A Map of the Lipid–Metabolite–Protein Network to Aid Multi-Omics Integration
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Construction of a Protein, Lipid, and Metabolite Network
2.2. Hyperbolic Embedding of the Network
2.3. Clustering in the Angular Similarity Dimension
2.4. Evaluation of Molecular Relationships Between Omics Layers
- -
- User-defined molecule subset (S): List of identifiers of one omics layer (proteins, lipids, or metabolites)
- -
- Hyperbolic coordinates dataset: Precomputed (r, θ) for all molecules across layers
- -
- n: Number of smallest distances to consider (default = 3)
- -
- Ranked lists of molecules of non-input omics layers, sorted by association strength
- Input Processing:
- Receive user input (S) and parameter n
- Validate identifiers in S against reference database
- Filter valid subset (S_valid) = S ∩ database_entries
- Distance Matrix Construction:For each target omics layer T ∉ input layer:
- Initialize distance matrix D with dimensions |S_valid| × |T|
- Compute hyperbolic distances between all pairs (s ∈ S_valid, t ∈ T):distance(s,t) = acosh[cosh(rs)cosh(rt) − sinh(rs)sinh(rt)cos(Δθ)]where Δθ = π − |π − |θs − θt||
- Association Score Calculation:For each molecule t in target layer T:
- Collect all distances from S_valid to t: {distance(s1,t), …, distance(sk,t)}
- Identify n smallest distances: d1 ≤ d2 ≤ … ≤ dn
- Compute association score: score(t) = 1/(Σn{i=1}di)
- Ranking and Output:
- Sort all molecules in T by descending score(t)
- Generate evidence strings for top associations:evidence(t) = [si:di (sorted)] for i = 1…n
- Return ranked list: (t, score(t), evidence(t)) ∀ t ∈ T
2.5. Functional Enrichment Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Software Implementation
3.2. Literature Discovery: Cardiovascular Disease Case Study
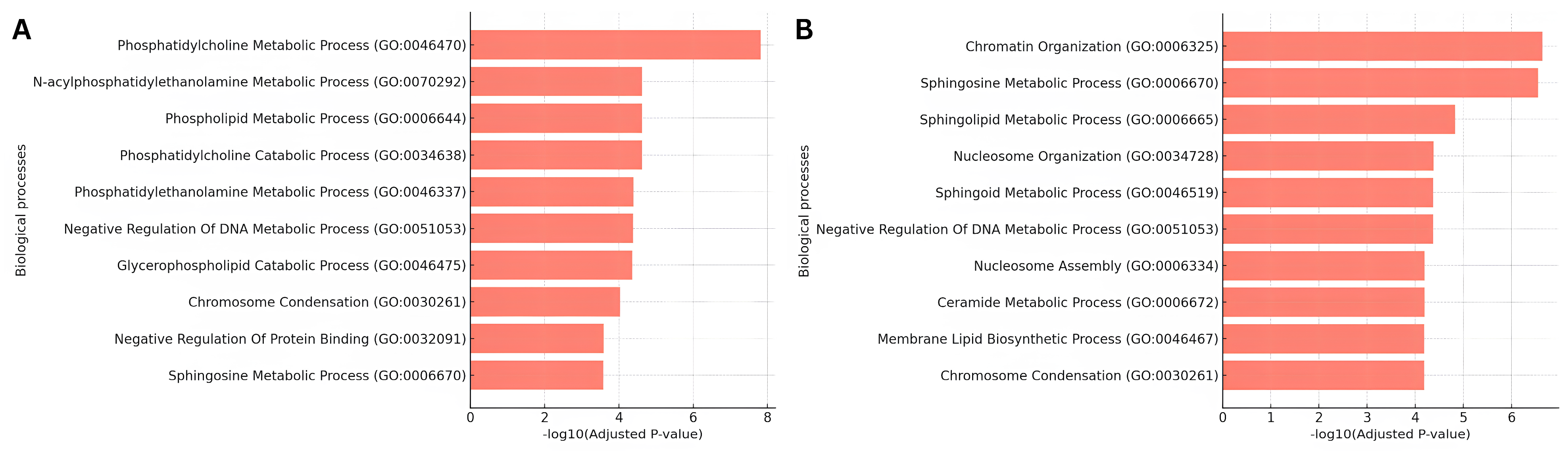
3.3. Functional Enrichment Analysis of Lipid Signatures
4. Discussion and Conclusions
4.1. Multi-Omics Integration for Disease Insights
4.2. Limitations of Our Approach
4.3. Advantages and Future Directions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vasaikar, S.; Huang, C.; Wang, X.; Petyuk, V.A.; Savage, S.R.; Wen, B.; Dou, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, Z.; Arshad, O.A.; et al. Proteogenomic Analysis of Human Colon Cancer Reveals New Therapeutic Opportunities. Cell 2019, 177, 1035–1049.e19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.V.; Hu, Y.J. Integrative Analysis of Multi-omics Data for Discovery and Functional Studies of Complex Human Diseases. Adv. Genet. 2016, 93, 147–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linda, A. Heffernan-Stroud, Lina, M. Obeid, Chapter Seven—Sphingosine Kinase 1 in Cancer. In Advances in Cancer Research; Norris, J.S., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2013; Volume 117, pp. 201–235. ISBN 9780123942746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Liu, B.; Zou, P.; Zhang, Y.; You, J.; Pei, F. Silencing of LASS2/TMSG1 enhances invasion and metastasis capacity of prostate cancer cell. J. Cell. Biochem. 2014, 115, 731–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Wang, J.; Wang, X.; Zhu, J.; Liu, Q.; Shi, Z.; Chambers, M.C.; Zimmerman, L.J.; Shaddox, K.F.; Kim, S.; et al. Proteogenomic characterization of human colon and rectal cancer. Nature 2014, 513, 382–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canzler, S.; Schor, J.; Busch, W.; Schubert, K.; Rolle-Kampczyk, U.E.; Seitz, H.; Kamp, H.; von Bergen, M.; Buesen, R.; Hackermüller, J. Prospects and challenges of multi-omics data integration in toxicology. Arch. Toxicol. 2020, 94, 371–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wörheide, M.A.; Krumsiek, J.; Kastenmüller, G.; Arnold, M. Multi-omics integration in biomedical research—A metabolomics-centric review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2021, 1141, 144–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López de Maturana, E.; Alonso, L.; Alarcón, P.; Martín-Antoniano, I.A.; Pineda, S.; Piorno, L.; Calle, M.L.; Malats, N. Challenges in the Integration of Omics and Non-Omics Data. Genes. 2019, 10, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fondi, M.; Liò, P. Multi-omics and metabolic modelling pipelines: Challenges and tools for systems microbiology. Microbiol. Res. 2015, 171, 52–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Liu, Q.; Xie, L. Hierarchical multi-omics data integration and modeling predict cell-specific chemical proteomics and drug responses. Cell Rep. Methods 2023, 3, 100452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Mou, M.; Hu, W.; Lu, M.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, H.; Luo, Y.; Xu, H.; Tao, L.; Dai, H.; et al. MOINER: A Novel Multiomics Early Integration Framework for Biomedical Classification and Biomarker Discovery. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2024, 64, 2720–2732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picard, M.; Scott-Boyer, M.P.; Bodein, A.; Périn, O.; Droit, A. Integration strategies of multi-omics data for machine learning analysis. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2021, 19, 3735–3746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, T.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, J.; Kang, Q.; Liu, L. Multi-omics integration for both single-cell and spatially resolved data based on dual-path graph attention auto-encoder. Brief. Bioinform. 2024, 25, bbae450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maitra, C.; Seal, D.B.; Das, V.; De, R.K. Unsupervised neural network for single cell Multi-omics INTegration (UMINT): An application to health and disease. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2023, 10, 1184748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bredikhin, D.; Kats, I.; Stegle, O. MUON: Multimodal omics analysis framework. Genome Biol. 2022, 23, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benkirane, H.; Pradat, Y.; Michiels, S.; Cournède, P.H. CustOmics: A versatile deep-learning based strategy for multi-omics integration. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2023, 19, e1010921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Huang, D.S.; Zhang, X. scmFormer Integrates Large-Scale Single-Cell Proteomics and Transcriptomics Data by Multi-Task Transformer. Adv. Sci. 2024, 11, e2307835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodam, P.; Sai Swaroop, R.; Pradhan, S.S.; Sivaramakrishnan, V.; Vadrevu, R. Integrated multi-omics analysis of Alzheimer’s disease shows molecular signatures associated with disease progression and potential therapeutic targets. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 3695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stahlschmidt, S.R.; Ulfenborg, B.; Synnergren, J. Multimodal deep learning for biomedical data fusion: A review. Brief. Bioinform. 2022, 23, bbab569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Wu, T.-Y.; Wan, S.; Yang, J.Y.H.; Wong, W.H.; Wang, Y.X.R. scJoint integrates atlas-scale single-cell RNA-seq and ATAC-seq data with transfer learning. Nat. Biotechnol. 2022, 40, 703–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Mann, K.K.; Wu, H.; Ding, J. scCross: A deep generative model for unifying single-cell multi-omics with seamless integration, cross-modal generation, and in silico exploration. Genome Biol. 2024, 25, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.J.; Gao, G. Multi-omics single-cell data integration and regulatory inference with graph-linked embedding. Nat. Biotechnol. 2022, 40, 1458–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ma, J.; Leng, L.; Han, M.; Li, M.; He, F.; Zhu, Y. MoGCN: A Multi-Omics Integration Method Based on Graph Convolutional Network for Cancer Subtype Analysis. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 806842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Yu, X.; Wang, X.; Song, J.; Yu, D.J.; Ge, F. MORE: A multi-omics data-driven hypergraph integration network for biomedical data classification and biomarker identification. Brief. Bioinform. 2024, 26, bbae658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palshikar, M.G.; Min, X.; Crystal, A.; Meng, J.; Hilchey, S.P.; Zand, M.S.; Thakar, J. Executable Network Models of Integrated Multiomics Data. J. Proteome Res. 2023, 22, 1546–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, H.; Liang, H.; Liu, H.; Fan, Z.; Wei, Y.; Yao, X.; Cong, S. TEMINET: A Co-Informative and Trustworthy Multi-Omics Integration Network for Diagnostic Prediction. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, D.; Yang, M.; Peng, D.; Yu, J.; Liu, Y.; Lv, J.; Chen, L.; Peng, X. scBridge embraces cell heterogeneity in single-cell RNA-seq and ATAC-seq data integration. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 6045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Salguero, P.; Petek, M.; Martinez-Mira, C.; Balzano-Nogueira, L.; Ramšak, Ž.; McIntyre, L.; Gruden, K.; Tarazona, S.; Conesa, A. PaintOmics 4: New tools for the integrative analysis of multi-omics datasets supported by multiple pathway databases. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, W551–W559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Ni, Q.; He, G.; Huang, J.; Chao, H.; Li, S.; Chen, M.; Hu, G.; Whelan, J.; Shou, H. SoyOD: An Integrated Soybean Multi-omics Database for Mining Genes and Biological Research. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2025, 22, qzae080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, L.; Zhou, Y.L.; Sun, H.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, C.; Wang, Z.; Xuan, B.; Zhao, Y.; Ma, Y.; Yan, Y.; et al. Microbiome and metabolome features in inflammatory bowel disease via multi-omics integration analyses across cohorts. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 7135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maghsoudi, Z.; Nguyen, H.; Tavakkoli, A.; Nguyen, T. A comprehensive survey of the approaches for pathway analysis using multi-omics data integration. Brief. Bioinform. 2022, 23, bbac435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alanis-Lobato, G.; Mier, P.; Andrade-Navarro, M. The latent geometry of the human protein interaction network. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 2826–2834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cannistraci, C.V.; Alanis-Lobato, G.; Ravasi, T. Minimum curvilinearity to enhance topological prediction of protein interactions by network embedding. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, i199–i209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vagiona, A.C.; Mier, P.; Petrakis, S.; Andrade-Navarro, M.A. Analysis of Huntington’s Disease Modifiers Using the Hyperbolic Mapping of the Protein Interaction Network. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zahra, N.U.A.; Vagiona, A.C.; Uddin, R.; Andrade-Navarro, M.A. Selection of Multi-Drug Targets against Drug-Resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis XDR1219 Using the Hyperbolic Mapping of the Protein Interaction Network. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 14050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deprince, A.; Haas, J.T.; Staels, B. Dysregulated lipid metabolism links NAFLD to cardiovascular disease. Mol. Metab. 2020, 42, 101092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Lima, E.P.; Moretti, R.C., Jr.; Torres Pomini, K.; Laurindo, L.F.; Sloan, K.P.; Sloan, L.A.; Castro, M.V.M.d.; Baldi, E., Jr.; Ferraz, B.F.R.; de Souza Bastos Mazuqueli Pereira, E.; et al. Glycolipid Metabolic Disorders, Metainflammation, Oxidative Stress, and Cardiovascular Diseases: Unraveling Pathways. Biology 2024, 13, 519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taube, A.; Schlich, R.; Sell, H.; Eckardt, K.; Eckel, J. Inflammation and metabolic dysfunction: Links to cardiovascular diseases. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2012, 302, H2148–H2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doran, S.; Arif, M.; Lam, S.; Bayraktar, A.; Turkez, H.; Uhlen, M.; Boren, J.; Mardinoglu, A. Multi-omics approaches for revealing the complexity of cardiovascular disease. Brief. Bioinform. 2021, 22, bbab061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, S.; Li, L.; Shen, X.; Li, Q.; Xu, W.; Wang, X.; Tao, Y.; Yin, H. An update on lipid oxidation and inflammation in cardiovascular diseases. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2019, 144, 266–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alanis-Lobato, G.; Andrade-Navarro, M.A.; Schaefer, M.H. HIPPIE v2.0: Enhancing meaningfulness and reliability of protein-protein interaction networks. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, D408–D414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaefer, M.H.; Fontaine, J.F.; Vinayagam, A.; Porras, P.; Wanker, E.E.; Andrade-Navarro, M.A. HIPPIE: Integrating protein interaction networks with experiment based quality scores. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e31826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anyaegbunam, U.A.; More, P.; Fontaine, J.F.; Cate, V.T.; Bauer, K.; Distler, U.; Araldi, E.; Bindila, L.; Wild, P.; Andrade-Navarro, M.A. A Systematic Review of Lipid-Focused Cardiovascular Disease Research: Trends and Opportunities. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2023, 45, 9904–9916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aimo, L.; Liechti, R.; Hyka-Nouspikel, N.; Niknejad, A.; Gleizes, A.; Götz, L.; Kuznetsov, D.; David, F.P.; van der Goot, F.G.; Riezman, H.; et al. The SwissLipids knowledgebase for lipid biology. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 2860–2866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadby, G.; Giles, C.; Melton, P.E.; Huynh, K.; Mellett, N.A.; Duong, T.; Nguyen, A.; Cinel, M.; Smith, A.; Olshansky, G.; et al. Comprehensive genetic analysis of the human lipidome identifies loci associated with lipid homeostasis with links to coronary artery disease. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 3124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Bezwada, D.; Cai, F.; Harris, R.C.; Ko, B.; Sondhi, V.; Pan, C.; Vu, H.S.; Nguyen, P.T.; Faubert, B.; et al. Electron transport chain inhibition increases cellular dependence on purine transport and salvage. Cell Metab. 2024, 36, 1504–1520.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Chen, J.; Cheng, T.; Gindulyte, A.; He, J.; He, S.; Li, Q.; Shoemaker, B.A.; Thiessen, P.A.; Yu, B.; et al. PubChem 2023 update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, D1373–D1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alanis-Lobato, G.; Mier, P.; Andrade-Navarro, M.A. Manifold learning and maximum likelihood estimation for hyperbolic network embedding. Appl. Netw. Sci. 2016, 1, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alanis-Lobato, G.; Mier, P.; Andrade-Navarro, M.A. Efficient embedding of complex networks to hyperbolic space via their Laplacian. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 30108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadopoulos, F.; Aldecoa, R.; Krioukov, D. Network geometry inference using common neighbors. Phys. Rev. E Stat. Nonlinear Soft Matter Phys. 2015, 92, 022807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadopoulos, F.; Kitsak, M.; Serrano, M.Á.; Boguñá, M.; Krioukov, D. Popularity versus similarity in growing networks. Nature 2012, 489, 537–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krioukov, D.; Papadopoulos, F.; Kitsak, M.; Vahdat, A.; Boguñá, M. Hyperbolic geometry of complex networks. Physical review. E Stat. Nonlinear Soft Matter Phys. 2010, 82 Pt 2, 036106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuleshov, M.V.; Jones, M.R.; Rouillard, A.D.; Fernandez, N.F.; Duan, Q.; Wang, Z.; Koplev, S.; Jenkins, S.L.; Jagodnik, K.M.; Lachmann, A.; et al. Enrichr: A comprehensive gene set enrichment analysis web server 2016 update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, W90–W97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wishart, D.S.; Guo, A.; Oler, E.; Wang, F.; Anjum, A.; Peters, H.; Dizon, R.; Sayeeda, Z.; Tian, S.; Lee, B.L.; et al. HMDB 5.0: The Human Metabolome Database for 2022. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, D622–D631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GTEx Consortium. The Genotype-Tissue Expression (GTEx) project. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 580–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, J.C.; Lim, T.Y.; Park, J.S.; Hah, Y.S.; Park, N.; Hong, S.G.; Park, J.Y.; Yoon, T.J. SYT14L, especially its C2 domain, is involved in regulating melanocyte differentiation. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2013, 72, 246–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuboi, T.; McMahon, H.T.; Rutter, G.A. Mechanisms of dense core vesicle recapture following “kiss and run” (“cavicapture”) exocytosis in insulin-secreting cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 47115–47124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhlén, M.; Fagerberg, L.; Hallström, B.M.; Lindskog, C.; Oksvold, P.; Mardinoglu, A.; Sivertsson, Å.; Kampf, C.; Sjöstedt, E.; Asplund, A.; et al. Proteomics. Tissue-based map of the human proteome. Science 2015, 347, 1260419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinman, B.; Lachin, J.M.; Inzucchi, S.E. Empagliflozin, Cardiovascular Outcomes, and Mortality in Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 374, 1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prochaska, J.H.; Jünger, C.; Schulz, A.; Arnold, N.; Müller, F.; Heidorn, M.W.; Baumkötter, R.; Zahn, D.; Koeck, T.; Tröbs, S.O.; et al. Effects of empagliflozin on left ventricular diastolic function in addition to usual care in individuals with type 2 diabetes mellitus-results from the randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled EmDia trial. Clin. Res. Cardiol. Off. J. Ger. Card. Soc. 2023, 112, 911–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jünger, C.; Prochaska, J.H.; Gori, T.; Schulz, A.; Binder, H.; Daiber, A.; Koeck, T.; Rapp, S.; Lackner, K.J.; Münzel, T.; et al. Rationale and design of the effects of EMpagliflozin on left ventricular DIAstolic function in diabetes (EmDia) study. J. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 23, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, P.; Markiel, A.; Ozier, O.; Baliga, N.S.; Wang, J.T.; Ramage, D.; Amin, N.; Schwikowski, B.; Ideker, T. Cytoscape: A software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 2498–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anyaegbunam, U.A. Omint. Available online: https://github.com/uchealex/Omint (accessed on 24 March 2025).
- Jeon, J.; Han, E.Y.; Jung, I. MOPA: An integrative multi-omics pathway analysis method for measuring omics activity. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0278272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paczkowska, M.; Barenboim, J.; Sintupisut, N.; Fox, N.S.; Zhu, H.; Abd-Rabbo, D.; Mee, M.W.; Boutros, P.C.; PCAWG Drivers and Functional Interpretation Working Group; Reimand, J.; et al. Integrative pathway enrichment analysis of multivariate omics data. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slobodyanyuk, M.; Bahcheli, A.T.; Klein, Z.P.; Bayati, M.; Strug, L.J.; Reimand, J. Directional integration and pathway enrichment analysis for multi-omics data. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 5690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

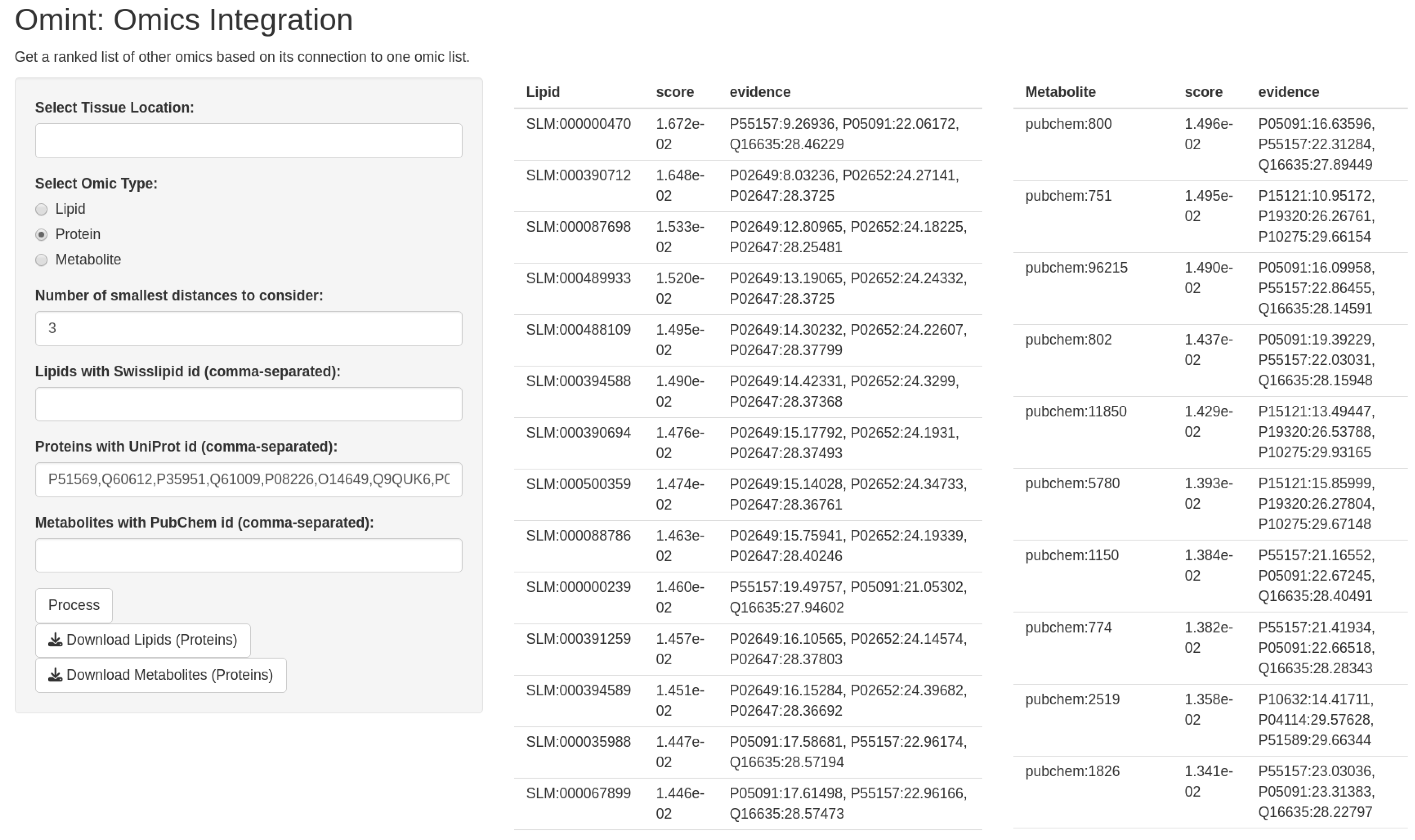
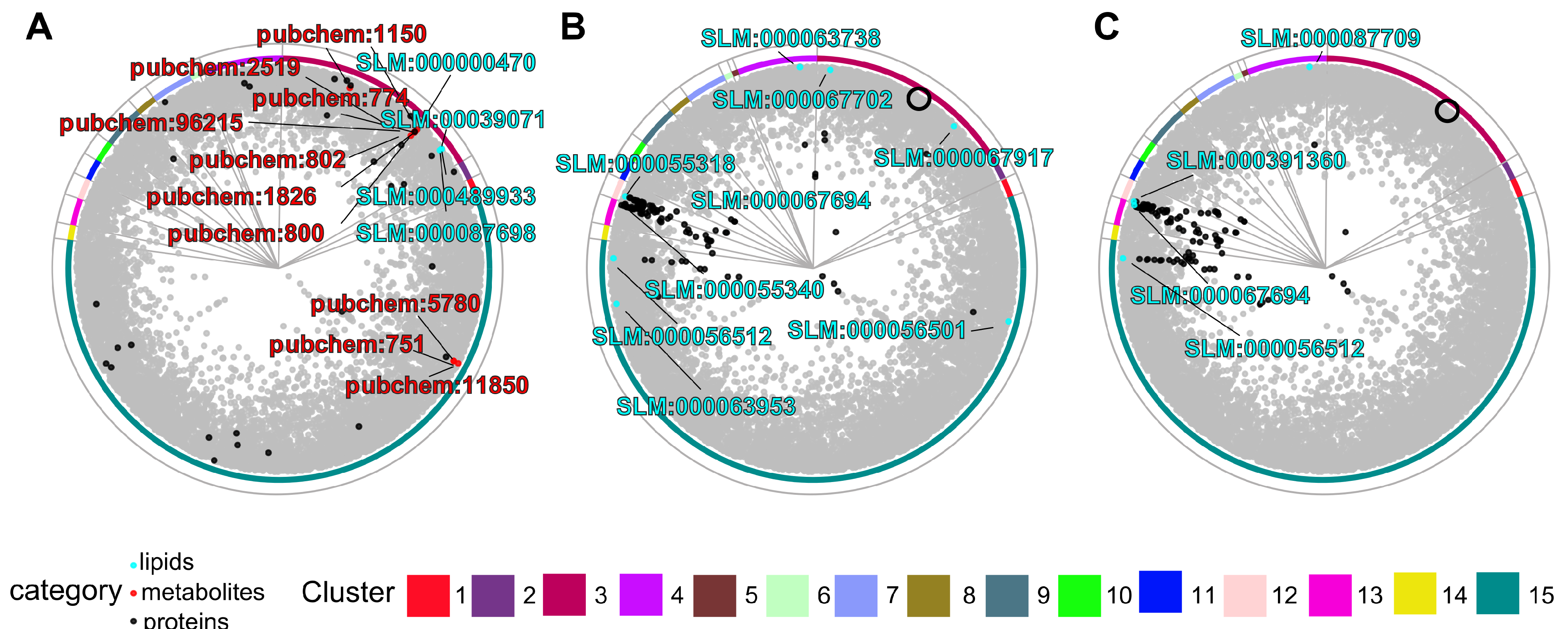
| Lipid | Score | Name | Number of Publications |
|---|---|---|---|
| SLM:000000470 | 0.01672 | Cholesterol esters | 184 |
| SLM:000390712 | 0.01648 | Sphingomyelin | 121 |
| SLM:000087698 | 0.01533 | Phosphatidylcholine | 295 |
| SLM:000489933 | 0.01520 | Ganglioside | 15 |
| Metabolite | Score | Name | Number of Publications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pubchem:800 | 0.01496 | Indoleacetaldehyde | 2 |
| Pubchem:751 | 0.01495 | Glyceraldehyde | 35 |
| Pubchem:96215 | 0.01490 | 4-imidazoleacetate | 1 |
| Pubchem:802 | 0.01437 | Indole-3-acetate | 24 |
| Pubchem:11850 | 0.01429 | Galactitol | 4 |
| Pubchem:5780 | 0.01393 | Sorbitol | 46 |
| Pubchem:1150 | 0.01384 | Tryptamine | 7 |
| Pubchem:774 | 0.01382 | Histamine | 166 |
| Pubchem:2519 | 0.01358 | Caffeine | 562 |
| Pubchem:1826 | 0.01341 | 5-hydroxyindoleacetate | 10 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Anyaegbunam, U.A.; Vagiona, A.-C.; ten Cate, V.; Bauer, K.; Schmidlin, T.; Distler, U.; Tenzer, S.; Araldi, E.; Bindila, L.; Wild, P.; et al. A Map of the Lipid–Metabolite–Protein Network to Aid Multi-Omics Integration. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 484. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15040484
Anyaegbunam UA, Vagiona A-C, ten Cate V, Bauer K, Schmidlin T, Distler U, Tenzer S, Araldi E, Bindila L, Wild P, et al. A Map of the Lipid–Metabolite–Protein Network to Aid Multi-Omics Integration. Biomolecules. 2025; 15(4):484. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15040484
Chicago/Turabian StyleAnyaegbunam, Uchenna Alex, Aimilia-Christina Vagiona, Vincent ten Cate, Katrin Bauer, Thierry Schmidlin, Ute Distler, Stefan Tenzer, Elisa Araldi, Laura Bindila, Philipp Wild, and et al. 2025. "A Map of the Lipid–Metabolite–Protein Network to Aid Multi-Omics Integration" Biomolecules 15, no. 4: 484. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15040484
APA StyleAnyaegbunam, U. A., Vagiona, A.-C., ten Cate, V., Bauer, K., Schmidlin, T., Distler, U., Tenzer, S., Araldi, E., Bindila, L., Wild, P., & Andrade-Navarro, M. A. (2025). A Map of the Lipid–Metabolite–Protein Network to Aid Multi-Omics Integration. Biomolecules, 15(4), 484. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15040484







