Recent Advances in Combination Therapy of YAP Inhibitors with Physical Anti-Cancer Strategies
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Discussion
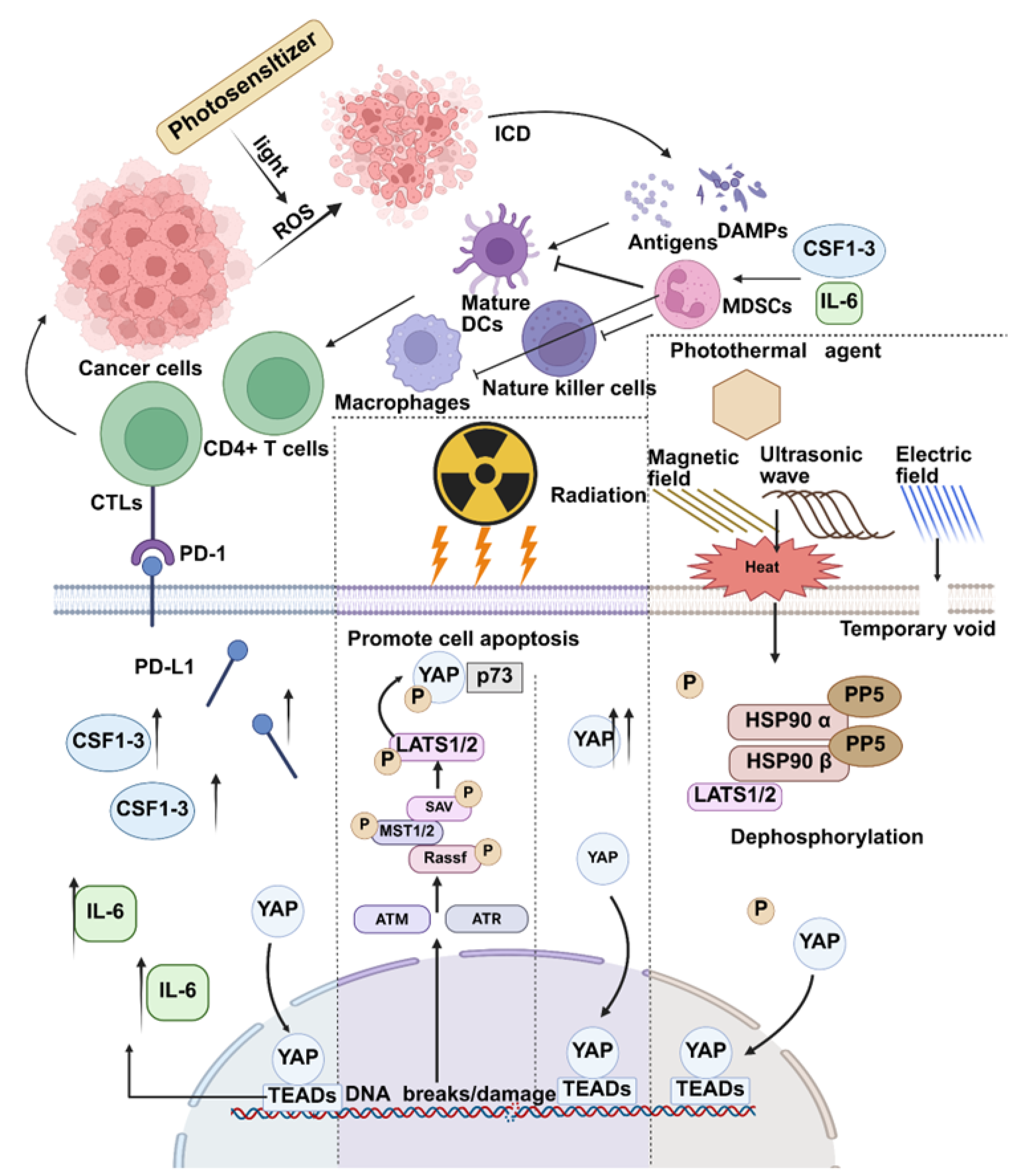
2.1. YAP and Photodynamic Therapy
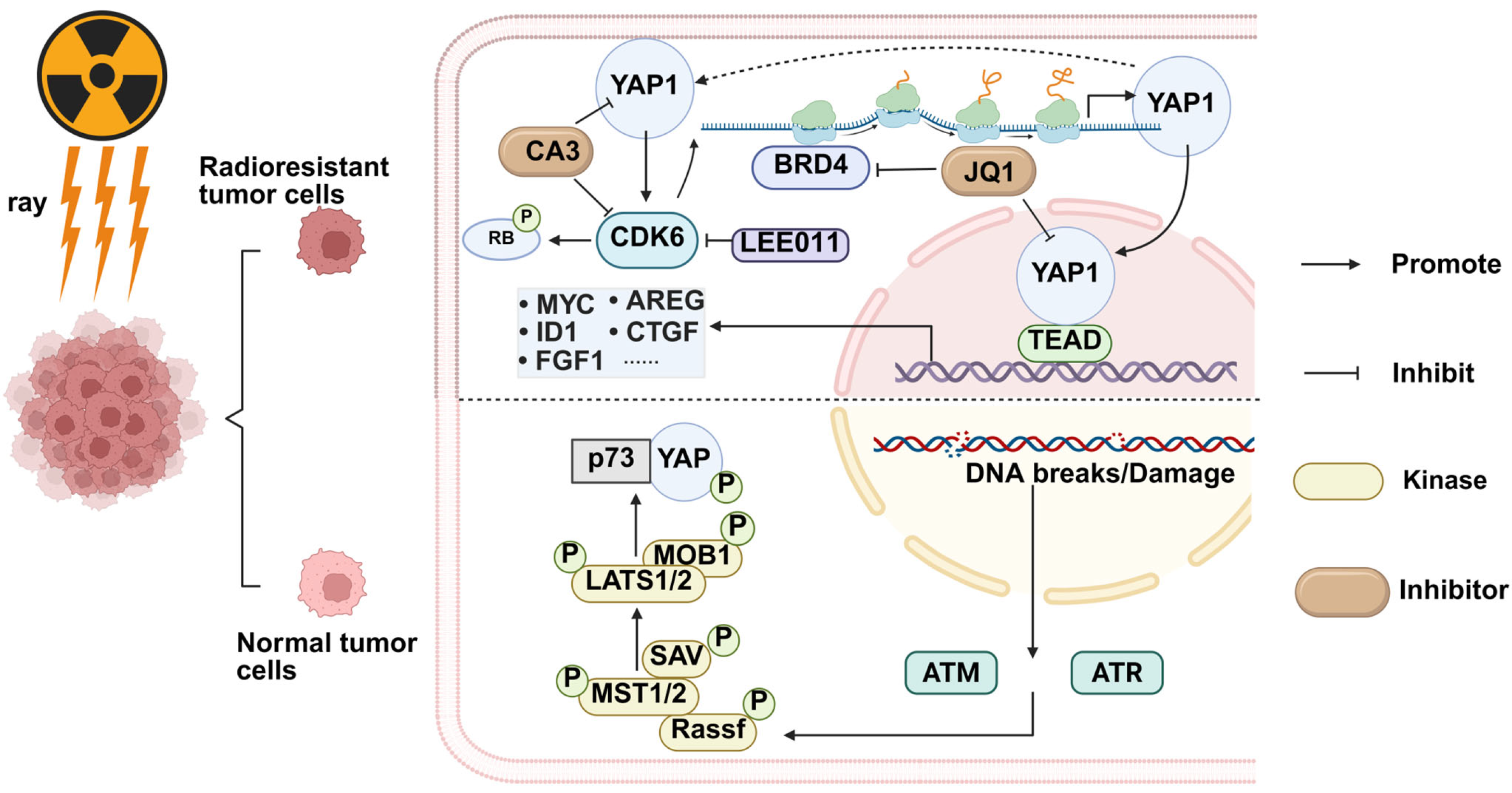
2.2. YAP and Radiation Therapy
2.3. YAP and Another Therapeutic Method: Hyperthermia and Electrochemotherapy
3. Summary and Outlook
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yu, X.T.; Sui, S.Y.; He, Y.X.; Yu, C.H.; Peng, Q. Nanomaterials-based photosensitizers and delivery systems for photodynamic cancer therapy. Biomater. Adv. 2022, 135, 212725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzeibak, R.; Mishchenko, T.A.; Shilyagina, N.Y.; Balalaeva, I.V.; Vedunova, M.V.; Krysko, D.V. Targeting immunogenic cancer cell death by photodynamic therapy: Past, present and future. J. Immunother. Cancer 2021, 9, e001926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boeer, B.; Oberlechner, E.; Rottscholl, R.; Gruber, I.; Guergan, S.; Brucker, S.; Hahn, M. Five-year follow-up after a single US-guided high intensity focused ultrasound treatment of breast fibroadenoma. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 18370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Wang, H.; Shi, J.; Chen, Z.; Wang, Y.; Gu, S.; Fu, Y.; Huang, J.; Ding, J.; Yu, L. An injectable and active hydrogel induces mutually enhanced mild magnetic hyperthermia and ferroptosis. Biomaterials 2023, 298, 122139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minnaar, C.A.; Kotzen, J.A.; Naidoo, T.; Tunmer, M.; Sharma, V.; Vangu, M.D.; Baeyens, A. Analysis of the effects of mEHT on the treatment-related toxicity and quality of life of HIV-positive cervical cancer patients. Int. J. Hyperth. 2020, 37, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peek, M.C.; Ahmed, M.; Scudder, J.; Baker, R.; Pinder, S.E.; Douek, M. High intensity focused ultrasound in the treatment of breast fibroadenomata: Results of the HIFU-F trial. Int. J. Hyperth. 2016, 32, 881–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahadoer, R.R.; Dijkstra, E.A.; van Etten, B.; Marijnen, C.A.M.; Putter, H.; Kranenbarg, E.M.; Roodvoets, A.G.H.; Nagtegaal, I.D.; Beets-Tan, R.G.H.; Blomqvist, L.K.; et al. Short-course radiotherapy followed by chemotherapy before total mesorectal excision (TME) versus preoperative chemoradiotherapy, TME, and optional adjuvant chemotherapy in locally advanced rectal cancer (RAPIDO): A randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2021, 22, 29–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Lovell, J.F.; Yoon, J.; Chen, X. Clinical development and potential of photothermal and photodynamic therapies for cancer. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 17, 657–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, J.A.; Correia, J.H. Photodynamic Therapy for Colorectal Cancer: An Update and a Look to the Future. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 12204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, B.; Wei, M.; Yang, B. Recent advances in nanomedicines for photodynamic therapy (PDT)-driven cancer immunotherapy. Theranostics 2022, 12, 434–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Yang, J.; Luo, L.; Jiang, M.; Qin, B.; Yin, H.; Zhu, C.; Yuan, X.; Zhang, J.; Luo, Z.; et al. Targeting photodynamic and photothermal therapy to the endoplasmic reticulum enhances immunogenic cancer cell death. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frey, B.; Weiss, E.M.; Rubner, Y.; Wunderlich, R.; Ott, O.J.; Sauer, R.; Fietkau, R.; Gaipl, U.S. Old and new facts about hyperthermia-induced modulations of the immune system. Int. J. Hyperth. 2012, 28, 528–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, P.C.; Miao, J.; Wang, Y.C.; Zhang, W.Q.; Yang, Y.L.; Wang, C.W.; Yang, C.T.; Huang, Z.; You, J.; Xu, Z.; et al. Inhibition of yes-associated protein down-regulates PD-L1 (CD274) expression in human malignant pleural mesothelioma. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2018, 22, 3139–3148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Yan, Z.; Hou, J.; Zhang, L.; Chen, Z.; Gao, C.; Ahmad, N.H.; Guo, M.; Wang, W.; Han, T.; et al. The Hippo-YAP signaling pathway drives CD24-mediated immune evasion in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma via macrophage phagocytosis. Oncogene 2024, 43, 495–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Lu, X.; Dey, P.; Deng, P.; Wu, C.C.; Jiang, S.; Fang, Z.; Zhao, K.; Konaparthi, R.; Hua, S.; et al. Targeting YAP-Dependent MDSC Infiltration Impairs Tumor Progression. Cancer Discov. 2016, 6, 80–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Wu, X.; Berry, K.; Zhao, C.; Xin, D.; Ogurek, S.; Liu, X.; Zhang, L.; Luo, Z.; Sakabe, M.; et al. Nuclear condensates of YAP fusion proteins alter transcription to drive ependymoma tumourigenesis. Nat. Cell Biol. 2023, 25, 323–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, D.; Feliciano, D.; Dong, P.; Flores, E.; Gruebele, M.; Porat-Shliom, N.; Sukenik, S.; Liu, Z.; Lippincott-Schwartz, J. Phase separation of YAP reorganizes genome topology for long-term YAP target gene expression. Nat. Cell Biol. 2019, 21, 1578–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Peng, Z.; Qin, M.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, C.; Lin, J.; Dong, T.; Wang, L.; Li, S.; et al. Interferon-γ induces tumor resistance to anti-PD-1 immunotherapy by promoting YAP phase separation. Mol. Cell 2021, 81, 1216–1230.e1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagenbeek, T.J.; Zbieg, J.R.; Hafner, M.; Mroue, R.; Lacap, J.A.; Sodir, N.M.; Noland, C.L.; Afghani, S.; Kishore, A.; Bhat, K.P.; et al. An allosteric pan-TEAD inhibitor blocks oncogenic YAP/TAZ signaling and overcomes KRAS G12C inhibitor resistance. Nat. Cancer 2023, 4, 812–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baroja, I.; Kyriakidis, N.C.; Halder, G.; Moya, I.M. Expected and unexpected effects after systemic inhibition of Hippo transcriptional output in cancer. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 2700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moya, I.M.; Castaldo, S.A.; Van den Mooter, L.; Soheily, S.; Sansores-Garcia, L.; Jacobs, J.; Mannaerts, I.; Xie, J.; Verboven, E.; Hillen, H.; et al. Peritumoral activation of the Hippo pathway effectors YAP and TAZ suppresses liver cancer in mice. Science 2019, 366, 1029–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Xu, N.; Yu, S.; Si, W.; Yang, M.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Zhao, S.; Shi, J.; Yuan, J. Hyaluronic acid-coated porphyrin nanoplatform with oxygen sustained supplying and glutathione depletion for enhancing photodynamic/ion/chemo synergistic cancer treatment. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 278, 134661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasu, J.P.; Tougeron, D.; Rols, M.P. Irreversible electroporation and electrochemotherapy in oncology: State of the art. Diagn. Interv. Imaging 2022, 103, 499–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, S.; Chang, L.; Liu, S.; Gao, T.; Sang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Mu, W.; Liu, X.; Liang, S.; Yang, H.; et al. Temperature sensitive liposome based cancer nanomedicine enables tumour lymph node immune microenvironment remodelling. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 2248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Han, G.; Li, X. Platinum-copper alloy nanoparticles armored with chloride ion transporter to promote electro-driven tumor inhibition. Bioact. Mater. 2022, 12, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moghassemi, S.; Dadashzadeh, A.; Azevedo, R.B.; Amorim, C.A. Nanoemulsion applications in photodynamic therapy. J. Control. Release 2022, 351, 164–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kessel, D. Photodynamic Therapy: A Brief History. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, C.; Ali, Z.; Detsky, J.; Sahgal, A.; David, E.; Kunz, M.; Akens, M.; Chow, E.; Whyne, C.; Burch, S.; et al. Photodynamic Therapy for the Treatment of Vertebral Metastases: A Phase I Clinical Trial. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 5766–5776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Day, R.F.; Pejnovic, T.M.; Isaacs, T.; Muecke, J.S.; Glasson, W.J.; Campbell, W.G. Australian and New Zealand Study of Photodynamic Therapy in Choroidal Amelanotic Melanoma. Retina 2020, 40, 972–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krajczewski, J.; Rucińska, K.; Townley, H.E.; Kudelski, A. Role of various nanoparticles in photodynamic therapy and detection methods of singlet oxygen. Photodiagn. Photodyn. Ther. 2019, 26, 162–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mroz, P.; Yaroslavsky, A.; Kharkwal, G.B.; Hamblin, M.R. Cell death pathways in photodynamic therapy of cancer. Cancers 2011, 3, 2516–2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, S.; Guo, X.; Wang, S.; Wei, Z.; Huang, D.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, T.C.; Huang, Z. Singlet Oxygen in Photodynamic Therapy. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartelmess, J.; Milcovich, G.; Maffeis, V.; d’Amora, M.; Bertozzi, S.M.; Giordani, S. Modulation of Efficient Diiodo-BODIPY in vitro Phototoxicity to Cancer Cells by Carbon Nano-Onions. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 573211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Jung, H.Y.; Park, H.J. Topical PDT in the Treatment of Benign Skin Diseases: Principles and New Applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 23259–23278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Xu, R.; Ding, Y.; Wang, C.; Zhang, S.; Sun, Z.; Chen, Y.; Mi, Y.; Gao, M.; Ma, X.; et al. Intelligent triggering of nanomicelles based on a ROS-activated anticancer prodrug and photodynamic therapy (PDT)-synergistic therapy for lung cancers. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 241, 114622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Wang, L.; Yang, Y.; Li, J.; Qi, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, H.; Li, J. An Assembled Nanocomplex for Improving both Therapeutic Efficiency and Treatment Depth in Photodynamic Therapy. Angew. Chem. 2018, 57, 7759–7763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, E.J.; Choi, D.G.; Shim, M.S. Targeted and effective photodynamic therapy for cancer using functionalized nanomaterials. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2016, 6, 297–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Song, Y.; Huang, Z.; Pu, X.; Wang, Y.; Yin, G.; Gou, L.; Weng, J.; Meng, X. Photothermal photodynamic therapy and enhanced radiotherapy of targeting copolymer-coated liquid metal nanoparticles on liver cancer. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2021, 207, 112023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, Y.J.; Yang, X.X.; Liu, R.Q.; Zhao, D.; Guo, C.X.; Zhu, A.C.; Wen, M.N.; Liu, Z.; Qu, G.F.; Meng, H.X. Pathological Mechanism of Photodynamic Therapy and Photothermal Therapy Based on Nanoparticles. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 15, 6827–6838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Jiang, W.; Zhou, R. DAMPs and DAMP-sensing receptors in inflammation and diseases. Immunity 2024, 57, 752–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.; Tait, S.W.G. Targeting immunogenic cell death in cancer. Mol. Oncol. 2020, 14, 2994–3006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunningham, R.; Hansen, C.G. The Hippo pathway in cancer: YAP/TAZ and TEAD as therapeutic targets in cancer. Clin. Sci. 2022, 136, 197–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Rensburg, H.J.J.; Azad, T.; Ling, M.; Hao, Y.; Snetsinger, B.; Khanal, P.; Minassian, L.M.; Graham, C.H.; Rauh, M.J.; Yang, X. The Hippo Pathway Component TAZ Promotes Immune Evasion in Human Cancer through PD-L1. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 1457–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, C.D.K.; Yi, C. YAP/TAZ Signaling and Resistance to Cancer Therapy. Trends Cancer 2019, 5, 283–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shibata, M.; Ham, K.; Hoque, M.O. A time for YAP1: Tumorigenesis, immunosuppression and targeted therapy. Int. J. Cancer 2018, 143, 2133–2144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stampouloglou, E.; Cheng, N.; Federico, A.; Slaby, E.; Monti, S.; Szeto, G.L.; Varelas, X. Yap suppresses T-cell function and infiltration in the tumor microenvironment. PLoS Biol. 2020, 18, e3000591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, L.; Ge, X.; Cao, J.; Teng, Y.; Tian, R. Combination of Molecule-Targeted Therapy and Photodynamic Therapy Using Nanoformulated Verteporfin for Effective Uveal Melanoma Treatment. Mol. Pharm. 2024, 21, 2340–2350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, F.; He, T.; Chen, Z.; Zuo, Q.; Wang, Y.; Li, Q.; Zhong, S.; Ou, Y. RhoA enhances osteosarcoma resistance to MPPa-PDT via the Hippo/YAP signaling pathway. Cell Biosci. 2021, 11, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Liu, L.; Liang, R.; Zhou, H.; Pan, H.; Zhang, S.; Cai, L. Tumor-targeted nanoplatform for in situ oxygenation-boosted immunogenic phototherapy of colorectal cancer. Acta Biomater. 2020, 104, 188–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, M.L.; Moen, E.; Ager, B.; Bajaj, B.; Poppe, M.; Russo, G.; Yock, T.I. Radiotherapy dosing in intracranial ependymoma using the national cancer database. J. Neuro-Oncol. 2024, 170, 387–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirose, K.; Konno, A.; Hiratsuka, J.; Yoshimoto, S.; Kato, T.; Ono, K.; Otsuki, N.; Hatazawa, J.; Tanaka, H.; Takayama, K.; et al. Boron neutron capture therapy using cyclotron-based epithermal neutron source and borofalan ((10)B) for recurrent or locally advanced head and neck cancer (JHN002): An open-label phase II trial. Radiother. Oncol. J. Eur. Soc. Ther. Radiol. Oncol. 2021, 155, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klopp, A.H.; Enserro, D.; Powell, M.; Randall, M.; Schink, J.C.; Mannel, R.S.; Holman, L.; Bender, D.; Kushnir, C.L.; Backes, F.; et al. Radiation Therapy With or Without Cisplatin for Local Recurrences of Endometrial Cancer: Results From an NRG Oncology/GOG Prospective Randomized Multicenter Clinical Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2024, 42, 2425–2435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Guo, J.H.; Zhu, H.D.; Zhu, G.Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, L.; Wang, C.; Pan, T.F.; Teng, G.J. Palliative treatment with radiation-emitting metallic stents in unresectable Bismuth type III or IV hilar cholangiocarcinoma. ESMO Open 2017, 2, e000242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunther, J.R.; Xu, J.; Bhutani, M.S.; Strati, P.; Fang, P.Q.; Wu, S.Y.; Dabaja, B.S.; Dong, W.; Bhosale, P.R.; Flowers, C.R.; et al. Response-adapted ultra-low-dose 4 Gy radiation as definitive therapy of gastric MALT lymphoma: A single-centre, pilot trial. Lancet Haematol. 2024, 11, e521–e529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hudson, J.M.; Loblaw, A.; McGuffin, M.; Chung, H.T.; Tseng, C.L.; Helou, J.; Cheung, P.; Szumacher, E.; Liu, S.; Zhang, L.; et al. Prostate high dose-rate brachytherapy as monotherapy for low and intermediate-risk prostate cancer: Efficacy results from a randomized phase II clinical trial of one fraction of 19 Gy or two fractions of 13.5 Gy: A 9-year update. Radiother. Oncol. J. Eur. Soc. Ther. Radiol. Oncol. 2024, 198, 110381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Odia, Y.; Gutierrez, A.N.; Kotecha, R. Surgically targeted radiation therapy (STaRT) trials for brain neoplasms: A comprehensive review. Neuro-Oncology 2022, 24, S16–S24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfouzan, A.F. Radiation therapy in head and neck cancer. Saudi Med. J. 2021, 42, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wirth, A.; Mikhaeel, N.G.; Aleman, B.M.P.; Pinnix, C.C.; Constine, L.S.; Ricardi, U.; Illidge, T.M.; Eich, H.T.; Hoppe, B.S.; Dabaja, B.; et al. Involved Site Radiation Therapy in Adult Lymphomas: An Overview of International Lymphoma Radiation Oncology Group Guidelines. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2020, 107, 909–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, S.; Saha, T.; Rama, N.; Acharya, A.; Le, T.; Bian, F.; Donovan, J.; Tan, L.A.; Vatner, R.; Kalinichenko, V.; et al. Ultra-high dose-rate proton FLASH improves tumor control. Radiother. Oncol. J. Eur. Soc. Ther. Radiol. Oncol. 2023, 186, 109741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerard, J.P.; Barbet, N.; Schiappa, R.; Magné, N.; Martel, I.; Mineur, L.; Deberne, M.; Zilli, T.; Dhadda, A.; Myint, A.S. Neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy with radiation dose escalation with contact x-ray brachytherapy boost or external beam radiotherapy boost for organ preservation in early cT2-cT3 rectal adenocarcinoma (OPERA): A phase 3, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 8, 356–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murthy, V.; Adsul, K.; Maitre, P.; Singla, A.; Singh, P.; Panigrahi, G.; Raveendran, V.; Phurailatpam, R. Acute and Late Adverse Effects of Prostate-Only or Pelvic Stereotactic Radiation Therapy in Prostate Cancer: A Comparative Study. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2022, 114, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welsh, J.; Bevelacqua, J.J.; Dobrzyński, L.; Farjadian, S.; Mortazavi, S.M.J. Abscopal Effect Following Radiation Therapy in Cancer Patients: A New Look from the Immunological Point of View. J. Biomed. Phys. Eng. 2020, 10, 537–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, G.S.; Ahn, W.G.; Kim, S.Y.; Kang, W.; Choi, C.; Park, H.C. Radiation-induced abscopal effect and its enhancement by programmed cell death 1 blockade in the hepatocellular carcinoma: A murine model study. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2021, 27, 144–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, M.; Yang, M.; Zhang, J.; Yin, Y.; Fan, X.; Zhang, Y.; Qin, S.; Zhang, H.; Yu, F. Immunogenic Cell Death Induction by Ionizing Radiation. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 705361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, K.; Sano, M.; Jenkins, C.H.; Zhang, G.; Vernekohl, D.; Zhao, W.; Wei, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, Y.; et al. Synergistically Enhancing the Therapeutic Effect of Radiation Therapy with Radiation Activatable and Reactive Oxygen Species-Releasing Nanostructures. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 4946–4958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pefani, D.E.; O’Neill, E. Hippo pathway and protection of genome stability in response to DNA damage. FEBS J. 2016, 283, 1392–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawamoto, R.; Nakano, N.; Ishikawa, H.; Tashiro, E.; Nagano, W.; Sano, K.; Irie, M.; Ikuta, M.; Kishi, F.; Nakane, T.; et al. Narciclasine is a novel YAP inhibitor that disturbs interaction between YAP and TEAD4. BBA Adv. 2021, 1, 100008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Cai, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Hu, N.; Ma, S.; Hu, S.; Zhu, P.; Wang, W.; Zhou, H. Yap promotes hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis and mobilization via governing cofilin/F-actin/lamellipodium axis by regulation of JNK/Bnip3/SERCA/CaMKII pathways. Redox Biol. 2018, 14, 59–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Li, Y.; Xu, Y.; Ma, L.; Pizzi, M.P.; Jin, J.; Scott, A.W.; Huo, L.; Wang, Y.; Lee, J.H.; et al. Targeting Hippo coactivator YAP1 through BET bromodomain inhibition in esophageal adenocarcinoma. Mol. Oncol. 2020, 14, 1410–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Xu, Y.; Liu, B.; Singh, P.K.; Zhao, W.; Jin, J.; Han, G.; Scott, A.W.; Dong, X.; Huo, L.; et al. YAP1-Mediated CDK6 Activation Confers Radiation Resistance in Esophageal Cancer—Rationale for the Combination of YAP1 and CDK4/6 Inhibitors in Esophageal Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 2264–2277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Zhang, Z.; Rodriguez-Barrueco, R.; Borczuk, A.; Liu, H.; Yu, J.; Silva, J.M.; Cheng, S.K.; Perez-Soler, R.; Halmos, B. Functional genomics screen identifies YAP1 as a key determinant to enhance treatment sensitivity in lung cancer cells. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 28976–28988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Peng, X.; Zheng, L.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, B.; Shi, Y.; Wu, H.; Xu, C. YAP nuclear translocation facilitates radiation resistance in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2023, 670, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filis, P.; Mauri, D.; Markozannes, G.; Tolia, M.; Filis, N.; Tsilidis, K. Hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy (HIPEC) for the management of primary advanced and recurrent ovarian cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized trials. ESMO Open 2022, 7, 100586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aronson, S.L.; Lopez-Yurda, M.; Koole, S.N.; van Leeuwen, J.H.S.; Schreuder, H.W.R.; Hermans, R.H.M.; de Hingh, I.; van Gent, M.; Arts, H.J.G.; van Ham, M.; et al. Cytoreductive surgery with or without hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy in patients with advanced ovarian cancer (OVHIPEC-1): Final survival analysis of a randomised, controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2023, 24, 1109–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwanenburg, E.S.; El Klaver, C.; Wisselink, D.D.; Punt, C.J.A.; Snaebjornsson, P.; Crezee, J.; Aalbers, A.G.J.; Brandt-Kerkhof, A.R.M.; Bremers, A.J.A.; Burger, P.; et al. Adjuvant Hyperthermic Intraperitoneal Chemotherapy in Patients With Locally Advanced Colon Cancer (COLOPEC): 5-Year Results of a Randomized Multicenter Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2024, 42, 140–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beik, J.; Abed, Z.; Ghoreishi, F.S.; Hosseini-Nami, S.; Mehrzadi, S.; Shakeri-Zadeh, A.; Kamrava, S.K. Nanotechnology in hyperthermia cancer therapy: From fundamental principles to advanced applications. J. Control. Release 2016, 235, 205–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adnan, A.; Muñoz, N.M.; Prakash, P.; Habibollahi, P.; Cressman, E.N.K.; Sheth, R.A. Hyperthermia and Tumor Immunity. Cancers 2021, 13, 2507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaupel, P.; Piazena, H.; Notter, M.; Thomsen, A.R.; Grosu, A.L.; Scholkmann, F.; Pockley, A.G.; Multhoff, G. From Localized Mild Hyperthermia to Improved Tumor Oxygenation: Physiological Mechanisms Critically Involved in Oncologic Thermo-Radio-Immunotherapy. Cancers 2023, 15, 1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Zhang, Q.; Dai, L.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, G.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, D.; Ji, X.; Sang, Y.; Nie, Z. Docetaxel-Encapsulated Catalytic Pt/Au Nanotubes for Synergistic Chemo-Photothermal Therapy of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2024, 13, e2400662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, C.; Wang, X.; Li, S.; Zhang, Z.; Li, J.; Deng, Q.; Chen, X.; Yang, X.; Li, Z. A cuproptosis-based nanomedicine suppresses triple negative breast cancers by regulating tumor microenvironment and eliminating cancer stem cells. Biomaterials 2024, 313, 122763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, T.; Yu, X.; Han, S.; Yang, B. Nanomedicine-based tumor photothermal therapy synergized immunotherapy. Biomater. Sci. 2020, 8, 5241–5259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.; Meng, Z.; Moroishi, T.; Lin, K.C.; Shen, G.; Mo, F.; Shao, B.; Wei, X.; Zhang, P.; Wei, Y.; et al. Heat stress activates YAP/TAZ to induce the heat shock transcriptome. Nat. Cell Biol. 2020, 22, 1447–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, P.; Luo, Y.; Luo, Y.; Ma, L. A “sandwich” cell culture platform with NIR-responsive dynamic stiffness to modulate macrophage phenotypes. Biomater. Sci. 2021, 9, 2553–2561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ijff, M.; Crezee, J.; Oei, A.L.; Stalpers, L.J.A.; Westerveld, H. The role of hyperthermia in the treatment of locally advanced cervical cancer: A comprehensive review. Int. J. Gynecol. Cancer 2022, 32, 288–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Rivera-Rodriguez, A.; Tay, Z.W.; Hensley, D.; Fung, K.L.B.; Colson, C.; Saayujya, C.; Huynh, Q.; Kabuli, L.; Fellows, B.; et al. Combining magnetic particle imaging and magnetic fluid hyperthermia for localized and image-guided treatment. Int. J. Hyperth. 2020, 37, 141–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalanda, R.; Bartolo, J.; Carvalhal, S.; Abecasis, N.; Farricha, V. Cutaneous and subcutaneous Kaposi’s sarcoma lesions treated with electrochemotherapy. Int. J. Dermatol. 2023, 62, 115–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kispál, M.; Czirbesz, K.; Baranyai, F.; Balatoni, T.; Liszkay, G. Electrochemotherapy in metastatic melanoma. Orvosi Hetil. 2023, 164, 1381–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mucha, M.; Štach, M.; Kaštánková, I.; Rychlá, J.; Vydra, J.; Lesný, P.; Otáhal, P. Good manufacturing practice-grade generation of CD19 and CD123-specific CAR-T cells using piggyBac transposon and allogeneic feeder cells in patients diagnosed with B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma and acute myeloid leukemia. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1415328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuan, C.Y.; Yang, I.H.; Chang, C.T.; Chen, Z.Y.; Lin, J.N.; Kuo, W.T.; Lin, Y.Y.; Yueh, A.; Lin, F.H. Enhanced non-viral gene delivery via calcium phosphate/DNA co-precipitates with low-voltage pulse electroporation in NK-92 cells for immunocellular therapy. APL Bioeng. 2024, 8, 036107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, B.M.; Boville, G.A.; Bernardos, G.B.; Marckert, X.A.; Roca, M.T.; Huerta, L.L.; Aubá, F.V.; Chillón, F.R.d.F.; Ortega, J.S.; Muela, M.A.; et al. Focal Therapy of Prostate Cancer Index Lesion with Irreversible Electroporation. A Prospective Study with a Median Follow-Up of 3 Years. J. Urol. 2023, 209, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Yang, X.; He, C.; Chen, Y.; Li, C.; Li, S.; Chen, Y.; Wu, Y.; Xiang, Z.; Kang, J.; et al. Rejuvenation of tendon stem/progenitor cells for functional tendon regeneration through platelet-derived exosomes loaded with recombinant Yap1. Acta Biomater. 2023, 161, 80–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.; Wang, M.F.; Yuan, S.J.; Li, K.; Zhang, Q.; Lei, H.M.; Wu, J.L.; Li, A.X.; Xu, Y.H.; Chen, X. Photo-controlled co-delivery of verteporfin and acriflavine via platelets achieves potentiated glioblastoma-targeted photodynamic therapy. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2025, 23, 371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, Y.; Lee, D.; Lee, J.E.; Park, H.S.; Jung, S.S.; Park, D.; Kang, D.H.; Lee, S.I.; Woo, S.D.; Chung, C. The Matrix Stiffness Coordinates the Cell Proliferation and PD-L1 Expression via YAP in Lung Adenocarcinoma. Cancers 2024, 16, 598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez, N.M.C.; Pujol-Solé, N.; Arifi, Q.; Coll, J.L.; le Clainche, T.; Broekgaarden, M. Increasing cancer permeability by photodynamic priming: From microenvironment to mechanotransduction signaling. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2022, 41, 899–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, M.; Jin, J.; An, D.Y.; Kim, D.H.; Lee, J.; Yun, J.W.; Hwang, I.; Park, J.S.; Kim, M.K.; Lee, Y.M.; et al. Targeting YAP Activity and Glutamine Metabolism Cooperatively Suppresses Tumor Progression by Preventing Extracellular Matrix Accumulation. Cancer Res. 2024, 84, 3388–3401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Zhou, X.; Xie, Q.; Sun, H.; Huang, K.; Chen, H.; Wang, W.; Zhou, B.; Wei, X.; Zeng, D.; et al. CD146 interaction with integrin β1 activates LATS1-YAP signaling and induces radiation-resistance in breast cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 2022, 546, 215856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| NCT Number | Study Status | Sponsor | Phases | Start Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT06791941 | RECRUITING | Regina Elena Cancer Institute | 7 March 2024 | |
| NCT05228015 | TERMINATED | Ikena Oncology | PHASE1 | 7 January 2022 |
| NCT04857372 | RECRUITING | Novartis Pharmaceuticals | PHASE1 | 21 October 2021 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, J.; Yu, C.; Yang, W.; Jiang, N.; Li, S.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, X. Recent Advances in Combination Therapy of YAP Inhibitors with Physical Anti-Cancer Strategies. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 945. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15070945
Zhou J, Yu C, Yang W, Jiang N, Li S, Liu Y, Zhu X. Recent Advances in Combination Therapy of YAP Inhibitors with Physical Anti-Cancer Strategies. Biomolecules. 2025; 15(7):945. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15070945
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Junchi, Changyan Yu, Wanhong Yang, Nian Jiang, Sanhua Li, Yun Liu, and Xinting Zhu. 2025. "Recent Advances in Combination Therapy of YAP Inhibitors with Physical Anti-Cancer Strategies" Biomolecules 15, no. 7: 945. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15070945
APA StyleZhou, J., Yu, C., Yang, W., Jiang, N., Li, S., Liu, Y., & Zhu, X. (2025). Recent Advances in Combination Therapy of YAP Inhibitors with Physical Anti-Cancer Strategies. Biomolecules, 15(7), 945. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15070945





