Capture of Pb2+ and Cu2+ Metal Cations by Neisseria meningitidis-type Capsular Polysaccharides
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
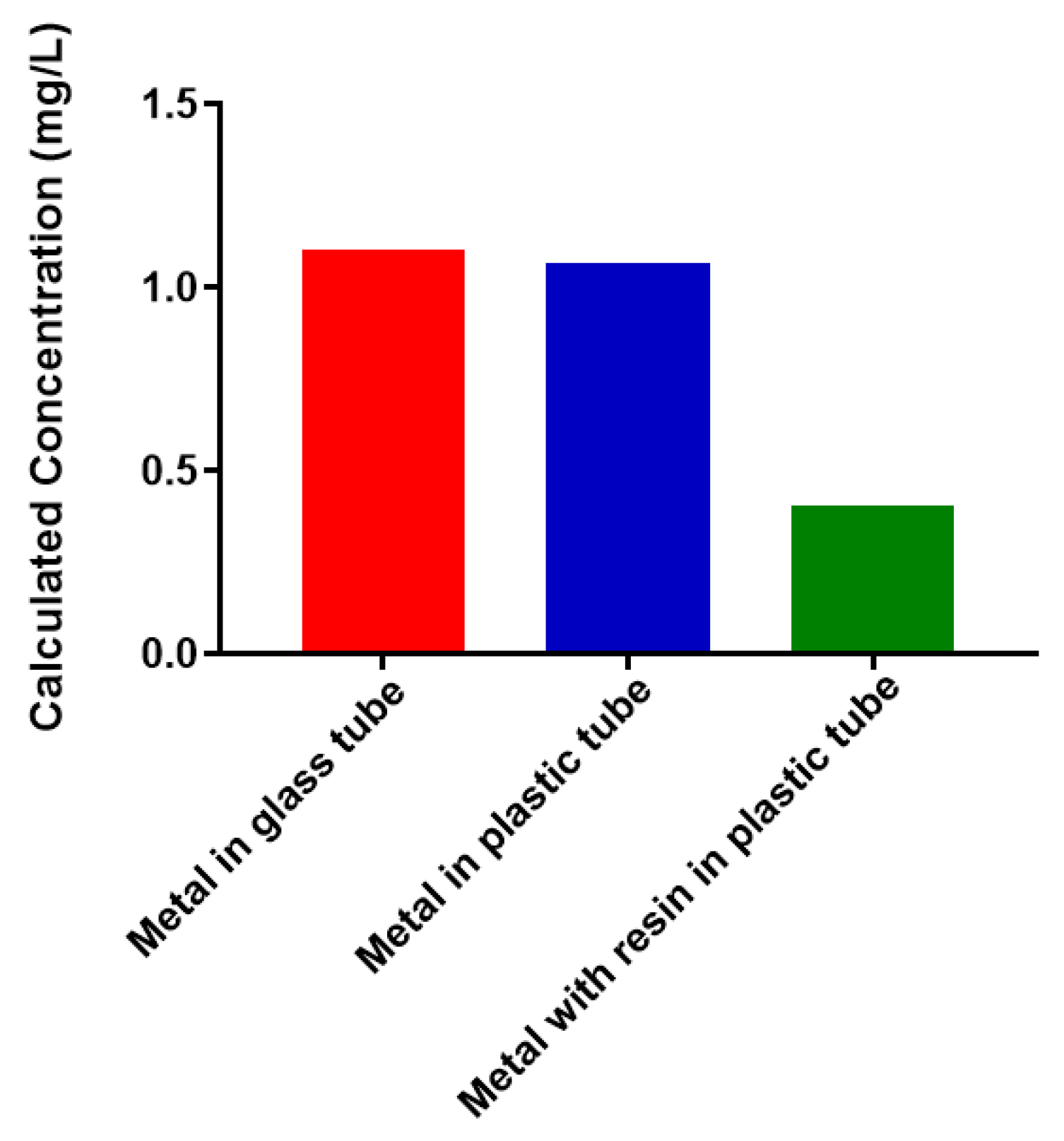
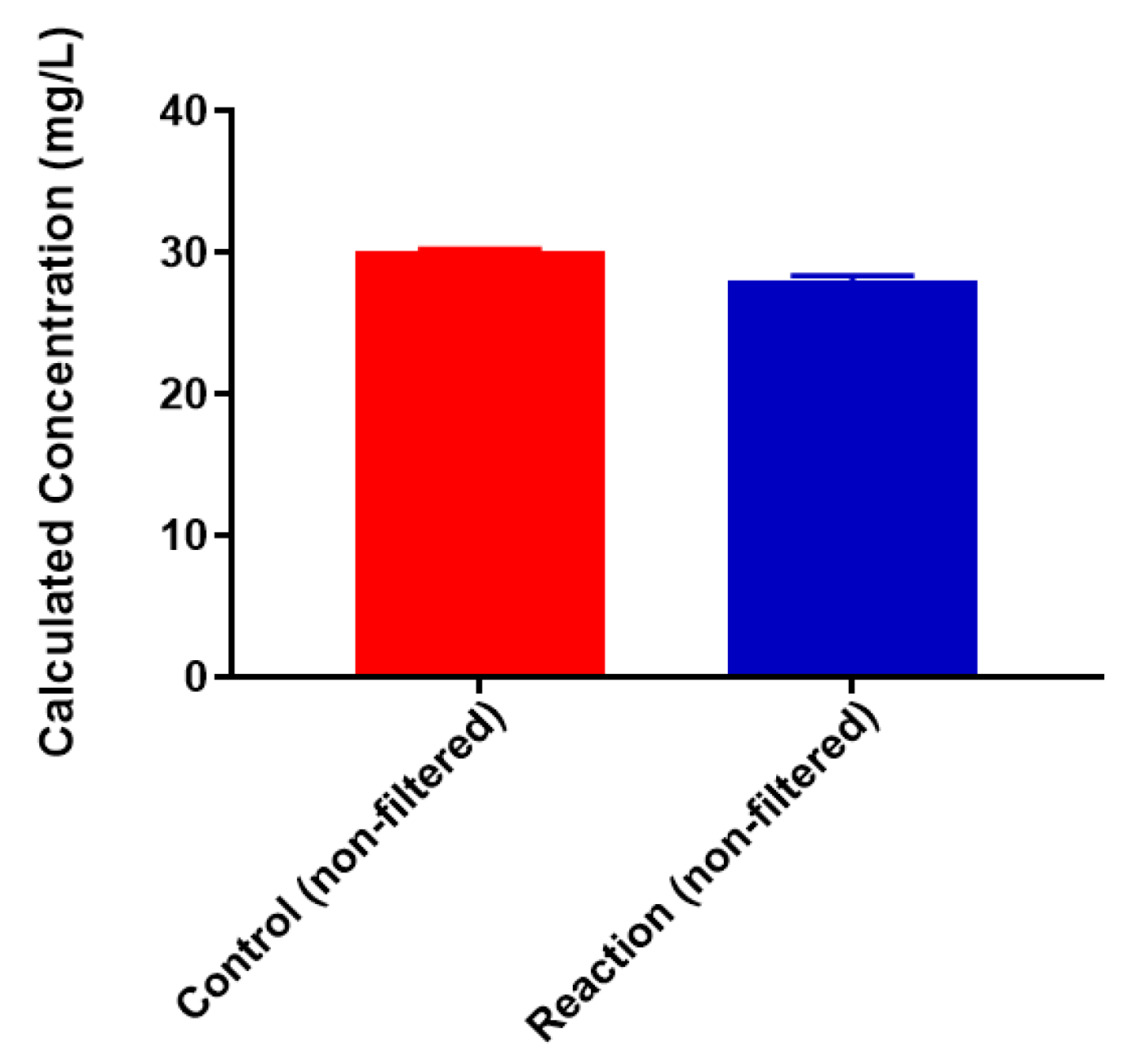
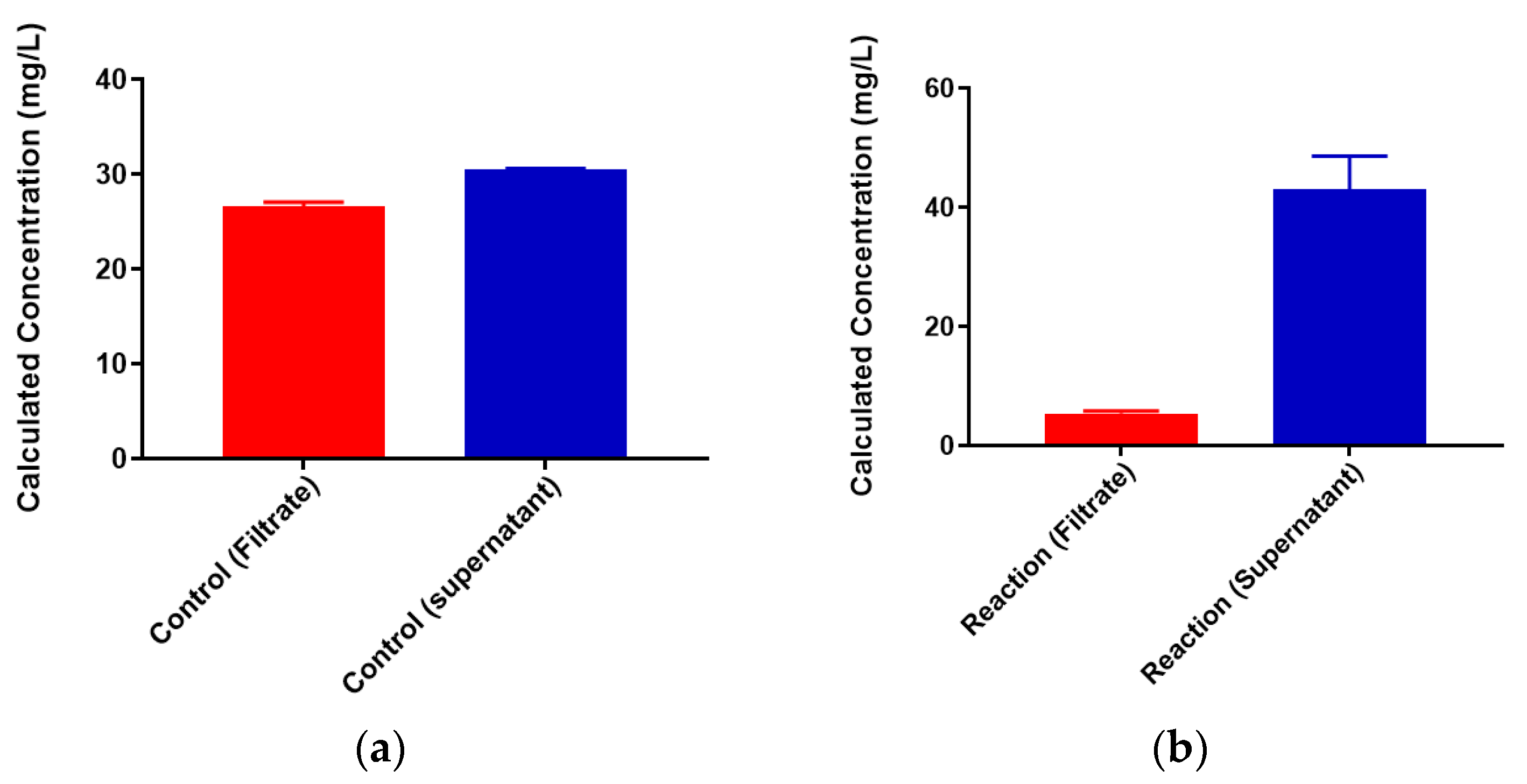
2.1. Free Metal Cations Are Sequestered by a Polymeric Resin
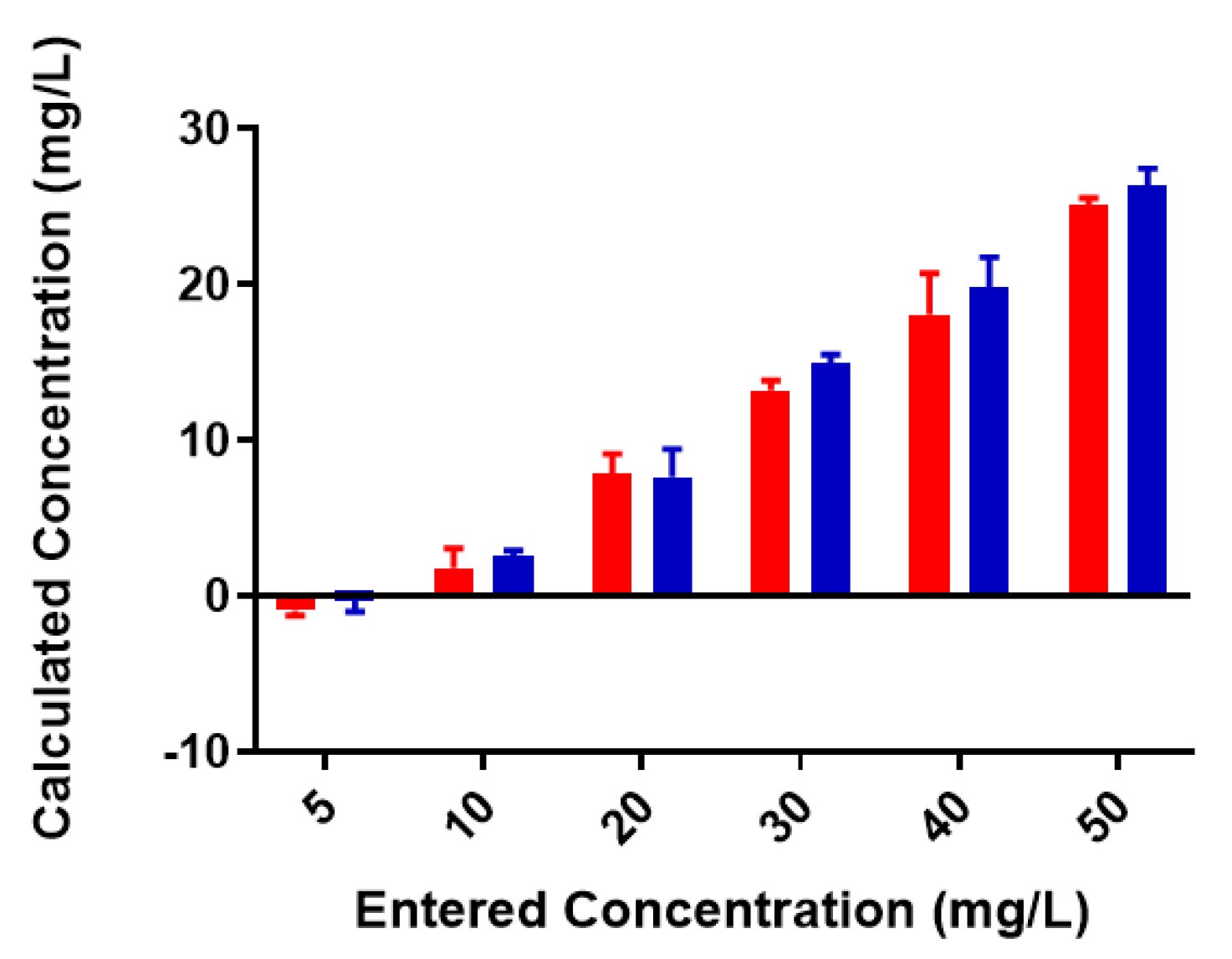
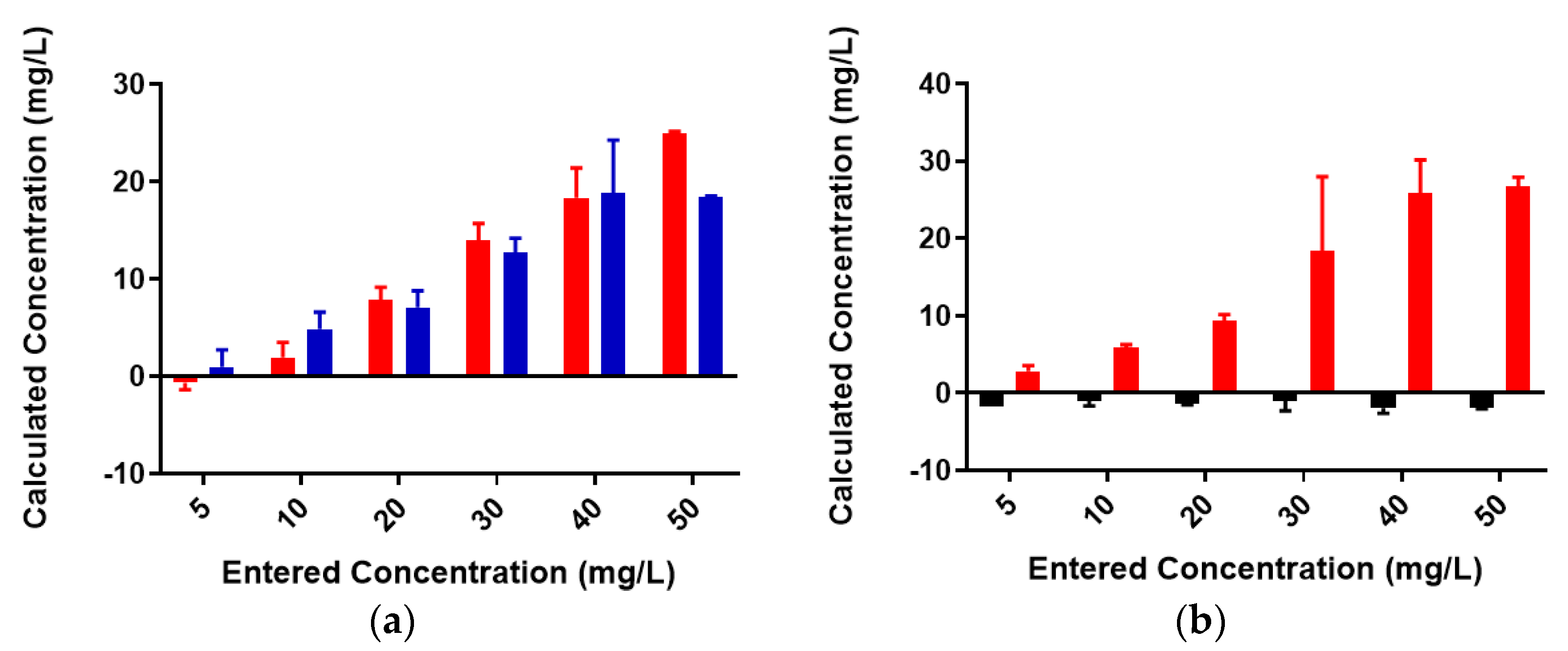
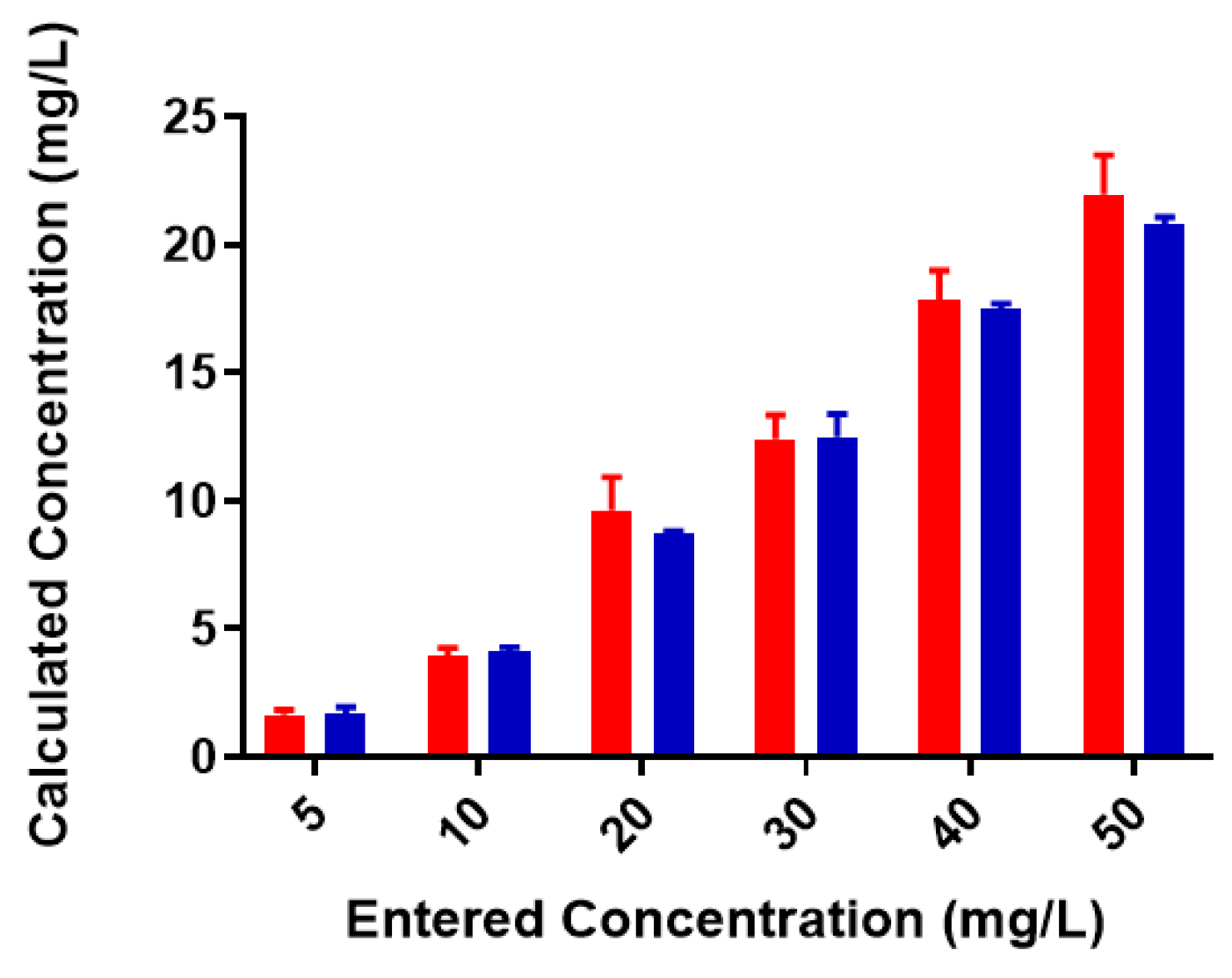
2.2. Colominic Acid Binds High Concentrations of Pb2+ and Cu2+
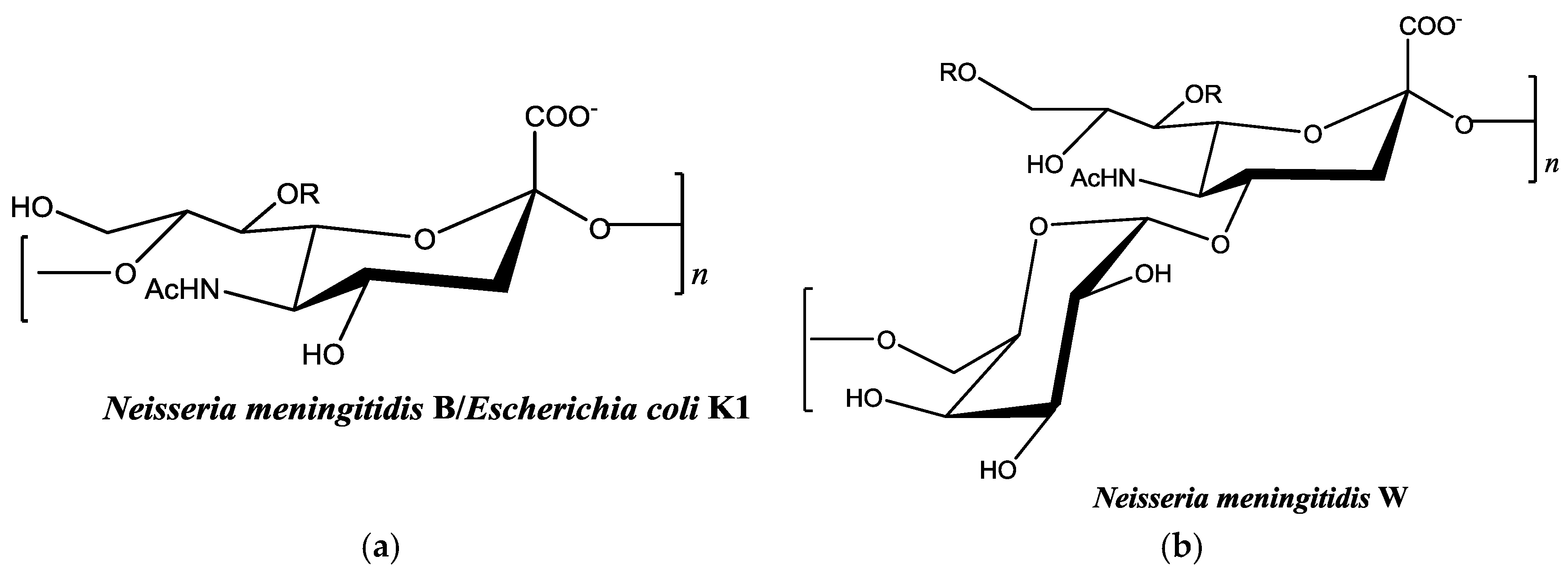
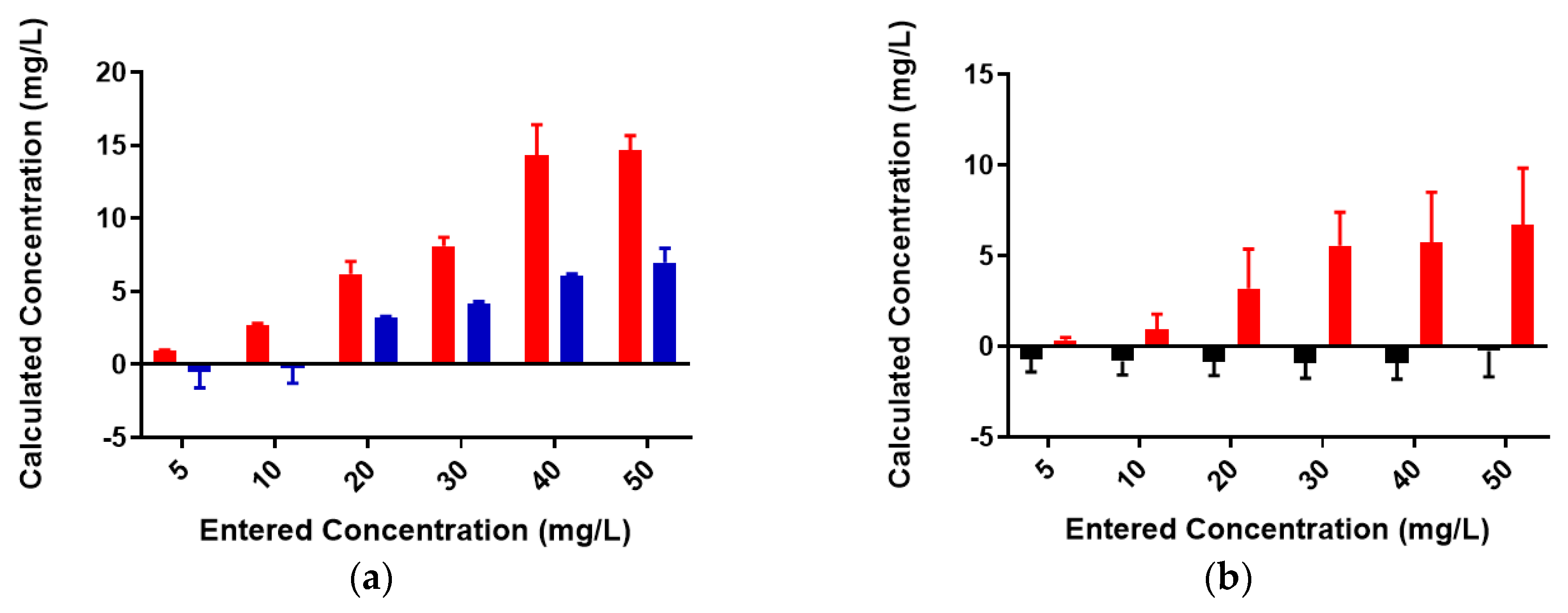
2.3. Neisseria meningitidis Serogroup W Capsular Polysaccharide Binds a High Concentration of Pb2+
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Metal Capture by Alkyne-Modified Solid Support
3.2. Binding of Heavy Metal Cations to Polysaccharide
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tchounwou, P.B.; Yedjou, C.G.; Patlolla, A.K.; Sutton, D.J. Heavy metal toxicity and the environment. In Molecular, Clinical and Environmental Toxicology; Springer: Basel, Switzerland, 2012; Volume 101, pp. 133–164. [Google Scholar]
- Blewett, T.A.; Leonard, E.M. Mechanisms of nickel toxicity to fish and invertebrates in marine and estuarine waters. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 223, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamas, M.J.; Fauvet, B.; Christen, P.; Goloubinoff, P. Misfolding and aggregation of nascent proteins: A novel mode of toxic cadmium action in vivo. Curr. Genet. 2018, 64, 177–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zefferino, R.; Piccoli, C.; Ricciardi, N.; Scrima, R.; Capitanio, N. Possible mechanisms of mercury toxicity and cancer promotion: Involvement of gap junction intercellular communications and inflammatory cytokines. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2017, 2017, 7028583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wessling-Resnick, M. Excess iron: Considerations related to development and early growth. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 106, 1600s–1605s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, X.; Fiati Kenston, S.S.; Kong, L.; Zhao, J. Molecular mechanisms of nickel induced neurotoxicity and chemoprevention. Toxicology 2017, 392, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rinaldi, M.; Micali, A.; Marini, H.; Adamo, E.B.; Puzzolo, D.; Pisani, A.; Trichilo, V.; Altavilla, D.; Squadrito, F.; Minutoli, L. Cadmium, organ toxicity and therapeutic approaches: A review on brain, kidney and testis damage. Curr. Med. Chem. 2017, 24, 3879–3893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cicero, C.E.; Mostile, G.; Vasta, R.; Rapisarda, V.; Signorelli, S.S.; Ferrante, M.; Zappia, M.; Nicoletti, A. Metals and neurodegenerative diseases. A systematic review. Environ. Res. 2017, 159, 82–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bulcke, F.; Dringen, R.; Scheiber, I.F. Neurotoxicity of copper. Adv. Neurobiol. Y 2017, 18, 313–343. [Google Scholar]
- Ojuederie, O.; Babalola, O. Microbial and plant-assisted bioremediation of heavy metal polluted environments: A review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayangbenro, A.S.; Babalola, O.O. A new strategy for heavy metal polluted environments: A review of microbial biosorbents. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nwodo, U.U.; Green, E.; Okoh, A.I. Bacterial exopolysaccharides: Functionality and prospects. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 14002–14015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flemming, H.C.; Neu, T.R.; Wozniak, D.J. The EPS matrix: The “house of biofilm cells”. J. Bacteriol. 2007, 189, 7945–7947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corbett, D.; Roberts, I.S. The role of microbial polysaccharides in host-pathogen interaction. F1000 Biol. Rep. 2009, 1, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Limoli, D.H.; Jones, C.J.; Wozniak, D.J. Bacterial extracellular polysaccharides in biofilm formation and function. Microbiol. Spectr. 2015, 3, 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, P.; Diwan, B. Bacterial exopolysaccharide mediated heavy metal removal: A review on biosynthesis, mechanism and remediation strategies. Biotechnol. Rep. 2017, 13, 58–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poli, A.; Anzelmo, G.; Nicolaus, B. Bacterial exopolysaccharides from extreme marine habitats: Production, characterization and biological activities. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 1779–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chug, R.; Gour, V.S.; Mathur, S.; Kothari, S.L. Optimization of extracellular polymeric substances production using Azotobacter beijreinckii and Bacillus subtilis and its application in chromium (vi) removal. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 214, 604–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhaskar, P.V.; Bhosle, N.B. Bacterial extracellular polymeric substance (eps): A carrier of heavy metals in the marine food-chain. Environ. Int. 2006, 32, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmid, J. Recent insights in microbial exopolysaccharide biosynthesis and engineering strategies. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2018, 53, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiebig, T.; Berti, F.; Freiberger, F.; Pinto, V.; Claus, H.; Romano, M.R.; Proietti, D.; Brogioni, B.; Stummeyer, K.; Berger, M.; et al. Functional expression of the capsule polymerase of Neisseria meningitidis serogroup X: A new perspective for vaccine development. Glycobiology 2014, 24, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiebig, T.; Freiberger, F.; Pinto, V.; Romano, M.R.; Black, A.; Litschko, C.; Bethe, A.; Yashunsky, D.; Adamo, R.; Nikolaev, A.; et al. Molecular cloning and functional characterization of components of the capsule biosynthesis complex of Neisseria meningitidis serogroup A: Toward in vitro vaccine production. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 19395–19407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ming, S.A.; Cottman-Thomas, E.; Black, N.C.; Chen, Y.; Veeramachineni, V.; Peterson, D.C.; Chen, X.; Tedaldi, L.M.; Wagner, G.K.; Cai, C.; et al. Interaction of Neisseria meningitidis group X N-acetylglucosamine-1-phosphotransferase with its donor substrate. Glycobiology 2018, 28, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muindi, K.M.; McCarthy, P.C.; Wang, T.; Vionnet, J.; Battistel, M.; Jankowska, E.; Vann, W.F. Characterization of the meningococcal serogroup X capsule N-acetylglucosamine-1-phosphotransferase. Glycobiology 2014, 24, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Peterson, D.C.; Arakere, G.; Vionnet, J.; McCarthy, P.C.; Vann, W.F. Characterization and acceptor preference of a soluble meningococcal group C polysialyltransferase. J. Bacteriol. 2011, 193, 1576–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Romanow, A.; Haselhorst, T.; Stummeyer, K.; Claus, H.; Bethe, A.; Muhlenhoff, M.; Vogel, U.; von Itzstein, M.; Gerardy-Schahn, R. Biochemical and biophysical characterization of the sialyl-/hexosyltransferase synthesizing the meningococcal serogroup W135 heteropolysaccharide capsule. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 11718–11730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCarthy, P.C.; Sharyan, A.; Sheikhi Moghaddam, L. Meningococcal vaccines: Current status and emerging strategies. Vaccines 2018, 6, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattacharjee, A.K.; Jennings, H.J.; Kenny, C.P.; Martin, A.; Smith, I.C. Structural determination of the sialic acid polysaccharide antigens of Neisseria meningitidis serogroups B and C with carbon 13 nuclear magnetic resonance. J. Biol. Chem. 1975, 250, 1926–1932. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bhattacharjee, A.K.; Jennings, H.J.; Kenny, C.P.; Martin, A.; Smith, I.C. Structural determination of the polysaccharide antigens of Neisseria meningitidis serogroups Y, W-135, and BO1. Can. J. Biochem. 1976, 54, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCarthy, P.C.; Saksena, R.; Peterson, D.C.; Lee, C.H.; An, Y.; Cipollo, J.F.; Vann, W.F. Chemoenzymatic synthesis of immunogenic meningococcal group C polysialic acid-tetanus Hc fragment glycoconjugates. Glycoconj. J. 2013, 30, 857–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andreishcheva, E.N.; Vann, W.F. Gene products required for de novo synthesis of polysialic acid in Escherichia coli K1. J. Bacteriol. 2006, 188, 1786–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, I.H.; Lin, J.; Choi, J.E.; Shin, J.S. Characterization of escherichia coli k1 colominic acid-specific murine antibodies that are cross-protective against Neisseria meningitidis groups B, C, and Y. Mol. Immunol. 2014, 59, 142–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loaëc, M.; Olier, R.; Guezennec, J. Uptake of lead, cadmium and zinc by a novel bacterial exopolysaccharide. Water Res. 1997, 31, 1171–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battistel, M.D.; Shangold, M.; Trinh, L.; Shiloach, J.; Freedberg, D.I. Evidence for helical structure in a tetramer of α2–8 sialic acid: Unveiling a structural antigen. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 10717–10720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ghimire, S.; McCarthy, P.C. Capture of Pb2+ and Cu2+ Metal Cations by Neisseria meningitidis-type Capsular Polysaccharides. Biomolecules 2018, 8, 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom8020023
Ghimire S, McCarthy PC. Capture of Pb2+ and Cu2+ Metal Cations by Neisseria meningitidis-type Capsular Polysaccharides. Biomolecules. 2018; 8(2):23. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom8020023
Chicago/Turabian StyleGhimire, Sujan, and Pumtiwitt C. McCarthy. 2018. "Capture of Pb2+ and Cu2+ Metal Cations by Neisseria meningitidis-type Capsular Polysaccharides" Biomolecules 8, no. 2: 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom8020023
APA StyleGhimire, S., & McCarthy, P. C. (2018). Capture of Pb2+ and Cu2+ Metal Cations by Neisseria meningitidis-type Capsular Polysaccharides. Biomolecules, 8(2), 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom8020023




