Heparin-Binding Hemagglutinin-Induced Trained Immunity in Macrophages: Implications for Antimycobacterial Defense
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Antibodies
2.2. Cell Lines and Cell Isolation
2.3. Trained Immunity in Macrophages and hPBMCs
2.4. Quantitative Real-Time PCR
2.5. Cytokine Assay
2.6. In Vitro Mtb Killing Assays
2.7. Determination of Lactate
2.8. ChIP Assay
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
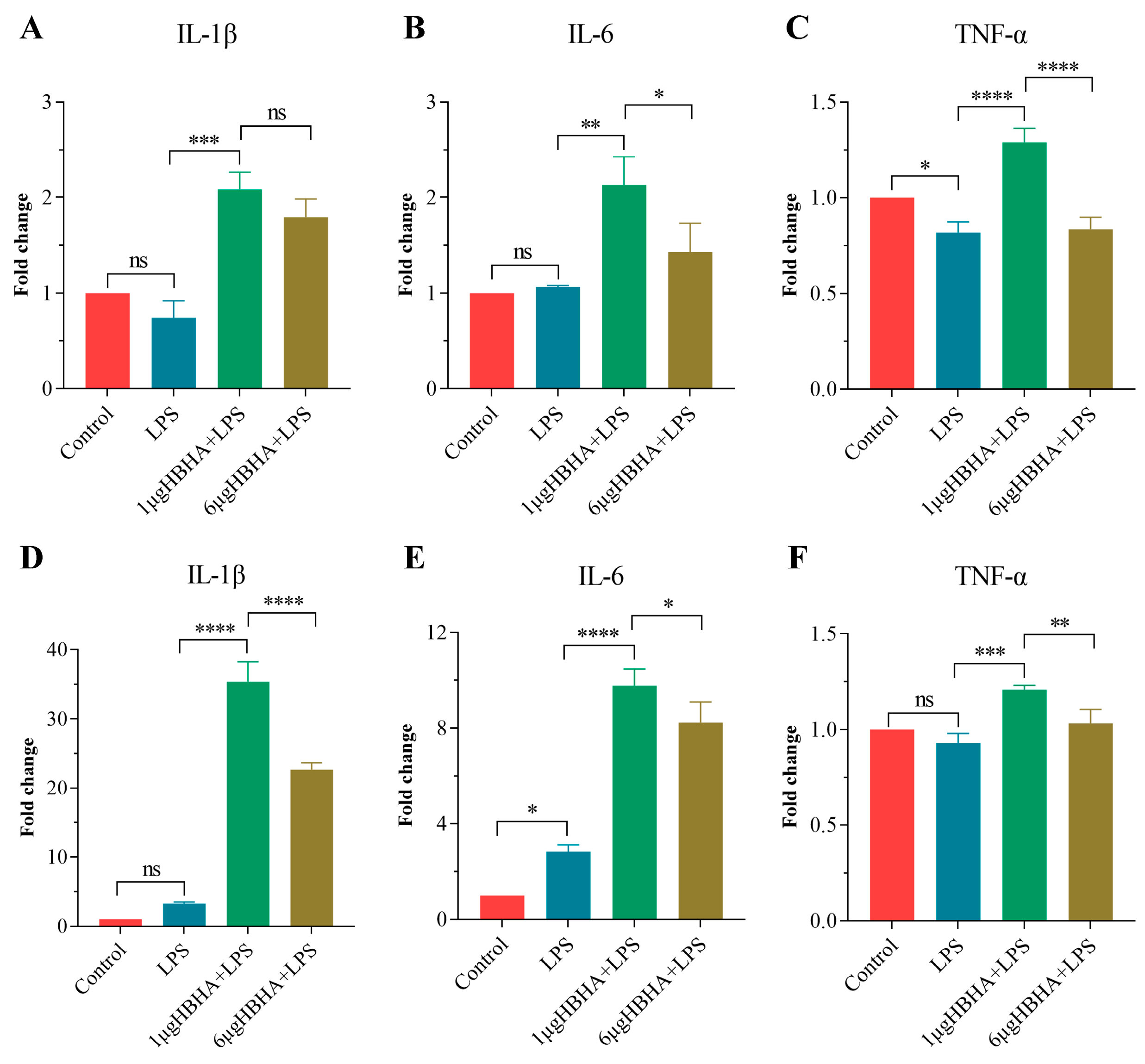
3.1. HBHA Training Enhances Production of Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines in RAW264.7
3.2. HBHA-Trained Macrophages Exhibit Enhanced Mycobacterial Killing Capacity
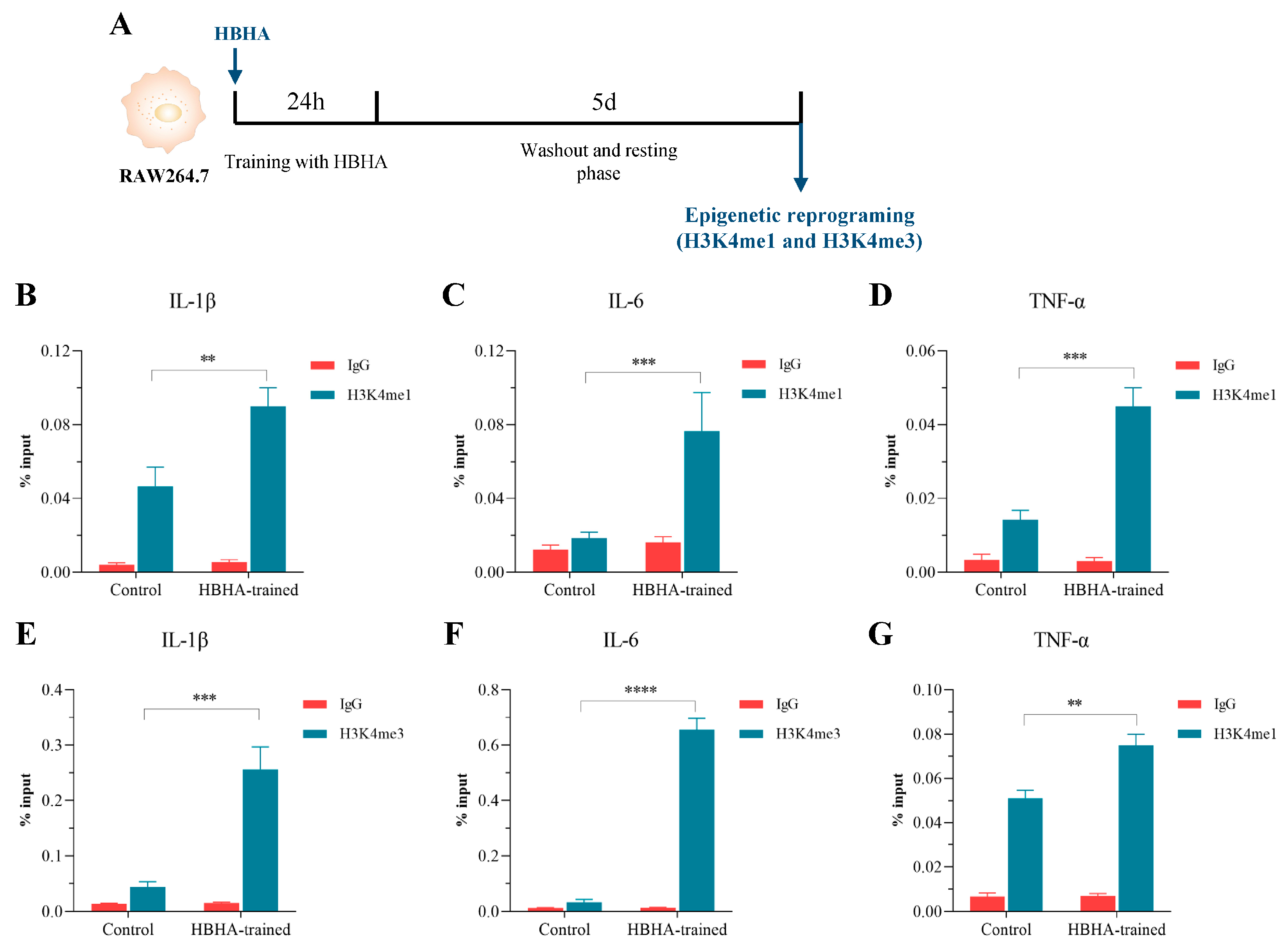
3.3. HBHA Training Triggers Epigenetic Modifications in RAW264.7 Macrophages
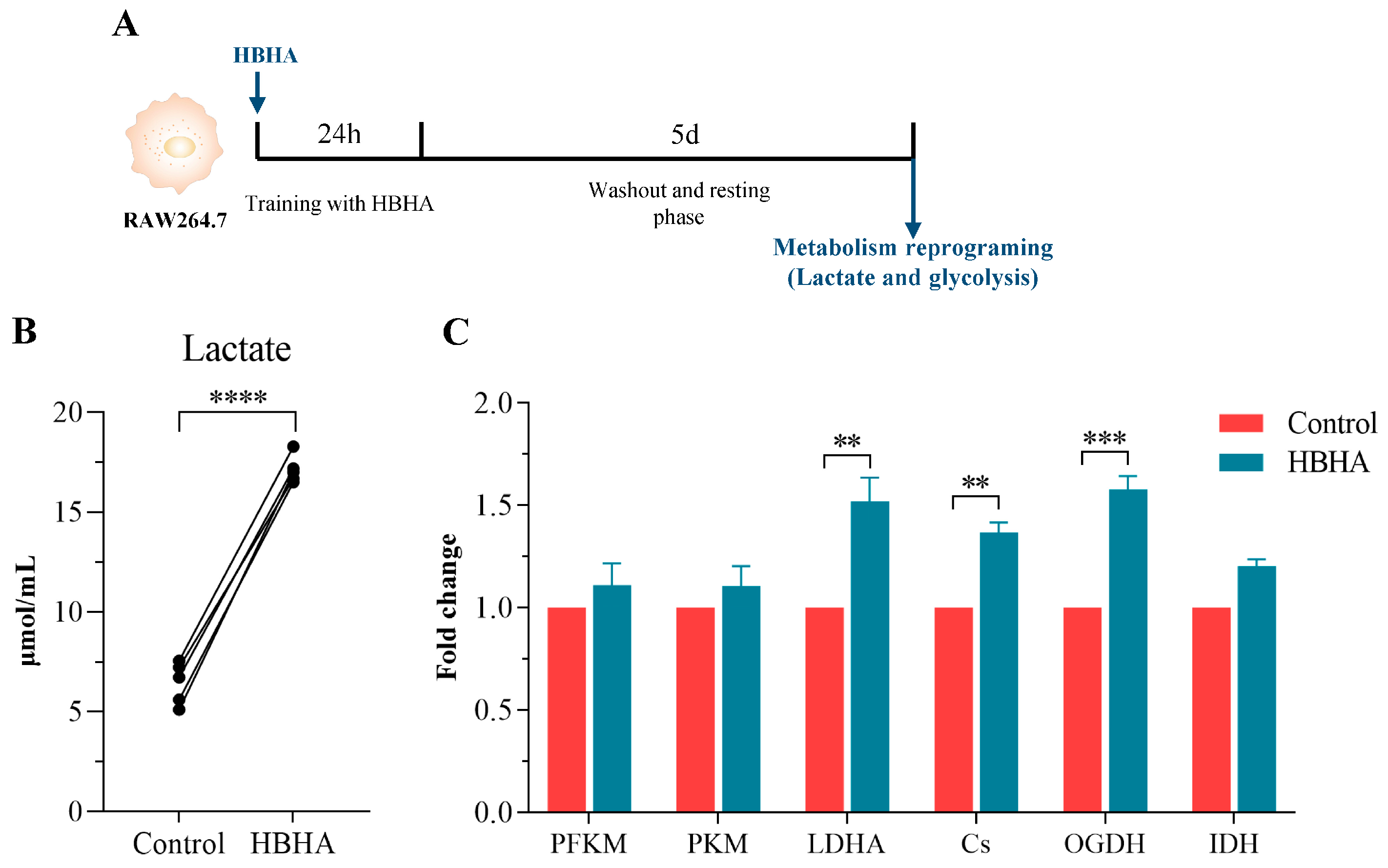
3.4. HBHA Training Induces Metabolic Reprogramming in RAW264.7 Macrophages
3.5. HBHA Induces Trained Immunity in Human-Derived Innate Immune Cells
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO. Global Tuberculosis Report 2024. Available online: https://www.who.int/teams/global-tuberculosis-programme/tb-reports/global-tuberculosis-report-2024 (accessed on 29 October 2024).
- Lange, C.; Aaby, P.; Behr, M.A.; Donald, P.R.; Kaufmann, S.H.E.; Netea, M.G.; Mandalakas, A.M. 100 years of Mycobacterium bovis bacille Calmette-Guérin. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2022, 22, e2–e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasiliu, A.; Martinez, L.; Gupta, R.K.; Hamada, Y.; Ness, T.; Kay, A.; Bonnet, M.; Sester, M.; Kaufmann, S.H.E.; Lange, C.; et al. Tuberculosis prevention: Current strategies and future directions. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2024, 30, 1123–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Netea, M.G.; Domínguez-Andrés, J.; Barreiro, L.B.; Chavakis, T.; Divangahi, M.; Fuchs, E.; Joosten, L.A.B.; van der Meer, J.W.M.; Mhlanga, M.M.; Mulder, W.J.M.; et al. Defining trained immunity and its role in health and disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2020, 20, 375–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domínguez-Andrés, J.; Dos Santos, J.C.; Bekkering, S.; Mulder, W.J.M.; van der Meer, J.W.M.; Riksen, N.P.; Joosten, L.A.B.; Netea, M.G. Trained immunity: Adaptation within innate immune mechanisms. Physiol. Rev. 2023, 103, 313–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuscan, P.; Kischkel, B.; Joosten, L.A.B.; Netea, M.G. Trained immunity: General and emerging concepts. Immunol. Rev. 2024, 323, 164–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, K.A.; Pernet, E.; Sadeghi, M.; Downey, J.; Chronopoulos, J.; Lapshina, E.; Tsai, O.; Kaufmann, E.; Ding, J.; Divangahi, M. BCG immunization induces CX3CR1(hi) effector memory T cells to provide cross-protection via IFN-γ-mediated trained immunity. Nat. Immunol. 2024, 25, 418–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Gao, L.; Wu, X.; Fan, Y.; Liu, M.; Peng, L.; Song, J.; Li, B.; Liu, A.; Bao, F. BCG-induced trained immunity: History, mechanisms and potential applications. J. Transl. Med. 2023, 21, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, C.; Shrestha, R.; Zhu, X.; Geller, A.E.; Wu, S.; Woeste, M.R.; Li, W.; Wang, H.; Yuan, F.; Xu, R.; et al. Inducing trained immunity in pro-metastatic macrophages to control tumor metastasis. Nat. Immunol. 2023, 24, 239–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roquilly, A.; Villadangos, J.A. Intestinal microbe-derived metabolites instruct macrophages in the lungs. Nat. Immunol. 2022, 23, 1662–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Z.; Afkhami, S.; Bavananthasivam, J.; Fritz, D.K.; D’Agostino, M.R.; Vaseghi-Shanjani, M.; Yao, Y.; Jeyanathan, M. Innate immune memory of tissue-resident macrophages and trained innate immunity: Re-vamping vaccine concept and strategies. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2020, 108, 825–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, L.; Yu, Y.; Yao, Y. Influenza-trained mucosal-resident alveolar macrophages confer long-term antitumor immunity in the lungs. Nat. Immunol. 2023, 24, 423–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, A.; Ye, G.; Afkhami, S.; Aleithan, F.; Singh, K.; Dvorkin-Gheva, A.; Berg, T.; Miller, M.S.; Jeyanathan, M.; Xing, Z. LPS-induced lung tissue-resident trained innate immunity provides differential protection against pneumococci and SARS-CoV-2. Cell Rep. 2024, 43, 114849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, S.B.; Gern, B.H.; Delahaye, J.L.; Adams, K.N.; Plumlee, C.R.; Winkler, J.K.; Sherman, D.R.; Gerner, M.Y.; Urdahl, K.B. Alveolar Macrophages Provide an Early Mycobacterium tuberculosis Niche and Initiate Dissemination. Cell Host Microbe 2018, 24, 439–446.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Agostino, M.R.; Lai, R.; Afkhami, S.; Khera, A.; Yao, Y.; Vaseghi-Shanjani, M.; Zganiacz, A.; Jeyanathan, M.; Xing, Z. Airway Macrophages Mediate Mucosal Vaccine-Induced Trained Innate Immunity against Mycobacterium tuberculosis in Early Stages of Infection. J. Immunol. 2020, 205, 2750–2762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, Q.; Wang, L.; Liu, C.H.; Ge, B. New insights into the evasion of host innate immunity by Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Cell Mol. Immunol. 2020, 17, 901–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fatima, S.; Kumari, A.; Das, G.; Dwivedi, V.P. Tuberculosis vaccine: A journey from BCG to present. Life Sci. 2020, 252, 117594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Jeyanathan, M.; Haddadi, S.; Barra, N.G.; Vaseghi-Shanjani, M.; Damjanovic, D.; Lai, R.; Afkhami, S.; Chen, Y.; Dvorkin-Gheva, A.; et al. Induction of Autonomous Memory Alveolar Macrophages Requires T Cell Help and Is Critical to Trained Immunity. Cell 2018, 175, 1634–1650.e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vierboom, M.P.M.; Dijkman, K.; Sombroek, C.C.; Hofman, S.O.; Boot, C.; Vervenne, R.A.W.; Haanstra, K.G.; van der Sande, M.; van Emst, L.; Domínguez-Andrés, J.; et al. Stronger induction of trained immunity by mucosal BCG or MTBVAC vaccination compared to standard intradermal vaccination. Cell Rep. Med. 2021, 2, 100185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanfranconi, M.P.; Arabolaza, A.; Gramajo, H.; Alvarez, H.M. Insights into the evolutionary history of the virulent factor HBHA of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Arch. Microbiol. 2021, 203, 2171–2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbière, V.; Segers, J.; Desmet, R.; Lecher, S.; Loyens, M.; Petit, E.; Melnyk, O.; Locht, C.; Mascart, F. Natural T Cell Epitope Containing Methyl Lysines on Mycobacterial Heparin-Binding Hemagglutinin. J. Immunol. 2020, 204, 1715–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zulueta, M.M.L.; Chyan, C.L.; Hung, S.C. Structural analysis of synthetic heparan sulfate oligosaccharides with fibroblast growth factors and heparin-binding hemagglutinin. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2018, 50, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Q.; Li, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Li, Y.; Gong, M.; Sun, H.; Deng, X.; Ma, Y. Heparin-Binding Hemagglutinin of Mycobacterium tuberculosis Inhibits Autophagy via Toll-like Receptor 4 and Drives M2 Polarization in Macrophages. J. Infect. Dis. 2024, 230, 323–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temmerman, S.; Pethe, K.; Parra, M.; Alonso, S.; Rouanet, C.; Pickett, T.; Drowart, A.; Debrie, A.S.; Delogu, G.; Menozzi, F.D.; et al. Methylation-dependent T cell immunity to Mycobacterium tuberculosis heparin-binding hemagglutinin. Nat. Med. 2004, 10, 935–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parra, M.; Pickett, T.; Delogu, G.; Dheenadhayalan, V.; Debrie, A.S.; Locht, C.; Brennan, M.J. The mycobacterial heparin-binding hemagglutinin is a protective antigen in the mouse aerosol challenge model of tuberculosis. Infect. Immun. 2004, 72, 6799–6805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Locht, C.; Hougardy, J.M.; Rouanet, C.; Place, S.; Mascart, F. Heparin-binding hemagglutinin, from an extrapulmonary dissemination factor to a powerful diagnostic and protective antigen against tuberculosis. Tuberculosis 2006, 86, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.; Shao, J.; Ma, F.; Lei, C.; Chang, H.; Zhang, Y. Enhanced efficacy of a multi-epitope vaccine for type A and O foot-and-mouth disease virus by fusing multiple epitopes with Mycobacterium tuberculosis heparin-binding hemagglutinin (HBHA), a novel TLR4 agonist. Mol. Immunol. 2020, 121, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuscino, N.; Fatima, A.; Di Pilato, V.; Bulati, M.; Alfano, C.; Monaca, E.; Di Mento, G.; Di Carlo, D.; Cardinale, F.; Monaco, F.; et al. Computational design and characterization of a multiepitope vaccine against carbapenemase-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae strains, derived from antigens identified through reverse vaccinology. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2022, 20, 4446–4463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minute, L.; Bergón-Gutiérrez, M.; Mata-Martínez, P.; Fernández-Pascual, J.; Terrón, V.; Bravo-Robles, L.; Bıçakcıoğlu, G.; Zapata-Fernández, G.; Aguiló, N.; López-Collazo, E.; et al. Heat-killed Mycobacterium tuberculosis induces trained immunity in vitro and in vivo administered systemically or intranasally. iScience 2024, 27, 108869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arts, R.J.W.; Moorlag, S.; Novakovic, B.; Li, Y.; Wang, S.Y.; Oosting, M.; Kumar, V.; Xavier, R.J.; Wijmenga, C.; Joosten, L.A.B.; et al. BCG Vaccination Protects against Experimental Viral Infection in Humans through the Induction of Cytokines Associated with Trained Immunity. Cell Host Microbe 2018, 23, 89–100.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Spandidos, A.; Wang, H.; Seed, B. PrimerBank: A PCR primer database for quantitative gene expression analysis, 2012 update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, D1144–D1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taing, L.; Dandawate, A.; L’Yi, S.; Gehlenborg, N.; Brown, M.; Meyer, C.A. Cistrome Data Browser: Integrated search, analysis and visualization of chromatin data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024, 52, D61–D66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raney, B.J.; Barber, G.P.; Benet-Pagès, A.; Casper, J.; Clawson, H.; Cline, M.S.; Diekhans, M.; Fischer, C.; Navarro Gonzalez, J.; Hickey, G.; et al. The UCSC Genome Browser database: 2024 update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024, 52, D1082–D1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soldi, M.; Mari, T.; Nicosia, L.; Musiani, D.; Sigismondo, G.; Cuomo, A.; Pavesi, G.; Bonaldi, T. Chromatin proteomics reveals novel combinatorial histone modification signatures that mark distinct subpopulations of macrophage enhancers. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, 12195–12213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haim, Y.; Tarnovscki, T.; Bashari, D.; Rudich, A. A chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) protocol for use in whole human adipose tissue. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 305, E1172–E1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dos Santos, J.C.; Barroso de Figueiredo, A.M.; Teodoro Silva, M.V.; Cirovic, B.; de Bree, L.C.J.; Damen, M.; Moorlag, S.; Gomes, R.S.; Helsen, M.M.; Oosting, M.; et al. β-Glucan-Induced Trained Immunity Protects against Leishmania braziliensis Infection: A Crucial Role for IL-32. Cell Rep. 2019, 28, 2659–2672.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ochando, J.; Mulder, W.J.M.; Madsen, J.C.; Netea, M.G.; Duivenvoorden, R. Trained immunity—Basic concepts and contributions to immunopathology. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2023, 19, 23–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Divangahi, M.; Aaby, P.; Khader, S.A.; Barreiro, L.B.; Bekkering, S.; Chavakis, T.; van Crevel, R.; Curtis, N.; DiNardo, A.R.; Dominguez-Andres, J.; et al. Trained immunity, tolerance, priming and differentiation: Distinct immunological processes. Nat. Immunol. 2021, 22, 2–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, P.; Grigsby, S.J.; Philips, J.A. Immune evasion and provocation by Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2022, 20, 750–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Species | Primer Name | Forward Primer (5′ to 3′) | Reverse Primer (5′ to 3′) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mouse | IL-1β | GCAACTGTTCCTGAACTCAACT | ATCTTTTGGGGTCCGTCAACT |
| IL-6 | TAGTCCTTCCTACCCCAATTTCC | TTGGTCCTTAGCCACTCCTTC | |
| TNF-α | CCCTCACACTCAGATCATCTTCT | GCTACGACGTGGGCTACAG | |
| PFKM | TGTGGTCCGAGTTGGTATCTT | GCACTTCCAATCACTGTGCC | |
| PKM | GCCGCCTGGACATTGACTC | CCATGAGAGAAATTCAGCCGAG | |
| LDHA | TGTCTCCAGCAAAGACTACTGT | GACTGTACTTGACAATGTTGGGA | |
| Cs | GGACAATTTTCCAACCAATCTGC | TCGGTTCATTCCCTCTGCATA | |
| OGDH | GTTTCTTCAAACGTGGGGTTCT | GCATGATTCCAGGGGTCTCAAA | |
| IDH1 | ATGCAAGGAGATGAAATGACACG | GCATCACGATTCTCTATGCCTAA | |
| Human | IL-1β | ATGATGGCTTATTACAGTGGCAA | GTCGGAGATTCGTAGCTGGA |
| IL-6 | ACTCACCTCTTCAGAACGAATTG | CCATCTTTGGAAGGTTCAGGTTG | |
| TNF | GAGGCCAAGCCCTGGTATG | CGGGCCGATTGATCTCAGC |
| Antibodies | Target Gene | Forward Primer (5′ to 3′) | Reverse Primer (5′ to 3′) |
|---|---|---|---|
| H3K4me1 | IL-1β | ATGAAACCTGTGTGGGAGCC | GCCTTGCTCCCAGGCTATTT |
| IL-6 | AAGGGCTTCTGGCTACCATTAG | TTGCATCTGGCTTTGTTCGC | |
| TNF-α | TGCTTGATCTCCCGTTATCTCC | TGTTCACACGTGGAGAGATCTG | |
| H3K4me3 | IL-1β | CAACATGGGGAACAGCATTAGG | AGCTCCTGTCTTGTAGGAAAGC |
| IL-6 | GGGCGTCCATTCATTCTCTTTG | CCACTCAAAACCAGCAAAGAGG | |
| TNF-α | CCTCATGTCTCTTTGCTCTGC | TTGTGTCTGTCTTGCGTTGG |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Y.; Jia, X.; Tang, J.; Qiao, H.; Zhou, J.; Ma, Y. Heparin-Binding Hemagglutinin-Induced Trained Immunity in Macrophages: Implications for Antimycobacterial Defense. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 959. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15070959
Li Y, Jia X, Tang J, Qiao H, Zhou J, Ma Y. Heparin-Binding Hemagglutinin-Induced Trained Immunity in Macrophages: Implications for Antimycobacterial Defense. Biomolecules. 2025; 15(7):959. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15070959
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Yongqiang, Xiuping Jia, Jinhua Tang, Huilian Qiao, Jiani Zhou, and Yueyun Ma. 2025. "Heparin-Binding Hemagglutinin-Induced Trained Immunity in Macrophages: Implications for Antimycobacterial Defense" Biomolecules 15, no. 7: 959. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15070959
APA StyleLi, Y., Jia, X., Tang, J., Qiao, H., Zhou, J., & Ma, Y. (2025). Heparin-Binding Hemagglutinin-Induced Trained Immunity in Macrophages: Implications for Antimycobacterial Defense. Biomolecules, 15(7), 959. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15070959







