Gold Nanoparticles-Enhanced Gene Transfer Driven by MHz-Frequency Nanosecond Pulsed Electric Fields
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
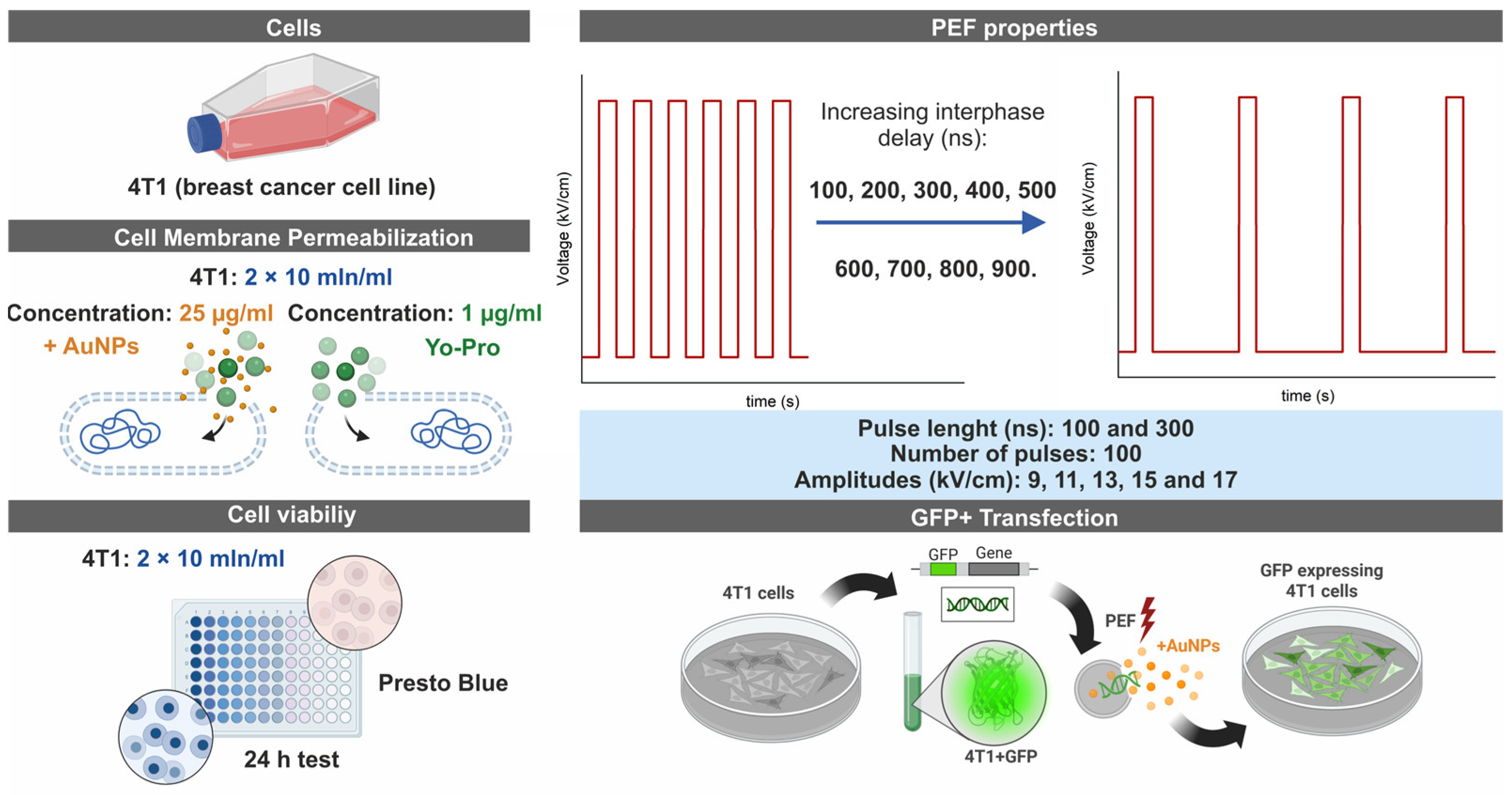
2.1. Cells
2.2. Electroporation Setup and Parameters
2.3. Cell Permeabilization Detection Assay Using Yo-Pro-1
2.4. Viability Assay
2.5. Gene Delivery Experiments
2.6. The Preparation of AuNPs
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Cell Membrane Permeabilization
3.2. Cell Viability with and Without AuNPs
3.3. Gene Electrotransfer
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kotnik, T.; Frey, W.; Sack, M.; Meglič, S.H.; Peterka, M.; Miklavčič, D. Electroporation-based applications in biotechnology. Trends Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 480–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Li, Y.; Sun, D.W.; Zhu, Z. Enhancing Food Processing by Pulsed and High Voltage Electric Fields: Principles and Applications. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2018, 58, 2285–2298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, F.; Qian, K.; Li, X.; Deng, H. Simulation study of cell transmembrane potential and electroporation induced by time-varying magnetic fields. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2022, 81, 103117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Movahed, S.; Li, D. A theoretical study of single-cell electroporation in a microchannel. J. Membr. Biol. 2013, 246, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aycock, K.N.; Campelo, S.N.; Davalos, R.V. A Comparative Modeling Study of Thermal Mitigation Strategies in Irreversible Electroporation Treatments. J. Heat Transfer 2022, 144, 031206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, J.; Wang, Y.; Rubinsky, B. A Study on Nonthermal Irreversible Electroporation of the Thyroid. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2019, 18, 1533033819876307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Velázquez, P.; Castellví, Q.; Villanueva, A.; Quesada, R.; Pañella, C.; Cáceres, M.; Dorcaratto, D.; Andaluz, A.; Moll, X.; Trujillo, M.; et al. Irreversible electroporation of the liver: Is there a safe limit to the ablation volume? Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 23781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Yao, C.; Mi, Y.; Dong, S.; Liu, H. Experimental study on the killing effect of the irreversible electroporation in different frequencies. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Pulsed Power Conference (PPC), Austin, TX, USA, 31 May–4 June 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neu, W.K.; Neu, J.C. Mechanism of Irreversible Electroporation in Cells: Insight from the Models. In Irreversible Electroporation; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 85–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagstaff, P.G.K.; Buijs, M.; van den Bos, W.; de Bruin, D.M.; Zondervan, P.J.; de la Rosette, J.J.M.C.H.; Laguna Pes, M.P. Irreversible electroporation: State of the art. Onco Targets Ther. 2016, 9, 2437–2446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotnik, T.; Rems, L.; Tarek, M.; Miklavčič, D.; Miklavcic, D. Membrane Electroporation and Electropermeabilization: Mechanisms and Models. Annu. Rev. Biophys. 2019, 48, 63–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiwani, T.; Dhesi, S.S.; Wah, T.M. Reversible electroporation for cancer therapy. Br. J. Radiol. 2025, 98, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, J.L.; Dean, D.A. Electroporation-Mediated Gene Delivery. Adv. Genet. 2015, 89, 49–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escoffre, J.M.; Portet, T.; Wasungu, L.; Teissié, J.; Dean, D.; Rols, M.P. What is (Still not) known of the mechanism by which electroporation mediates gene transfer and expression in cells and tissues. Mol. Biotechnol. 2009, 41, 286–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, K.H. Gene Transfer Technologies and their Applications: Roles in Human Diseases. Asian J. Exp. Biol. Sci. 2010, 1, 208–218. [Google Scholar]
- Heller, R.; Heller, L.C. Gene Electrotransfer Clinical Trials. In Advances in Genetics; Elsevier Ltd.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heller, L.C.; Heller, R. Electroporation Gene Therapy Preclinical and Clinical Trials for Melanoma. Curr. Gene Ther. 2010, 10, 312–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prud’homme, G.; Glinka, Y.; Khan, A.; Draghia-Akli, R. Electroporation-Enhanced Nonviral Gene Transfer for the Prevention or Treatment of Immunological, Endocrine and Neoplastic Diseases. Curr. Gene Ther. 2006, 6, 243–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Covello, G.; Siva, K.; Adami, V.; Denti, M.A. An electroporation protocol for efficient DNA transfection in PC12 cells. Cytotechnology 2014, 66, 543–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maja, M.; De Robertis, M.; Heller, L.C.; Heller, R.; Gong, X.; Chen, Z.; Hu, J.J.; Liu, C. Advances of Electroporation-Related Therapies and the Synergy with Immunotherapy in Cancer Treatment. Vaccines 2022, 10, 1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvet, C.Y.; André, F.M.; Mir, L.M. Dual therapeutic benefit of electroporation-mediated DNA vaccination in vivo. Oncoimmunology 2014, 3, e28540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yen, H.H.; Scheerlinck, J.P.Y. Co-delivery of plasmid-encoded cytokines modulates the immune response to a DNA vaccine delivered by in vivo electroporation. Vaccine 2007, 25, 2575–2582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burkart, C.; Mukhopadhyay, A.; Shirley, S.A.; Connolly, R.J.; Wright, J.H.; Bahrami, A.; Campbell, J.S.; Pierce, R.H.; Canton, D.A. Improving therapeutic efficacy of IL-12 intratumoral gene electrotransfer through novel plasmid design and modified parameters. Gene Ther. 2018, 25, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Danishmalik, S.N.; Sin, J.I. DNA vaccines, electroporation and their applications in cancer treatment. Hum. Vaccin. Immunother. 2015, 11, 1889–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Zhang, N.; Liang, X.; Li, J.; Gong, P.; Yu, X.; Ma, G.; Ryan, U.M.; Zhang, X. Transient transfection of Cryptosporidium parvum using green fluorescent protein (GFP) as a marker. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 2009, 168, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva-Pilipich, N.; Lasarte-Cía, A.; Lozano, T.; Martín-Otal, C.; Lasarte, J.J.; Smerdou, C. Intratumoral electroporation of a self-amplifying RNA expressing IL-12 induces antitumor effects in mouse models of cancer. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2022, 29, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Divangahi, M.; Ngai, P.; Santosuosso, M.; Millar, J.; Zganiacz, A.; Wang, J.; Bramson, J.; Xing, Z. Intramuscular immunization with a monogenic plasmid DNA tuberculosis vaccine: Enhanced immunogenicity by electroporation and co-expression of GM-CSF transgene. Vaccine 2007, 25, 1342–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balantič, K.; Miklavčič, D.; Križaj, I.; Kramar, P. The Good and the Bad of Cell Membrane Electroporation. Acta Chim. Slov. 2021, 68, 753–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherba, J.J.; Hogquist, S.; Lin, H.; Shan, J.W.; Shreiber, D.I.; Zahn, J.D. The effects of electroporation buffer composition on cell viability and electro-transfection efficiency. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 3053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chicaybam, L.; Barcelos, C.; Peixoto, B.; Carneiro, M.; Limia, C.G.; Redondo, P.; Lira, C.; Paraguassú-Braga, F.; De Vasconcelos, Z.F.M.; Barros, L.; et al. An Efficient Electroporation Protocol for the Genetic Modification of Mammalian Cells. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2017, 4, 229100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, F.; Xie, X.; Gollan, T.; Zhao, L.; Narsinh, K.; Lee, R.J.; Wu, J.C. Comparison of gene-transfer efficiency in human embryonic stem cells. Mol. Imaging Biol. 2010, 12, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roos, A.K.; Eriksson, F.; Timmons, J.A.; Gerhardt, J.; Nyman, U.; Gudmundsdotter, L.; Bråve, A.; Wahren, B.; Pisa, P. Skin Electroporation: Effects on Transgene Expression, DNA Persistence and Local Tissue Environment. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e7226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisec, B.; Markelc, B.; Valentinuzzi, K.U.; Sersa, G.; Cemazar, M. The effectiveness of calcium electroporation combined with gene electrotransfer of a plasmid encoding IL-12 is tumor type-dependent. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 2694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado-Cañedo, A.; Santos, D.G.D.; Chies, J.A.B.; Kvitko, K.; Nardi, N.B. Optimization of an electroporation protocol using the K562 cell line as a model: Role of cell cycle phase and cytoplasmic DNAses. Cytotechnology 2006, 51, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Caro, A.; Bellard, E.; Kolosnjaj-Tabi, J.; Golzio, M.; Rols, M.P. Gene Electrotransfer Efficiency in 2D and 3D Cancer Cell Models Using Different Electroporation Protocols: A Comparative Study. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chopinet, L.; Wasungu, L.; Rols, M.P. First explanations for differences in electrotransfection efficiency in vitro and in vivo using spheroid model. Int. J. Pharm. 2012, 423, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavlin, M.; Flisar, K.; Kandušer, M. The role of electrophoresis in gene electrotransfer. J. Membr. Biol. 2010, 236, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsong, T.Y. Electroporation of cell membranes. Biophys. J. 1991, 60, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golberg, A.; Rubinsky, B. Towards electroporation based treatment planning considering electric field induced muscle contractions. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2012, 11, 189–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cvetkoska, A.; Maček-Lebar, A.; Trdina, P.; Miklavčič, D.; Reberšek, M. Muscle contractions and pain sensation accompanying high-frequency electroporation pulses. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 8019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakhomova, O.N.; Khorokhorina, V.A.; Bowman, A.M.; Rodaite-Riševičiene, R.; Saulis, G.; Xiao, S.; Pakhomov, A.G. Oxidative effects of nanosecond pulsed electric field exposure in cells and cell-free media. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2012, 527, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhonsle, S.P.; Arena, C.B.; Sweeney, D.C.; Davalos, R.V. Mitigation of impedance changes due to electroporation therapy using bursts of high-frequency bipolar pulses. Biomed. Eng. Online 2015, 14, S3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šatkauskas, S.; André, F.; Bureau, M.F.; Scherman, D.; Miklavčič, D.; Mir, L.M. Electrophoretic component of electric pulses determines the efficacy of in vivo DNA electrotransfer. Hum. Gene Ther. 2005, 16, 1194–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Jackson, D.L.; Burcus, N.I.; Chen, Y.J.; Xiao, S.; Heller, R. Gene electrotransfer enhanced by nanosecond pulsed electric fields. Mol. Ther. Methods Clin. Dev. 2014, 1, 14043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chopinet, L.; Batista-Napotnik, T.; Montigny, A.; Rebersek, M.; Teissié, J.; Rols, M.P.; Miklavčič, D. Nanosecond electric pulse effects on gene expression. J. Membr. Biol. 2013, 246, 851–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potočnik, T.; Lebar, A.M.; Kos, Š.; Reberšek, M.; Pirc, E.; Serša, G.; Miklavčič, D. Effect of Experimental Electrical and Biological Parameters on Gene Transfer by Electroporation: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 2700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potočnik, T.; Miklavčič, D.; Lebar, A.M. Gene transfer by electroporation with high frequency bipolar pulses in vitro. Bioelectrochemistry 2021, 140, 34–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novickij, V.; Ruzgys, P.; Grainys, A.; Šatkauskas, S. High frequency electroporation efficiency is under control of membrane capacitive charging and voltage potential relaxation. Bioelectrochemistry 2018, 119, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorbel, A.; Mir, L.M.; García-Sánchez, T. Conductive nanoparticles improve cell electropermeabilization. Nanotechnology 2019, 30, 495101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kus-liśkiewicz, M.; Fickers, P.; Tahar, I.B. Biocompatibility and Cytotoxicity of Gold Nanoparticles: Recent Advances in Methodologies and Regulations. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Deshmukh, H.; Rajagopalan, K.K.; Wang, S. Gold nanoparticles electroporation enhanced polyplex delivery to mammalian cells. Electrophoresis 2014, 35, 1837–1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lekešytė, B.; Mickevičiūtė, E.; Malakauskaitė, P.; Szewczyk, A.; Radzevičiūtė-Valčiukė, E.; Malyško-Ptašinskė, V.; Želvys, A.; German, N.; Ramanavičienė, A.; Kulbacka, J.; et al. Application of Gold Nanoparticles for Improvement of Electroporation-Assisted Drug Delivery and Bleomycin Electrochemotherapy. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radzevičiūtė, E.; Malyško-Ptašinskė, V.; Novickij, J.; Novickij, V.; Girkontaitė, I. Transfection by Electroporation of Cancer and Primary Cells Using Nanosecond and Microsecond Electric Fields. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radzevičiūtė-Valčiukė, E.; Mickevičiūtė, E.; Želvys, A.; Lekešytė, B.; Malakauskaitė, P.; Gečaitė, J.; Malyško-Ptašinskė, V.; German, N.; Žalnėravičius, R.; Kašėta, V.; et al. Improving bleomycin electrochemotherapy with gold nanoparticles: First in vivo study on intra-tumoral field amplification. Bioelectrochemistry 2025, 165, 108999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novickij, V.; Staigvila, G.; Murauskas, A.; Rembialkowska, N.; Kulbacka, J.; Novickij, J. High Frequency Bipolar Electroporator with Double-Crowbar Circuit for Load-Independent Forming of Nanosecond Pulses. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radzevičiūtė-Valčiukė, E.; Gečaitė, J.; Želvys, A.; Zinkevičienė, A.; Žalnėravičius, R.; Malyško-Ptašinskė, V.; Nemeikaitė-Čenienė, A.; Kašėta, V.; German, N.; Novickij, J.; et al. Improving NonViral Gene Delivery Using MHz Bursts of Nanosecond Pulses and Gold Nanoparticles for Electric Field Amplification. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- German, N.; Kausaite-Minkstimiene, A.; Ramanavicius, A.; Semashko, T.; Mikhailova, R.; Ramanaviciene, A. The use of different glucose oxidases for the development of an amperometric reagentless glucose biosensor based on gold nanoparticles covered by polypyrrole. Electrochim. Acta 2015, 169, 326–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szostková, M.; Horáková, D. The effect of plasmid DNA sizes and other factors on electrotransformation of Escherichia coli JM109. Bioelectrochemistry Bioenerg. 1998, 47, 319–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores-Romero, H.; Ros, U.; Garcia-Saez, A.J. Pore formation in regulated cell death. EMBO J. 2020, 39, EMBJ2020105753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandušer, M.; Šentjurc, M.; Miklavčič, D. Cell membrane fluidity related to electroporation and resealing. Eur. Biophys. J. 2005, 35, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dermol, J.; Pakhomova, O.N.; Pakhomov, A.G.; Miklavěiě, D. Cell Electrosensitization Exists Only in Certain Electroporation Buffers. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0159434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benz, R.; Zimmermann, U. The resealing process of lipid bilayers after reversible electrical breakdown. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Biomembr. 1981, 640, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lekner, J. Electroporation in cancer therapy without insertion of electrodes. Phys. Med. Biol. 2016, 59, 6031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perera, Y.R.; Xu, J.X.; Amarasekara, D.L.; Hughes, A.C.; Abbood, I.; Fitzkee, N.C. Understanding the Adsorption of Peptides and Proteins onto PEGylated Gold Nanoparticles. Molecules 2021, 26, 5788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polajžer, T.; Kranjc, M.; Kralj, S.; Caf, M.; Romih, R.; Hudoklin, S.; Rocca, F.; Miklavčič, D. Limited Efficacy of Nanoparticle-Assisted Electroporation for Membrane Permeabilization and Gene Electrotransfer. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carnerero, J.M.; Jimenez-Ruiz, A.; Castillo, P.M.; Prado-Gotor, R. Covalent and Non-Covalent DNA–Gold-Nanoparticle Interactions: New Avenues of Research. ChemPhysChem 2017, 18, 17–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soloviev, A.; Ivanova, I.; Sydorenko, V.; Sukhanova, K.; Melnyk, M.; Dryn, D.; Zholos, A. Calcium-dependent modulation of BKCa channel activity induced by plasmonic gold nanoparticles in pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells and hippocampal neurons. Acta Physiol. 2023, 237, e13922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorbel, A.; André, F.M.; Mir, L.M.; García-Sánchez, T. Electrophoresis-assisted accumulation of conductive nanoparticles for the enhancement of cell electropermeabilization. Bioelectrochemistry 2021, 137, 107642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheri, E.; Sameiyan, E.; Hassibian, S.; Amin, M.; Alibolandi, M.; Ramezani, M.; Taghdisi, S.M.; Abnous, K. Modification of Cell Membrane-Coated Platforms for Targeted Drug Delivery. ACS Symp. Ser. 2024, 1464, 57–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthika, V.; Jo, S.H.; Yadav, S.; Reddy, O.S.; Lim, H.G.; Lee, W.K.; Park, S.H.; Lim, K.T. Self-Signal-Triggered Drug Delivery System for Tumor Therapy Using Cancer Cell Membrane-Coated Biocompatible Mn3O4 Nanocomposites. Adv. Biol. 2024, 8, 2300375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Sun, M.; Fan, Z.; Du, J. Recent Advances and Future Prospects in Biological-Membrane-Targeted Polymers. Polym. Sci. Technol. 2025, 2025, 584–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honary, S.; Zahir, F. Effect of Zeta Potential on the Properties of Nano-Drug Delivery Systems—A Review (Part 1). Trop. J. Pharm. Res. 2013, 12, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Ma, G.; Wei, W. Simulation of nanoparticles interacting with a cell membrane: Probing the structural basis and potential biomedical application. NPG Asia Mater. 2021, 13, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Z.G.; Wei, W.; Lv, P.P.; Yue, H.; Wang, L.Y.; Su, Z.G.; Ma, G.H. Surface Charge Affects Cellular Uptake and Intracellular Trafficking of Chitosan-Based Nanoparticles. Biomacromolecules 2011, 12, 2440–2446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gambinossi, F.; Mylon, S.E.; Ferri, J.K. Aggregation kinetics and colloidal stability of functionalized nanoparticles. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 222, 332–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| PEF Protocol | Viability (%) × Transfection Efficiency (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Without AuNPs | With AuNPs | Improvement with AuNPs | |
| 15 kV/cm × 100 ns × 100 (delay 100 ns) | 6.9% | 12.0% | 1.74-fold |
| 9 kV/cm × 300 ns × 100 (delay 500 ns) | 17.1% | 26.0% | 1.52-fold |
| 9 kV/cm × 300 ns × 100 (delay 900 ns) | 15.0% | 26.4% | 1.76-fold |
| 1.2 kV/cm × 100 μs × 8 (delay 1 s) | 24.9% | 43.9% | 1.76-fold |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Malyško-Ptašinskė, V.; Radzevičiūtė-Valčiukė, E.; Szewczyk, A.; Lekešytė, B.; Malakauskaitė, P.; Mickevičiūtė-Zinkuvienė, E.; Želvys, A.; German, N.; Kulbacka, J.; Novickij, V. Gold Nanoparticles-Enhanced Gene Transfer Driven by MHz-Frequency Nanosecond Pulsed Electric Fields. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 1736. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15121736
Malyško-Ptašinskė V, Radzevičiūtė-Valčiukė E, Szewczyk A, Lekešytė B, Malakauskaitė P, Mickevičiūtė-Zinkuvienė E, Želvys A, German N, Kulbacka J, Novickij V. Gold Nanoparticles-Enhanced Gene Transfer Driven by MHz-Frequency Nanosecond Pulsed Electric Fields. Biomolecules. 2025; 15(12):1736. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15121736
Chicago/Turabian StyleMalyško-Ptašinskė, Veronika, Eivina Radzevičiūtė-Valčiukė, Anna Szewczyk, Barbora Lekešytė, Paulina Malakauskaitė, Eglė Mickevičiūtė-Zinkuvienė, Augustinas Želvys, Natalija German, Julita Kulbacka, and Vitalij Novickij. 2025. "Gold Nanoparticles-Enhanced Gene Transfer Driven by MHz-Frequency Nanosecond Pulsed Electric Fields" Biomolecules 15, no. 12: 1736. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15121736
APA StyleMalyško-Ptašinskė, V., Radzevičiūtė-Valčiukė, E., Szewczyk, A., Lekešytė, B., Malakauskaitė, P., Mickevičiūtė-Zinkuvienė, E., Želvys, A., German, N., Kulbacka, J., & Novickij, V. (2025). Gold Nanoparticles-Enhanced Gene Transfer Driven by MHz-Frequency Nanosecond Pulsed Electric Fields. Biomolecules, 15(12), 1736. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15121736











