E.; et al. Matrix cross-linking lysyl oxidases are induced in response to myocardial infarction and promote cardiac dysfunction. Cardiovasc. Res. 2016, 109, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badenhorst, D.; Maseko, M.; Tsotetsi, O.J.; Naidoo, A.; Brooksbank, R.; Norton, G.R.; Woodiwiss, A.J. Cross-linking influences the impact of quantitative changes inmyocardial collagen on cardiac stiffness and remodelling in hypertension in rats. Cardiovasc. Res. 2003, 57, 632–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanon, I.; Valero-Muñoz, M.; Fernandes, A.A.; Ribeiro, R.F., Jr.; Rodríguez, C.; Miana, M.; Martínez-González, J.; Spalenza, J.S.; Lahera, V.; Vassallo, P.F.; et al. Left and right ventricle late remodeling following myocardial infarction in rats. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e64986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norton, G.R.; Tsotetsi, J.; Trifunovic, B.; Hartford, C.; Candy, G.P.; Woodiwiss, A.J. Myocardial stiffness is attributed to alterations in cross-linked collagen rather than total collagen or phenotypes in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Circulation 1997, 96, 1991–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López, B.; Querejeta, R.; González, A.; Larman, M.; Díez, J. Collagen cross-linking but not collagen amount associates with elevated filling pressures in hypertensive patients with stage C heart failure: Potential role of lysyl oxidase. Hypertension 2012, 60, 677–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasner, M.; Westermann, D.; Lopez, B.; Gaub, R.; Escher, F.; Kühl, U.; Schultheiss, H.P.; Tschöpe, C. Diastolic tissue Doppler indexes correlate with the degree of collagen expression and crosslinking in heart failure and normal ejection fraction. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2011, 57, 977–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galán, M.; Varona, S.; Guadall, A.; Orriols, M.; Navas, M.; Aguiló, S.; de Diego, A.; Navarro, M.A.; García-Dorado, D.; Rodríguez-Sinovas, A.; et al. Lysyl oxidase over-expression accelerates cardiac remodelling and aggravates angiotensin II-induced hypertrophy. FASEB J. 2017, 31, 3787–3799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Savvatis, K.; Kang, J.S.; Fan, P.; Zhong, H.; Schwartz, K.; Barry, V.; Mikels-Vigdal, A.; Karpinski, S.; Kornyeyev, D.; et al. Targeting LOXL2 for cardiac interstitial fibrosis and heart failure treatment. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 13710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Putten, S.; Shafieyan, Y.; Hinz, B. Mechanical control of cardiac myofibroblasts. J. Mol. Cell Cardiol. 2016, 93, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voloshenyuk, T.G.; Landesman, E.S.; Khoutorova, E.; Hart, A.D.; Gardner, J.D. Induction of cardiac fibroblast lysyl oxidase by TGF-β1 requires PI3K/Akt, Smad3, and MAPK signaling. Cytokine 2011, 55, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Qin, Q.; Yao, J.; Sun, L.; Qin, X. Induction of LOX by TGF-β1/Smad/AP-1 signaling aggravates rat myocardial fibrosis and heart failure. IUBMB Life 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubota, T.; McTiernan, C.F.; Frye, C.S.; Slawson, S.E.; Lemster, B.H.; Koretsky, A.P.; Demetris, A.J.; Feldman, A.M. Dilated cardiomyopathy in transgenic mice with cardiac-specific overexpression of tumor necrosis factor-alpha. Circ. Res. 1997, 81, 627–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voloshenyuk, T.G.; Hart, A.D.; Khoutorova, E.; Gardner, J.D. TNF-α increases cardiac fibroblast lysyl oxidase expression through TGF-β and PI3Kinase signaling pathways. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2011, 413, 370–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, B.; González, A.; Lindner, D.; Westermann, D.; Ravassa, S.; Beaumont, J.; Gallego, I.; Zudaire, A.; Brugnolaro, C.; Querejeta, R.; et al. Osteopontin-mediated myocardial fibrosis in heart failure: A role for lysyl oxidase? Cardiovasc. Res. 2013, 99, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Q.; Vazquez, R.; Zabadi, S.; Watson, R.R.; Larson, D.F. T-lymphocytes mediate left ventricular fibrillar collagen cross-linking and diastolic dysfunction in mice. Matrix Biol. 2010, 29, 511–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahsan, T.; Lottman, L.M.; Harwood, F.; Amiel, D.; Sah, R.L. Integrative cartilage repair: Inhibition by beta-aminopropionitrile. J. Orthop. Res. 1999, 17, 850–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spencer, P.S.; Schaumburg, H.H. Lathyrism: A neurotoxic disease. Neurobehav. Toxicol. Teratol. 1983, 5, 625–629. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Turecek, C.; Fratzl-Zelman, N.; Rumpler, M.; Buchinger, B.; Spitzer, S.; Zoehrer, R.; Durchschlag, E.; Klaushofer, K.; Paschalis, E.P.; Varga, F. Collagen cross-linking influences osteoblastic differentiation. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2008, 82, 392–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dasler, W. Isolation of toxic crystals from sweet peas (Lathyrus odoratus). Science 1954, 120, 307–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fickert, P. Is this the last requiem for Simtuzumab? Hepatology 2019, 69, 476–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowbottom, M.W.; Bain, G.; Calderon, I.; Lasof, T.; Lonergan, D.; Lai, A.; Huang, F.; Darlington, J.; Prodanovich, P.; Santini, A.M.; et al. Identification of 4-(aminomethyl)-6-(trifluoromethyl)-2-(phenoxy)pyridine derivatives as potent, selective, and orally efficacious inhibitors of the copper-dependent amine oxidase, lysyl oxidase-like 2 (LOXL2). J. Med. Chem. 2017, 60, 4403–4423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, B.; Querejeta, R.; González, A.; Beaumont, J.; Larman, M.; Díez, J. Impact of treatment on myocardial lysyl oxidase expression and collagen cross-linking in patients with heart failure. Hypertension 2009, 53, 236–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miguel-Carrasco, J.L.; Beaumont, J.; San José, G.; Moreno, M.U.; López, B.; González, A.; Zalba, G.; Díez, J.; Fortuño, A.; Ravassa, S. Mechanisms underlying the cardiac antifibrotic effects of losartan metabolites. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 41865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Martínez-González, J.; Varona, S.; Cañes, L.; Galán, M.; Briones, A.M.; Cachofeiro, V.; Rodríguez, C. Emerging Roles of Lysyl Oxidases in the Cardiovascular System: New Concepts and Therapeutic Challenges. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 610. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom9100610
Martínez-González J, Varona S, Cañes L, Galán M, Briones AM, Cachofeiro V, Rodríguez C. Emerging Roles of Lysyl Oxidases in the Cardiovascular System: New Concepts and Therapeutic Challenges. Biomolecules. 2019; 9(10):610. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom9100610
Chicago/Turabian StyleMartínez-González, José, Saray Varona, Laia Cañes, María Galán, Ana M Briones, Victoria Cachofeiro, and Cristina Rodríguez. 2019. "Emerging Roles of Lysyl Oxidases in the Cardiovascular System: New Concepts and Therapeutic Challenges" Biomolecules 9, no. 10: 610. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom9100610
APA StyleMartínez-González, J., Varona, S., Cañes, L., Galán, M., Briones, A. M., Cachofeiro, V., & Rodríguez, C. (2019). Emerging Roles of Lysyl Oxidases in the Cardiovascular System: New Concepts and Therapeutic Challenges. Biomolecules, 9(10), 610. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom9100610







