Abstract
With its increasing prevalence, metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) has emerged as a major global public health concern over the past few decades. Growing evidence has proposed the microbiota-derived metabolites short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) as a potential factor in the pathophysiology of MASLD and related metabolic conditions, such as obesity and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). By influencing key pathways involved in energy homeostasis, insulin sensitivity, and inflammation, SCFAs play an important role in gut microbiota composition, intestinal barrier function, immune modulation, and direct metabolic signaling. Furthermore, recent animal and human studies on therapeutic strategies targeting SCFAs demonstrate their potential for treating these metabolic disorders.
1. Introduction
Short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) are a group of saturated aliphatic acids with fewer than six carbon atoms, including acetate (C2), propionate (C3), and butyrate (C4) [1]. They are primarily produced through microbial fermentation of dietary fibers in the gut and play a crucial role in gut health, energy metabolism, and immune regulation [2,3]. SCFAs serve as key signaling molecules influencing host physiology by modulating inflammatory responses, maintaining intestinal barrier integrity, and regulating metabolic pathways [4]. Their impact extends beyond the gut, with emerging research linking SCFAs to systemic effects on metabolism, neurobiology, and chronic disease [5].
Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD), previously known as nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), is a spectrum of liver conditions characterized by excessive fat accumulation in the liver, ranging from simple hepatic steatosis to more severe forms, such as metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH), formerly termed nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), which can eventually lead to liver fibrosis, cirrhosis, and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) [6,7,8]. Furthermore, the recent change in nomenclature also led to a change in the definition of MASLD to include the presence of at least one of five cardiometabolic risk factors, namely (1) body mass index (BMI) ≥ 25 kg/m2 or waist circumference (WC) > 94 cm (male) or > 80 cm (female); (2) fasting serum glucose ≥ 100 mg/dL or HbA1C ≥ 5.7% or diagnosis of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) or treatment for T2DM; (3) blood pressure ≥ 130/85 mmHg or specific antihypertensive drug treatment; (4) plasma triglycerides ≥ 150 mg/dL or lipid-lowering treatment; and (5) plasma HDL-cholesterol ≤ 40 mg/dL (male) or ≤50 mg/dL (female) or lipid-lowering treatment [7,9,10,11].
Over the past few decades, MASLD has emerged as a major global public health concern, with its prevalence and annual direct medical costs steadily increasing [12,13,14]. A recent meta-analysis by Younossi et al. based on MASLD studies from 1990 to 2019 revealed that the global prevalence of MASLD increased by over 50% from 25.26% in 1990–2006 to 38.00% in 2016–2019 [12]. Similar but lower increases by 26% from 3.73% to 4.71% global prevalence were also reported in pediatric MASLD during the same time frame [13]. Moreover, MASLD has become a major cause of chronic liver disease (CLD), with approximately one-quarter of subjects with simple steatosis progressing to MASH, and again, more than a quarter of those developing severe fibrosis [15,16,17,18]. From 2016 to 2019, CLD moved from being the twelfth leading cause of death to the tenth leading cause of death [19].
In recent years, the human microbiome and the gut–liver axis have also come into focus in scientific research, with studies suggesting the involvement of short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), a product of bacterial fermentation in the gut, in various cellular processes [20,21].
In this context, this review aims to provide detailed information on MASLD and SCFAs in general, as well as their role in MASLD and other metabolic diseases associated with MASLD.
2. Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease
2.1. Pathogenesis and Progression of Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease
The pathogenesis of MASLD is complex and involves an interplay of multiple factors, supporting a “multiple-parallel hit” model [22,23,24,25,26]. Key aspects of MASLD pathogenesis include lipid accumulation and insulin resistance. Insulin resistance reduces glucose uptake by muscle and adipose tissue, leading to peripheral lipolysis, which in turn raises the liver’s exposure to both glucose and free fatty acids. Likewise, excessive caloric intake results in higher levels of free fatty acids in the bloodstream, leading to increased ectopic fat accumulation, including in hepatocytes [23,25]. Free fatty acids are not only stored in the liver in the form of triglycerides but can also directly generate oxidative stress and activate inflammatory pathways in the liver. High levels of free fatty acids overload the mitochondria, where β-oxidation normally takes place, thus leading to the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS). These ROS drive oxidative stress, trigger inflammatory pathways, and cause mitochondrial damage, which reduces the proliferation rate of hepatocytes, resulting in reduced endogenous liver repair [27]. Further, hyperinsulinemia and hyperlipidemia can trigger endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress, activating pathways that lead to inflammation and apoptosis [28]. Additionally, damaged hepatocytes release extracellular vesicles, inflammatory cytokines, and damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs), activating Kupffer cells and promoting inflammation [25,27]. Another important aspect in the pathogenesis of MASLD is gut microbiota dysbiosis, or a microbial imbalance with reduced concentrations of beneficial microbes and an increased abundance of potentially pathogenic microbes [21,29,30]. Dysbiosis contributes to the development of MASLD by disrupting gut–liver homeostasis. This includes compromising the gut barrier, facilitating the portal transport of microbial products including lipopolysaccharides (LPS) to the liver, altering bile acid (BA) profiles, and reducing short-chain fatty acid (SCFA) levels [31,32]. Aside from environmental and other factors, genetic predisposition plays a role in the pathogenesis of MASLD. A twin study revealed that both hepatic steatosis and hepatic fibrosis in MASLD are heritable traits [33]. For example, variations in genes related to hepatic lipid metabolism, such as patatin-like phospholipase domain-containing protein 3 (PNPLA3), transmembrane 6 superfamily member 2 (TM6SF2), membrane-bound O-acyltransferase domain-containing protein 7 (MBOAT7), and glucokinase regulatory protein (GCKR), are associated with increased susceptibility to MASLD [34].
2.2. Metabolic Comorbidities Associated with Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease
MASLD is closely associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD), with evidence linking it to both fatal and non-fatal cardiovascular events [35,36,37]. A meta-analysis from 2016 including 16 studies revealed that individuals with MASLD had a 64% higher risk of experiencing cardiovascular events, whether fatal or non-fatal, compared with those without the disease. Further, more severe forms of MASLD were associated with an even greater risk [35]. Additionally, MASLD has been linked to several markers of subclinical atherosclerosis, including increased carotid artery intimal-medial thickness, reduced flow-mediated vasodilation, and increased coronary artery calcification, suggesting a heightened burden of early-stage cardiovascular damage [38]. Additional studies have also found a higher prevalence of clinically manifest CVD, including high-risk coronary plaques (59.3% in patients with MASLD vs. 19.0% in patients without MASLD), in patients with MASLD, independent of traditional CVD risk factors [39,40,41]. As a result, MASLD is now recognized as a significant risk factor for major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE), which are the leading cause of mortality in affected individuals [42,43].
The relationship between type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) and MASLD, including MASH, has recently been described as bidirectional and is increasingly recognized as a critical aspect of their pathophysiology [44,45,46,47]. Hence, T2DM not only accelerates the progression of MASLD, but MASLD also heightens the risk of developing T2DM and worsens glycemic control in individuals already diagnosed with the disease [45,46]. A recent globally representative meta-analysis involving nearly 50,000 patients revealed that the prevalence of MASLD among those with T2DM was over two times higher than in the general population (55.5%), with rates of MASH and advanced fibrosis reaching 37.3% and 17%, respectively [48]. Also, T2DM was shown to be a significant risk factor for the development of severe hepatic complications, such as cirrhosis and liver-related mortality [46,49]. Patients with MASH, on the other hand, had a two times higher risk of developing T2DM, and the severity of hepatic steatosis and liver fibrosis was shown to correlate with an increased risk of developing T2DM [50]. Lastly, a study by Sung et al. evaluating the combined influence of insulin resistance, obesity, and MASLD on the risk of T2DM showed a 14-fold increased risk of T2DM when all three factors were present simultaneously [51].
Another major contributor to the development and progression of MASLD is obesity. The relationship between obesity and MASLD is largely mediated by excess adiposity, which promotes hepatic fat accumulation and insulin resistance. Diet plays a critical role in this process, with high consumption of sugary foods, refined carbohydrates, and caloric excess being key drivers of hepatic steatosis [52,53]. Recent studies have shown that MASLD is present in about 75% of individuals with overweight and obesity [54].
Furthermore, MASLD is associated with an increased risk of HCC and various extrahepatic cancers [37,55]. A comprehensive meta-analysis of 10 cohort studies involving more than 180,000 individuals and approximately 8500 incident cases of extrahepatic cancers demonstrated that MASLD significantly raises the risk of developing several types of cancer, including thyroid cancer, gastrointestinal cancers, and cancers in other systems [56].
2.3. Therapeutic Management of Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease
Therapeutic strategies for managing MASLD, as well as MASH, focus on addressing both lifestyle factors and pharmacological targets. Weight loss through lifestyle modification is a cornerstone of treatment, with reductions in body weight of more than 10% resulting in a 100% improvement in steatosis, a 90% resolution of MASH, and the reversal of liver fibrosis by at least one stage in 81% of individuals [57,58]. Additionally, weight loss interventions such as bariatric surgery, endoscopic bariatric interventions, and anti-obesity drugs have been shown to improve MASLD [59,60]. Pharmacological treatments for MASLD include insulin sensitizers, such as pioglitazone and metformin; lipid-lowering agents, such as statins and ezetimibe; antioxidants; and medications aimed at modulating liver fat metabolism and inflammation (e.g., aramchol, elafibranor, and obeticholic acid) [61].
Further, glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1RAs), including both short-acting (e.g., exenatide) and long-acting (e.g., liraglutide, semaglutide) formulations, are emerging as effective therapies for MASLD and MASH. These incretin mimetics work by activating GLP-1 receptors, which are widely expressed on various cell types throughout the body, including hepatocytes [62,63,64]. Central GLP-1 receptor activation in regions of the hypothalamus and brainstem promotes satiety and reduces appetite, facilitating weight loss [65,66]. Beyond their central effects, GLP-1RAs directly influence the lipid metabolism by oxidizing fatty acids and reducing their influx into hepatocytes, thereby mitigating hepatic fat accumulation and improving liver lipid metabolism [67,68,69,70]. Furthermore, GLP-1RAs have been shown to reduce lipotoxicity and the lipid stress response in hepatocytes, ultimately preventing or delaying the progression of MASLD [71]. GLP-1RAs have demonstrated efficacy in reversing steatohepatitis and improving liver biochemistry, and there are indications that some might even improve fibrosis [72]. However, semaglutide does not improve MASH-related cirrhosis [73]. Moreover, combination therapies, such as semaglutide with cilofexor and/or firsocostat and semaglutide with cagrilintide, have shown promising results in enhancing improvements in liver steatosis and non-invasive tests of fibrosis. Combination therapies furthermore resulted in greater weight reduction and glycemic control compared with semaglutide monotherapy [74,75]. Furthermore, tirzepatide, a novel GLP-1 and glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) receptor agonist used for treating T2DM and promoting weight loss, showed promising effects in patients with MASH and stage 2–3 fibrosis in a recent phase 2 trial [76].
In March 2024, resmetirom (MGL-3196), a liver-directed selective thyroid hormone receptor beta (THR-β) agonist, received accelerated approval in the United States for the treatment of adults with MASH and stage 2 or 3 fibrosis and is to date the only drug approved by the Food and Drug Administration for a subset of MASLD [77]. Since thyroid hormones regulate many processes in the hepatic lipid and cholesterol metabolism, MASLD is thought to arise from a state of hepatic hypothyroidism characterized by diminished thyroid hormone levels in the liver [78]. By selectively targeting THR-β, a receptor highly expressed in the liver and crucial for regulating lipid metabolism and inflammation, resmetirom addresses this pathophysiological abnormality. Resmetirom modulates genes involved in lipid metabolism, enhancing hepatic fat oxidation, reducing lipotoxicity, and thereby decreasing hepatic fat accumulation and inflammation [79,80,81]. In a recent phase 3 trial, patients treated with 80–100 mg resmetirom daily for 52 weeks showed MASH resolution without worsening of fibrosis in 25.9–29.9% of cases, compared with 9.7% in the placebo group, as well as fibrosis improvement by at least one stage without NAS worsening in 24.2–25.9%, as compared with 14.2% in the placebo group [82]. Notably, resmetirom has 28-fold selectivity for THR-β over THR-α, which may help prevent the adverse systemic effects of thyroid hormone excess, such as those on the heart and bones, which are mediated primarily by THR-α [83,84].
3. Short-Chain Fatty Acids in Metabolic Disease
3.1. Short-Chain Fatty Acids
Short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) are key metabolites produced by the gut microbiota during the fermentation of dietary fiber and proteins, primarily in the cecum and proximal colon, but can also be produced by bacteria of the skin and vagina [85,86]. Bacteria involved in the production of SCFAs include Clostridial clusters IV and XIVa of Firmicutes, encompassing genera such as Eubacterium, Roseburia, Faecalibacterium, and Coprococcus [87,88,89]. SCFAs are organic compounds with a carboxyl group (COOH) bound to a short carbon chain of between one and five atoms and include formate (C1), acetate (C2), propionate (C3), butyrate (C4), and valerate (C5) [1,86,90]. The most abundant SCFAs—acetate (C2H4O2), propionate (C3H6O2), and butyrate (C4H8O2)—account for approximately 95% of SCFAs in the body. Of this 95%, acetate makes up 60%, while propionate and butyrate each account for 20% on average in the healthy adult population [91,92]. They exert a wide range of beneficial effects on human health [85,93]. These include anti-inflammatory, immunoregulatory, anti-obesity, anti-diabetes, and neuroprotective properties, alongside potential cardiovascular and hepatoprotective roles [85]. SCFAs influence gene expression and cellular processes through multiple mechanisms, notably by activating G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) such as the free fatty acid receptors (FFARs) FFAR3 (GPR41) and FFAR2 (GPR43), which are expressed on epithelial cells, immune cells, and adipose tissue [94]. Additionally, SCFAs, particularly butyrate, inhibit histone deacetylases, leading to enhanced histone acetylation and modulation of gene expression [5,95,96,97,98,99,100]. This results in potential biological functions such as inhibiting the growth of pathogens, stimulating water and sodium absorption, decreasing colonic pH, and providing energy to colonic epithelial cells [87,88,89]. These actions contribute to the regulation of immune responses, intestinal barrier function, and metabolism, with implications for conditions such as obesity, insulin resistance, and inflammatory bowel diseases. Furthermore, SCFAs may influence appetite regulation and energy homeostasis [5,20,98,101].
3.2. Short-Chain Fatty Acid-Producing Bacteria
SCFAs are primarily produced by anaerobic bacteria in the large intestine through the fermentation of indigestible dietary fibers and resistant starches [102,103]. Throughout the human life cycle, the gut microbiome undergoes substantial changes that impact both the production and diversity of SCFAs. As individuals transition through different life stages, dietary changes—such as the shift from breastfeeding to solid foods—alter the types and amounts of substrates accessible to SCFA-producing bacteria. These dietary modifications play a crucial role in shaping the composition of the microbiota and, consequently, its metabolic outputs [104]. In early life (0–3 years), for instance, the microbiota is characterized by low diversity and primarily dominated by Enterobacteriaceae, which gradually shifts toward Bifidobacteriaceae as the child grows [105,106,107]. Following the transition to solid foods, microbial diversity as well as the abundance of Firmicutes increases, reflecting the dietary shift towards more complex carbohydrates [104,105,108]. In the elderly, however, the microbiota shifts again, with Enterobacteriaceae becoming more prevalent [109]. These dynamic changes in the microbiome are mirrored in SCFA production, with varying concentrations of acetate, propionate, and butyrate [106].
Acetate, the most abundant SCFA, accounts for nearly 60% of all SCFAs in the human body and is produced by a variety of gut bacteria, with significant implications for host health (Figure 1). The primary acetate-producing bacteria span several phyla, including Bacteroidetes (e.g., Bacteroides and Prevotella species), Actinobacteria (e.g., Bifidobacterium species), Verrucomicrobia (e.g., Akkermansia muciniphila), and Firmicutes (e.g., Ruminococcus species) [110,111,112]. Among these, Bifidobacterium species, particularly B. bifidum, B. infantis, and B. breve, are especially prominent in early life, where they dominate the infant gut microbiota and produce acetate through the bifid-shunt pathway [111,113]. This pathway, unique to Bifidobacteria, is centered around the key enzyme fructose-6-phosphate phosphoketolase and involves the fermentation of various carbohydrates, including resistant starches, polysaccharides, and simple sugars, including human milk oligosaccharides [114]. Moreover, acetate can be produced by bacteria through several additional pathways, which often coexist within the same microorganism. The two main pathways in the production of acetate include the acetate kinase-phosphotransacetylase (AckA-Pta) pathway and the pyruvate:menaquinone oxidoreductase (PoxB/CidC) pathway [112,115,116] (Figure 1). The capacity to generate acetate through various pathways allows the microbiota to adjust to fluctuating environmental conditions and helps to maintain metabolic flexibility [117]. In addition to its role in energy production, acetate plays an important role in maintaining gut health by protecting against infections such as Escherichia coli (E. coli) and promoting the growth of other SCFA-producing bacteria and thus contributing to gut microbiota diversity and stability [118,119,120,121].
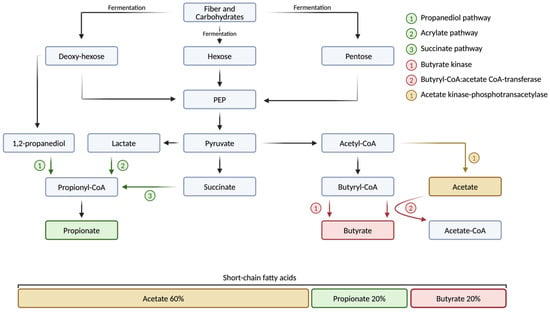
Figure 1.
Production of short-chain fatty acids by the human gut microbiota. Dietary fiber and complex carbohydrates, which are indigestible by the human gut, are fermented by the gut microbiota and broken down into monosaccharides, such as hexoses and pentoses. These monosaccharides are further processed through various metabolic pathways. The production of acetate involves the enzymes acetate kinase and phosphotransacetylase, which convert acetyl-CoA into acetyl phosphate, ultimately leading to acetate. The primary pathways for propionate production include the propanediol, acrylate, and succinate pathways. In the production of butyrate, key enzymes such as butyrate kinase and butyryl-CoA:acetate CoA-transferase play crucial roles. Acetate, propionate, and butyrate are the three most abundant short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) in the human body, collectively accounting for 95% of all SCFAs. Of this 95%, acetate makes up 60%, while propionate and butyrate each account for 20% on average in healthy adults. Acetate-CoA, acetate coenzyme A; acetyl-CoA, acetyl coenzyme A; butyryl-CoA, butyryl coenzyme A; PEP, phosphoenol-pyruvate; propionyl-CoA, propionyl coenzyme A. Created with a license from BioRender.com (accessed on 5 March 2025).
Similar to acetate, propionate is produced by a variety of gut bacteria, with production levels increasing after the cessation of breastfeeding and the introduction of a more diverse diet [122]. In adults, propionate makes up about 20% of SCFAs in the human gut microbiome (Figure 1). Key propionate-producing bacteria are found across multiple phyla, including Bacteroidetes (e.g., Bacteroides and Prevotella species), Firmicutes (e.g., the Lachnospiraceae family, Ruminococcus obeum, Coprococcus cactus, and Veillonella parvula), Verrucomicrobia (e.g., Akkermansia muciniphila), and Negativicutes (e.g., Megasphaera elsdenii) [123,124,125]. Propionate is produced through three primary metabolic pathways: the succinate pathway, employed by Bacteroidetes and some Firmicutes to convert succinate to propionate; the acrylate pathway, used by bacteria such as Coprococcus cactus to convert lactate into propionate; and the propanediol pathway, which involves bacteria such as Ruminococcus obeum that ferment fucose to produce propionate [123,124,125,126,127,128] (Figure 1). While the production of propionate is influenced by several factors, including the availability of substrates and the structure and diversity of the gut microbiome, the consumption of prebiotic fibers such as beta-glucan has also been shown to stimulate propionate production [129,130].
Butyrate is predominantly produced by anaerobic bacteria within the Firmicutes phylum, including key species such as Faecalibacterium prausnitzii, Eubacterium rectale, Eubacterium hallii, Roseburia species, Clostridium butyricum, Coprococcus species, and Anaerostipes species [131,132,133]. In this, Faecalibacterium prausnitzii, which belongs to the Ruminococcaceae family, is one of the most abundant butyrate-producing bacteria, comprising about 5% of the gut microbiome [134]. In addition, some members of other phyla such as Actinobacteria, Bacteroidetes, Fusobacteria, and Proteobacteria are also capable of producing butyrate [132]. While butyrate production in the gut occurs through several pathways, the primary route for butyrate production is the acetyl-CoA pathway, which involves two enzymes, butyryl-CoA:acetate CoA-transferase and butyrate kinase [135,136,137] (Figure 1). In this context, lactate and acetate, both byproducts of fermenting dietary fibers and resistant starches, serve as substrates for microbial communities, where they are further processed and ultimately converted into butyrate [138] (Figure 1). Butyrate plays a key role in maintaining an anaerobic gut environment, which helps to prevent the establishment of harmful pathogens including Salmonella and E. coli [131,132,139]. Furthermore, butyrate provides energy for colonocytes and supports the intestinal barrier by increasing tight junction proteins and mucin 2, a glycoprotein in the intestinal mucus layer [140]. Additionally, butyrate’s beneficial effects on metabolic health have been demonstrated in studies where capsaicin supplementation increased the abundance of butyrate-producing bacteria in mice, leading to lower metabolic endotoxemia and reduced body weight gain [141].
Interactions between SCFA-producing bacteria in the gut play a crucial role in shaping microbial communities and enhancing metabolic functions. One of the most significant interactions is cross-feeding, where the production of one SCFA supports the growth of bacteria that produce other SCFAs. For example, acetate produced by Bifidobacterium supports the growth of propionate and butyrate producers, while butyrate, in turn, promotes the growth of Bifidobacterium species [119]. Lactate produced by Bifidobacterium, on the other hand, can be used by bacteria such as Eubacterium hallii and Anaerostipes caccae to produce butyrate and propionate [125]. Additionally, certain bacterial species engage in cooperative metabolism, such as Roseburia and acetogenic species, which collaborate to produce butyrate in the absence of hydrogen [142]. Furthermore, some fibers act as prebiotics, selectively stimulating beneficial bacteria. The fermentation of fibers and resistant starches also lowers gut pH, which affects microbial composition and favors the growth of butyrate-producing bacteria [102]. A recent animal study further demonstrated that prolonged feeding of a high-fat diet resulted in a reduction of bile acid levels, disrupting gut microbiota balance and ultimately contributing to metabolic disorders and obesity [143].
3.3. The Role of Short-Chain Fatty Acids in Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease
SCFAs play a crucial role in the pathophysiology and potential treatment of MASLD. A recent clinical study involving over 100 individuals, both with and without MASLD, demonstrated significant alterations in gut microbiota composition in the MASLD cohort, with a marked decrease in bacterial richness compared with healthy controls. Namely, four bacterial genera—Faecalibacterium, Subdoligranulum, Haemophilus, and Roseburia—were notably reduced across all three MASLD subtypes (mild, moderate, and severe), suggesting a consistent microbial dysbiosis in MASLD. Additionally, SCFAs, including acetic acid and butyric acid, were significantly lower in MASLD patients across all stages, with more pronounced reductions observed in moderate-to-severe cases [144]. In line with these findings, other studies showed a decrease in SCFAs in subjects with MASLD compared with healthy controls [145,146]. Further, a recent clinical trial involving patients with liver steatosis and metabolic disease showed that supplementation of a butyrate-based formula significantly improved liver parameters, such as cholesterol, triglycerides, or gamma-glutamyl transferase, compared with baseline parameters [147] (Table 1). SCFAs influence MASLD pathophysiology through various mechanisms. SCFAs regulate hepatic metabolism by suppressing hepatic gluconeogenesis and lipogenesis, enhancing hepatic uptake of cholesterol, and increasing leptin secretion [148,149,150,151,152,153] (Figure 2). SCFAs also play a role in the regulation of the immune system. Through binding to FFARs, SCFAs regulate the production and release of anti- and pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines [154,155,156]. Further mechanisms influencing the inflammatory response include the inhibition of histone deacetylases (HDACs) and the activation of nuclear factor kappa β (NF-κB) in macrophages by butyrate, the production of transforming growth factor beta 1 (TGFβ1), and the reduction of the luminal pH [148,157,158,159,160]. Moreover, SCFAs, in particular butyrate, maintain the homeostasis of the gut barrier and the integrity of gut mucosa by increasing tight junctions, such as claudin-1, claudin-7, zonula occludens-1 (ZO-1), ZO-2, and occludin [161,162,163] (Figure 2). Mucin 2 is the most abundant glycoprotein in the intestinal mucus layer and plays a role in liver disease [164,165]. Butyrate increases the production of mucin 2, strengthening the intestinal mucus layer and preventing toxic substances and inflammatory mediators from entering the bloodstream and finally the liver [148,166,167,168,169] (Figure 2). In recent animal studies investigating the MASH phenotype, administration of SCFAs resulted in a reduction of liver steatosis in diet-induced steatohepatitis [166,170,171]. In humans, vinegar, which is rich in acetate, has been shown to reduce BMI, visceral fat, and serum triglyceride levels [172].

Table 1.
Clinical trials of SCFA supplementation in metabolic diseases (selected articles).
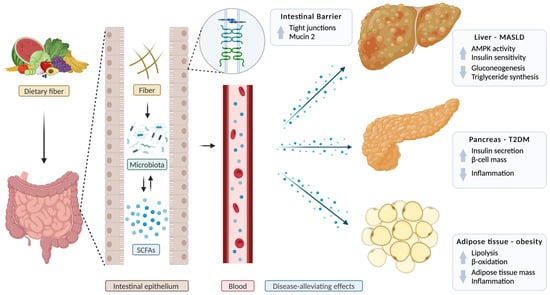
Figure 2.
Short-chain fatty acids in metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease, type 2 diabetes mellitus, and obesity. Short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), produced by the gut microbiota from dietary fiber, are transported through the bloodstream to various organs or directly act on the intestinal epithelium. They improve intestinal barrier function by increasing the expression of tight-junction proteins such as claudin-1, claudin-7, zonula occludens-1, zonula occludens-2, and occludin, and by strengthening the intestinal mucus layer by increasing mucin 2 secretion. In the liver, SCFAs improve metabolic dysfunction-associated liver disease (MASLD) by activating 5′ adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK), a key enzyme that regulates liver metabolism, enhancing insulin sensitivity, reducing gluconeogenesis, and inhibiting fat production. In the pancreas, SCFAs boost insulin secretion, promote β-cell expansion, and reduce inflammation, all of which contribute to the prevention of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). In adipose tissue, SCFAs reduce inflammation and decrease fat mass by upregulating lipolysis and β-oxidation, thereby helping to alleviate obesity. AMPK, 5′ adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase; SCFA, short-chain fatty acids. Created with a license from BioRender.com (accessed on 5 March 2025).
3.4. The Role of Short-Chain Fatty Acids in Obesity
SCFAs play a complex and dual role in the context of obesity, with both protective and potentially adverse effects reported in various studies [179]. On the one hand, SCFAs help prevent obesity through multiple mechanisms, including appetite regulation, modulation of lipid and glucose metabolism, and the enhancement of fat oxidation [180,181] (Figure 2). Thus, dietary SCFA supplementation in diet-induced obese mouse models has been shown to increase triglyceride hydrolysis and promote fatty acid oxidation in adipose tissue, contributing to weight management (Figure 2). Additionally, SCFAs stimulate beige adipogenesis, mitochondrial biogenesis, and reduce chronic inflammation, all of which are key processes in obesity prevention [181,182,183,184] (Figure 2). However, excess SCFA production may also contribute to obesity by increasing energy absorption, potentially promoting weight gain [185,186,187]. Furthermore, a human study involving 60 patients with obesity demonstrated that supplementation with 10 g/day of inulin-propionate significantly stimulated postprandial secretion of the satiety hormones peptide YY (PYY) and glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) compared with inulin controls. This supplementation also non-significantly reduced weight gain and increased weight loss. Additionally, treatment with inulin-propionate significantly decreased intrahepatocellular lipid content, measured using magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS), from 22.1% pre-intervention to 15.9% post-intervention in patients with obesity and MASLD [173] (Table 1). Moreover, supplementation with sodium butyrate reduced fat mass (p = 0.027), in particular visceral fat (p = 0.026), and increased fat-free mass (p = 0.032) in adults with obesity [174] (Table 1). In another clinical trial, oral supplementation of butyrate in both healthy individuals and patients with metabolic syndrome was shown to affect immune response. Specifically, it reduced the training capacity of monocytes induced by β-glucan and oxidized low-density lipoprotein [175] (Table 1). Similarly, studies in pediatric patients with obesity showed a significant decrease in BMI by 2.26, BMI z-score by 0.31, waist circumference (−5.07 cm), and insulin level (−5.41 μU/mL) when treated with sodium butyrate for 6 months, compared with the placebo-treated group [176] (Table 1). SCFAs may stimulate the release of gut-derived satiety hormones, such as PYY and GLP-1, by binding to the FFAR2 and FFAR3 receptors or directly inhibiting HDAC [188,189]. These hormones influence appetite regulation through several mechanisms: they activate proopiomelanocortin (POMC) neurons in the hypothalamus, suppress neuropeptide Y (NPY), and delay gastric emptying [190,191]. However, the relationship between SCFAs and obesity is not straightforward. Some studies report higher fecal SCFA concentrations in obese individuals, while others show lower levels, indicating a more complex interaction [179,192,193]. De la Cuesta-Zuluaga et al. found a correlation between increased fecal SCFA levels and obesity, metabolic dysregulation, and other comorbidities, while Müller et al. reported that circulating, rather than fecal, SCFAs are associated with metabolic health [194]. Furthermore, obesity is often associated with reduced microbial diversity and dysbiosis, as well as a decline in SCFAs and SCFA-producing bacteria [192]. In obese humans, a diverse microbiota and a high Akkermansia muciniphila abundance were linked to the healthiest metabolic status [195]. In an animal model, Ley et al. furthermore demonstrated a reduction in the abundance of Bacteroidetes and an increase in Firmicutes in obese ob/ob mice compared with lean control mice, highlighting an imbalance in the gut microbiota [196,197]. In another animal study, Cani et al. demonstrated that mice on high-fat diet (HFD) exhibited a decrease in Bifidobacterium spp., leading to increased endotoxemia and elevated proinflammatory cytokines [198]. However, excess SCFA production may also contribute to obesity by increasing energy absorption, potentially promoting weight gain [185,186,187]. However, supplementation with SCFAs led to significant alterations in gut microbiota composition, including a reduced Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes ratio [181], which can be viewed as a positive effect, as the Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes ratio is frequently high in obese mice, as stated above [196]. SCFA treatment can also reduce opportunistic pathogen concentrations in vitro and in vivo, such as Clostridioides difficile, E. coli, Salmonella enterica, or Klebsiella pneumoniae, among others [199,200]. On the other hand, treatment with SCFAs can also decrease the relative abundance of SCFA-producing microbes (e.g., Odoribacter, Rikenella) in mice despite the beneficial effects of the SCFA treatment itself [181]. SCFAs influence obesity-related processes through various pathways, including inducing a switch from lipid synthesis to utilization by decreasing peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARγ) expression and activity, activation of 5′ adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK) to stimulate oxidative metabolism, and the reduction of cholesterol levels [152,192,201] (Figure 2). Moreover, Sanna et al. demonstrated in a clinical study involving nearly 1000 individuals that increased gut production of butyrate is correlated with improved insulin sensitivity [202]. As mentioned previously, SCFAs exert their functions by activating FFARs. Consistent with this, FFAR2-deficient mice on a normal diet gained weight, whereas FFAR2-overexpressing mice remained lean despite being fed a high-fat diet [203]. However, butyrate and propionate administration in FFAR3-deficient mice still resulted in decreased food intake and body weight [204].
3.5. The Role of Short-Chain Fatty Acids in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is associated with alterations in gut microbiota composition, specifically a decrease in butyrate-producing bacteria, leading to reduced SCFA production. This dysbiosis may contribute to the development and progression of T2DM by impairing key metabolic processes [205,206,207,208,209]. SCFAs, particularly butyrate, play a critical role in improving glucose homeostasis by enhancing insulin sensitivity, reducing fasting insulin concentrations, promoting glucose uptake, and reducing hepatic glucose production [210,211,212] (Figure 2). In a mouse model assessing the impact of acetic acid on glucose regulation, acetic acid-treated mice exhibited lower fasting plasma glucose and HbA1c levels compared with control mice. This effect is associated with the activation of AMPK in the liver by acetate. AMPK, an energy-sensing enzyme in the liver, plays a key role in glucose homeostasis by regulating diverse metabolic processes, such as the expression of glucose transporter protein-4 (GLUT4) [151,213,214,215]. Despite its limitations by low palatability and unpleasant odor, animal as well as human studies have shown that butyrate supplementation improves insulin sensitivity, reduces diastolic blood pressure, and increases energy consumption, which may aid in managing obesity, a key risk factor for T2DM [177,210,216]. Furthermore, SCFAs have anti-inflammatory properties that help mitigate the chronic low-grade inflammation often seen in T2DM, a key driver of insulin resistance [206] (Figure 2). Additionally, SCFAs stimulate the secretion of GLP-1 and PYY, which are known for their role in insulin secretion, inhibition of glucagon secretion in the pancreas, and appetite suppression, by binding to GPRs in the gut [173,177,207]. SCFAs act by binding to the FFAR2 receptor on the surface of pancreatic β-cells, which triggers a signaling cascade that enhances insulin secretion and promotes the expansion of β-cell mass, potentially contributing to a long-term improvement in insulin sensitivity [217] (Figure 2). Recent findings also suggest that SCFAs, which are elevated in individuals with better glucose control, may represent a promising target for T2DM prevention and treatment [211]. Thus, a human study involving 60 patients with T2DM showed that treatment with sodium butyrate and inulin resulted in a decrease in fasting blood sugar in comparison with the placebo group (p = 0.049) [177] (Table 1). In another recent randomized clinical trial, Khosravi et al. reported decreased postprandial blood sugar levels (p = 0.016), as well as increased insulin levels (p = 0.047) and homeostatic model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) (p = 0.008) in patients with T2DM treated with sodium butyrate compared to baseline [178] (Table 1).
4. Conclusions
In conclusion, SCFAs play an important role in the regulation of metabolic health. Through their effects on gut microbiota composition, intestinal barrier function, immune modulation, and direct metabolic signaling, SCFAs influence key pathways involved in energy homeostasis, insulin sensitivity, and inflammation. Furthermore, dysregulation of SCFA production and composition of the gut microbiome has been linked to the pathogenesis of metabolic diseases, such as MASLD, obesity, and T2DM. Therapeutic approaches involving SCFAs hold promise for the treatment of those metabolic conditions. However, despite promising preclinical and some clinical evidence, significant gaps remain in our understanding. The mechanisms underlying SCFA effects require further investigation, as does the optimal strategy for increasing SCFA levels—whether through dietary fiber, probiotics, or direct supplementation—particularly in terms of long-term safety and efficacy. Thus, additional human trials are needed to establish effective dosages, potential side effects, and interactions with existing treatments.
Author Contributions
E.M. was responsible for writing the manuscript; P.H. edited the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by National Institutes of Health (NIH) grant K12 HD105271, University of California San Diego Altman Clinical and Translational Research Institute (ACTRI)/NIH grant KL2TR001444, and Pinnacle Research Award in Liver Diseases Grant #PNC22-159963 from the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases Foundation (to P.H.) and services provided by NIH center P30 DK120515. E.M. was supported by a scholarship from the German Society for Gastroenterology, Digestive and Metabolic Diseases (DGVS).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
No new data were created or analyzed in this study.
Conflicts of Interest
P.H.’s institution, UCSD, has received grant support from Nterica Bio.
Abbreviations
BMI, body mass index; CLD, chronic liver disease; CVD, cardiovascular disease; FFAR, free fatty acid receptors; GLP-1RA, glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist; GPCR, G-protein-coupled receptor; HCC, hepatocellular carcinoma; MACE, major adverse cardiovascular events; MASH, metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis; MASLD, metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease; NAFLD, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease; NAS, NAFLD activity score; ROS, reactive oxygen species; SCFA, short-chain fatty acid; T2DM, type 2 diabetes mellitus; THR, thyroid hormone receptor.
References
- Chen, X.-F.; Chen, X.; Tang, X. Short-chain fatty acid, acylation and cardiovascular diseases. Clin. Sci. 2020, 134, 657–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.H. Complex regulatory effects of gut microbial short-chain fatty acids on immune tolerance and autoimmunity. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2023, 20, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.-F.; Shao, J.-H.; Liao, Y.-T.; Wang, L.-N.; Jia, Y.; Dong, P.-J.; Liu, Z.-Z.; He, D.-D.; Li, C.; Zhang, X. Regulation of short-chain fatty acids in the immune system. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1186892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Lu, Y.; Xue, G.; Han, L.; Jia, H.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Liu, P.; Yang, C.; Zhou, Y. Role of short-chain fatty acids in host physiology. Anim. Model. Exp. Med. 2024, 7, 641–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.; McKenzie, C.; Potamitis, M.; Thorburn, A.N.; Mackay, C.R.; Macia, L. The role of short-chain fatty acids in health and disease. Adv. Immunol. 2014, 121, 91–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinella, M.E. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A systematic review. JAMA 2015, 313, 2263–2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinella, M.E.; Lazarus, J.V.; Ratziu, V.; Francque, S.M.; Sanyal, A.J.; Kanwal, F.; Romero, D.; Abdelmalek, M.F.; Anstee, Q.M.; Arab, J.P.; et al. A multisociety Delphi consensus statement on new fatty liver disease nomenclature. Hepatology 2023, 78, 1966–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunt, E.M.; Wong, V.W.-S.; Nobili, V.; Day, C.P.; Sookoian, S.; Maher, J.J.; Bugianesi, E.; Sirlin, C.B.; Neuschwander-Tetri, B.A.; Rinella, M.E. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2015, 1, 15080. [Google Scholar]
- Eslam, M.; Newsome, P.N.; Sarin, S.K.; Anstee, Q.M.; Targher, G.; Romero-Gomez, M.; Zelber-Sagi, S.; Wong, V.W.-S.; Dufour, J.-F.; Schattenberg, J.M.; et al. A new definition for metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease: An international expert consensus statement. J. Hepatol. 2020, 73, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.; Sun, L.; Hao, Y.; Li, P.; Zhou, Y.; Liang, X.; Hu, J.; Wei, H. From NAFLD to MASLD: When metabolic comorbidity matters. Ann. Hepatol. 2024, 29, 101281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, P.B.; Davis, A.M.; Kumar, S. Diagnosis and Management of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. JAMA 2023, 330, 1687–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Younossi, Z.M.; Golabi, P.; Paik, J.M.; Henry, A.; Van Dongen, C.; Henry, L. The global epidemiology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH): A systematic review. Hepatology 2023, 77, 1335–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartmann, P.; Zhang, X.; Loomba, R.; Schnabl, B. Global and national prevalence of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in adolescents: An analysis of the global burden of disease study 2019. Hepatology 2023, 78, 1168–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Younossi, Z.M.; Blissett, D.; Blissett, R.; Henry, L.; Stepanova, M.; Younossi, Y.; Racila, A.; Hunt, S.; Beckerman, R. The economic and clinical burden of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in the United States and Europe. Hepatology 2016, 64, 1577–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.-Y.; Li, Y.; Li, L.-Q.; Zheng, Y.; Lv, J.-H.; Huang, S.-C.; Zhang, W.; Liu, L.; Zhao, L.; Liu, Z.; et al. Risk factors and biomarkers of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: An observational cross-sectional population survey. BMJ Open 2018, 8, e019974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kupčová, V.; Fedelešová, M.; Bulas, J.; Kozmonová, P.; Turecký, L. Overview of the Pathogenesis, Genetic, and Non-Invasive Clinical, Biochemical, and Scoring Methods in the Assessment of NAFLD. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 3570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golabi, P.; Paik, J.M.; AlQahtani, S.; Younossi, Y.; Tuncer, G.; Younossi, Z.M. Burden of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in Asia, the Middle East and North Africa: Data from Global Burden of Disease 2009–2019. J. Hepatol. 2021, 75, 795–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paik, J.M.; Golabi, P.; Younossi, Y.; Srishord, M.; Mishra, A.; Younossi, Z.M. The Growing Burden of Disability Related to Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Data From the Global Burden of Disease 2007–2017. Hepatol. Commun. 2020, 4, 1769–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asrani, S.K.; Devarbhavi, H.; Eaton, J.; Kamath, P.S. Burden of liver diseases in the world. J. Hepatol. 2019, 70, 151–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, E.R.; Lam, Y.K.; Uhlig, H.H. Short-chain fatty acids: Linking diet, the microbiome and immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2024, 24, 577–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufmann, B.; Seyfried, N.; Hartmann, D.; Hartmann, P. Probiotics, prebiotics, and synbiotics in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and alcohol-associated liver disease. Am. J. Physiol. Liver Physiol. 2023, 325, G42–G61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, J.; Zhang, X.-J.; Li, H. The Role of Innate Immune Cells in Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. Hepatology 2019, 70, 1026–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, K.E.; Shah, V.H. Pathogenesis and pathways: Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease & alcoholic liver disease. Transl. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 5, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loomba, R.; Friedman, S.L.; Shulman, G.I. Mechanisms and disease consequences of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Cell 2021, 184, 2537–2564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.H.; Lee, M.-S. Pathogenesis of Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis and Hormone-Based Therapeutic Approaches. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilg, H.; Moschen, A.R. Evolution of inflammation in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: The multiple parallel hits hypothesis. Hepatology 2010, 52, 1836–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowman, J.K.; Tomlinson, J.; Newsome, P. Pathogenesis of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. QJM Int. J. Med. 2009, 103, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ron, D. Translational control in the endoplasmic reticulum stress response. J. Clin. Investig. 2002, 110, 1383–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, P.; Schnabl, B. Risk factors for progression of and treatment options for NAFLD in children. Clin. Liver Dis. 2018, 11, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, P.; Schnabl, B. New Developments in Microbiome in Alcohol-Associated and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Semin. Liver Dis. 2021, 41, 087–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokuhara, D. Role of the Gut Microbiota in Regulating Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Children and Adolescents. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 70058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safari, Z.; Gérard, P. The links between the gut microbiome and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2019, 76, 1541–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loomba, R.; Schork, N.; Chen, C.-H.; Bettencourt, R.; Bhatt, A.; Ang, B.; Nguyen, P.; Hernandez, C.; Richards, L.; Salotti, J.; et al. Heritability of Hepatic Fibrosis and Steatosis Based on a Prospective Twin Study. Gastroenterology 2015, 149, 1784–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eslam, M.; Valenti, L.; Romeo, S. Genetics and epigenetics of NAFLD and NASH: Clinical impact. J. Hepatol. 2018, 68, 268–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Targher, G.; Byrne, C.D.; Lonardo, A.; Zoppini, G.; Barbui, C. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and risk of incident cardiovascular disease: A meta-analysis. J. Hepatol. 2016, 65, 589–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lonardo, A.; Nascimbeni, F.; Mantovani, A.; Targher, G. Hypertension, diabetes, atherosclerosis and NASH: Cause or consequence? J. Hepatol. 2018, 68, 335–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Targher, G.; Byrne, C.D.; Tilg, H. MASLD: A systemic metabolic disorder with cardiovascular and malignant complications. Gut 2024, 73, 691–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oni, E.T.; Agatston, A.S.; Blaha, M.J.; Fialkow, J.; Cury, R.; Sposito, A.; Erbel, R.; Blankstein, R.; Feldman, T.; Al-Mallah, M.H.; et al. A systematic review: Burden and severity of subclinical cardiovascular disease among those with nonalcoholic fatty liver; Should we care? Atherosclerosis 2013, 230, 258–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puchner, S.B.; Lu, M.T.; Mayrhofer, T.; Liu, T.; Pursnani, A.; Ghoshhajra, B.B.; Truong, Q.A.; Wiviott, S.D.; Fleg, J.L.; Hoffmann, U.; et al. High-Risk coronary plaque at coronary CT angiography is associated with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, independent of coronary plaque and stenosis burden: Results from the ROMICAT II trial. Radiology 2015, 274, 693–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballestri, S.; Lonardo, A.; Bonapace, S.; Byrne, C.D.; Loria, P.; Targher, G. Risk of cardiovascular, cardiac and arrhythmic complications in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 1724–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrne, C.D.; Targher, G. NAFLD: A multisystem disease. J. Hepatol. 2015, 62 (Suppl. 1), S47–S64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angulo, P.; Kleiner, D.E.; Dam-Larsen, S.; Adams, L.A.; Björnsson, E.S.; Charatcharoenwitthaya, P.; Mills, P.R.; Keach, J.C.; Lafferty, H.D.; Stahler, A.; et al. Liver Fibrosis, but No Other Histologic Features, Is Associated With Long-term Outcomes of Patients With Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Gastroenterology 2015, 149, 389–397.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, L.A.; Anstee, Q.M.; Tilg, H.; Targher, G. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and its relationship with cardiovascular disease and other extrahepatic diseases. Gut 2017, 66, 1138–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Younossi, Z.M.; Henry, L. The Impact of Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes on Chronic Liver Disease. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 114, 1714–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantovani, A.; Taverna, A.; Cappelli, D.; Beatrice, G.; Csermely, A.; Sani, E.; Byrne, C.D.; Targher, G. Long-Term Adverse Effect of Liver Stiffness on Glycaemic Control in Type 2 Diabetic Patients with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Pilot Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 12481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, X.; Li, J.; Caussy, C.; Teng, G.-J.; Loomba, R. Epidemiology, screening, and co-management of type 2 diabetes mellitus and metabolic dysfunction–associated steatotic liver disease. Hepatology 2024, 8, 00913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, K.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, D.; Kahn, M.; ter Horst, K.W.; Rodrigues, M.R.; Gaspar, R.C.; Hirabara, S.M.; Luukkonen, P.K.; Lee, S.; et al. A Membrane-Bound Diacylglycerol Species Induces PKCϵ-Mediated Hepatic Insulin Resistance. Cell Metab. 2020, 32, 654–664.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younossi, Z.M.; Golabi, P.; de Avila, L.; Paik, J.M.; Srishord, M.; Fukui, N.; Qiu, Y.; Burns, L.; Afendy, A.; Nader, F. The global epidemiology of NAFLD and NASH in patients with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Hepatol. 2019, 71, 793–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarvis, H.; Craig, D.; Barker, R.; Spiers, G.; Stow, D.; Anstee, Q.M.; Hanratty, B. Metabolic risk factors and incident advanced liver disease in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD): A systematic review and meta-analysis of population-based observational studies. PLoS Med. 2020, 17, e1003100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantovani, A.; Petracca, G.; Beatrice, G.; Tilg, H.; Byrne, C.D.; Targher, G. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and risk of incident diabetes mellitus: An updated meta-analysis of 501 022 adult individuals. Gut 2021, 70, 962–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, K.-C.; Jeong, W.-S.; Wild, S.H.; Byrne, C.D. Combined influence of insulin resistance, overweight/obesity, and fatty liver as risk factors for type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2012, 35, 717–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.; Wu, F.; Ding, Y.; Hou, J.; Bi, J.; Zhang, Z. Association of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease with major adverse cardiovascular events: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 33386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, R.J.; Aguilar, M.; Cheung, R.; Perumpail, R.B.; Harrison, S.A.; Younossi, Z.M.; Ahmed, A. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis is the second leading etiology of liver disease among adults awaiting liver transplantation in the United States. Gastroenterology 2015, 148, 547–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quek, J.; Chan, K.E.; Wong, Z.Y.; Tan, C.; Tan, B.; Lim, W.H.; Tan, D.J.H.; Tang, A.S.P.; Tay, P.; Xiao, J.; et al. Global prevalence of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis in the overweight and obese population: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 8, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younossi, Z.M.; Otgonsuren, M.; Henry, L.; Venkatesan, C.; Mishra, A.; Erario, M.; Hunt, S. Association of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) in the United States from 2004 to 2009. Hepatology 2015, 62, 1723–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantovani, A.; Petracca, G.; Beatrice, G.; Csermely, A.; Tilg, H.; Byrne, C.D.; Targher, G. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and increased risk of incident extrahepatic cancers: A meta-analysis of observational cohort studies. Gut 2022, 71, 778–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilar-Gomez, E.; Martinez-Perez, Y.; Calzadilla-Bertot, L.; Torres-Gonzalez, A.; Gra-Oramas, B.; Gonzalez-Fabian, L.; Friedman, S.L.; Diago, M.; Romero-Gomez, M. Weight Loss Through Lifestyle Modification Significantly Reduces Features of Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. Gastroenterology 2015, 149, 367–378.e5; quiz e14-5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilar-Gomez, E.; Nephew, L.D.; Vuppalanchi, R.; Gawrieh, S.; Mladenovic, A.; Pike, F.; Samala, N.; Chalasani, N. High-quality diet, physical activity, and college education are associated with low risk of NAFLD among the US population. Hepatology 2022, 75, 1491–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lassailly, G.; Caiazzo, R.; Buob, D.; Pigeyre, M.; Verkindt, H.; Labreuche, J.; Raverdy, V.; Leteurtre, E.; Dharancy, S.; Louvet, A.; et al. Bariatric Surgery Reduces Features of Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis in Morbidly Obese Patients. Gastroenterology 2015, 149, 379–388; quiz e15-6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jirapinyo, P.; McCarty, T.R.; Dolan, R.D.; Shah, R.; Thompson, C.C. Effect of Endoscopic Bariatric and Metabolic Therapies on Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 20, 511–524.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumida, Y.; Yoneda, M. Current and future pharmacological therapies for NAFLD/NASH. J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 53, 362–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzook, A.; Tomas, A.; Jones, B. The Interplay of Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Trafficking and Signalling in Pancreatic Beta Cells. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 678055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, S.S.; Ibrahim, R.S.; Arabi, B.; Brockmueller, A.; Shakibaei, M.; Büsselberg, D. The effect of GLP-1R agonists on the medical triad of obesity, diabetes, and cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2024, 43, 1297–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Z.; Zong, Y.; Ma, Y.; Tian, Y.; Pang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Gao, J. Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor: Mechanisms and advances in therapy. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drucker, D.J. GLP-1 physiology informs the pharmacotherapy of obesity. Mol. Metab. 2022, 57, 101351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannakogeorgou, A.; Roden, M. Role of lifestyle and glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists for weight loss in obesity, type 2 diabetes and steatotic liver diseases. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2024, 59, S52–S75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacDonald, P.E.; El-Kholy, W.; Riedel, M.J.; Salapatek, A.M.F.; Light, P.E.; Wheeler, M.B. The multiple actions of GLP-1 on the process of glucose-stimulated insulin secretion. Diabetes 2002, 51, S434–S442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, T.; Sun, Z.; Pan, Y.; Deng, X.; Yuan, G. Glucagon-Like Peptide-1: New Regulator in Lipid Metabolism. Diabetes Metab. J. 2024, 48, 354–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; Li, J.; Liu, X.; Ma, Y.; Han, C.; Zhang, L.; Zheng, L. Exenatide ameliorates hepatic steatosis and attenuates fat mass and FTO gene expression through PI3K signaling pathway in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2018, 51, e7299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, N.D.; Cuthbertson, D.J.; Kemp, G.J.; Pugh, C.; Green, D.J.; Cable, N.T.; Jones, H. Effects of 6 months glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist treatment on endothelial function in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2013, 15, 770–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Mells, J.E.; Fu, P.P.; Saxena, N.K.; Anania, F.A. GLP-1 analogs reduce hepatocyte steatosis and improve survival by enhancing the unfolded protein response and promoting macroautophagy. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e25269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novo Nordisk. ESSENCE Phase 3 Trial Results Demonstrating Statistically Significant and Superior Improvements with Semaglutide 2.4 mg in People with MASH Presented at AASLD 2024—The Liver Meeting®. Novo Nordisk. Available online: https://www.novonordisk-us.com/media/news-archive/news-details.html?id=171986 (accessed on 3 January 2025).
- Loomba, R.; Abdelmalek, M.F.; Armstrong, M.J.; Jara, M.; Kjær, M.S.; Krarup, N.; Lawitz, E.; Ratziu, V.; Sanyal, A.J.; Schattenberg, J.M.; et al. Semaglutide 2·4 mg once weekly in patients with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis-related cirrhosis: A randomised, placebo-controlled phase 2 trial. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 8, 511–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frias, J.P.; Deenadayalan, S.; Erichsen, L.; Knop, F.K.; Lingvay, I.; Macura, S.; Mathieu, C.; Pedersen, S.D.; Davies, M. Efficacy and safety of co-administered once-weekly cagrilintide 2·4 mg with once-weekly semaglutide 2·4 mg in type 2 diabetes: A multicentre, randomised, double-blind, active-controlled, phase 2 trial. Lancet 2023, 402, 720–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alkhouri, N.; Herring, R.; Kabler, H.; Kayali, Z.; Hassanein, T.; Kohli, A.; Huss, R.S.; Zhu, Y.; Billin, A.N.; Damgaard, L.H.; et al. Safety and efficacy of combination therapy with semaglutide, cilofexor and firsocostat in patients with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis: A randomised, open-label phase II trial. J. Hepatol. 2022, 77, 607–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loomba, R.; Hartman, M.L.; Lawitz, E.J.; Vuppalanchi, R.; Boursier, J.; Bugianesi, E.; Yoneda, M.; Behling, C.; Cummings, O.W.; Tang, Y.; et al. Tirzepatide for Metabolic Dysfunction—Associated Steatohepatitis with Liver Fibrosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2024, 391, 299–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keam, S.J. Resmetirom: First Approval. Drugs 2024, 84, 729–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, R.A.; Bruinstroop, E.; Singh, B.K.; Yen, P.M. Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Hypercholesterolemia: Roles of Thyroid Hormones, Metabolites, and Agonists. Thyroid® 2019, 29, 1173–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokkorakis, M.; Boutari, C.; Hill, M.A.; Kotsis, V.; Loomba, R.; Sanyal, A.J.; Mantzoros, C.S. Resmetirom, the first approved drug for the management of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis: Trials, opportunities, and challenges. Metabolism 2024, 154, 155835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, S.A.; Bashir, M.R.; Guy, C.D.; Zhou, R.; Moylan, C.A.; Frias, J.P.; Alkhouri, N.; Bansal, M.B.; Baum, S.; A Neuschwander-Tetri, B.; et al. Resmetirom (MGL-3196) for the treatment of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis: A multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 2 trial. Lancet 2019, 394, 2012–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, S.A.; Taub, R.; Neff, G.W.; Lucas, K.J.; Labriola, D.; Moussa, S.E.; Alkhouri, N.; Bashir, M.R. Resmetirom for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 3 trial. Nat. Med. 2023, 29, 2919–2928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, S.A.; Bedossa, P.; Guy, C.D.; Schattenberg, J.M.; Loomba, R.; Taub, R.; Labriola, D.; Moussa, S.E.; Neff, G.W.; Rinella, M.E.; et al. A Phase 3, Randomized, Controlled Trial of Resmetirom in NASH with Liver Fibrosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2024, 390, 497–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karim, G.; Bansal, M.B. Resmetirom: An Orally Administered, Small-molecule, Liver-directed, β-selective THR Agonist for the Treatment of Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Non-alcoholic Steatohepatitis. Eur. Endocrinol. 2023, 19, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, M.J.; Pietranico-Cole, S.; Larigan, J.D.; Haynes, N.-E.; Reynolds, C.H.; Scott, N.; Vermeulen, J.; Dvorozniak, M.; Conde-Knape, K.; Huang, K.-S.; et al. Discovery of 2-[3,5-dichloro-4-(5-isopropyl-6-oxo-1,6-dihydropyridazin-3-yloxy)phenyl]-3,5-dioxo-2,3,4,5-tetrahydro [1,2,4]triazine-6-carbonitrile (MGL-3196), a Highly Selective Thyroid Hormone Receptor β agonist in clinical trials for the treatment of dyslipidemia. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 3912–3923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, R.-G.; Zhou, D.-D.; Wu, S.-X.; Huang, S.-Y.; Saimaiti, A.; Yang, Z.-J.; Shang, A.; Zhao, C.-N.; Gan, R.-Y.; Li, H.-B. Health Benefits and Side Effects of Short-Chain Fatty Acids. Foods 2022, 11, 2863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, J.K.; Holmes, E.; Kinross, J.; Burcelin, R.; Gibson, G.; Jia, W.; Pettersson, S. Host-gut microbiota metabolic interactions. Science 2012, 336, 1262–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuel, B.S.; Shaito, A.; Motoike, T.; Rey, F.E.; Backhed, F.; Manchester, J.K.; Hammer, R.E.; Williams, S.C.; Crowley, J.; Yanagisawa, M.; et al. Effects of the gut microbiota on host adiposity are modulated by the short-chain fatty-acid binding G protein-coupled receptor, Gpr41. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 16767–16772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, J.M.W.; de Souza, R.; Kendall, C.W.C.; Emam, A.; Jenkins, D.J.A. Colonic health: Fermentation and short chain fatty acids. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2006, 40, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, Y.P.; Bernardi, A.; Frozza, R.L. The Role of Short-Chain Fatty Acids From Gut Microbiota in Gut-Brain Communication. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Layden, B.T.; Angueira, A.R.; Brodsky, M.; Durai, V.; Lowe, W.L., Jr. Short chain fatty acids and their receptors: New metabolic targets. Transl. Res. 2013, 161, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Zhang, P.; Shen, L.; Niu, L.; Tan, Y.; Chen, L.; Zhao, Y.; Bai, L.; Hao, X.; Li, X.; et al. Short-Chain Fatty Acids and Their Association with Signalling Pathways in Inflammation, Glucose and Lipid Metabolism. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Den Besten, G.; van Eunen, K.; Groen, A.K.; Venema, K.; Reijngoud, D.-J.; Bakker, B.M. The role of short-chain fatty acids in the interplay between diet, gut microbiota, and host energy metabolism. J. Lipid Res. 2013, 54, 2325–2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, S.P.; Denu, J.M.; States, U. Short-chain fatty acids activate acetyltransferase p300. eLife 2021, 10, e72171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura, I.; Ichimura, A.; Ohue-Kitano, R.; Igarashi, M. Free Fatty Acid Receptors in Health and Disease. Physiol. Rev. 2020, 100, 171–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koh, A.; De Vadder, F.; Kovatcheva-Datchary, P.; Bäckhed, F. From Dietary Fiber to Host Physiology: Short-Chain Fatty Acids as Key Bacterial Metabolites. Cell 2016, 165, 1332–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Wu, W.; Liu, Z.; Cong, Y. Microbiota metabolite short chain fatty acids, GPCR, and inflammatory bowel diseases. J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 52, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.Y.; de Zoete, M.R.; van Putten, J.P.M.; Strijbis, K. Redirection of Epithelial Immune Responses by Short-Chain Fatty Acids through Inhibition of Histone Deacetylases. Front. Immunol. 2015, 6, 554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Li, Q.; Yang, Y.; Guo, A. Biological Function of Short-Chain Fatty Acids and Its Regulation on Intestinal Health of Poultry. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 736739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; van Esch, B.C.A.M.; Henricks, P.A.J.; Folkerts, G.; Garssen, J. The Anti-inflammatory Effects of Short Chain Fatty Acids on Lipopolysaccharide- or Tumor Necrosis Factor α-Stimulated Endothelial Cells via Activation of GPR41/43 and Inhibition of HDACs. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fellows, R.; Denizot, J.; Stellato, C.; Cuomo, A.; Jain, P.; Stoyanova, E.; Balázsi, S.; Hajnády, Z.; Liebert, A.; Kazakevych, J.; et al. Microbiota derived short chain fatty acids promote histone crotonylation in the colon through histone deacetylases. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Jian, Y.-P.; Zhang, Y.-N.; Li, Y.; Gu, L.-T.; Sun, H.-H.; Liu, M.-D.; Zhou, H.-L.; Wang, Y.-S.; Xu, Z.-X. Short-chain fatty acids in diseases. Cell Commun. Signal. 2023, 21, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deleu, S.; Machiels, K.; Raes, J.; Verbeke, K.; Vermeire, S. Short chain fatty acids and its producing organisms: An overlooked therapy for IBD? EBioMedicine 2021, 66, 103293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ríos-Covián, D.; Ruas-Madiedo, P.; Margolles, A.; Gueimonde, M.; De Los Reyes-Gavilán, C.G.; Salazar, N. Intestinal Short Chain Fatty Acids and their Link with Diet and Human Health. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santoro, A.; Ostan, R.; Candela, M.; Biagi, E.; Brigidi, P.; Capri, M.; Franceschi, C. Gut microbiota changes in the extreme decades of human life: A focus on centenarians. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2018, 75, 129–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, C.J.; Ajami, N.J.; O’brien, J.L.; Hutchinson, D.S.; Smith, D.P.; Wong, M.C.; Ross, M.C.; Lloyd, R.E.; Doddapaneni, H.; Metcalf, G.A.; et al. Temporal development of the gut microbiome in early childhood from the TEDDY study. Nature 2018, 562, 583–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsukuda, N.; Yahagi, K.; Hara, T.; Watanabe, Y.; Matsumoto, H.; Mori, H.; Higashi, K.; Tsuji, H.; Matsumoto, S.; Kurokawa, K.; et al. Key bacterial taxa and metabolic pathways affecting gut short-chain fatty acid profiles in early life. ISME J. 2021, 15, 2574–2590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odamaki, T.; Kato, K.; Sugahara, H.; Hashikura, N.; Takahashi, S.; Xiao, J.-Z.; Abe, F.; Osawa, R. Age-related changes in gut microbiota composition from newborn to centenarian: A cross-sectional study. BMC Microbiol. 2016, 16, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrmann, E.; Young, W.; Reichert-Grimm, V.; Weis, S.; Riedel, C.U.; Rosendale, D.; Stoklosinski, H.; Hunt, M.; Egert, M. In Vivo Assessment of Resistant Starch Degradation by the Caecal Microbiota of Mice Using RNA-Based Stable Isotope Probing—A Proof-of-Principle Study. Nutrients 2018, 10, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, T.S.; Shanahan, F.; O’toole, P.W. The gut microbiome as a modulator of healthy ageing. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 19, 565–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogal, A.; Louca, P.; Zhang, X.; Wells, P.M.; Steves, C.J.; Spector, T.D.; Falchi, M.; Valdes, A.M.; Menni, C. Circulating Levels of the Short-Chain Fatty Acid Acetate Mediate the Effect of the Gut Microbiome on Visceral Fat. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 711359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Callaghan, A.; van Sinderen, D. Bifidobacteria and Their Role as Members of the Human Gut Microbiota. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosmer, J.; McEwan, A.G.; Kappler, U. Bacterial acetate metabolism and its influence on human epithelia. Emerg. Top. Life Sci. 2024, 8, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Xiao, M.; Zhang, C.; Duan, H.; Narbad, A.; Zhao, J.; Chen, W.; Zhai, Q.; Yu, L.; Tian, F. Cross-feeding of bifidobacteria promotes intestinal homeostasis: A lifelong perspective on the host health. npj Biofilms Microbiomes 2024, 10, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devika, N.T.; Raman, K. Deciphering the metabolic capabilities of Bifidobacteria using genome-scale metabolic models. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 18222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Bayles, K.W.; Luca, S. Staphylococcus aureus CidC Is a Pyruvate:Menaquinone Oxidoreductase. Biochemistry 2017, 56, 4819–4829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferry, J.G. Acetate kinase and phosphotransacetylase. Methods Enzymol. 2011, 494, 219–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martino, C.; Zaramela, L.S.; Gao, B.; Embree, M.; Tarasova, J.; Parker, S.J.; Wang, Y.; Chu, H.; Chen, P.; Lee, K.-C.; et al. Acetate reprograms gut microbiota during alcohol consumption. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 4630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimura, K.; Matsui, T.; Itoh, K. Prevention of Escherichia coli O157:H7 infection in gnotobiotic mice associated with Bifidobacterium strains. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2010, 97, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rios-Covian, D.; Gueimonde, M.; Duncan, S.H.; Flint, H.J.; De Los Reyes-Gavilan, C.G. Enhanced butyrate formation by cross-feeding between Faecalibacterium prausnitzii and Bifidobacterium adolescentis. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2015, 362, fnv176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasubuchi, M.; Hasegawa, S.; Hiramatsu, T.; Ichimura, A.; Kimura, I. Dietary gut microbial metabolites, short-chain fatty acids, and host metabolic regulation. Nutrients 2015, 7, 2839–2849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratajczak, W.; Rył, A.; Mizerski, A.; Walczakiewicz, K.; Sipak, O.; Laszczyńska, M. Immunomodulatory potential of gut microbiome-derived short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs). Acta Biochim. Pol. 2019, 66, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conlon, M.A.; Bird, A.R. The impact of diet and lifestyle on gut microbiota and human health. Nutrients 2014, 7, 17–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kircher, B.; Woltemate, S.; Gutzki, F.; Schlüter, D.; Geffers, R.; Bähre, H.; Vital, M. Predicting butyrate- and propionate-forming bacteria of gut microbiota from sequencing data. Gut Microbes 2022, 14, 2149019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Hage, R.; Hernandez-Sanabria, E.; Arroyo, M.C.; Props, R.; Van de Wiele, T. Propionate-Producing Consortium Restores Antibiotic-Induced Dysbiosis in a Dynamic in vitro Model of the Human Intestinal Microbial Ecosystem. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reichardt, N.; Duncan, S.H.; Young, P.; Belenguer, A.; McWilliam Leitch, C.; Scott, K.P.; Flint, H.J.; Louis, P. Phylogenetic distribution of three pathways for propionate production within the human gut microbiota. ISME J. 2014, 8, 1323–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Vadder, F.; Kovatcheva-Datchary, P.; Zitoun, C.; Duchampt, A.; Bäckhed, F.; Mithieux, G. Microbiota-Produced Succinate Improves Glucose Homeostasis via Intestinal Gluconeogenesis. Cell Metab. 2016, 24, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salonen, A.; Lahti, L.; Salojärvi, J.; Holtrop, G.; Korpela, K.; Duncan, S.H.; Date, P.; Farquharson, F.; Johnstone, A.M.; Lobley, G.E.; et al. Impact of diet and individual variation on intestinal microbiota composition and fermentation products in obese men. ISME J. 2014, 8, 2218–2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louis, P.; Flint, H.J. Formation of propionate and butyrate by the human colonic microbiota. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 19, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, J.L.; Erickson, J.M.; Hess, J.M.; Gould, T.J.; Slavin, J.L. Prebiotic Dietary Fiber and Gut Health: Comparing the In Vitro Fermentations of Beta-Glucan, Inulin and Xylooligosaccharide. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velikonja, A.; Lipoglavšek, L.; Zorec, M.; Orel, R.; Avguštin, G. Alterations in gut microbiota composition and metabolic parameters after dietary intervention with barley beta glucans in patients with high risk for metabolic syndrome development. Anaerobe 2019, 55, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.-B.; Zhang, Y.-C.; Huang, H.-H.; Lin, J. Prospects for clinical applications of butyrate-producing bacteria. World J. Clin. Pediatr. 2021, 10, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.; Lee, G.; Son, H.; Koh, H.; Kim, E.S.; Unno, T.; Shin, J.-H. Butyrate producers, “The Sentinel of Gut”: Their intestinal significance with and beyond butyrate, and prospective use as microbial therapeutics. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1103836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoeva, M.K.; Garcia-So, J.; Justice, N.; Myers, J.; Tyagi, S.; Nemchek, M.; McMurdie, P.J.; Kolterman, O.; Eid, J. Butyrate-producing human gut symbiont, Clostridium butyricum, and its role in health and disease. Gut Microbes 2021, 13, 1907272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martín, R.; Bermúdez-Humarán, L.G.; Langella, P. Searching for the Bacterial Effector: The Example of the Multi-Skilled Commensal Bacterium Faecalibacterium prausnitzii. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, S.; Kaur, H.; Mande, S.S. Comparative In silico Analysis of Butyrate Production Pathways in Gut Commensals and Pathogens. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kullberg, R.F.J.; Wikki, I.; Haak, B.W.; Kauko, A.; Galenkamp, H.; Peters-Sengers, H.; Butler, J.M.; Havulinna, A.S.; Palmu, J.; McDonald, D.; et al. Association between butyrate-producing gut bacteria and the risk of infectious disease hospitalisation: Results from two observational, population-based microbiome studies. Lancet Microbe 2024, 5, 100864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singhal, R.; Donde, H.; Ghare, S.; Stocke, K.; Zhang, J.; Vadhanam, M.; Reddy, S.; Gobejishvili, L.; Chilton, P.; Joshi-Barve, S.; et al. Decrease in acetyl-CoA pathway utilizing butyrate-producing bacteria is a key pathogenic feature of alcohol-induced functional gut microbial dysbiosis and development of liver disease in mice. Gut Microbes 2021, 13, 1946367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Detman, A.; Mielecki, D.; Chojnacka, A.; Salamon, A.; Błaszczyk, M.K.; Sikora, A. Cell factories converting lactate and acetate to butyrate: Clostridium butyricum and microbial communities from dark fermentation bioreactors. Microb. Cell Factories 2019, 18, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera-Chávez, F.; Zhang, L.F.; Faber, F.; Lopez, C.A.; Byndloss, M.X.; Olsan, E.E.; Xu, G.; Velazquez, E.M.; Lebrilla, C.B.; Winter, S.E.; et al. Depletion of Butyrate-Producing Clostridia from the Gut Microbiota Drives an Aerobic Luminal Expansion of Salmonella. Cell Host Microbe 2016, 19, 443–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litvak, Y.; Byndloss, M.X.; Bäumler, A.J. Colonocyte metabolism shapes the gut microbiota. Science 2018, 362, eaat9076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, C.; Wang, B.; Kaliannan, K.; Wang, X.; Lang, H.; Hui, S.; Huang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, M.; Chen, M.; et al. Gut Microbiota Mediates the Protective Effects of Dietary Capsaicin against Chronic Low-Grade Inflammation and Associated Obesity Induced by High-Fat Diet. mBio 2017, 8, e00470-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chassard, C.; Bernalier-Donadille, A. H2 and acetate transfers during xylan fermentation between a butyrate-producing xylanolytic species and hydrogenotrophic microorganisms from the human gut. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2006, 254, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, H.; Zhang, J.; Liu, C.; Le, T.N.; Lu, Y.; Feng, F.; Zhao, M. High-Fat Diet-Induced Decreased Circulating Bile Acids Contribute to Obesity Associated with Gut Microbiota in Mice. Foods 2024, 13, 699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Wu, J.; Yang, L.; Hu, Q.; Li, L.; Yang, Y.; Hu, J.; Pan, D.; Zhao, Q. Altered gut microbial profile accompanied by abnormal short chain fatty acid metabolism exacerbates nonalcoholic fatty liver disease progression. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, e0261222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, H.-J.; Hung, W.-C.; Hung, W.-W.; Lee, Y.-J.; Chen, Y.-C.; Lee, C.-Y.; Tsai, Y.-C.; Dai, C.-Y. Circulating Short-Chain Fatty Acids and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Severity in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.; Hou, H.; Zhang, W.; Liu, T.; Li, Y.; Wang, S.; Wang, B.; Cao, H. Microbial Metabolites: Critical Regulators in NAFLD. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 567654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fogacci, F.; Giovannini, M.; Di Micoli, V.; Grandi, E.; Borghi, C.; Cicero, A.F.G. Effect of Supplementation of a Butyrate-Based Formula in Individuals with Liver Steatosis and Metabolic Syndrome: A Randomized Double-Blind Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial. Nutrients 2024, 16, 2454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; He, M.; Yi, X.; Lu, X.; Zhu, M.; Xue, M.; Tang, Y.; Zhu, Y. Short-chain fatty acids in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: New prospects for short-chain fatty acids as therapeutic targets. Heliyon 2024, 10, e26991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.D.; Prykhodko, O.; Hållenius, F.F.; Nyman, M. Monobutyrin Reduces Liver Cholesterol and Improves Intestinal Barrier Function in Rats Fed High-Fat Diets. Nutrients 2019, 11, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Liu, J.; Hao, W.; Zhu, H.; Liang, N.; He, Z.; Ma, K.Y.; Chen, Z.-Y. Structure-Specific Effects of Short-Chain Fatty Acids on Plasma Cholesterol Concentration in Male Syrian Hamsters. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 10984–10992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, H.; Ishii, M.; Akagawa, M. Propionate suppresses hepatic gluconeogenesis via GPR43/AMPK signaling pathway. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2019, 672, 108057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- den Besten, G.; Bleeker, A.; Gerding, A.; Van Eunen, K.; Havinga, R.; Van Dijk, T.H.; Oosterveer, M.H.; Jonker, J.W.; Groen, A.K.; Reijngoud, D.-J.; et al. Short-Chain Fatty Acids Protect Against High-Fat Diet–Induced Obesity via a PPARgamma-Dependent Switch from Lipogenesis to Fat Oxidation. Diabetes 2015, 64, 2398–2408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weitkunat, K.; Schumann, S.; Nickel, D.; Kappo, K.A.; Petzke, K.J.; Kipp, A.P.; Blaut, M.; Klaus, S. Importance of propionate for the repression of hepatic lipogenesis and improvement of insulin sensitivity in high-fat diet-induced obesity. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2016, 60, 2611–2621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macia, L.; Tan, J.; Vieira, A.T.; Leach, K.; Stanley, D.; Luong, S.; Maruya, M.; McKenzie, C.l.; Hijikata, A.; Wong, C.; et al. Metabolite-sensing receptors GPR43 and GPR109A facilitate dietary fibre-induced gut homeostasis through regulation of the inflammasome. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atarashi, K.; Tanoue, T.; Oshima, K.; Suda, W.; Nagano, Y.; Nishikawa, H.; Fukuda, S.; Saito, T.; Narushima, S.; Hase, K.; et al. Treg induction by a rationally selected mixture of Clostridia strains from the human microbiota. Nature 2013, 500, 232–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; He, C.; An, Y.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Fu, W.; Wang, M.; Shan, Z.; Xie, J.; Yang, Y.; et al. The Role of Short Chain Fatty Acids in Inflammation and Body Health. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 7379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thing, M.; Werge, M.P.; Kimer, N.; Hetland, L.E.; Rashu, E.B.; Nabilou, P.; Junker, A.E.; Galsgaard, E.D.; Bendtsen, F.; Laupsa-Borge, J.; et al. Targeted metabolomics reveals plasma short-chain fatty acids are associated with metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease. BMC Gastroenterol. 2024, 24, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lührs, H.; Gerke, T.; Müller, J.G.; Melcher, R.; Schauber, J.; Boxberger, F.; Scheppach, W.; Menzel, T. Butyrate inhibits NF-κB activation in lamina propria macrophages of patients with ulcerative colitis. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2002, 37, 458–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, T.; Towatari, M.; Kosugi, H.; Saito, H. Up-regulation of costimulatory/adhesion molecules by histone deacetylase inhibitors in acute myeloid leukemia cells. Blood 2000, 96, 3847–3856. [Google Scholar]
- Slavin, J. Fiber and Prebiotics: Mechanisms and Health Benefits. Nutrients 2013, 5, 1417–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Shi, P.; Zuo, L.; Dong, J.; Zhao, J.; Liu, Q.; Zhu, W. Dietary Non-digestible Polysaccharides Ameliorate Intestinal Epithelial Barrier Dysfunction in IL-10 Knockout Mice. J. Crohn’s Colitis 2016, 10, 1076–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Hung, T.; Suzuki, T. Dietary Fermentable Fibers Attenuate Chronic Kidney Disease in Mice by Protecting the Intestinal Barrier. J. Nutr. 2018, 148, 552–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Ran, X.; Li, B.; Li, Y.; He, D.; Huang, B.; Fu, S.; Liu, J.; Wang, W. Sodium Butyrate Inhibits Inflammation and Maintains Epithelium Barrier Integrity in a TNBS-induced Inflammatory Bowel Disease Mice Model. EBioMedicine 2018, 30, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartmann, P.; Seebauer, C.T.; Mazagova, M.; Horvath, A.; Wang, L.; Llorente, C.; Varki, N.M.; Brandl, K.; Ho, S.B.; Schnabl, B. Deficiency of intestinal mucin-2 protects mice from diet-induced fatty liver disease and obesity. Am. J. Physiol. Liver Physiol. 2016, 310, G310–G322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, P.; Chen, P.; Wang, H.J.; Wang, L.; McCole, D.F.; Brandl, K.; Stärkel, P.; Belzer, C.; Hellerbrand, C.; Tsukamoto, H.; et al. Deficiency of intestinal mucin-2 ameliorates experimental alcoholic liver disease in mice. Hepatology 2013, 58, 108–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pohl, K.; Moodley, P.; Dhanda, A. The effect of increasing intestinal short-chain fatty acid concentration on gut permeability and liver injury in the context of liver disease: A systematic review. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 37, 1498–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamer, H.M.; Jonkers, D.; Venema, K.; Vanhoutvin, S.; Troost, F.J.; Brummer, R.-J. Review article: The role of butyrate on colonic function. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2008, 27, 104–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaudier, E.; Jarry, A.; Blottière, H.M.; de Coppet, P.; Buisine, M.P.; Aubert, J.P.; Laboisse, C.; Cherbut, C.; Hoebler, C. Butyrate specifically modulates MUC gene expression in intestinal epithelial goblet cells deprived of glucose. Am. J. Physiol. Liver Physiol. 2004, 287, G1168–G1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.; Liu, L.; Zhou, W.; Yang, C.; Mai, G.; Li, H.; Chen, Y. Gut microbiota-derived butyrate regulates gut mucus barrier repair by activating the macrophage/WNT/ERK signaling pathway. Clin. Sci. 2022, 136, 291–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, H.; Masujima, Y.; Ushiroda, C.; Mizushima, R.; Taira, S.; Ohue-Kitano, R.; Kimura, I. Dietary short-chain fatty acid intake improves the hepatic metabolic condition via FFAR3. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, M.; Qu, F.; Chen, L.; Liu, C.; Zhang, M.; Ren, F.; Guo, H.; Zhang, H.; Ge, S.; Wu, C.; et al. SCFAs alleviated steatosis and inflammation in mice with NASH induced by MCD. J. Endocrinol. 2020, 245, 425–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondo, T.; Kishi, M.; Fushimi, T.; Ugajin, S.; Kaga, T. vinegar intake reduces body weight, body fat mass, and serum triglyceride levels in obese Japanese subjects. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2009, 73, 1837–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chambers, E.S.; Viardot, A.; Psichas, A.; Morrison, D.J.; Murphy, K.G.; Zac-Varghese, S.E.K.; MacDougall, K.; Preston, T.; Tedford, C.; Finlayson, G.S.; et al. Effects of targeted delivery of propionate to the human colon on appetite regulation, body weight maintenance and adiposity in overweight adults. Gut 2015, 64, 1744–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amiri, P.; Hosseini, S.A.; Saghafi-Asl, M.; Akbari-Naserkiadeh, A.; Zavieh, S.A.J.; Arefhosseini, S.; Asghari, S.; Roshanravan, N. Expression of lipid metabolism- related genes, body composition and inflammation: Effects of sodium butyrate supplementation in subjects with obesity. J. Funct. Foods 2024, 124, 106645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleophas, M.C.P.; Ratter, J.M.; Bekkering, S.; Quintin, J.; Schraa, K.; Stroes, E.S.; Netea, M.G.; Joosten, L.A.B. Effects of oral butyrate supplementation on inflammatory potential of circulating peripheral blood mononuclear cells in healthy and obese males. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppola, S.; Nocerino, R.; Paparo, L.; Bedogni, G.; Calignano, A.; Di Scala, C.; Severina, A.F.d.G.d.S.; De Filippis, F.; Ercolini, D.; Canani, R.B. Therapeutic Effects of Butyrate on Pediatric Obesity. JAMA Netw. Open 2022, 5, e2244912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roshanravan, N.; Mahdavi, R.; Alizadeh, E.; Jafarabadi, M.A.; Hedayati, M.; Ghavami, A.; Alipour, S.; Alamdari, N.M.; Barati, M.; Ostadrahimi, A. Effect of Butyrate and Inulin Supplementation on Glycemic Status, Lipid Profile and Glucagon-Like Peptide 1 Level in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Randomized Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Horm. Metab. Res. 2017, 49, 886–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khosravi, Z.; Hadi, A.; Tutunchi, H.; Asghari-Jafarabadi, M.; Naeinie, F.; Roshanravan, N.; Ostadrahimi, A.; Fadel, A. The effects of butyrate supplementation on glycemic control, lipid profile, blood pressure, nitric oxide level and glutathione peroxidase activity in type 2 diabetic patients: A randomized triple -blind, placebo-controlled trial. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2022, 49, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.N.; Yao, Y.; Ju, S.Y. Short Chain Fatty Acids and Fecal Microbiota Abundance in Humans with Obesity: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdes, A.M.; Walter, J.; Segal, E.; Spector, T.D. Role of the gut microbiota in nutrition and health. BMJ 2018, 361, k2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Fan, C.; Li, P.; Lu, Y.; Chang, X.; Qi, K. Short Chain Fatty Acids Prevent High-fat-diet-induced Obesity in Mice by Regulating G Protein-coupled Receptors and Gut Microbiota. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 37589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henagan, T.M.; Stefanska, B.; Fang, Z.; Navard, A.M.; Ye, J.; Lenard, N.R.; Devarshi, P.P. Sodium butyrate epigenetically modulates high-fat diet-induced skeletal muscle mitochondrial adaptation, obesity and insulin resistance through nucleosome positioning. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 172, 2782–2798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonomo, R.R.; Cook, T.M.; Gavini, C.K.; White, C.R.; Jones, J.R.; Bovo, E.; Zima, A.V.; Brown, I.A.; Dugas, L.R.; Zakharian, E.; et al. Fecal transplantation and butyrate improve neuropathic pain, modify immune cell profile, and gene expression in the PNS of obese mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 26482–26493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Z.; Yin, J.; Zhang, J.; Ward, R.E.; Martin, R.J.; Lefevre, M.; Cefalu, W.T.; Ye, J. butyrate improves insulin sensitivity and increases energy expenditure in mice. Diabetes 2009, 58, 1509–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tirosh, A.; Calay, E.S.; Tuncman, G.; Claiborn, K.C.; Inouye, K.E.; Eguchi, K.; Alcala, M.; Rathaus, M.; Hollander, K.S.; Ron, I.; et al. The short-chain fatty acid propionate increases glucagon and FABP4 production, impairing insulin action in mice and humans. Sci. Transl. Med. 2019, 11, eaav0120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, R.J.; Peng, L.; Barry, N.A.; Cline, G.W.; Zhang, D.; Cardone, R.L.; Petersen, K.F.; Kibbey, R.G.; Goodman, A.L.; Shulman, G.I. Acetate mediates a microbiome–brain–β-cell axis to promote metabolic syndrome. Nature 2016, 534, 213–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwiertz, A.; Taras, D.; Schäfer, K.; Beijer, S.; Bos, N.A.; Donus, C.; Hardt, P.D. Microbiota and SCFA in Lean and Overweight Healthy Subjects. Obesity 2010, 18, 190–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larraufie, P.; Martin-Gallausiaux, C.; Lapaque, N.; Dore, J.; Gribble, F.M.; Reimann, F.; Blottiere, H.M. SCFAs strongly stimulate PYY production in human enteroendocrine cells. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Hee, B.; Wells, J.M. Microbial Regulation of Host Physiology by Short-chain Fatty Acids. Trends Microbiol. 2021, 29, 700–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Silva, A.; Bloom, S.R. Gut Hormones and Appetite Control: A Focus on PYY and GLP-1 as Therapeutic Targets in Obesity. Gut Liver 2012, 6, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puddu, A.; Sanguineti, R.; Montecucco, F.; Viviani, G.L. Evidence for the gut microbiota short-chain fatty acids as key pathophysiological molecules improving diabetes. Mediat. Inflamm. 2014, 2014, 162021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ecklu-Mensah, G.; Choo-Kang, C.; Maseng, M.G.; Donato, S.; Bovet, P.; Viswanathan, B.; Bedu-Addo, K.; Plange-Rhule, J.; Boateng, P.O.; Forrester, T.E.; et al. Gut microbiota and fecal short chain fatty acids differ with adiposity and country of origin: The METS-microbiome study. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 5160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, R.K.; Lane, A.I.; Weninger, S.N.; Martinez, T.M.; Kangath, A.; Laubitz, D.; Duca, F.A. Oligofructose restores postprandial short-chain fatty acid levels during high-fat feeding. Obesity 2022, 30, 1442–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De la Cuesta-Zuluaga, J.; Mueller, N.T.; Álvarez-Quintero, R.; Velásquez-Mejía, E.P.; Sierra, J.A.; Corrales-Agudelo, V.; Carmona, J.A.; Abad, J.M.; Escobar, J.S. Higher Fecal Short-Chain Fatty Acid Levels Are Associated with Gut Microbiome Dysbiosis, Obesity, Hypertension and Cardiometabolic Disease Risk Factors. Nutrients 2018, 11, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dao, M.C.; Everard, A.; Aron-Wisnewsky, J.; Sokolovska, N.; Prifti, E.; Verger, E.O.; Kayser, B.D.; Levenez, F.; Chilloux, J.; Hoyles, L.; et al. Akkermansia muciniphila and improved metabolic health during a dietary intervention in obesity: Relationship with gut microbiome richness and ecology. Gut 2016, 65, 426–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ley, R.E.; Bäckhed, F.; Turnbaugh, P.; Lozupone, C.A.; Knight, R.D.; Gordon, J.I. Obesity alters gut microbial ecology. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 11070–11075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, M.; Hernández, M.A.G.; Goossens, G.H.; Reijnders, D.; Holst, J.J.; Jocken, J.W.E.; Van Eijk, H.; Canfora, E.E.; Blaak, E.E. Circulating but not faecal short-chain fatty acids are related to insulin sensitivity, lipolysis and GLP-1 concentrations in humans. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 12515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cani, P.D.; Neyrinck, A.M.; Fava, F.; Knauf, C.; Burcelin, R.G.; Tuohy, K.M.; Gibson, G.R.; Delzenne, N.M. Selective increases of bifidobacteria in gut microflora improve high-fat-diet-induced diabetes in mice through a mechanism associated with endotoxaemia. Diabetologia 2007, 50, 2374–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, J.A.; Mullish, B.H.; Pechlivanis, A.; Liu, Z.; Brignardello, J.; Kao, D.; Holmes, E.; Li, J.V.; Clarke, T.B.; Thursz, M.R.; et al. Inhibiting Growth of Clostridioides difficile by Restoring Valerate, Produced by the Intestinal Microbiota. Gastroenterology 2018, 155, 1495–1507.e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, K.C.; Nagarajan, N.; Gan, Y.-H. Short-chain fatty acids of various lengths differentially inhibit Klebsiella pneumoniae and Enterobacteriaceae species. mSphere 2024, 9, e0078123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vourakis, M.; Mayer, G.; Rousseau, G. The Role of Gut Microbiota on Cholesterol Metabolism in Atherosclerosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanna, S.; Van Zuydam, N.R.; Mahajan, A.; Kurilshikov, A.; Vila, A.V.; Võsa, U.; Mujagic, Z.; Masclee, A.A.M.; Jonkers, D.M.A.E.; Oosting, M.; et al. Causal relationships among the gut microbiome, short-chain fatty acids and metabolic diseases. Nat. Genet. 2019, 51, 600–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura, I.; Ozawa, K.; Inoue, D.; Imamura, T.; Kimura, K.; Maeda, T.; Terasawa, K.; Kashihara, D.; Hirano, K.; Tani, T.; et al. The gut microbiota suppresses insulin-mediated fat accumulation via the short-chain fatty acid receptor GPR43. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.V.; Frassetto, A.; Kowalik, E.J., Jr.; Nawrocki, A.R.; Lu, M.M.; Kosinski, J.R.; Hubert, J.A.; Szeto, D.; Yao, X.; Forrest, G.; et al. Butyrate and propionate protect against diet-induced obesity and regulate gut hormones via free fatty acid receptor 3-independent mechanisms. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e35240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.; Li, Y.; Cai, Z.; Li, S.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, F.; Liang, S.; Zhang, W.; Guan, Y.; Shen, D.; et al. A metagenome-wide association study of gut microbiota in type 2 diabetes. Nature 2012, 490, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Ouyang, J.; Sun, F.; Yang, J. Short-Chain Fatty Acids: A Soldier Fighting Against Inflammation and Protecting From Tumorigenesis in People With Diabetes. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 590685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salamone, D.; Rivellese, A.A.; Vetrani, C. The relationship between gut microbiota, short-chain fatty acids and type 2 diabetes mellitus: The possible role of dietary fibre. Acta Diabetol. 2021, 58, 1131–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Tremaroli, V.; Schmidt, C.; Lundqvist, A.; Olsson, L.M.; Krämer, M.; Gummesson, A.; Perkins, R.; Bergström, G.; Bäckhed, F. The Gut Microbiota in Prediabetes and Diabetes: A Population-Based Cross-Sectional Study. Cell Metab. 2020, 32, 379–390.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlsson, F.H.; Tremaroli, V.; Nookaew, I.; Bergström, G.; Behre, C.J.; Fagerberg, B.; Nielsen, J.; Bäckhed, F. Gut metagenome in European women with normal, impaired and diabetic glucose control. Nature 2013, 498, 99–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, R.; Li, L. Modulation of Short-Chain Fatty Acids as Potential Therapy Method for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Can. J. Infect. Dis. Med. Microbiol. 2021, 2021, 6632266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslamy, A.; Wood, A.C.; Jensen, E.T.; Bertoni, A.G.; Sheridan, P.A.; Wong, K.E.; Ramesh, G.; Rotter, J.I.; Chen, Y.-D.I.; Goodarzi, M.O. Increased Plasma Branched Short-Chain Fatty Acids and Improved Glucose Homeostasis: The Microbiome and Insulin Longitudinal Evaluation Study (MILES). Diabetes 2024, 73, 385–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, N.H.T.; Joglekar, M.V.; Wong, W.K.M.; Nassif, N.T.; Simpson, A.M.; Hardikar, A.A. Short-chain fatty acids and insulin sensitivity: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Nutr. Rev. 2023, 82, 193–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakakibara, S.; Yamauchi, T.; Oshima, Y.; Tsukamoto, Y.; Kadowaki, T. Acetic acid activates hepatic AMPK and reduces hyperglycemia in diabetic KK-A(y) mice. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006, 344, 597–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Yang, K.; Fan, H.; Wei, M.; Xiong, Q. Targeting the gut microbiota and its metabolites for type 2 diabetes mellitus. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1114424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Chen, H.; Zhang, M.; Wu, T.; Liu, R. Altered short chain fatty acid profiles induced by dietary fiber intervention regulate AMPK levels and intestinal homeostasis. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 7174–7187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shashni, B.; Tajika, Y.; Nagasaki, Y. Design of enzyme-responsive short-chain fatty acid-based self-assembling drug for alleviation of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Biomaterials 2021, 275, 120877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pingitore, A.; Chambers, E.S.; Hill, T.; Maldonado, I.R.; Liu, B.; Bewick, G.; Morrison, D.J.; Preston, T.; Wallis, G.A.; Tedford, C.; et al. The diet-derived short chain fatty acid propionate improves beta-cell function in humans and stimulates insulin secretion from human islets in vitro. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2017, 19, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).