Glucocorticoid-Induced Muscle Satellite Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Mediate Skeletal Muscle Atrophy via the miR-335-5p/MAPK11/iNOS Pathway
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Isolation, Culture, and Treatment of Primary Skeletal Muscle Cells
2.3. Quantitative Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (qRT-PCR)
2.4. Western Blot
2.5. Immunofluorescence
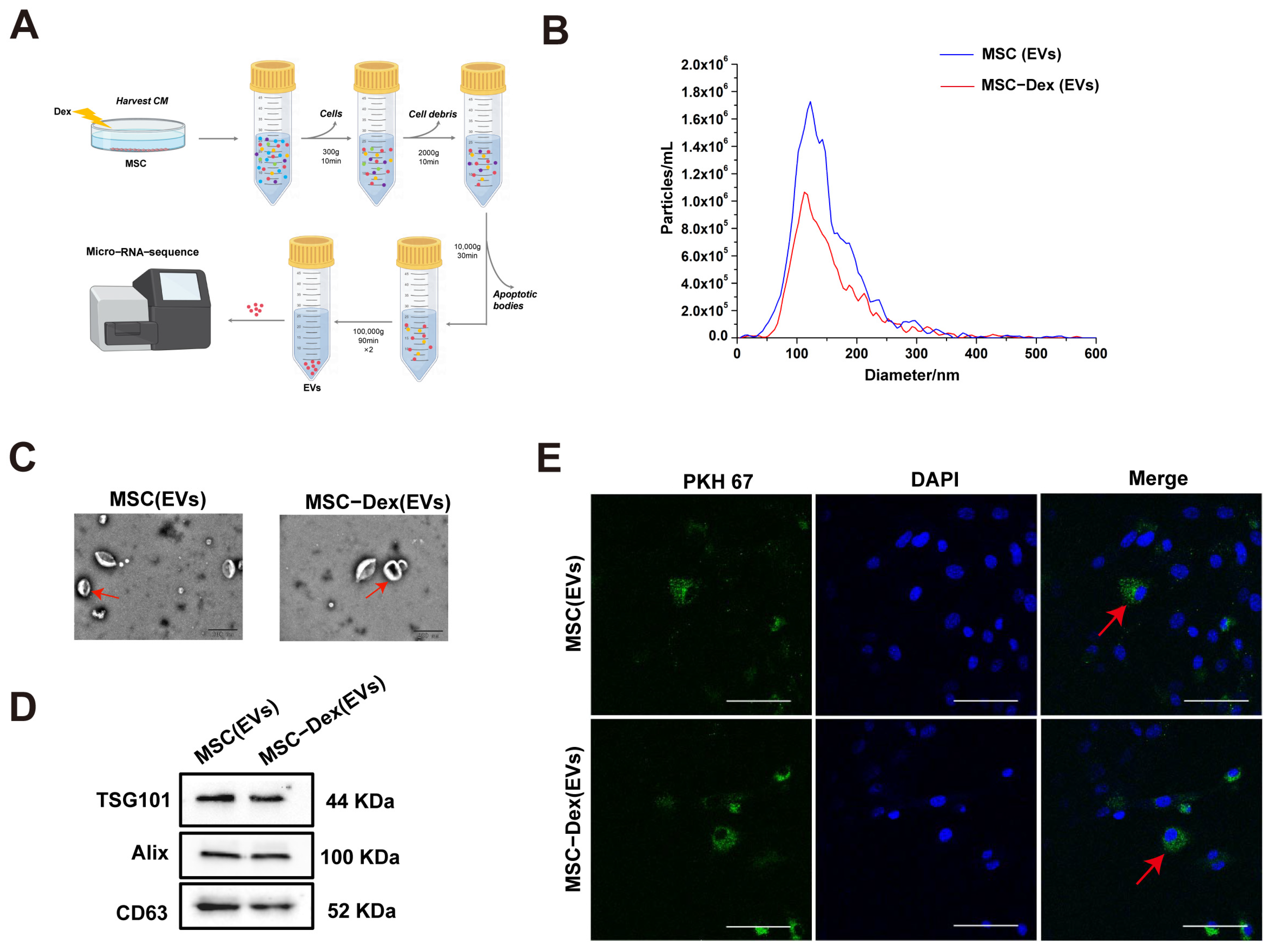
2.6. EV Isolation and Characterization
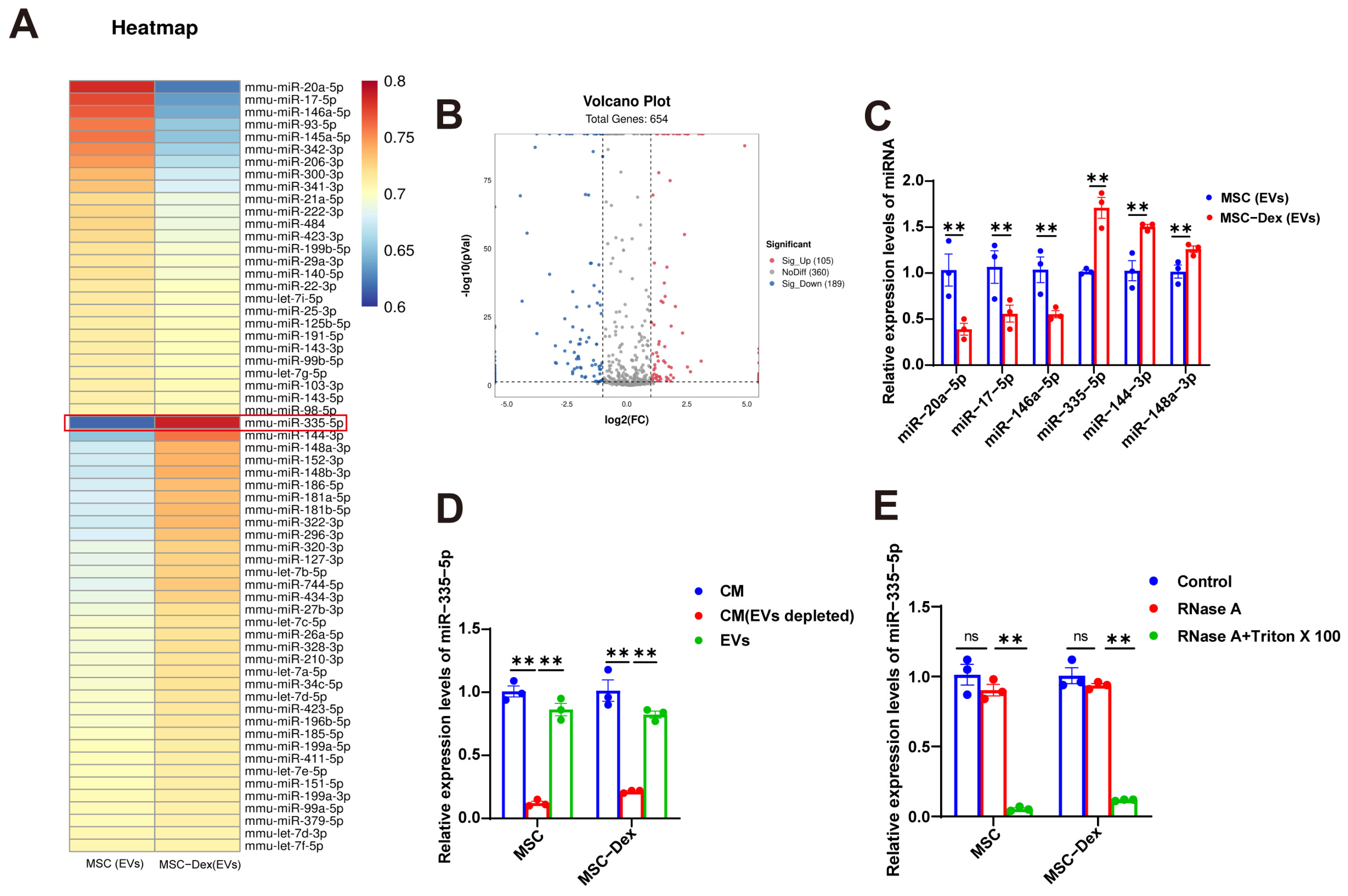
2.7. miRNA Sequencing of MSC-Derived EVs
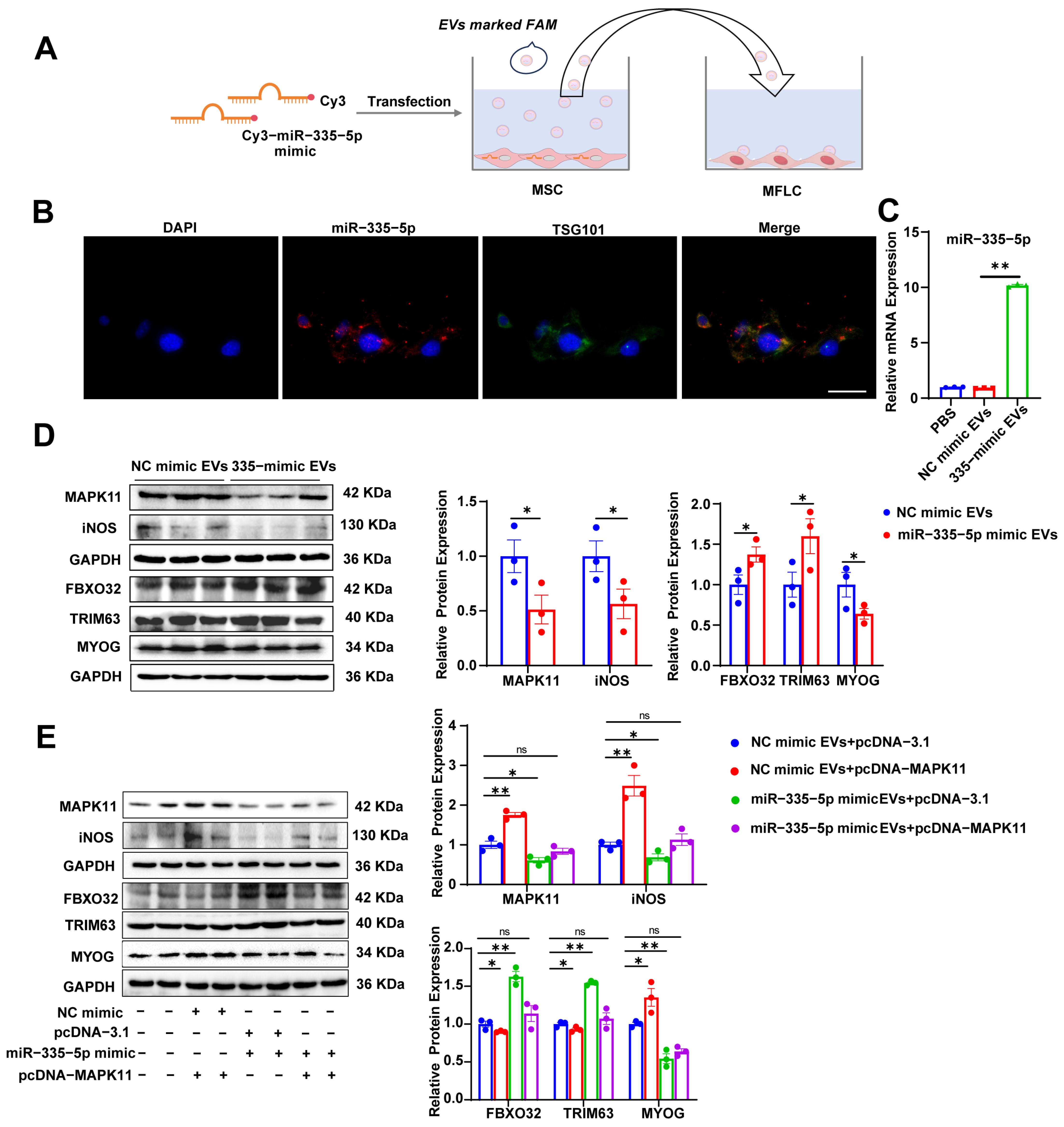
2.8. EV Uptake
2.9. miRNA Intervention
2.10. Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization (FISH)
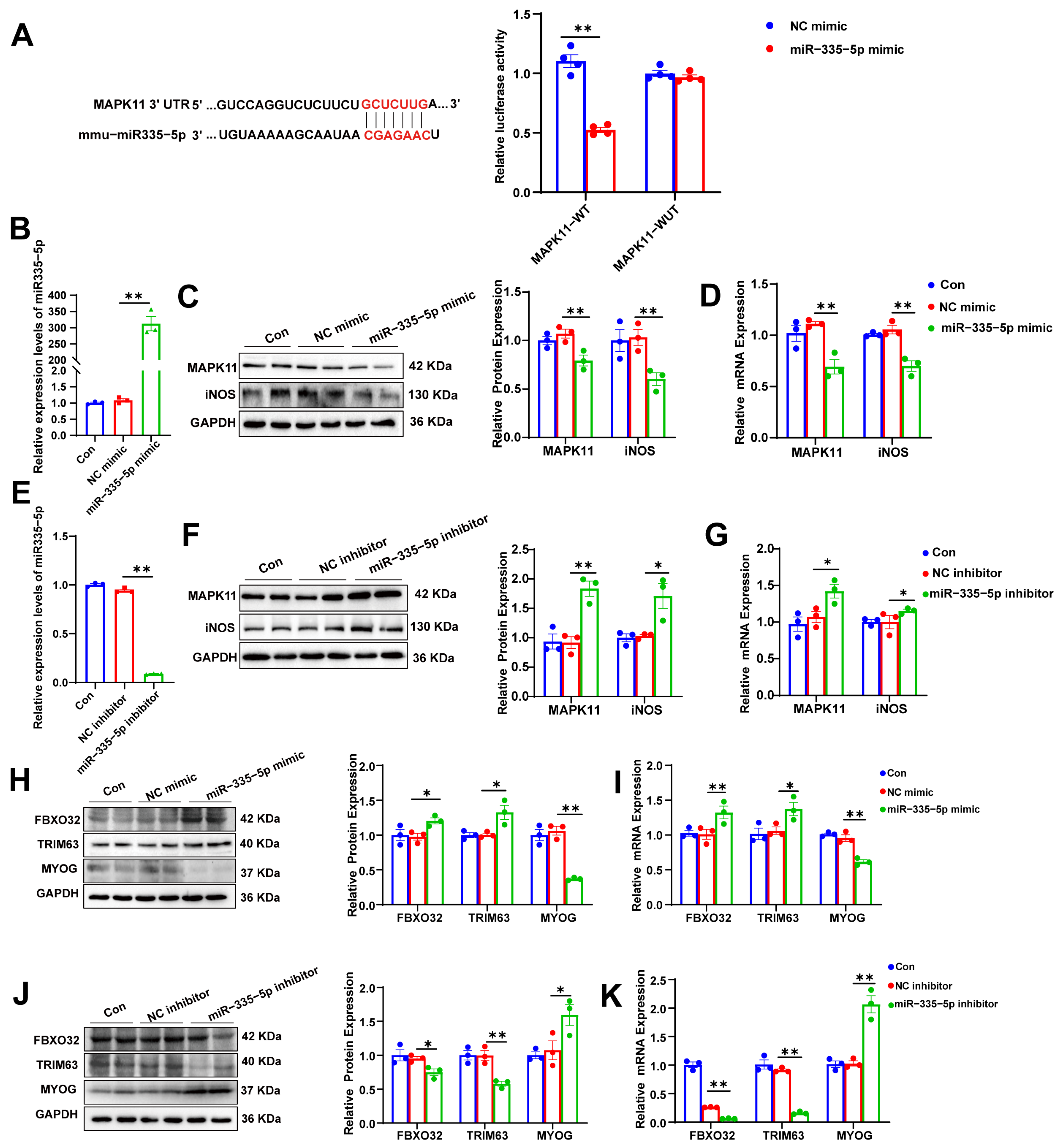
2.11. Dual-Luciferase Reporter Assay
2.12. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Isolation and Characterization of Primary MFLCs and MSCs from Skeletal Muscle
3.2. Characterization of Dex-Induced MSC-Derived EVs
3.3. Dex-Induced MSC-Derived EVs Cause Protein Degradation in MFLC via iNOS
3.4. Dex Alters miRNA Cargo in MSC-Derived EVs
3.5. miR-335-5p Targets MAPK11/iNOS, Inducing Protein Degradation in MFLCs
3.6. MSC-Derived EVs Carrying miR-335-5p Induce Protein Degradation in MFLCs via the MAPK11/iNOS Pathway
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, M.; Fu, W.; Xu, H.; Liu, C.J. Pathogenic mechanisms of glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2023, 70, 54–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogel, F.; Reincke, M. Endocrine risk factors for COVID-19: Endogenous and exogenous glucocorticoid excess. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2022, 23, 233–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, A.; Kim, J.I.; Lee, H.; Nirmala, F.S.; Hahm, J.H.; Seo, H.D.; Jung, C.H.; Ha, T.Y.; Ahn, J. Gromwell ameliorates glucocorticoid-induced muscle atrophy through the regulation of Akt/mTOR pathway. Chin. Med. 2024, 19, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Betters, J.L.; Long, J.H.; Howe, K.S.; Braith, R.W.; Soltow, Q.A.; Lira, V.A.; Criswell, D.S. Nitric oxide reverses prednisolone-induced inactivation of muscle satellite cells. Muscle Nerve Off. J. Am. Assoc. Electrodiagn. Med. 2008, 37, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, G.; Pfeilschifter, J.; Otten, U.; Kunz, D. Proteolytic cleavage of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) by calpain I. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Gen. Subj. 2001, 1568, 216–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandri, M. Protein breakdown in muscle wasting: Role of autophagy-lysosome and ubiquitin-proteasome. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2013, 45, 2121–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foletta, V.C.; White, L.J.; Larsen, A.E.; Léger, B.; Russell, A.P. The role and regulation of MAFbx/atrogin-1 and MuRF1 in skeletal muscle atrophy. Pflügers Arch. Eur. J. Physiol. 2011, 461, 325–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, R.M.; Freire de Carvalho, J. Glucocorticoid-induced myopathy. Jt. Bone Spine 2011, 78, 41–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frontera, W.R.; Ochala, J. Skeletal muscle: A brief review of structure and function. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2015, 96, 183–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sousa-Victor, P.; García-Prat, L.; Muñoz-Cánoves, P. Control of satellite cell function in muscle regeneration and its disruption in ageing. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2022, 23, 204–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mytidou, C.; Koutsoulidou, A.; Katsioloudi, A.; Prokopi, M.; Kapnisis, K.; Michailidou, K.; Anayiotos, A.; Phylactou, L.A. Muscle-derived exosomes encapsulate myomiRs and are involved in local skeletal muscle tissue communication. FASEB J. 2021, 35, e21279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frattini, P.; Villa, C.; De Santis, F.; Meregalli, M.; Belicchi, M.; Erratico, S.; Bella, P.; Raimondi, M.T.; Lu, Q.; Torrente, Y. Autologous intramuscular transplantation of engineered satellite cells induces exosome-mediated systemic expression of Fukutin-related protein and rescues disease phenotype in a murine model of limb-girdle muscular dystrophy type 2I. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2017, 26, 3682–3698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, R.; Liu, S.; Feng, X.; Luo, W.; Zhang, H.; Wu, Y.; Chen, S.; Shang, X. The Revolution of exosomes: From biological functions to therapeutic applications in skeletal muscle diseases. J. Orthop. Transl. 2024, 45, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, N.; Cui, G.; Zhao, S.; Li, Y.; Liu, Q.; Liu, X.; Zhao, C.; Feng, R.; Kuang, M.; Han, S. Therapeutic Effects of Mechanical Stress-Induced C2C12-Derived Exosomes on Glucocorticoid-Induced Osteoporosis Through miR-92a-3p/PTEN/AKT Signaling Pathway. Int. J. Nanomed. 2023, 18, 7583–7603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalluri, R.; LeBleu, V.S. The biology, function, and biomedical applications of exosomes. Science 2020, 367, eaau6977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Yuan, S.; Liu, G.; Li, J.; Zheng, K.; Zhang, Z.; Zheng, S.; Yin, L.; Li, Y. Satellite Cell-Derived Exosomes: A Novel Approach to Alleviate Skeletal Muscle Atrophy and Fibrosis. Adv. Biol. 2024, 8, e2300558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franco, C.; Giannella, A.; Gasparotto, M.; Zanatta, E.; Ghirardello, A.; Pettorossi, F.; Rahmè, Z.; Depascale, R.; Ragno, D.; Bevilacqua, G.; et al. Circulating extracellular vesicles and small non-coding RNAs cargo in idiopathic inflammatory myopathies reveal differences across myositis subsets. J. Autoimmun. 2024, 147, 103255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safwat, S.M.; Abdel Ghaffar, D.M.; Eldesoqui, M.; Mostafa, S.A.; Farrag, E.A.E.; El-Senduny, F.; Osman, B.; Nashar, E.M.E.; Alshehri, S.H.; Alhefzi, A.; et al. Platelet-rich plasma ameliorates dexamethasone-induced myopathy by suppressing autophagy and enhancing myogenic potential through modulation of Myo-D, Pax-7, and myogenin expression. Tissue Cell 2024, 91, 102602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Y.; Pan, J.S.; Zhang, L. Myostatin suppression of Akirin1 mediates glucocorticoid-induced satellite cell dysfunction. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e58554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gharaibeh, B.; Lu, A.; Tebbets, J.; Zheng, B.; Feduska, J.; Crisan, M.; Péault, B.; Cummins, J.; Huard, J. Isolation of a slowly adhering cell fraction containing stem cells from murine skeletal muscle by the preplate technique. Nat. Protoc. 2008, 3, 1501–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Chan, M.C.; Yu, Y.; Bei, Y.; Chen, P.; Zhou, Q.; Cheng, L.; Chen, L.; Ziegler, O.; Rowe, G.C.; et al. miR-29b contributes to multiple types of muscle atrophy. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Ji, J.; Zheng, D.; Su, L.; Peng, T.; Tang, J. Protective role of endothelial calpain knockout in lipopolysaccharide-induced acute kidney injury via attenuation of the p38-iNOS pathway and NO/ROS production. Exp. Mol. Med. 2020, 52, 702–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, C.; Zheng, S.; Luo, Y.; Wang, B. Exosome Theranostics: Biology and Translational Medicine. Theranostics 2018, 8, 237–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casadei, L.; Calore, F.; Creighton, C.J.; Guescini, M.; Batte, K.; Iwenofu, O.H.; Zewdu, A.; Braggio, D.A.; Bill, K.L.; Fadda, P.; et al. Exosome-Derived miR-25-3p and miR-92a-3p Stimulate Liposarcoma Progression. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 3846–3856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferguson, S.W.; Nguyen, J. Exosomes as therapeutics: The implications of molecular composition and exosomal heterogeneity. J. Control. Release 2016, 228, 179–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rome, S.; Forterre, A.; Mizgier, M.L.; Bouzakri, K. Skeletal Muscle-Released Extracellular Vesicles: State of the Art. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aswad, H.; Forterre, A.; Wiklander, O.P.; Vial, G.; Danty-Berger, E.; Jalabert, A.; Lamazière, A.; Meugnier, E.; Pesenti, S.; Ott, C.; et al. Exosomes participate in the alteration of muscle homeostasis during lipid-induced insulin resistance in mice. Diabetologia 2014, 57, 2155–2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, J.E. A role for nitric oxide in muscle repair: Nitric oxide-mediated activation of muscle satellite cells. Mol. Biol. Cell 2000, 11, 1859–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Auger, J.P.; Zimmermann, M.; Faas, M.; Stifel, U.; Chambers, D.; Krishnacoumar, B.; Taudte, R.V.; Grund, C.; Erdmann, G.; Scholtysek, C.; et al. Metabolic rewiring promotes anti-inflammatory effects of glucocorticoids. Nature 2024, 629, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsuyama, K.; Shichiri, M.; Kato, H.; Imai, T.; Marumo, F.; Hirata, Y. Differential inhibitory actions by glucocorticoid and aspirin on cytokine-induced nitric oxide production in vascular smooth muscle cells. Endocrinology 1999, 140, 2183–2190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasudevan, S.; Tong, Y.; Steitz, J.A. Switching from repression to activation: microRNAs can up-regulate translation. Science 2007, 318, 1931–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ørom, U.A.; Nielsen, F.C.; Lund, A.H. MicroRNA-10a binds the 5′UTR of ribosomal protein mRNAs and enhances their translation. Mol. Cell 2008, 30, 460–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horak, M.; Novak, J.; Bienertova-Vasku, J. Muscle-specific microRNAs in skeletal muscle development. Dev. Biol. 2016, 410, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ono, K.; Han, J. The p38 signal transduction pathway: Activation and function. Cell. Signal. 2000, 12, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennett, A.M.; Tonks, N.K. Regulation of distinct stages of skeletal muscle differentiation by mitogen-activated protein kinases. Science 1997, 278, 1288–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lacham-Kaplan, O.; Camera, D.M.; Hawley, J.A. Divergent Regulation of Myotube Formation and Gene Expression by E2 and EPA during In-Vitro Differentiation of C2C12 Myoblasts. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.; Zhang, D.; Li, L.; Xin, T.; Zhao, Y.; Ma, R.; Du, J. Exosomal microRNA-144 from bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells inhibits the progression of non-small cell lung cancer by targeting CCNE1 and CCNE2. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2020, 11, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, K.; Li, G.; Chen, W.; Song, L.; Wei, T.; Li, Z.; Gong, R.; Lei, J.; Shi, H.; Zhu, J. Plasma Exosomal miR-146b-5p and miR-222-3p are Potential Biomarkers for Lymph Node Metastasis in Papillary Thyroid Carcinomas. OncoTargets Ther. 2020, 13, 1311–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.J.; Yang, G.; Yan, Q.Q.; Zhao, J.; Li, S. Exosome-encapsulated microRNAs as promising biomarkers for Alzheimer’s disease. Rev. Neurosci. 2019, 31, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.; Ge, X.; Yu, J.; Han, Z.; Yin, Z.; Li, Y.; Chen, F.; Wang, H.; Zhang, J.; Lei, P. Increased miR-124-3p in microglial exosomes following traumatic brain injury inhibits neuronal inflammation and contributes to neurite outgrowth via their transfer into neurons. FASEB J. 2018, 32, 512–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, B.; Yang, H.; Wang, J.; Ru, W.; Wu, J.; Huang, Y.; Lan, X.; Lei, C.; Chen, H. Exosome biogenesis, secretion and function of exosomal miRNAs in skeletal muscle myogenesis. Cell Prolif. 2020, 53, e12857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, C.; Hou, Y.X.; Shi, P.X.; Zhu, C.H.; Lu, X.; Wang, X.L.; Que, L.L.; Zhu, G.Q.; Liu, L.; Chen, Q.; et al. Cardiomyocyte-specific Peli1 contributes to the pressure overload-induced cardiac fibrosis through miR-494-3p-dependent exosomal communication. FASEB J. 2023, 37, e22699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, E.; Ryu, G.R.; Ko, S.H.; Ahn, Y.B.; Song, K.H. Pancreatic stellate cells promote pancreatic β-cell death through exosomal microRNA transfer in hypoxia. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2023, 572, 111947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nan, K.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, D.; Zhao, Y.; Jing, Z.; Liu, K.; Shang, D.; Geng, Z.; Fan, L. Exosomes from miRNA-378-modified adipose-derived stem cells prevent glucocorticoid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head by enhancing angiogenesis and osteogenesis via targeting miR-378 negatively regulated suppressor of fused (Sufu). Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2021, 12, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biggar, W.D.; Skalsky, A.; McDonald, C.M. Comparing Deflazacort and Prednisone in Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy. J. Neuromuscul. Dis. 2022, 9, 463–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| miRNA or Gene Name | Primer Sequences (5′ to 3′) |
|---|---|
| iNOS-F | GTTCTCAGCCCAACAATACAAGA |
| iNOS-R | GTGGACGGGTCGATGTCAC |
| β-actin-F | TTGCTGACAGGATGCAGAAG |
| β-actin-R | ACATCTGCTGGAAGGTGGAC |
| FBXO32-F | CAGCTTCGTGAGCGACCTC |
| FBXO32-R | GGCAGTCGAGAAGTCCAGTC |
| TRIM63-F | GTGTGAGGTGCCTACTTGCTC |
| TRIM63-R | GCTCAGTCTTCTGTCCTTGGA |
| MYOG-F | CAGCTTCGTGAGCGACCTC |
| MYOG-R | GGCAGTCGAGAAGTCCAGTC |
| MAPK11-F | GTGTGAGGTGCCTACTTGCTC |
| MAPK11-R | GAGCAGACTGAGCCGTAGG |
| miR-335-5p | CGCGTCAAGAGCAATAACGAA |
| miR-144-3p | GCGCGCGTACAGTATAGATGA |
| miR-148a-3p | GCGCGTCAGTGCACTACAGAA |
| miR-20a-5p | CGCGCGTAAAGTGCTTATAGTG |
| miR-17-5p | GCGCAAAGTGCTTACAGTGC |
| miR-146a-5p | CGCGTGAGAACTGAATTCCA |
| U6-F | CTCGCTTCGGCAGCACA |
| U6-R | AACGCTTCACGAATTTGCGT |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, P.; Wu, J.; Zhou, R.; Xue, L.; Luo, X.; Yan, Y.; Lu, J.; Dong, Y.; Geng, J.; Wang, H. Glucocorticoid-Induced Muscle Satellite Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Mediate Skeletal Muscle Atrophy via the miR-335-5p/MAPK11/iNOS Pathway. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 1072. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15081072
Ma P, Wu J, Zhou R, Xue L, Luo X, Yan Y, Lu J, Dong Y, Geng J, Wang H. Glucocorticoid-Induced Muscle Satellite Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Mediate Skeletal Muscle Atrophy via the miR-335-5p/MAPK11/iNOS Pathway. Biomolecules. 2025; 15(8):1072. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15081072
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Pei, Jiarui Wu, Ruiyuan Zhou, Linli Xue, Xiaomao Luo, Yi Yan, Jiayin Lu, Yanjun Dong, Jianjun Geng, and Haidong Wang. 2025. "Glucocorticoid-Induced Muscle Satellite Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Mediate Skeletal Muscle Atrophy via the miR-335-5p/MAPK11/iNOS Pathway" Biomolecules 15, no. 8: 1072. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15081072
APA StyleMa, P., Wu, J., Zhou, R., Xue, L., Luo, X., Yan, Y., Lu, J., Dong, Y., Geng, J., & Wang, H. (2025). Glucocorticoid-Induced Muscle Satellite Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Mediate Skeletal Muscle Atrophy via the miR-335-5p/MAPK11/iNOS Pathway. Biomolecules, 15(8), 1072. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15081072






