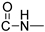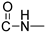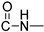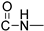The chemicals used for the synthesis of the novel compounds were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (Burlington, MA, USA), Fluka (Buchs, Switzerland), Alfa-Aesar (Lancashire, UK) and Acros (Fukuoka, Japan) and were used without further purification. The synthesized compounds were structurally characterized using 300 MHz and 600 MHz Varian NMR spectrometer using DMSO-d6 and CDCl3-d1 99.9 atom % D as solvents. 1HNMR spectra were acquired at 298 K using a spectral width of −2–20 ppm and 32 number of scans. Coupling constants (J) are reported in Hertz (Hz) and chemical shifts (δ) are given in parts per million (ppm) units, relative to the solvent. Spectra processing was performed using MestReNova version number11.0.0 software. HR-MS spectra were recorded on a UHPLC-MSn Orbitrap Velos-Thermo mass spectrometer (Thermo Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). FTIR spectroscopy was performed on a JASCO FT/IR-4200 spectrometer (JASCO, Easton, MD, USA) in the form of KBr pellets, in the scanning range of 400–4000 cm−1. Melting points were measured on a Gallenkamp MFB-595 melting point apparatus and are reported uncorrected. The used cell lines in our experiments were a kind offer from Associate Professor A. Pappa (Department of Molecular Biology & Genetics, Faculty of Health Sciences, Democritus University of Thrace, 68100 Alexandroupolis, Greece): (I) The human cancer cell lines A549 (non-small cell lung adenocarcinoma, ATCC CCL-185) were obtained from the American Type Culture Collection (Rockville, MD, USA). (ΙΙ) The A375 cells were obtained from the American Type Culture Collection (ATCC; Cat No: CRL-1619, Manassas, VA, USA). (IIΙ) The human immortalized keratinocyte (HaCaT) cell line was kindly provided by Dr Sharon Broby (Dermal Toxicology & Effects Group; Centre for Radiation, Chemical and Environmental Hazards; Public Health England, Didcot, UK).
2.1. Synthesis and General Procedures
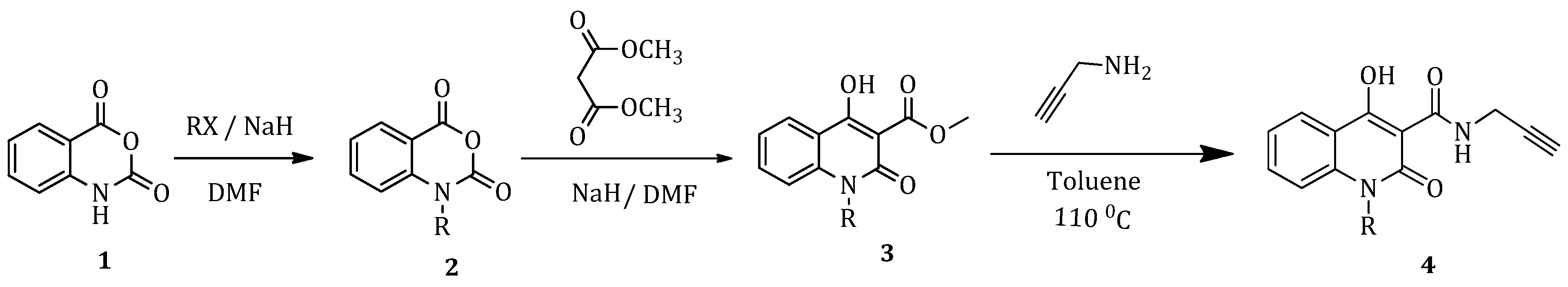
2.1.1. General Method (A): Synthesis of N-Substituted Isatoic Anhydrides (2a–2g)
The desired alkyl halide was added to a stirred solution of isatoic anhydride (1) and sodium hydride (NaH), in dry dimethylformamide (DMF), under cooling. The reaction mixture was then refluxed or stirred at room temperature for 24 h, under inert atmosphere and monitored by Thin-Layer Chromatography (TLC). Upon completion, the mixture was poured into a conical flask containing water and ice and then extracted three times with diethyl ether (Et2O). The combined organic phases were dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate (Na2SO4) and concentrated under reduced pressure. The final product (2) was obtained as a solid after additional rinsing with Et2O and used in the next step without further purification.
1-methyl-1H-benzo[d][1,3]oxazine-2,4-dione (2a)
Prepared according to the general method (A), isatoic anhydride (1) (5 g, 30.6 mmol) was added at room temperature to a mixture of NaH (1.1 g, 45.9 mol, 60% w/w in oil) and 125 mL dry DMF, followed by the addition of iodomethane (2.3 mL, 36.7 mmol) at 0 °C. The product (2a) was obtained after the appropriate treatment in the form of a beige solid. Yield: 64% (3.729 g). 1H NMR (600 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ (ppm) 8.00 (dd, J = 7.8, 1.2 Hz, 1H, Ar-H), 7.78 (td, J = 8.4, 1.2 Hz, 1H, Ar-H), 7.44 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 1H, Ar-H), 7.34 (d, J = 7.2 Hz, 1H, Ar-H), 3.46 (s, 3H, N-CH3); 13C NMR (150 MHz, DMS-d6) δ (ppm) 159.0, 147.7, 142.2, 137.2, 129.3, 123.6, 114.8, 111.5, 31.7.
1-benzyl-1H-benzo[d][1,3]oxazine-2,4-dione (2b)
Prepared according to the general method (A), isatoic anhydride (1) (3 g, 18.4 mmol) was added at room temperature to a mixture of NaH (662.4 mg, 27.6 mol, 60% w/w in oil) and 75 mL dry DMF, followed by the addition of benzyl bromide (2.6 mL, 24.6 mmol) at 0 °C. The product (2b) was obtained after the appropriate treatment in the form of a beige solid. Yield: 51% (2.3842 g). 1H NMR (600 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ (ppm) 8.04 (dd, J = 7.8, 1.8 Hz, 1H, Ar-H), 7.63 (td, J = 8.4, 1.2 Hz, 1H, Ar-H), 7.41 (d, J = 7.8 Hz, 2H, Ar-H), 7.34 (t, J = 7.8 Hz, 2H, Ar-H), 7.31 (t, J = 7.8 Hz, 1H, Ar-H), 7.27 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, 1H, Ar-H), 7.24 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 1H, Ar-H), 5.29 (s, 2H, N-CH2-Ar); 13C NMR (150 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ (ppm) 158.9, 148.3, 141.4, 137.0, 135.3, 129.5, 128.6, 127.4, 126.6, 123.7, 115.1, 112.1, 47.6.
1-ethyl-1H-benzo[d][1,3]oxazine-2,4-dione (2c)
Prepared according to the general method (A), isatoic anhydride (1) (2 g, 12.3 mmol) was added at room temperature to a mixture of NaH (444 mg, 18.5 mol, 60% w/w in oil) and 50 mL dry DMF, followed by the addition of iodoethane (1.2 mL, 14.8 mmol) at 0 °C. The product (2c) was obtained after the appropriate treatment in the form of a beige solid. Yield: 36% (840 mg). 1H NMR (600 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ (ppm) 8.0 (d, J = 7.8, 1H, Ar-H), 7.85 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, 1H, Ar-H), 7.50 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 1H, Ar-H), 7.33 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, 1H, Ar-H), 4.06 (q, J = 5.4 Hz, 2H, N-CH2-), 1.23 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, 3H, -CH3); 13C NMR (150 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ (ppm) 159.0, 147.3, 141.1, 137.2, 129.6, 123.5, 114.6, 111.8, 11.90.
1-(3-methylbut-2-en-1-yl)-1H-benzo[d][1,3]oxazine-2,4-dione (2d)
Prepared according to the general method (A), isatoic anhydride (1) (4 g, 24.5 mmol) was added at room temperature to a mixture of NaH (883.2 mg, 36.8 mol, 60% w/w in oil) and 100 mL dry DMF, followed by the addition of prenyl bromide (4.3 mL, 36.8 mmol) at 0 °C. The product (2d) was obtained after the appropriate treatment in the form of a beige solid. Yield: 32% (680.9 mg). 1H NMR (600 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ (ppm) 8.01 (d, J = 7.8 Hz, 1H, Ar-H), 7.85 (t, J = 7.8 Hz, 1H, Ar-H), 7.33 (t, J = 7.8 Hz, 1H, Ar-H), 7.29 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 1H, Ar-H), 5.19–5.17 (m, 1H, N-CH2-CH=), 4.64 (d, J = 6.0 Hz, 2H, N-CH2-CH=), 1.81 (s, 3H, -CH3), 1.70 (s, 3H, -CH3); 13C NMR (150 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ (ppm) 158.9, 147.6, 141.3, 137.14, 136.4, 129.6, 123.6, 118.2, 114.8, 111.8, 42.7, 25.3, 18.1.
1-octyl-1H-benzo[d][1,3]oxazine-2,4-dione (2e)
Prepared according to the general method (A), isatoic anhydride (
1) (2 g, 12.3 mmol) was added at room temperature to a mixture of NaH (444 mg, 18.5 mol, 60%
w/
w in oil) and 100 mL dry DMF, followed by the addition of 1-bromooctane (3.2 mL, 18.5 mmol) at 0 °C. The product (
2e) was obtained after the appropriate treatment in the form of a beige solid. Yield: 25% (813.8 mg).
1H NMR (600 MHz, CDCl
3)
δ (ppm) 8.16 (dd,
J = 7.8, 1.8 Hz, 1H, Ar-H), 7.75 (ddd,
J = 7.8, 7.2, 1.8 Hz, 1H, Ar-H), 7.28 (t,
J = 7.8 Hz, 1H, Ar-H), 7.16 (d,
J = 8.4 Hz, 1H, Ar-H), 4.04 (t,
J = 7.8 Hz, 2H, N-CH
2-), 1.75 (quint,
J = 7.8 Hz, 2H, N-CH
2-
CH2-), 1.44–1.40 (m, 2H, -CH
2-), 1.30–1.24 (m, 8H, 4×-CH
2-), 0.87 (t,
J = 7.2 Hz, 3H, -CH
3).
13C NMR (150 MHz, CDCl
3)
δ (ppm) 158.7, 147.8, 141.5, 137.3, 131.1, 124.0, 114.0, 112.0, 77.2, 45.1, 31.9, 29.3, 28.9, 27.0, 27.8, 22.7, 14.2 [
53].
1-(3-phenylpropyl)-1H-benzo[d][1,3]oxazine-2,4-dione (2f)
Prepared according to the general method (A), isatoic anhydride (
1) (4 g, 24.5 mmol) was added at room temperature to a mixture of NaH (883.2 mg, 36.8 mol, 60%
w/
w in oil) and 100 mL dry DMF, followed by the addition of 1-bromo3-phenylpropane (5.6 mL, 36.8 mmol) at 0 °C. The product (
2f) was obtained after the appropriate treatment in the form of a beige solid. Yield: 30% (2.1 g).
1H NMR (600 MHz, DMSO-d
6)
δ (ppm) 8.00 (d,
J = 7.8 Hz, 1H, Ar-H), 7.82 (t,
J = 8.4 Hz, 1H, Ar-H), 7.42 (d,
J = 8.4 Hz, 1H, Ar-H), 7.32 (t,
J = 7.8 Hz, 1H, Ar-H), 7.28–7.26 (m, 2H, Ar-H), 7.23 (d,
J = 7.2 Hz, 2H, Ar-H), 7.17 (t,
J = 7.8 Hz, 1H, Ar-H), 4.05 (t,
J = 7.2 Hz, 2H, N-CH
2-), 2.73 (t,
J = 7.8 Hz, 2H, -CH
2-Ar), 1.95 (t,
J = 7.8 Hz, 2H, N-CH
2-C
H2-);
13C NMR (150 MHz, DMSO-d
6)
δ (ppm) 159.0, 147.5, 141.3, 141.2, 137.1, 129.6, 128.3, 128.2, 125.9, 123.5, 114.7, 111.8, 44.0, 32.0, 28.0 [
54].
(E)-1-(3-phenylprop-1-en-1-yl)-1H-benzo[d][1,3]oxazine-2,4-dione (2g)
Prepared according to the general method (A), isatoic anhydride (1) (1 g, 6.1 mmol) was added at room temperature to a mixture of NaH (219.6 mg, 9.2 mol, 60% w/w in oil) and 25 mL dry DMF, followed by the addition of 3-bromo-1-phenyl-1-propene (3.2 mL, 9.2 mmol) at 0 °C. The product (2g) was obtained after the appropriate treatment in the form of a beige solid. Yield: 31% (520.0 mg). 1H NMR (600 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ (ppm) 8.15 (dd, J = 7.8, 1.2 Hz, 1H, Ar-H), 7.73 (ddd, J = 8.4, 7.8, 1.2 Hz, 1H, Ar-H), 7.34–7.33 (m, 2H, Ar-H), 7.30–7.27 (m, 3H, Ar-H), 7.26–7.23 (m, 2H, Ar-H), 6.66 (d, J = 15.6Hz, 1H, =CH-Ar), 6.24 (dt, J = 16.2, 5.4 Hz, 1H, N-CH2-CH=), 4.85 (dd, J = 6.0, 1.8 Hz, 2H, N-CH2-); 13C NMR (150 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ (ppm) 158.5, 147.9, 141.4, 137.4, 135.7, 134.2, 131.0, 128.7, 128.4, 126.6, 124.2, 121.2, 114.5, 111.9, 77.2, 46.9.
2.1.2. General Method (Β): Synthesis of N-Substituted 4-Hydroxy-Quinolinones (3a–3g)
Sodium hydride (NaH) was suspended in dry DMF in a round-bottom flask and 1 eq. of N-substituted isatoic anhydride (2) and 5 eq. of dimethyl malonate were added at 0 °C. The mixture was refluxed at 80 °C under inert atmosphere for 2–2.5 h, with the reaction progress monitored by TLC. After completion of the reaction, the mixture was cooled in an ice-water bath, acidified with HCl (10% aqueous solution) and then extracted with Et2O; the organic layer was collected, dried over Na2SO4, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The desired quinolinone product (3) was obtained in a solid form and it was further purified through recrystallization from methanol/dichloromethane.
Methyl 4-hydroxy-1-methyl-2-oxo-1,2-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylate (3a)
Prepared according to the general method (B), N-methyl-isatoic anhydride (
2a) (444.3 mg, 2.5 mmol) was added to a mixture of NaH (120.5 mg, 5.0 mmol, 60%
w/
w in oil) in 20 mL of dry DMF, followed by the addition of dimethyl malonate (1.4 mL, 12.6 mmol) under cooling. After the work-up procedure, the product (
3a) was obtained upon recrystallization from methanol as a white solid. Yield: 52%; M.p. 160–162 °C;
1H NMR (600 MHz, CDCl
3):
δ (ppm) 14.06 (s, 1H, -OH), 8.19 (d,
J = 7.8Hz, 1H, Ar-H), 7.69 (t,
J = 7.8Hz, 1H, Ar-H), 7.32 (d,
J = 8.4 Hz, 1H, Ar-H), 7.26 (br, 1H, Ar-H), 4.03 (s, 3H, C=O-O-CH
3), 3.65 (s, 3H, N-CH
3);
13C NMR (75 MHz, CDCl
3)
δ (ppm) 173.9, 171.9, 159.5, 141.0, 134.5, 126.0, 122.0, 115.1, 114.7, 97.9, 53.2, 25.8 [
52].
Methyl 1-benzyl-4-hydroxy-2-oxo-1,2-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylate (3b)
Prepared according to the general method (B), N-benzyl-isatoic anhydride (
2b) (2.38 g, 9.4 mmol) was added to a mixture of NaH (451.2 mg, 18.8 mmol, 60%
w/
w in oil) in 70 mL of dry DMF, followed by the addition of dimethyl malonate (5.4 mL, 47.0 mmol) under cooling. After the work-up procedure, the product (
3b) was obtained upon recrystallization from methanol as a white solid. Yield: 46%; M.p. 151–152 °C;
1H NMR (600 MHz, CDCl
3):
δ (ppm) 8.20 (dd,
J = 8.4, 1.8 Hz, 1H, Ar-H), 7.55 (td,
J = 8.4, 1.8 Hz, 1H, Ar-H), 7.30–7.28 (m, 1H), 7.23–7.21 (m, 5H), 5.50 (s, 2H, N-CH
2-Ar), 4.05 (s, 3H, C=O-O-CH
3);
13C NMR (75 MHz, CDCl
3)
δ (ppm) 173.2, 171.8., 159.6, 141.2, 136.7, 134.6, 128.6, 128.6, 126.3, 126.1, 122.0, 115.1, 114.2, 97.8, 53.2, 45.1; HR-MS calcd for C
18H
16O
4N (Μ + H)
+: 310.1074, found: 310.1069 [
55].
Methyl 1-ethyl-4-hydroxy-2-oxo-1,2-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylate (3c)
Prepared according to the general method (B), N-ethyl-isatoic anhydride (
2c) (1.5429 g, 8.1 mmol) was added to a mixture of NaH (388.8 mg, 16.2 mmol, 60%
w/
w in oil) in 60 mL of dry DMF, followed by the addition of dimethyl malonate (4.7 mL, 40.5 mmol) under cooling. The product (
3c) was obtained after the work-up procedure in the form of a white solid. Yield: 40% (449.4 mg); M.p. 133–134 °C;
1H NMR (600 MHz, CDCl
3):
δ (ppm) 8.20 (dd,
J = 8.4, 1.8 Hz, 1H, Ar-H), 7.68 (td,
J = 8.4, 1.2 Hz, 1H, Ar-H), 7.33 (d,
J = 8.4 Hz, 1H, Ar-H), 7.24–7.25 (m, 1H, Ar-H), 4.31 (q,
J = 7.2 Hz, 2H, N-
CH2-CH
3), 4.04 (s, 3H, C=O-O-
CH3), 1.33 (t,
J = 7.2 Hz, 3H, N-
CH2-CH
3);
13C NMR (75 MHz, CDCl
3)
δ (ppm) 173.0, 171.9, 159.6, 141.0, 134.6, 126.0, 122.0, 115.2, 114.8, 98.0, 50.2, 25.9, 18.5; HR-MS calcd for C
13H
14O
4N (Μ + H)
+:
m/
z: 248.0917, found: 248.0916 [
52].
Methyl 4-hydroxy-1-(3-methylbut-2-en-1-yl)-2-oxo-1,2-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylate (3d)
Prepared according to the general method (B), N-prenyl-isatoic anhydride (2d) (680.9 mg, 2.9 mmol) was added to a mixture of NaH (139.2 mg, 5.8 mmol, 60% w/w in oil) in 22 mL of dry DMF, followed by the addition of dimethyl malonate (1.7 mL, 14.5 mmol) under cooling. After the work-up procedure, the product (3d) was obtained as a white solid. Yield: 32%; M.p. 119–121 °C; 1H NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3): δ (ppm) 8.19 (dd, J = 7.8, 1.2 Hz, 1H, Ar-H), 7.65 (td, J = 8.4, 1.2 Hz, 1H), 7.27–7.23 (m, 2H, Ar-H), 5.12 (t, J = 8.4 Hz, 1H, N-CH2-CH=), 4.87 (d, J = 5.4 Hz, 2H, N-CH2-CH=), 4.03 (s, 3H, C=O-O-CH3), 1.88 (s, 3H, -CH3), 1.71 (s, 3H, -CH3); 13C NMR (151 MHz, CDCl3): δ (ppm) 173.25, 171.84, 159.51, 140.95, 136.13, 134.49, 125.96, 121.96, 119.38, 115.13, 114.70, 97.88, 53.15, 40.89, 25.77, 18.46; HR-MS calcd for C16H18O4N (Μ + H)+: m/z: 288.1230, found: 288.1226.
Methyl 4-hydroxy-1-octyl-2-oxo-1,2-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylate (3e)
Prepared according to the general method (B), N-octyl-isatoic anhydride (2e) (813.8 mg, 3.0 mmol) was added to a mixture of NaH (144.0 mg, 6.0 mmol, 60% w/w in oil) in 22 mL of dry DMF, followed by the addition of dimethyl malonate (1.7 mL, 15.0 mmol) under cooling. After the work-up procedure, the product (3e) was obtained as a white solid. Yield: 19%; M.p. 69–71 °C; 1H NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3): δ (ppm) 8.20 (dd, J = 7.8, 1.2 Hz, 1H, Ar-H), 7.68 (td, J = 8.4, 1.2 Hz, 1H, Ar-H), 7.30 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 1H, Ar-H), 7.24 (t, J = 7.8 Hz, 1H, Ar-H), 4.20 (t, J = 7.8 Hz, 2H, N-CH2-), 4.03 (s, 3H, C=O-O-CH3), 1.71 (quint, J = 7.8 Hz, 2H, N-CH2-CH2-), 1.45 (quint, J = 7.8 Hz, 2H, N-CH2-CH2-CH2-), 1.36 (quint, J = 7.2 Hz, 2H, N-(CH2)3-CH2-), 1.33–1.25 (m, 6H, N-(CH2)4-(CH2)3-CH3), 0.88 (t, J = 6.6 Hz, 3H, -CH3); 13C NMR (150 MHz, CDCl3): δ (ppm) 173.25, 171.73, 159.51, 140.80, 134.54, 126.07, 121.89, 115.11, 114.33, 97.85, 53.15, 42.63, 31.94, 29.47, 29.38, 27.63, 27.21, 22.77, 14.23; HR-MS calcd for C19H26O4N (Μ + H)+: m/z: 332.1856, found: 332.1850.
Methyl 4-hydroxy-2-oxo-1-(3-phenylpropyl)-1,2-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylate (3f)
Prepared according to the general method (B), N-phenylpropyl-isatoic anhydride (2f) (2.1 g, 7.5 mmol) was added to a mixture of NaH (360.0 mg, 15.0 mmol, 60% w/w in oil) in 56 mL of dry DMF, followed by the addition of dimethyl malonate (4.3 mL, 37.5 mmol) under cooling. After the work-up procedure, the product (3f) was obtained as a white solid. Yield: 56%; M.p. 101–104 °C; 1H NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3): δ (ppm) 8.18 (dd, J = 7.8, 1.2 Hz, 1H, Ar-H), 7.59 (td, J = 8.4, 1.2 Hz, 1H, Ar-H), 7.30 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, 2H, Ar-H), 7.24–7.20 (m, 4H, Ar-H), 7.06 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 1H, Ar-H), 4.24 (t, J = 7.8 Hz, 2H, N-CH2-), 4.04 (s, 3H, C=O-O-CH3), 2.80 (t, J = 7.8 Hz, 2H, -CH2-Ar), 2.05 (quint, J = 7.8 Hz, 2H, N-CH2-CH2-CH2-Ar); 13C NMR (150 MHz, CDCl3): δ (ppm) 173.19, 171.77, 159.53, 141.19, 140.62, 134.55, 128.59, 128.52, 126.23, 126.05, 121.91, 115.08, 114.14, 97.78, 53.16, 42.00, 33.38, 28.89; HR-MS calcd for C20H20O4N (Μ + H)+: m/z: 338.1387, found: 338.1382.
Methyl 1-cinnamyl-4-hydroxy-2-oxo-1,2-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylate (3g)
Prepared according to the general method (B), N-cinnamyl-isatoic anhydride (2g) (520.0 mg, 1.9 mmol) was added to a mixture of NaH (91.2 mg, 3.8 mmol, 60% w/w in oil) in 14 mL of dry DMF, followed by the addition of dimethyl malonate (1.1 mL, 9.3 mmol) under cooling. After the work-up procedure, the product (3g) was obtained as a white solid. Yield: 41%; M.p. 177–178 °C; 1H NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3): δ (ppm) 14.18 (brs, 1H, -OH) 8.22 (dd, J = 7.8, 1.2 Hz, 1H, Ar-H), 7.66 (td, J = 9, 1.8 Hz, 1H, Ar-H), 7.38 (d, J = 9 Hz, 1H, Ar-H), 7.32–7.31 (m, 2H, Ar-H), 7.28–7.25 (m, 3H, Ar-H), 7.20 (t, J = 7.8 Hz, 1H, Ar-H), 6.55 (d, J = 16.2 Hz, 1H, N-CH2-CH=CH-Ar), 6.29 (dt, J = 16.2, 6 Hz, 1H, N-CH2-CH=CH-Ar), 5.06 (d, J = 4.8 Hz, 2H, N-CH2-), 4.05 (s, 3H, C=O-O-CH3); 13C NMR (150 MHz, CDCl3): δ (ppm) 173.20, 172.11, 159.54, 140.91, 136.43, 134.67, 132.77, 128.65, 127.90, 126.53, 126.04, 123.55, 122.22, 115.19, 114.84, 97.82, 53.22, 44.31; HR-MS calcd for C20H18O4N (Μ + H)+: m/z: 336.1230, found: 336.1230.
2.1.3. General Method (C): Synthesis of Carboxamides (4a–4g)
To a stirred solution of 1 eq of N-substituted-4-hydroxy-quinolinone (3), dissolved in toluene, 2 eq of propargylamine was added. The reaction mixture was refluxed at 110 °C under inert atmosphere for 2–2.5 h. The completion of the reaction was monitored by TLC. At the end of the reaction, the mixture was cooled to 0 °C (ice-water bath) and the precipitate formed was filtered and washed with Et2O. The product (4) was obtained in solid form and used without purification in the next step.
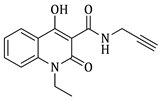
4-hydroxy-1-methyl-2-oxo-N-(prop-2-yn-1-yl)-1,2-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxamide (4a)
Prepared according to the general method (C), N-methyl-quinolinone (3a) (508 mg, 2.2 mmol) was dissolved in 12 mL toluene, followed by the addition of propargylamine (281 μL, 4.4 mmol). After the work-up procedure, the product (4a) was obtained as an orange-brown solid. Yield: 82% (463.1 mg); M.p. 195.0–198.0 °C; 1H NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3): δ (ppm) 16.52 (s, 1H, -OH), 10.51 (brs, 1H, -NH), 8.21 (dd, J = 8.4, 1.2 Hz, 1H, Ar-H), 7.70 (ddd, J = 8.4, 7.8, 1.2 Hz, 1H, Ar-H), 7.36 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 1H, Ar-H), 7.31 (t, J = 7.8 Hz, 1H, Ar-H), 4.24 (dd, J = 5.4, 2.4 Hz, 2H, NH-CH2-), 3.68 (s, 3H, N-CH3), 2.27 (br, 1H, -C≡CH); 13C NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3) δ (ppm) 171.8, 171.0, 162.7, 140.1, 134.1, 125.7, 122.6, 116.1, 114.4, 97.0, 79.2, 71.7, 29.3, 28.8; HR-MS calcd for C14H13O3N2 (Μ + H)+: m/z: 257.0926, found: 257.0925.
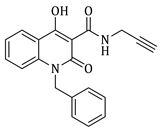
1-benzyl-4-hydroxy-2-oxo-N-(prop-2-yn-1-yl)-1,2-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxamide (4b)
Prepared according to the general method (C), N-benzyl-quinolinone (3b) (521 mg, 1.7 mmol) was dissolved in 12 mL toluene, followed by the addition of propargylamine (218 μL, 3.4 mmol). After the work-up procedure, the product (4b) was obtained as an orange-brown solid. Yield: 71% (402.0 mg); M.p. 178–182 °C; 1H NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3): δ (ppm) 16.67 (s, 1H, -OH), 10.53 (brs, 1H, -NH), 8.24 (d, J = 7.8 Hz, 1H, Ar-H), 7.56 (ddd, J = 8.4, 7.8, 1.2 Hz, 1H, Ar-H), 7.32–7.30 (m, 2H, Ar-H), 7.28–7.25 (m, 3H, Ar-H), 7.19–7.18 (m, 2H, Ar-H), 5.52 (s, 2H, N-CH2-Ar), 4.25 (dd, J = 5.4, 2.4 Hz, 2H, -NH-CH2-), 2.27 (br, 1H, -C≡CH); 13C NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3): δ (ppm) 172.2, 171.0, 162.8, 139.7, 136.1, 134.0, 129.1, 127.6, 126.2, 125.7, 122.7, 116.4, 115.2, 96.8, 71.7, 45.9, 28.8; HR-MS calcd for C20H17O3N2 (Μ + H)+: m/z: 333.1239, found: 333.1234.
1-ethyl-4-hydroxy-2-oxo-N-(prop-2-yn-1-yl)-1,2-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxamide (4c)
Prepared according to the general method (C), N-ethyl-quinolinone (3c) (402.4 mg, 1.6 mmol) was dissolved in 10 mL toluene, followed by the addition of propargylamine (215 μL, 3.2 mmol). After the work-up procedure, the product (4c) was obtained as an orange-brown solid. Yield: 77% (338.7 mg); M.p. 190–195 °C; 1H NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3): δ (ppm) 16.48 (s, 1H, -OH), 10.59 (brs, 1H, -NH), 8.24 (dd, J = 7.8, 1.2 Hz, 1H, Ar-H), 7.69 (ddd, J = 9.0, 8.1, 1.8 Hz, 1H, Ar-H), 7.38 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 1H, Ar-H), 7.30 (t, J = 7.8 Hz, 1H, Ar-H), 4.33 (q, J = 7.2 Hz, 2H, N-CH2), 4.24 (dd, J = 5.4, 2.4 Hz, 2H, NH-CH2), 2.27 (br, 1H, -C≡CH), 1.36 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, 3H, -CH3); 13C NMR (150 MHz, CDCl3): δ (ppm) 171.7, 171.0, 162.3, 139.1, 134.0, 125.9, 122.4, 116.4, 114.3, 96.9, 79.3, 71.7, 37.4, 28.8, 13.0; HR-MS calcd for C15H15O3N2 (Μ + H)+: m/z: 271.1086, found: 271.1076.
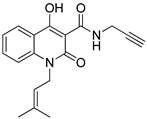
4-hydroxy-1-(3-methylbut-2-en-1-yl)-2-oxo-N-(prop-2-yn-1-yl)-1,2-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxamide (4d)
Prepared according to the general method (C), N-prenyl-quinolinone (3d) (228.8 mg, 0.8 mmol) was dissolved in 8 mL toluene, followed by the addition of propargylamine (102.5 μL, 1.6 mmol). After the work-up procedure, the product (4d) was obtained as an orange-brown solid. Yield: 55% (136.6 mg); M.p. 150.0–153.0 °C; 1H NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3): δ (ppm) 16.51 (s, 1H, -OH), 10.57 (brs, 1H, -NH), 8.22 (dd, J = 7.8, 1.2 Hz, 1H, Ar-H), 7.66 (ddd, J = 8.4, 7.8, 1.2 Hz, 1H, Ar-H), 7.31–7.28 (m, 2H, Ar-H), 5.10 (t, J = 6.0Hz, 1H, -CH=C), 4.90 (d, J = 4.2 Hz, 2H, N-CH2-), 4.23 (dd, J = 5.4, 2.4 Hz, 2H, NH-CH2-), 2.26 (br, 1H, -C≡CH), 1.89 (s, 3H, -CH3), 1.74 (s, 3H, -CH3); 13C NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3): δ (ppm) 171.8, 171.0, 162.4, 139.5, 136.4, 133.9, 125.7, 122.4, 119.3, 116.3, 114.8, 96.9, 79.3, 71.6, 40.9, 28.7, 25.7, 18.5; HR-MS calcd for C18H19O3N2 (Μ + H)+: m/z: 311.1390, found: 311.1391.
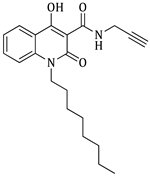
4-hydroxy-1-octyl-2-oxo-N-(prop-2-yn-1-yl)-1,2-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxamide (4e)
Prepared according to the general method (C), N-octyl-quinolinone (3e) (180.0 mg, 0.5 mmol) was dissolved in 7 mL toluene, followed by the addition of propargylamine (69.0 μL, 1.1 mmol). After the work-up procedure, the product (4e) was obtained as an orange-brown solid. Yield: 10% (14.3 mg); M.p. 47.0–49.0 °C; 1H NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3): δ (ppm) 16.49 (s, 1H, -OH), 10.59 (brs, 1H, -NH), 8.23 (dd, J = 7.8, 1.2 Hz, 1H, Ar-H), 7.69 (ddd, J = 9.0, 8.1, 1.8 Hz, 1H, Ar-H), 7.35 (d, J = 9.0 Hz, 1H, Ar-H), 7.30 (t, J = 7.8 Hz, 1H, Ar-H), 4.24–4.23 (m, 4H, N-CH2, NH-CH2-), 2.27 (br, 1H, -C≡CH), 1.72 (quint, J = 7.8 Hz, 2H, N-CH2-CH2-), 1.46 (quint, J = 7.2 Hz, 2H, N-(CH2)2-CH2-), 1.38 (quint, J = 7.2Hz, 2H, N-(CH2)3-CH2-), 1.29 (m, 6H, 3×-CH2-), 0.89 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, 3H, -CH3); 13C NMR (75 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ (ppm) 171.0, 170.4, 161.3, 139.0, 134.5, 124.8, 122.5, 115.3, 115.1, 95.9, 80.1, 73.8, 41.6, 34.1, 31.2, 28.7, 28.2, 27.2, 26.3, 22.1, 14.0; HR-MS calcd for C21H27O3N2 (Μ + H)+: m/z: 355.2022, found: 355.2014.
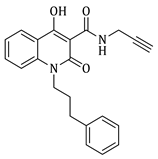
4-hydroxy-2-oxo-1-(3-phenylpropyl)-N-(prop-2-yn-1-yl)-1,2-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxamide (4f)
Prepared according to the general method (C), N-phenylpropyl-quinolinone (3f) (700.0 mg, 2.1 mmol) was dissolved in 15 mL toluene, followed by the addition of propargylamine (269.0 μL, 4.2 mmol). After the work-up procedure, the product (4f) was obtained as an orange-brown solid. Yield: 70% (521.8 mg); M.p. 84.0–86.0 °C; 1H NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3): δ (ppm) 16.49 (s, 1H, -OH), 10.57 (brs, 1H, -NH), 8.21 (dd, J = 7.8, 1.2 Hz, 1H, Ar-H), 7.60 (ddd, J = 8.4, 7.8, 1.2 Hz, 1H, Ar-H), 7.33–7.30 (m, 2H, Ar-H), 7.28–7.22 (m, 4H, Ar-H), 7.10 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 1H, Ar-H), 4.28–4.23 (m, 4H, N-CH2, NH-CH2-), 2.80 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, 2H, -CH2-Ar), 2.28 (br, 1H, -C≡CH), 2.06 (quint, J = 7.8 Hz, 2H, N-CH2-CH2-); 13C NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3): δ (ppm) 171.7, 171.0, 162.4, 141.0, 139.2, 134.0, 128.6, 128.5, 126.3, 125.8, 122.4, 116.3, 114.2, 96.8, 79.2, 71.7, 41.8, 33.3, 29.0, 28.7; HR-MS calcd for C22H21O3N2 (Μ + H)+: m/z: 361.1552, found: 361.1546.
1-cinnamyl-4-hydroxy-2-oxo-N-(prop-2-yn-1-yl)-1,2-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxamide (4g)
Prepared according to the general method (C), N-cinnamyl-quinolinone (3g) (175.0 mg, 0.5 mmol) was dissolved in 7 mL toluene, followed by the addition of propargylamine (76.0 μL, 1.2 mmol). After the work-up procedure, the product (4g) was obtained as an orange-brown solid. Yield: 48% (90.0 mg); M.p. 93.5–97.0 °C; 1H NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3): δ (ppm) 16.61 (s, 1H, -OH), 10.53 (brs, 1H, -NH), 8.25 (dd, J = 8.4, 1.2 Hz, 1H, Ar-H), 7.67 (ddd, J = 8.4, 7.8, 1.2 Hz, 1H, Ar-H), 7.41 (d, J = 9.0Hz, 1H, Ar-H), 7.33–7.31 (m, 3H, Ar-H), 7.30–7.27 (m, 2H, Ar-H), 7.22 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, 1H, Ar-H), 6.49 (d, J = 16.2 Hz, 1H, -CH-Ar), 6.30 (dt, J = 16.2, 5.4 Hz, 1H, -CH=CH-Ar), 5.08 (d, J = 4.2 Hz, 2H, N-CH2-), 4.25 (dd, J = 4.8, 2.4 Hz, 2H, NH-CH2-), 2.27 (br, 1H, -C≡CH); 13C NMR (150 MHz, CDCl3): δ (ppm) 172.0, 170.9, 162.3, 139.4, 136.1, 133.9, 132.4, 128.5, 127.9, 126.4, 125.7, 123.0, 122.5, 116.2, 114.8, 96.7, 79.0, 77.5, 77.0, 76.6, 71.6, 44.1, 28.7. HR-MS calcd for C22H19O3N2 (Μ + H)+: m/z: 359.1396, found: 359.1390.
2.1.4. General Method (D): Synthesis of Quinolinone–triazoles (5a–5j)
In a quartz μW-reaction tube, equimolar quantities of sodium azide (NaN3), triethylamine (Et3N), the appropriate alkyl bromide and carboxamide (4), along with the appropriate amount of copper sulfate (CuSO4), and sodium ascorbate as catalyst, were added to a mixture t-BuOH:H2O in a ratio 1:1. The reaction mixture was stirred under microwave radiation at 80 °C, 100 W for 10 min. The completion of the reaction was monitored by TLC. At the end of the reaction, the mixture was cooled to 0 °C (ice-water bath) and the precipitate formed was filtered and washed with water. The precipitate underwent a silica gel column chromatography in order to obtain the product (5) in high purity as a white solid.
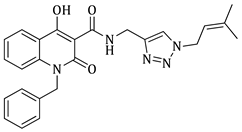
N-((1-benzyl-1H-1,2,3-triazol-4-yl)methyl)-4-hydroxy-1-methyl-2-oxo-1,2-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxamide (5a)
Prepared according to the general method (D), in a quartz vessel, 1.75 mmol (113.8 mg) NaN
3, 1.75 mmol (244.0 μL) Et
3N, 1.75 mmol (208.0 μL) benzyl bromide, 0.35 mmol (69.3mg) sodium ascorbate, 0.35 mmol (55.9 mg) CuSO
4 and 1.75 mmol (449.0 mg) of carboxamide (
4a) were dissolved in about 7mL of 1:1 t-BuOH/H
2O solution. After the work-up procedure, the product (
5a) was subjected to further purification via column chromatography, using PE/EtOAc 50:50 as eluent and was obtained as white solid. Yield: 40% (272.2 mg); M.p. 146.2–146.7 °C;
1H NMR (600 MHz, CDCl
3):
δ (ppm), 16.72 (s, 1H, 4-OH), 10.73 (brs, 1H,N-H), 8.19 (dd,
J = 7.8, 1.2 Hz, 1H, Ar-H), 7.68 (ddd,
J = 8.4, 7.8, 1.2 Hz, 1H, Ar-H), 7.52 (s, 1H, N-
CH=C-), 7.38–7.34 (m, 4H, Ar-H), 7.31–7.26 (m, 3H, Ar-H), 5.51 (s, 2H, N-
CH2-Ar), 4.74 (br, 2H, NH-
CH2-), 3.65 (s, 3H, N-
CH3);
13C NMR (75 MHz, CDCl
3):
δ (ppm) 171.8, 171.2, 162.6, 145.1, 140.0, 134.7, 133.9, 129.2, 128.8, 128.2, 125.5, 122.5, 122.2, 116.1, 114.3, 96.9, 54.3, 34.9, 29.2; IR 3118.33 cm
−1 (
, aromatic C-H), 2935.13 cm
−1 (
, aliphatic C-H), 1631.43 cm
−1 (
,
![Biomolecules 16 00029 i001 Biomolecules 16 00029 i001]()
), 1590.99 cm−1 (, N=N), 1563.99 cm−1 (, N-H), 1340.28 cm−1 (, C-N), 711.604 cm−1 (, aromatic monosubstitution); HR-MS calcd for C21H18O3N5 (Μ − H)−: m/z: 388.1410, found: 388.1407.
1-benzyl-N-((1-benzyl-1H-1,2,3-triazol-4-yl)methyl)-4-hydroxy-2-oxo-1,2-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxamide (5b)
Prepared according to the general method (D), in a quartz vessel, 1.20 mmol (401.0 mg) NaN
3, 1.20 mmol (167.0 μL) Et
3N, 1.20 mmol (143.0 μL) benzyl bromide, 0.24 mmol (47.5mg) sodium ascorbate, 0.24 mmol (38.3 mg) CuSO
4 and 1.20 mmol (401.0 mg) of carboxamide (
4b) were dissolved in about 7mL of 1:1 t-BuOH/H
2O solution. After the work-up procedure, the product (
5b) was subjected to further purification via column chromatography, using PE/EtOAc 50:50 as eluent and was obtained as white solid. Yield: 18% (100.2 mg); M.p. 187.6–188.4 °C;
1H NMR (600 MHz, CDCl
3):
δ (ppm), 16.91 (s, 1H, 4-OH), 10.69 (brs, 1H, -NH), 8.22 (dd,
J = 7.8, 0.6 Hz, 1H, Ar-H), 7.54 (ddd,
J = 8.4, 7.8, 1.2 Hz, 1H, Ar-H), 7.50 (s, 1H, N-
CH=C-), 7.38–7.34 (m, 3H, Ar-H), 7.31–7.27 (m, 4H, Ar-H), 7.25–7.23 (m, 3H, Ar-H), 7.16 (m, 2H, Ar-H), 5.51 (s, 4H, 2x N-
CH-Ar), 4.73 (br, 2H, NH-
CH2-);
13C NMR (75 MHz, CDCl
3):
δ (ppm) 172.3, 171.3, 162.9, 145.0, 139.7, 136.2, 134.7, 134.0, 129.2, 129.0, 128.9, 128.2, 127.5, 126.4, 125.7, 122.6, 122.2, 166.5, 115.2, 96.8, 54.3, 45.8, 35.0; IR 3126.04 cm
−1 (
aromatic C-H), 1660.77 cm
−1 (
,
![Biomolecules 16 00029 i002 Biomolecules 16 00029 i002]()
), 1589.06 cm−1 (, N=N), 1535.06 cm−1 (, N-H), 1328.71 cm−1 (, C-N), 725.104 cm−1 (, aromatic monosubstitution); HR-MS calcd for C27H24O3N5 (Μ + H)+: m/z: 466.1879, found: 466.1873.
N-((1-benzyl-1H-1,2,3-triazol-4-yl)methyl)-1-ethyl-4-hydroxy-2-oxo-1,2-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxamide (5c)
Prepared according to the general method (D), in a quartz vessel, 0.60 mmol (39.1 mg) NaN
3, 0.60 mmol (84.0 μL) Et
3N, 0.60 mmol (71.0 μL) benzyl bromide, 0.12 mmol (23.8 mg) sodium ascorbate, 0.12 mmol (19.2 mg) CuSO
4 and 0.60 mmol (162.0 mg) of carboxamide (
4c) were dissolved in about 7mL of 1:1 t-BuOH/H
2O solution. After the work-up procedure, the product (
5c) was subjected to further purification via column chromatography, using PE/EtOAc 50:50 as eluent and was obtained as white solid. Yield: 32% (77.5 mg); M.p. 144.0–144.5 °C;
1H NMR (600 MHz, CDCl
3):
δ (ppm) 16.67 (s, 1H, 4-OH), 10.76 (brs, 1H, -NH), 8.21 (dd,
J = 7.8, 1.2 Hz, 1H, Ar-H), 7.68 (ddd,
J = 7.2, 1.8 Hz, 1H, Ar-H), 7.52 (s, 1H, N-
CH=C-), 7.38–7.34 (m, 4H, Ar-H), 7.30–7.26 (m, 3H, Ar-H), 5.51 (s, 2H, N-
CH2-Ar), 4.73 (br, 2H, NH-
CH2-), 4.29 (q,
J = 7.2 Hz, 2H, -
CH2-CH
3), 1.32 (t,
J = 6.6 Hz, 3H, -CH
2-
CH3);
13C NMR (75 MHz, CDCl
3):
δ (ppm) 171.7, 171.3, 162.2, 145.1, 139.1, 134.7, 133.9, 129.2, 128.8, 128.2, 125.8, 122.3, 122.2, 116.4, 114.2, 97.0, 54.3, 37.3, 34.9, 13.0; IR 3442.31 cm
−1 (
, R-OH), 3168.47 cm
−1 (
, aromatic C-H), 2980.45 cm
−1 (
, aliphatic C-H), 1644.02 cm
−1 (
,
![Biomolecules 16 00029 i003 Biomolecules 16 00029 i003]()
), 1580.88 cm−1 (, N=N), 1536.99 cm−1 (, N-H), 1327.75 cm−1 (, C-N), 767.53 cm−1 (, aromatic monosubstitution); HR-MS calcd for C22H22O3N5 (Μ + H)+: m/z: 404.1723, found: 404.1716.
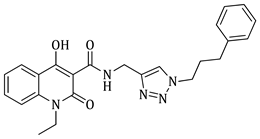
1-ethyl-4-hydroxy-2-oxo-N-((1-(3-phenylpropyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazol-4-yl)methyl)-1,2-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxamide (5d)
Prepared according to the general method (D), in a quartz vessel, 1.23 mmol (80.0 mg) NaN
3, 1.23 mmol (171.6 μL) Et
3N, 1.23 mmol (187.2 μL) 1-bromo-3-phenylpropane, 0.25 mmol (49.5 mg) sodium ascorbate, 0.25 mmol (39.9 mg) CuSO
4 and 1.23 mmol (333.0 mg) of carboxamide (
4c) were dissolved in about 7mL of 1:1 t-BuOH/H
2O solution. After the work-up procedure, the product (
5d) was subjected to further purification via column chromatography, using PE/EtOAc 60:40 as eluent and was obtained as white solid. Yield: 48% (254.7 mg); M.p. 84.0–86.0 °C;
1H NMR (600 MHz, CDCl
3):
δ (ppm), 16.75 (s, 1H, 4-OH), 10.78 (brs, 1H, -NH), 8.23 (d,
J = 7.8 Hz, 1H, Ar-H), 7.68 (t,
J = 8.4 Hz, 1H, Ar-H), 7.58 (brs, 1H, N-
CH=C-), 7.37 (d,
J = 8.4 Hz, 1H, Ar-H), 7.30–7.28 (m, 3H, Ar-H), 7.21–7.17 (m, 3H, Ar-H), 4.75 (s, 2H, NH-
CH2-), 4.32 (m, 4H, 2x N-
CH2-), 2.66 (t,
J = 6.6 Hz, 2H, N-CH
2-CH
2-
CH2-Ar), 2.26 (t,
J = 5.4 Hz, 2H, N-CH
2-
CH2-CH
2-Ar), 1.33 (t,
J = 6.6 Hz, N-CH
2-
CH3);
13C NMR (75 MHz, CDCl
3):
δ (ppm) 171.7, 171.3, 162.2, 140.2, 139.1, 133.9, 128.7, 128.5, 126.4, 125.8, 122.3, 116.4, 114.2, 96.9, 49.6, 37.3, 34.9, 32.6, 31.7, 12.9; IR 3145.33 cm
−1 (
, aromatic C-H), 2935.13 cm
−1 (
, aliphatic C-H), 1637.27 cm
−1 (
,
![Biomolecules 16 00029 i004 Biomolecules 16 00029 i004]()
), 1587.13 cm−1 (, N=N), 1554.34 cm−1 (, N-H), 1334.50 cm−1 (, C-N), 748.245 cm−1 (, aromatic monosubstitution); HR-MS calcd for C24H26O3N5 (Μ + H)+: m/z: 432.2036, found: 432.2025.
(E)-N-((1-cinnamyl-1H-1,2,3-triazol-4-yl)methyl)-1-ethyl-4-hydroxy-2-oxo-1,2-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxamide (5e)
Prepared according to the general method (D), in a quartz vessel, 0.30 mmol (19.5 mg) NaN
3, 0.30 mmol (41.9 μL) Et
3N, 0.30 mmol (59.1 mg) cinnamyl bromide, 0.06 mmol (11.9 mg) sodium ascorbate, 0.06 mmol (9.6 mg) CuSO
4 and 0.30 mmol (67.5 mg) of carboxamide (
4c) were dissolved in about 7mL of 1:1 t-BuOH/H
2O solution. After the work-up procedure, the product (
5e) was subjected to further purification via column chromatography, using PE/EtOAc 50:50 as eluent and was obtained as white solid. Yield: 52% (70.0 mg); M.p. 130.0–136.0 °C;
1H NMR (600 MHz, CDCl
3):
δ (ppm), 16.69 (s, 1H, 4-OH), 10.79 (brs, 1H, -NH), 8.22 (dd,
J = 7.8, 1.2 Hz, 1H, Ar-H), 7.68 (ddd,
J = 8.4, 1.8 Hz, 1H, Ar-H), 7.65 (s, 1H, N-
CH=C-), 7.39–7.35 (m, 3H, Ar-H), 7.34–7.31 (m, 2H, Ar-H), 7.30–7.28 (m, 2H, Ar-H), 6.67 (d,
J = 15.6 Hz, 1H, N-CH
2-CH=
CH-Ar), 6.34 (dt,
J = 15.6, 6.6 Hz, 1H, N-CH
2-
CH=CH-Ar), 5.12 (br, 2H, NH-
CH2-), 4.78 (d,
J = 5.4 Hz, 2H, N-
CH2-CH=CH-Ar), 4.30 (q,
J = 7.2 Hz, 2H, N-
CH2-CH
3), 1.32 (t,
J = 7.2 Hz, 3H, N-CH
2-
CH3);
13C NMR (75 MHz, CDCl
3):
δ (ppm) 171.5, 171.4, 162.0, 144.4, 139.0, 136.1, 135.2, 133.9, 128.7, 128.6, 126.8, 125.7, 122.8, 122.2, 121.1, 116.2, 96.8, 53.0, 37.2, 34.3, 12.8; IR 3083.62 cm
−1 (
, aromatic C-H), 2983.34 cm
−1 (
, aliphatic C-H), 1648.91 cm
−1 (
,
![Biomolecules 16 00029 i005 Biomolecules 16 00029 i005]()
), 1581.34 cm−1 (, N=N), 1536.99 cm−1 (, N-H), 1326.79 cm−1 (, C-N), 763.673 cm−1 (, aromatic monosubstitution); HR-MS calcd for C24H24O3N5 (Μ + H)+: m/z: 430.1879, found: 430.1871.
N-((1-benzyl-1H-1,2,3-triazol-4-yl)methyl)-4-hydroxy-2-oxo-1-(3-phenylpropyl)-1,2-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxamide (5f)
Prepared according to the general method (D), in a quartz vessel, 0.55 mmol (35.8 mg) NaN
3, 0.55 mmol (76.8 μL) Et
3N, 0.55 mmol (65.3.0 μL) benzyl bromide, 0.11 mmol (21.8 mg) sodium ascorbate, 0.11 mmol (17.6 mg) CuSO
4 and 0.55 mmol (200.0 mg) of carboxamide (
4f) were dissolved in about 7mL of 1:1 t-BuOH/H
2O solution. After the work-up procedure, the product (
5f) was subjected to further purification via column chromatography, using PE/EtOAc 60:40 as eluent and was obtained as white solid. Yield: 45% (122.2 mg); M.p. 101.0–104.5 °C;
1HNMR (600 MHz, CDCl
3):
δ (ppm), 16.71 (s, 1H, 4-OH), 10.74 (brs, 1H, -NH), 8.19 (d,
J = 7.8 Hz, 1H, Ar-H), 7.58 (t,
J = 8.4 Hz, 1H, Ar-H), 7.51 (brs, 1H, N-
CH=C-), 7.38–7.33 (m, 3H, Ar-H), 7.32–7.27 (m, 4H, Ar-H), 7.24–7.21 (m, 4H, Ar-H), 7.08 (d,
J = 8.4 Hz, 1H, Ar-H), 5.51 (s, 2H, N-
CH2-Ar), 4.73 (s, 2H, NH-
CH2), 4.23 (t,
J = 6 Hz
, 2H, N-
CH2-), 2.66 (t,
J = 6.6 Hz, 2H, N-CH
2-CH
2-
CH2-Ar), 2.78 (t,
J = 7.2 Hz, 2H, -
CH2-Ar), 2.03 (m, 2H, N-CH
2-
CH2-CH
2-Ar);
13C NMR (75 MHz, CDCl
3):
δ (ppm) 171.7, 171.4, 141.0, 139.2, 134.3, 133.9, 129.3, 129.0, 128.6, 128.5, 128.3, 126.3, 125.7, 122.3, 116.3, 114.2, 96.8, 54.7, 41.8, 34.6, 33.2, 29.8, 28.9; IR 3122.19 cm
−1 (
, aromatic C-H), 2973.7 cm
−1 (
, aliphatic C-H), 1619.91 cm
−1 (
,
![Biomolecules 16 00029 i006 Biomolecules 16 00029 i006]()
), 1563.99 cm−1 (, N-H), 1328.71 cm−1 (, C-N), 759.816 cm−1 (, aromatic monosubstitution); HR-MS calcd for C29H28O3N5 (Μ + H)+: m/z: 494.2192, found: 494.2184.
N-((1-benzyl-1H-1,2,3-triazol-4-yl)methyl)-4-hydroxy-1-(3-methylbut-2-en-1-yl)-2-oxo-1,2-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxamide (5g)
Prepared according to the general method (D), in a quartz vessel, 0.44 mmol (28.6 mg) NaN
3, 0.44 mmol (61.3 μL) Et
3N, 0.4 mmol (52.3 μL) benzyl bromide, 0.09 mmol (17.8 mg) sodium ascorbate, 0.11 mmol (14.4 mg) CuSO
4 and 0.44 mmol (136.6 mg) of carboxamide (
4d) were dissolved in about 7mL of 1:1 t-BuOH/H
2O solution. After the work-up procedure, the product (
5g) was subjected to further purification via column chromatography, using PE/EtOAc 60:40 as eluent and was obtained as white solid. Yield: 52% (101.5 mg); M.p. 109–114 °C;
1HNMR (600 MHz, CDCl
3):
δ (ppm) 16.72 (s, 1H, C-OH), 10.74 (brs, 1H, -NH), 8.20 (d,
J = 7.8 Hz, 1H, Ar-H), 7.65 (t,
J = 7.8 Hz, 1H, Ar-H), 7.50 (s, 1H, N-
CH=C-), 7.38–7.34 (m, 3H, Ar-H), 7.29–7.27 (m, 4H, Ar-H), 5.50 (s, 2H, N-
CH2-Ar), 5.08 (t,
J = 5.4 Hz, 1H, N-CH
2-
CH=), 4.86 (d,
J = 4.8 Hz, 2H, N-
CH2-CH=), 4.72 (br, 2H, NH-
CH2-), 1.87 (s, 3H, -CH
3), 1.72 (s, 3H, -CH
3);
13C NMR (75 MHz, CDCl
3):
δ (ppm) 171.8, 171.3, 162.4, 145.2, 139.5, 136.3, 134.7, 133.8, 129.2, 128.8, 128.2, 125.6, 122.3, 119.3, 116.4, 114.8, 96.9, 54.3, 40.8, 34.9, 25.7, 18.5; IR > 3000 cm
−1 (
, aromatic C-H), 2973.7 cm
−1 (
, aliphatic C-H), 1646.91 cm
−1 (
,
![Biomolecules 16 00029 i007 Biomolecules 16 00029 i007]()
), 1563.99 cm−1 (, N-H), 1319.07 cm−1 (, C-N), 757.888 cm−1 (, aromatic monosubstitution); HR-MS calcd for C25H26O3N5 (Μ + H)+: m/z: 444.2036, found: 444.2026.
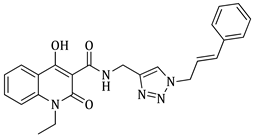
1-cinnamyl-4-hydroxy-N-((1-(3-methylbut-2-en-1-yl)-1H-1,2,3-triazol-4-yl)methyl)-2-oxo-1,2-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxamide (5h)
Prepared according to the general method (D), in a quartz vessel, 0.25 mmol (24.7 mg) NaN3, 0.25 mmol (34.9 μL) Et3N, 0.25 mmol (44.2 μL) prenyl bromide, 0.05 mmol (9.9 mg) sodium ascorbate, 0.05 mmol (8.0 mg) CuSO4 and 0.25 mmol (90.0 mg) of carboxamide (4g) were dissolved in about 7mL of 1:1 t-BuOH/H2O solution. After the work-up procedure, the product (5h) was subjected to further purification via column chromatography, using PE/EtOAc 60:40 as eluent and was obtained as white solid. Yield: 33% (38.7 mg); M.p. 92.0–95.5 °C; 1H NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3): δ (ppm) 16.89 (s, 1H, -OH), 10.70 (brs, 1H, -NH), 8.24 (d, J = 7.8 Hz, 1H, Ar-H), 7.66 (t, J = 8.4 Hz, 1H, Ar-H), 7.55 (s, 1H, N-CH=C-), 7.40 (d, J = 9.0 Hz, 1H, Ar-H), 7.32–7.31 (m, 3H, Ar-H), 7.29–7.27 (m, 2H, Ar-H), 7.22–7.20 (m, 1H, Ar-H), 6.48 (d, J = 15.6 Hz, 1H, N-CH2-CH=CH-Ar), 6.28 (dt, J = 16.2, 5.4 Hz, 1H, N-CH2-CH=CH-Ar), 5.42 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, 1H, N-CH2-CH=C-), 5.06 (d, J = 4.2 Hz, 2H, N-CH2-CH=CH-Ar), 4.94 (br, 2H, NH-CH2), 4.76 (d, J = 6.0 Hz, 2H, N-CH2-CH=C-), 1.79 (br, 6H, 2x -CH3); 13C NMR (150 MHz, CDCl3): δ (ppm) 172.2, 171.3, 162.5, 144.6, 139.9, 139.6, 136.2, 134.0, 132.6, 128.7, 128.0, 126.5, 125.8, 123.2, 122.6, 121.7, 117.4, 116.5, 115.0, 96.9, 48.2, 44.1, 35.0, 25.9, 18.2; HR-MS calcd for C27H28O3N5 (Μ − H)−: m/z: 468.2036, found: 468.2033.
1-ethyl-4-hydroxy-N-((1-(3-methylbut-2-en-1-yl)-1H-1,2,3-triazol-4-yl)methyl)-2-oxo-1,2-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxamide (5i)
Prepared according to the general method (D), in a quartz vessel, 0.80 mmol (52.0 mg) NaN3, 0.80 mmol (111.7 μL) Et3N, 0.80 mmol (87.5 μL) prenyl bromide, 0.08 mmol (15.8 mg) sodium ascorbate, 0.08 mmol (12.8 mg) CuSO4 and 0.80 mmol (200.0 mg) of carboxamide (4c) were dissolved in about 7mL of 1:1 t-BuOH/H2O solution. After the work-up procedure, the product (5i) was subjected to further purification via column chromatography, using PE/EtOAc 60:40 as eluent and was obtained as white solid. Yield: 30% (91.5 mg); M.p. 100–104 °C; 1H NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3): δ (ppm) 16.74 (s, 1H, -OH), 10.76 (brs, 1H, -NH), 8.24 (dd, J = 7.8, 1.2 Hz, 1H, Ar-H), 7.69 (ddd, J = 8.1, 7.4, 1.8 Hz, 1H, Ar-H), 7.55 (s, 1H, H-5′), 7.37 (d, J = 9.0 Hz, 1H, Ar-H), 7.30 (t, J = 7.8 Hz, 1H, Ar-H), 5.43 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, 1H, N-CH2-CH=), 4.93 (br, 2H, NH-CH2-), 4.74 (d, J = 6.0 Hz, 2H, N-CH2-CH=), 4.31 (q, J = 7.2 Hz, 2H, N-CH2-CH3), 1.79 (br, 6H, H-15, CH=C-(CH3)2), 1.33 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, 3H, N-CH2-CH3); 13C NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3): δ (ppm) 171.8, 171.3, 162.3, 144.7, 139.8, 139.2, 133.9, 125.8, 122.3, 121.7, 117.4, 116.5, 114.2, 97.0, 48.2, 37.3, 35.0, 25.8, 18.2, 13.0; HR-MS calcd for C20H23N5O3 (Μ + H)+: m/z: 382.1879, found: 382.1872.
1-benzyl-4-hydroxy-N-((1-(3-methylbut-2-en-1-yl)-1H-1,2,3-triazol-4-yl)methyl)-2-oxo-1,2-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxamide (5j)
Prepared according to the general method (D), in a quartz vessel, 0.60 mmol (39.0 mg) NaN3, 0.60 mmol (83.8 μL) Et3N, 0.60 mmol (65.6 μL) prenyl bromide, 0.06 mmol (11.9 mg) sodium ascorbate, 0.06 mmol (9.6 mg) CuSO4 and 0.60 mmol (200.0 mg) of carboxamide (4b) were dissolved in about 7mL of 1:1 t-BuOH/H2O solution. After the work-up procedure, the product (5j) was subjected to further purification via column chromatography, using PE/EtOAc 60:40 as eluent and was obtained as white solid. Yield: 22% (58.5 mg); M.p. 120.0–122.0 °C; 1H NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3): δ (ppm) 16.93 (s, 1H, -OH), 10.69 (brs, 1H, -NH), 8.21 (dd, J = 8.4, 1.2 Hz, 1H, Ar-H), 7.56 (s, 1H, H-5′), 7.54 (td, J = 8.4, 1.21 Hz, 1H, Ar-H), 7.30–7.25 (m, 3H, Ar-H), 7.24–7.22 (m, 2H, Ar-H), 7.16 (d, J = 7.2 Hz, 2H, Ar-H), 5.48 (br, 2H, N-CH2-Ar), 5.42 (t, J = 6.6 Hz, 1H, N-CH2-CH=), 4.93 (d, J = 7.8 Hz, 2H, N-CH2-CH=), 4.75 (d, J = 6 Hz, 2H, NH-CH2-), 1.79 (s, 3H, -CH3), 1.78 (s, 3H, -CH3); 13C NMR (150 MHz, CDCl3): δ (ppm) 172.3, 171.2, 162.8, 144.5, 139.8, 139.6, 136.2, 134.0, 129.0, 127.5, 1263, 125.7, 122.6, 121.7, 117.3, 116.5, 115.2, 96.8, 48.1, 45.8, 35.0, 25.8, 18.2; HR-MS calcd for C20H23N5O3 (Μ − H)−: m/z: 442.1879, found: 442.1878.