Inhibiting miR-200a-3p Increases Sirtuin 1 and Mitigates Kidney Injury in a Tubular Cell Model of Diabetes and Hypertension-Related Renal Damage
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Urine Sample Processing and UAE Data Measurements
2.3. Renal Proximal Tubular Epithelial Cell (RPTEC) Culture and Treatment
2.4. Cell Apoptosis Analysis
2.5. Transfection of RPTEC with miR-200a-3p Mimic and Inhibitor
2.6. EV Isolation from RPTEC Cultures and Patients’ Urine
2.7. EV Concentration Assessment
2.8. RNA Isolation and cDNA Synthesis
2.9. Quantitative Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-qPCR)
2.10. Homogenization of Samples, Gel Electrophoresis, and Western Blot Analyses
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. miR-200a-3p Expression in Patients’ Urinary Exosomes
3.2. Cell Line and EV Characterisation
3.3. Effect of Treatments on RPTECs
3.4. miR-200a-3p Expression in Treated RPTECs, Exosomes, and Target Analyses
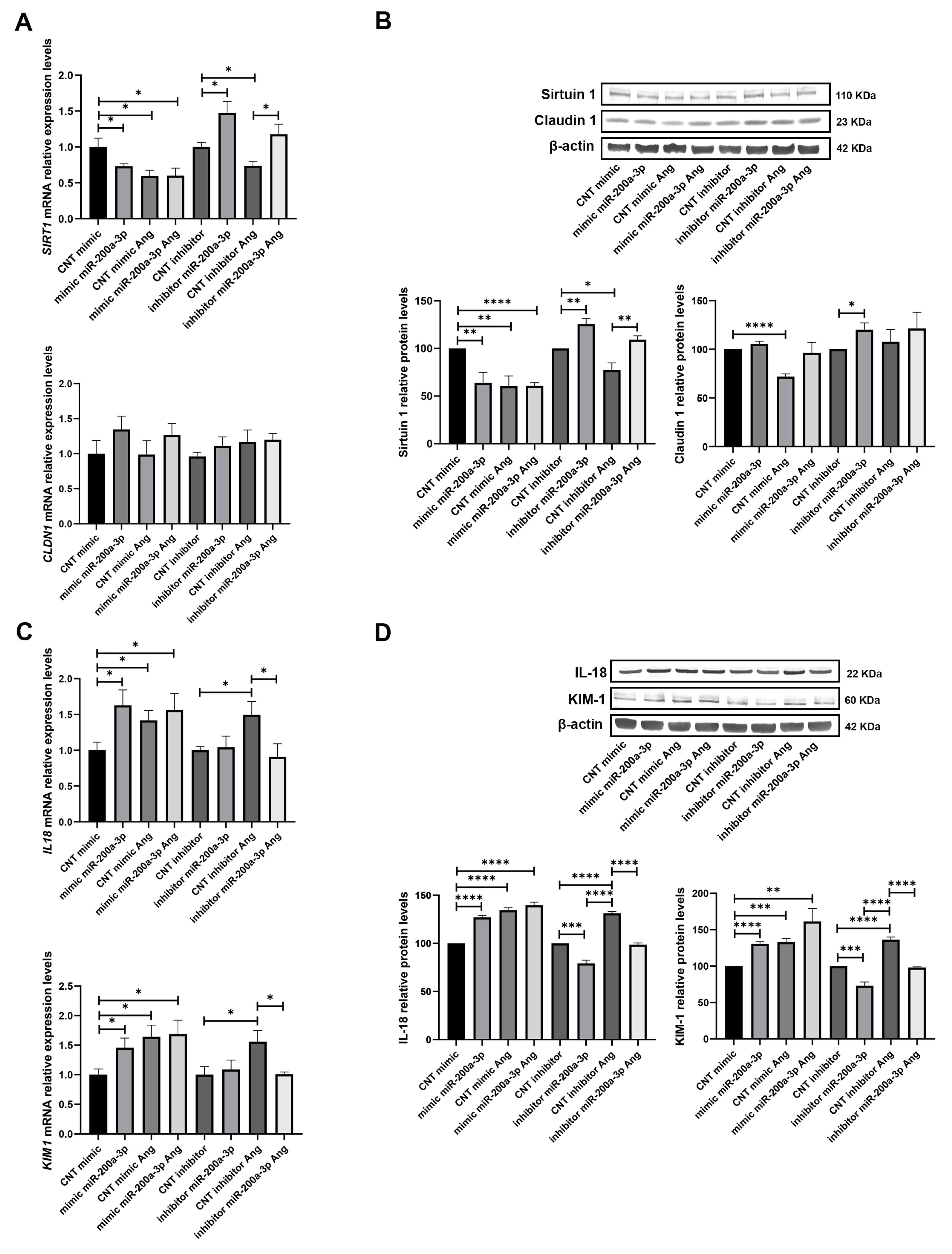
3.5. miR-200a-3p Overexpression and Inhibition Effects on SIRT1 and Tubular Damage
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACR: | Albumin/creatinine ratio |
| ACTB | β-Actin |
| AQP1 | Aquaporin 1 |
| AUC | Area under the curve |
| Ang II | Angiotensin II |
| B2MG | β2-microglobulin |
| BSA | Bovine serum albumin |
| CDH1 | E-cadherin |
| CI | Confidence interval |
| CLDN1 | Claudin 1 |
| CNT | Control |
| DBP | Diastolic blood pressure |
| DM | Diabetes mellitus |
| DMEM | Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle Medium |
| DTT | Dithiothreitol |
| EV | Extracellular vesicle |
| EXO-U | Exosome derived from patient urine |
| FC | Fold change |
| FBS | Foetal bovine serum |
| GFR | Glomerular filtration rate |
| hEGF | Human epidermal growth factor |
| HG | High glucose |
| HTN | Hypertension |
| ITS | Insulin transferrin selenium |
| miRNAs | MicroRNAs |
| NAD | Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide |
| NG | Normal glucose |
| PBS | Phosphate-buffered saline |
| PVDF | Polyvinylidene difluoride |
| P/S | Penicillin/streptomycin |
| UAE | Urinary albumin excretion |
| ROC | Receiver Operating Characteristic |
| RPTEC | Renal proximal tubular epithelial cell |
| RT | Room temperature |
| RT-qPCR | Quantitative Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction |
| SEM | Standard error of the mean |
| SIRT 1 | Sirtuin 1 |
| SBP | Systolic blood pressure |
| TBS-T | Tris-buffered saline with Tween |
| 7-AAD | 7-amino-actinomycin D |
References
- Webster, A.C.; Nagler, E.V.; Morton, R.L.; Masson, P. Chronic Kidney Disease. Lancet 2017, 389, 1238–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohishi, M. Hypertension with diabetes mellitus: Physiology and pathology. Hypertens. Res. 2018, 41, 389–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, D.M.; Bose, M.; Cooper, M.E. Glucose and Blood Pressure-Dependent Pathways-The Progression of Diabetic Kidney Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.C.; Tang, T.T.; Lv, L.L.; Lan, H.Y. Renal tubule injury: A driving force toward chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2018, 93, 568–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, T.X.; Rothenberg, M.E. MicroRNA. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018, 141, 1202–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.L.; Lv, L.L.; Tang, T.T.; Wang, B.; Feng, Y.; Zhou, L.T.; Cao, J.Y.; Tang, R.N.; Wu, M.; Liu, H.; et al. HIF-1alpha inducing exosomal microRNA-23a expression mediates the cross-talk between tubular epithelial cells and macrophages in tubulointerstitial inflammation. Kidney Int. 2019, 95, 388–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Zhao, S.; Li, W.; Ruan, Y.; Yuan, R.; Ning, J.; Jiang, K.; Xie, J.; Yao, X.; Li, H.; et al. Tubular cell-derived exosomal miR-150-5p contributes to renal fibrosis following unilateral ischemia-reperfusion injury by activating fibroblast in vitro and in vivo. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 17, 4021–4033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zheng, Z.J.; Jia, Y.J.; Yang, Y.L.; Xue, Y.M. Role of p53/miR-155-5p/sirt1 loop in renal tubular injury of diabetic kidney disease. J. Transl. Med. 2018, 16, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, J.; Shi, J. MicroRNA-25 inhibits high glucose-induced apoptosis in renal tubular epithelial cells via PTEN/AKT pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 96, 471–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, K.; Breyne, K.; Ughetto, S.; Laurent, L.C.; Breakefield, X.O. RNA delivery by extracellular vesicles in mammalian cells and its applications. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020, 21, 585–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Arroyo, O.; Ortega, A.; Forner, M.J.; Cortes, R. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles as Non-Coding RNA Therapeutic Vehicles in Autoimmune Diseases. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez-Arroyo, O.; Ortega, A.; Redon, J.; Cortes, R. Therapeutic Potential of Extracellular Vesicles in Hypertension-Associated Kidney Disease. Hypertension 2021, 77, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, T.T.; Lv, L.L.; Lan, H.Y.; Liu, B.C. Extracellular Vesicles: Opportunities and Challenges for the Treatment of Renal Diseases. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdbrugger, U.; Le, T.H. Extracellular vesicles as a novel diagnostic and research tool for patients with HTN and kidney disease. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2019, 317, F641–F647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erdbrugger, U.; Le, T.H. Extracellular Vesicles in Renal Diseases: More than Novel Biomarkers? J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2016, 27, 12–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Niel, G.; D’Angelo, G.; Raposo, G. Shedding light on the cell biology of extracellular vesicles. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2018, 19, 213–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thery, C.; Witwer, K.W.; Aikawa, E.; Alcaraz, M.J.; Anderson, J.D.; Andriantsitohaina, R.; Antoniou, A.; Arab, T.; Archer, F.; Atkin-Smith, G.K.; et al. Minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles 2018 (MISEV2018): A position statement of the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles and update of the MISEV2014 guidelines. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2018, 7, 1535750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, L.L.; Feng, Y.; Wu, M.; Wang, B.; Li, Z.L.; Zhong, X.; Wu, W.J.; Chen, J.; Ni, H.F.; Tang, T.T.; et al. Exosomal miRNA-19b-3p of tubular epithelial cells promotes M1 macrophage activation in kidney injury. Cell Death Differ. 2020, 27, 210–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Hernandez, J.; Riffo-Campos, A.L.; Ortega, A.; Martinez-Arroyo, O.; Perez-Gil, D.; Olivares, D.; Solaz, E.; Martinez, F.; Martinez-Hervas, S.; Chaves, F.J.; et al. Urinary- and Plasma-Derived Exosomes Reveal a Distinct MicroRNA Signature Associated With Albuminuria in Hypertension. Hypertension 2021, 77, 960–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riffo-Campos, A.L.; Perez-Hernandez, J.; Ortega, A.; Martinez-Arroyo, O.; Flores-Chova, A.; Redon, J.; Cortes, R. Exosomal and Plasma Non-Coding RNA Signature Associated with Urinary Albumin Excretion in Hypertension. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Arroyo, O.; Flores-Chova, A.; Mendez-Debaets, M.; Martinez-Hervas, S.; Martinez, F.; Forner, M.J.; Redon, J.; Ortega, A.; Cortes, R. Enrichment of RedoxifibromiR miR-21-5p in Plasma Exosomes of Hypertensive Patients with Renal Injury. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez-Arroyo, O.; Ortega, A.; Galera, M.; Solaz, E.; Martinez-Hervas, S.; Redon, J.; Cortes, R. Decreased Urinary Levels of SIRT1 as Non-Invasive Biomarker of Early Renal Damage in Hypertension. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kume, S.; Haneda, M.; Kanasaki, K.; Sugimoto, T.; Araki, S.; Isshiki, K.; Isono, M.; Uzu, T.; Guarente, L.; Kashiwagi, A.; et al. SIRT1 inhibits transforming growth factor beta-induced apoptosis in glomerular mesangial cells via Smad7 deacetylation. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasegawa, K.; Wakino, S.; Simic, P.; Sakamaki, Y.; Minakuchi, H.; Fujimura, K.; Hosoya, K.; Komatsu, M.; Kaneko, Y.; Kanda, T.; et al. Renal tubular Sirt1 attenuates diabetic albuminuria by epigenetically suppressing Claudin-1 overexpression in podocytes. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 1496–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, C.H.; Kim, S.; Kim, G.H. Claudins in kidney health and disease. Kidney Res. Clin. Pract. 2022, 41, 275–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Shen, L.; Yu, X.; Wu, J.; Zha, L.; Xia, Y.; Luo, H. miR-200a attenuated oxidative stress, inflammation, and apoptosis in dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis through activation of Nrf2. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1196065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.S.; Liu, W.; Lu, G.X. miR-200a-3p promotes b-Amyloid-induced neuronal apoptosis through down-regulation of SIRT1 in Alzheimer’s disease. J. Biosci. 2017, 42, 397–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, P.; Chen, H.; Han, W.; Deng, J. miR-200a-3p overexpression alleviates diabetic cardiomyopathy injury in mice by regulating autophagy through the FOXO3/Mst1/Sirt3/AMPK axis. PeerJ 2023, 11, e15840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, L.; Xiong, C.; Li, J.; Ren, Y.; Zhang, L.; Jiao, K.; Chen, C.; Ding, P. miR-200-3p suppresses cell proliferation and reduces apoptosis in diabetic retinopathy via blocking the TGF-beta2/Smad pathway. Biosci. Rep. 2020, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, B.; Mancia, G.; Spiering, W.; Agabiti Rosei, E.; Azizi, M.; Burnier, M.; Clement, D.L.; Coca, A.; de Simone, G.; Dominiczak, A.; et al. 2018 ESC/ESH Guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension. Eur. Heart J. 2018, 39, 3021–3104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Diabetes, A. 2. Classification and Diagnosis of Diabetes: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes-2018. Diabetes Care 2018, 41, S13–S27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wieser, M.; Stadler, G.; Jennings, P.; Streubel, B.; Pfaller, W.; Ambros, P.; Riedl, C.; Katinger, H.; Grillari, J.; Grillari-Voglauer, R. hTERT alone immortalizes epithelial cells of renal proximal tubules without changing their functional characteristics. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2008, 295, F1365–F1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Arroyo, O.; Flores-Chova, A.; Sanchez-Garcia, B.; Redon, J.; Cortes, R.; Ortega, A. Rab3A/Rab27A System Silencing Ameliorates High Glucose-Induced Injury in Podocytes. Biology 2023, 12, 690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.; Wang, C.; Zhu, L.; Yang, Y. Emerging Sensing and In Situ Detection Technologies for the Analysis of Extracellular Vesicle miRNAs. Adv. Nanobiomed Res. 2024, 4, 202300067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Kannisto, E.; Patnaik, S.K.; Reid, M.E.; Li, L.; Wu, Y. Ultrafast Detection of Exosomal RNAs via Cationic Lipoplex Nanoparticles in a Micromixer Biochip for Cancer Diagnosis. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2021, 4, 2806–2819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eades, G.; Yao, Y.; Yang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Chumsri, S.; Zhou, Q. miR-200a regulates SIRT1 expression and epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT)-like transformation in mammary epithelial cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 25992–26002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zeng, Z.; Guan, L.; Ao, R. GRHL2 induces liver fibrosis and intestinal mucosal barrier dysfunction in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease via microRNA-200 and the MAPK pathway. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 6107–6119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Q.; Ma, F.; Liu, T.; Yang, L.; Mao, H.; Wang, Y.; Peng, L.; Li, P.; Zhan, Y. Sirtuins in kidney diseases: Potential mechanism and therapeutic targets. Cell Commun. Signal 2024, 22, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivares, D.; Perez-Hernandez, J.; Forner, M.J.; Perez-Soriano, C.; Tormos, M.C.; Saez, G.T.; Chaves, F.J.; Redon, J.; Cortes, R. Urinary levels of sirtuin-1 associated with disease activity in lupus nephritis. Clin. Sci. 2018, 132, 569–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.H.; Jung, Y.J.; Lee, J.E.; Lee, A.S.; Kang, K.P.; Lee, S.; Park, S.K.; Han, M.K.; Lee, S.Y.; Ramkumar, K.M.; et al. SIRT1 activation by resveratrol ameliorates cisplatin-induced renal injury through deacetylation of p53. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2011, 301, F427–F435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Sun, W.; Cheng, Y.; Xu, Z.; Cai, L. Role of sirtuin-1 in diabetic nephropathy. J. Mol. Med. 2019, 97, 291–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, X.; Li, Y.; Wu, J.; Liao, L.; Lu, D.; Qiu, P.; Yang, H.L.; Tang, M.W.; Liang, X.Y.; Liu, D. Dulaglutide restores endothelial progenitor cell levels in diabetic mice and mitigates high glucose-induced endothelial injury through SIRT1-mediated mitochondrial fission. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2024, 716, 150002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazyluk, A.; Malyszko, J.; Hryszko, T.; Zbroch, E. State of the art—Sirtuin 1 in kidney pathology—Clinical relevance. Adv. Med. Sci. 2019, 64, 356–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Wang, J.; Zhao, A.; Li, J. SIRT1 activation inhibits hyperglycemia-induced apoptosis by reducing oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction in human endothelial cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 16, 3331–3338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kida, Y.; Zullo, J.A.; Goligorsky, M.S. Endothelial sirtuin 1 inactivation enhances capillary rarefaction and fibrosis following kidney injury through Notch activation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016, 478, 1074–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Tang, C.; Cai, J.; Chen, G.; Dong, Z. p53/sirtuin 1/NF-kappaB Signaling Axis in Chronic Inflammation and Maladaptive Kidney Repair After Cisplatin Nephrotoxicity. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 925738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, L.; Zha, D.; Wu, X. Inhibition of miRNA-135a-5p ameliorates TGF-beta1-induced human renal fibrosis by targeting SIRT1 in diabetic nephropathy. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2020, 46, 1063–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemoto, S.; Fergusson, M.M.; Finkel, T. SIRT1 functionally interacts with the metabolic regulator and transcriptional coactivator PGC-1alpha. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 16456–16460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olmos, Y.; Sanchez-Gomez, F.J.; Wild, B.; Garcia-Quintans, N.; Cabezudo, S.; Lamas, S.; Monsalve, M. SirT1 regulation of antioxidant genes is dependent on the formation of a FoxO3a/PGC-1alpha complex. Antioxid. Redox Signal 2013, 19, 1507–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Wu, J.; Ma, F.; Jiang, J.; Xu, L.; Du, L.; Huang, W.; Wang, Z.; Jia, Y.; Lu, L.; et al. MicroRNA-200a improves diabetic endothelial dysfunction by targeting KEAP1/NRF2. J. Endocrinol. 2020, 245, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, M.; Jiang, L.; Zhou, Y.; Qiu, W.; Fang, L.; Tan, R.; Wen, P.; Yang, J. The miR-200 family regulates TGF-beta1-induced renal tubular epithelial to mesenchymal transition through Smad pathway by targeting ZEB1 and ZEB2 expression. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2012, 302, F369–F379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, Y.; Lee, K.; He, J.C. SIRT1 Is a Potential Drug Target for Treatment of Diabetic Kidney Disease. Front Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelaala, N.; El-Shoura, E.A.M.; Khalaf, M.M.; Zafaar, D.; A, A.N.A.; Atwa, A.M.; Abdel-Wahab, B.A.; Ahmed, Y.H.; Abomandour, A.; Salem, E.A. Reno-protective impact of diosmin and perindopril in amikacin-induced nephrotoxicity rat model: Modulation of SIRT1/p53/C-FOS, NF-kappaB-p65, and keap-1/Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathways. Immunopharmacol. Immunotoxicol. 2025, 24, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohmmed Hegab, A.M.; Hassanin, S.O.; Mekky, R.H.; Abuzahrah, S.S.; Hamza, A.A.; Talaat, I.M.; Amin, A. Withania somnifera Ameliorates Doxorubicin-Induced Nephrotoxicity and Potentiates Its Therapeutic Efficacy Targeting SIRT1/Nrf2, Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, and Apoptosis. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Zhao, Y.; Hu, S.; Yuan, J.B.; Xie, K.J.; Cai, S.N.; Zhu, X.Y.; Du, J.K.; Xu, P.B. Inhibition of SIRT1/HSF1 pathway contributes to doxorubicin-induced nephrotoxicity in ovarian tumor-bearing mice. Apoptosis 2025, 30, 1572–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasegawa, K.; Wakino, S.; Yoshioka, K.; Tatematsu, S.; Hara, Y.; Minakuchi, H.; Sueyasu, K.; Washida, N.; Tokuyama, H.; Tzukerman, M.; et al. Kidney-specific overexpression of Sirt1 protects against acute kidney injury by retaining peroxisome function. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 13045–13056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.; Zhang, K.; Wang, X.; Li, J.; Zou, H.; Yuan, Y.; Gu, J.; Zhu, J.; Liu, G.; Liu, Z.; et al. SIRT1 alleviates Cd nephrotoxicity through NF-kappaB/p65 deacetylation-mediated pyroptosis in rat renal tubular epithelial cells. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 929, 172392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, P.; Xiao, L.; Liu, Y.; Yang, J.; Li, S.; Wang, L. Morusin ameliorates tubulointerstitial damage in diabetic mice through SIRT1/HIF-1alpha/IL-16 signaling pathway. Phytomedicine 2025, 142, 156781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Niu, Q.; Mi, X.; Yang, B.; Cai, M.; Liang, Y. Sirt1 activation prevents high glucose-induced angiotensin converting enzyme 2 downregulation in renal tubular cells by regulating the TIMP3/ADAM17 pathway. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2024, 51, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Medical, A. World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki: Ethical principles for medical research involving human subjects. JAMA 2013, 310, 2191–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
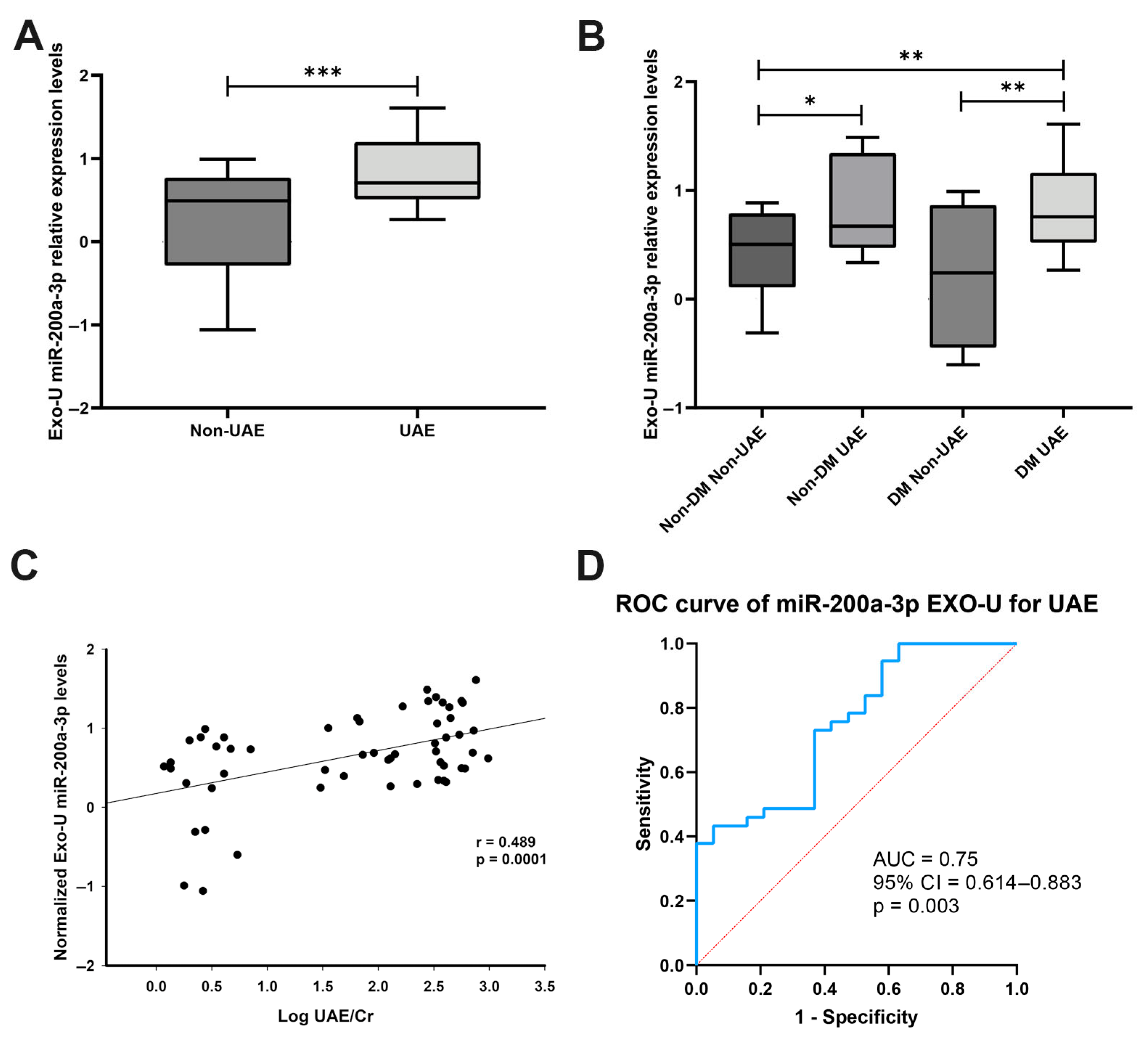
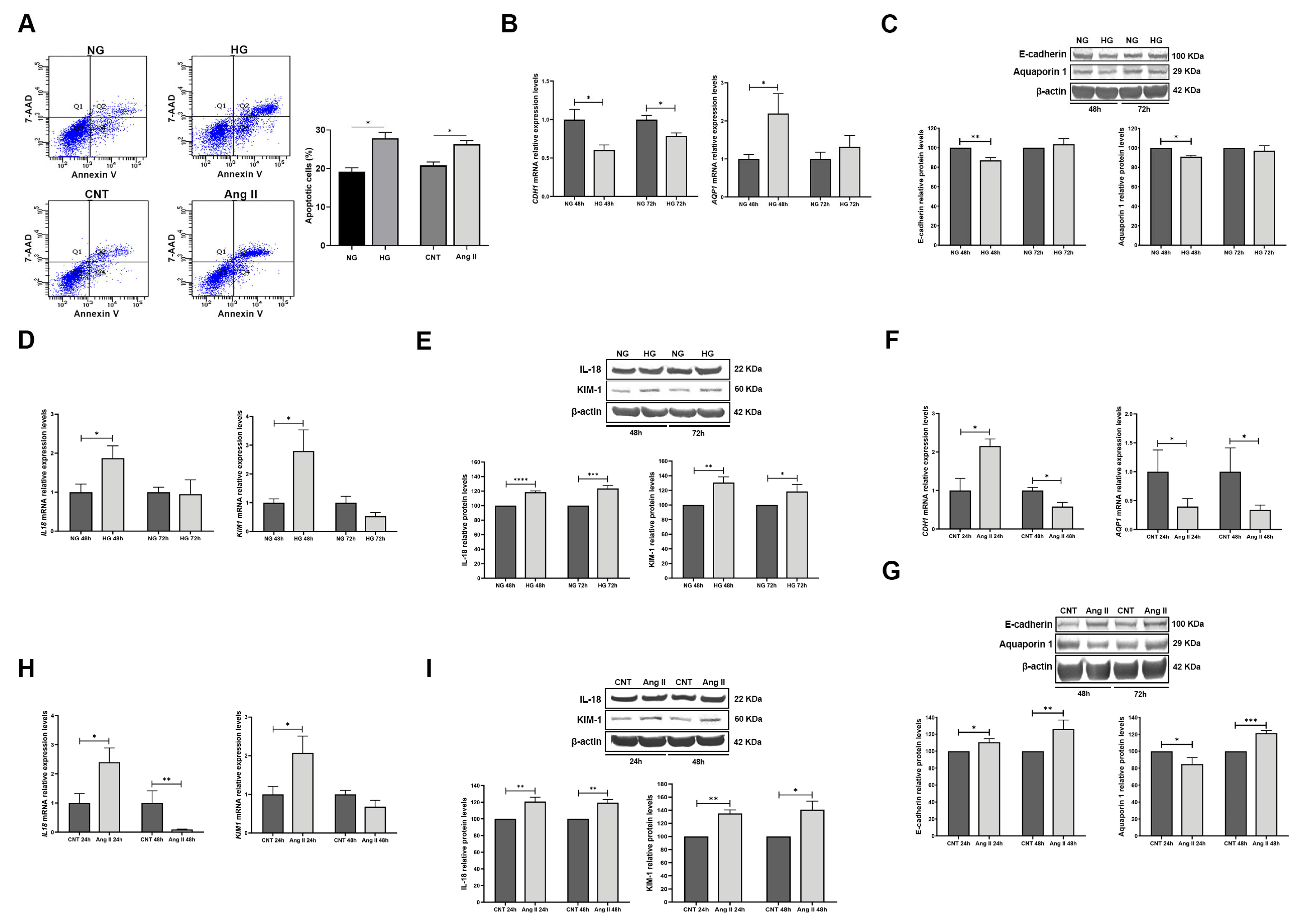
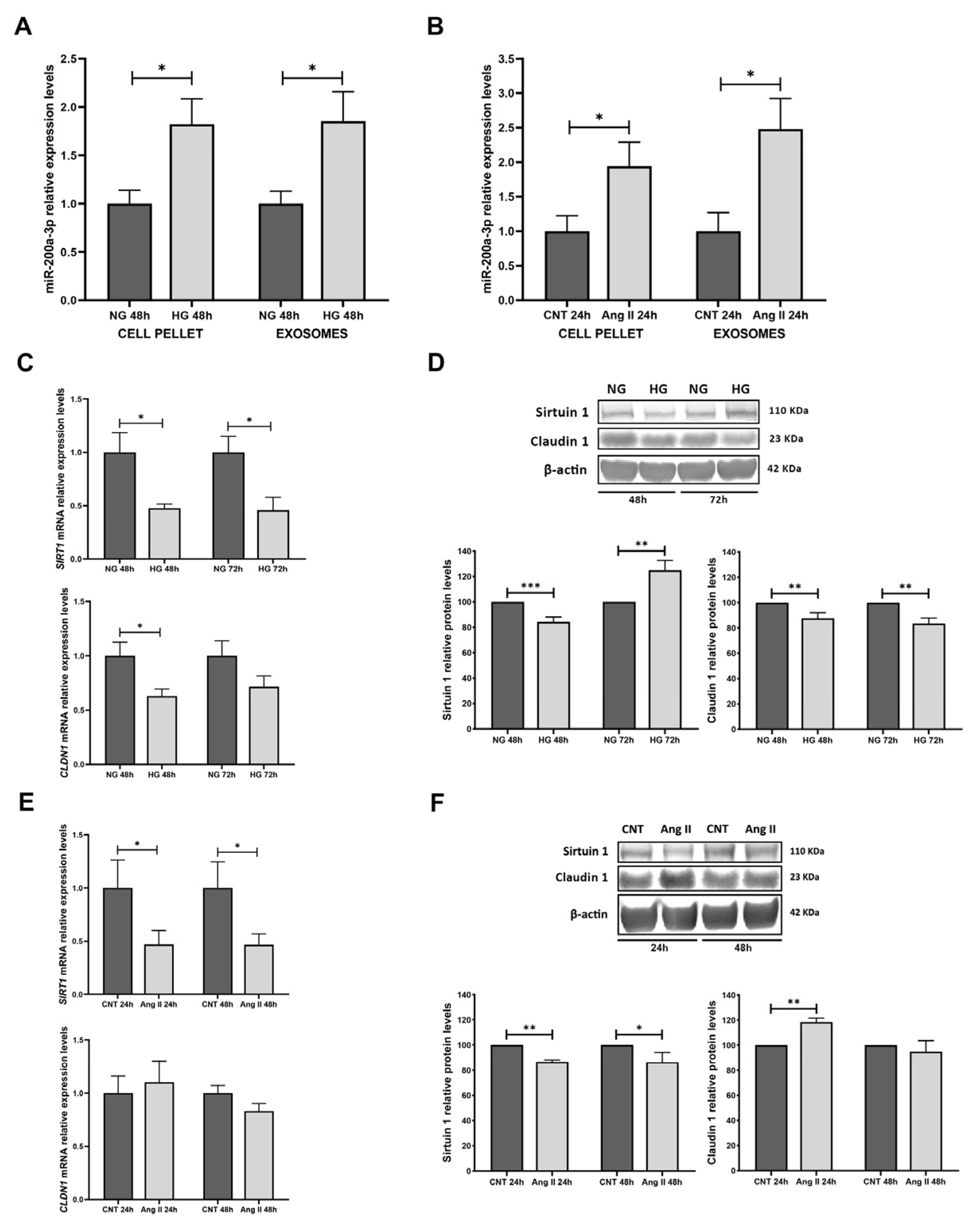
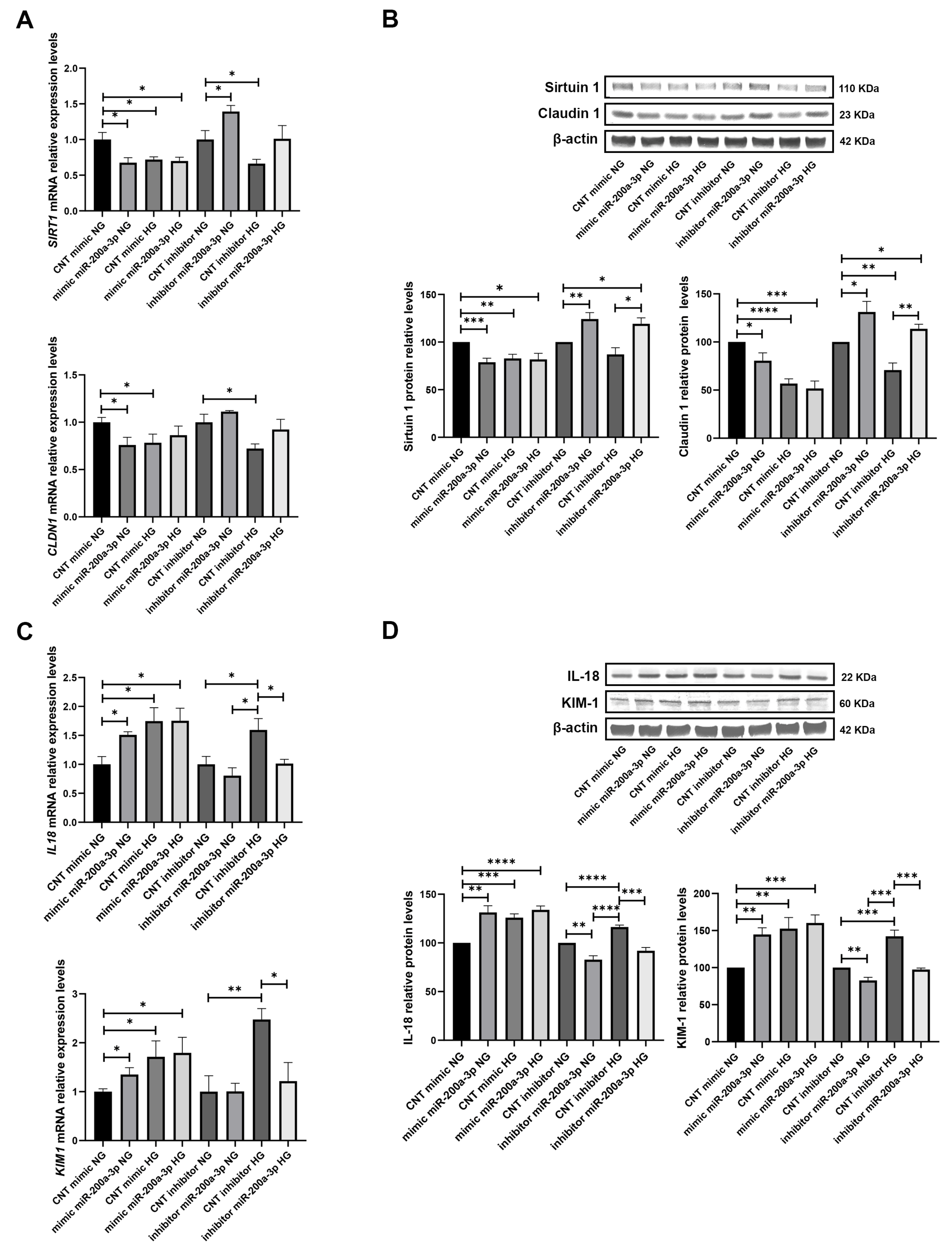
| Variables | Non-Diabetic | Diabetic | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Non-UAE (n = 19) | Increased UAE (n = 14) | Non-UAE (n = 9) | Increased UAE (n = 27) | |
| Age (years) | 54.45 ± 6.04 | 50.79 ± 9.26 | 54.78 ± 4.15 | 63.96 ± 10.99 †‡‡‡ |
| Gender (male, %) | 60 | 64.3 | 77.8 | 81.5 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 30.6 ± 6.49 | 29.46 ± 5.01 | 29.51 ± 4.66 | 34.01 ± 7.05 ‡ |
| Obesity (%) | 40 | 42.9 | 44.4 | 63 |
| SBP (mmHg) | 134.05 ± 18.55 | 130.79 ± 10.59 | 140.78 ± 34.06 | 141.33 ± 21.56 ‡ |
| DBP (mmHg) | 88.00 ± 13.53 | 82.5 ± 8.86 | 89.00 ± 18.04 | 82.74 ± 11.70 |
| Smoking (%) | 40 | 57.1 | 55.6 | 22.2 |
| Glucose (mg/dL) | 103.65 ± 9.51 | 97.43 ± 17.46 | 149.11 ± 59.53 §§ | 149.33 ± 51.76 ‡‡‡ |
| Glycated Hb (%) | 3.37 ± 2.83 | 0.82 ± 2.09 * | 6.49 ± 1.06 §§ | 7.09 ± 1.14 ‡‡‡ |
| Plasma Cr (mg/dL) | 0.85 ± 0.17 | 0.91 ± 0.34 | 0.99 ± 0.28 | 1.17 ± 0.59 |
| GFR (mL/min/1.73 m2) | 89.58 ± 16.97 | 92.04 ± 29.28 | 82.81 ± 23.51 | 78.95 ± 31.61 |
| Ratio UAE/Cr (mg/g) | 4.84 ± 6.45 | 126.67 ± 203.4 | 3.02 ± 1.48 | 361.97 ± 252.13 †††‡‡ |
| Dyslipidaemia (%) | 75 | 85.7 | 100 | 96.3 |
| T Cholesterol (mg/dL) | 184 ± 22.66 | 204.86 ± 35.98 | 150.67 ± 25.18 | 172.59 ± 35.32 |
| LDL (mg/dL) | 116.85 ± 19.74 | 133.43 ± 30.13 | 86.00 ± 20.58 § | 104.22 ± 30.69 ‡‡ |
| HDL (mg/dL) | 51.30 ± 10.85 | 56.00 ± 13.80 | 43.67 ± 8.60 | 43.56 ± 11.18 ‡‡ |
| TG (mg/dL) | 121.40 ± 57.47 | 113.86 ± 44.12 | 159.00 ± 65.02 | 214.89 ± 177.86 ‡ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Martinez-Arroyo, O.; Flores-Chova, A.; Mendez-Debaets, M.; Garcia-Ferran, L.; Escrivá, L.; Forner, M.J.; Redón, J.; Cortes, R.; Ortega, A. Inhibiting miR-200a-3p Increases Sirtuin 1 and Mitigates Kidney Injury in a Tubular Cell Model of Diabetes and Hypertension-Related Renal Damage. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 995. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15070995
Martinez-Arroyo O, Flores-Chova A, Mendez-Debaets M, Garcia-Ferran L, Escrivá L, Forner MJ, Redón J, Cortes R, Ortega A. Inhibiting miR-200a-3p Increases Sirtuin 1 and Mitigates Kidney Injury in a Tubular Cell Model of Diabetes and Hypertension-Related Renal Damage. Biomolecules. 2025; 15(7):995. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15070995
Chicago/Turabian StyleMartinez-Arroyo, Olga, Ana Flores-Chova, Marta Mendez-Debaets, Laia Garcia-Ferran, Lesley Escrivá, Maria Jose Forner, Josep Redón, Raquel Cortes, and Ana Ortega. 2025. "Inhibiting miR-200a-3p Increases Sirtuin 1 and Mitigates Kidney Injury in a Tubular Cell Model of Diabetes and Hypertension-Related Renal Damage" Biomolecules 15, no. 7: 995. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15070995
APA StyleMartinez-Arroyo, O., Flores-Chova, A., Mendez-Debaets, M., Garcia-Ferran, L., Escrivá, L., Forner, M. J., Redón, J., Cortes, R., & Ortega, A. (2025). Inhibiting miR-200a-3p Increases Sirtuin 1 and Mitigates Kidney Injury in a Tubular Cell Model of Diabetes and Hypertension-Related Renal Damage. Biomolecules, 15(7), 995. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15070995









