Dermatan Sulfate: Structure, Biosynthesis, and Biological Roles
Abstract
1. Introduction
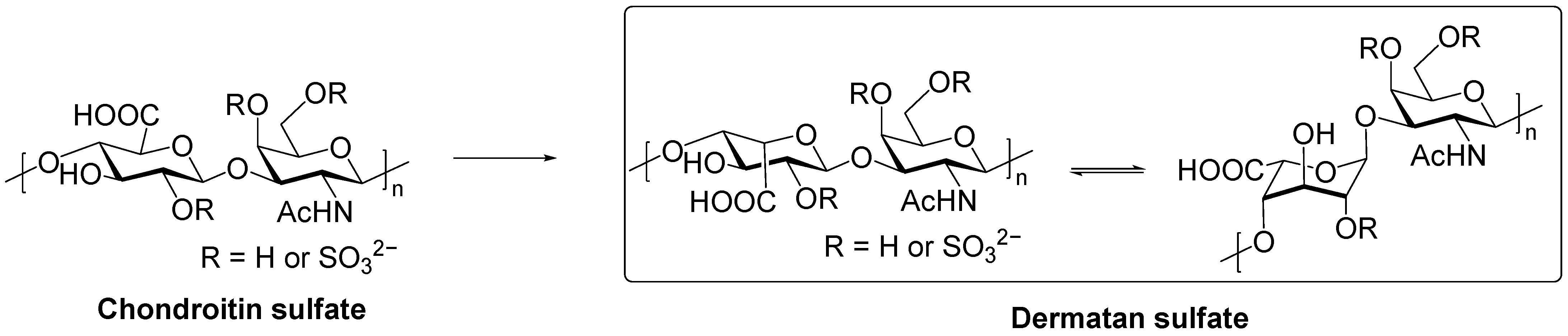
2. Structure of DS
2.1. Primary Structure and Sulfation
2.2. Structural Heterogeneity and Physicochemical Properties
3. Biosynthesis of DS
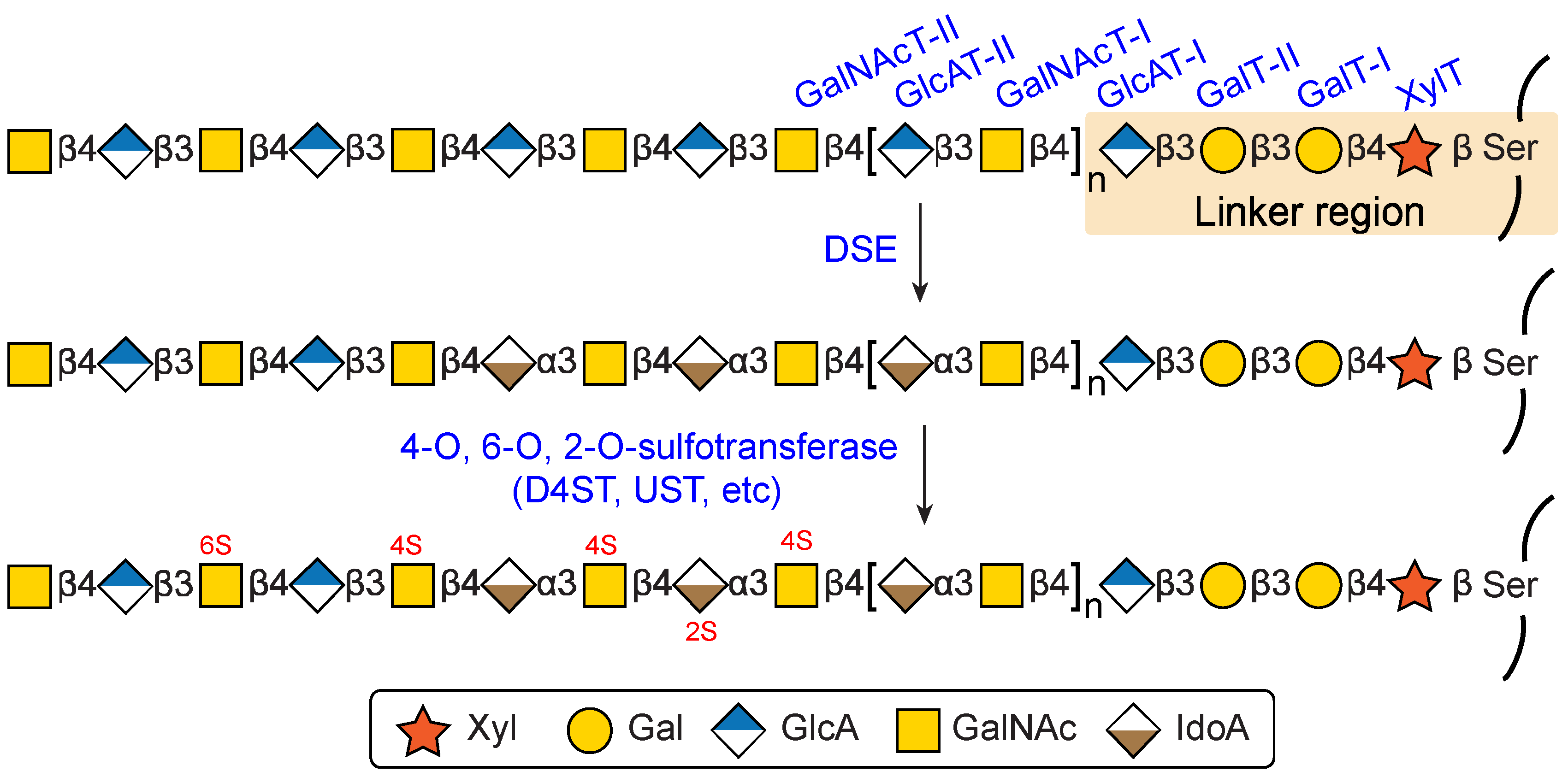
3.1. Biosynthesis of Common Glycosaminoglycan-Protein Linker Region
3.2. Biosynthesis of the Repeating Disaccharide Region
3.3. Epimerazation and Sulfation
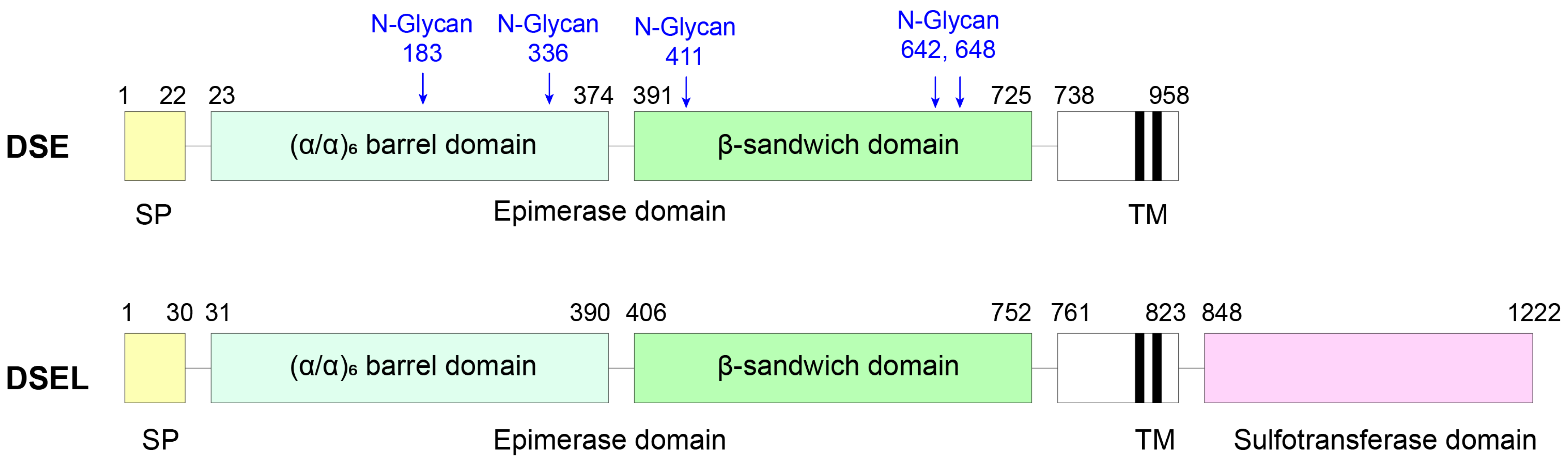
3.3.1. DS Epimerase 1
3.3.2. DS Epimerase 2
3.3.3. Dermatan-4-O-Sulfotransferase 1
4. Preparation and Characterization of DS
4.1. Tissue Extraction
4.2. Chemical and Enzymatic Synthesis
4.3. Characterization
5. Biological Functions
5.1. DS in Extracellular Matrix
5.2. DS in Wound Healing
5.3. DS in Anti-Aging and Cosmetic Applications
5.4. Anticoagulant and Hemostatic Regulation
5.5. Disease Pathophysiology
5.6. Role in Cancer
5.7. DS in Nervous System Development and Function
5.8. DS and Signaling Molecules
5.9. Other Biological Roles and Regulatory Functions
6. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| GAGs | Glycosaminoglycans |
| DS | Dermatan Sulfate |
| CS | Chondroitin sulfate |
| HA | hyaluronic acid |
| HP | Heparan |
| HS | Heparan sulfate |
| KS | keratan sulfate |
| IdoA | L-iduronic acid |
| GlcA | D-glucuronic acid |
| GalNAc | N-acetylgalactosamine |
| GlcNAc | N-acetylglucosamine |
| DSE | Dermatan sulfate epimerase |
| D4ST | Dermatan 4-O-sulfotransferase |
| ECM | Extracellular matrix |
References
- Volpi, N. Dermatan sulfate: Recent structural and activity data. Carbohydr. Polym. 2010, 82, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, S.; Makshakova, O.; Angulo, J.; Bedini, E.; Bisio, A.; de Paz, J.L.; Fadda, E.; Guerrini, M.; Hricovini, M.; Hricovini, M.; et al. Glycosaminoglycans: What Remains to Be Deciphered? JACS Au 2023, 3, 628–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, K.; Chaffee, E. The Mucopolysaccharides of Skin. J. Biol. Chem. 1941, 138, 491–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, K.; Rapport, M.M. The Mucopolysaccharides of the Ground Substance of Connective Tissue. Science 1951, 113, 596–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trowbridge, J.M.; Gallo, R.L. Dermatan sulfate: New functions from an old glycosaminoglycan. Glycobiology 2002, 12, 117R–125R. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikami, T.; Kitagawa, H. Biosynthesis and function of chondroitin sulfate. BBA—Gen. Subj. 2013, 1830, 4719–4733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayes, A.J.; Melrose, J. Glycans and glycosaminoglycans in neurobiology: Key regulators of neuronal cell function and fate. Biochem. J. 2018, 475, 2511–2545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizumoto, S.; Kosho, T.; Yamada, S.; Sugahara, K. Pathophysiological Significance of Dermatan Sulfate Proteoglycans Revealed by Human Genetic Disorders. Pharmaceuticals 2017, 10, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, A.; Sugahara, K.; Farrugia, B.; Whitelock, J.M.; Caterson, B.; Melrose, J. Biodiversity of CS–proteoglycan sulphation motifs: Chemical messenger recognition modules with roles in information transfer, control of cellular behaviour and tissue morphogenesis. Biochem. J. 2018, 475, 587–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizumoto, S.; Yamada, S. The Specific Role of Dermatan Sulfate as an Instructive Glycosaminoglycan in Tissue Development. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 7485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babuty, A.; Zykwinska, A.; Samsonov, S.A.; Candia, N.; Veinstein, C.; Pugnière, M.; Ngo, T.H.G.; Sinquin, C.; Muñoz-Garcia, J.; Colliec-Jouault, S.; et al. Anticoagulant Potential of Modified Sulfated Exopolysaccharides from Deep-Sea Bacteria: Toward Non-Animal Heparin Alternatives. Polysaccharides 2025, 6, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Sun, Z.; Yang, Q.; Xiao, W.; Deng, S. Dermatan sulfate regulates apoptosis and osteogenic differentiation of hBMSCs through estrogen-like effects. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 319, 145368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stachtea, X.N.; Tykesson, E.; van Kuppevelt, T.H.; Feinstein, R.; Malmström, A.; Reijmers, R.M.; Maccarana, M. Dermatan Sulfate-Free Mice Display Embryological Defects and Are Neonatal Lethal Despite Normal Lymphoid and Non-Lymphoid Organogenesis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0140279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, S.; Sugahara, K. Potential Therapeutic Application of Chondroitin Sulfate/Dermatan Sulfate. Curr. Drug Discov. Technol. 2008, 5, 289–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malmström, A.; Bartolini, B.; Thelin, M.A.; Pacheco, B.; Maccarana, M. Iduronic Acid in Chondroitin/Dermatan Sulfate:Biosynthesis and Biological Function. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2012, 60, 916–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosho, T.; Mizumoto, S.; Watanabe, T.; Yoshizawa, T.; Miyake, N.; Yamada, S. Recent Advances in the Pathophysiology of Musculocontractural Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome. Genes 2020, 11, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Syx, D.; Delbaere, S.; Bui, C.; De Clercq, A.; Larson, G.; Mizumoto, S.; Kosho, T.; Fournel-Gigleux, S.; Malfait, F. Alterations in glycosaminoglycan biosynthesis associated with the Ehlers-Danlos syndromes. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2022, 323, C1843–C1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arunkumar, N.; Vu, D.C.; Khan, S.; Kobayashi, H.; Ngoc Can, T.B.; Oguni, T.; Watanabe, J.; Tanaka, M.; Yamaguchi, S.; Taketani, T.; et al. Diagnosis of Mucopolysaccharidoses and Mucolipidosis by Assaying Multiplex Enzymes and Glycosaminoglycans. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silipo, A.; Zhang, Z.; Cañada, F.J.; Molinaro, A.; Linhardt, R.J.; Jiménez-Barbero, J. Conformational Analysis of a Dermatan Sulfate-Derived Tetrasaccharide by NMR, Molecular Modeling, and Residual Dipolar Couplings. ChemBioChem 2008, 9, 240–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Shi, L.; Qin, Y.; Li, F. Research and Application of Chondroitin Sulfate/Dermatan Sulfate-Degrading Enzymes. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 560442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Tang, H.; Ma, H.; Liu, Z.; Huang, J.; Yang, X.; Zhao, L.; Yuan, Q. Chondroitin Sulfate/Dermatan Sulfate Hybrid Chains from Swim Bladder: Isolation, Structural Analysis, and Anticoagulant Activity. Mar. Drugs 2024, 22, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ustyuzhanina, N.E.; Bilan, M.I.; Dmitrenok, A.S.; Tsvetkova, E.A.; Nifantiev, N.E.; Usov, A.I. Oversulfated dermatan sulfate and heparinoid in the starfish Lysastrosoma anthosticta: Structures and anticoagulant activity. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 261, 117867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizumoto, S.; Yamada, S. Histories of Dermatan Sulfate Epimerase and Dermatan 4-O-Sulfotransferase from Discovery of Their Enzymes and Genes to Musculocontractural Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome. Genes 2023, 14, 509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pągielska, M.; Samsonov, S.A. Molecular Dynamics-Based Comparative Analysis of Chondroitin and Dermatan Sulfates. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, R.; Jonniya, N.A.; Kar, P. Effect of Sulfation on the Conformational Dynamics of Dermatan Sulfate Glycosaminoglycan: A Gaussian Accelerated Molecular Dynamics Study. J. Phys. Chem. B 2022, 126, 3852–3866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanthamurthy, C.D.; Gimeno, A.; Leviatan Ben-Arye, S.; Kumar, N.V.; Jain, P.; Padler-Karavani, V.; Jiménez-Barbero, J.; Kikkeri, R. Sulfation Code and Conformational Plasticity of l-Iduronic Acid Homo-Oligosaccharides Mimic the Biological Functions of Heparan Sulfate. ACS Chem. Biol. 2021, 16, 2481–2489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavão, M.S.G.; Vilela-Silva, A.C.; Mourão, P.A.S. Biosynthesis of Chondroitin Sulfate: From the Early, Precursor Discoveries to Nowadays, Genetics Approaches. Adv. Pharmacol. 2006, 53, 117–140. [Google Scholar]
- Grebner, E.E.; Hall, C.W.; Neufeld, E.F. Glycosylation of serine residues by a uridine diphosphate-xylose: Protein xylosyltransferase from mouse mastocytoma. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1966, 116, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grebner, E.E.; Hall, C.W.; Neufeld, E.F. Incorporation of D-xylose-C14 into glycoprotein by particles from hen oviduct. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1966, 22, 672–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, R.; Levery, S.B.; Mandel, U.; Kresse, H.; Schwientek, T.; Bennett, E.P.; Clausen, H. Cloning and Expression of a Proteoglycan UDP-Galactose:β-Xylose β1,4-Galactosyltransferase I: A seventh member of the human β4-galactosyltransferase gene family. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 26165–26171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Zhou, D.; Brown, J.R.; Crawford, B.E.; Hennet, T.; Esko, J.D. Biosynthesis of the Linkage Region of Glycosaminoglycans: Cloning and activity of galactosyltransferase ii, the sixth member of the β1,3-galactosyltransferase family (β3GalT6). J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 48189–48195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitagawa, H.; Tone, Y.; Tamura, J.; Neumann, K.W.; Ogawa, T.; Oka, S.; Kawasaki, T.; Sugahara, K. Molecular Cloning and Expression of Glucuronyltransferase I Involved in the Biosynthesis of the Glycosaminoglycan-Protein Linkage Region of Proteoglycans. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 6615–6618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silbert, J.E.; Sugumaran, G. Biosynthesis of Chondroitin/Dermatan Sulfate. IUBMB Life 2002, 54, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rohrmann, K.; Niemann, R.; Buddecke, E. Two N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase are involved in the biosynthesis of chondroitin sulfate. Eur. J. Biochem. 1985, 148, 463–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugahara, K.; Kitagawa, H. Recent advances in the study of the biosynthesis and functions of sulfated glycosaminoglycans. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2000, 10, 518–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malmström, A.; Aberg, L. Biosynthesis of dermatan sulphate. Assay and properties of the uronosyl C-5 epimerase. Biochem. J. 1982, 201, 489–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maccarana, M.; Malmström, A. Dermatan Sulfate Epimerases (DSE, DSEL). In Handbook of Glycosyltransferases and Related Genes; Taniguchi, N., Honke, K., Fukuda, M., Narimatsu, H., Yamaguchi, Y., Angata, T., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 935–945. [Google Scholar]
- Mikami, T.; Mizumoto, S.; Kago, N.; Kitagawa, H.; Sugahara, K. Specificities of Three Distinct Human Chondroitin/Dermatan N-Acetylgalactosamine 4-O-Sulfotransferases Demonstrated Using Partially Desulfated Dermatan Sulfate as an Acceptor: Implication of differential roles in dermatan sulfate biosynthesis. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 36115–36127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tykesson, E.; Hassinen, A.; Zielinska, K.; Thelin, M.A.; Frati, G.; Ellervik, U.; Westergren-Thorsson, G.; Malmström, A.; Kellokumpu, S.; Maccarana, M. Dermatan sulfate epimerase 1 and dermatan 4-O-sulfotransferase 1 form complexes that generate long epimerized 4-O-sulfated blocks. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 13725–13735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malmström, A.; Fransson, L.A. Biosynthesis of dermatan sulfate. I. Formation of L-iduronic acid residues. J. Biol. Chem. 1975, 250, 3419–3425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maccarana, M.; Olander, B.; Malmström, J.; Tiedemann, K.; Aebersold, R.; Lindahl, U.; Li, J.-P.; Malmström, A. Biosynthesis of Dermatan Sulfate: Chondroitin-glucuronate C5-epimerase is identical to SART2. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 11560–11568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakao, M.; Shichijo, S.; Imaizumi, T.; Inoue, Y.; Matsunaga, K.; Yamada, A.; Kikuchi, M.; Tsuda, N.; Ohta, K.; Takamori, S.; et al. Identification of a Gene Coding for a New Squamous Cell Carcinoma Antigen Recognized by the CTL. J. Immun. 2000, 164, 2565–2574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tykesson, E.; Mao, Y.; Maccarana, M.; Pu, Y.; Gao, J.; Lin, C.; Zaia, J.; Westergren-Thorsson, G.; Ellervik, U.; Malmström, L.; et al. Deciphering the mode of action of the processive polysaccharide modifying enzyme dermatan sulfate epimerase 1 by hydrogen–deuterium exchange mass spectrometry. Chem. Sci. 2016, 7, 1447–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malmström, A. Biosynthesis of dermatan sulfate. II. Substrate specificity of the C-5 uronosyl epimerase. J. Biol. Chem. 1984, 259, 161–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasan, M.; Khakzad, H.; Happonen, L.; Sundin, A.; Unge, J.; Mueller, U.; Malmström, J.; Westergren-Thorsson, G.; Malmström, L.; Ellervik, U.; et al. The structure of human dermatan sulfate epimerase 1 emphasizes the importance of C5-epimerization of glucuronic acid in higher organisms. Chem. Sci. 2021, 12, 1869–1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pacheco, B.; Maccarana, M.; Goodlett, D.R.; Malmström, A.; Malmström, L. Identification of the Active Site of DS-epimerase 1 and Requirement of N-Glycosylation for Enzyme Function. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 1741–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goossens, D.; Van Gestel, S.; Claes, S.; De Rijk, P.; Souery, D.; Massat, I.; Van den Bossche, D.; Backhovens, H.; Mendlewicz, J.; Van Broeckhoven, C.; et al. A novel CpG-associated brain-expressed candidate gene for chromosome 18q-linked bipolar disorder. Mol. Psychiatry 2003, 8, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartolini, B.; Thelin, M.A.; Rauch, U.; Feinstein, R.; Oldberg, Å.; Malmström, A.; Maccarana, M. Mouse development is not obviously affected by the absence of dermatan sulfate epimerase 2 in spite of a modified brain dermatan sulfate composition. Glycobiology 2012, 22, 1007–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akatsu, C.; Mizumoto, S.; Kaneiwa, T.; Maccarana, M.; Malmström, A.; Yamada, S.; Sugahara, K. Dermatan sulfate epimerase 2 is the predominant isozyme in the formation of the chondroitin sulfate/dermatan sulfate hybrid structure in postnatal developing mouse brain. Glycobiology 2010, 21, 565–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacheco, B.; Malmström, A.; Maccarana, M. Two Dermatan Sulfate Epimerases Form Iduronic Acid Domains in Dermatan Sulfate. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 9788–9795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thelin, M.A.; Bartolini, B.; Axelsson, J.; Gustafsson, R.; Tykesson, E.; Pera, E.; Oldberg, Å.; Maccarana, M.; Malmstrom, A. Biological functions of iduronic acid in chondroitin/dermatan sulfate. FEBS J. 2013, 280, 2431–2446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evers, M.R.; Xia, G.; Kang, H.-G.; Schachner, M.; Baenziger, J.U. Molecular Cloning and Characterization of a Dermatan-specific N-Acetylgalactosamine 4-O-Sulfotransferase. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 36344–36353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pacheco, B.; Maccarana, M.; Malmström, A. Dermatan 4-O-sulfotransferase 1 is pivotal in the formation of iduronic acid blocks in dermatan sulfate. Glycobiology 2009, 19, 1197–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mende, M.; Bednarek, C.; Wawryszyn, M.; Sauter, P.; Biskup, M.B.; Schepers, U.; Bräse, S. Chemical Synthesis of Glycosaminoglycans. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 8193–8255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tykesson, E.; Maccarana, M.; Thorsson, H.; Liu, J.; Malmström, A.; Ellervik, U.; Westergren-Thorsson, G. Recombinant dermatan sulfate is a potent activator of heparin cofactor II-dependent inhibition of thrombin. Glycobiology 2019, 29, 446–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paththuwe Arachchi, M.J.; Subash, A.; Bamigbade, G.B.; Abdin, M.; Ulla, N.; Ayyash, M. Fish byproducts as a sustainable source of glycosaminoglycans: Extraction processes, food applications, nutraceutical advancements, and challenges. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2025, 159, 104963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Q.; Shi, X.; Ma, H.; Yao, Y.; Zhang, B.; Zhao, L. Recent progress in marine chondroitin sulfate, dermatan sulfate, and chondroitin sulfate/dermatan sulfate hybrid chains as potential functional foods and therapeutic agents. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 262, 129969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarannum, A.; Ballav, S.; Rao, J.R.; Fathima, N.N. Extraction of dermatan sulfate using ionic liquid-assisted enzymatic digestion: An efficient approach. Carbohydr. Res. 2023, 531, 108897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osborne, S.A.; Daniel, R.A.; Chen, W.; Stockwell, P.; Tyrrell, K.; Desilva, K.; Seymour, R.B. Extraction, purification and characterisation of dermatan sulphate from bovine collagen waste liquor. Food Bioprod. Process. 2016, 99, 244–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeda-Okuda, N.; Yeon, S.-J.; Matsumi, Y.; Matsuura, Y.; Hosaka, Y.Z.; Tamura, J.-I. Quantitative, compositional, and immunohistochemical analyses of chondroitin sulfate, dermatan sulfate, and hyaluronan in internal organs of deer (Cervus nippon centralis and C. n. yesoensis) and cattle (Bos taurus). Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 261, 129680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeanneret, R.A.; Dalton, C.E.; Gardiner, J.M. Synthesis of Heparan Sulfate- and Dermatan Sulfate-Related Oligosaccharides via Iterative Chemoselective Glycosylation Exploiting Conformationally Disarmed [2.2.2] l-Iduronic Lactone Thioglycosides. J. Org. Chem. 2019, 84, 15063–15078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Sorum, A.W.; Huang, B.-S.; Kern, M.K.; Su, G.; Pawar, N.; Huang, X.; Liu, J.; Pohl, N.L.B.; Hsieh-Wilson, L.C. Efficient platform for synthesizing comprehensive heparan sulfate oligosaccharide libraries for decoding glycosaminoglycan–protein interactions. Nat. Chem. 2023, 15, 1108–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baryal, K.N.; Ramadan, S.; Su, G.; Huo, C.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, J.; Hsieh-Wilson, L.C.; Huang, X. Synthesis of a systematic 64-membered heparan sulfate tetrasaccharide library. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202211985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wang, S.; Fu, X.; Liu, X.; Wang, P.G.; Fang, J. Sequential one-pot multienzyme synthesis of hyaluronan and its derivative. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 178, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wang, S.; Qu, J.; Han, J.; Yang, L.; Li, Y.; Li, L.; Jia, Q.; Chen, C.; Ling, P.; et al. Programmable one cycle–one disaccharide unit modular synthesis of hyaluronan and chondroitin hybrid glycans. Green Chem. 2023, 25, 2021–2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Su, G.; Liu, J. Enzymatic Synthesis of Homogeneous Chondroitin Sulfate Oligosaccharides. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 11784–11787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Wang, S.; Chen, C.; Liu, C.; Wang, X.; Li, S.; Li, Y.; Ling, P.; Wang, Z.; Fang, J. Programmable Enzymatic Toolbox for the Assembly of Fucosylated Chondroitin Derivatives. ACS Catal. 2024, 14, 670–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.-Q.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.-J.; Cao, Y.-L.; Xin, S.-Y.; Li, X.-Y.; Xi, R.-M.; Wang, F.-S.; Sheng, J.-Z. Biosynthetic production of anticoagulant heparin polysaccharides through metabolic and sulfotransferases engineering strategies. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 3755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Bosman, G.P.; Chapla, D.; Huang, C.; Moremen, K.W.; de Vries, R.P.; Boons, G.-J. A biomimetic synthetic strategy can provide keratan sulfate I and II oligosaccharides with diverse fucosylation and sulfation patterns. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2024, 146, 9230–9240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Bosman, G.P.; Vos, G.M.; Uslu, E.; Chapla, D.; Huang, C.; Moremen, K.W.; Boons, G.-J. Chemoenzymatic synthesis of keratan sulfate oligosaccharides using UDP-Galactose-6-aldehyde to control sulfation at galactosides. Org. Lett. 2024, 26, 8272–8277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.O.; Gunay, N.S.; Toida, T.; Kuberan, B.; Yu, G.; Kim, Y.S.; Linhardt, R.J. Preparation and structural determination of dermatan sulfate–derived oligosaccharides. Glycobiology 2000, 10, 1033–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasgupta, F.; Irene Masada, R.; Starr, C.M.; Kuberan, B.; Yang, H.-O.; Linhardt, R.J. Chemoenzymatic preparation of dermatan sulfate oligosaccharides as arylsulfatase B and α-L-iduronidase substrates. Glycoconj. J. 2000, 17, 829–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, M.; Xu, Y.-Y.; Li, Y.-N.; Yu, S.; Wang, Y.-L.; Ma, X.-L.; Zhang, Y.-W. Engineering of Substrate-Binding Domain to Improve Catalytic Activity of Chondroitin B Lyase with Semi-Rational Design. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2024, 46, 9916–9927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Chi, L. Chondroitin Sulfate/Dermatan Sulfate-Protein Interactions and Their Biological Functions in Human Diseases: Implications and Analytical Tools. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 693563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishihara, S.; Angata, K.; Aoki-Kinoshita, K.F.; Hirabayashi, J. Glycoscience Protocols (GlycoPODv2) [Internet]; Japan Consortium for Glycobiology and Glycotechnology: Saitama, Japan, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Cahyadi, D.D.; Warita, K.; Takeda-Okuda, N.; Tamura, J.-I.; Hosaka, Y.Z. Qualitative and quantitative analyses in sulfated glycosaminoglycans, chondroitin sulfate/dermatan sulfate, during 3 T3-L1 adipocytes differentiation. Anim. Sci. J. 2023, 94, e13894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, X. Study on the interaction between agglutinin and chondroitin sulfate and dermatan sulfate using multiple methods. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 272, 132624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, R.; Xu, X.; Li, F. Classification and characteristics of bacterial glycosaminoglycan lyases, and their therapeutic and experimental applications. J. Cell Sci. 2025, 138, JCS263489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarbu, M.; Seidler, D.G.; Clemmer, D.E.; Zamfir, A.D. Introducing Ion Mobility Mass Spectrometry in Brain Glycosaminoglycomics: Application to Chondroitin/Dermatan Sulfate Octasaccharide Domains. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2024, 35, 2102–2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarbu, M.; Ica, R.; Sharon, E.; Clemmer, D.E.; Zamfir, A.D. Identification and Structural Characterization of Novel Chondroitin/Dermatan Sulfate Hexassacharide Domains in Human Decorin by Ion Mobility Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Molecules 2022, 27, 6026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devlin, A.; Green, F.; Takats, Z. Mass Spectrometry Imaging with Trapped Ion Mobility Spectrometry Enables Spatially Resolved Chondroitin, Dermatan, and Hyaluronan Glycosaminoglycan Oligosaccharide Analysis In Situ. Anal. Chem. 2024, 96, 17969–17977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Xu, Q.; Liu, X.; Wang, K. Quantitative Analysis of Chondroitin Sulfate and Dermatan Sulfate Using Capillary Electrophoresis with Gaussian Distribution-Based Peak Fitting for Improved Peak Resolution. Sep. Sci. Plus 2024, 7, e202300244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamfir, A.D. Capillary Zone Electrophoresis–Electrospray Ionization Tandem Mass Spectrometry for Total Analysis of Chondroitin/Dermatan Sulfate Oligosaccharides. In Capillary Electrophoresis-Mass Spectrometry: Methods and Protocols; Neusüß, C., Jooß, K., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 163–184. [Google Scholar]
- García-Jiménez, M.J.; Gil-Caballero, S.; Maza, S.; Corzana, F.; Juárez-Vicente, F.; Miles, J.R.; Sakamoto, K.; Kadomatsu, K.; García-Domínguez, M.; de Paz, J.L.; et al. Midkine Interaction with Chondroitin Sulfate Model Synthetic Tetrasaccharides and Their Mimetics: The Role of Aromatic Interactions. Chem. Eur. J. 2021, 27, 12395–12409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Jiménez, M.J.; Torres-Rico, M.; de Paz, J.L.; Nieto, P.M. The Interaction between Chondroitin Sulfate and Dermatan Sulfate Tetrasaccharides and Pleiotrophin. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Bollas, A.; Wang, Y.; Au, K.F. Nanopore sequencing technology, bioinformatics and applications. Nat. Biotechnol. 2021, 39, 1348–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, G.; Ke, W.; Xia, B.; Gao, Z. Nanopore-based glycan sequencing: State of the art and future prospects. Chem. Sci. 2024, 15, 6229–6243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, K.; Hagan, J.T.; Fu, L.; Sheetz, B.S.; Bhattacharya, S.; Zhang, F.; Dwyer, J.R.; Linhardt, R.J. Synthetic heparan sulfate standards and machine learning facilitate the development of solid-state nanopore analysis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2022806118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Im, J.; Lindsay, S.; Wang, X.; Zhang, P. Single Molecule Identification and Quantification of Glycosaminoglycans Using Solid-State Nanopores. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 6308–6318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayat, P.; Rambaud, C.; Priem, B.; Bourderioux, M.; Bilong, M.; Poyer, S.; Pastoriza-Gallego, M.; Oukhaled, A.; Mathé, J.; Daniel, R. Comprehensive structural assignment of glycosaminoglycan oligo- and polysaccharides by protein nanopore. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 5113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivas, F.; Zahid, O.K.; Reesink, H.L.; Peal, B.T.; Nixon, A.J.; DeAngelis, P.L.; Skardal, A.; Rahbar, E.; Hall, A.R. Label-free analysis of physiological hyaluronan size distribution with a solid-state nanopore sensor. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.-F.; Mizumoto, S.; Fujita, M. Novel Insight Into Glycosaminoglycan Biosynthesis Based on Gene Expression Profiles. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 709018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persson, A.; Nikpour, M.; Vorontsov, E.; Nilsson, J.; Larson, G. Domain Mapping of Chondroitin/Dermatan Sulfate Glycosaminoglycans Enables Structural Characterization of Proteoglycans. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2021, 20, 100074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persson, A.; Vorontsov, E.; Larson, G.; Nilsson, J. Glycosaminoglycan Domain Mapping of Cellular Chondroitin/Dermatan Sulfates. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 3506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, L.; Xu, Y.; Du, M.; Fan, Y.; Zou, R.; Xu, X.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, Y.-Z.; Wang, W.; Li, F. A novel 4-O-endosulfatase with high potential for the structure-function studies of chondroitin sulfate/dermatan sulfate. Carbohydr. Polym. 2023, 305, 120508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Xu, Y.; Du, M.; Fan, Y.; Zou, R.; Xu, X.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, Y.-Z.; Wang, W.; Li, F. Data on cloning, expression and biochemical characteristics of a chondroitin sulfate/dermatan sulfate 4-O-endosulfatase. Data Brief 2023, 48, 109139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karamanos, N.K.; Piperigkou, Z.; Theocharis, A.D.; Watanabe, H.; Franchi, M.; Baud, S.; Brézillon, S.; Götte, M.; Passi, A.; Vigetti, D.; et al. Proteoglycan Chemical Diversity Drives Multifunctional Cell Regulation and Therapeutics. Chem. Rev. 2018, 118, 9152–9232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizumoto, S.; Yamada, S.; Sugahara, K. Molecular interactions between chondroitin–dermatan sulfate and growth factors/receptors/matrix proteins. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2015, 34, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miguez, P.A.; Bash, E.; Musskopf, M.L.; Tuin, S.A.; Rivera-Concepcion, A.; Chapple, I.L.C.; Liu, J. Control of tissue homeostasis by the extracellular matrix: Synthetic heparan sulfate as a promising therapeutic for periodontal health and bone regeneration. Periodontology 2000 2024, 94, 510–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jyothsna, K.M.; Sarkar, P.; Jha, K.K.; A.S., L.K.; Raghunathan, V.; Bhat, R. A biphasic response of polymerized Type 1 collagen architectures to dermatan sulfate. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2021, 109, 1646–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortes-Medina, M.; Bushman, A.R.; Beshay, P.E.; Adorno, J.J.; Menyhert, M.M.; Hildebrand, R.M.; Agarwal, S.S.; Avendano, A.; Friedman, A.K.; Song, J.W. Chondroitin sulfate, dermatan sulfate, and hyaluronic acid differentially modify the biophysical properties of collagen-based hydrogels. Acta Biomater. 2024, 174, 116–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallet, S.D.; Berthollier, C.; Ricard-Blum, S. The glycosaminoglycan interactome 2.0. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2022, 322, C1271–C1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, T.; Heinemann, S.; Mietrach, C.; Hempel, U.; Bierbaum, S.; Scharnweber, D.; Worch, H. Interactions of Collagen Types I and II with Chondroitin Sulfates A−C and Their Effect on Osteoblast Adhesion. Biomacromolecules 2007, 8, 1085–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouignard, N.; Maccarana, M.; Strate, I.; von Stedingk, K.; Malmström, A.; Pera, E.M. Musculocontractural Ehlers–Danlos syndrome and neurocristopathies: Dermatan sulfate is required for Xenopus neural crest cells to migrate and adhere to fibronectin. Dis. Models Mech. 2016, 9, 607–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.H.; Oh, J.-H.; Chung, J.H. Glycosaminoglycan and proteoglycan in skin aging. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2016, 83, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Chen, S.; Goldoni, S.; Calder, B.W.; Simpson, H.C.; Owens, R.T.; McQuillan, D.J.; Young, M.F.; Iozzo, R.V.; Birk, D.E. Genetic Evidence for the Coordinated Regulation of Collagen Fibrillogenesis in the Cornea by Decorin and Biglycan. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 8888–8897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, C.C.; Iozzo, R.V. The role of decorin in collagen fibrillogenesis and skin homeostasis. Glycoconj. J. 2002, 19, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gubbiotti, M.A.; Vallet, S.D.; Ricard-Blum, S.; Iozzo, R.V. Decorin interacting network: A comprehensive analysis of decorin-binding partners and their versatile functions. Matrix Biol. 2016, 55, 7–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svensson, L.; Heineg, D.; Oldberg. Decorin-binding Sites for Collagen Type I Are Mainly Located in Leucine-rich Repeats 4-5. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 20712–20716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rühland, C.; Schönherr, E.; Robenek, H.; Hansen, U.; Iozzo, R.V.; Bruckner, P.; Seidler, D.G. The glycosaminoglycan chain of decorin plays an important role in collagen fibril formation at the early stages of fibrillogenesis. FEBS J. 2007, 274, 4246–4255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirose, T.; Mizumoto, S.; Hashimoto, A.; Takahashi, Y.; Yoshizawa, T.; Nitahara-Kasahara, Y.; Takahashi, N.; Nakayama, J.; Takehana, K.; Okada, T.; et al. Systematic investigation of the skin in Chst14−/− mice: A model for skin fragility in musculocontractural Ehlers–Danlos syndrome caused by CHST14 variants (mcEDS-CHST14). Glycobiology 2020, 31, 137–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, F.; Takahashi, Y.; Shimada, S.; Mizumoto, S.; Miyata, S.; Nitahara-Kasahara, Y.; Yamada, S.; Okada, T.; Kosho, T.; Yoshizawa, T. Carbohydrate sulfotransferase 14 gene deletion induces dermatan sulfate deficiency and affects collagen structure and bowel contraction. PLoS ONE 2025, 20, e0320943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Bai, X.; Dai, X.; Li, Y. The Biological Processes During Wound Healing. Regen. Med. 2021, 16, 373–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorg, H.; Sorg, C.G.G. Skin Wound Healing: Of Players, Patterns, and Processes. Eur. Surg. Res. 2022, 64, 141–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almadani, Y.H.; Vorstenbosch, J.; Davison, P.G.; Murphy, A.M. Wound Healing: A Comprehensive Review. Semin. Plast. Surg. 2021, 35, 141–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plichta, J.K.; Radek, K.A. Sugar-Coating Wound Repair: A Review of FGF-10 and Dermatan Sulfate in Wound Healing and Their Potential Application in Burn Wounds. J. Burn Care Res. 2012, 33, 299–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galvez-Martin, P.; Martinez-Puig, D.; Soto-Fernández, C.; Romero-Rueda, J. In vitroevaluation of anti-aging and regenerative properties of dermatan sulfate for skin care. FASEB J. 2022, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuwaba, K.; Kobayashi, M.; Nomura, Y.; Irie, S.; Koyama, Y.-I. Size control of decorin dermatan sulfate during remodeling of collagen fibrils in healing skin. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2002, 29, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares da Costa, D.; Reis, R.L.; Pashkuleva, I. Sulfation of glycosaminoglycans and its implications in human gealth and disorders. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2017, 19, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chocarro-Wrona, C.; Pleguezuelos-Beltrán, P.; López de Andrés, J.; Antich, C.; de Vicente, J.; Jiménez, G.; Arias-Santiago, S.; Gálvez-Martín, P.; López-Ruiz, E.; Marchal, J.A. A bioactive three-layered skin substitute based on ECM components effectively promotes skin wound healing and regeneration. Mater. Today Bio 2025, 31, 101592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanitphakdeedecha, R.; Eimpunth, S.; Manuskiatti, W. The Effects of Mucopolysaccharide Polysulphate on Hydration and Elasticity of Human Skin. Dermatol. Res. Pract. 2011, 2011, 807906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, J.-H.; Kim, Y.K.; Jung, J.-Y.; Shin, J.-E.; Kim, K.H.; Cho, K.H.; Eun, H.C.; Chung, J.H. Intrinsic aging- and photoaging-dependent level changes of glycosaminoglycans and their correlation with water content in human skin. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2011, 62, 192–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.T.; Hoe, N.B.; Betts, R.J. Glycosaminoglycans: Sweet as Sugar Targets for Topical Skin Anti-Aging. Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dermatol. 2021, 14, 1227–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Q.; Ding, D.; Loka, R.S.; Wang, S.; Ling, P. Recent advances in exploring the properties and applications of hyaluronan. J. Dermatol. Sci. Cosmet. Technol. 2024, 1, 100039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augustyniak, A.; McMahon, H. Effect of Marine-Derived Saccharides on Human Skin Fibroblasts and Dermal Papilla Cells. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Giri, T.K.; Vicente, C.P.; Tollefsen, D.M. Vascular dermatan sulfate regulates the antithrombotic activity of heparin cofactor II. Blood 2008, 111, 4118–4125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böhm, E.W.; Buonfiglio, F.; Korb, C.A.; Dauth, A.; Pfeiffer, N.; Bręborowicz, A.; Gericke, A. Potential of Sulodexide in the Treatment of Diabetic Retinopathy and Retinal Vein Occlusion. Thromb. Haemost. 2024, 125, 291–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Li, R.; Liu, Y.; Li, G.; Liu, S. Diversity, mechanism and structure-activity relationships of marine anticoagulant-active polysaccharides: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 306, 141742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chikha, S.B.; Bougatef, H.; Capitani, F.; Ben Amor, I.; Maccari, F.; Gargouri, J.; Sila, A.; Volpi, N.; Bougatef, A. Composition and Anticoagulant Potential of Chondroitin Sulfate and Dermatan Sulfate from Inedible Parts of Garfish (Belone belone). Foods 2023, 12, 3887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valcarcel, J.; Novoa-Carballal, R.; Pérez-Martín, R.I.; Reis, R.L.; Vázquez, J.A. Glycosaminoglycans from marine sources as therapeutic agents. Biotechnol. Adv. 2017, 35, 711–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizumoto, S.; Yamada, S. Congenital Disorders of Deficiency in Glycosaminoglycan Biosynthesis. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 717535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizumoto, S.; Yamada, S. An Overview of in vivo Functions of Chondroitin Sulfate and Dermatan Sulfate Revealed by Their Deficient Mice. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 764781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshizawa, T.; Kosho, T. Mouse Models of Musculocontractural Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome. Genes 2023, 14, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, T.; Mizumoto, S.; Suresh, I.; Komatsu, Y.; Vodopiutz, J.; Dundar, M.; Straub, V.; Lingenhel, A.; Melmer, A.; Lechner, S.; et al. Loss of dermatan sulfate epimerase (DSE) function results in musculocontractural Ehlers–Danlos syndrome. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2013, 22, 3761–3772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubaski, F.; de Oliveira Poswar, F.; Michelin-Tirelli, K.; Matte, U.D.S.; Horovitz, D.D.; Barth, A.L.; Baldo, G.; Vairo, F.; Giugliani, R. Mucopolysaccharidosis Type I. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maciej-Hulme, M.L.; Melrose, J.; Farrugia, B.L. Arthritis and Duchenne muscular dystrophy: The role of chondroitin sulfate and its associated proteoglycans in disease pathology and as a diagnostic marker. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2023, 324, C142–C152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, E.B.; Trier, K.; Eldov, K.; Ammitzbøll, T. Glycosaminoglycans in human breast cancer. Acta Obstet. Gynecol. Scand. 1988, 67, 539–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Q.; Wang, J.; Liu, C.; Meng, L.-X.; Qian, R.-K.; Gao, H.-J.; Qin, W.; Zhou, C.-J.; Qiao, S.; Wang, H.-Y.; et al. Exploring the sulfate patterns of chondroitin sulfate/dermatan sulfate and keratan sulfate in human pancreatic cancer. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2021, 205, 114339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pál, D.; Bugyi, F.; Virág, D.; Szabó, D.; Schlosser, G.; Kovalszky, I.; Harkó, T.; Moldvay, J.; Turiák, L. Analysis and characterization of chondroitin/dermatan sulfate composition of lung adenocarcinoma tissues with different types of genetic alterations in ALK, EGFR and KRAS oncogenes. Carbohydr. Polym. Technol. Appl. 2025, 10, 100826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Entezarian, M.; Ameli, F.; Masir, N.; Geok Chin, T. Significance of Endocan Expression in Various Types of Epithelial Ovarian Tumors. Iran. J. Pathol. 2022, 17, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastola, S.; Pavlyukov, M.S.; Sharma, N.; Ghochani, Y.; Nakano, M.A.; Muthukrishnan, S.D.; Yu, S.Y.; Kim, M.S.; Sohrabi, A.; Biscola, N.P.; et al. Endothelial-secreted Endocan activates PDGFRA and regulates vascularity and spatial phenotype in glioblastoma. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Yang, Q.; Yu, S.; Zhang, X. Endocan: A new marker for cancer and a target for cancer therapy (Review). Biomed. Rep. 2015, 3, 279–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, K.-F.; Yang, Y.-C.; Lee, W.-J.; Hua, K.-T.; Chien, M.-H. Proteoglycan Endocan: A multifaceted therapeutic target in Cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Rev. Cancer 2022, 1877, 188672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wisowski, G.; Pudełko, A.; Olczyk, K.; Paul-Samojedny, M.; Koźma, E.M. Dermatan Sulfate Affects Breast Cancer Cell Function via the Induction of Necroptosis. Cells 2022, 11, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wisowski, G.; Pudełko, A.; Paul-Samojedny, M.; Komosińska-Vassev, K.; Koźma, E.M. Dermatan Sulfate Affects the Activation of the Necroptotic Effector MLKL in Breast Cancer Cell Lines via the NFκB Pathway and Rac-Mediated Oxidative Stress. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blachman, A.; Birocco, A.M.; Curcio, S.; Camperi, S.A.; Gianvincenzo, P.D.; Rodriguez, J.A.; Barredo-Vacchelli, G.R.; Cenci, G.; Sosnik, A.; Moya, S.; et al. Dermatan Sulfate/Chitosan Nanoparticles Loaded with an Anti-Inflammatory Peptide Increase the Response of Human Colorectal Cancer Cells to 5-Fluorouracil. Macromol. Biosci. 2023, 23, 2300193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Zhang, F.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, Q. A dermatan sulfate-functionalized biomimetic nanocarrier for melanoma targeted chemotherapy. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 235, 115983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Li, S.; Ren, J.; He, X.; Shi, H.; Zhang, F.; Li, H.; Tong, R. ROS-triggered nanoinducer based on dermatan sulfate enhances immunogenic cell death in melanoma. J. Control. Release 2022, 348, 22–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayes, A.J.; Melrose, J. Neural Tissue Homeostasis and Repair Is Regulated via CS and DS Proteoglycan Motifs. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 696640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugahara, K.; Mikami, T. Chondroitin/dermatan sulfate in the central nervous system. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2007, 17, 536–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Bai, T.; Feng, J. Endocan, a novel glycoprotein with multiple biological activities, may play important roles in neurological diseases. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2024, 16, 1438367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogura, C.; Hirano, K.; Mizumoto, S.; Yamada, S.; Nishihara, S. Dermatan sulphate promotes neuronal differentiation in mouse and human stem cells. J. Biochem. 2020, 169, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medeiros, T.B.; Cosendey, P.; Gerin, D.R.; de Sousa, G.F.; Portal, T.M.; Monteiro-de-Barros, C. The effect of the sulfation patterns of dermatan and chondroitin sulfate from vertebrates and ascidians on their neuritogenic and neuroprotective properties. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 247, 125830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Sousa, G.F.; Palmero, C.Y.; de Souza-Menezes, J.; Araujo, A.K.; Guimarães, A.G.; de Barros, C.M. Dermatan sulfate obtained from the Phallusia nigra marine organism is responsible for antioxidant activity and neuroprotection in the neuroblastoma-2A cell lineage. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 164, 1099–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, P.B.; Lax, I.; Reshetnyak, A.; Ligon, G.F.; Lillquist, J.S.; Natoli, E.J.; Shi, X.; Folta-Stogniew, E.; Gunel, M.; Alvarado, D.; et al. Heparin is an activating ligand of the orphan receptor tyrosine kinase ALK. Sci. Signal. 2015, 8, ra6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machino, M.; Gong, Y.; Ozaki, T.; Suzuki, Y.; Watanabe, E.; Imagama, S.; Kadomatsu, K.; Sakamoto, K. Dermatan sulphate is an activating ligand of anaplastic lymphoma kinase. J. Biochem. 2021, 170, 631–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramasamy, R.; Yan, S.F.; Herold, K.; Clynes, R.; Schmidt, A.M. Receptor for Advanced Glycation End Products. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2008, 1126, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizumoto, S.; Sugahara, K. Glycosaminoglycans are functional ligands for receptor for advanced glycation end-products in tumors. FEBS J. 2013, 280, 2462–2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Young, J.H.; Krahn, J.M.; Song, D.; Corbett, K.D.; Chazin, W.J.; Pedersen, L.C.; Esko, J.D. Stable RAGE-heparan sulfate complexes are essential for signal transduction. ACS Chem. Biol. 2013, 8, 1611–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizumoto, S.; Takahashi, J.; Sugahara, K. Receptor for Advanced Glycation End Products (RAGE) Functions as Receptor for Specific Sulfated Glycosaminoglycans, and Anti-RAGE Antibody or Sulfated Glycosaminoglycans Delivered in Vivo Inhibit Pulmonary Metastasis of Tumor Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 18985–18994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billiau, A.; Matthys, P. Interferon-γ: A historical perspective. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2009, 20, 97–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, B.; Briggs, D.M.; Eastmond, N.C.; Fernig, D.G.; Coleman, J.W. Presentation of IFN-γ to Nitric Oxide-Producing Cells: A Novel Function for Mast Cells1. J. Immun. 2000, 164, 573–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocian, C.; Urbanowitz, A.-K.; Owens, R.T.; Iozzo, R.V.; Götte, M.; Seidler, D.G. Decorin Potentiates Interferon-γ Activity in a Model of Allergic Inflammation. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 12699–12711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshauer, C.; Morgan, A.M.; Ryan, E.O.; Handel, T.M.; Prestegard, J.H.; Wang, X. Interactions of the Chemokine CCL5/RANTES with Medium-Sized Chondroitin Sulfate Ligands. Structure 2015, 23, 1066–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Proudfoot, A.E.I.; Fritchley, S.; Borlat, F.; Shaw, J.P.; Vilbois, F.; Zwahlen, C.; Trkola, A.; Marchant, D.; Clapham, P.R.; Wells, T.N.C. The BBXB Motif of RANTES Is the Principal Site for Heparin Binding and Controls Receptor Selectivity. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 10620–10626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Rho, J.-H.; Roehrl, M.H.; Wang, J.Y. Dermatan Sulfate Is a Potential Regulator of IgH via Interactions with Pre-BCR, GTF2I, and BiP ER Complex in Pre-B Lymphoblasts. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 680212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stojnić, B.; Galmés, S.; Serrano, A.; Sulli, M.; Sušak, L.; Seye, N.; Palou, A.; Diretto, G.; Bonet, M.L.; Ribot, J. Glycosaminoglycan dermatan sulfate supplementation decreases diet-induced obesity and metabolic dysfunction in mice. BioFactors 2024, 50, 493–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Lin, N.; Liang, X.; Zhang, H. Dermatan sulfate and chondroitin sulfate from Lophius litulon alleviate the allergy sensitized by major royal jelly protein 1. Food Funct. 2022, 13, 587–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafuente-Merchan, M.; Ruiz-Alonso, S.; Zabala, A.; Gálvez-Martín, P.; Marchal, J.A.; Vázquez-Lasa, B.; Gallego, I.; Saenz-del-Burgo, L.; Pedraz, J.L. Chondroitin and Dermatan Sulfate Bioinks for 3D Bioprinting and Cartilage Regeneration. Macromol. Biosci. 2022, 22, 2100435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McEwan, T.B.-D.; De Oliveira, D.M.P.; Stares, E.K.; Hartley-Tassell, L.E.; Day, C.J.; Walker, M.J.; Jennings, M.P.; Sluyter, R.; Sanderson-Smith, M.L. Group A Streptococcus interacts with glycosaminoglycans via M proteins to modulate bacterial adherence in vitro. FEBS J. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Unit | Sequence |
|---|---|
| iO unit | IdoAα1-3GalNAc |
| iA unit | IdoAα1-3GalNAc4S |
| iB unit | IdoA2Sα1-3GalNAc4S |
| iC unit | IdoAα1-3GalNAc6S |
| iD unit | IdoA2Sα1-3GalNAc6S |
| iE unit | IdoAα1-3GalNAc4S6S |
| iU unit | IdoA2Sα1-3GalNAc |
| iT unit | IdoA2Sα1-3GalNAc4S6S |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, C.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, W.; Ding, D.; Loka, R.S.; Zhao, K.; Ling, P.; Wang, S. Dermatan Sulfate: Structure, Biosynthesis, and Biological Roles. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 1158. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15081158
Chen C, Zhang X, Zhang W, Ding D, Loka RS, Zhao K, Ling P, Wang S. Dermatan Sulfate: Structure, Biosynthesis, and Biological Roles. Biomolecules. 2025; 15(8):1158. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15081158
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Congcong, Xuyang Zhang, Weiting Zhang, Dahai Ding, Ravi Sankar Loka, Kun Zhao, Peixue Ling, and Shuaishuai Wang. 2025. "Dermatan Sulfate: Structure, Biosynthesis, and Biological Roles" Biomolecules 15, no. 8: 1158. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15081158
APA StyleChen, C., Zhang, X., Zhang, W., Ding, D., Loka, R. S., Zhao, K., Ling, P., & Wang, S. (2025). Dermatan Sulfate: Structure, Biosynthesis, and Biological Roles. Biomolecules, 15(8), 1158. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15081158






