M6A Demethylase ALKBH5 in Human Diseases: From Structure to Mechanisms
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Structural Features and Catalytic Mechanisms of ALKBH5
3. Biological Functions of ALKBH5
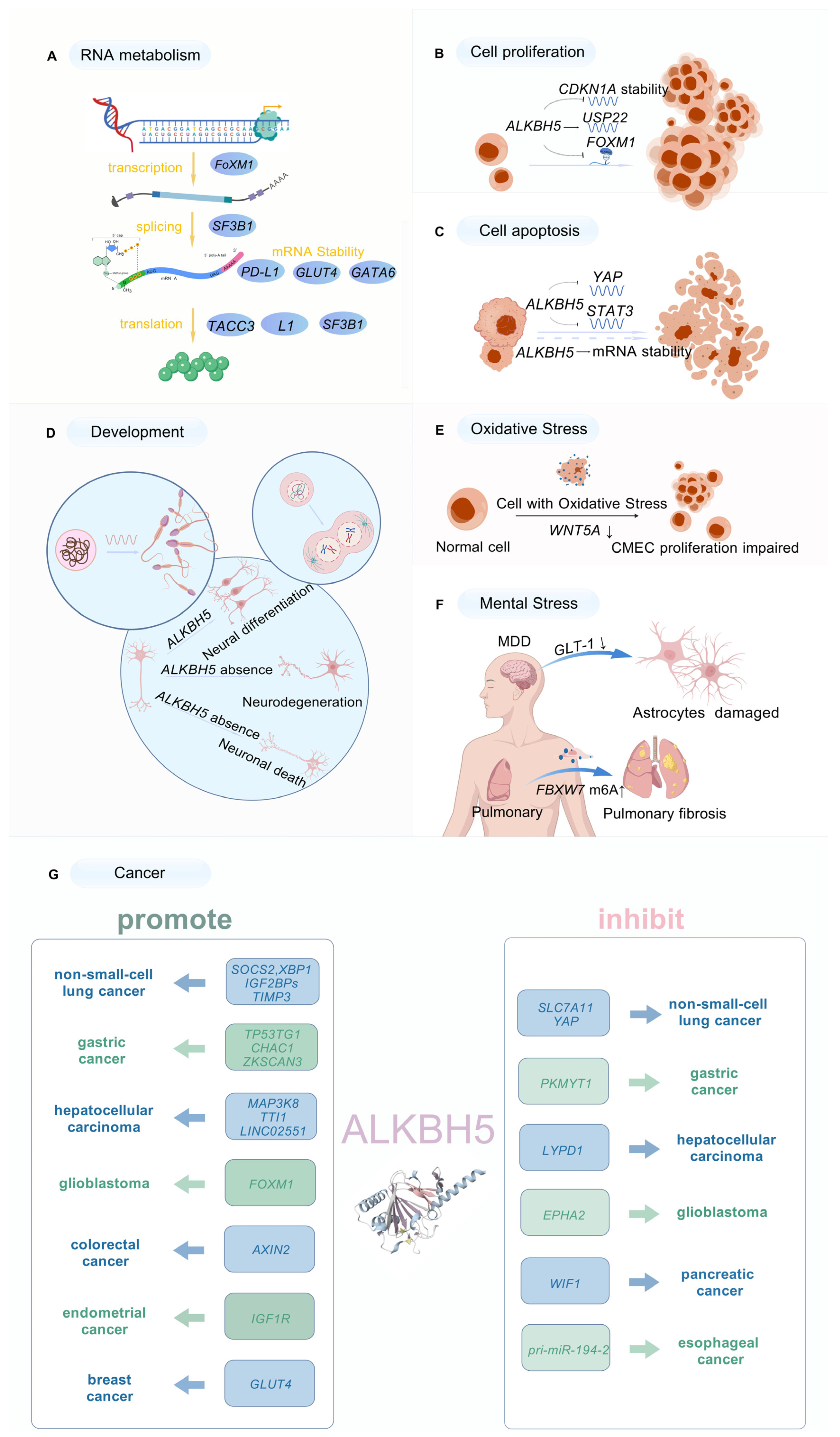
3.1. Roles of ALKBH5 in RNA Metabolism
3.2. ALKBH5 Mediation of Cell Proliferation
3.3. Association of ALKBH5 with Apoptosis
3.4. Involvement of ALKBH5 in Development
3.5. ALKBH5 Regulation of Oxidative Stress Response
3.6. ALKBH5 Regulation of Mental Stress Response
3.7. Impact of ALKBH5 on Cancer
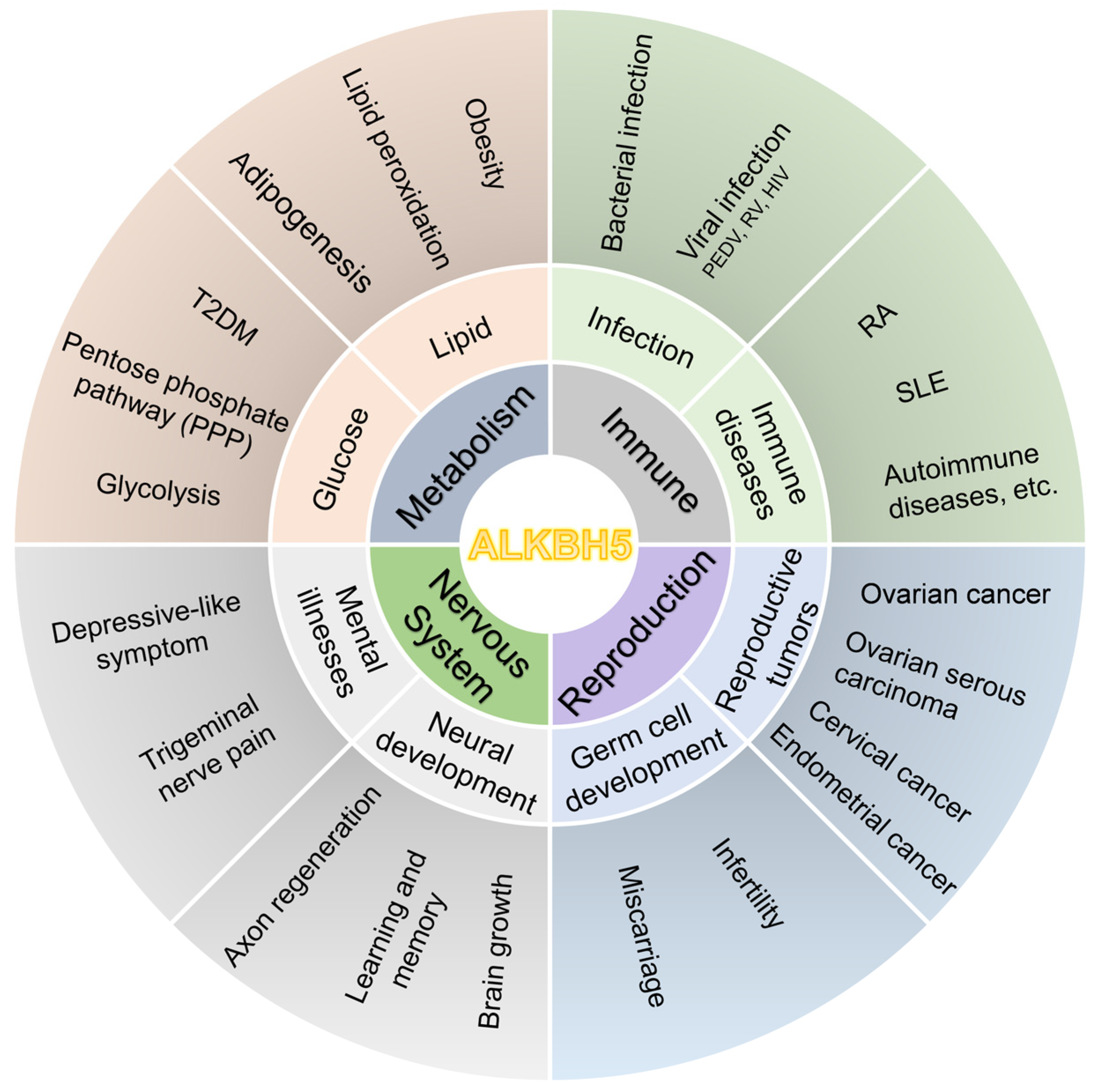
4. Research on ALKBH5 in Human Diseases
4.1. Association of ALKBH5 with Metabolic Disorders
4.1.1. ALKBH5 and Glucose Metabolism
4.1.2. ALKBH5 and Lipid Metabolism
4.1.3. ALKBH5 and T2DM
4.2. ALKBH5 and Immune System Disorders
4.3. ALKBH5 and Reproductive System Disorders
4.4. ALKBH5 and Nervous System Disorders
5. Development and Potential Applications of ALKBH5 Inhibitors
6. Conclusions and Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jiang, X.; Liu, B.; Nie, Z.; Duan, L.; Xiong, Q.; Jin, Z.; Yang, C.; Chen, Y. The Role of m6A Modification in the Biological Functions and Diseases. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Hsu, P.J.; Chen, Y.; Yang, Y. Dynamic Transcriptomic m6A Decoration: Writers, Erasers, Readers and Functions in RNA Metabolism. Cell Res. 2018, 28, 616–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheehan, C.J.; Marayati, B.F.; Bhatia, J.; Meyer, K.D. In Situ Visualization of m6A Sites in Cellular mRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, e101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Jiang, Y.; Sun, X.; Wu, Y.; Chen, Z. METTL3 Is Required for Maintaining β-Cell Function. Metabolism 2021, 116, 154702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.; Li, M.; Chang, H.; Wang, R.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, J.; He, Y.; Ma, H. The m6A Demethylase ALKBH5 Promotes Tumor Progression by Inhibiting RIG-I Expression and Interferon Alpha Production through the IKKε/TBK1/IRF3 Pathway in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Mol. Cancer 2022, 21, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Che, K.; Wu, J.; Yang, B. Construction of m6A-Related Gene Prediction Model and Subtype Analysis in Non-Obstructive Azoospermia Based on Bioinformatics. Am. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2024, 92, e13892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Gong, C.; Li, Z.; Liu, J.; Chen, Y.; Huang, Y.; Luo, Q.; Wang, S.; Hou, Y.; Yang, S.; et al. Demethylase ALKBH5 Suppresses Invasion of Gastric Cancer via PKMYT1 m6A Modification. Mol. Cancer 2022, 21, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.; Wu, R.; Ming, L. The Role of m6A RNA Methylation in Cancer. Biomed. Pharmacother. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 112, 108613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onalan, E.; Yakar, B.; Onalan, E.E.; Karakulak, K.; Kaymaz, T.; Donder, E. m6A RNA, FTO, ALKBH5 Expression in Type 2 Diabetic and Obesity Patients. J. Coll. Physicians Surg.—Pak. JCPSP 2022, 32, 1143–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benak, D.; Benakova, S.; Plecita-Hlavata, L.; Hlavackova, M. The Role of m6A and m6Am RNA Modifications in the Pathogenesis of Diabetes Mellitus. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1223583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Cai, J.; Yang, X.; Wang, K.; Sun, K.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Yang, L.; Gu, C.; Huang, X.; et al. Dysregulated m6A Modification Promotes Lipogenesis and Development of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Mol. Ther. J. Am. Soc. Gene Ther. 2022, 30, 2342–2353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, S.; Chen, C.; Ji, X.; Liu, J.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, G.; Yuan, W.; Kan, Q.; Sun, Z. The Interplay between m6A RNA Methylation and Noncoding RNA in Cancer. J. Hematol. Oncol. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2019, 12, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Weng, H.; Chen, J. m6A Modification in Coding and Non-Coding RNAs: Roles and Therapeutic Implications in Cancer. Cancer Cell 2020, 37, 270–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, J.; Hou, K.; Mi, S.; Ji, H.; Ma, S.; Ba, Y.; Hu, S.; Xie, R.; Chen, L. Malignant Evaluation and Clinical Prognostic Values of m6A RNA Methylation Regulators in Glioblastoma. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, J.; Yan, H.; Hou, Y.; Cao, W.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, E.; He, J.; Cai, Z. RNA Demethylase ALKBH5 in Cancer: From Mechanisms to Therapeutic Potential. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2022, 15, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aik, W.; Scotti, J.S.; Choi, H.; Gong, L.; Demetriades, M.; Schofield, C.J.; McDonough, M.A. Structure of Human RNA N6-Methyladenine Demethylase ALKBH5 Provides Insights into Its Mechanisms of Nucleic Acid Recognition and Demethylation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, 4741–4754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedeles, B.I.; Singh, V.; Delaney, J.C.; Li, D.; Essigmann, J.M. The AlkB Family of Fe(II)/α-Ketoglutarate-Dependent Dioxygenases: Repairing Nucleic Acid Alkylation Damage and Beyond. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 20734–20742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, D.; Wang, B.; Gao, Y.; Zhao, L.; Bi, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, N.; Kang, H.; Pang, J.; Liu, Y.; et al. Detailed Resume of RNA m6A Demethylases. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2022, 12, 2193–2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, S.; Tam, N.Y.; McDonough, M.A.; Schofield, C.J.; Aik, W.S. Mechanisms of Substrate Recognition and N6-Methyladenosine Demethylation Revealed by Crystal Structures of ALKBH5-RNA Complexes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, 4148–4160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clifton, I.J.; McDonough, M.A.; Ehrismann, D.; Kershaw, N.J.; Granatino, N.; Schofield, C.J. Structural Studies on 2-Oxoglutarate Oxygenases and Related Double-Stranded Beta-Helix Fold Proteins. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2006, 100, 644–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsujikawa, K.; Koike, K.; Kitae, K.; Shinkawa, A.; Arima, H.; Suzuki, T.; Tsuchiya, M.; Makino, Y.; Furukawa, T.; Konishi, N.; et al. Expression and Sub-Cellular Localization of Human ABH Family Molecules. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2007, 11, 1105–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toh, J.D.W.; Crossley, S.W.M.; Bruemmer, K.J.; Ge, E.J.; He, D.; Iovan, D.A.; Chang, C.J. Distinct RNA N-Demethylation Pathways Catalyzed by Nonheme Iron ALKBH5 and FTO Enzymes Enable Regulation of Formaldehyde Release Rates. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 25284–25292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, L.; Song, C.; He, C.; Zhang, Y. Mechanism and Function of Oxidative Reversal of DNA and RNA Methylation. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2014, 83, 585–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, K.D.; Jaffrey, S.R. The Dynamic Epitranscriptome: N6-Methyladenosine and Gene Expression Control. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2014, 15, 313–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, G.; Dahl, J.A.; Niu, Y.; Fedorcsak, P.; Huang, C.; Li, C.; Vågbø, C.B.; Shi, Y.; Wang, W.; Song, S.; et al. ALKBH5 Is a Mammalian RNA Demethylase That Impacts RNA Metabolism and Mouse Fertility. Mol. Cell 2013, 49, 18–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Huo, F.; Zhang, J.; Shan, H.; Pei, D. Crosstalk between m6A Modification and Alternative Splicing during Cancer Progression. Clin. Transl. Med. 2023, 13, e1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.; Klukovich, R.; Peng, H.; Wang, Z.; Yu, T.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, H.; Klungland, A.; Yan, W. ALKBH5-Dependent m6A Demethylation Controls Splicing and Stability of Long 3’-UTR mRNAs in Male Germ Cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E325–E333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papaemmanuil, E.; Cazzola, M.; Boultwood, J.; Malcovati, L.; Vyas, P.; Bowen, D.; Pellagatti, A.; Wainscoat, J.S.; Hellstrom-Lindberg, E.; Gambacorti-Passerini, C.; et al. Somatic SF3B1 Mutation in Myelodysplasia with Ring Sideroblasts. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 365, 1384–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cieśla, M.; Ngoc, P.C.T.; Muthukumar, S.; Todisco, G.; Madej, M.; Fritz, H.; Dimitriou, M.; Incarnato, D.; Hellström-Lindberg, E.; Bellodi, C. m6A-Driven SF3B1 Translation Control Steers Splicing to Direct Genome Integrity and Leukemogenesis. Mol. Cell 2023, 83, 1165–1179.e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, S.Y.; Jung, H.; Mun, S.; Lee, S.; Park, K.; Baek, S.C.; Moon, H.C.; Kim, H.; Kim, B.; Choi, Y.; et al. L1 Retrotransposons Exploit RNA m6A Modification as an Evolutionary Driving Force. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Z.; Huang, T.; Li, W.; Ma, Z.; Wang, K.; Zhai, Z.; Fan, Y.; Fu, Y.; Wang, X.; Qin, Y.; et al. ALKBH5 Governs Human Endoderm Fate by Regulating the DKK1/4-Mediated Wnt/β-Catenin Activation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024, 52, gkae707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, X.; Yang, S.; Wang, S.; Wu, J.; Zheng, B.; Wang, K.; Shen, S.; Jeong, S.; Li, Z.; Zhu, Y.; et al. M6A Demethylase ALKBH5 Regulates PD-L1 Expression and Tumor Immunoenvironment in Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma. Cancer Res. 2021, 81, 4778–4793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Lyu, H.; Jiang, G.; Chen, D.; Ruan, S.; Liu, S.; Zhou, L.; Yang, M.; Zeng, S.; He, Z.; et al. ALKBH5-Mediated m6A Demethylation of GLUT4 mRNA Promotes Glycolysis and Resistance to HER2-Targeted Therapy in Breast Cancer. Cancer Res. 2022, 82, 3974–3986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, L.; Zhao, L.; Wang, Q.; Yang, C.; Zhang, M.; Wang, B.; Jiang, K.; Ye, Y.; Wang, S.; et al. N6-Methyladenosine Demethylase ALKBH5 Suppresses Colorectal Cancer Progression Potentially by Decreasing PHF20 mRNA Methylation. Clin. Transl. Med. 2022, 12, e940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Zhao, J.; Deng, H.; Zhong, Y.; Chen, M.; Chi, L.; Luo, G.; Cao, C.; Yu, C.; Liu, H.; et al. N6-Methyladenosine Modification of PLOD2 Causes Spermatocyte Damage in Rats with Varicocele. Cell. Mol. Biol. Lett. 2023, 28, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.; Sheng, Y.; Zhu, A.C.; Robinson, S.; Jiang, X.; Dong, L.; Chen, H.; Su, R.; Yin, Z.; Li, W.; et al. RNA Demethylase ALKBH5 Selectively Promotes Tumorigenesis and Cancer Stem Cell Self-Renewal in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Cell Stem Cell 2020, 27, 64–80.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, S.; Huang, S. FoxM1: A Potential Drug Target for Glioma. Future Oncol. Lond. Engl. 2012, 8, 223–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhao, B.; Zhou, A.; Lin, K.; Zheng, S.; Lu, Z.; Chen, Y.; Sulman, E.P.; Xie, K.; Bögler, O.; et al. m6A Demethylase ALKBH5 Maintains Tumorigenicity of Glioblastoma Stem-like Cells by Sustaining FOXM1 Expression and Cell Proliferation Program. Cancer Cell 2017, 31, 591–606.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagaki, Y.; Motoyama, S.; Yamaguchi, T.; Hoshizaki, M.; Sato, Y.; Sato, T.; Koizumi, Y.; Wakita, A.; Kawakita, Y.; Imai, K.; et al. M6 A Demethylase ALKBH5 Promotes Proliferation of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Associated with Poor Prognosis. Genes Cells Devoted Mol. Cell. Mech. 2020, 25, 547–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, P.; Subbarayalu, P.; Medina, D.; Nirzhor, S.; Timilsina, S.; Rajamanickam, S.; Eedunuri, V.K.; Gupta, Y.; Zheng, S.; Abdelfattah, N.; et al. M6A RNA Methylation Regulates Histone Ubiquitination to Support Cancer Growth and Progression. Cancer Res. 2022, 82, 1872–1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, P.; Han, G.; Zhang, T.; Chang, J.; Yin, R.; Shan, Y.; Wen, J.; Xie, X.; et al. Leukemogenic Chromatin Alterations Promote AML Leukemia Stem Cells via a KDM4C-ALKBH5-AXL Signaling Axis. Cell Stem Cell 2020, 27, 81–97.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Y.; Yan, G.; He, M.; Lei, H.; Li, L.; Wang, Y.; He, X.; Li, G.; Wang, Q.; Gao, Y.; et al. ALKBH5 Suppresses Tumor Progression via an m6A-Dependent Epigenetic Silencing of Pre-miR-181b-1/YAP Signaling Axis in Osteosarcoma. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Cai, Z.; Yang, C.; Luo, Z.; Bao, X. ALKBH5 Regulates STAT3 Activity to Affect the Proliferation and Tumorigenicity of Osteosarcoma via an m6A-YTHDF2-Dependent Manner. EBioMedicine 2022, 80, 104019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Jin, F.; Wang, B.; Yin, X.; Hong, W.; Tian, F. The m6A Demethylase ALKBH5 Controls Trophoblast Invasion at the Maternal-Fetal Interface by Regulating the Stability of CYR61 mRNA. Theranostics 2019, 9, 3853–3865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, L.; Xiang, Y.; Tang, M.; Liu, S.; Chen, Q.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, M.; Wan, S.; Sang, Y.; Li, Q.; et al. ALKBH5 Controls the Meiosis-Coupled mRNA Clearance in Oocytes by Removing the N 6-Methyladenosine Methylation. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 6532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Chang, M.; Lv, H.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, W.; He, X.; Wu, G.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, D.; et al. RNA m6A Methylation Participates in Regulation of Postnatal Development of the Mouse Cerebellum. Genome Biol. 2018, 19, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Mo, Y.; Li, D.; Yu, Q.; Wang, L.; Lin, F.; Kong, C.; Balelang, M.F.; Zhang, A.; Chen, S.; et al. N6-Methyladenosine Demethylases Alkbh5/Fto Regulate Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury. Ther. Adv. Chronic Dis. 2020, 11, 2040622320916024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Hu, J.; Sun, X.; Yang, K.; Yang, L.; Kong, L.; Zhang, B.; Li, F.; Li, C.; Shi, B.; et al. Loss of m6A Demethylase ALKBH5 Promotes Post-Ischemic Angiogenesis via Post-Transcriptional Stabilization of WNT5A. Clin. Transl. Med. 2021, 11, e402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Kang, N.; Wang, R.; Li, M.; Chen, L.; Zhou, P.; Xu, D.; Zhao, H.; Fu, L. ALKBH5 SUMOylation-Mediated FBXW7 m6A Modification Regulates Alveolar Cells Senescence during 1-Nitropyrene-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 468, 133704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, T.; Rao, S.; Wu, L.; Ye, N.; Liu, Z.; Hu, H.; Xiu, J.; Shen, Y.; Xu, Q. An Association Study of the m6A Genes with Major Depressive Disorder in Chinese Han Population. J. Affect. Disord. 2015, 183, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Fan, J.; Liu, J.; Kong, P.; Ren, J.; Mo, J.; Lu, C.; Zhong, Q.; Chen, L.; Jiang, H.; et al. Astrocytic ALKBH5 in Stress Response Contributes to Depressive-like Behaviors in Mice. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 4347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, C.; Wang, B.; Peng, D.; Zhang, X.; Li, Z.; Luo, L.; He, Y.; Liang, H.; Du, X.; Li, S.; et al. Pan-Cancer Analysis Shows That ALKBH5 Is a Potential Prognostic and Immunotherapeutic Biomarker for Multiple Cancer Types Including Gliomas. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 849592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Wang, P.; Yang, Y.; Du, X.; Xia, H.; Liu, J.; Lu, L.; Wu, H.; Liu, Q. Smoking-Induced M2-TAMs, via circEML4 in EVs, Promote the Progression of NSCLC through ALKBH5-Regulated m6A Modification of SOCS2 in NSCLC Cells. Adv. Sci. Weinh. Baden-Wurtt. Ger. 2023, 10, e2300953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, H.; Zhang, C.; Hu, M.; Hu, F.; Wang, S.; Wei, W.; Hu, W. ALKBH5-Mediated m6A Modification of XBP1 Facilitates NSCLC Progression Through the IL-6-JAK-STAT3 Pathway. Mol. Carcinog. 2025, 64, 57–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuchiya, K.; Yoshimura, K.; Iwashita, Y.; Inoue, Y.; Ohta, T.; Watanabe, H.; Yamada, H.; Kawase, A.; Tanahashi, M.; Ogawa, H.; et al. m6A Demethylase ALKBH5 Promotes Tumor Cell Proliferation by Destabilizing IGF2BPs Target Genes and Worsens the Prognosis of Patients with Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Cancer Gene Ther. 2022, 29, 1355–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, Y.; Wen, D.; Zeng, L.; Lu, J.; Xiao, X.; Chen, Y.; Song, H.; Liu, Z. ALKBH5/MAP3K8 Axis Regulates PD-L1+ Macrophage Infiltration and Promotes Hepatocellular Carcinoma Progression. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2022, 18, 5001–5018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, J.; Chen, H.; Wong, C.C.; Peng, Y.; Gou, H.; Zhang, J.; Pan, Y.; Chen, D.; Lin, Y.; Wang, S.; et al. ALKBH5 Drives Immune Suppression Via Targeting AXIN2 to Promote Colorectal Cancer and Is a Target for Boosting Immunotherapy. Gastroenterology 2023, 165, 445–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Huang, Y.; Jiang, M.; Tang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Bai, L.; Yu, C.; Yang, X.; Ding, K.; Wang, W.; et al. The Demethylase ALKBH5 Mediates ZKSCAN3 Expression through the m6A Modification to Activate VEGFA Transcription and Thus Participates in MNNG-Induced Gastric Cancer Progression. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 473, 134690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, X.; Gu, Z.; Gu, Z. ALKBH5 Regulates IGF1R Expression to Promote the Proliferation and Tumorigenicity of Endometrial Cancer. J. Cancer 2020, 11, 5612–5622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Ren, C.; Jiang, A.; Sun, Y.; Lu, J.; Ling, X.; Lu, C.; Yu, Z. Arginine Methylation of ALKBH5 by PRMT6 Promotes Breast Tumorigenesis via LDHA-Mediated Glycolysis. Front. Med. 2024, 18, 344–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, D.; Guo, J.; Wu, Y.; Yang, L.; Wang, X.; Du, J.; Dai, J.; Chen, W.; Gong, K.; Miao, S.; et al. Correction: m6A Demethylase ALKBH5 Inhibits Tumor Growth and Metastasis by Reducing YTHDFs-Mediated YAP Expression and Inhibiting miR-107/LATS2-Mediated YAP Activity in NSCLC. Mol. Cancer 2022, 21, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, P.; Li, S.; Zhang, K.; Zhao, R.; Cui, J.; Zhou, W.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Cheng, Y. N6-Methyladenosine Demethylase ALKBH5 Suppresses Malignancy of Esophageal Cancer by Regulating microRNA Biogenesis and RAI1 Expression. Oncogene 2021, 40, 5600–5612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, B.; Yang, Y.; Kang, M.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Bi, Y.; He, S.; Shimamoto, F. m6A Demethylase ALKBH5 Inhibits Pancreatic Cancer Tumorigenesis by Decreasing WIF-1 RNA Methylation and Mediating Wnt Signaling. Mol. Cancer 2020, 19, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, K.; Wu, W.; Zhu, K.; Lu, L.; Lv, Z. Identification and Characterization of a Glucometabolic Prognostic Gene Signature in Neuroblastoma Based on N6-Methyladenosine Eraser ALKBH5. J. Cancer 2022, 13, 2105–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouché, C.; Serdy, S.; Kahn, C.R.; Goldfine, A.B. The Cellular Fate of Glucose and Its Relevance in Type 2 Diabetes. Endocr. Rev. 2004, 25, 807–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Yang, X.; Tang, J.; Si, S.; Zhou, Z.; Lu, J.; Han, J.; Yuan, B.; Wu, Q.; Lu, Q.; et al. ALKBH5 Inhibited Cell Proliferation and Sensitized Bladder Cancer Cells to Cisplatin by m6A-CK2α-Mediated Glycolysis. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2021, 23, 27–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, D.; Si, Q.; Yu, C.; Han, Z.; Zang, L. USF1-mediated ALKBH5 stabilizes FLII mRNA in an m6A-YTHDF2-dependent manner to repress glycolytic activity in prostate adenocarcinoma. Mol. Carcinog. 2023, 62, 1700–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, M.; Chen, J.; Lu, F.; Zhao, M.; Wu, S.; Hu, C.; Yu, P.; Kan, J.; Bai, J.; Tian, Y.; et al. Down-Regulated FTO and ALKBH5 Co-Operatively Activates FOXO Signaling through m6A Methylation Modification in HK2 mRNA Mediated by IGF2BP2 to Enhance Glycolysis in Colorectal Cancer. Cell Biosci. 2023, 13, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Chen, Y.; Wang, L.; Ji, S. ALKBH5 Promotes the Proliferation of Glioma Cells via Enhancing the mRNA Stability of G6PD. Neurochem. Res. 2021, 46, 3003–3011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, F.; Huang, W.; Huang, J.; Xiong, J.; Yang, Y.; Wu, K.; Jia, G.; Chen, J.; Feng, Y.; Yuan, B.; et al. Decreased N(6)-Methyladenosine in Peripheral Blood RNA from Diabetic Patients Is Associated with FTO Expression Rather than ALKBH5. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 100, E148–E154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Yang, J.; Liu, X.; Liu, G.; He, Z.; Gu, S. Changes of m6A Regulatory Proteins and Nrf2 Signaling Molecules in Liver Tissue of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Rats. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 2024, 82, 2217–2226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chao, X.; Guo, L.; Ye, C.; Liu, A.; Wang, X.; Ye, M.; Fan, Z.; Luan, K.; Chen, J.; Zhang, C.; et al. ALKBH5 Regulates Chicken Adipogenesis by Mediating LCAT mRNA Stability Depending on m6A Modification. BMC Genom. 2024, 25, 634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cen, S.; Li, J.; Cai, Z.; Pan, Y.; Sun, Z.; Li, Z.; Ye, G.; Zheng, G.; Li, M.; Liu, W.; et al. TRAF4 Acts as a Fate Checkpoint to Regulate the Adipogenic Differentiation of MSCs by Activating PKM2. EBioMedicine 2020, 54, 102722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wu, R.; Chen, W.; Liu, Y.; Liao, X.; Zeng, B.; Guo, G.; Lou, F.; Xiang, Y.; Wang, Y.; et al. Curcumin Prevents Obesity by Targeting TRAF4-Induced Ubiquitylation in M6 A-Dependent Manner. EMBO Rep. 2021, 22, e52146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Ye, M.; Bai, J.; Gong, Z.; Yan, L.; Gu, D.; Hu, C.; Lu, F.; Yu, P.; Xu, L.; et al. ALKBH5 Enhances Lipid Metabolism Reprogramming by Increasing Stability of FABP5 to Promote Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Neoplasms Progression in an m6A-IGF2BP2-Dependent Manner. J. Transl. Med. 2023, 21, 741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.; Song, C.; Liu, J.; Chen, F.; Zhu, Y.; Fang, X.; Cao, Q.; Ma, D.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, C. Chlorogenic Acid Modulates Autophagy by Inhibiting the Activity of ALKBH5 Demethylase, Thereby Ameliorating Hepatic Steatosis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 15073-15086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, C.; Xu, H.; Yu, Z.; Roulis, M.; Qu, R.; Zhou, J.; Oh, J.; Crawford, J.; Gao, Y.; Jackson, R.; et al. RNA m6A Demethylase ALKBH5 Regulates the Development of Γδ T Cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2203318119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Song, R.; Lu, Z.; Zhao, L.; Zhan, X.; Li, Y.; Cao, X. The RNA m6A Demethylase ALKBH5 Drives Emergency Granulopoiesis and Neutrophil Mobilization by Upregulating G-CSFR Expression. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2024, 1, 6–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Liu, N.; Zhu, X.; Yang, L.; Ye, B.; Li, H.; Zhu, P.; Lu, T.; Tian, Y.; Fan, Z. Circular RNA circZbtb20 Maintains ILC3 Homeostasis and Function via Alkbh5-Dependent m6A Demethylation of Nr4a1 mRNA. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2021, 18, 1412–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Xu, N.; Zhou, J.; He, Z.; Lenahan, C.; Wang, C.; Ji, H.; Liu, B.; Zou, Y.; Zeng, H.; et al. ALKBH5 Promotes PD-L1-Mediated Immune Escape through m6A Modification of ZDHHC3 in Glioma. Cell Death Discov. 2022, 8, 497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.; Xu, C.; Wu, S.; Wu, Z.; Wu, S.; Sun, M.; Bao, W. m6A Demethylase ALKBH5 Restrains PEDV Infection by Regulating GAS6 Expression in Porcine Alveolar Macrophages. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 6191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, A.; Tao, W.; Tong, J.; Gao, J.; Wang, J.; Hou, G.; Qian, C.; Zhang, G.; Li, R.; Wang, D.; et al. m6A Modifications Regulate Intestinal Immunity and Rotavirus Infection. eLife 2022, 11, e73628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Kumar, S.; Espada, C.E.; Tirumuru, N.; Cahill, M.P.; Hu, L.; He, C.; Wu, L. N6-Methyladenosine Modification of HIV-1 RNA Suppresses Type-I Interferon Induction in Differentiated Monocytic Cells and Primary Macrophages. PLoS Pathog. 2021, 17, e1009421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Q.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, L.; Rao, J.; Guo, Y.; Huang, Z.; Li, J. Decreased ALKBH5, FTO, and YTHDF2 in Peripheral Blood Are as Risk Factors for Rheumatoid Arthritis. BioMed Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 5735279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Rao, J.; Zhang, L.; Fu, B.; Guo, Y.; Huang, Z.; Li, J. The Study of METTL14, ALKBH5, and YTHDF2 in Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells from Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Mol. Genet. Genomic Med. 2020, 8, e1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Fu, B.; Zhang, L.; Guo, Y.; Huang, Z.; Li, J. Decreased Peripheral Blood ALKBH5 Correlates with Markers of Autoimmune Response in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Dis. Markers 2020, 2020, 8193895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barro, M.; Patton, J.T. Rotavirus Nonstructural Protein 1 Subverts Innate Immune Response by Inducing Degradation of IFN Regulatory Factor 3. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 4114–4119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, X.; Xu, Q.; Wu, R.; Sun, W.; Gu, Y.; Zhu, S.; Liu, X.; Lv, T.; Song, Y. ALKBH5 Promotes Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Progression and Susceptibility to Anti-PD-L1 Therapy by Modulating Interactions between Tumor and Macrophages. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. CR 2024, 43, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Zhang, X.; Hu, J.; Qu, R.; Yu, Z.; Xu, H.; Chen, H.; Yan, L.; Ding, C.; Zou, Q.; et al. m6A Demethylase ALKBH5 Controls CD4+ T Cell Pathogenicity and Promotes Autoimmunity. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabg0470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, R.; Zhao, J.; Gao, C.; Qin, Q.; Zhang, J. Inclusion of ALKBH5 as a Candidate Gene for the Susceptibility of Autoimmune Thyroid Disease. Adv. Med. Sci. 2021, 66, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Q.; Wu, X.; Deng, C.; Zhao, L.; Peng, L.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, W.; Zhao, Y.; Fei, Y. The Potential Role of RNA N6-Methyladenosine in Primary Sjögren’s Syndrome. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 959388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, H.; Gan, X.; Jiang, X.; Diao, S.; Wu, H.; Hu, J. ALKBH5 Inhibited Autophagy of Epithelial Ovarian Cancer through miR-7 and BCL-2. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. CR 2019, 38, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Wan, Y.; Gong, M.; Zhou, S.; Qiu, J.; Cheng, W. RNA Demethylase ALKBH5 Promotes Ovarian Carcinogenesis in a Simulated Tumour Microenvironment through Stimulating NF-κB Pathway. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 6137–6148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, R.; Yuan, L.; Jiang, Y.; Wan, Y.; Ma, X.; Yang, J.; Sun, G.; Zhou, S.; Wang, H.; Qiu, J.; et al. ALKBH5 activates FAK signaling through m6A demethylation in ITGB1 mRNA and enhances tumor-associated lymphangiogenesis and lymph node metastasis in ovarian cancer. Theranostics 2023, 13, 833–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Q.; Yang, F.; Gan, H.; Jin, L. Hypoxia induced ALKBH5 prevents spontaneous abortion by mediating m6A-demethylation of SMAD1/5 mRNAs. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2022, 1869, 119316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.; Zhu, Y.; Li, J.; Zeng, J.; Wu, L. ALKBH5-Mediated m6A Modification of circCCDC134 Facilitates Cervical Cancer Metastasis by Enhancing HIF1A Transcription. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. CR 2022, 41, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, Z.; Kong, B.; Song, C.; Cong, J.; Hou, J.; Wang, S. Reduced m6A mRNA Methylation Is Correlated with the Progression of Human Cervical Cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 98918–98930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Wu, G.; Peng, B.; Li, J.; Zeng, S.; Yan, Y.; Xu, Z. Expression and Molecular Profiles of the AlkB Family in Ovarian Serous Carcinoma. Aging 2021, 13, 9679–9692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, T.; Li, G.; Yang, J.; Ma, K. RNA demethylase Alkbh5 is widely expressed in neurons and decreased during brain development. Brain Res. Bull. 2020, 163, 150–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Zheng, T.; Zhou, S.; Liu, M.; Liu, Y.; Gu, X.; Mao, S.; Yu, B. Promoting Axon Regeneration by Inhibiting RNA N6-Methyladenosine Demethylase ALKBH5. eLife 2023, 12, e85309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, W.; Chen, Y.; Li, W.; Peng, K.; Xu, H.; Yang, Y.; Shan, X.; Huo, W.; et al. Identification of Differential m6A RNA Methylomes and ALKBH5 as a Potential Prevention Target in the Developmental Neurotoxicity Induced by Multiple Sevoflurane Exposures. FASEB J. 2024, 38, e23793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, Y.; Fan, Y.; Huang, G.; Liu, J. N6-Methyladenosine Demethylase ALKBH5 Homologous Protein Protects against Cerebral I/R Injury Though Suppressing SNHG3-Mediated Neural PANoptosis: Involvement of m6A-Related Macromolecules in the Diseases of Nervous System. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 274, 133815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, S.; Qi, R.; Tao, Y.; Sun, Y.; Jiang, D.; Jiang, X.; Tao, J. FOXD3-Mediated Transactivation of ALKBH5 Promotes Neuropathic Pain via m6A-Dependent Stabilization of 5-HT3A mRNA in Sensory Neurons. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2024, 121, e2312861121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.; Liu, K.; Tempel, W.; Demetriades, M.; Aik, W.; Schofield, C.J.; Min, J. Structures of Human ALKBH5 Demethylase Reveal a Unique Binding Mode for Specific Single-Stranded N6-Methyladenosine RNA Demethylation. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 17299–17311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Kennedy, S.; Hajian, T.; Gibson, E.; Seitova, A.; Xu, C.; Arrowsmith, C.H.; Vedadi, M. A Radioactivity-Based Assay for Screening Human m6A-RNA Methyltransferase, METTL3-METTL14 Complex, and Demethylase ALKBH5. J. Biomol. Screen. 2016, 21, 290–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Xu, C.; Yang, K.; Gao, R.; Cao, Y.; Liang, L.; Chen, S.; Xu, S.; Rong, R.; Wang, J.; et al. Inhibition of ALKBH5 Attenuates I/R-Induced Renal Injury in Male Mice by Promoting Ccl28 m6A Modification and Increasing Treg Recruitment. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Cao, Q.; Ji, J.; Jiang, C.; Yuan, S.; Chen, X.; et al. ALKBH5 Causes Retinal Pigment Epithelium Anomalies and Choroidal Neovascularization in Age-Related Macular Degeneration via the AKT/mTOR Pathway. Cell Rep. 2023, 42, 112779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Lu, Y. Dexmedetomidine Suppressed the Biological Behavior of HK-2 Cells Treated with LPS by Down-Regulating ALKBH5. Inflammation 2020, 43, 2256–2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Kang, Y.; Wang, L.; Huff, S.; Tang, R.; Hui, H.; Agrawal, K.; Gonzalez, G.M.; Wang, Y.; Patel, S.P.; et al. ALKBH5 Regulates Anti-PD-1 Therapy Response by Modulating Lactate and Suppressive Immune Cell Accumulation in Tumor Microenvironment. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 20159–20170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Z.; Mu, B.; Liu, Y.; Guo, N.; Xiong, L.; Guo, Y.; Xia, A.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, H.; Yao, R.; et al. Discovery of a Potent, Selective and Cell Active Inhibitor of m6A Demethylase ALKBH5. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 238, 114446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Yan, F.; Geng, Y.; Cheng, X.; Zhang, S.; Zhao, T.; Guo, J.; Dai, Z.; Gao, J.; Yue, X.; et al. ALKBH5 Deficiency Attenuates Oxygen-Glucose Deprivation-Induced Injury in Mouse Brain Microvascular Endothelial Cells in an m6A Dependent Manner. Exp. Neurol. 2024, 380, 114910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, H.; Hase, H.; Yoshida, T.; Tashiro, J.; Hirade, Y.; Kitae, K.; Tsujikawa, K. Discovery of Two Novel ALKBH5 Selective Inhibitors That Exhibit Uncompetitive or Competitive Type and Suppress the Growth Activity of Glioblastoma Multiforme. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2022, 100, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, R.; Xu, J.; Gu, J.; Jiang, Z.; Jiang, Z.; You, Q.; Guo, X. Discovery of Pyrazolo [1,5-a] Pyrimidine Derivative as a Novel and Selective ALKBH5 Inhibitor for the Treatment of AML. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 66, 15944–15959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selberg, S.; Seli, N.; Kankuri, E.; Karelson, M. Rational Design of Novel Anticancer Small-Molecule RNA m6A Demethylase ALKBH5 Inhibitors. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 13310–13320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, G.; Li, Y.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, T.; Gao, J.; Zhou, H.; Yang, C. A Covalent Compound Selectively Inhibits RNA Demethylase ALKBH5 Rather than FTO. RSC Chem. Biol. 2024, 5, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malacrida, A.; Rivara, M.; Di Domizio, A.; Cislaghi, G.; Miloso, M.; Zuliani, V.; Nicolini, G. 3D Proteome-Wide Scale Screening and Activity Evaluation of a New ALKBH5 Inhibitor in U87 Glioblastoma Cell Line. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2020, 28, 115300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malacrida, A.; Di Domizio, A.; Bentivegna, A.; Cislaghi, G.; Messuti, E.; Tabano, S.M.; Giussani, C.; Zuliani, V.; Rivara, M.; Nicolini, G. MV1035 Overcomes Temozolomide Resistance in Patient-Derived Glioblastoma Stem Cell Lines. Biology 2022, 11, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
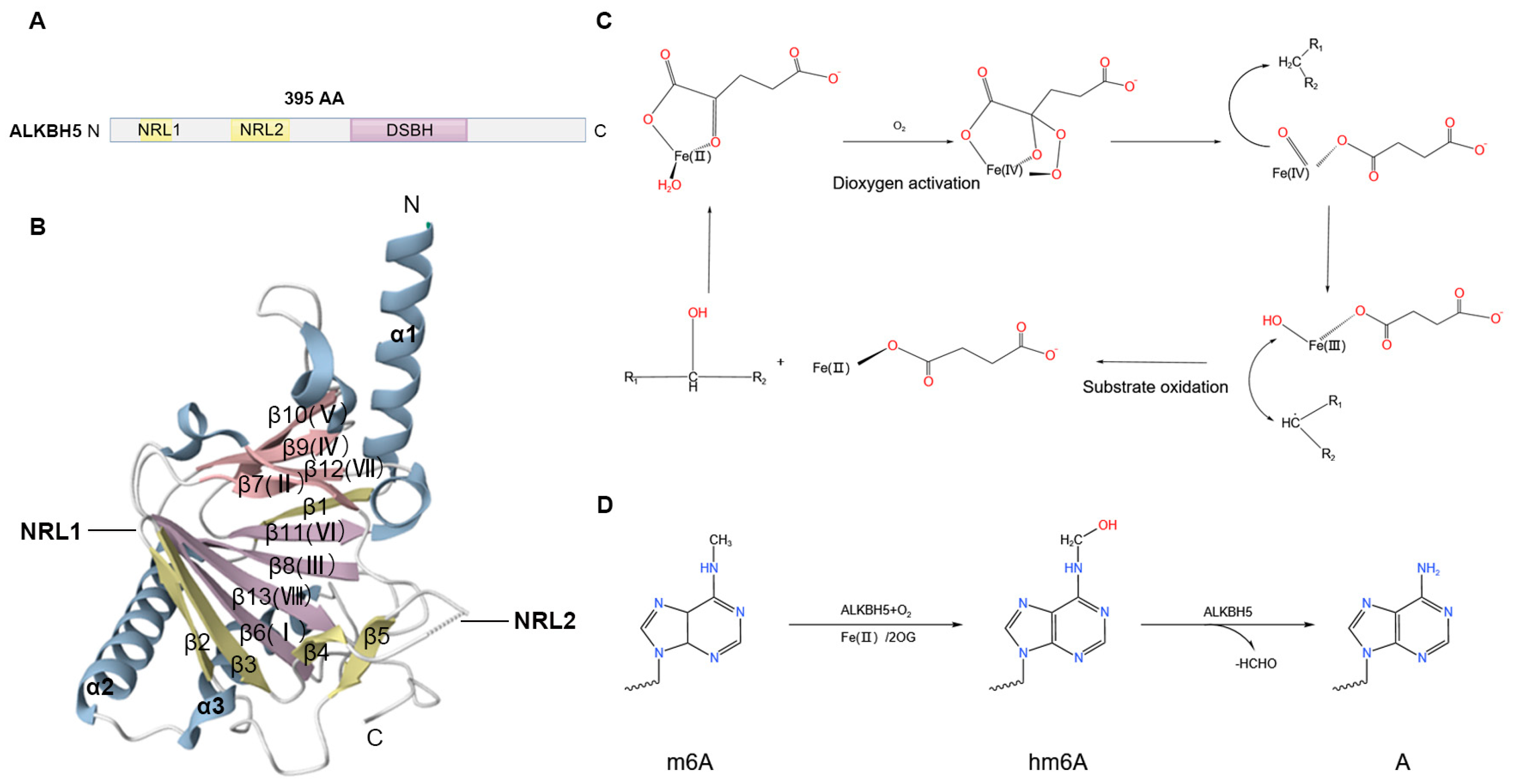
| Glucose Metabolism | ALKBH5 | Target | Function | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Enhanced Glycolysis | down | CK2α | Downregulated ALKBH5 promoted bladder cancer development through modulating the glycolysis pathway mediated by CK2α in an m6A-dependent manner. | [66] |
| down | FLII | The USF1-mediated downregulation of ALKBH5 stabilized FLII mRNA in a YTHDF2-dependent manner to repress glycolytic activity, subsequently inhibiting prostate adenocarcinoma. | [67] | |
| down | HK2 | In a high-fat environment, the diminished expression of FTO and ALKBH5 cooperatively activated FOXO signaling through IGF2BP2-mediated m6A methylation in HK2 mRNA, which boosted glycolysis in colorectal cancer. | [68] | |
| up | GLUT4 | The increased expression of ALKBH5 promoted the m6A demethylation and stability of GLUT4 mRNA in a YTHDF2-dependent manner, leading to enhanced glycolysis in drug-resistant breast cancer cells. | [33] | |
| Aerobic Glycolysis | up | LDHA | PRMT6 directly methylated ALKBH5 at Arg283, which strengthened the stability of LDHA mRNA, leading to increased aerobic glycolysis in breast cancer cells. | [60] |
| Pentose Phosphate Pathway (PPP) | up | G6PD | Upregulated ALKBH5 demethylated G6PD mRNA and enhanced the stability and expression of G6PD, which activated the pentose phosphate pathway and stimulated the proliferation of glioma cells. | [69] |
| T2DM (Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus) | down | - | The expression of FTO and ALKBH5 mRNA in peripheral blood was lower in the T2DM group compared to the healthy group. | [9] |
| unchanged | - | The reduced m6A content in the peripheral blood of patients with T2DM and diabetic rats was only related to increased FTO mRNA expression, but not ALKBH5. | [70] | |
| up | - | FTO and Alkbh5 quantities in the liver of T2DM rats were higher than those in the control group. | [71] |
| Lipid Metabolism | ALKBH5 | Target | Function | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adipogenesis | down | LCAT | Low expression of ALKBH5 reinforced the m6A methylation of LCAT to improve the stability of its mRNA, which promoted preadipocyte differentiation and thus enhanced adipogenesis. | [72] |
| down | TRAF4 | Downregulated ALKBH5 enhanced TRAF4 m6A modification, thus reducing the expression of TRAF4, and the PKM2/TRAF4 interaction, which weakened the kinase activity of PKM2 and obstructed β-catenin signal transduction, thus promoting the fat formation of MSCs. | [73] | |
| up | TRAF4 | Curcumin reduced the expression of ALKHB5, leading to an increase in m6A-modified TRAF4 mRNA and promoting its translation, which promoted the degradation of adipocyte differentiation regulator PPARγ through a ubiquitin–proteasome pathway, thereby inhibiting adipogenesis. | [74] | |
| Lipid metabolism | up | FABP5 | Upregulated ALKBH5 significantly increased FABP5 expression in an m6A-IGF2BP2-dependent manner, thereby activating the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway and enhancing lipid metabolism in pNENs. | [75] |
| Lipid deposition | up | AXL | The weakened activity of ALKBH5 mediated by CGA reduced the stability and expression of AXL mRNA in hepatocytes, which further suppressed the MAPK/ERK signaling pathway, thus reducing liver lipid deposition and, finally, improving HFD-induced MASLD. | [76] |
| Disease | ALKBH5 | Target | Function | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Systemic bacterial infection | down | CSF3R | When systemic bacterial infection occurred, ALKBH5 enhanced the expression of pro-neutrophil-migration molecules such as CXCR2, thereby promoting the recruitment of neutrophils to the infection area to remove bacteria. | [78] |
| C. rodentium infection | down | Nr4a1 | High expression of Alkbh5 reduced the m6A level of Nr4a1 mRNA and heightened its stability, which activated Notch2 signaling, maintaining the homeostasis of group 3 innate lymphocyte cells (ILC3s), thereby reducing susceptibility to C. rodentium infection. | [79] |
| Gastrointestinal Salmonella typhimurium infection | up | Jagged1 and Notch2 | Alkbh5-deficient mice exhibited a protective effect against Salmonella typhimurium infection through the downregulation of Jagged1 and Notch2. | [77] |
| PEDV infection | down | GAS6 | ALKBH5 modulated the expression of GAS6, which attenuated the ability of PEDV to infect lung tissue and the 3D4/21 alveolar macrophage cell line. | [81] |
| RV infection | down | NSP1 | ALKBH5 expression was predominantly diminished in the RV-infected IECs of mice due to NSP1, which facilitated the RV virus in evading antiviral immune defense. | [82] |
| HIV-1 infection | down | IFN-I | ALKBH5 reduced the m6A level of HIV-1 RNA to enhance the expression of IFN-I by activating transcription factors IRF3 and IRF7, thus promoting the antiviral immunity of bone marrow cells. | [83] |
| RA | down | - | A decreased peripheral blood expression of ALKBH5 was a dangerous factor for rheumatoid arthritis. | [84] |
| SLE | down | - | ALKBH5 mRNA expression was cardinally cut down in the peripheral blood mononuclear cells of patients with SLE, implicating ALKBH5 as one of the potential risk factors of SLE. | [85,86] |
| Disorder | ALKBH5 | Target | Function | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Epithelial ovarian cancer | up | BCL-2 | ALKBH5 promoted the stability of BCL-2 mRNA and thus enhanced the binding of Bcl-2 and Beclin1, which eventually prohibited autophagy and aggravated epithelial ovarian cancer. | [92] |
| Ovarian cancer | up | NANOG | ALKBH5 enhanced NANOG expression through the demethylation of NANOG mRNA, which accelerated ovarian cancer development. | [93] |
| Metastatic ovarian cancer | up | ITGB1 | ALKBH5 inhibited the degradation of ITGB1 and enhanced its expression, which augmented the phosphorylation of focal adhesion kinase (FAK) and Src proto-oncogene proteins, and promoted lymph node metastasis. | [94] |
| Endometrial cancer | up | IGF1R | ALKBH5 promoted the proliferation and invasion of endometrial cancer via the erasing of IGF1R m6A modifications. | [59] |
| Infertility | down | - | ALKBH5 KO in mice affected the output of mRNA and thus suppressed sperm development and quality, ultimately inhibiting fertility. | [25] |
| down | Unc50 and Traf3ip1 | The inactivation of Alkbh5 in spermatocytes and round sperm nuclei led to abnormal splicing and the production of shorter transcripts, resulting in male infertility in mice. | [27] | |
| down | Atp5j2, Birc5, Esrrb, and Rpl39 | The loss of Alkbh5 caused oocyte meiosis defects, leading to impaired RNA clearance and female infertility. | [45] | |
| Recurrent miscarriage (RM) | up | CYR61 | In the trophoblast of patients with RM, upregulated ALKBH5 shortened the half-life of CYR61 mRNA and inhibited its expression, thereby inhibiting trophoblast invasion. | [44] |
| Recurrent spontaneous abortion (RSA) | down | SMAD1 / 5 | The trophoblast-specific knockdown of ALKBH5 in mouse placenta attenuated the translation of SMAD1/5 by increasing m6A modification, thereby inhibiting trophoblast cell activity and significantly leading to fetal abortion. | [95] |
| Process or Disease | ALKBH5 | Target | Function | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brain development | down | - | Alkbh5 protein decreased dramatically during brain development. | [99] |
| Optic nerve injury | up | Lpin2 | ALKBH5 increased the stability of Lpin2 mRNA and thus hindered the regenerative growth associated with lipid metabolism in neurons, thereby inhibiting survival and axonal regeneration after neuronal injury in rodents. | [100] |
| Learning and memory impairments | up | - | In hippocampal neuronal injury mice, Alkbh5 expression was increased in the hippocampus, accompanied by learning and memory impairments. | [101] |
| Cerebral I/R injury | down | SNHG3 | ALKBH5 induced SNHG3 mRNA demethylation to inhibit its expression, thereby protecting against damage and PANoptosis in a cerebral I/R injury model. | [102] |
| Major depression disorder (MDD) | up | GLT-1 | ALKBH5 lowered GLT-1 m6A modification and increased the expression of GLT-1 in astrocytes, thereby impairing glutamate uptake and, finally, promoting depressive-like behaviors. | [51] |
| Neuropathic pain | up | Htr3a | The FOXD3-mediated transactivation of ALKBH5 promoted neuropathic pain through the m6A-dependent stabilization of Htr3a mRNA in trigeminal ganglion (TG) neurons. | [103] |
| Inhibitor | Type | Selectivity | Diseases | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Citrate | Natural inhibitor | - | - | [104] |
| CGA | Natural inhibitor | No | MASLD | [76] |
| IOX1 | Competitive inhibitor | No | I/R-induced renal injury | [105] |
| AKI | [106] | |||
| AMD | [107] | |||
| Dexmedetomidine | Demethylase activity inhibitor | No | Sepsis | [108] |
| ALK-04 | Small-molecule inhibitor | No | Melanoma | [109] |
| 20m | Novel inhibitor | Yes | OGD-induced BMEC injury | [110,111] |
| Ena21 | Competitive inhibitor | No | GBM | [112] |
| Ena15 | Non-competitive inhibitor | Yes | GBM | [112] |
| DO-2728 | Competitive inhibitor | Yes | AML | [113] |
| cmp-3 and cmp-6 | Novel inhibitor | Yes | Leukemia and GBM | [114] |
| TD19 | Covalent inhibitor | Yes | AML | [115] |
| MV1035 | Competitive inhibitor | Yes | GBM | [116,117] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fang, M.; Ye, L.; Zhu, Y.; Huang, L.; Xu, S. M6A Demethylase ALKBH5 in Human Diseases: From Structure to Mechanisms. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 157. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15020157
Fang M, Ye L, Zhu Y, Huang L, Xu S. M6A Demethylase ALKBH5 in Human Diseases: From Structure to Mechanisms. Biomolecules. 2025; 15(2):157. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15020157
Chicago/Turabian StyleFang, Miaochun, Liwen Ye, Yue Zhu, Linying Huang, and Shun Xu. 2025. "M6A Demethylase ALKBH5 in Human Diseases: From Structure to Mechanisms" Biomolecules 15, no. 2: 157. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15020157
APA StyleFang, M., Ye, L., Zhu, Y., Huang, L., & Xu, S. (2025). M6A Demethylase ALKBH5 in Human Diseases: From Structure to Mechanisms. Biomolecules, 15(2), 157. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15020157






