Administration of Purified Alpha-1 Antitrypsin in Salt-Loaded Hypertensive 129Sv Mice Attenuates the Expression of Inflammatory Associated Proteins in the Kidney
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals and Treatments
2.2. Blood Pressure Measurements
2.3. Urinary Creatine Measurements
2.4. SDS-PAGE, Western Blotting, and Densitometric Analysis
2.5. Immunofluorescence
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. hAAT Reduces Systolic Blood Pressure in Salt-Loaded Hypertensive 129Sv Mice
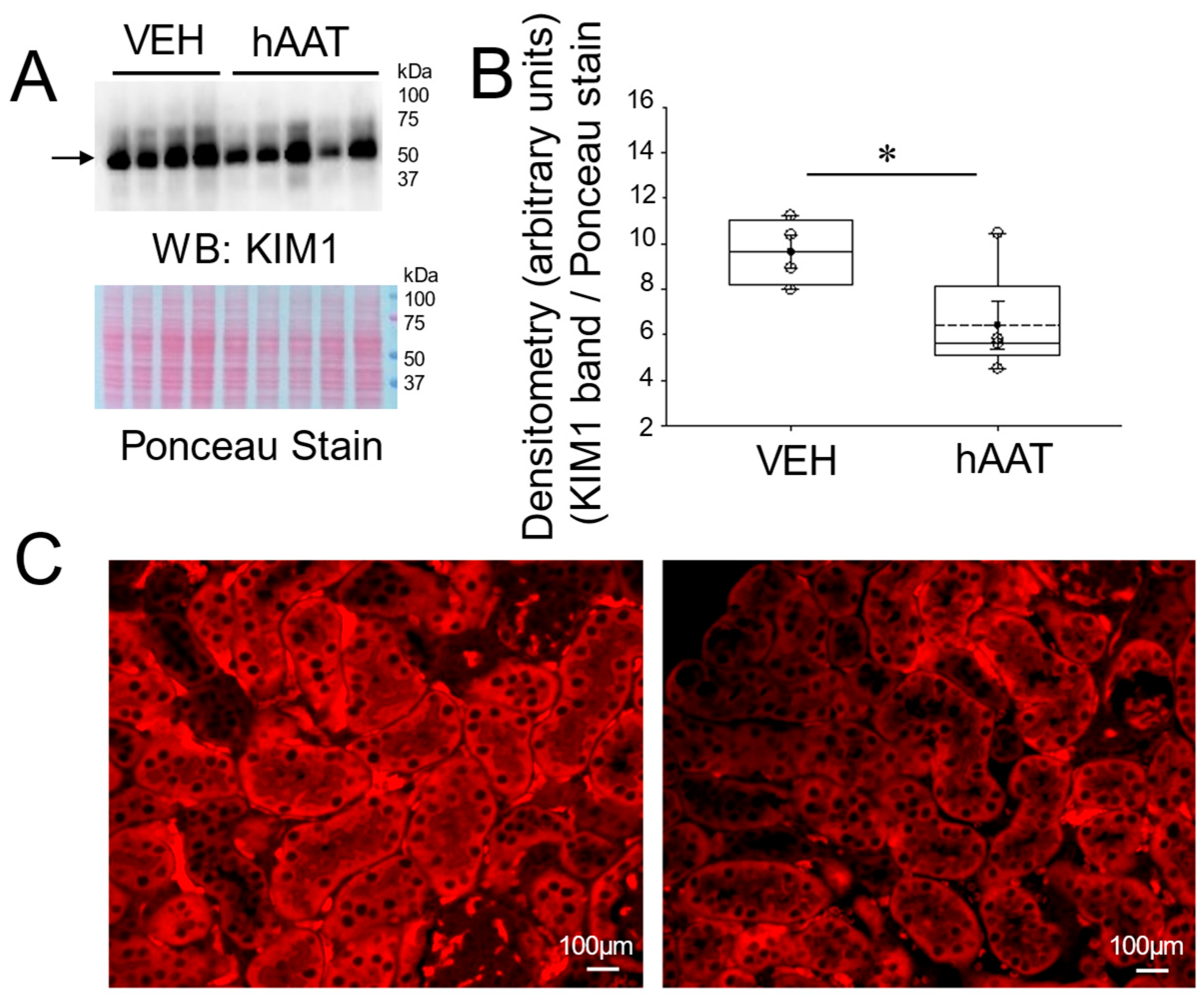
3.2. hAAT Attenuates Renal KIM1 Protein Expression in the Kidney of Salt-Loaded 129Sv Mice
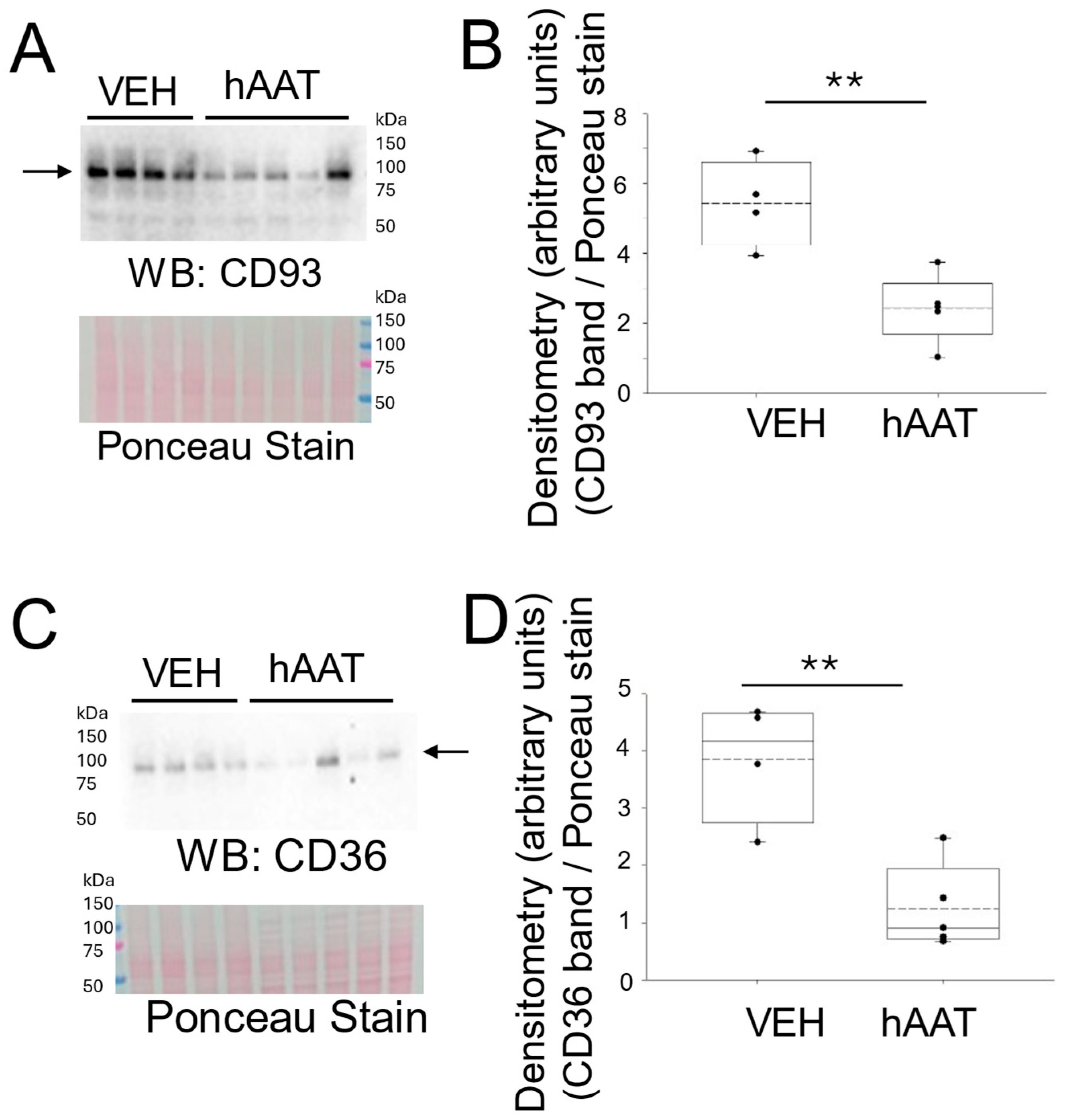
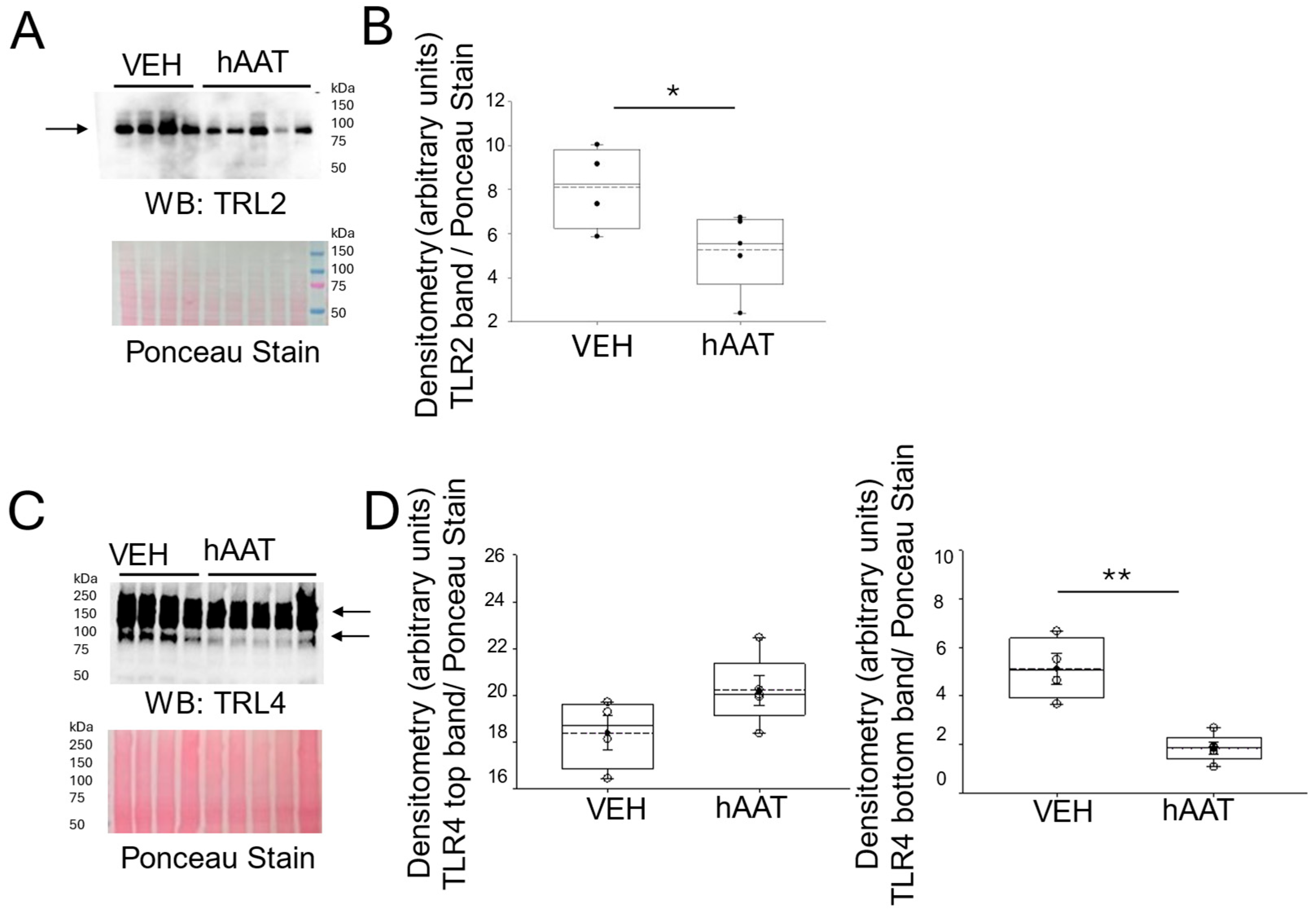
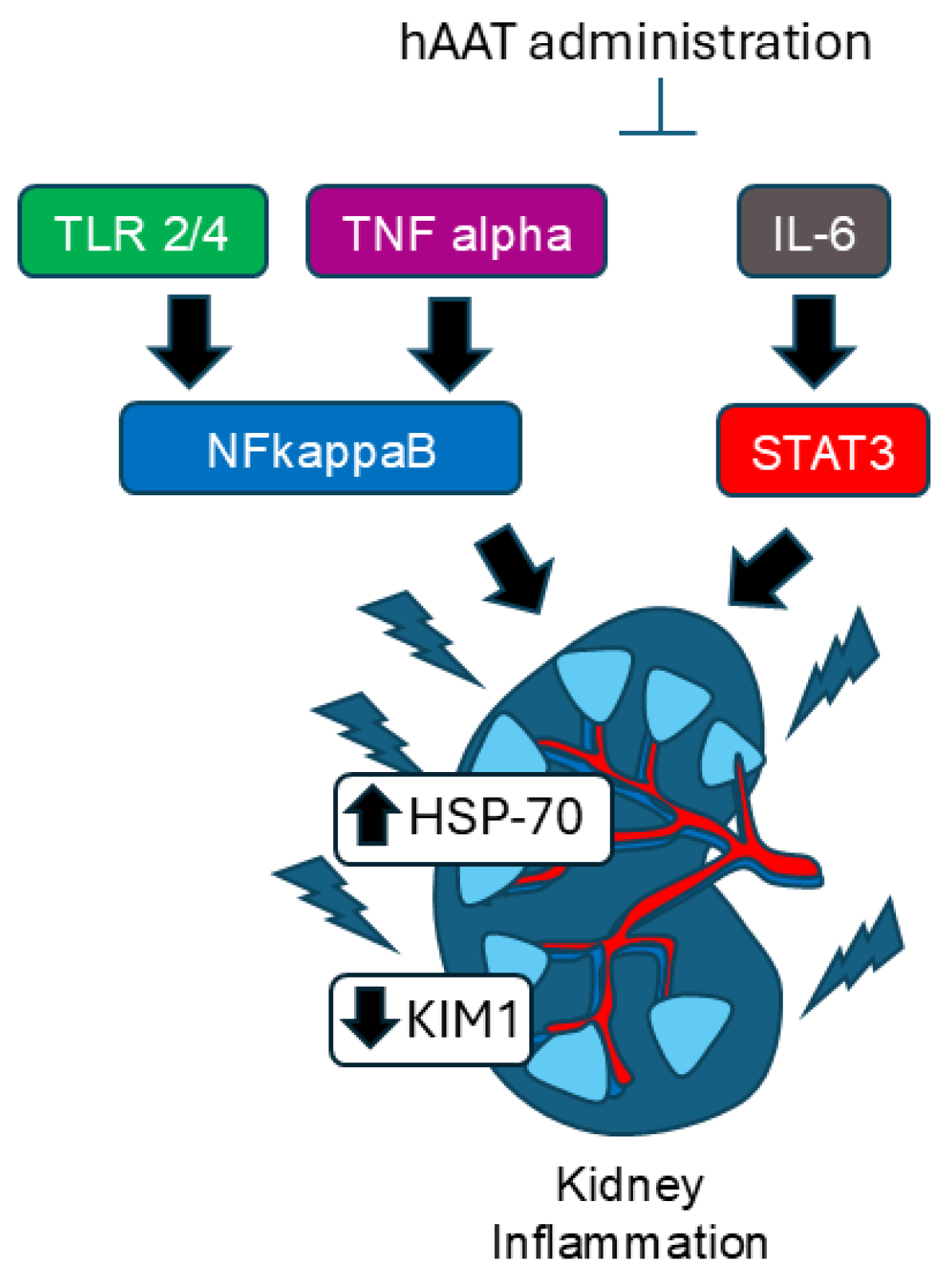
3.3. hAAT Attenuates Expression of Inflammatory Signaling Proteins in the Kidney of Salt-Loaded 129Sv Mice
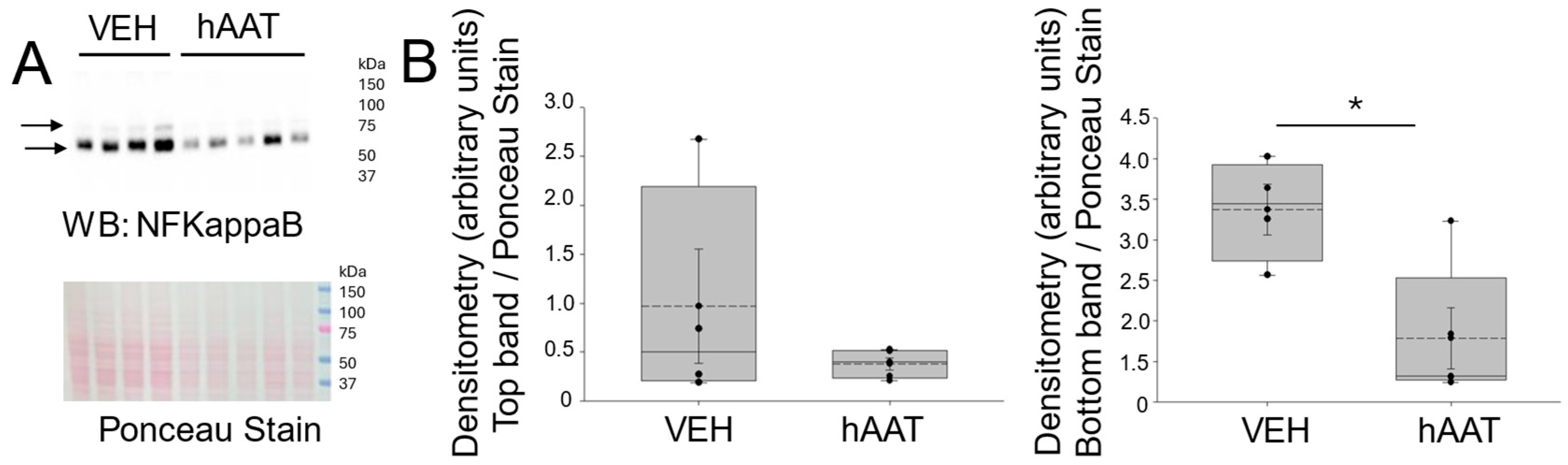
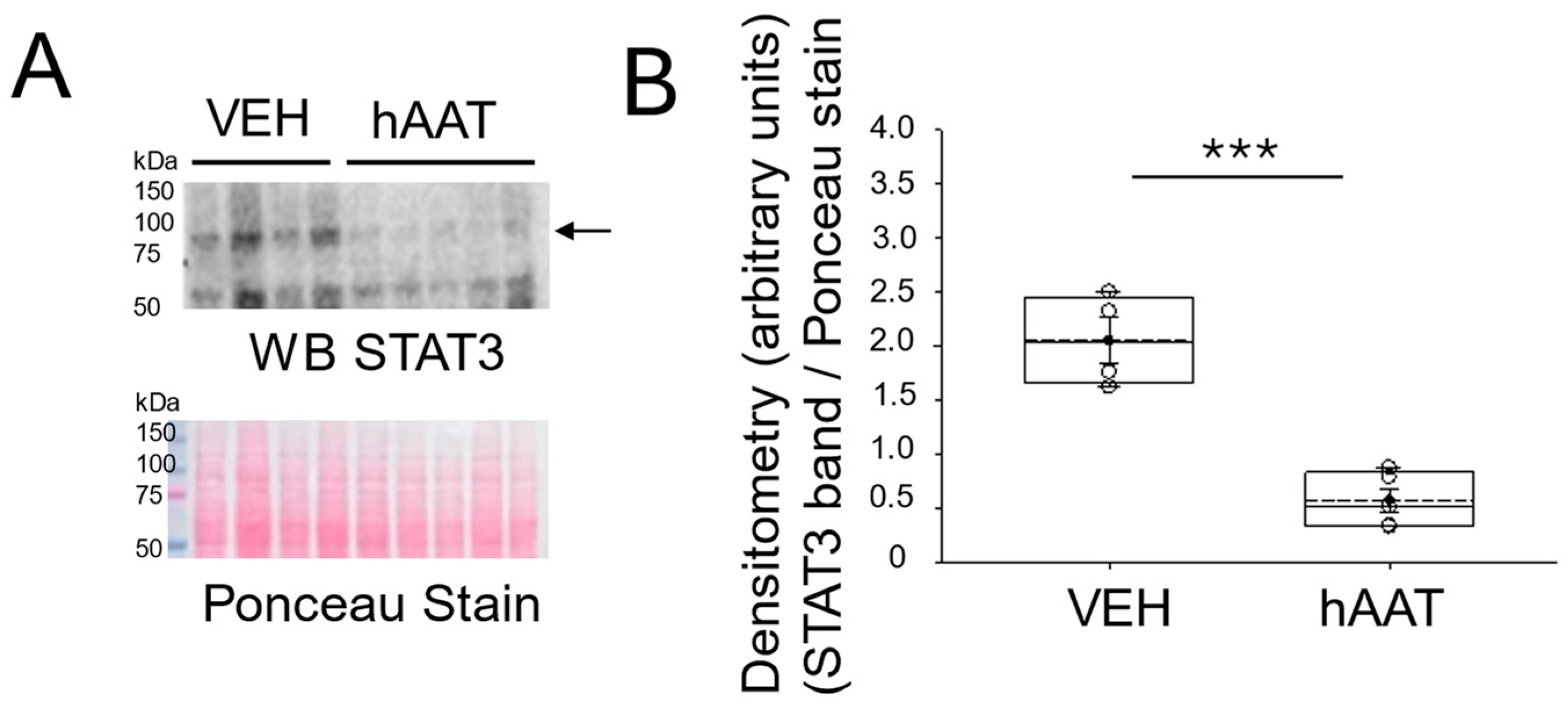
3.4. hAAT Administration Decreases the Level of NF-Kappab and STAT3 Protein Expression in the Kidney Cortex of Salt-Loaded 129Sv Mice
3.5. Purified hAAT Reduces TLR2/4 Expression in the Kidney of Salt-Loaded 129Sv Mice
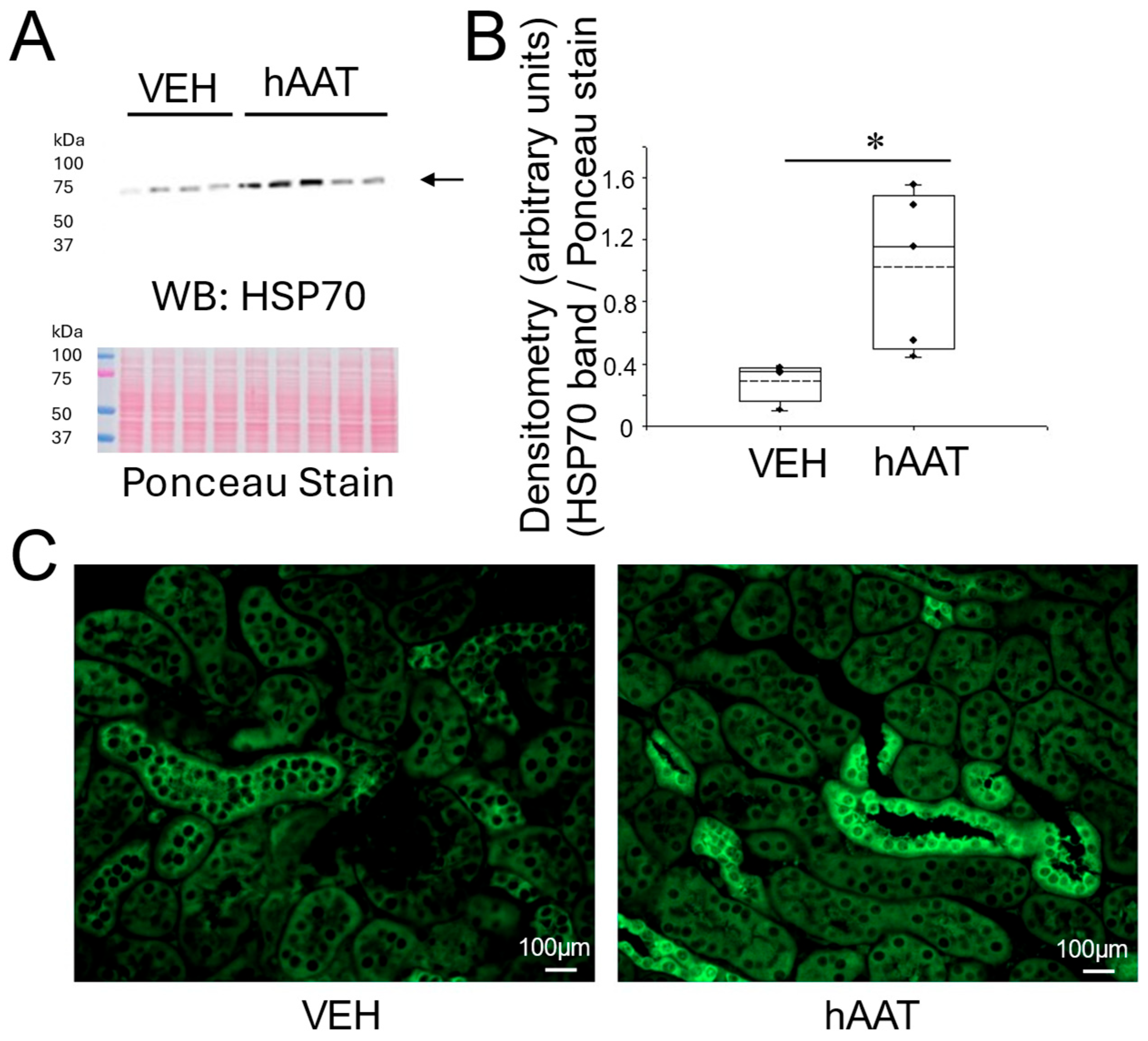
3.6. Purified hAAT Augments HSP-70 Protein Expression in the Kidney of Salt-Loaded 129Sv Mice
3.7. Administration of hAAT Augments the IGF-1 Protein Expression in the Kidney of 129Sv Mice
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AAT | alpha-1 antitrypsin |
| TLR | toll-like receptor |
| HSP | heat shock proteins |
| IL-6 | interleukin-6 |
| MDPI | multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute |
| TNF-α | tumor necrosis factor-alpha |
| CD | cluster of differentiation |
| KIM-1 | kidney injury molecule |
| STAT3 | signal transducer and activator of transcript 3 |
References
- Mishra, S.R.; Satheesh, G.; Khanal, V.; Nguyen, T.N.; Picone, D.; Chapman, N.; Lindley, R.I. Closing the Gap in Global Disparities in Hypertension Control. Hypertension 2025, 82, 407–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grillo, A.; Salvi, L.; Coruzzi, P.; Salvi, P.; Parati, G. Sodium Intake and Hypertension. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skov, K.; Mulvany, M.J.; Korsgaard, N. Morphology of renal afferent arterioles in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Hypertension 1992, 20, 821–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gigante, A.; Perrotta, A.M.; De Marco, O.; Rosato, E.; Lai, S.; Cianci, R. Sonographic evaluation of hypertension: Role of atrophic index and renal resistive index. J. Clin. Hypertens. 2022, 24, 955–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, W.P.; Kett, M.M.; Evans, R.G.; Alcorn, D. Pre-glomerular structural changes in the renal vasculature in hypertension. Blood Press. Suppl. 1995, 2, 74–80. [Google Scholar]
- Harris, R.C.; Neilson, E.G. Toward a unified theory of renal progression. Annu. Rev. Med. 2006, 57, 365–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banek, C.T.; Gauthier, M.M.; Van Helden, D.A.; Fink, G.D.; Osborn, J.W. Renal Inflammation in DOCA-Salt Hypertension. Hypertension 2019, 73, 1079–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Kirabo, A.; Wu, J.; Saleh, M.A.; Zhu, L.; Wang, F.; Takahashi, T.; Loperena, R.; Foss, J.D.; Mernaugh, R.L.; et al. Renal Denervation Prevents Immune Cell Activation and Renal Inflammation in Angiotensin II-Induced Hypertension. Circ. Res. 2015, 117, 547–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.; Crowley, S.D. Renal effects of cytokines in hypertension. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 2018, 27, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, W.K.; Bailly, V.; Abichandani, R.; Thadhani, R.; Bonventre, J.V. Kidney Injury Molecule-1 (KIM-1): A novel biomarker for human renal proximal tubule injury. Kidney Int. 2002, 62, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, A.I.; Tang, S.C.; Lai, K.N.; Leung, J.C. Kidney injury molecule-1: More than just an injury marker of tubular epithelial cells? J. Cell Physiol. 2013, 228, 917–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jonigk, D.; Al-Omari, M.; Maegel, L.; Muller, M.; Izykowski, N.; Hong, J.; Hong, K.; Kim, S.H.; Dorsch, M.; Mahadeva, R.; et al. Anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory properties of alpha1-antitrypsin without inhibition of elastase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 15007–15012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okamura, D.M.; Pennathur, S.; Pasichnyk, K.; Lopez-Guisa, J.M.; Collins, S.; Febbraio, M.; Heinecke, J.; Eddy, A.A. CD36 regulates oxidative stress and inflammation in hypercholesterolemic CKD. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2009, 20, 495–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, X.; Xia, M.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, T.; Zhang, Y.; Qian, Z.; Bao, J.; Li, H. Deficiency of CD93 exacerbates inflammation-induced activation and migration of BV2 microglia by regulating the TAK1/NF-κB pathway. Neurosci. Lett. 2022, 791, 136914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.; Huang, L.; Luo, W.; Yu, W.; Hu, X.; Guan, X.; Cai, Y.; Zou, C.; Yin, H.; Xu, Z.; et al. Inhibition of STAT3 in tubular epithelial cells prevents kidney fibrosis and nephropathy in STZ-induced diabetic mice. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.P.; Gholam, M.F.; Elshikha, A.S.; Kawakibi, T.; Elmoujahid, N.; Moussa, H.H.; Song, S.; Alli, A.A. Transgenic Mice Overexpressing Human Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Exhibit Low Blood Pressure and Altered Epithelial Transport Mechanisms in the Inactive and Active Cycles. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 710313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lugo, C.I.; Liu, L.P.; Bala, N.; Morales, A.G.; Gholam, M.F.; Abchee, J.C.; Elmoujahid, N.; Elshikha, A.S.; Avdiaj, R.; Searcy, L.A.; et al. Human Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Attenuates ENaC and MARCKS and Lowers Blood Pressure in Hypertensive Diabetic db/db Mice. Biomolecules 2022, 13, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohnlein, T.; Welte, T. Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency: Pathogenesis, clinical presentation, diagnosis, and treatment. Am. J. Med. 2008, 121, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.H.; Oh, E.J.; Oh, S.H.; Jung, H.Y.; Choi, J.Y.; Cho, J.H.; Park, S.H.; Kim, Y.L.; Kim, C.D. Renoprotective Effects of Alpha-1 Antitrypsin against Tacrolimus-Induced Renal Injury. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zager, R.A.; Johnson, A.C.; Frostad, K.B. Rapid renal alpha-1 antitrypsin gene induction in experimental and clinical acute kidney injury. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e98380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacquier-Sarlin, M.R.; Fuller, K.; Dinh-Xuan, A.T.; Richard, M.J.; Polla, B.S. Protective effects of hsp70 in inflammation. Experientia 1994, 50, 1031–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manucha, W. HSP70 Family in the Renal Inflammatory Response. Inflamm. Allergy Drug Targets 2014, 13, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.G.; Cho, E.J.; Lee, J.W.; Ko, Y.S.; Lee, H.L.; Jo, S.K.; Cho, W.Y.; Kim, H.K. The heat-shock protein-70-induced renoprotective effect is partially mediated by CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ regulatory T cells in ischemia/reperfusion-induced acute kidney injury. Kidney Int. 2014, 85, 62–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruchalski, K.; Mao, H.; Li, Z.; Wang, Z.; Gillers, S.; Wang, Y.; Mosser, D.D.; Gabai, V.; Schwartz, J.H.; Borkan, S.C. Distinct hsp70 domains mediate apoptosis-inducing factor release and nuclear accumulation. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 7873–7880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Zhang, Y.; Pei, Q.; Zheng, L.; Wang, M.; Shi, Y.; Wu, S.; Ni, W.; Fu, X.; Peng, Y.; et al. HSP70 alleviates sepsis-induced cardiomyopathy by attenuating mitochondrial dysfunction-initiated NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated pyroptosis in cardiomyocytes. Burns Trauma 2022, 10, tkac043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ran, R.; Lu, A.; Zhang, L.; Tang, Y.; Zhu, H.; Xu, H.; Feng, Y.; Han, C.; Zhou, G.; Rigby, A.C.; et al. Hsp70 promotes TNF-mediated apoptosis by binding IKK gamma and impairing NF-kappa B survival signaling. Genes. Dev. 2004, 18, 1466–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, C.A.; Rasband, W.S.; Eliceiri, K.W. NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Yu, J.; Prayogo, G.W.; Cao, W.; Wu, Y.; Jia, Z.; Zhang, A. Understanding kidney injury molecule 1: A novel immune factor in kidney pathophysiology. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2019, 11, 1219–1229. [Google Scholar]
- Dogan, Y.E.; Bala, N.; Galban, E.S.; Lewis, R.L.; Denslow, N.D.; Song, S.; Alli, A.A. Alpha 1-antitrypsin mitigates salt-sensitive hypertension in juvenile mice by reducing diacylglycerol concentrations and protein kinase C activity in kidney membranes. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2024, 11, 1485506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenlee, M.C.; Sullivan, S.A.; Bohlson, S.S. Detection and characterization of soluble CD93 released during inflammation. Inflamm. Res. 2009, 58, 909–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.J.; Han, H.; Lee, S.C.; Son, Y.W.; Sim, D.W.; Park, K.H.; Park, Y.H.; Jeong, K.Y.; Park, J.W.; Lee, J.H. Soluble CD93 in Serum as a Marker of Allergic Inflammation. Yonsei Med. J. 2017, 58, 598–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sigari, N.; Jalili, A.; Mahdawi, L.; Ghaderi, E.; Shilan, M. Soluble CD93 as a Novel Biomarker in Asthma Exacerbation. Allergy Asthma Immunol. Res. 2016, 8, 461–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Zhang, C.; Luo, X.; Wang, P.; Zhou, W.; Zhong, S.; Xie, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Yang, P.; Tang, R.; et al. CD36 palmitoylation disrupts free fatty acid metabolism and promotes tissue inflammation in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. J. Hepatol. 2018, 69, 705–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasimsetty, S.G.; Hawkes, A.; Barekatain, K.; Soo, E.; Welch, A.K.; McKay, D.B. TLR2 and NODs1 and 2 cooperate in inflammatory responses associated with renal ischemia reperfusion injury. Transpl. Immunol. 2020, 58, 101260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruemmer-Smith, S.; Stuber, F.; Schroeder, S. Protective functions of intracellular heat-shock protein (HSP) 70-expression in patients with severe sepsis. Intensive Care Med. 2001, 27, 1835–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, L.; Mann, D.; Imig, J.D.; Emmett, N.; Gibbons, G.; Jin, L.M. Glomerular expression of kidney injury molecule-1 and podocytopenia in diabetic glomerulopathy. Am. J. Nephrol. 2011, 34, 268–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maicas, N.; van der Vlag, J.; Bublitz, J.; Florquin, S.; Bakker-van Bebber, M.; Dinarello, C.A.; Verweij, V.; Masereeuw, R.; Joosten, L.A.; Hilbrands, L.B. Human Alpha-1-Antitrypsin (hAAT) therapy reduces renal dysfunction and acute tubular necrosis in a murine model of bilateral kidney ischemia-reperfusion injury. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0168981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadioglu, T.; Uzunlulu, M.; Kaya, S.Y.; Oguz, A.; Ggonenli, G.; Isbilen, B.; Isman, F. Urinary kidney injury molecule-1 levels as a marker of early kidney injury in hypertensive patients. Minerva Urol. Nefrol. 2016, 68, 456–461. [Google Scholar]
- Elshikha, A.S.; Abboud, G.; Avdiaj, R.; Morel, L.; Song, S. The Inhibitory Effects of Alpha 1 Antitrypsin on Endosomal TLR Signaling Pathways. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Mao, R.; Yang, J. NF-κB and STAT3 signaling pathways collaboratively link inflammation to cancer. Protein Cell 2013, 4, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, G.; Karin, M. NF-κB and STAT3-key players in liver inflammation and cancer. Cell Res. 2011, 21, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.M.; Mao, J.W.; Zhu, J.Z.; Xie, C.C.; Yao, J.Y.; Yang, X.Q.; Xiang, M.; He, Y.F.; Tong, X.; Litifu, D.; et al. DZ2002 alleviates corneal angiogenesis and inflammation in rodent models of dry eye disease via regulating STAT3-PI3K-Akt-NF-κB pathway. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2024, 45, 166–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Wang, F.; Han, Y.; Zhai, J.; Jin, Y.; Liu, R.; Niu, Y.; Yao, Z.; Zhao, J. Nitazoxanide reduces inflammation and bone erosion in mice with collagen-induced arthritis via inhibiting the JAK2/STAT3 and NF-κB pathways in fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2024, 171, 116195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Xue, P.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Han, X.; Xing, J. Esmolol upregulates the α7 nAChR/STAT3/NF-κB pathway by decreasing the ubiquitin and increasing the ChAT+CD4+ T lymphocyte to alleviate inflammation in septic cardiomyopathy. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2025, 148, 114043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, H.; Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Liu, B.; Yuan, Y.; Zuo, X. Curcumin attenuates inflammation and cell apoptosis through regulating NF-κB and JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway against acute kidney injury. Cell Cycle 2020, 19, 1941–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Van Belkum, M.; O’Brien, A.; Garcia, A.; Troncoso, K.; Elshikha, A.S.; Zhou, L.; Song, S. Human Alpha 1 Antitrypsin Suppresses NF-κB Activity and Extends Lifespan in Adult Drosophila. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Okamura, D.M.; Lu, X.; Chen, Y.; Moorhead, J.; Varghese, Z.; Ruan, X.Z. CD36 in chronic kidney disease: Novel insights and therapeutic opportunities. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2017, 13, 769–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanke, F.; Janciauskiene, S.; Tamm, S.; Wrenger, S.; Raddatz, E.L.; Jonigk, D.; Braubach, P. Effect of Alpha-1 Antitrypsin on CFTR Levels in Primary Human Airway Epithelial Cells Grown at the Air-Liquid-Interface. Molecules 2021, 26, 2639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Yuan, H.; Cao, W.; Wang, T.; Chen, W.; Yu, H.; Fu, Y.; Jiang, B.; Zhou, H.; Guo, H.; et al. Blocking interleukin-6 trans-signaling protects against renal fibrosis by suppressing STAT3 activation. Theranostics 2019, 9, 3980–3991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; DiCiaccio, B.; Li, Y.; Elshikha, A.S.; Titov, D.; Brenner, B.; Seifer, L.; Pan, H.; Karic, N.; Akbar, M.A.; et al. Anti-inflammaging effects of human alpha-1 antitrypsin. Aging Cell 2018, 17, e12694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costantino, V.V.; Gil Lorenzo, A.F.; Bocanegra, V.; Valles, P.G. Molecular Mechanisms of Hypertensive Nephropathy: Renoprotective Effect of Losartan through Hsp70. Cells 2021, 10, 3146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrizo, L.C.; Ruete, C.M.; Manucha, W.A.; Ciocca, D.R.; Valles, P.G. Heat shock protein 70 expression is associated with inhibition of renal tubule epithelial cell apoptosis during recovery from low-protein feeding. Cell Stress. Chaperones 2006, 11, 309–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Gall, J.M.; Bonegio, R.G.; Havasi, A.; Hunt, C.R.; Sherman, M.Y.; Schwartz, J.H.; Borkan, S.C. Induction of heat shock protein 70 inhibits ischemic renal injury. Kidney Int. 2011, 79, 861–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, X.M.; Liu, Y.; Hailaiti, D.; Gong, Y.; Zhang, X.D.; Yue, B.N.; Liu, J.P.; Wu, X.L.; Yang, K.Z.; Wang, J.; et al. Mechanisms of inflammation modulation by different immune cells in hypertensive nephropathy. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1333170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Wang, Q.; Han, B.; Chen, Y.; Qiao, X.; Wang, L. CD36 promotes NLRP3 inflammasome activation via the mtROS pathway in renal tubular epithelial cells of diabetic kidneys. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Antibody | Company | Catalog Number |
|---|---|---|
| HSP70 | Cell Signaling Tech (Danvers, MA, USA) | 4872P |
| STAT3 | Abcam (Waltham, MA, USA) | ab76315 |
| TIM1/KIM1 | Novus Biologicals (Centennial, CO, USA) | NBP1-76701 |
| CD93 | Santa Cruz Biotech (Dallas, TX, USA) | SC-365172 |
| CD36 | Santa Cruz Biotech | SC-7309 |
| TLR2 | Santa Cruz Biotech | SC-166900 |
| NF-KappaB p65 | Protein Tech (Rosemont, IL, USA) | 80979-1-RR |
| Physiological Parameter | hAAT Administration | VEH Administration | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Systolic blood pressure (mmHg) | 118.9 +/− 1.24 | 149.12 +/− 7.76 | 0.003 |
| Urine creatinine (mg/dL) | 7.47 +/− 1.05 | 6.01 +/− 1.94 | 0.506 |
| Urinary sodium excretion (mEq/24-h) | 1.14 +/− 0.34 | 0.45 +/− 0.042 | 0.124 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nguyen, V.-A.L.; Dogan, Y.E.; Bala, N.; Galban, E.S.; Song, S.; Alli, A.A. Administration of Purified Alpha-1 Antitrypsin in Salt-Loaded Hypertensive 129Sv Mice Attenuates the Expression of Inflammatory Associated Proteins in the Kidney. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 951. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15070951
Nguyen V-AL, Dogan YE, Bala N, Galban ES, Song S, Alli AA. Administration of Purified Alpha-1 Antitrypsin in Salt-Loaded Hypertensive 129Sv Mice Attenuates the Expression of Inflammatory Associated Proteins in the Kidney. Biomolecules. 2025; 15(7):951. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15070951
Chicago/Turabian StyleNguyen, Van-Anh L., Yunus E. Dogan, Niharika Bala, Erika S. Galban, Sihong Song, and Abdel A. Alli. 2025. "Administration of Purified Alpha-1 Antitrypsin in Salt-Loaded Hypertensive 129Sv Mice Attenuates the Expression of Inflammatory Associated Proteins in the Kidney" Biomolecules 15, no. 7: 951. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15070951
APA StyleNguyen, V.-A. L., Dogan, Y. E., Bala, N., Galban, E. S., Song, S., & Alli, A. A. (2025). Administration of Purified Alpha-1 Antitrypsin in Salt-Loaded Hypertensive 129Sv Mice Attenuates the Expression of Inflammatory Associated Proteins in the Kidney. Biomolecules, 15(7), 951. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15070951





