Modulation of Intestinal Barrier and Bacterial Endotoxin Production Contributes to the Beneficial Effect of Nicotinic Acid on Alcohol-Induced Endotoxemia and Hepatic Inflammation in Rats
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Nicotinic Acid Supplementation Prevents Alcohol-Induced Elevation of Blood Endotoxin Level and Hepatic Endotoxin Signaling
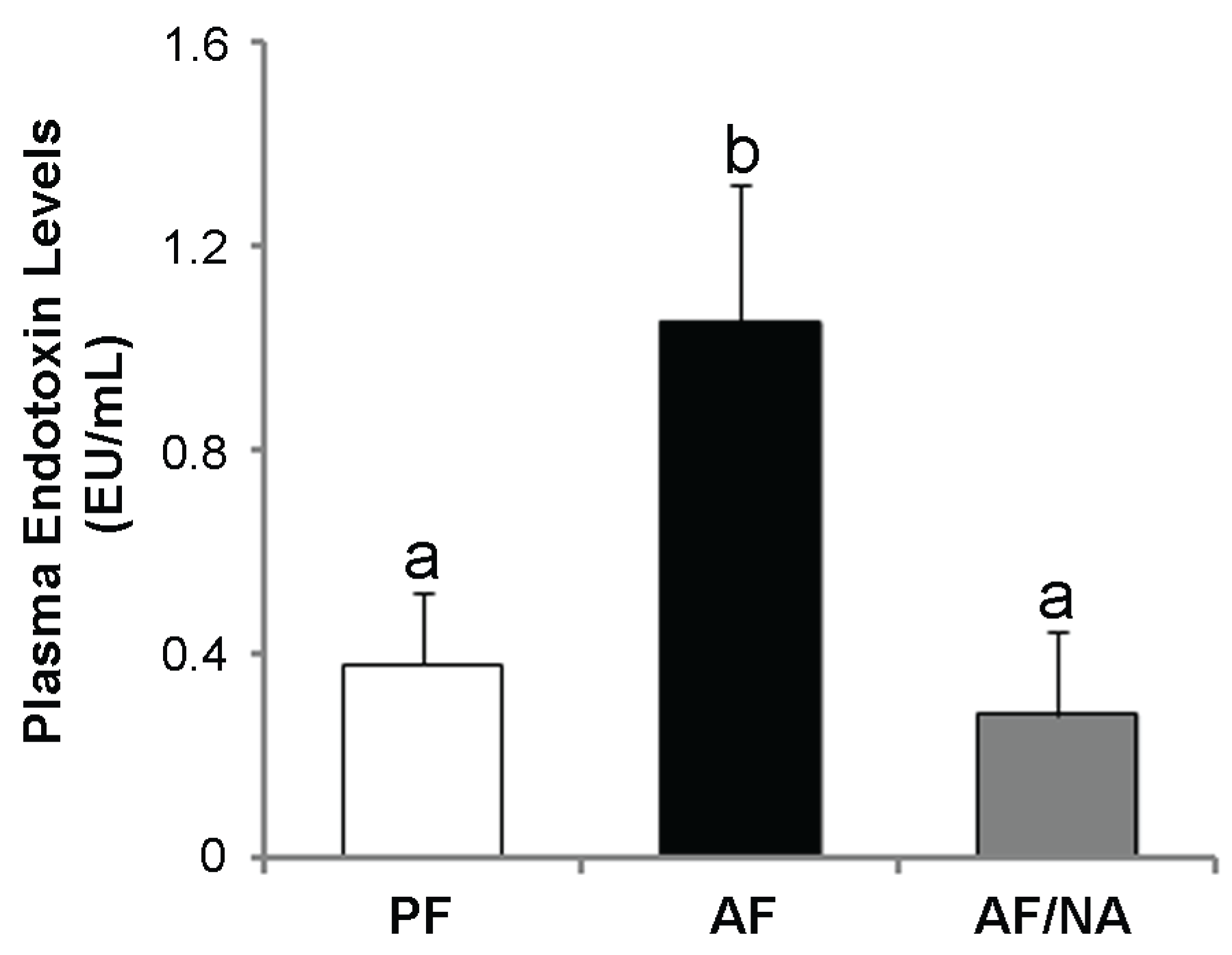
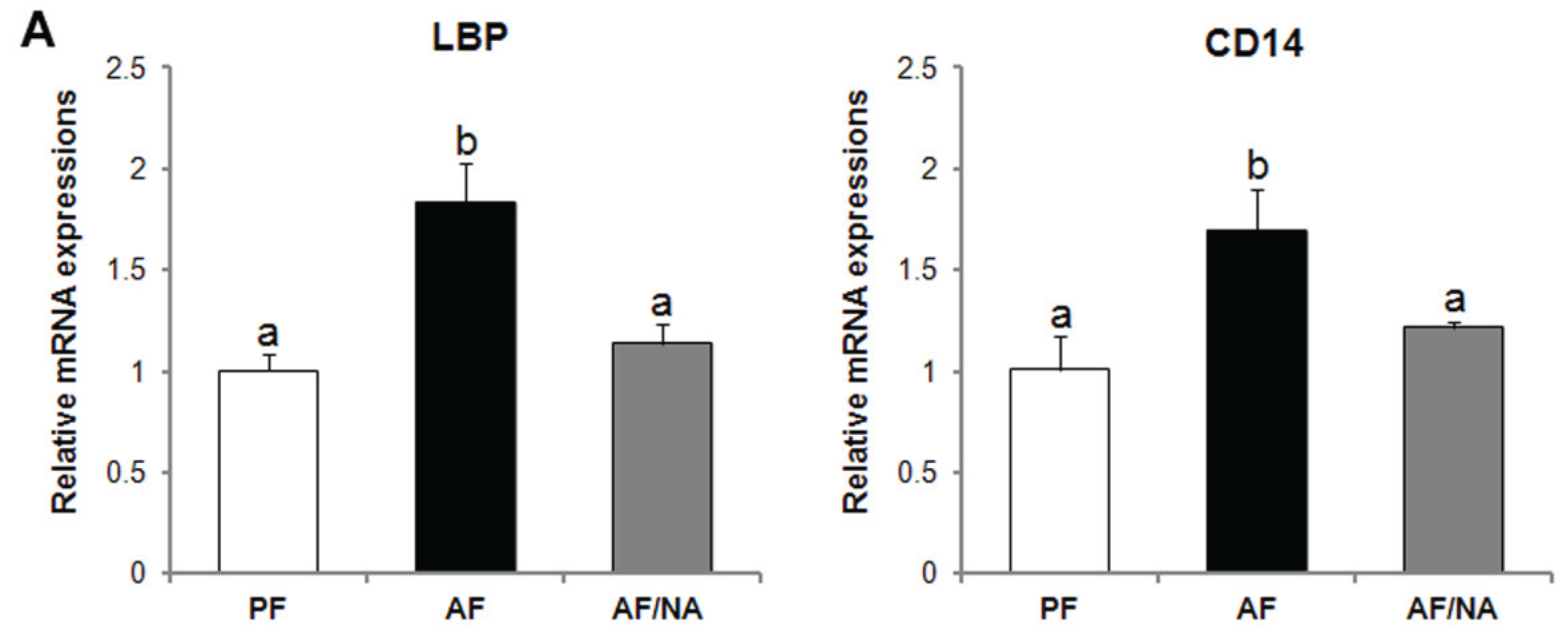
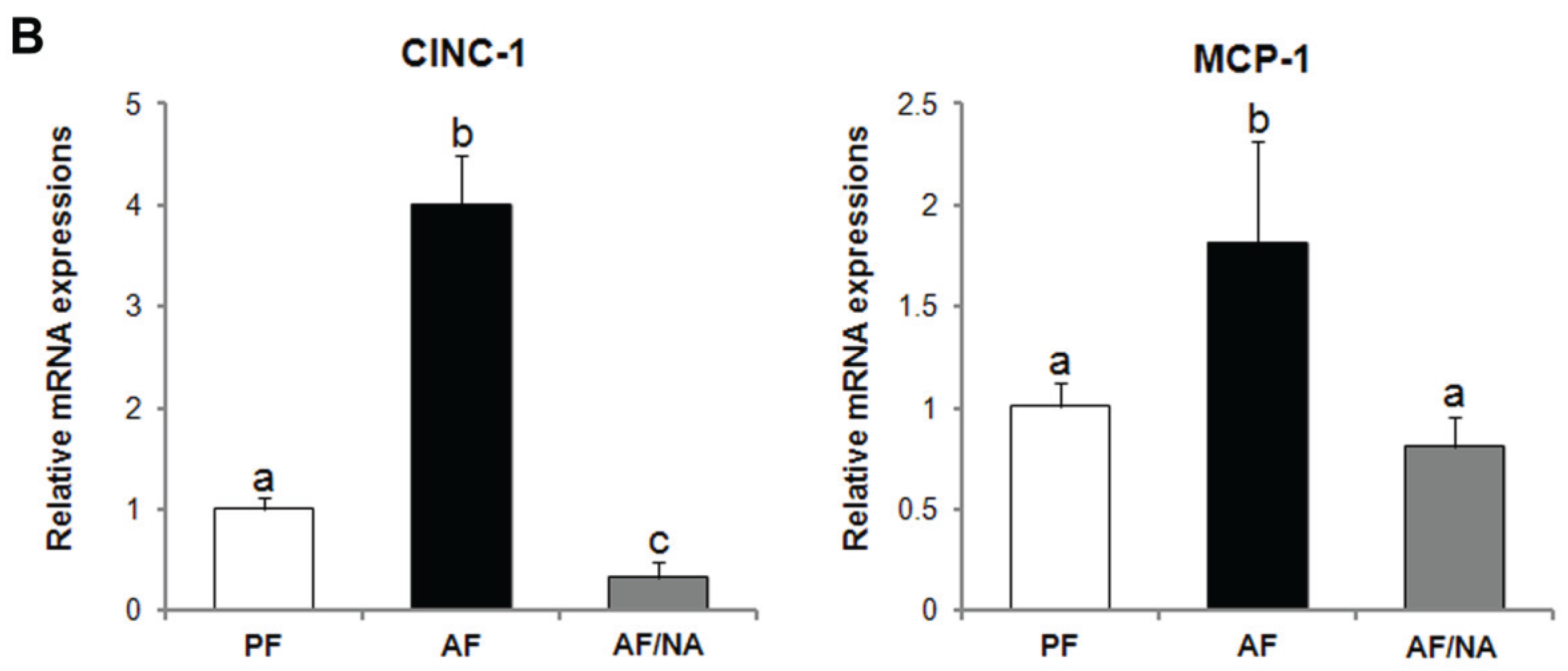
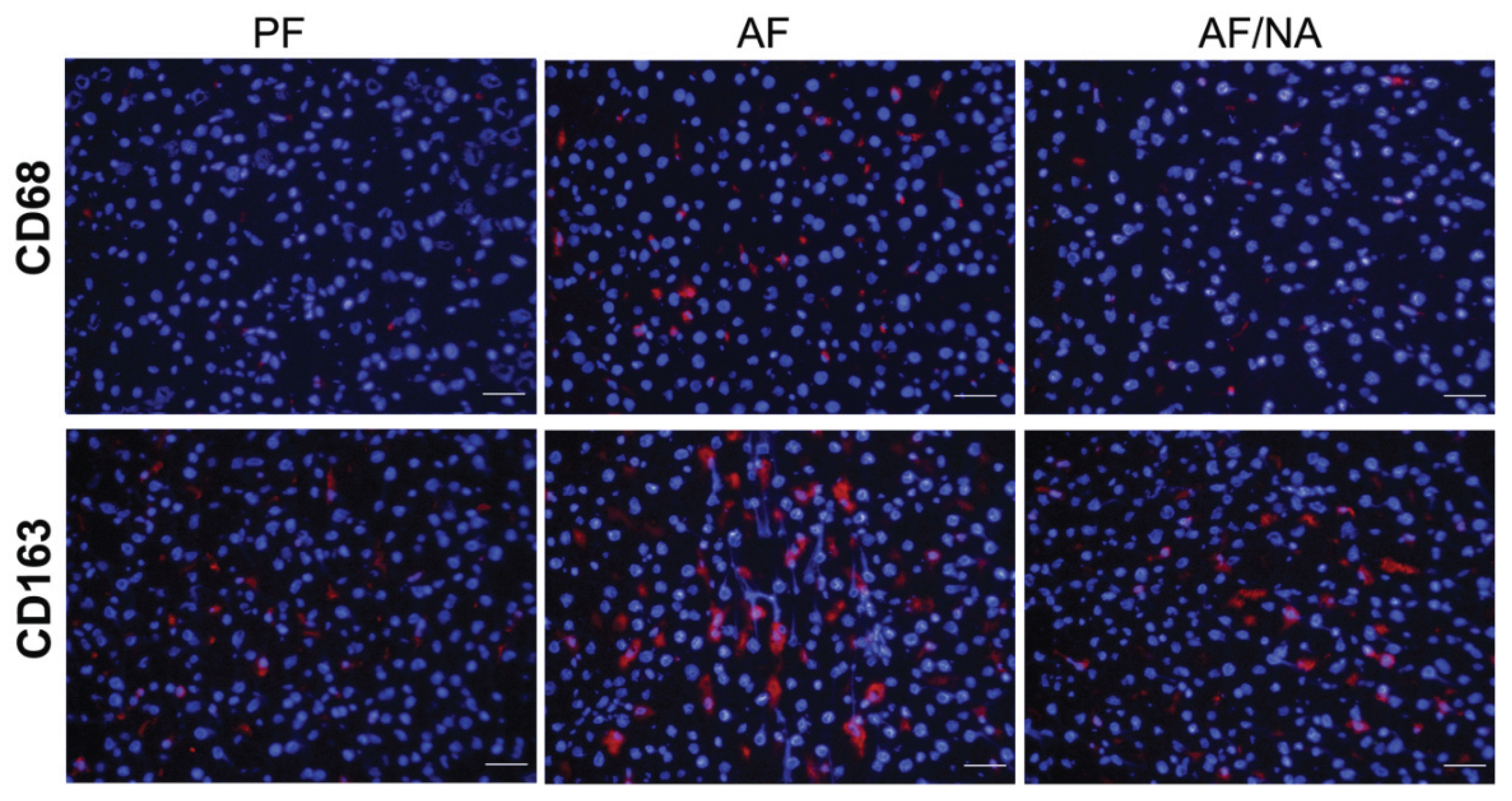
2.2. Nicotinic Acid Supplementation Upregulates Intestinal Tight Junction Proteins and Reduces Intestinal Luminal Endotoxin Level

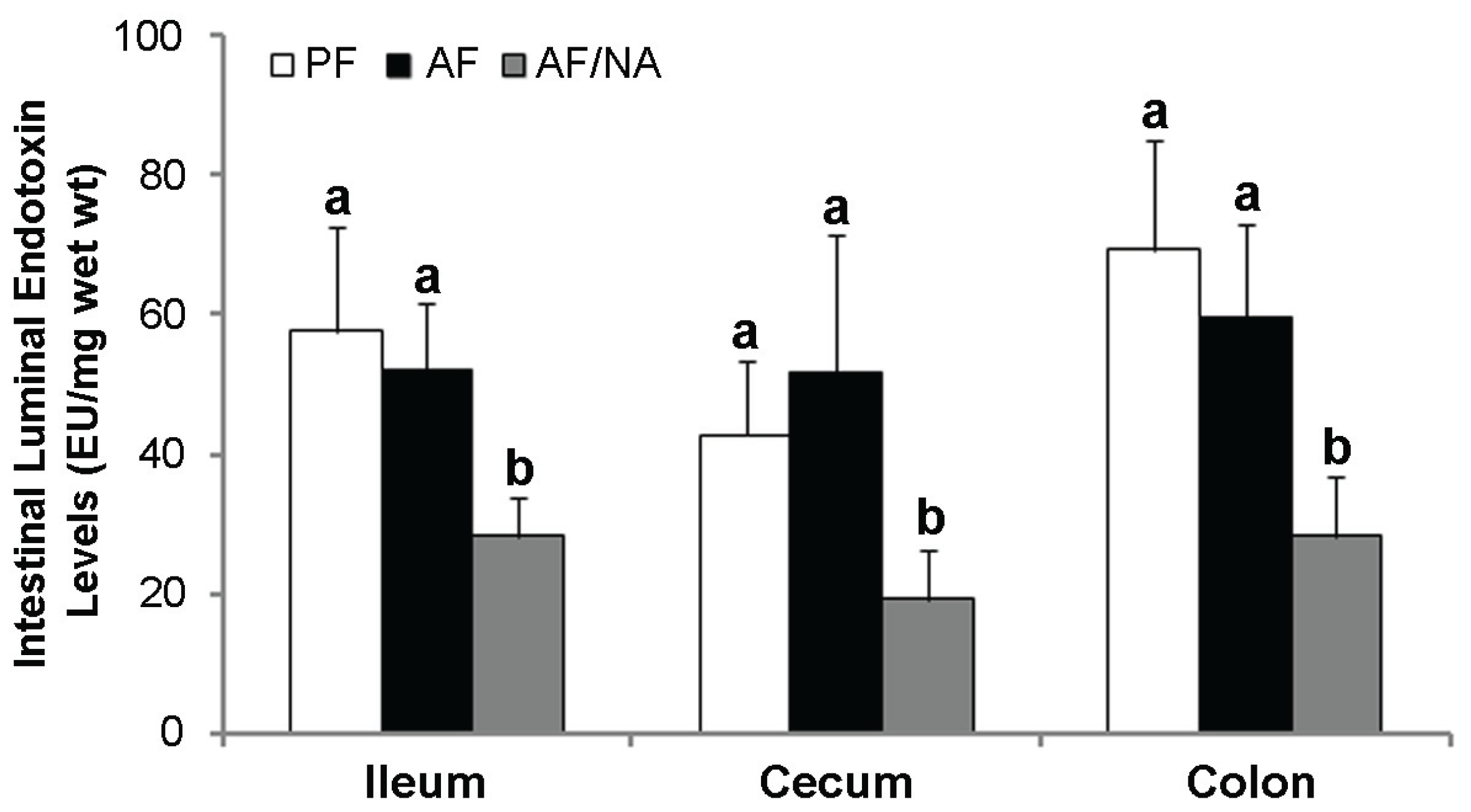
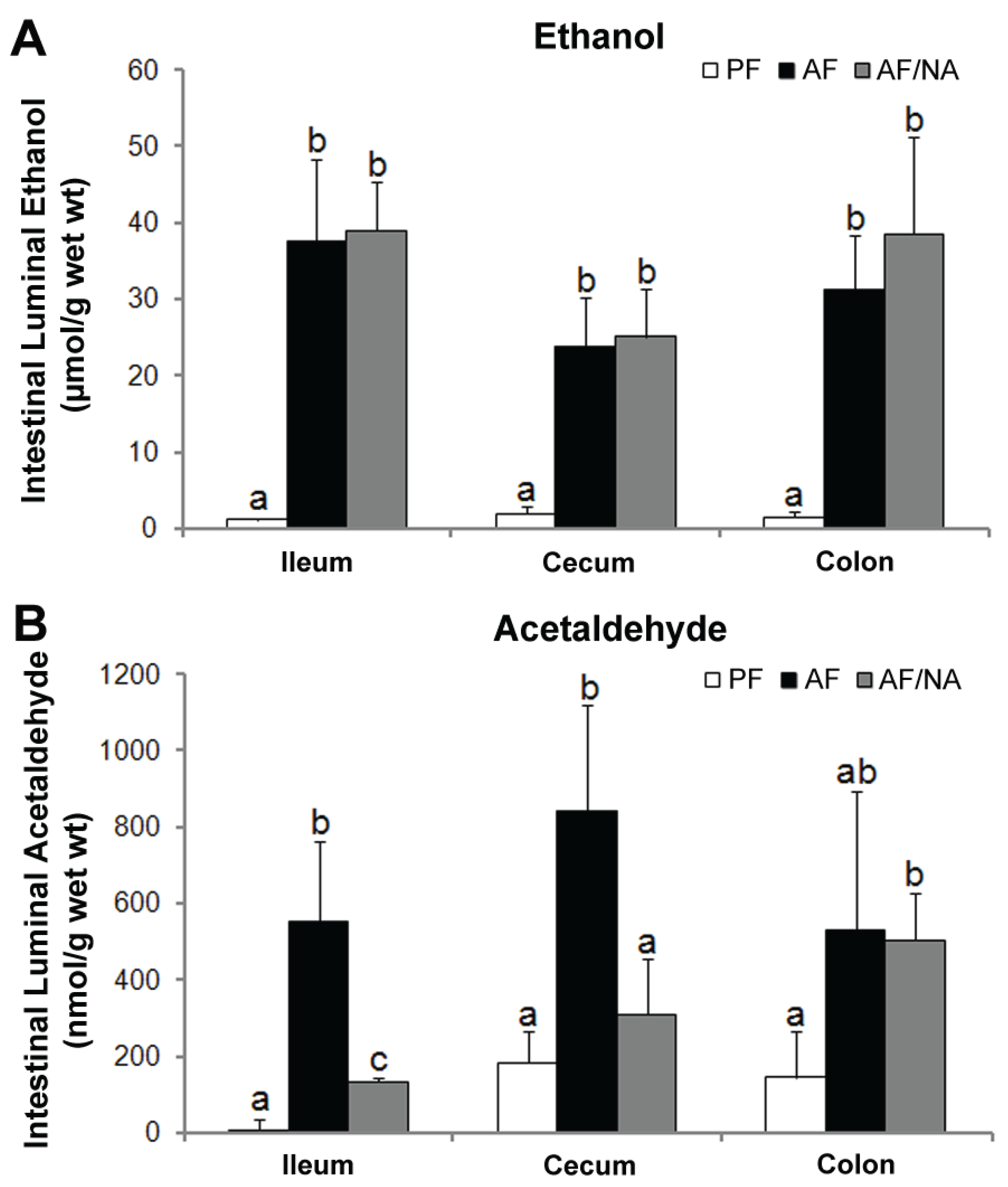
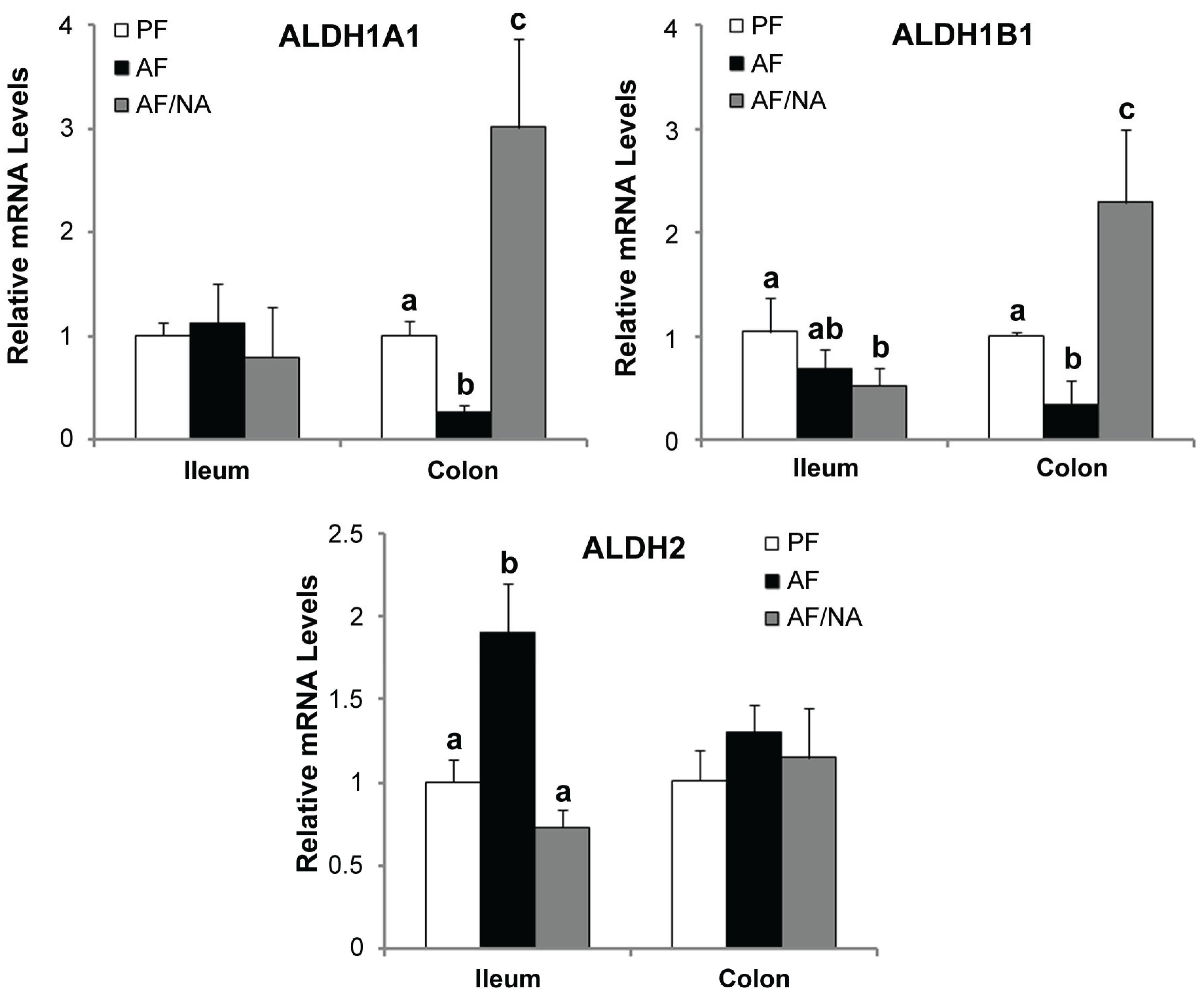
2.3. Nicotinic Acid Supplementation Modulates Intestinal ALDH Genes and Reduces Intestinal Luminal Acetaldehyde Level
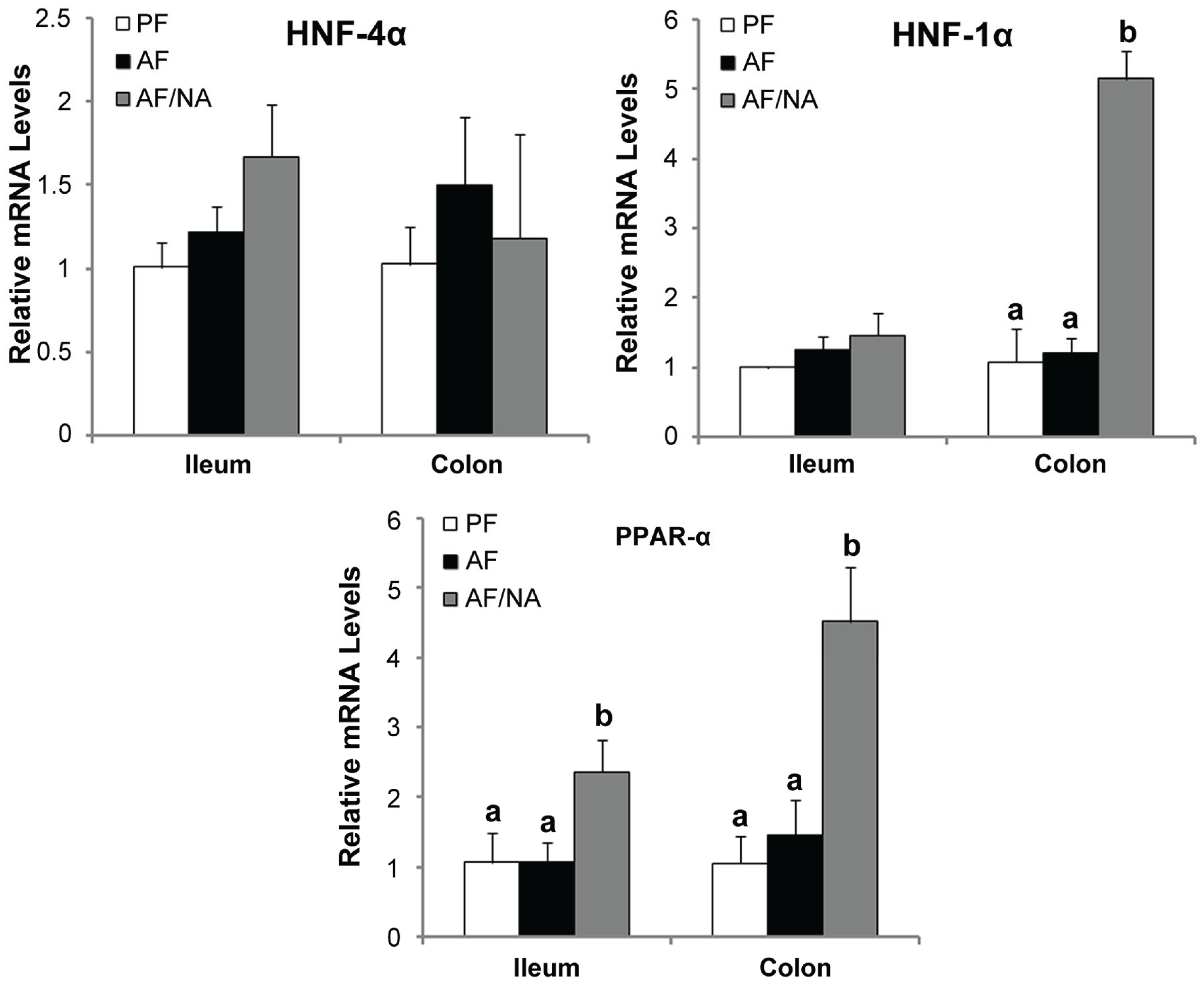
2.4. Nicotinic Acid Supplementation Upregulates Intestinal HNF-1α and PPAR-α
3. Discussion
4. Experimental Section
4.1. Animals and Alcohol Feeding Experiments
4.2. Endotoxin Assay
4.3. qPCR Analysis
4.4. Immunofluorescence Procedure
| Gene | Genebank Accession No. | Forward Primer (5'–3')/Reverse Primer (5'–3') | Amplicon Size |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aldh1a1 | NM_022407 | GGGAAAGAGCCCTTGCATTGTGTT/ | 170 bp |
| TGGCTCGCTCAACACTCTTTCTCA | |||
| Aldh1b1 | NM_001011975 | AACAATACCAGGTACGGCTTGGCT/ | 163 bp |
| TGCCATTGCCGGATTCCTTAAAGC | |||
| Aldh2 | NM_032416 | ATTGGCTGATCTCATCGAACGGGA/ | 147 bp |
| TACTTGTCAGCCCAGCCAGCATAA | |||
| Claudin-1/Cldn1 | NM_031699 | AGGCAACCAGAGCCTTGATGGTAA/ | 83 bp |
| CATGCACTTCATGCCAATGGTGGA | |||
| Claudin-5/Cldn5 | NM_031701 | AATTCTGGGTCTGGTGCTGTGTCT/ | 102 bp |
| ACGATATTGTGGTCCAGGAAGGCA | |||
| CINC-1/Cxcl1 | NM_030845 | ACCCAAACCGAAGTCATAGCCAC/ | 181 bp |
| ACTAGTGTTGTCAGAAGCCAGCGT | |||
| Hnf1α | NM_012669 | ACATTGAGCACAGAGGATGTGCCT/ | 105 bp |
| GGAGCTGTCAGTGCGTTGTTGTTT | |||
| Hnf4α | NM_022180 | ATTCGGGCCAAGAAGATTGCCAAC/ | 108 bp |
| AAGTTCACAGAAGGCCGGGATGTA | |||
| LBP/Lbp | NM_017208 | TGACATGTTACCGCCTGACTCCAA/ | 119 bp |
| AGACCACTGTTCCAAGAAGCTCCA | |||
| MCP-1/Ccl2 | NM_031530 | TGCTGTCTCAGCCAGATGCAGTTA/ | 131 bp |
| TACAGCTTCTTTGGGACACCTGCT | |||
| Pparα | NM_013196 | AGCTCAGGACACAAGACGTTGTCA/ | 136 bp |
| AGGGACTTTCCAGGTCATCTGCTT | |||
| Tnfα | NM_012675 | AGAACAGCAACTCCAGAACACCCT/ | 160 bp |
| TGCCAGTTCCACATCTCGGATCAT | |||
| ZO-1/Tjp1 | NM_001106266 | AAGATGGGATTCTTAGGCCCAGCA/ | 136 bp |
| TCTTTGGCTGCAGGGCTATCTTCT | |||
| 18s rRNA/Rn18s | NR_046237 | ACGGACCAGAGCGAAAGCAT/ | 152 bp |
| TGTCAATCCTGTCCGTGTCC |
4.5. Ethanol and Acetaldehyde Assay
4.6. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflict of Interest
References
- Ceni, E.; Mello, T.; Galli, A. Pathogenesis of alcoholic liver disease: Role of oxidative metabolism. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 17756–17772. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rocco, A.; Compare, D.; Angrisani, D.; Sanduzzi Zamparelli, M.; Nardone, G. Alcoholic disease: Liver and beyond. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 14652–14659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barry, R.E. Role of acetaldehyde in the pathogenesis of alcoholic liver disease. Br. J. Addict. 1988, 83, 1381–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.S.; Oyama, T.; Isse, T.; Kitagawa, K.; Pham, T.T.; Tanaka, M.; Kawamoto, T. Formation of acetaldehyde-derived DNA adducts due to alcohol exposure. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2010, 188, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keshavarzian, A.; Holmes, E.W.; Patel, M.; Iber, F.; Fields, J.Z.; Pethkar, S. Leaky gut in alcoholic cirrhosis: A possible mechanism for alcohol-induced liver damage. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 1999, 94, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, R. Endotoxemia and gut barrier dysfunction in alcoholic liver disease. Hepatology 2009, 50, 638–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szabo, G. Gut-liver axis in alcoholic liver disease. Gastroenterology 2015, 148, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szabo, G.; Bala, S. Alcoholic liver disease and the gut-liver axis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 16, 1321–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wheeler, M.D. Endotoxin and Kupffer cell activation in alcoholic liver disease. Alcohol Res. Health 2003, 27, 300–306. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fujimoto, M.; Uemura, M.; Nakatani, Y.; Tsujita, S.; Hoppo, K.; Tamagawa, T.; Kitano, H.; Kikukawa, M.; Ann, T.; Ishii, Y.; et al. Plasma endotoxin and serum cytokine levels in patients with alcoholic hepatitis: Relation to severity of liver disturbance. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2000, 24, 48S–54S. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hanck, C.; Rossol, S.; Bocker, U.; Tokus, M.; Singer, M.V. Presence of plasma endotoxin is correlated with tumour necrosis factor receptor levels and disease activity in alcoholic cirrhosis. Alcohol Alcohol. 1998, 33, 606–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urbaschek, R.; McCuskey, R.S.; Rudi, V.; Becker, K.P.; Stickel, F.; Urbaschek, B.; Seitz, H.K. Endotoxin, endotoxin-neutralizing-capacity, sCD14, sICAM-1, and cytokines in patients with various degrees of alcoholic liver disease. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2001, 25, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.; Wang, L.; Song, Z.; Lambert, J.C.; McClain, C.J.; Kang, Y.J. A critical involvement of oxidative stress in acute alcohol-induced hepatic TNF-alpha production. Am. J. Pathol. 2003, 163, 1137–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, G.P. Intestinal barrier dysfunction, endotoxemia, and gastrointestinal symptoms: The “canary in the coal mine” during exercise-heat stress? Med. Sport Sci. 2008, 53, 61–73. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rao, R.K.; Seth, A.; Sheth, P. Recent advances in alcoholic liver disease I. Role of intestinal permeability and endotoxemia in alcoholic liver disease. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2004, 286, G881–G884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bjarnason, I.; Peters, T.J.; Wise, R.J. The leaky gut of alcoholism: Possible route of entry for toxic compounds. Lancet 1984, 1, 179–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keshavarzian, A.; Fields, J.Z.; Vaeth, J.; Holmes, E.W. The differing effects of acute and chronic alcohol on gastric and intestinal permeability. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 1994, 89, 2205–2211. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Parlesak, A.; Schafer, C.; Schutz, T.; Bode, J.C.; Bode, C. Increased intestinal permeability to macromolecules and endotoxemia in patients with chronic alcohol abuse in different stages of alcohol-induced liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2000, 32, 742–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, W.; McClain, C.J.; Cave, M.; Kang, Y.J.; Zhou, Z. The role of zinc deficiency in alcohol-induced intestinal barrier dysfunction. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2010, 298, G625–G633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nanji, A.A.; Khettry, U.; Sadrzadeh, S.M. Lactobacillus feeding reduces endotoxemia and severity of experimental alcoholic liver (disease). Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 1994, 205, 243–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adachi, Y.; Moore, L.E.; Bradford, B.U.; Gao, W.; Thurman, R.G. Antibiotics prevent liver injury in rats following long-term exposure to ethanol. Gastroenterology 1995, 108, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World, M.J.; Ryle, P.R.; Thomson, A.D. Alcoholic malnutrition and the small intestine. Alcohol Alcohol. 1985, 20, 89–124. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Badawy, A.A. Pellagra and alcoholism: A biochemical perspective. Alcohol Alcohol. 2014, 49, 238–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Xie, G.; Zhang, W.; Zhong, W.; Sun, X.; Tan, X.; Sun, X.; Jia, W.; Zhou, Z. Dietary nicotinic acid supplementation ameliorates chronic alcohol-induced fatty liver in rats. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2014, 38, 1982–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nanji, A.A.; Zakim, D.; Rahemtulla, A.; Daly, T.; Miao, L.; Zhao, S.; Khwaja, S.; Tahan, S.R.; Dannenberg, A.J. Dietary saturated fatty acids down-regulate cyclooxygenase-2 and tumor necrosis factor alfa and reverse fibrosis in alcohol-induced liver disease in the rat. Hepatology 1997, 26, 1538–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kono, H.; Enomoto, N.; Connor, H.D.; Wheeler, M.D.; Bradford, B.U.; Rivera, C.A.; Kadiiska, M.B.; Mason, R.P.; Thurman, R.G. Medium-chain triglycerides inhibit free radical formation and TNF-alpha production in rats given enteral ethanol. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2000, 278, G467–G476. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nanji, A.A.; Jokelainen, K.; Tipoe, G.L.; Rahemtulla, A.; Dannenberg, A.J. Dietary saturated fatty acids reverse inflammatory and fibrotic changes in rat liver despite continued ethanol administration. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2001, 299, 638–644. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhong, W.; Li, Q.; Xie, G.; Sun, X.; Tan, X.; Sun, X.; Jia, W.; Zhou, Z. Dietary fat sources differentially modulate intestinal barrier and hepatic inflammation in alcohol-induced liver injury in rats. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol 2013, 305, G919–G932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathurin, P.; Deng, Q.G.; Keshavarzian, A.; Choudhary, S.; Holmes, E.W.; Tsukamoto, H. Exacerbation of alcoholic liver injury by enteral endotoxin in rats. Hepatology 2000, 32, 1008–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitic, L.L.; van Itallie, C.M.; Anderson, J.M. Molecular physiology and pathophysiology of tight junctions I. Tight junction structure and function: Lessons from mutant animals and proteins. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2000, 279, G250–G254. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Farhadi, A.; Banan, A.; Fields, J.; Keshavarzian, A. Intestinal barrier: An interface between health and disease. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2003, 18, 479–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Angelo, A.; Bluteau, O.; Garcia-Gonzalez, M.A.; Gresh, L.; Doyen, A.; Garbay, S.; Robine, S.; Pontoglio, M. Hepatocyte nuclear factor 1alpha and beta control terminal differentiation and cell fate commitment in the gut epithelium. Development 2010, 137, 1573–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piomelli, D. A fatty gut feeling. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 24, 332–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, P.; Schnabl, B. Host-microbiome interactions in alcoholic liver disease. Gut Liver 2014, 8, 237–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabbard, S.L.; Lacy, B.E.; Levine, G.M.; Crowell, M.D. The impact of alcohol consumption and cholecystectomy on small intestinal bacterial overgrowth. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2014, 59, 638–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bode, J.C.; Bode, C.; Heidelbach, R.; Durr, H.K.; Martini, G.A. Jejunal microflora in patients with chronic alcohol abuse. Hepato-Gastroenterol. 1984, 31, 30–34. [Google Scholar]
- Casafont Morencos, F.; de las Heras Castano, G.; Martin Ramos, L.; Lopez Arias, M.J.; Ledesma, F.; Pons Romero, F. Small bowel bacterial overgrowth in patients with alcoholic cirrhosis. Dig. Dis. Sci. 1996, 41, 552–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, A.W.; Fouts, D.E.; Brandl, J.; Starkel, P.; Torralba, M.; Schott, E.; Tsukamoto, H.; Nelson, K.E.; Brenner, D.A.; Schnabl, B. Enteric dysbiosis associated with a mouse model of alcoholic liver disease. Hepatology 2011, 53, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bull-Otterson, L.; Feng, W.; Kirpich, I.; Wang, Y.; Qin, X.; Liu, Y.; Gobejishvili, L.; Joshi-Barve, S.; Ayvaz, T.; Petrosino, J.; et al. Metagenomic analyses of alcohol induced pathogenic alterations in the intestinal microbiome and the effect of Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG treatment. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e53028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mutlu, E.A.; Gillevet, P.M.; Rangwala, H.; Sikaroodi, M.; Naqvi, A.; Engen, P.A.; Kwasny, M.; Lau, C.K.; Keshavarzian, A. Colonic microbiome is altered in alcoholism. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver physiol. 2012, 302, G966–G978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bode, C.; Bode, J.C. Effect of alcohol consumption on the gut. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2003, 17, 575–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunagan, M.; Chaudhry, K.; Samak, G.; Rao, R.K. Acetaldehyde disrupts tight junctions in Caco-2 cell monolayers by a protein phosphatase 2A-dependent mechanism. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2012, 303, G1356–G1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samak, G.; Aggarwal, S.; Rao, R.K. ERK is involved in EGF-mediated protection of tight junctions, but not adherens junctions, in acetaldehyde-treated Caco-2 cell monolayers. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2011, 301, G50–G59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basuroy, S.; Sheth, P.; Mansbach, C.M.; Rao, R.K. Acetaldehyde disrupts tight junctions and adherens junctions in human colonic mucosa: Protection by EGF and L-glutamine. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2005, 289, G367–G375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baraona, E.; Julkunen, R.; Tannenbaum, L.; Lieber, C.S. Role of intestinal bacterial overgrowth in ethanol production and metabolism in rats. Gastroenterology 1986, 90, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Visapaa, J.P.; Tillonen, J.; Salaspuro, M. Microbes and mucosa in the regulation of intracolonic acetaldehyde concentration during ethanol challenge. Alcohol Alcohol. 2002, 37, 322–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tillonen, J.; Vakevainen, S.; Salaspuro, V.; Zhang, Y.; Rautio, M.; Jousimies-Somer, H.; Lindros, K.; Salaspuro, M. Metronidazole increases intracolonic but not peripheral blood acetaldehyde in chronic ethanol-treated rats. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2000, 24, 570–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visapaa, J.P.; Jokelainen, K.; Nosova, T.; Salaspuro, M. Inhibition of intracolonic acetaldehyde production and alcoholic fermentation in rats by ciprofloxacin. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 1998, 22, 1161–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koivisto, T.; Salaspuro, M. Aldehyde dehydrogenases of the rat colon: Comparison with other tissues of the alimentary tract and the liver. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 1996, 20, 551–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nosova, T.; Jokelainen, K.; Kaihovaara, P.; Heine, R.; Jousimies-Somer, H.; Salaspuro, M. Characteristics of aldehyde dehydrogenases of certain aerobic bacteria representing human colonic flora. Alcohol Alcohol. 1998, 33, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhong, W.; Li, Q.; Zhang, W.; Sun, Q.; Sun, X.; Zhou, Z. Modulation of Intestinal Barrier and Bacterial Endotoxin Production Contributes to the Beneficial Effect of Nicotinic Acid on Alcohol-Induced Endotoxemia and Hepatic Inflammation in Rats. Biomolecules 2015, 5, 2643-2658. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom5042643
Zhong W, Li Q, Zhang W, Sun Q, Sun X, Zhou Z. Modulation of Intestinal Barrier and Bacterial Endotoxin Production Contributes to the Beneficial Effect of Nicotinic Acid on Alcohol-Induced Endotoxemia and Hepatic Inflammation in Rats. Biomolecules. 2015; 5(4):2643-2658. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom5042643
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhong, Wei, Qiong Li, Wenliang Zhang, Qian Sun, Xinguo Sun, and Zhanxiang Zhou. 2015. "Modulation of Intestinal Barrier and Bacterial Endotoxin Production Contributes to the Beneficial Effect of Nicotinic Acid on Alcohol-Induced Endotoxemia and Hepatic Inflammation in Rats" Biomolecules 5, no. 4: 2643-2658. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom5042643
APA StyleZhong, W., Li, Q., Zhang, W., Sun, Q., Sun, X., & Zhou, Z. (2015). Modulation of Intestinal Barrier and Bacterial Endotoxin Production Contributes to the Beneficial Effect of Nicotinic Acid on Alcohol-Induced Endotoxemia and Hepatic Inflammation in Rats. Biomolecules, 5(4), 2643-2658. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom5042643





