Abstract
Alternative therapeutic approaches against chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection need to be urgently developed because current therapies are only virostatic. In this context, cell penetration peptides (CPPs) and their Peptide Nucleic Acids (PNAs) cargoes appear as a promising novel class of biologically active compounds. In this review we summarize different in vitro and in vivo studies, exploring the potential of CPPs as vehicles for intracellular delivery of PNAs targeting hepadnaviral replication. Thus, studies conducted in the duck HBV (DHBV) infection model showed that conjugation of (D-Arg)8 CPP to PNA targeting viral epsilon (ε) were able to efficiently inhibit viral replication in vivo following intravenous administration to ducklings. Unexpectedly, some CPPs, (D-Arg)8 and Decanoyl-(D-Arg)8, alone displayed potent antiviral effect, altering late stages of DHBV and HBV morphogenesis. Such antiviral effects of CPPs may affect the sequence-specificity of CPP-PNA conjugates. By contrast, PNA conjugated to (D-Lys)4 inhibited hepadnaviral replication without compromising sequence specificity. Interestingly, Lactose-modified CPP mediated the delivery of anti-HBV PNA to human hepatoma cells HepaRG, thus improving its antiviral activity. In light of these promising data, we believe that future studies will open new perspectives for translation of CPPs and CPP-PNA based technology to therapy of chronic hepatitis B.
1. Introduction
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection is still a major public health issue, with over 240 million virus carriers worldwide. Indeed, chronic HBV infection significantly increases the risk for the development of end stage liver diseases such as cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) []. Currently, there are two major types of anti-HBV therapeutic strategies, nucleos(t)ide analogues (NAs) that inhibit viral reverse transcriptase and the immune-based treatments such as interferon-α and pegylated-interferon alpha (pegylated-IFN-α). These antiviral therapies are only partially effective as they are unable to eradicate the viral persistence reservoir, an episomal covalently closed circular (ccc) DNA in the infected cells that is responsible for viral relapse after treatment cessation [,].
Moreover, the long-term use of these therapies increases the risk of drug resistance and of serious side effects. Therefore, alternative therapeutic approaches need to be urgently developed to eradicate chronic hepatitis B infection.
In recent years, cell penetrating peptides (CPP)s appeared of interest for non-viral delivery of different antisense macromolecules targeting HBV replication. Within different antisense agents, peptide nucleic acids (PNAs) provide a potentially promising approach to treat chronic HBV infection. Indeed, PNAs are DNA mimics containing an uncharged pseudopeptide backbone with N-(2-aminoethyl)-glycine units to which the nucleobases are attached via methylene carbonyl linkers []. These nucleic analogues are capable of sequence-specific recognition of DNA and RNA through Watson-Crick base pairing [,]. Furthermore, PNAs have attractive potential as antiviral agents because of their high hybridization affinity and specificity. Importantly, PNAs exhibit resistance to protease and nuclease degradation in the cells, fluids, and tissues, showing an exceptional stability in biological environments [,,]. Thus, we have previously demonstrated a potent effect of PNA targeting of the hepadnaviral ε sequence, leading to sequence-specific inhibition of viral reverse transcription in a cell-free system [,].
However, the application of PNAs as antiviral therapeutics has been hampered by their poor cell uptake and biodistribution due to their uncharged structure. To overcome these difficulties, the conjugation of PNAs to CPPs appears as a strategy of choice to enhance their delivery into cells [,].
In this context, several studies documented the role of CPPs in intracellular delivery of biologically active cargos such as PNAs to the host tissues. Thus, different CPPs such as oligoarginine [,,] and oligolysine [,] were shown to efficiently internalize PNAs through the cell membrane. These CPPs are small in size (less than 30 residues) and have been shown to considerably increase the cellular uptake and antisense activity of their cargos. However, data on antiviral activity of CPP-PNAs conjugates in the control of HBV infection were scarce and limited to the murine model.
We explored the ability of CPP-PNA conjugates to inhibit HBV replication. Because HBV, displays an extremely narrow host range, infecting only humans and chimpanzee, we have chosen the closely related duck HBV (DHBV) as a model virus. DHBV belongs to the Hepadnaviridae family, encompassing mammalian and avian viruses. Hepadnaviruses are small, enveloped DNA viruses that replicate in the liver of their hosts []. The Eastern woodchuck and Pekin duck, which are natural hosts of DHBV and woodchuck hepatitis B virus (WHV), respectively, played an important role in the understanding of the hepadnaviral replication pathway and in the in vivo evaluation of novel therapeutic approaches against chronic hepatitis B infection. Both DHBV and WHV share with the human HBV a similar genome organization and replication pathway via the reverse transcription of pregenomic RNA [].
Interestingly, the DHBV model allows study of innovative anti-HBV strategies both in vivo in DHBV-carrier ducklings and in vitro in primary duck hepatocytes (PDH) or stably transfected cell lines. Thus, DHBV represents an attractive model system validated by us and others for the evaluation of novel anti-HBV strategies in preclinical studies [,,,,,].
Because the major problem of in vivo PNAs delivery is a poor cellular uptake, as a first step, we investigated in Pekin ducklings the uptake and biodistribution of fluorescein isothiocyante (FITC)-labeled PNA (FITC-PNA) administrated via different routes [].
Next, we evaluated in this model the antiviral activity of different CPPs for delivery to hepatocytes of a PNA targeting hepadnaviral encapsidation signal (ε). The results generated in vitro in DHBV-infected PDH cultures and in vivo virus-carrier ducklings allowed identification of a CPP-PNA conjugate that specifically inhibited DHBV replication following low-dose administration [].
Surprisingly, in a pilot study we observed an anti-DHBV activity of (DArg)8 CPP alone when used as a control in the absence of its PNA cargo [,]. Based on this unexpected finding, we have further investigated the antiviral activity of different CPPs and their lipid domain conjugates (CatLips). The detailed analysis of impact of these CatLips on different steps in hepadnaviral replication allowed us to identify their novel mechanism of action [].
In addition, sugar-based CPP conjugated to a PNA targeting the HBV surface (S) gene was evaluated in this report. Our preliminary findings demonstrated that treatment of HBV-infected HepaRG cells by CPP-PNA conjugate coupled to Lactose inhibited HBV surface antigen (HBsAg) release.
This review focuses on the crucial role of cationic polymers as cargos and on the advantage of their modifications for intracellular delivery of PNAs targeting hepadnaviral RNA and envelope proteins. Thus, CPPs can mediate intracellular uptake of bioactive agents and consequently improve their biological activities. Moreover, some CPPs exhibit a potent antiviral activity on hepadnavirus replication, which can alter the specificity of viral inhibition displayed by their antisense PNA cargo. This antiviral activity can be strongly increased when these CPPs were modified by the fatty acid domains. In addition, the anti-HBV activity of CPP-PNA conjugated to another delivery system such as sugar moieties is also documented in this report.
2. Why Cell Penetrating Peptides Are of Particular Interest for Delivery of Bioactive Molecules
Various bioactive molecules, including PNAs, need to cross the cellular membrane to exhibit their activity. In this view, different CPPs also termed PTDs (for protein transduction domains), MTSs (for membrane translocation sequences), or CTPs (for cytoplasmic transduction peptides) [,] are short cationic sequences that are able to cross the cellular plasma membranes and transport bioactive molecules into a variety of cells without detectable toxicity [,,,].
To date, several cationic peptides have been described such as the transactivator of transcription (TAT) peptide from Human Immunodeficiency Virus’ (HIV’s) transactivator of transcription protein. TAT peptide represents the first cationic CPP discovered that was able to cross the lipid bilayer cell membrane and powerfully enter into the cells [,]. Thus, Song et al. reported that camptothecin (CPT) coupled to a TAT peptide (TAT-CPT and TAT-2CPT) could kill cancer cells by releasing the CPT after entering the cells []. In addition, the gold nanoparticles (AuNP) coupled to two derivatives of TAT peptide of 5 nm diameter (AuNP-CPPs) exhibited a strong fluorescent signal in Gram positive and Gram negative bacterial strains. The confocal microscopy data showed that the derivatives of the TAT peptide improve nanoparticle internalization into bacterial cells [].
Identification of TAT was rapidly followed by the discovery of other cationic peptides displaying comparable uptake activity, including VP22, a herpes virus protein [], and Antennapedia, a transcription factor from drosophila, termed penetratin (pAntp) [,].
Recently, a novel CPP, designated X-pep, found at the extreme N-terminus of the X-protein of the HBV has been identified. Moreover, the truncated form of this X-pep peptide (Met-Ala-Ala-Arg-Leu amino acids (MAARL) sequence) was able to readily penetrate into hepatoblastoma G2 (HepG2) cells. Further truncation by removal of the terminal leucine amino acid reduced the cell-penetrating activity of this peptide, indicating that the MAARL sequence is the active core of this peptide [].
Importantly, the ability of these CPPs to translocate across the lipid bilayer of cell membranes was conferred by a short sequence rich in basic residues [].
4. Anti-Duck Hepatitis B Virus Effect of Peptide Nucleic Acids coupled to Cell Penetrating Peptides Conjugates
Antisense strategies appear to have promise for the control of chronic viral infections. In this view, we initially evaluated the antiviral potential of different antisense molecules such as phosphodiester oligodeoxynucleotides (ODNs), targeting the DHBV large envelope gene. Using the DHBV infection model, we demonstrated that such antisense ODNs complexed to polyethylenimine and administrated to neonatal ducklings via the i.v route were able to drastically inhibit hepadnaviral replication [].
The pregenomic RNA and hepadnaviral encapsidation signal ε play an important role in initiation of hepadnaviral reverse transcription (RT), and they appear as interesting targets for antiviral therapy [,]. To explore the capacity of anti-ε PNAs to inhibit viral replication, we first investigated their antiviral activity in vitro, in a cell-free system for enzymatically active DHBV RT expression. Our results indicated that PNA that targeted the bulge and upper stem of epsilon exhibited a potent and sequence-specific inhibitory effect on DHBV reverse transcriptase [].
Next, to investigate the in vivo antiviral effect of PNAs, we coupled the anti-ε PNA to a cationic CPP (D-Arg)8 to increase its cellular uptake. Indeed, the main difficulty in the use of PNAs as antivirals is their poor transport across the cell membrane and their limited intracellular biodistribution. To optimize the in vivo delivery of PNA-CPP conjugates and their bioavailability, we administrated PNA-CPP coupled to FITC or PNA-FITC in vivo to DHBV-free neonatal ducklings. The hepatocyte-associated fluorescence was analyzed by fluorescence microscopy 48 hours later. The results showed little or no hepatocyte-associated fluorescence after i.v injection of FITC-PNA not conjugated to (D-Arg)8, whereas the injection of FITC-CPP-PNA resulted in a high level of hepatocyte-associated fluorescence. This finding indicates that (D-Arg)8 CPP is able to efficiently deliver anti-ε PNA to the liver following intravenous injection ([] and unpublished observations). Moreover, the i.v injection of a FITC-PNA(D-Arg)8 to ducklings was more effective than the intraperitoneal (i.p.) route as only following i.v administration was the FITC-PNA detected in the hepatocytes []. This differs from the mouse model in which i.p. injection resulted in better delivery of PNAs. In addition, our findings demonstrated for the first time that intravenous administration of CPP-PNA conjugates to ducklings, i.e. larger animals than mice, resulted in an effective delivery of these conjugates to hepatocytes that was associated with an antiviral effect [].
We next asked whether such anti-ε PNA conjugated to (D-Arg)8 inhibits hepadnaviral replication in vivo in the DHBV infection model []. Thus, DHBV-infected ducklings were treated with this (D-Arg)8-PNA conjugate (1 μg/g body weight/day) for six days. At the end of this treatment, the analysis of serum and liver DNA revealed a marked decrease in viremia and liver DHBV DNA, i.e. a decrease of about 50% in treated animals compared with the untreated controls (Table 1).
Surprisingly, 2 nt mismatched PNA coupled to the same (DArg)8 CPP and used as control also inhibited viral replication. Therefore, an antiviral activity of (D-Arg)8 was suspected. Indeed, the i.v administration of (DArg)8 alone to DHBV-infected ducklings resulted in a decrease in viremia, confirming the ability of this CPP to inhibit hepadnaviral replication (as detailed above). Altogether, these findings indicate that anti-DHBV activity exhibited by (DArg)8 CPP alone may explain the limited sequence specificity of this CPP-PNA conjugate. No loss of weight was observed in all treated animals compared with the untreated control animals during the six days of treatment (data not shown), showing the absence of in vivo toxicity of (DArg)8-PNA conjugates and of (DArg)8 alone.
To better understand the role of CPPs used as a vehicle in delivery of PNAs, we examined the antiviral activity of the same anti-ε PNA but conjugated to another cationic CPP, (D-Lys)4 in vitro, in PDH. Moreover, the antiviral activity of this (D-Lys)4 CPP alone was analyzed. Thus, treatment of DHBV-infected PDH by (D-Lys)4-PNA conjugates led to a marked inhibition of DHBV release in cell culture supernatants and to a decrease in intracellular viral replication.
Interestingly, this inhibition was specific, since a 2-nucleotides mismatched PNA conjugated to the same (D-Lys)4 CPP, displayed no pronounced inhibitory activity on DHBV secretion and on intracellular DHBV DNA. Importantly, the treatment of the same cells by (D-Lys)4 CPP alone did not affect viral replication []. Remarkably, neither (D-Lys)4 and its corresponding bonding CPP-PNA conjugates displayed toxicity in PDH cells, as assessed by Neutral Red test [].
Collectively, these findings demonstrate that the antiviral activity of some cationic CPPs such as (DArg)8, used as vehicles to improve cellular uptake of their bioactive PNA cargos, may reduce the sequence-specificity of CPP-PNA conjugates. In contrast, in the absence of the inhibitory effect exhibited by these cationic CPPs, the CPP-PNA conjugates are able to specifically inhibit hepadnaviral replication [].
Other preclinical studies demonstrated the benefit of CPP or PTD peptides used as vehicles. Indeed, PTD-p53 conjugates effectively suppressed production of HBV messenger RNAs (mRNAs), as well as HBsAg, HBeAg, and HBcAg, both in vitro and in vivo []. Also, CTP peptides improved Tapasin uptake and enhanced cytotoxic T lymphocyte activity []. Interestingly, the single-chain antibody targeting the hepatitis B core protein and coupled to the CPP was internalized into HepG2.2.15 cells and inhibited HBV replication in vitro [].
5. Sugar Modified CPP-PNA Uptake and Their Anti-HBV Activity in HepaRG Cells
The asialoglycoproteins receptors (ASGP-R) were the first mammalian lectins described [] and are found on the hepatocellular membranes. Thus, ASGP-R are known to facilitate the uptake into the hepatocytes through receptor-mediated endocytosis of a variety of ligands such as glycoproteins having a galactose-terminal carbohydrate. Indeed, the d-galactose-(poly)Lys- bovine serum albumin (BSA) complex improved the intracellular expression of the IX human factor gene in HepG2 cells []. Moreover, PNAs uptake by hepatocytes was enhanced following their incubation with an asialofetuin–oligonucleotide complex (AF/ODN) []. In addition, the sugar-dependent nuclear import of neoglycoproteins was shown to increase the expression of transferred genes [].
In another study, PNAs hybridized to the AF/ODN conjugates were efficiently internalized into murine primary hepatocytes and in HepG2 cells through receptor-mediated endocytosis. Indeed, after a 4-h incubation, PNAs were mainly localized in the nuclei of the cells. In addition, more than 70% inhibition of telomerase activity was detected when anti-human telomerase PNA was carried to HepG2 cells using AF/ODN. An in vivo study showed that the AF/ODN-PNAs conjugates led to an effective delivery of PNAs to the liver after intravenous injection into mice [].
We evaluated the anti-HBV activity of sugar-modified CPP-PNA conjugates in the HepaRG human hepatoma cell line. We chose HepaRG cells for this study since these cells when differentiated share different common features with human hepatocytes, including the expression of ASGP-R on their surface. Differentiated HepaRG cells can be effectively infected with HBV, reproducing a full viral replication cycle and cccDNA formation. Moreover, HepaRG are considered as a reference in vitro cell culture model for anti-HBV drug evaluation [,].
Therefore, we investigated in differentiated HepaRG cells whether a PNA that targets an HBV envelope protein coupled to a Lactose and Lysine, (Lac-(Lys)3-PNA), could HBsAg release. We first investigated the cellular uptake of Lac-(Lys)3-PNA coupled to FITC that was incubated with uninfected HepaRG cells. Our preliminary results showed uptake of fluorescein-labeled PNA indicating that Lac-CPP-PNA conjugates can enter into the HepaRG cells (Figure 1).
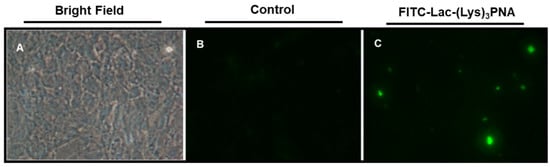
Figure 1.
Uptake of FITC-Lac-PNA in HepaRG cells. HepaRG cells were plated and incubated at 37 °C, 5% of CO2 with FITC-Lac-(Lys)3-PNA conjugates for 24 h. At the end of treatment, cells were observed by fluorescence microscopy (A) Bright field; (B) Control cells; (C) FITC-Lac-(Lys)3-PNA. FITC = fluorescein isothiocyante; Lac = lactose; PNA = peptide nucleic acids; Lys = lysine.
Next, the antiviral effect of this Lac-(Lys)3-PNA conjugate was evaluated in HBV-infected HepaRG cells. As illustrated in Figure 2, a marked decrease in the release of HBsAg into cell culture supernatants was observed, which was estimated at 53% inhibition as compared with untreated controls. Moreover, the inhibition was specific since a 2-nt mismatched PNA conjugated to the same vehicle (Lac-(Lys)3-mismatch peptide nucleic acid (MM PNA)) showed a far less marked (3%) inhibitory effect on the release of HBsAg.
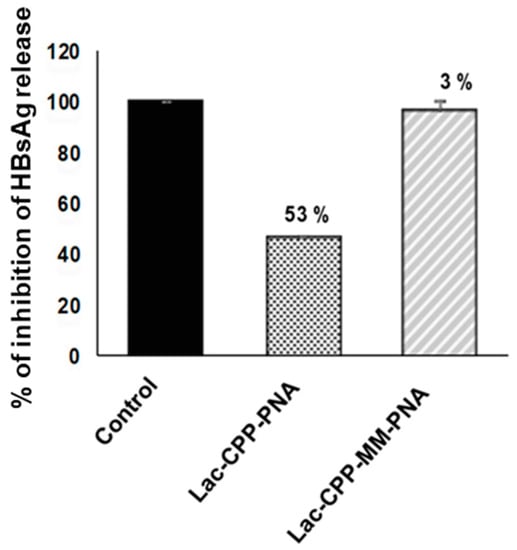
Figure 2.
Antiviral effect of Lac(Lys)3-PNA conjugates in vitro, in HBV-infected cells. HepaRG, human hepatocyte like cells, were plated and infected with HBV followed by treatment with Lac(Lys)3-PNA (Lac-CPP-PNA) or with its corresponding mismatch control (Lac-CPP-MMPNA). The cell culture supernatants were harvested daily and Hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) was quantified. Untreated HBV-infected control cells were considered as 100% and percentages of inhibition are indicated above the bars. The error bars display the standard deviation of duplicates.
Our preliminary results suggest an uptake of Lac-(Lys)3-PNA into hepatocytes via interaction of the Lactose moiety with ASGP-R, probably through receptor-mediated endocytosis. Altogether, these data demonstrate that treatment of HBV-infected HepaRG cells by anti-S PNA coupled to Lactose increases its uptake and decreases HBsAg release, although internalization and inhibitory potential of this novel conjugate need to be further investigated.
7. Conclusions
Taken together, different studies demonstrated an important role of CPPs or modified-CPPs in the intracellular delivery of PNAs that target the hepadnaviral replication pathway. Indeed, in the DHBV infection model, PNA that targets the viral encapsidation ε signal and is coupled to CPPs decreased viral replication in vitro in PDHs and in vivo in ducklings. Interestingly, some CPPs, (D-Arg)8 and Decanoyl-(D-Arg)8, alone displayed a potent antiviral effect, altering the late stages of DHBV and HBV morphogenesis. In addition, lipid and sugar domain-conjugated CPPs delivered their PNA cargos into hepatocytes and displayed an increased antiviral activity. Importantly, an anti-HBV PNA coupled to Lactose exhibited a high affinity to the asialoglycoprotein receptor on hepatocellular membranes and was shown to enter into the human hepatoma HepaRG cells and inhibit HBsAg release.
Thus, these different preclinical studies provide the evidence that CPPs, modified-CPP, and CPP-PNAs conjugates represent pertinent molecular tools for future development of novel therapeutic approaches to fight chronic hepatitis B infection. Further studies are warranted to explore the antiviral potency of these compounds, targeting different steps of hepadnaviral replication, which could be used in combination with immune therapies able to break immune tolerance in HBV-carrier patients and to enhance viral infection clearance.
Moreover, CPPs and modified CPPs appear of promise for development of novel antiviral strategies against different RNA and DNA viruses.
Author Contributions
B.N. performed experiments, analyzed data and wrote the paper; O.H. and G.J.L. provided materials and conceptual advice; L.C., designed experiments and wrote the paper.
Funding
This work was supported by INSERM.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Peter E. Nielsen and Fabien Abdul for stimulating discussion and Eric Duverger for the design and synthesis of Lactose-conjugated PNAs.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Trépo, C.; Chan, H.L.; Lok, A. Hepatitis B virus infection. Lancet 2014, 384, 2053–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoulim, F.; Locarnini, S. Hepatitis B virus resistance to nucleos(t)ide analogues. Gastroenterology 2009, 137, 1593–1608.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scaglione, S.J.; Lok, A.S. Effectiveness of hepatitis B treatment in clinical practice. Gastroenterology 2012, 142, 1360–1368.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, P.E.; Egholm, M.; Berg, R.H.; Buchardt, O. Sequence-selective recognition of DNA by strand displacement with a thymine-substituted polyamide. Science 1991, 254, 1497–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egholm, M.; Buchardt, O.; Christensen, L.; Behrens, C.; Freier, S.M.; Driver, D.A.; Berg, R.H.; Kim, S.K.; Norden, B.; Nielsen, P.E. PNA hybridizes to complementary oligonucleotides obeying the Watson-Crick hydrogen-bonding rules. Nature 1993, 365, 566–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, K.K.; Orum, H.; Nielsen, P.E.; Nordén, B. Kinetics for hybridization of peptide nucleic acids (PNA) with DNA and RNA studied with the BIAcore technique. Biochemistry 1997, 36, 5072–5077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demidov, V.V.; Potaman, V.N.; Frank-Kamenetskii, M.D.; Egholm, M.; Buchard, O.; Sönnichsen, S.H.; Nielsen, P.E. Stability of peptide nucleic acids in human serum and cellular extracts. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1994, 48, 1310–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robaczewska, M.; Narayan, R.; Seigneres, B.; Schorr, O.; Thermet, A.; Podhajska, A.J.; Trepo, C.; Zoulim, F.; Nielsen, P.E.; Cova, L. Sequence-specific inhibition of duck hepatitis B virus reverse transcription by peptide nucleic acids (PNA). J. Hepatol. 2005, 42, 180–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ndeboko, B.; Lemamy, G.J.; Nielsen, P.E.; Cova, L. Therapeutic Potential of Cell Penetrating Peptides (CPPs) and Cationic Polymers for Chronic Hepatitis B. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 28230–28241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ndeboko, B.; Ramamurthy, N.; Lemamy, G.J.; Jamard, C.; Nielsen, P.E.; Cova, L. Role of Cell-Penetrating Peptides in Intracellular Delivery of Peptide Nucleic Acids Targeting Hepadnaviral Replication. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2017, 9, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.H.; Chen, C.P.; Chan, M.H.; Chang, M.; Hou, Y.W.; Chen, H.H.; Hsu, H.R.; Liu, K.; Lee, H.J. Arginine-rich intracellular delivery peptides noncovalently transport protein into living cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006, 346, 758–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, Y.; Kogure, K.; Futaki, S.; Harashima, H. Octaarginine-modified multifunctional envelope-type nano device for siRNA. J. Control. Release 2007, 119, 360–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalil, I.A.; Kogure, K.; Futaki, S.; Harashima, H. Octaarginine-modified liposomes: Enhanced cellular uptake and controlled intracellular trafficking. Int. J. Pharm. 2008, 354, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gemignani, F.; Kang, S.H.; Maier, M.A.; Manoharan, M.; Persmark, M.; Bortner, D.; Kole, R. Systemically delivered antisense oligomers upregulate gene expression in mouse tissues. Nat. Biotechnol. 2002, 20, 1228–1233. [Google Scholar]
- Abes, S.; Williams, D.; Prevot, P.; Thierry, A.; Gait, M.J.; Lebleu, B. Endosome trapping limits the efficiency of splicing correction by PNA-oligolysine conjugates. J. Control. Release 2006, 110, 595–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zoulim, F.; Saade, F.; Buronfosse, T.; Abdul, F.; Cova, L. Animal models for the study of infection. In Hepatitis B Virus; Locarnini, S., Lai, C.L., Eds.; International Medical Press: London, UK, 2008; Volume I, pp. 6.1–6.20. [Google Scholar]
- Rollier, C.; Sunyach, C.; Barraud, L.; Madani, N.; Jamard, C.; Trepo, C.; Cova, L. Protective and therapeutic effect of DNA-based immunization against hepadnavirus large envelope protein. Gastroenterology 1999, 116, 658–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robaczewska, M.; Narayan, R.; Seigneres, B.; Schorr, O.; Thermet, A.; Podhajska, A.J.; Trepo, C.; Zoulim, F.; Nielsen, P.E.; Cova, L. Inhibition of hepadnaviral replication by polyethylenimine-based intravenous delivery of antisense phosphodiester oligodeoxynucleotides to the liver. Gene Ther. 2001, 8, 874–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borel, C.; Schorr, O.; Durand, I.; Zoulim, F.; Kay, A.; Trepo, C.; Hantz, O. Initial amplification of duck hepatitis B virus covalently closed circular DNA after in vitro infection of embryonic duck hepatocytes is increased by cell cycle progression. Hepatology 2001, 34, 168–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seignères, B.; Martin, P.; Werle, B.; Schorr, O.; Jamard, C.; Rimsky, L.; Trépo, C.; Zoulim, F. Effects of pyrimidine and purine analog combinations in the duck hepatitis B virus infection model. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2003, 47, 1842–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cova, L.; Zoulim, F. Duck hepatitis B virus model in the study of hepatitis B virus. Methods Mol. Med. 2004, 96, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Quinet, J.; Jamard, C.; Burtin, M.; Lemasson, M.; Guerret, S.; Sureau, C.; Vaillant, A.; Cova, L. Nucleic acid polymer REP 2139 and nucleos(T)ide analogues act synergistically against chronic hepadnaviral infection in vivo in Pekin ducks. Hepatology 2018, 67, 2127–2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdul, F.; Ndeboko, B.; Buronfosse, T.; Zoulim, F.; Kann, M.; Nielsen, P.E.; Cova, L. Potent inhibition of late stages of hepadnavirus replication by a modified cell penetrating peptide. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e48721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sebbage, V. Cell-penetrating peptides and their therapeutic applications. Biosci. Horiz. 2009, 2, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xun, Y.; Pan, Q.; Tang, Z.; Chen, X.; Yu, Y.; Xi, M.; Zang, G. Intracellular-delivery of a single-chain antibody against hepatitis B core protein via cell-penetrating peptide inhibits hepatitis B virus replication in vitro. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2013, 31, 369–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holm, T.; Johansson, H.; Lundberg, P.; Pooga, M.; Lindgren, M.; Langel, U. Studying the uptake of cell-penetrating peptides. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 1001–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mae, M.; Langel, U. Cell-penetrating peptides as vectors for peptide, protein and oligonucleotide delivery. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2006, 6, 509–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bendifallah, N.; Rasmussen, F.W.; Zachar, V.; Ebbesen, P.; Nielsen, P.E.; Koppelhus, U. Evaluation of cell-penetrating peptides (CPPs) as vehicles for intracellular delivery of antisense peptide nucleic acid (PNA). Bioconjugate Chem. 2006, 17, 750–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruczynski, J.; Wierzbicki, P.M.; Kogut-Wierzbicka, M.; Mucha, P.; Siedlecka-Kroplewska, K.; Rekowski, P. Cell-penetrating peptides as a promising tool for delivery of various molecules into the cells. Folia Histochem. Cytobiol. 2014, 52, 257–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, M.; Loewenstein, P.M. Autonomous functional domains of chemically synthesized human immunodeficiency virus TAT trans-activator protein. Cell 1988, 55, 1179–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frankel, A.D.; Pabo, C.O. Cellular uptake of the TAT protein from human immunodeficiency virus. Cell 1988, 55, 1189–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Chen, J.; Yang, X.; Ma, P.; Zhang, B.; Liu, B.; Ni, J.; Wang, R. Cell penetrating peptide TAT can kill cancer cells via membrane disruption after attachment of camptothecin. Peptides 2015, 63, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, M.; Tegge, W.; Wangoo, N.; Jain, R.; Sharma, R.K. Insights into cell penetrating peptide conjugated gold nanoparticles for internalization into bacterial cells. Biophys. Chem. 2018, 237, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elliott, G.; O’Hare, P. Intercellular trafficking and protein delivery by a herpesvirus structural protein. Cell 1997, 88, 223–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joliot, A.; Pernelle, C.; Deagostini-Bazin, H.; Prochiantz, A. Antennapedia homeobox peptide regulates neural morphogenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 1864–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derossi, D.; Joliot, A.H.; Chassaing, G.; Prochiantz, A. The third helix of the Antennapedia homeodomain translocates through biological membranes. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 10444–10450. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Montrose, K.; Yang, Y.; Krissansen, G.W. X-pep, a novel cell-penetrating peptide motif derived from the hepatitis B virus. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2014, 453, 64–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarze, S.R.; Ho, A.; Vocero-Akbani, A.; Dowdy, S.F. In vivo protein transduction: Delivery of a biologically active protein into the mouse. Science 1999, 285, 1569–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zorko, M.; Langel, U. Cell-penetrating peptides: Mechanism and kinetics of cargo delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2005, 57, 529–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, K.L.; Hancock, R.E. Cationic host defense (antimicrobial) peptides. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2006, 18, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, H.L. Herpes simplex virus type 1 morphogenesis and virus-cell interactions: Significance of cytoskeleton and methodological aspects. APMIS Suppl. 2006, 114, 7–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lizzi, A.R.; Carnicelli, V.; Clarkson, M.M.; Di Giulio, A.; Oratore, A. Lactoferrin derived peptides: Mechanisms of action and their perspectives as antimicrobial and antitumoral agents. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2009, 9, 687–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egal, M.; Conrad, M.; MacDonald, D.L.; Maloy, W.L.; Motley, M.; Genco, C.A. Antiviral effects of synthetic membrane-active peptides on herpes simplex virus, type 1. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 1999, 13, 57–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albiol Matanic, V.C.; Castilla, V. Antiviral activity of antimicrobial cationic peptides against Junin virus and herpes simplex virus. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2004, 23, 382–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roisin, A.; Robin, J.P.; Dereuddre-Bosquet, N.; Vitte, A.L.; Dormont, D.; Clayette, P.; Jalinot, P. Inhibition of HIV-1 replication by cell-penetrating peptides binding Rev. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 9208–9214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hancock, R.E.; Diamond, G. The role of cationic antimicrobial peptides in innate host defences. Trends Microbiol. 2000, 8, 402–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Lee, R.J.; Teng, L. Fatty acid modified octa-arginine for delivery of siRNA. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 495, 527–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruss, V. Envelopment of the hepatitis B virus nucleocapsid. Virus Res. 2004, 106, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambert, C.; Döring, T.; Prange, R. Hepatitis B virus maturation is sensitive to functional inhibition of ESCRT-III, Vps4, and γ2-adaptin. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 9050–9060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, X.B.; Wei, L.; Han, J.C.; Ma, H.; Deng, K.; Cong, X. Artificial recombinant cell-penetrating peptides interfere with envelopment of hepatitis B virus nucleocapsid and viral production. Antivir. Res. 2011, 89, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mhamdi, M.; Funk, A.; Hohenberg, H.; Will, H.; Sirma, H. Assembly and budding of a hepatitis B virus is mediated by a novel type of intracellular vesicles. Hepatology 2007, 46, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Köck, J.; Rösler, C.; Zhang, J.J.; Blum, H.E.; Nassal, M.; Thoma, C. Generation of covalently closed circular DNA of hepatitis B viruses via intracellular recycling is regulated in a virus specific manner. PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6, e1001082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.H.; Seeger, C. Novel mechanism for reverse transcription in hepatitis B viruses. J. Virol. 1993, 67, 6507–6512. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nassal, M.; Junker-Niepmann, M.; Schaller, H. Translational inactivation of RNA function: Discrimination against a subset of genomic transcripts during HBV nucleocapsid assembly. Cell 1990, 63, 1357–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, X.; Wu, B.; Fan, H.; Hou, J.; Hao, J.; Hu, J.; Wang, B.; Liu, G.; Li, C.; Meng, S. PTD-fused p53 as a potential antiviral agent directly suppresses HBV transcription and expression. Antivir. Res. 2016, 127, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Liu, H.; Tang, Z.; Yu, Y.; Zang, G. The modification of Tapasin enhances cytotoxic T lymphocyte activity of intracellularly delivered CTL epitopes via cytoplasmic transduction peptide. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2013, 45, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morell, A.G.; Irvine, R.A.; Sternlieb, I.; Scheinberg, I.H.; Ashwell, G. Physical and chemical studies on ceruloplasmin. V. Metabolic studies on sialic acid-free ceruloplasmin in vivo. J. Biol. Chem. 1968, 243, 155–159. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Faivre, V.; Fessi, H. Thérapie génique et vecteurs non-viraux: Ière partie—Des systèmes multiples. Lyon Pharm. 2000, 51, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Obara, K.; Ishihara, T.; Akaike, T.; Maruyama, A. Protein/oligonucleotide conjugates as a cell specific PNA carrier. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001, 1, 217–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monsigny, M.; Rondanino, C.; Duverger, E.; Fajac, I.; Roche, A.C. Glyco-dependent nuclear import of glycoproteins, glycoplexes and glycosylated plasmids. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2004, 1673, 94–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishihara, T.; Kano, A.; Obara, K.; Saito, M.; Chen, X.; Park, T.G.; Akaike, T.; Maruyama, A. Nuclear localization and antisense effect of PNA internalized by ASGP-R-mediated endocytosis with protein/DNA conjugates. J. Control. Release 2011, 155, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gripon, P.; Rumin, S.; Urban, S.; Le Seyec, J.; Glaise, D.; Cannie, I.; Guyomard, C.; Lucas, J.; Trepo, C.; Guguen-Guillouzo, C. Infection of a human hepatoma cell line by hepatitis B virus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 15655–15660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hantz, O.; Parent, R.; Durantel, D.; Gripon, P.; Guguen-Guillouzo, C.; Zoulim, F. Persistence of the hepatitis B virus covalently closed circular DNA in HepaRG human hepatocyte-like cells. J. Gen. Virol. 2009, 90 Pt 1, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, S.A.; Teow, S.Y.; Omar, T.C.; Khoo, A.S.; Choon, T.S.; Yusoff, N.M. A Cell Internalizing Antibody Targeting Capsid Protein (p24) Inhibits the Replication of HIV-1 in T Cells Lines and PBMCs: A Proof of Concept Study. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0145986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keogan, S.; Passic, S.; Krebs, F.C. Infection by CXCR4-Tropic Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 Is Inhibited by the Cationic Cell-Penetrating Peptide Derived from HIV-1 Tat. Int. J. Pept. 2012, 349427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bivalkar-Mehla, S.; Mehla, R.; Chauhan, A. Chimeric peptide-mediated siRNA transduction to inhibit HIV-1 infection. J. Drug Target. 2017, 25, 307–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, J.S.; Kim, C.M.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, J.Y.; Oh, J.W. Inhibition of Japanese encephalitis virus replication by peptide nucleic acids targeting cis-acting elements on the plus- and minus-strands of viral RNA. Antivir. Res. 2009, 82, 122–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mino, T.; Mori, T.; Aoyama, Y.; Sera, T. Development of protein-based antiviral drugs for human papillomaviruses. Nucleic Acids Symp. Ser. 2007, 51, 427–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mino, T.; Mori, T.; Aoyama, Y.; Sera, T. Cell-permeable artificial zinc-finger proteins as potent antiviral drugs for human papillomaviruses. Arch. Virol. 2008, 153, 1291–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
