Galectin-12 in the Regulation of Sebocyte Proliferation, Lipid Metabolism, and Immune Responses
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Role of Galectin-12 in Sebaceous Glands
3. Role of Galectin-12 in Sebaceous Gland Immune Responses
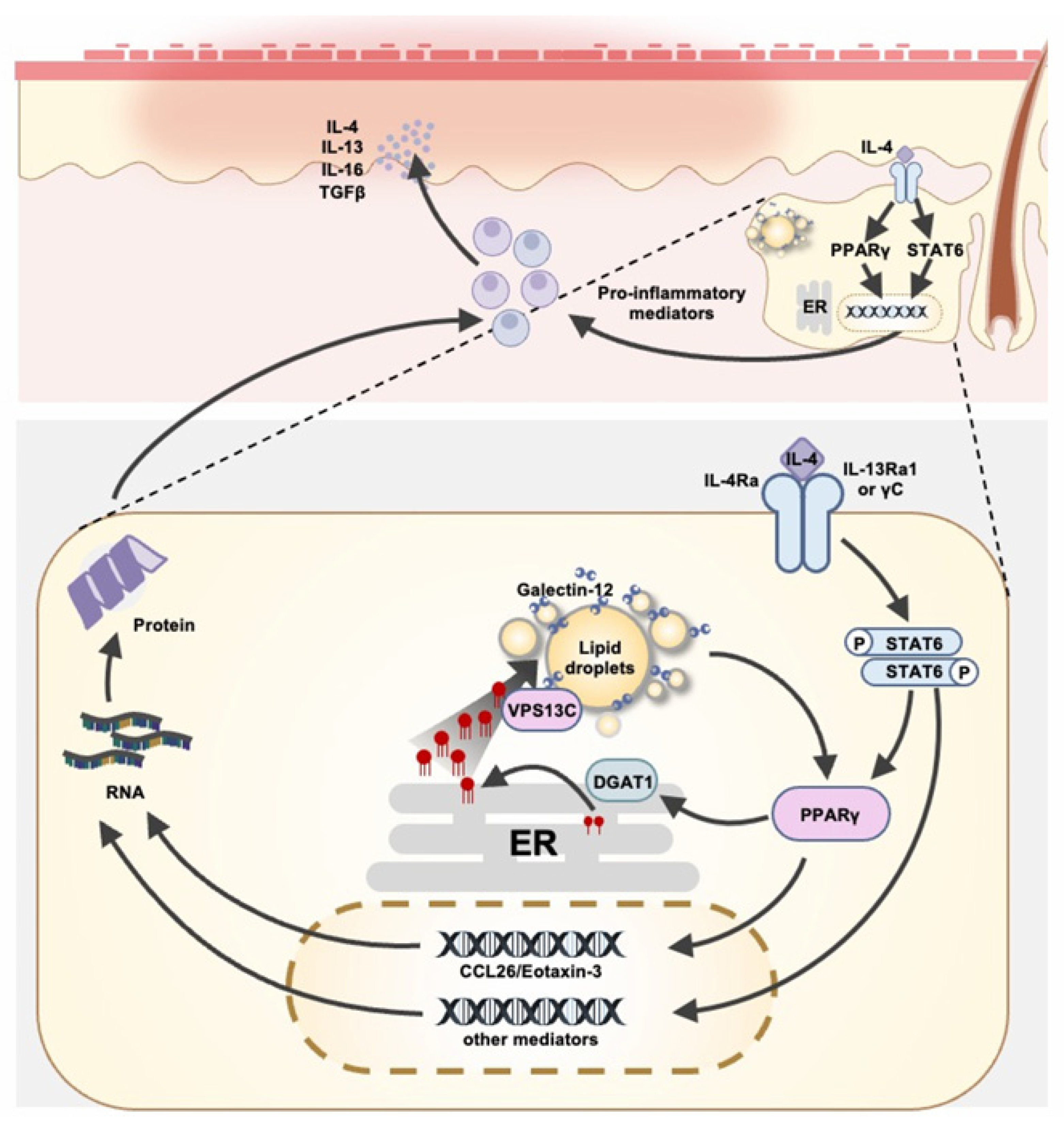
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement:
Data Availability Statement:
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cummings, R.D.; Liu, F.-T.; Rabinovich, G.A.; Stowell, S.R.; Vasta, G.R. Galectins. In Essentials of Glycobiology, 4th ed.; Ajit Varki, R.D.C., Esko, J.D., Stanley, P., Hart, G.W., Aebi, M., Mohnen, D., Kinoshita, T., Packer, N.H., Prestegard, J.H., Schnaar, R.L., et al., Eds.; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: Cold Spring Harbor, NY, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, F.T.; Stowell, S.R. The role of galectins in immunity and infection. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2023, 23, 479–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaminker, J.D.; Timoshenko, A.V. Expression, Regulation, and Functions of the Galectin-16 Gene in Human Cells and Tissues. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirabayashi, J.; Hashidate, T.; Arata, Y.; Nishi, N.; Nakamura, T.; Hirashima, M.; Urashima, T.; Oka, T.; Futai, M.; Muller, W.E.; et al. Oligosaccharide specificity of galectins: A search by frontal affinity chromatography. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2002, 1572, 232–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, T.J.; Lin, H.Y.; Tu, Z.; Huang, B.S.; Wu, S.C.; Lin, C.H. Structural Basis Underlying the Binding Preference of Human Galectins-1, -3 and -7 for Galbeta1-3/4GlcNAc. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0125946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cagnoni, A.J.; Massaro, M.; Cutine, A.M.; Gimeno, A.; Perez-Saez, J.M.; Manselle Cocco, M.N.; Maller, S.M.; Di Lella, S.; Jimenez-Barbero, J.; Arda, A.; et al. Exploring galectin interactions with human milk oligosaccharides and blood group antigens identifies BGA6 as a functional galectin-4 ligand. J. Biol. Chem. 2024, 300, 107573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.C.; Ho, A.D.; Kamili, N.A.; Wang, J.; Murdock, K.L.; Cummings, R.D.; Arthur, C.M.; Stowell, S.R. Full-Length Galectin-3 Is Required for High Affinity Microbial Interactions and Antimicrobial Activity. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 731026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maller, S.M.; Cagnoni, A.J.; Bannoud, N.; Sigaut, L.; Perez Saez, J.M.; Pietrasanta, L.I.; Yang, R.Y.; Liu, F.T.; Croci, D.O.; Di Lella, S.; et al. An adipose tissue galectin controls endothelial cell function via preferential recognition of 3-fucosylated glycans. FASEB J. 2020, 34, 735–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johannes, L.; Jacob, R.; Leffler, H. Galectins at a glance. J. Cell Sci. 2018, 131, jcs208884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Troncoso, M.F.; Elola, M.T.; Blidner, A.G.; Sarrias, L.; Espelt, M.V.; Rabinovich, G.A. The universe of galectin-binding partners and their functions in health and disease. J. Biol. Chem. 2023, 299, 105400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.Y.; Hsu, D.K.; Yu, L.; Ni, J.; Liu, F.T. Cell cycle regulation by galectin-12, a new member of the galectin superfamily. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 20252–20260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.Y.; Rabinovich, G.A.; Liu, F.T. Galectins: Structure, function and therapeutic potential. Expert Rev. Mol. Med. 2008, 10, e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, L.; Yang, R.Y.; Liu, F.T. Galectin-12 in Cellular Differentiation, Apoptosis and Polarization. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.Y.; Shyu, A.B. AU-rich elements: Characterization and importance in mRNA degradation. Trends Biochem. Sci. 1995, 20, 465–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotta, K.; Funahashi, T.; Matsukawa, Y.; Takahashi, M.; Nishizawa, H.; Kishida, K.; Matsuda, M.; Kuriyama, H.; Kihara, S.; Nakamura, T.; et al. Galectin-12, an Adipose-expressed Galectin-like Molecule Possessing Apoptosis-inducing Activity. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 34089–34097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.Y.; Hsu, D.K.; Yu, L.; Chen, H.Y.; Liu, F.T. Galectin-12 is required for adipogenic signaling and adipocyte differentiation. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 29761–29766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, R.Y.; Yu, L.; Graham, J.L.; Hsu, D.K.; Lloyd, K.C.; Havel, P.J.; Liu, F.T. Ablation of a galectin preferentially expressed in adipocytes increases lipolysis, reduces adiposity, and improves insulin sensitivity in mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 18696–18701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Yin, Y.; Xu, K.; Peng, Y.; Zhang, J. Knockdown of LGALS12 inhibits porcine adipocyte adipogenesis via PKA-Erk1/2 signaling pathway. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2018, 50, 960–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Zhang, D.; Yin, Y.; Ji, M.; Xu, K.; Huang, X.; Peng, Y.; Zhang, J. Comprehensive transcriptomic view of the role of the LGALS12 gene in porcine subcutaneous and intramuscular adipocytes. BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, R.Y.; Xue, H.; Yu, L.; Velayos-Baeza, A.; Monaco, A.P.; Liu, F.T. Identification of VPS13C as a Galectin-12-Binding Protein That Regulates Galectin-12 Protein Stability and Adipogenesis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0153534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonangelino, C.J.; Chavez, E.M.; Bonifacino, J.S. Genomic screen for vacuolar protein sorting genes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol. Biol. Cell 2002, 13, 2486–2501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gambardella, S.; Biagioni, F.; Ferese, R.; Busceti, C.L.; Frati, A.; Novelli, G.; Ruggieri, S.; Fornai, F. Vacuolar Protein Sorting Genes in Parkinson’s Disease: A Re-appraisal of Mutations Detection Rate and Neurobiology of Disease. Front. Neurosci. 2016, 10, 532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haft, C.R.; de la Luz Sierra, M.; Bafford, R.; Lesniak, M.A.; Barr, V.A.; Taylor, S.I. Human orthologs of yeast vacuolar protein sorting proteins Vps26, 29, and 35: Assembly into multimeric complexes. Mol. Biol. Cell 2000, 11, 4105–4116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, N.; Leonzino, M.; Hancock-Cerutti, W.; Horenkamp, F.A.; Li, P.; Lees, J.A.; Wheeler, H.; Reinisch, K.M.; De Camilli, P. VPS13A and VPS13C are lipid transport proteins differentially localized at ER contact sites. J. Cell Biol. 2018, 217, 3625–3639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Roberts, M.A.; Chen, C.Y.; Markmiller, S.; Wei, H.G.; Yeo, G.W.; Granneman, J.G.; Olzmann, J.A.; Ferro-Novick, S. VPS13A and VPS13C Influence Lipid Droplet Abundance. Contact 2022, 5, 25152564221125613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leonzino, M.; Reinisch, K.M.; De Camilli, P. Insights into VPS13 properties and function reveal a new mechanism of eukaryotic lipid transport. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2021, 1866, 159003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesage, S.; Drouet, V.; Majounie, E.; Deramecourt, V.; Jacoupy, M.; Nicolas, A.; Cormier-Dequaire, F.; Hassoun, S.M.; Pujol, C.; Ciura, S.; et al. Loss of VPS13C Function in Autosomal-Recessive Parkinsonism Causes Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Increases PINK1/Parkin-Dependent Mitophagy. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2016, 98, 500–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schröder, L.F.; Peng, W.; Gao, G.; Wong, Y.C.; Schwake, M.; Krainc, D. VPS13C regulates phospho-Rab10-mediated lysosomal function in human dopaminergic neurons. J. Cell Biol. 2024, 223, e202304042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katzenmaier, E.M.; Fuchs, V.; Warnken, U.; Schnolzer, M.; Gebert, J.; Kopitz, J. Deciphering the galectin-12 protein interactome reveals a major impact of galectin-12 on glutamine anaplerosis in colon cancer cells. Exp. Cell Res. 2019, 379, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, M.R.; Zouboulis, C.C. Primary sebocytes and sebaceous gland cell lines for studying sebaceous lipogenesis and sebaceous gland diseases. Exp. Dermatol. 2018, 27, 484–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinde, E.; Haslam, I.S.; Schneider, M.R.; Langan, E.A.; Kloepper, J.E.; Schramm, C.; Zouboulis, C.C.; Paus, R. A practical guide for the study of human and murine sebaceous glands in situ. Exp. Dermatol. 2013, 22, 631–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picardo, M.; Ottaviani, M.; Camera, E.; Mastrofrancesco, A. Sebaceous gland lipids. Dermato-Endocrinology 2009, 1, 68–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fluhr, J.W.; Mao-Qiang, M.; Brown, B.E.; Wertz, P.W.; Crumrine, D.; Sundberg, J.P.; Feingold, K.R.; Elias, P.M. Glycerol regulates stratum corneum hydration in sebaceous gland deficient (asebia) mice. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2003, 120, 728–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovaszi, M.; Szegedi, A.; Zouboulis, C.C.; Torocsik, D. Sebaceous-immunobiology is orchestrated by sebum lipids. Dermato-Endocrinology 2017, 9, e1375636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilgram, G.S.; van der Meulen, J.; Gooris, G.S.; Koerten, H.K.; Bouwstra, J.A. The influence of two azones and sebaceous lipids on the lateral organization of lipids isolated from human stratum corneum. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2001, 1511, 244–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, M.R. Lipid droplets and associated proteins in sebocytes. Exp. Cell Res. 2016, 340, 205–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.F.; Cai, X.L.; Jing, K.P.; Pi, X.X.; Liao, P.Y.; Li, S.J.; Wen, L.; Cai, C.C.; Quan, J.H.; Fan, Y.M.; et al. Differentiation Model Establishment and Differentiation-Related Protein Screening in Primary Cultured Human Sebocytes. BioMed Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 7174561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okoro, O.E.; Adenle, A.; Ludovici, M.; Truglio, M.; Marini, F.; Camera, E. Lipidomics of facial sebum in the comparison between acne and non-acne adolescents with dark skin. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 16591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.K.; Bluhm, R.; Cooper, E.A.; Summerbell, R.C.; Batra, R. Seborrheic dermatitis. Dermatol. Clin. 2003, 21, 401–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirth, H.; Gloor, M.; Stoika, D. Sebaceous glands in uninvolved skin of patients suffering from atopic dermatitis. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 1981, 270, 167–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christofides, A.; Konstantinidou, E.; Jani, C.; Boussiotis, V.A. The role of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPAR) in immune responses. Metabolism 2021, 114, 154338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toobian, D.; Ghosh, P.; Katkar, G.D. Parsing the Role of PPARs in Macrophage Processes. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 783780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briganti, S.; Mosca, S.; Di Nardo, A.; Flori, E.; Ottaviani, M. New Insights into the Role of PPARgamma in Skin Physiopathology. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trivedi, N.R.; Cong, Z.; Nelson, A.M.; Albert, A.J.; Rosamilia, L.L.; Sivarajah, S.; Gilliland, K.L.; Liu, W.; Mauger, D.T.; Gabbay, R.A.; et al. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors increase human sebum production. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2006, 126, 2002–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zouboulis, C.C.; Coenye, T.; He, L.; Kabashima, K.; Kobayashi, T.; Niemann, C.; Nomura, T.; Olah, A.; Picardo, M.; Quist, S.R.; et al. Sebaceous immunobiology—Skin homeostasis, pathophysiology, coordination of innate immunity and inflammatory response and disease associations. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1029818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yen, C.L.; Stone, S.J.; Koliwad, S.; Harris, C.; Farese, R.V., Jr. Thematic review series: Glycerolipids. DGAT enzymes and triacylglycerol biosynthesis. J. Lipid Res. 2008, 49, 2283–2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, G.; Schoonjans, K.; Lefebvre, A.M.; Staels, B.; Auwerx, J. Coordinate regulation of the expression of the fatty acid transport protein and acyl-CoA synthetase genes by PPARalpha and PPARgamma activators. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 28210–28217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferre, P. The biology of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors: Relationship with lipid metabolism and insulin sensitivity. Diabetes 2004, 53 (Suppl. 1), S43–S50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fenske, N.A.; Lober, C.W. Structural and functional changes of normal aging skin. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 1986, 15, 571–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harada, K.; Kato, Y.; Kato, Y.; Tsuboi, R. Hair Follicle Nevus with Sebaceous Hyperplasia: A Dermoscopic Observation. Case Rep. Dermatol. 2015, 7, 358–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolova, M.; Tawab, A.; Marie-Cardine, A.; Bagot, M.; Boumsell, L.; Bensussan, A. Increased expression of a novel early activation surface membrane receptor in cutaneous T cell lymphoma cells. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2001, 116, 731–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thody, A.J.; Shuster, S. Control and function of sebaceous glands. Physiol. Rev. 1989, 69, 383–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zouboulis, C.C.; Boschnakow, A. Chronological ageing and photoageing of the human sebaceous gland. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2001, 26, 600–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zouboulis, C.C.; Jourdan, E.; Picardo, M. Acne is an inflammatory disease and alterations of sebum composition initiate acne lesions. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2014, 28, 527–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collier, P.M.; James, M.P. Pseudopelade of Brocq occurring in two brothers in childhood. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 1994, 19, 61–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamp, S.; Fiehn, A.M.; Stenderup, K.; Rosada, C.; Pakkenberg, B.; Kemp, K.; Dam, T.N.; Jemec, G.B. Hidradenitis suppurativa: A disease of the absent sebaceous gland? Sebaceous gland number and volume are significantly reduced in uninvolved hair follicles from patients with hidradenitis suppurativa. Br. J. Dermatol. 2011, 164, 1017–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liakou, A.I.; Nyengaard, J.R.; Bonovas, S.; Knolle, J.; Makrantonaki, E.; Zouboulis, C.C. Marked Reduction of the Number and Individual Volume of Sebaceous Glands in Psoriatic Lesions. Dermatology 2016, 232, 415–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsao, C.H.; Hsieh, W.C.; Yang, R.Y.; Lo, Y.H.; Tu, T.J.; Ke, L.Y.; Zouboulis, C.C.; Liu, F.T. Galectin-12 modulates sebocyte proliferation and cell cycle progression by regulating cyclin A1 and CDK2. Glycobiology 2022, 32, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertoli, C.; Skotheim, J.M.; de Bruin, R.A. Control of cell cycle transcription during G1 and S phases. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2013, 14, 518–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seiringer, P.; Hillig, C.; Schabitz, A.; Jargosch, M.; Pilz, A.C.; Eyerich, S.; Szegedi, A.; Sochorova, M.; Gruber, F.; Zouboulis, C.C.; et al. Spatial transcriptomics reveals altered lipid metabolism and inflammation-related gene expression of sebaceous glands in psoriasis and atopic dermatitis. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1334844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, V.Y.; Leo, M.; Hassoun, L.; Chahal, D.S.; Maibach, H.I.; Sivamani, R.K. Role of sebaceous glands in inflammatory dermatoses. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2015, 73, 856–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsao, C.H.; Hsieh, W.C.; Lin, F.J.; Yang, R.Y.; Chang, M.T.; Apaya, M.K.; Shyur, L.F.; Ke, L.Y.; Zouboulis, C.C.; Liu, F.T. The Critical Role of Galectin-12 in Modulating Lipid Metabolism in Sebaceous Glands. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2023, 143, 913–924.E4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tazhitdinova, R.; Cristiano, S.; Yi, J.; Zhurov, V.; DeKoter, R.P.; Timoshenko, A.V. Expression and secretion of galectin-12 in the context of neutrophilic differentiation of human promyeloblastic HL-60 cells. J. Cell Physiol. 2024, 239, e31288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buschmann, C.; Unverdorben, L.; Knabl, J.; Hutter, S.; Meister, S.; Beyer, S.; Burgmann, M.; Zati Zehni, A.; Schmoeckel, E.; Kessler, M.; et al. Placental expression of inflammatory Galectin-12 is associated with gestational diabetes. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2024, 163, 104240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.L.; Wang, Y.C.; Hsu, Y.A.; Chen, C.S.; Weng, R.C.; Lu, Y.P.; Chuang, C.Y.; Wan, L. Galectin-12 modulates Kupffer cell polarization to alter the progression of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Glycobiology 2023, 33, 673–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowowiejska, J.; Baran, A.; Hermanowicz, J.M.; Sieklucka, B.; Pawlak, D.; Flisiak, I. Evaluation of Plasma Concentrations of Galectins-1, 2 and 12 in Psoriasis and Their Clinical Implications. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanford, J.A.; O’Neill, A.M.; Zouboulis, C.C.; Gallo, R.L. Short-Chain Fatty Acids from Cutibacterium acnes Activate Both a Canonical and Epigenetic Inflammatory Response in Human Sebocytes. J. Immunol. 2019, 202, 1767–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zouboulis, C.C.; Oeff, M.K.; Hiroi, N.; Makrantonaki, E.; Bornstein, S.R. Involvement of Pattern Recognition Receptors in the Direct Influence of Bacterial Components and Standard Antiacne Compounds on Human Sebaceous Gland Cells. Skin Pharmacol. Physiol. 2021, 34, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, F.J.; Huang, Y.H.; Tsao, C.H.; Hsieh, W.C.; Lo, Y.H.; Zouboulis, C.C.; Chen, H.L.; Liu, F.T. Galectin-12 Regulates Immune Responses in the Skin through Sebaceous Glands. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2023, 143, 2120–2131.E7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baumann, A.; Burger, K.; Brandt, A.; Staltner, R.; Jung, F.; Rajcic, D.; Lorenzo Pisarello, M.J.; Bergheim, I. GW9662, a peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma antagonist, attenuates the development of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Metabolism 2022, 133, 155233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Kaufman, R.J. From endoplasmic-reticulum stress to the inflammatory response. Nature 2008, 454, 455–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, R.B. The role of PPARs in inflammation and immunity. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2002, 71, 388–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniel, B.; Nagy, G.; Czimmerer, Z.; Horvath, A.; Hammers, D.W.; Cuaranta-Monroy, I.; Poliska, S.; Tzerpos, P.; Kolostyak, Z.; Hays, T.T.; et al. The Nuclear Receptor PPARgamma Controls Progressive Macrophage Polarization as a Ligand-Insensitive Epigenomic Ratchet of Transcriptional Memory. Immunity 2018, 49, 615–626.E6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.; Kaufman, R.J. The role of ER stress in lipid metabolism and lipotoxicity. J. Lipid Res. 2016, 57, 1329–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Wang, S.; Malhotra, J.; Hassler, J.R.; Back, S.H.; Wang, G.; Chang, L.; Xu, W.; Miao, H.; Leonardi, R.; et al. The unfolded protein response transducer IRE1alpha prevents ER stress-induced hepatic steatosis. EMBO J. 2011, 30, 1357–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, M.R.; Paus, R. Sebocytes, multifaceted epithelial cells: Lipid production and holocrine secretion. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2010, 42, 181–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tsao, C.-H.; Hsieh, W.-C.; Lin, F.-J.; Liu, F.-T.; Yang, R.-Y. Galectin-12 in the Regulation of Sebocyte Proliferation, Lipid Metabolism, and Immune Responses. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 837. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15060837
Tsao C-H, Hsieh W-C, Lin F-J, Liu F-T, Yang R-Y. Galectin-12 in the Regulation of Sebocyte Proliferation, Lipid Metabolism, and Immune Responses. Biomolecules. 2025; 15(6):837. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15060837
Chicago/Turabian StyleTsao, Ching-Han, Wei-Chen Hsieh, Feng-Jen Lin, Fu-Tong Liu, and Ri-Yao Yang. 2025. "Galectin-12 in the Regulation of Sebocyte Proliferation, Lipid Metabolism, and Immune Responses" Biomolecules 15, no. 6: 837. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15060837
APA StyleTsao, C.-H., Hsieh, W.-C., Lin, F.-J., Liu, F.-T., & Yang, R.-Y. (2025). Galectin-12 in the Regulation of Sebocyte Proliferation, Lipid Metabolism, and Immune Responses. Biomolecules, 15(6), 837. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15060837





