Optimized Production of Xylitol from Xylose Using a Hyper-Acidophilic Candida tropicalis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
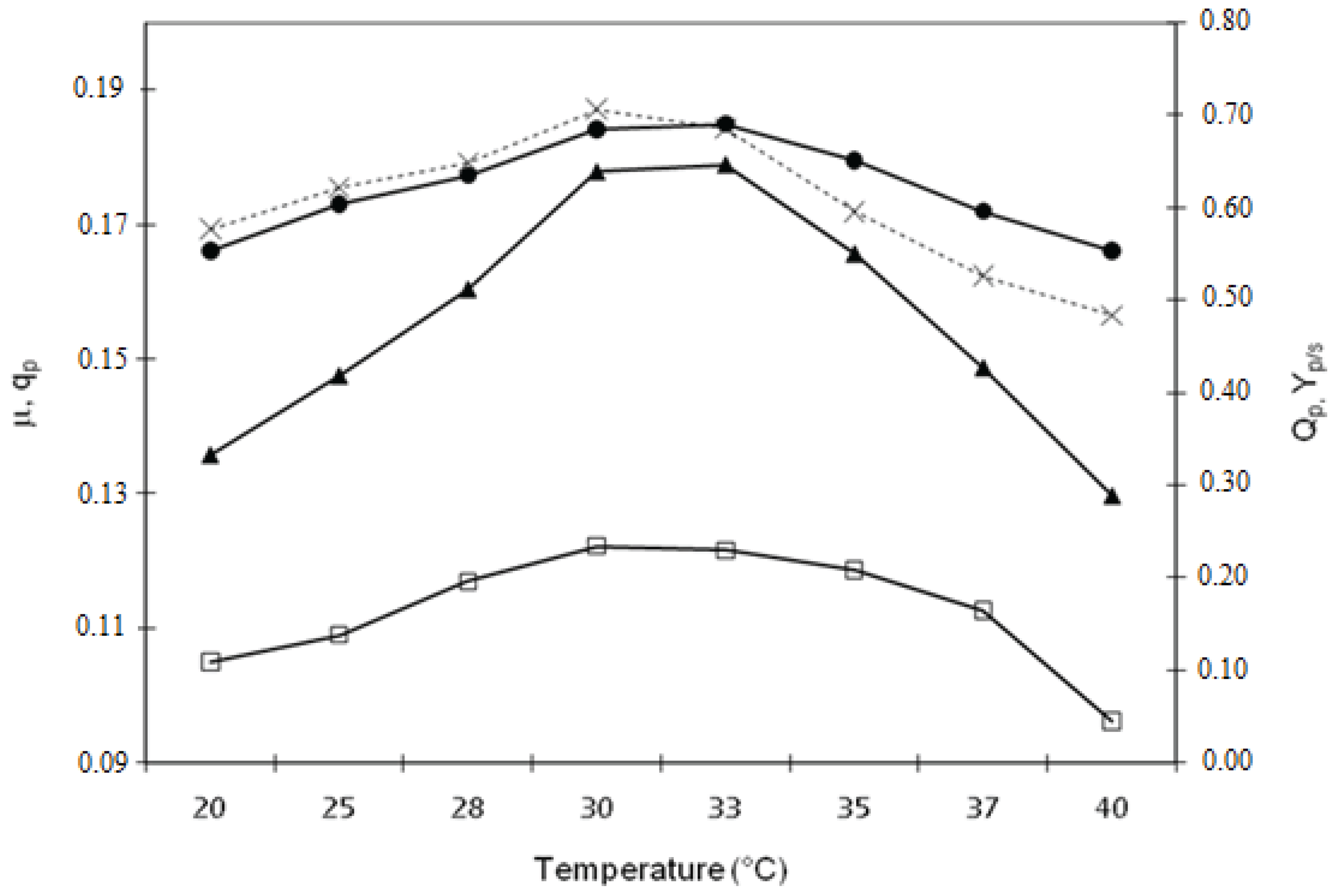
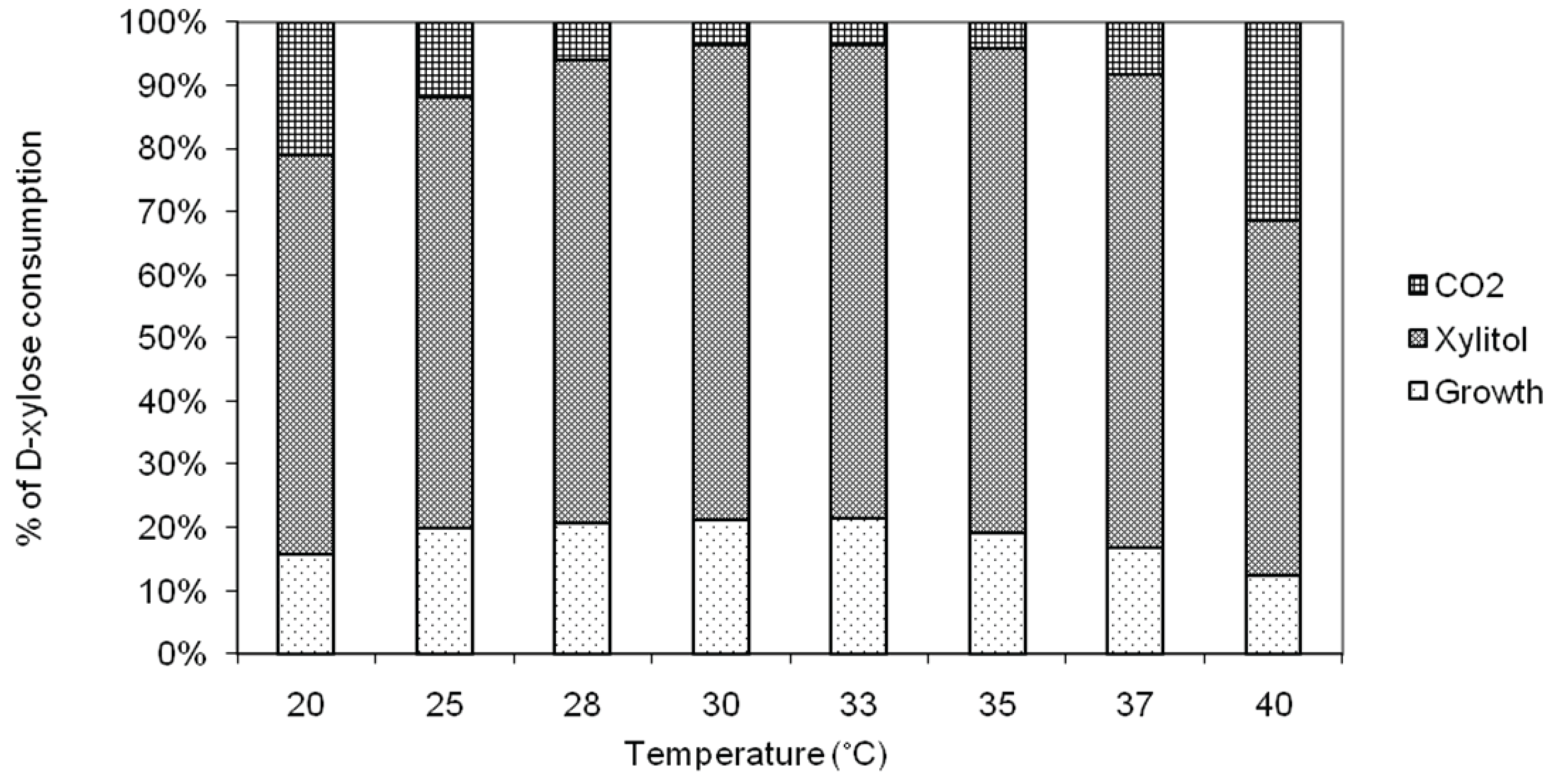
2.1. Effect of Temperature
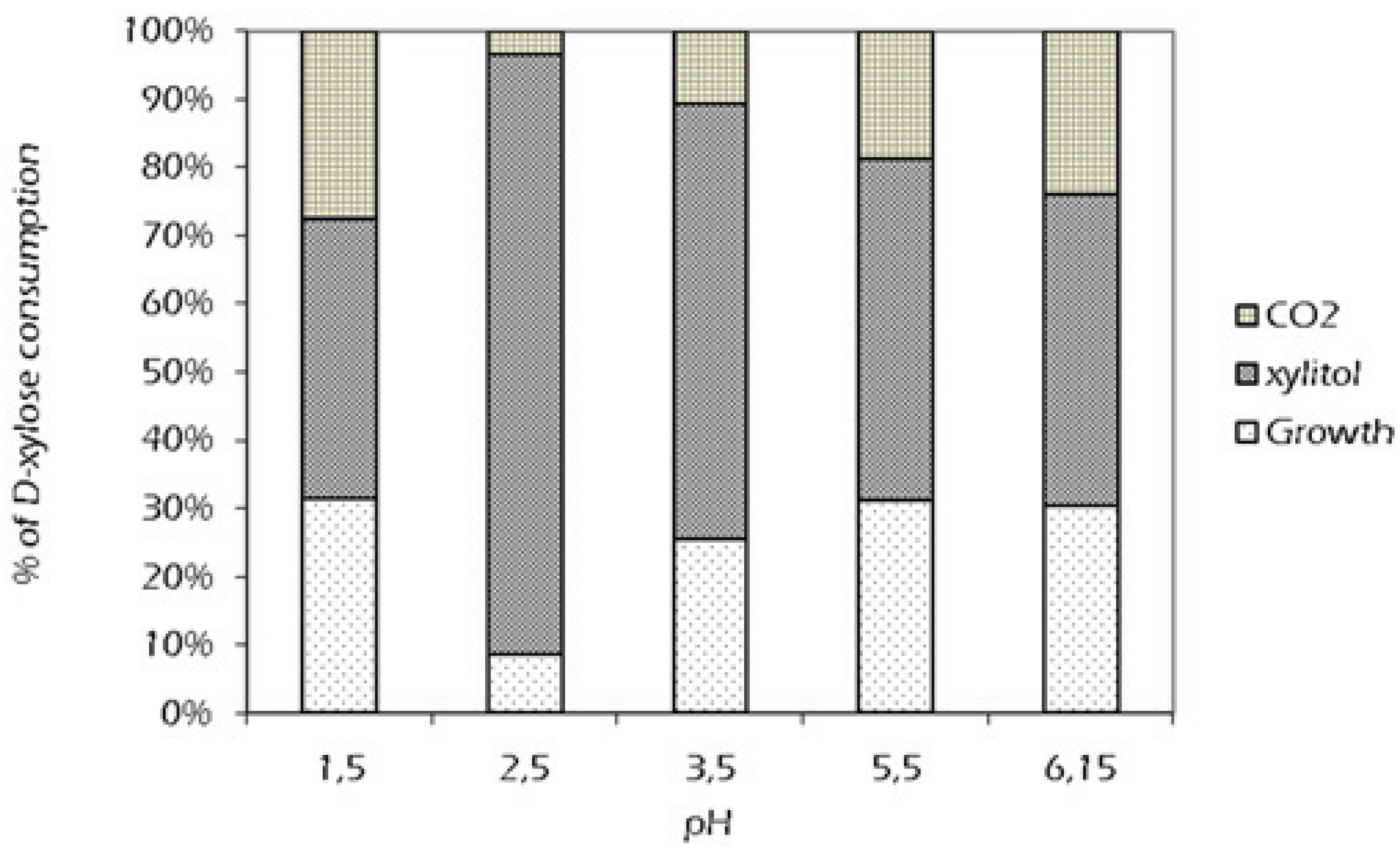
2.2. Effect of External pH
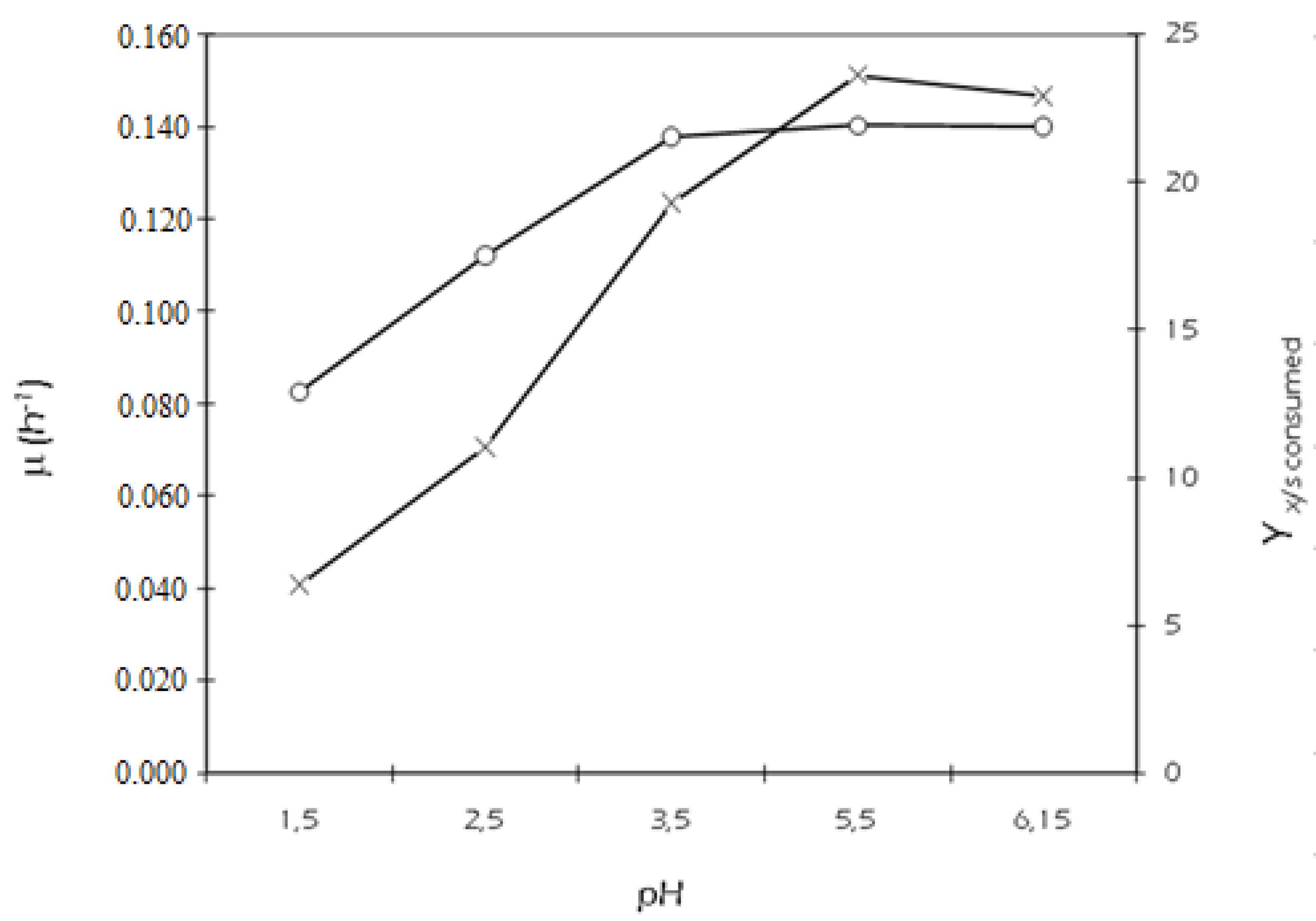
| pH | Yp/s initial | Yp/x | qs (g/g h) | Qp (g/L h) | qp (g/g h) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.5 | 0.08 | 1.57 | 0.162 | 0.096 | 0.060 |
| 2.5 | 0.61 | 6.40 | 0.349 | 0.815 | 0.246 |
| 3.5 | 0.32 | 3.30 | 0.199 | 0.515 | 0.116 |
| 5.5 | 0.25 | 2.70 | 0.163 | 0.392 | 0.074 |
| 6.15 | 0.16 | 1.80 | 0.140 | 0.385 | 0.070 |
2.3. Effect of Initial Xylose Concentration on Xylitol Yield
| S (g/L) | µ (1/h) | Yp/s initial | Yp/s consumed | qs (g/g h) | Qp (g/L h) | qp (g/g h) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15 | 0.031 | 30.13 | 30.13 | 0.027 | 0.073 | 0.008 |
| 30 | 0.034 | 33.80 | 33.80 | 0.035 | 0.141 | 0.012 |
| 40 | 0.034 | 43.78 | 48.62 | 0.035 | 0.204 | 0.017 |
| 50 | 0.034 | 49.18 | 52.67 | 0.048 | 0.297 | 0.025 |
| 60 | 0.030 | 71.52 | 71.52 | 0.083 | 0.512 | 0.059 |
| 70 | 0.033 | 65.76 | 74.35 | 0.068 | 0.557 | 0.051 |
| 80 | 0.033 | 54.99 | 83.66 | 0.067 | 0.616 | 0.056 |
| 100 | 0.017 | 42.33 | 67.82 | 0.029 | 0.236 | 0.020 |
| 150 | 0.010 | 25.17 | 64.10 | 0.017 | 0.142 | 0.011 |
| 200 | 0.007 | 12.50 | 35.71 | 0.015 | 0.070 | 0.005 |
| 300 | 0.004 | 3.33 | 29.41 | 0.020 | 0.028 | 0.006 |

2.4. Set Up of Fed-Batch Fermentation
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Strain and Chemicals
3.2. Xylitol Production
3.3. Analytical Methods
3.4. Calculation of Yields, Kinetic Parameters and Carbon Material Balances
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ahmad, I.; Shim, W.Y.; Jeon, W.Y.; Yoon, B.H.; Kim, J.H. Enhancement of xylitol production in Candida tropicalis by co-expression of two genes involved in pentose phosphate pathway. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2012, 35, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mäkinen, K.K. The rocky road of xylitol to its clinical application. J. Dent. Res. 2000, 79, 1352–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parajo, J.C.; Dominguez, H.; Dominguez, J.M. Biotechnological production of xylitol. Part1: Interest of xylitol and fundamentals of its biosynthesis. Bioresour. Technol. 1998, 65, 91–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkelhausen, E.; Kuzmanova, S. Microbial conversion of d-xylose to xylitol. J. Ferment. Bioeng. 1998, 86, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havenaar, R.; Huis In, T.; Veld, J.H.J.; Stoppelaar, I.D.; Backer DirKs, O. Anticariogenic and remineralizing properties of xylitol in combination with sucrose in rats inoculated with Streptococcus mutans. Caries Res. 1984, 18, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry. Policy on the use of xylitol in caries prevention. Pediatr. Dent. 2010, 36, 3236–3238. [Google Scholar]
- Nayak, P.A.; Nayak, U.A.; Khandelwal, V. The effect of xylitol on dental caries and oral flora. Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dent. 2014, 6, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Eys, J.; Wang, Y.M.; Chan, S.; Tanphaichitr, V.S.; King, S.M. Xylitol as a therapeutic agent on glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency. In Sugars in Nutrition; Sipple, H.L., McNutt, K.W., Eds.; Academic Press: London, UK, 1974; pp. 613–621. [Google Scholar]
- Grembecka, M.; Lebiedzińska, A.; Szefer, P. Simultaneous separation and determination of erythritol, xylitol, sorbitol, mannitol, maltitol, fructose, glucose, sucrose and maltose in food products by high performance liquid chromatography coupled to charged aerosol detector. Microchem. J. 2014, 117, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granström, T.B.; Izumori, K.; Leisola, M. A rare sugar xylitol. Part II: Biotechnological production and future applications of xylitol. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2007, 74, 273–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prakasham, R.S.; Rao, R.S.; Hobbs, P.J. Current trends in biotechnology production of xylitol and future prospects. Curr. Trends Biotechnol. Pharm. 2009, 3, 8–36. [Google Scholar]
- Park, Y.C.; Kim, S.K.; Seo, J.H. Recent Advances for Microbial Production of Xylitol. In Bioprocessing of Renewable Resources to Commodity Bioproducts; Bisaria, V.S., Kondo, A., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Chichester, UK, 2014; pp. 497–518. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Geng, A.; Yao, C.; Lu, Y.; Li, Q. Xylitol production from d-xylose and horticultural waste hemicellulosic hydrolysate by a new isolate of Candida athensensis SB18. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 105, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamad, N.L.; Mustapa Kamal, S.M.; Mokhtar, M.N. Xylitol biological production: A review of recent studies. Food Rev. Intl. 2015, 31, 74–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Mello Lourenço, M.V.; Dini-Andreote, F.; Aguilar-Vildoso, C.I.; Basso, L.C. Biotechnological potential of Candida spp. for the bioconversion of d-xylose to xylitol. Afr. J. Microbiol. Res. 2014, 8, 2030–2036. [Google Scholar]
- Jeffries, T.W.; Jin, Y.S. Metabolic engineering for improved fermentation of pentoses by yeasts. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2004, 63, 495–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sampaio, F.C.; Chaves-Alves, V.M.; Converti, A.; Lopes Passos, F.M.; Cavalcante Cohelo, J.L. Influences of cultivation conditions on xylose-to-xylitol bioconversion by a new isolate of Debaryomyces hanseii. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 502–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, C.J.S.M.; Mussatto, S.I.; Roberto, I.C. Study of xylitol production by Candida guilliermondii on a bench reactor. J. Food Eng. 2006, 75, 115–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, B.S.; Rhee, C.H.; Kim, J.H. Enhancement of xylitol productivity and yield using a xylitol dehydrogenase gene-disrupted mutant of Candida tropicalis under fully aerobic conditions. Biotechnol. Lett. 2006, 28, 1159–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horitsu, H.; Yahashi, Y.; Takamizawa, K.; Kawai, K.; Suzuki, T.; Watanabe, N. Production of xylitol from d-xylose by candida tropicalis: Optimization of production rate. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 1992, 40, 1085–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Guo, X.; Feng, X.; Li, C. An environment friendly and efficient process for xylitol bioconversion from enzymatic corncob hydrolysate by adapted Candida tropicalis. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 263, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misra, S.; Gupta, P.; Raghuwanshi, S.; Dutt, K.; Saxena, R.K. Comparative study on different strategies involved for xylitol purification from culture media fermented by Candida tropicalis. Separation Purif. Technol. 2011, 78, 266–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, S.S.; Afschar, A.S. Microbial production of xylitol from d-xylose using Candida tropicalis. Bioprocess Eng. 1994, 11, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, S.; Nadeem, M.; Ahmad, F.; Mushtaq, Z. Biotechnological production of xylitol from banana peel and its impact on physicochemical properties of rusks. J. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2013, 15, 747–756. [Google Scholar]
- Suomalainen, H.; Oura, E. Yeast nutrition and solute uptake. In Yeast; Rose, A.H., Harrison, J.S., Eds.; Academic Press: London, UK, 1971; Volume 2, pp. 38–45. [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez, S.; Bravo, V.; Castro, E.; Moya, A.; Camacho, F. The influence of pH and aeration rate on the fermentation of d-xylose by Candida shehatae. Enzym. Microbiol. Technol. 1997, 21, 355–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Converti, A.; Dominguez, J.M. Influence of temperature and pH on xylitol production from xylose by Debaryomyces hansenii. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2001, 75, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyrial, V.; Delgenes, J.P.; Moletta, R.; Navarro, J.M.; Inra, J.A.A. Xylitol production from d-xylose by Candida guillermondii: Fermentation behaviour. Biotechnol. Lett. 1991, 13, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nolleau, V.; Preziosi-Belloy, L.; Delgenes, J.P.; Navarro, J.M. Fermentation of hemicellulosic sugars and sugar mixtures to xylitol by Candida parapsilosis. Curr. Microbiol. 1991, 27, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamburini, E.; Bianchini, E.; Bruni, A.; Forlani, G. Cosubstrate effect on xylose reductase and xylitol dehydrogenase activity levels, and its consequence on xylitol production by Candida tropicalis. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2010, 46, 352–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Converti, A.; Perego, P.; Sordi, A.; Torre, P. Effect of starting xylose concentration on the microaerobic metabolism of Debaryomyces hansenii. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2002, 101, 15–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roels, J.A. Energetics and Kinetics in Biotechnology; Elsevier Biomedical Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Barbosa, M.F.S.; de Medeiros, M.B.; de Mancilha, I.M.; Schneider, H.; Lee, H. Screening of yeast for production of xylitol from d-xylose and some factors which affect xylitol yield in Candida guillermondii. J. Ind. Microbiol. 1998, 3, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tamburini, E.; Costa, S.; Marchetti, M.G.; Pedrini, P. Optimized Production of Xylitol from Xylose Using a Hyper-Acidophilic Candida tropicalis. Biomolecules 2015, 5, 1979-1989. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom5031979
Tamburini E, Costa S, Marchetti MG, Pedrini P. Optimized Production of Xylitol from Xylose Using a Hyper-Acidophilic Candida tropicalis. Biomolecules. 2015; 5(3):1979-1989. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom5031979
Chicago/Turabian StyleTamburini, Elena, Stefania Costa, Maria Gabriella Marchetti, and Paola Pedrini. 2015. "Optimized Production of Xylitol from Xylose Using a Hyper-Acidophilic Candida tropicalis" Biomolecules 5, no. 3: 1979-1989. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom5031979
APA StyleTamburini, E., Costa, S., Marchetti, M. G., & Pedrini, P. (2015). Optimized Production of Xylitol from Xylose Using a Hyper-Acidophilic Candida tropicalis. Biomolecules, 5(3), 1979-1989. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom5031979








