Enhanced Anti-Nociception by Novel Dual Antagonists for 5-HT2AR and mGluR5 in Preclinical Models of Pain
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Reagents
2.3. 5-HT2AR Overexpression Cell (HEK293T Cell) and Ip1 Assay
2.4. Target Selectivity
2.5. Primary Neuronal Culture
2.6. Western Blot
2.7. Slice Preparation
2.8. Electrophysiology
2.9. In Vivo Studies for SNL and Formalin-Induced Pain Models
2.10. Intravenous Self-Administration (IVSA) Study
2.11. Pharmacokinetic Analysis
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
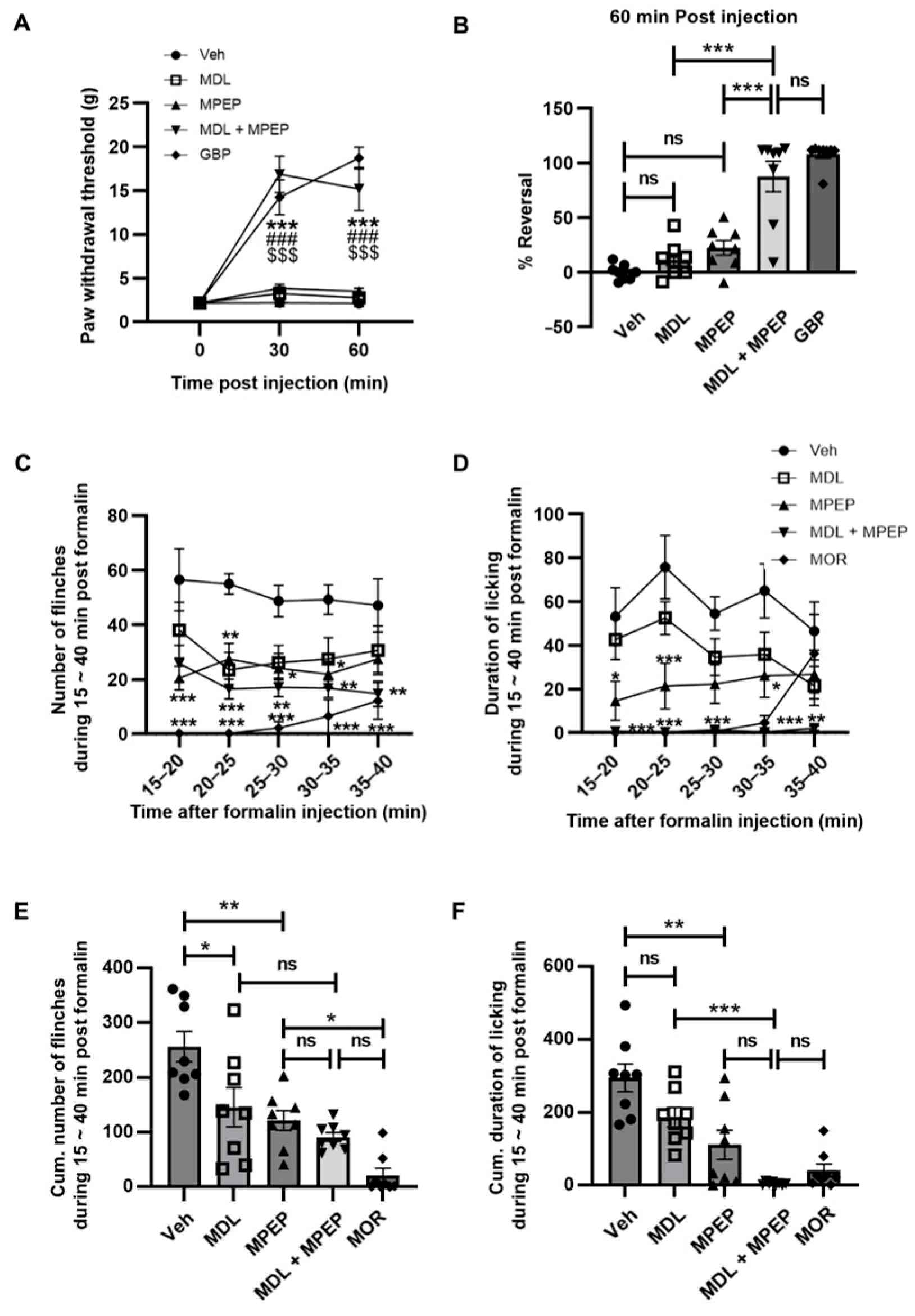
3.1. Enhanced Effects of mGluR5 and 5-HT2AR Antagonism Alleviates the Neuropathic Pain
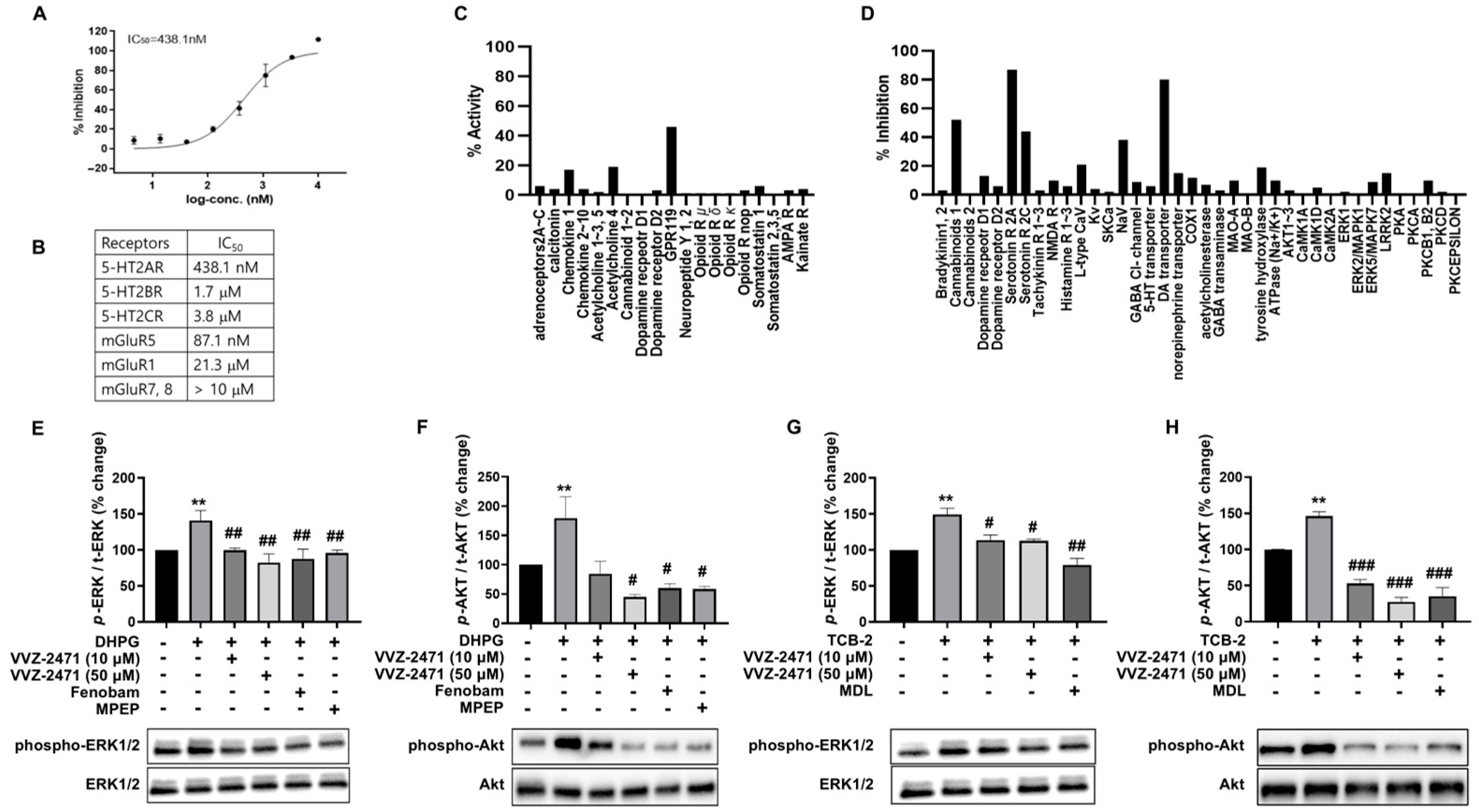
3.2. Development of Dual Antagonists for 5-HT2AR and mGluR5
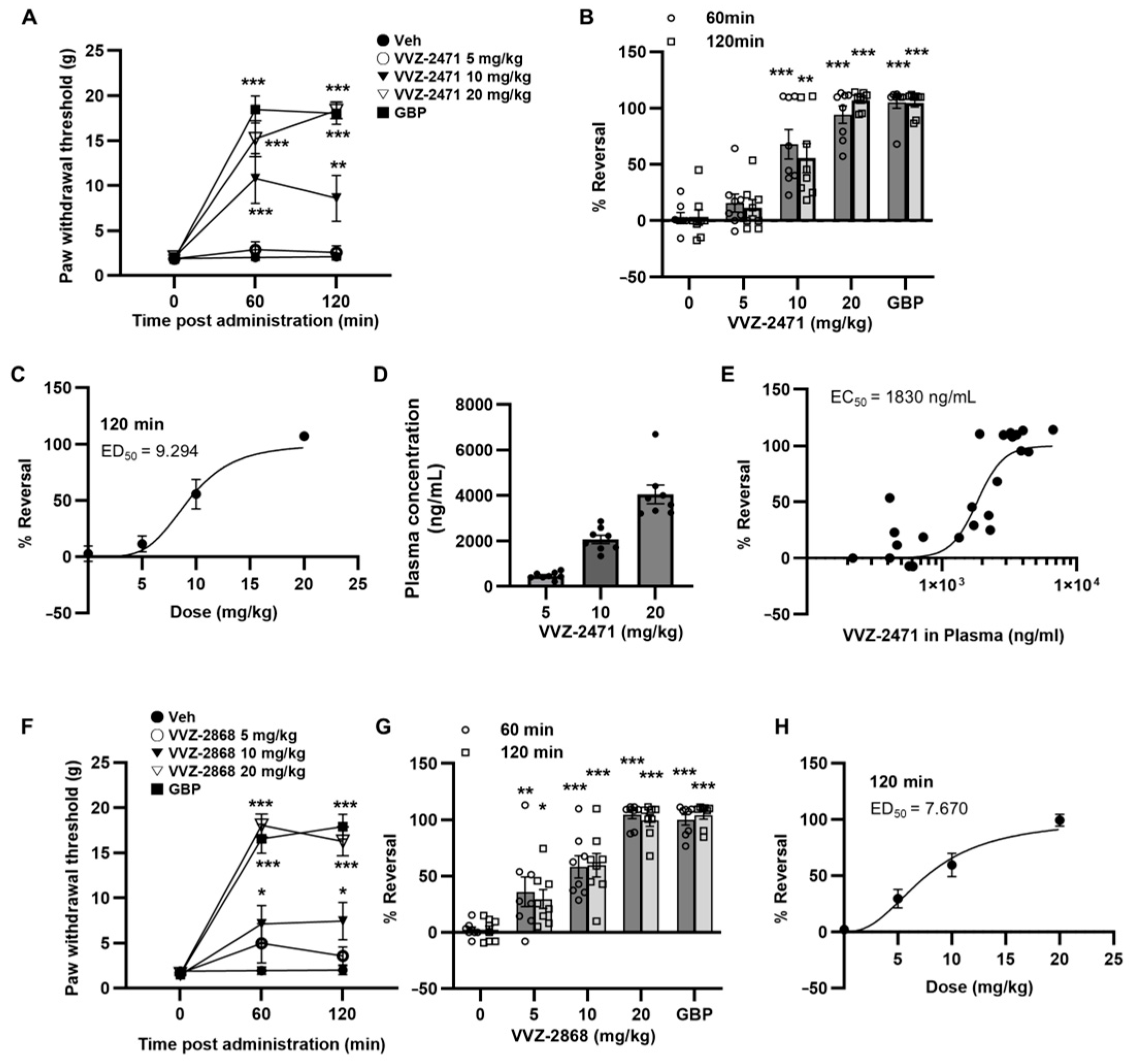
3.3. Pharmacokinetic Profile of VVZ-2471 Supports Its Suitability for Oral Pain Treatment
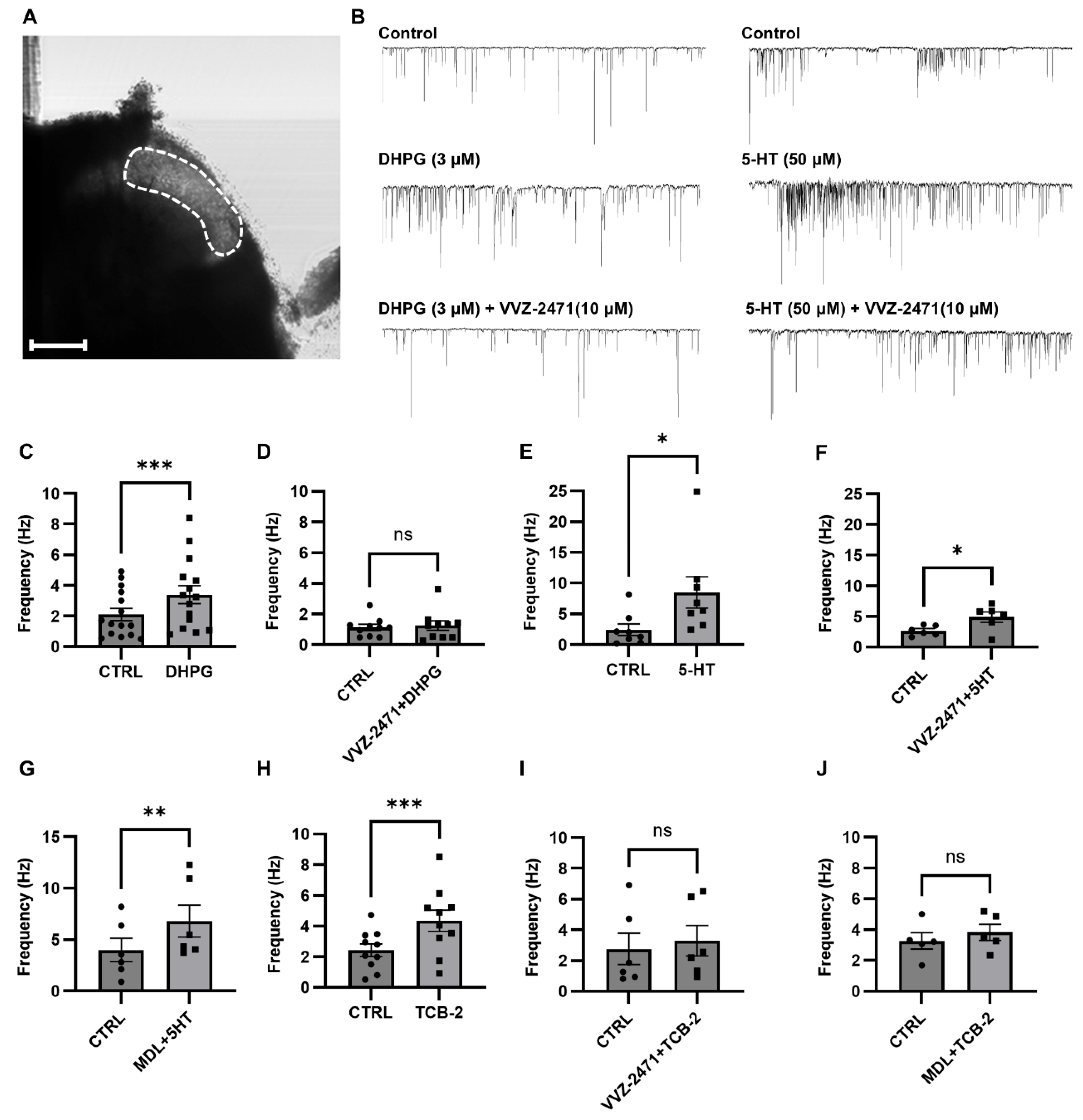
3.4. The Dual Antagonist Inhibits Synaptic Functions Mediated by 5-HT2AR and mGluR5
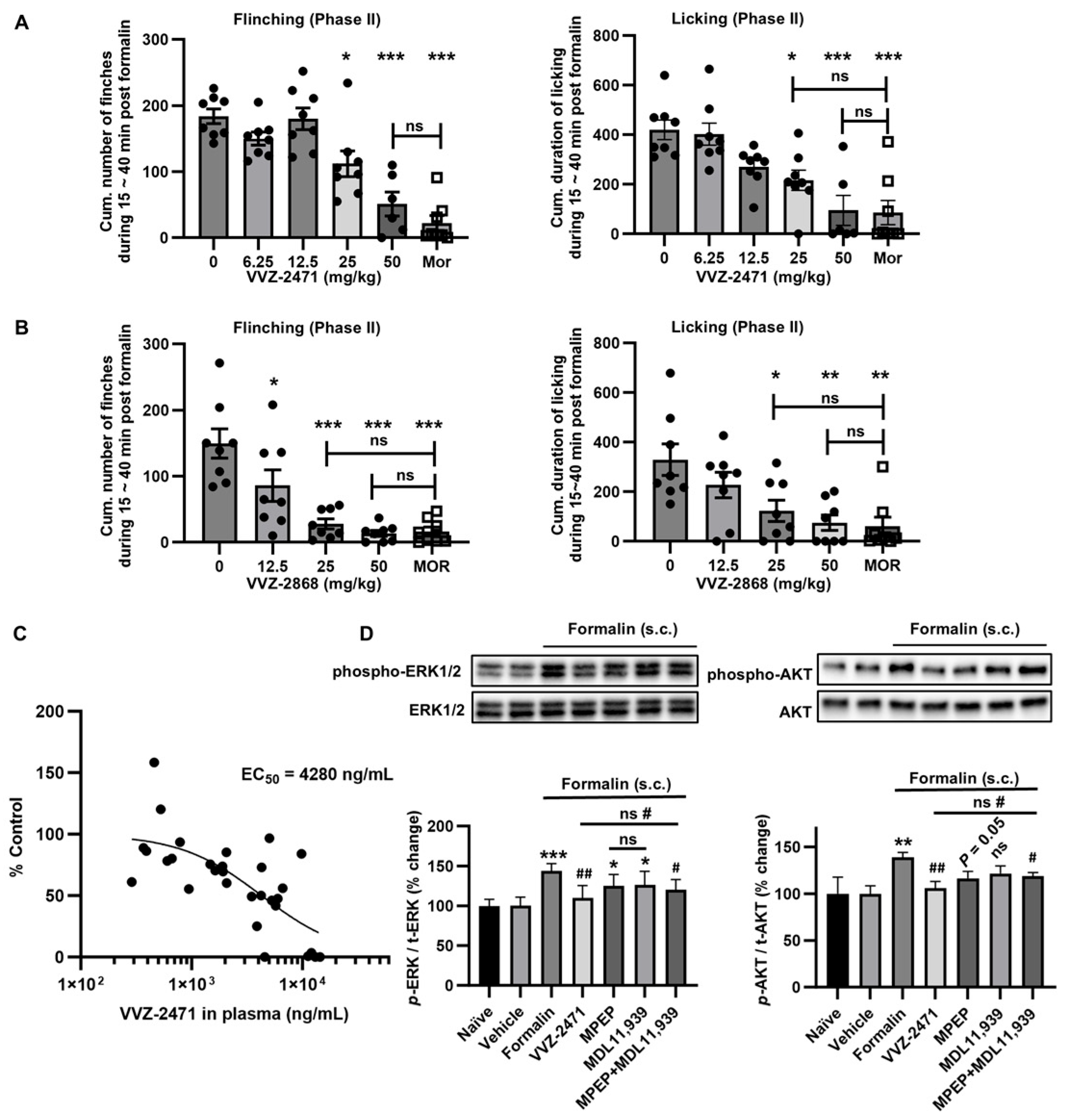
3.5. Dual-Antagonist Effects in Spinal Nerve Ligation and Formalin-Induced Pain Models
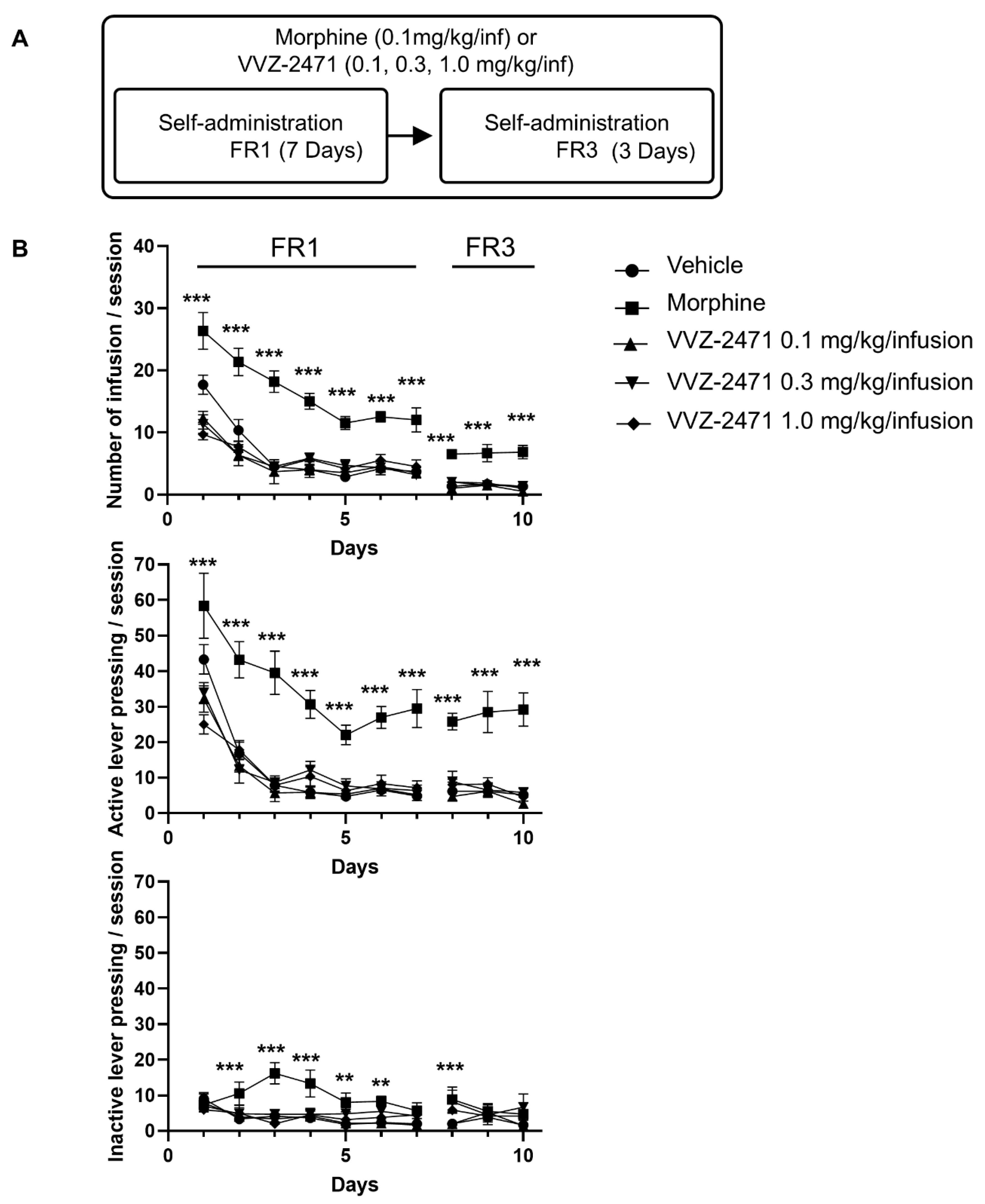
3.6. The Dual Antagonist Demonstrates No Tolerance and Low Abuse Liability in Rats
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sommer, C. Serotonin in pain and analgesia: Actions in the periphery. Mol. Neurobiol. 2004, 30, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inquimbert, P.; Bartels, K.; Babaniyi, O.B.; Barrett, L.B.; Tegeder, I.; Scholz, J. Peripheral nerve injury produces a sustained shift in the balance between glutamate release and uptake in the dorsal horn of the spinal cord. Pain 2012, 153, 2422–2431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyce, G.M.; Yaksh, T.L. Monoamine release from cat spinal cord by somatic stimuli: An intrinsic modulatory system. J. Physiol. 1981, 314, 513–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Steenwinckel, J.; Noghero, A.; Thibault, K.; Brisorgueil, M.J.; Fischer, J.; Conrath, M. The 5-HT2A receptor is mainly expressed in nociceptive sensory neurons in rat lumbar dorsal root ganglia. Neuroscience 2009, 161, 838–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thibault, K.; Van Steenwinckel, J.; Brisorgueil, M.J.; Fischer, J.; Hamon, M.; Calvino, B.; Conrath, M. Serotonin 5-HT2A receptor involvement and Fos expression at the spinal level in vincristine-induced neuropathy in the rat. Pain. 2008, 140, 305–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Chen, Y.; Hong, Y. The contribution of peripheral 5-hydroxytryptamine2A receptor to carrageenan-evoked hyperalgesia, inflammation and spinal Fos protein expression in the rat. Neuroscience 2005, 132, 1073–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitanda, A.; Yasunami, N.; Tokumo, K.; Fujii, H.; Hirai, T.; Nishio, H. Contribution of the peripheral 5-HT 2A receptor to mechanical hyperalgesia in a rat model of neuropathic pain. Neurochem. Int. 2005, 47, 394–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, F.V.; Hong, Y.; Blier, P. Activation of 5-HT2A receptors potentiates pain produced by inflammatory mediators. Neuropharmacology 1996, 35, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salzer, I.; Gantumur, E.; Yousuf, A.; Boehm, S. Control of sensory neuron excitability by serotonin involves 5HT2C receptors and Ca(2+)-activated chloride channels. Neuropharmacology 2016, 110 Pt A, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, A.; Kumamoto, E.; Takeda, M.; Shibata, K.; Sagai, H.; Yoshimura, M. Mechanisms for ovariectomy-induced hyperalgesia and its relief by calcitonin: Participation of 5-HT1A-like receptor on C-afferent terminals in substantia gelatinosa of the rat spinal cord. J. Neurosci. 2000, 20, 6302–6308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okubo, M.; Yamanaka, H.; Kobayashi, K.; Noguchi, K. Differential expression of mGluRs in rat spinal dorsal horns and their modulatory effects on nocifensive behaviors. Mol. Pain. 2019, 15, 1744806919875026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudson, L.J.; Bevan, S.; McNair, K.; Gentry, C.; Fox, A.; Kuhn, R.; Winter, J. Metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 upregulation in A-fibers after spinal nerve injury: 2-methyl-6-(phenylethynyl)-pyridine (MPEP) reverses the induced thermal hyperalgesia. J. Neurosci. 2002, 22, 2660–2668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, K.; Coderre, T.J. Hyperalgesia and allodynia induced by intrathecal (RS)-dihydroxyphenylglycine in rats. Neuroreport 1998, 9, 1169–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghelardini, C.; Menicacci, C.; Cerretani, D.; Bianchi, E. Spinal administration of mGluR5 antagonist prevents the onset of bortezomib induced neuropathic pain in rat. Neuropharmacology 2014, 86, 294–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dogrul, A.; Ossipov, M.H.; Lai, J.; Malan, T.P., Jr.; Porreca, F. Peripheral and spinal antihyperalgesic activity of SIB-1757, a metabotropic glutamate receptor (mGLUR(5)) antagonist, in experimental neuropathic pain in rats. Neurosci. Lett. 2000, 292, 115–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, J.D.; Chen, S.R.; Pan, H.L. Presynaptic mGluR5 receptor controls glutamatergic input through protein kinase C-NMDA receptors in paclitaxel-induced neuropathic pain. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 20644–20654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.Q.; Chen, S.R.; Chen, H.; Cai, Y.Q.; Pan, H.L. Regulation of increased glutamatergic input to spinal dorsal horn neurons by mGluR5 in diabetic neuropathic pain. J. Neurochem. 2010, 112, 162–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, M.H.; Kim, Y.; Jung, K.W.; Cho, S.; Lee, D.H. A series of case studies: Practical methodology for identifying antinociceptive multi-target drugs. Drug Discov. Today 2012, 17, 425–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nedeljkovic, S.S.; Correll, D.J.; Bao, X.; Zamor, N.; Zeballos, J.L.; Zhang, Y.; Young, M.J.; Ledley, J.; Sorace, J.; Eng, K.; et al. Randomised, double-blind, parallel group, placebo-controlled study to evaluate the analgesic efficacy and safety of VVZ-149 injections for postoperative pain following laparoscopic colorectal surgery. BMJ Open 2017, 7, e011035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nedeljkovic, S.S.; Song, I.; Bao, X.; Zeballos, J.L.; Correll, D.J.; Zhang, Y.; Ledley, J.S.; Bhandari, A.; Bai, X.; Lee, S.R.; et al. Exploratory study of VVZ-149, a novel analgesic molecule, in the affective component of acute postoperative pain after laparoscopic colorectal surgery. J. Clin. Anesth. 2022, 76, 110576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, I.; Cho, S.; Nedeljkovic, S.S.; Lee, S.R.; Lee, C.; Kim, J.; Bai, S.J. Role of VVZ-149, a Novel Analgesic Molecule, in the Affective Component of Pain: Results from an Exploratory Proof-of-Concept Study of Postoperative Pain following Laparoscopic and Robotic-Laparoscopic Gastrectomy. Pain Med. 2021, 22, 2037–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.J.; Sim, J.Y.; Song, I.; Nedeljkovic, S.S.; Kim, D.K.; Oh, A.Y.; Yoon, S.Z.; Moon, Y.J.; Park, M.H.; Park, I.; et al. Reduction of postoperative pain and opioid consumption by VVZ-149, first-in-class analgesic molecule: A confirmatory phase 3 trial of laparoscopic colectomy. J. Clin. Anesth. 2025, 101, 111729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stachowicz, K.; Golembiowska, K.; Sowa, M.; Nowak, G.; Chojnacka-Wojcik, E.; Pilc, A. Anxiolytic-like action of MTEP expressed in the conflict drinking Vogel test in rats is serotonin dependent. Neuropharmacology 2007, 53, 741–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palazzo, E.; Genovese, R.; Mariani, L.; Siniscalco, D.; Marabese, I.; De Novellis, V.; Rossi, F.; Maione, S. Metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 and dorsal raphe serotonin release in inflammatory pain in rat. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2004, 492, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, S.; Lee, H.; Song, I.; Kim, J.; Lee, S.R.; Cho, S.; Yu, K.S.; Chung, J.Y. Evaluation of Safety, Pharmacokinetic, and Pharmacodynamic Characteristics of a Novel Dual mGluR5/5-HT2AR Antagonist (VVZ-2471) in a Randomized, Double-Blind, First-in-Human Study. CNS Drugs 2025, 39, 583–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Brott, B.K.; Kirkby, L.A.; Adelson, J.D.; Cheng, S.; Feller, M.B.; Datwani, A.; Shatz, C.J. Synapse elimination and learning rules co-regulated by MHC class I H2-Db. Nature 2014, 509, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Chung, J. An experimental model for peripheral neuropathy produced by segmental spinal nerve ligation in the rat. Pain 1992, 50, 355–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaplan, S.R.; Bach, F.W.; Pogrel, J.W.; Chung, J.M.; Yaksh, T.L. Quantitative assessment of tactile allodynia in the rat paw. J. Neurosci. Methods 1994, 53, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deuis, J.R.; Dvorakova, L.S.; Vetter, I. Methods Used to Evaluate Pain Behaviors in Rodents. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2017, 10, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, J.M.; Kim, H.K.; Chung, K. Segmental spinal nerve ligation model of neuropathic pain. Methods Mol. Med. 2004, 99, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanlon, K.E.; Herman, D.S.; Agnes, R.S.; Largent-Milnes, T.M.; Kumarasinghe, I.R.; Ma, S.W.; Guo, W.; Lee, Y.S.; Ossipov, M.H.; Hruby, V.J.; et al. Novel peptide ligands with dual acting pharmacophores designed for the pathophysiology of neuropathic pain. Brain Res. 2011, 1395, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubuisson, D.; Dennis, S.G. The formalin test: A quantitative study of the analgesic effects of morphine, meperidine, and brain stem stimulation in rats and cats. Pain 1977, 4, 161–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hur, K.H.; Lee, Y.; Donio, A.L.; Ma, S.X.; Lee, B.R.; Kim, S.K.; Lee, J.G.; Kim, Y.J.; Kim, M.; Yoon, S.; et al. Mepirapim, a Novel Synthetic Cannabinoid, Induces Addiction-Related Behaviors through Neurochemical Maladaptation in the Brain of Rodents. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waters, N.J.; Jones, R.; Williams, G.; Sohal, B. Validation of a rapid equilibrium dialysis approach for the measurement of plasma protein binding. J. Pharm. Sci. 2008, 97, 4586–4595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knights, K.M.; Stresser, D.M.; Miners, J.O.; Crespi, C.L. In Vitro Drug Metabolism Using Liver Microsomes. Curr. Protoc. Pharmacol. 2016, 74, 7–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caterina, J.J.; Yamada, S.; Caterina, N.C.; Longenecker, G.; Holmback, K.; Shi, J.; Yermovsky, A.E.; Engler, J.A.; Birkedal-Hansen, H. Inactivating mutation of the mouse tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-2(Timp-2) gene alters proMMP-2 activation. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 26416–26422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lagerstrom, M.C.; Rogoz, K.; Abrahamsen, B.; Persson, E.; Reinius, B.; Nordenankar, K.; Olund, C.; Smith, C.; Mendez, J.A.; Chen, Z.F.; et al. VGLUT2-dependent sensory neurons in the TRPV1 population regulate pain and itch. Neuron 2010, 68, 529–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Abdel Samad, O.; Zhang, L.; Duan, B.; Tong, Q.; Lopes, C.; Ji, R.R.; Lowell, B.B.; Ma, Q. VGLUT2-dependent glutamate release from nociceptors is required to sense pain and suppress itch. Neuron 2010, 68, 543–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacDonald, D.I.; Jayabalan, M.; Seaman, J.T.; Balaji, R.; Nickolls, A.R.; Chesler, A.T. Pain persists in mice lacking both Substance P and CGRPalpha signaling. Elife 2025, 13, RP93754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hori, Y.; Endo, K.; Takahashi, T. Long-lasting synaptic facilitation induced by serotonin in superficial dorsal horn neurones of the rat spinal cord. J. Physiol. 1996, 492 Pt 3, 867–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.Y.; Bai, H.H.; Guo, Z.; Li, H.L.; He, Y.T.; Duan, X.L.; Suo, Z.W.; Yang, X.; He, Y.X.; Hu, X.D. mGluR5/ERK signaling regulated the phosphorylation and function of glycine receptor alpha1ins subunit in spinal dorsal horn of mice. PLoS Biol. 2019, 17, e3000371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Chen, T.; Gao, Y.; Quirion, R.; Hong, Y. Inhibition of SNL-induced upregulation of CGRP and NPY in the spinal cord and dorsal root ganglia by the 5-HT(2A) receptor antagonist ketanserin in rats. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2012, 101, 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pehek, E.A.; Nocjar, C.; Roth, B.L.; Byrd, T.A.; Mabrouk, O.S. Evidence for the preferential involvement of 5-HT2A serotonin receptors in stress- and drug-induced dopamine release in the rat medial prefrontal cortex. Neuropsychopharmacology 2006, 31, 265–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flaisher-Grinberg, S.; Klavir, O.; Joel, D. The role of 5-HT2A and 5-HT2C receptors in the signal attenuation rat model of obsessive-compulsive disorder. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2008, 11, 811–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, S.; Sigtermans, M.J.; Dahan, A.; Zuurmond, W.W.; Perez, R.S. NMDA receptor antagonists for the treatment of neuropathic pain. Pain Med. 2010, 11, 1726–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eide, P.K.; Stubhaug, A.; Oye, I.; Breivik, H. Continuous subcutaneous administration of the N-methyl-D-aspartic acid (NMDA) receptor antagonist ketamine in the treatment of post-herpetic neuralgia. Pain 1995, 61, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheeler-Aceto, H.; Cowan, A. Standardization of the rat paw formalin test for the evaluation of analgesics. Psychopharmacology 1991, 104, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevostianova, N.; Danysz, W.; Bespalov, A.Y. Analgesic effects of morphine and loperamide in the rat formalin test: Interactions with NMDA receptor antagonists. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2005, 525, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coderre, T.J.; Melzack, R. The contribution of excitatory amino acids to central sensitization and persistent nociception after formalin-induced tissue injury. J. Neurosci. 1992, 12, 3665–3670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coderre, T.J.; Vaccarino, A.L.; Melzack, R. Central nervous system plasticity in the tonic pain response to subcutaneous formalin injection. Brain Res. 1990, 535, 155–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Coppes, O.J.M.; Urman, R.D. Receptor and Molecular Targets for the Development of Novel Opioid and Non-Opioid Analgesic Therapies. Pain Physician 2021, 24, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kissin, I. Scientometrics of drug discovery efforts: Pain-related molecular targets. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2015, 9, 3393–3404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reichel, A. The role of blood-brain barrier studies in the pharmaceutical industry. Curr. Drug Metab. 2006, 7, 183–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karim, F.; Wang, C.C.; Gereau, R.W.t. Metabotropic glutamate receptor subtypes 1 and 5 are activators of extracellular signal-regulated kinase signaling required for inflammatory pain in mice. J. Neurosci. 2001, 21, 3771–3779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.P.; Zhou, Y.Q.; Liu, D.Q.; Zhang, W.; Manyande, A.; Guan, X.H.; Tian, Y.K.; Ye, D.W.; Omar, D.M. PI3K/Akt Pathway: A Potential Therapeutic Target for Chronic Pain. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2017, 23, 1860–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Liu, S.S.; Wei, J.; Jiao, Z.Y.; Mo, C.; Lv, C.M.; Huang, A.L.; Chen, Q.B.; Ma, L.; Guan, X.H. Role of Spinal Cord Akt-mTOR Signaling Pathways in Postoperative Hyperalgesia Induced by Plantar Incision in Mice. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, R.H.; Jaeschke, G.; Spooren, W.; Ballard, T.M.; Buttelmann, B.; Kolczewski, S.; Peters, J.U.; Prinssen, E.; Wichmann, J.; Vieira, E.; et al. Fenobam: A clinically validated nonbenzodiazepine anxiolytic is a potent, selective, and noncompetitive mGlu5 receptor antagonist with inverse agonist activity. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2005, 315, 711–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djouhri, L.; Koutsikou, S.; Fang, X.; McMullan, S.; Lawson, S.N. Spontaneous pain, both neuropathic and inflammatory, is related to frequency of spontaneous firing in intact C-fiber nociceptors. J. Neurosci. 2006, 26, 1281–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.H.; Bennett, G.J. Chemotherapy-evoked neuropathic pain: Abnormal spontaneous discharge in A-fiber and C-fiber primary afferent neurons and its suppression by acetyl-L-carnitine. Pain 2008, 135, 262–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sotgiu, M.L.; Bellomi, P.; Biella, G.E. The mGluR5 selective antagonist 6-methyl-2-(phenylethynyl)-pyridine reduces the spinal neuron pain-related activity in mononeuropathic rats. Neurosci. Lett. 2003, 342, 85–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLean, T.H.; Parrish, J.C.; Braden, M.R.; Marona-Lewicka, D.; Gallardo-Godoy, A.; Nichols, D.E. 1-Aminomethylbenzocycloalkanes: Conformationally restricted hallucinogenic phenethylamine analogues as functionally selective 5-HT2A receptor agonists. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 49, 5794–5803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgan, M.M.; Christie, M.J. Analysis of opioid efficacy, tolerance, addiction and dependence from cell culture to human. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 164, 1322–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoedel, K.A.; Sellers, E.M. Assessing abuse liability during drug development: Changing standards and expectations. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2008, 83, 622–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaparro, L.E.; Wiffen, P.J.; Moore, R.A.; Gilron, I. Combination pharmacotherapy for the treatment of neuropathic pain in adults. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2012, 2012, CD008943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafra, F.; Ibanez, I.; Gimenez, C. Glycinergic transmission: Glycine transporter GlyT2 in neuronal pathologies. Neuronal Signal. 2016, 1, NS20160009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valerio, A.; Rizzonelli, P.; Paterlini, M.; Moretto, G.; Knopfel, T.; Kuhn, R.; Memo, M.; Spano, P. mGluR5 metabotropic glutamate receptor distribution in rat and human spinal cord: A developmental study. Neurosci. Res. 1997, 28, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vuckovic, S.; Srebro, D.; Vujovic, K.S.; Vucetic, C.; Prostran, M. Cannabinoids and Pain: New Insights From Old Molecules. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urbi, B.; Sapaen, V.; Hughes, I.; Owusu, M.A.; Sabet, A.; Broadley, S.A. Effect of cannabinoids on glutamate levels in the human brain: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Cannabis Res. 2025, 7, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alba-Delgado, C.; Mountadem, S.; Mermet-Joret, N.; Monconduit, L.; Dallel, R.; Artola, A.; Antri, M. 5-HT(2A) Receptor-Induced Morphological Reorganization of PKCgamma-Expressing Interneurons Gates Inflammatory Mechanical Allodynia in Rat. J. Neurosci. 2018, 38, 10489–10504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pogorelov, V.M.; Rodriguiz, R.M.; Cheng, J.; Huang, M.; Schmerberg, C.M.; Meltzer, H.Y.; Roth, B.L.; Kozikowski, A.P.; Wetsel, W.C. 5-HT(2C) Agonists Modulate Schizophrenia-Like Behaviors in Mice. Neuropsychopharmacology 2017, 42, 2163–2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, R.; Rygh, L.J.; Dickenson, A.H. Bad news from the brain: Descending 5-HT pathways that control spinal pain processing. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2004, 25, 613–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kargbo, R.B. 5-HT(2C) Receptor Agonists for the Treatment of Obesity. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2018, 9, 864–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonhaus, D.W.; Weinhardt, K.K.; Taylor, M.; DeSouza, A.; McNeeley, P.M.; Szczepanski, K.; Fontana, D.J.; Trinh, J.; Rocha, C.L.; Dawson, M.W.; et al. RS-102221: A novel high affinity and selective, 5-HT2C receptor antagonist. Neuropharmacology 1997, 36, 621–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirk, S.L.; Glazebrook, J.; Grayson, B.; Neill, J.C.; Reynolds, G.P. Olanzapine-induced weight gain in the rat: Role of 5-HT2C and histamine H1 receptors. Psychopharmacology 2009, 207, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Reith, M.E. Role of the dopamine transporter in the action of psychostimulants, nicotine, and other drugs of abuse. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 2008, 7, 393–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siciliano, C.A.; Calipari, E.S.; Ferris, M.J.; Jones, S.R. Biphasic mechanisms of amphetamine action at the dopamine terminal. J. Neurosci. 2014, 34, 5575–5582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crits-Christoph, P.; Newberg, A.; Wintering, N.; Ploessl, K.; Gibbons, M.B.; Ring-Kurtz, S.; Gallop, R.; Present, J. Dopamine transporter levels in cocaine dependent subjects. Drug Alcohol. Depend. 2008, 98, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halberstadt, A.L.; Lehmann-Masten, V.D.; Geyer, M.A.; Powell, S.B. Interactive effects of mGlu5 and 5-HT2A receptors on locomotor activity in mice. Psychopharmacology 2011, 215, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, K.; Sekiguchi, M.; Kikuchi, S.; Konno, S. The effect of a 5-HT2A receptor antagonist on pain-related behavior, endogenous 5-hydroxytryptamine production, and the expression 5-HT2A receptors in dorsal root ganglia in a rat lumbar disc herniation model. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2015, 40, 357–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mixcoatl-Zecuatl, T.; Jolivalt, C.G. A spinal mechanism of action for duloxetine in a rat model of painful diabetic neuropathy. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 164, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dolan, S.; Nolan, A.M. Blockade of metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 activation inhibits mechanical hypersensitivity following abdominal surgery. Eur. J. Pain 2007, 11, 644–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finnerup, N.B.; Attal, N.; Haroutounian, S.; McNicol, E.; Baron, R.; Dworkin, R.H.; Gilron, I.; Haanpaa, M.; Hansson, P.; Jensen, T.S.; et al. Pharmacotherapy for neuropathic pain in adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Neurol. 2015, 14, 162–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fornasari, D. Pharmacotherapy for Neuropathic Pain: A Review. Pain Ther. 2017, 6 (Suppl. 1), 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacks, G.M. Unmet need in the treatment of postherpetic neuralgia. Am. J. Manag. Care 2013, 19 (Suppl. 1), S207–S213. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]

| Dose (mg/kg) | Cmax (ng/mL) a | Tmax (h) b | AUCinf (h∙ng/mL) c | t1/2 (h) d |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 1731 ± 252 | 0.5–2 | 9248 ± 1756 | 1.53 ± 0.41 |
| 25 | 4850 ± 1200 | 2–4 | 46,446 ± 15,281 | 3.52 ± 1.81 |
| 50 | 8720 ± 1520 | 4–8 | 114,261 ± 16,684 | 3.44 ± 0.34 |
| Plasma Protein Binding (%) e | Liver Microsomal Stability f (Half-life, Minute) | Brain-to-Plasma Ratio g | ||
| Rat | 98.1 ± 0.5 | 80.4 | 1.87 ± 0.17 | |
| Dog | 96.6 ± 0.1 | 212.1 | ||
| Human | 98.7 ± 0.4 | 417.6 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Choi, D.; Heo, H.J.; Shin, H.; Im, J.; Lee, G.; Kim, A.H.; Hur, K.-H.; Nho, Y.; Jang, C.-G.; Lee, H. Enhanced Anti-Nociception by Novel Dual Antagonists for 5-HT2AR and mGluR5 in Preclinical Models of Pain. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 1456. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15101456
Choi D, Heo HJ, Shin H, Im J, Lee G, Kim AH, Hur K-H, Nho Y, Jang C-G, Lee H. Enhanced Anti-Nociception by Novel Dual Antagonists for 5-HT2AR and mGluR5 in Preclinical Models of Pain. Biomolecules. 2025; 15(10):1456. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15101456
Chicago/Turabian StyleChoi, Daekyu, Hyun Jin Heo, Haeyoung Shin, Jayzoon Im, Geonho Lee, Ah Hyun Kim, Kwang-Hyun Hur, Yoonmi Nho, Choon-Gon Jang, and Hanmi Lee. 2025. "Enhanced Anti-Nociception by Novel Dual Antagonists for 5-HT2AR and mGluR5 in Preclinical Models of Pain" Biomolecules 15, no. 10: 1456. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15101456
APA StyleChoi, D., Heo, H. J., Shin, H., Im, J., Lee, G., Kim, A. H., Hur, K.-H., Nho, Y., Jang, C.-G., & Lee, H. (2025). Enhanced Anti-Nociception by Novel Dual Antagonists for 5-HT2AR and mGluR5 in Preclinical Models of Pain. Biomolecules, 15(10), 1456. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15101456






