EC359 Enhances Trametinib Efficacy in Ras/Raf-Driven Ovarian Cancer by Suppressing LIFR Signaling
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture and Reagents
2.2. Cell Viability, Colony Formation, and Apoptosis Assays
2.3. Western Blotting
2.4. RNA Sequencing
2.5. Cell Line-Derived and Patient-Derived Xenograft Studies
2.6. Statistical Ananlyses
3. Results
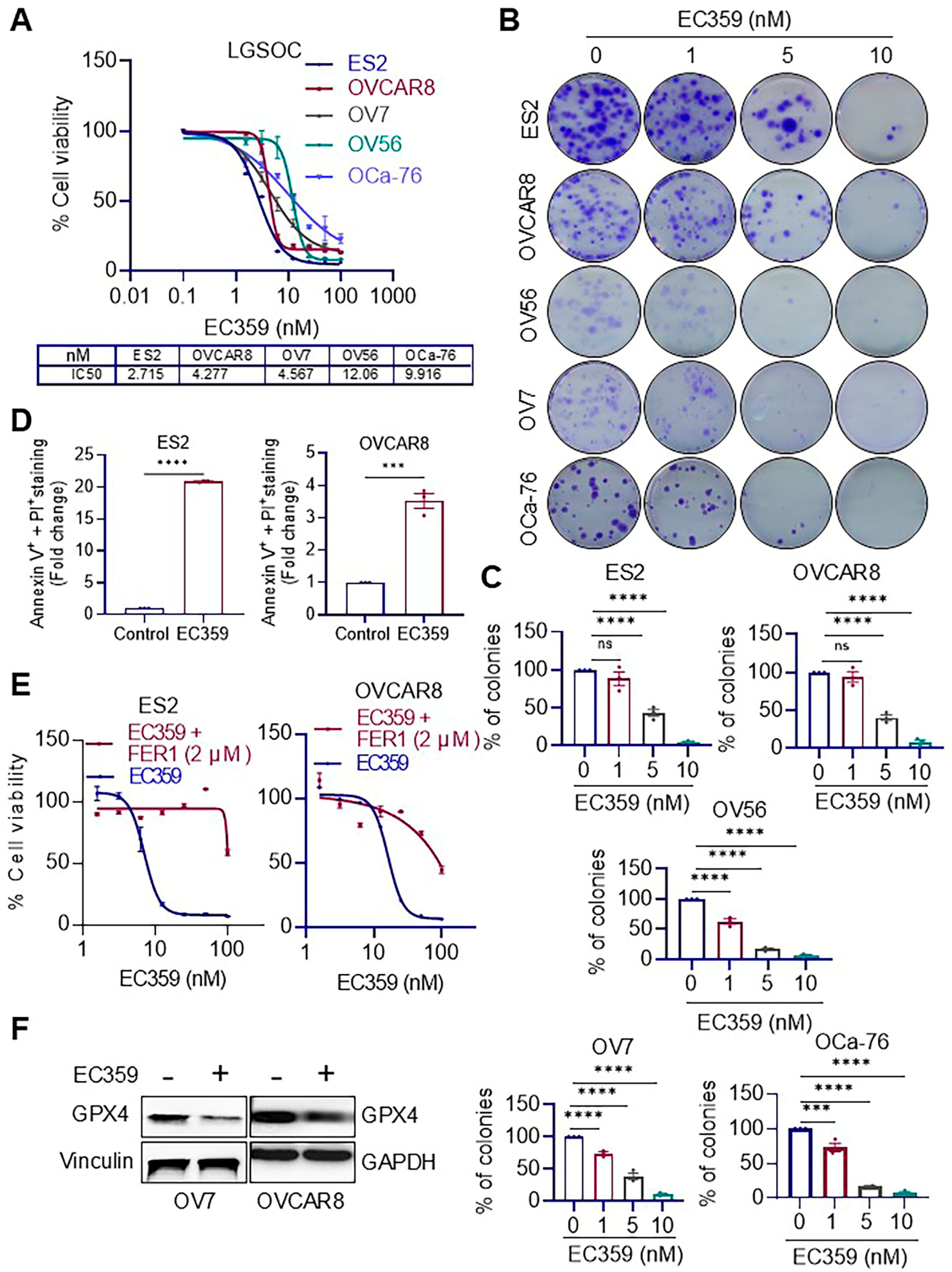
3.1. EC359 Treatment Reduces Cell Viability, Clonogenic Survival, and Promote Apoptosis in Ras/Raf-Mutant OCa Cells
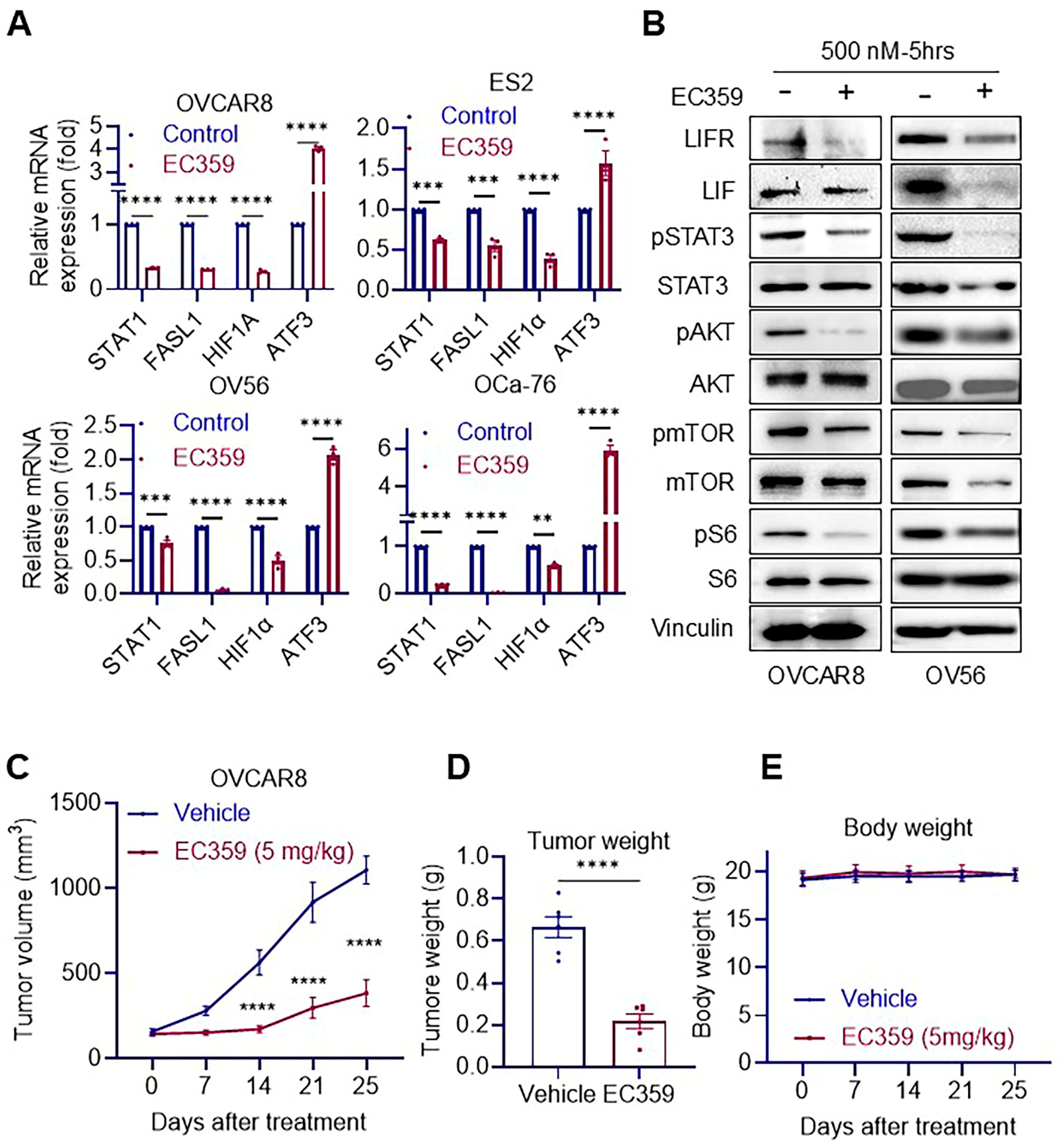
3.2. EC359 Suppresses LIFR Downstream Signaling and Inhibits Tumor Growth in Ras/Raf-Mutant OCa Xenografts
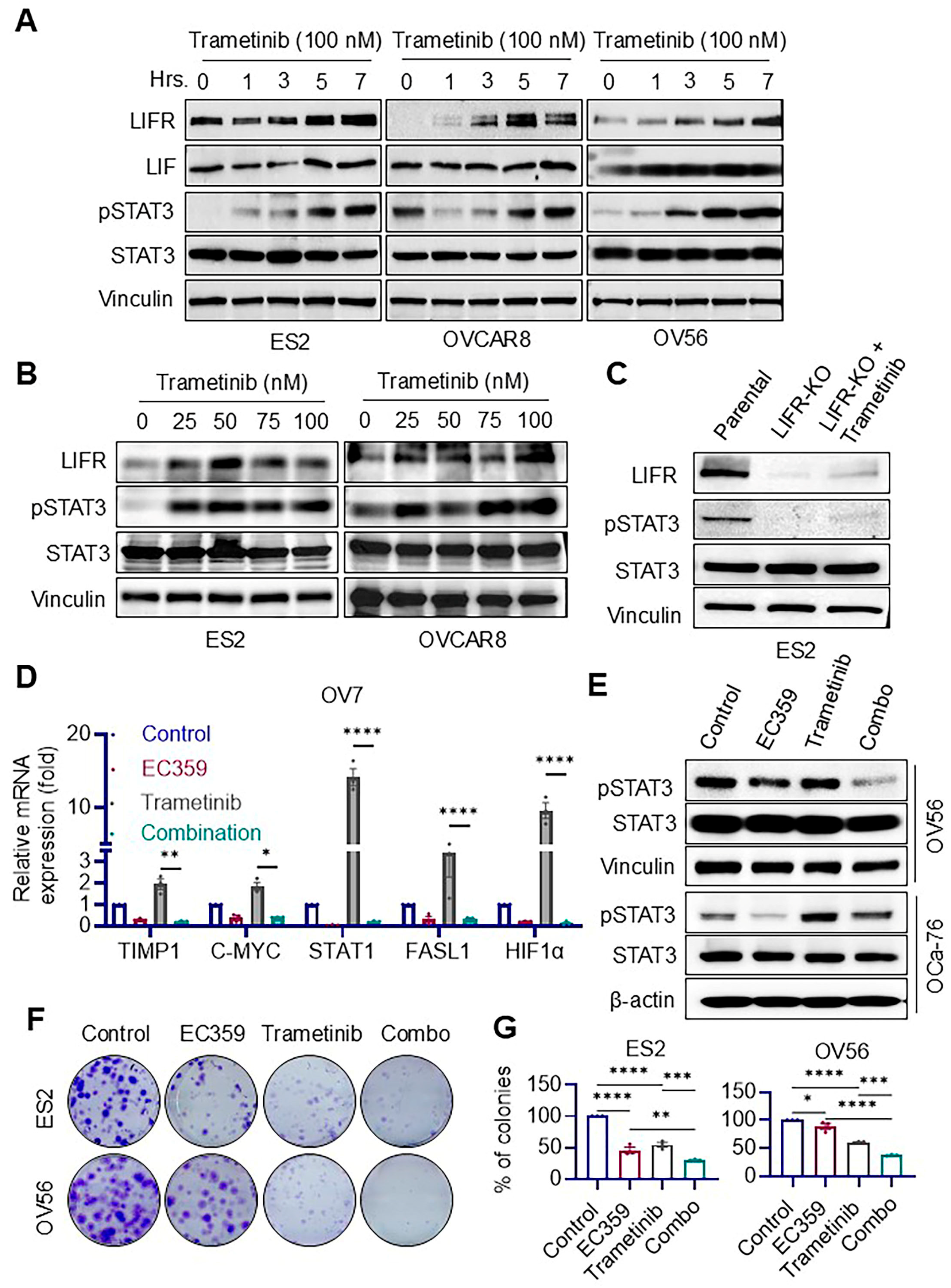
3.3. Trametinib Induces Aberrant Activation of LIFR Signaling in Ras/Raf-Mutant Ovarian Cancer Cells, Which Is Effectively Suppressed by EC359
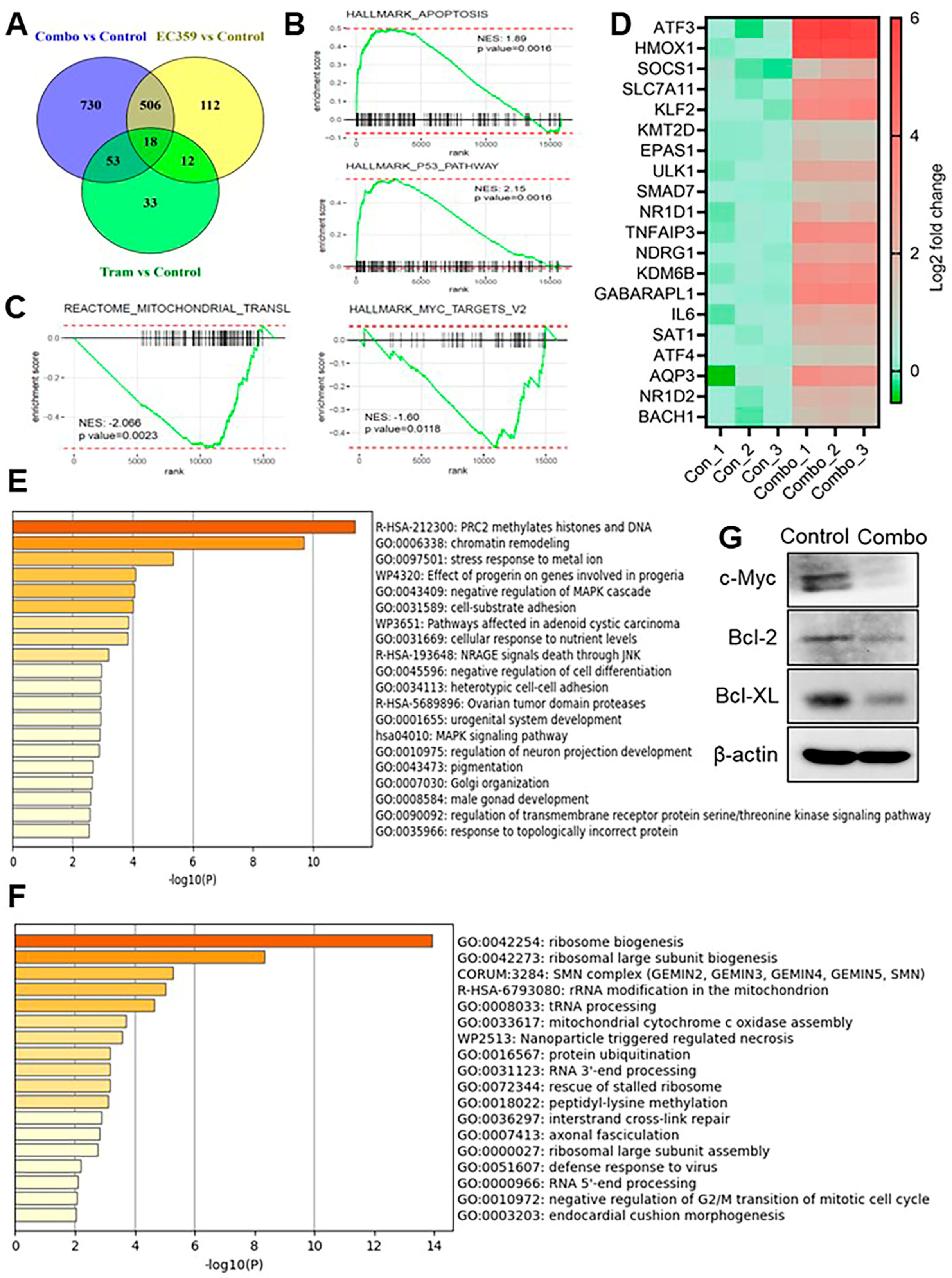
3.4. Combination Therapy with Trametinib and EC359 Modulates Transcriptional Programs Associated with Apoptosis and Ribosome Biogenesis
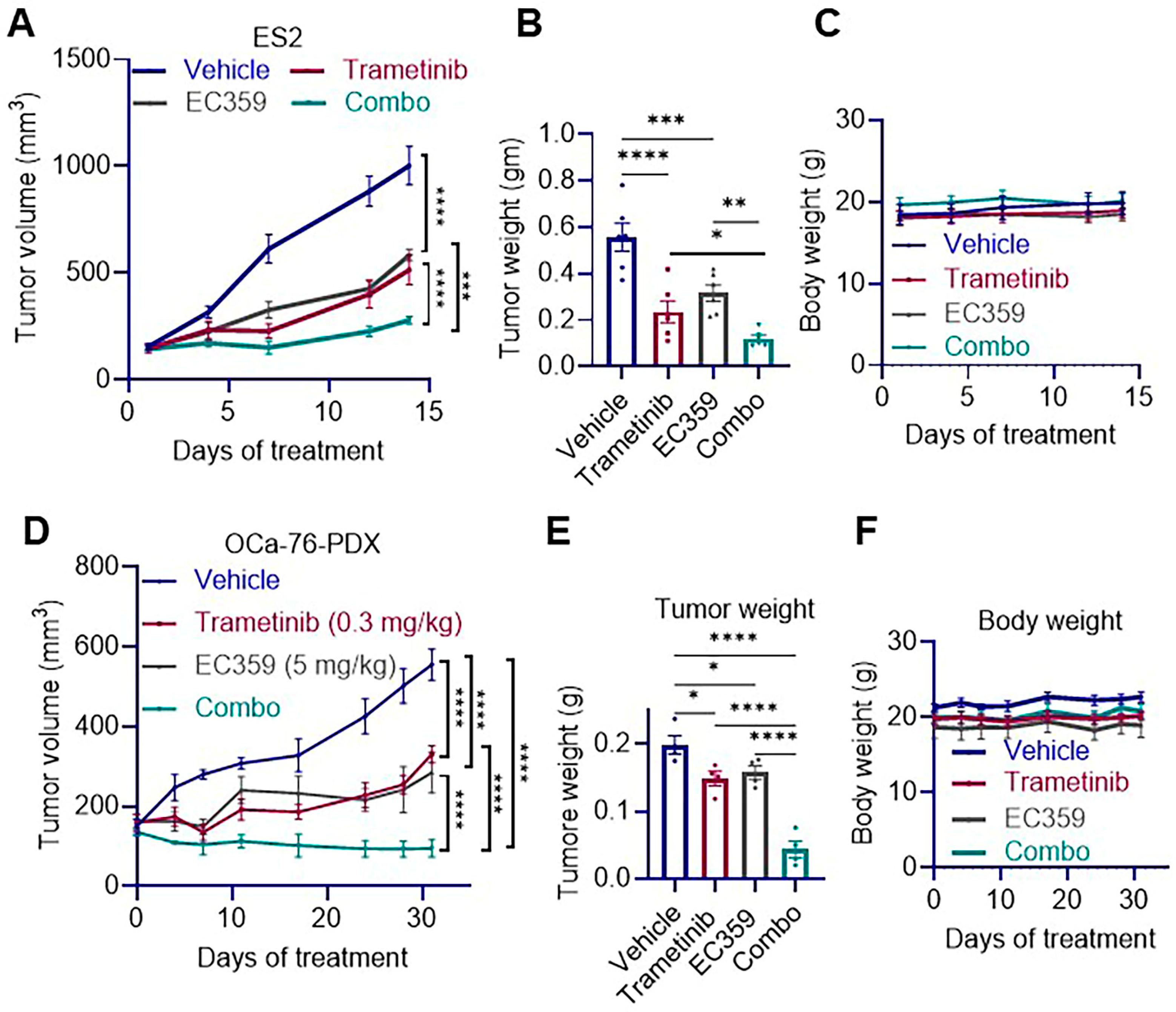
3.5. Combination Therapy of EC359 and Trametinib Reduces Tumor Growth in Ras/Raf Mutant OCa Xenografts
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AKT | Protein Kinase B |
| ANOVA | Analysis of Variance |
| ATCC | American Type Culture Collection |
| ATF3 | Activating Transcription Factor 3 |
| BRAF | B-Raf Proto-Oncogene, Serine/Threonine Kinase |
| EOC | Epithelial Ovarian Cancer |
| ENOC | Endometrioid Ovarian Cancer |
| FASL1 | Fas Ligand 1 |
| GEO | Gene Expression Omnibus |
| GPX4 | Glutathione Peroxidase 4 |
| HGSOC | High-Grade Serous Ovarian Cancer |
| HIF1α | Hypoxia-Inducible Factor 1-alpha |
| IC50 | Half-Maximal Inhibitory Concentration |
| IP | Intraperitoneal |
| JAK | Janus Kinase |
| KRAS | Kirsten Rat Sarcoma Viral Oncogene Homolog |
| LGSOC | Low-Grade Serous Ovarian Cancer |
| LIF | Leukemia Inhibitory Factor |
| LIFR | Leukemia Inhibitory Factor Receptor |
| MEK | Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Kinase |
| MOC | Mucinous Ovarian Cancer |
| mTOR | Mechanistic Target of Rapamycin |
| MTT | 3-(4,5-Dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-Diphenyltetrazolium Bromide |
| OCa | Ovarian Cancer |
| OCCC | Ovarian Clear Cell Carcinoma |
| PI3K | Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase |
| RNA-seq | RNA Sequencing |
| RT-qPCR | Reverse Transcription Quantitative PolymeRase Chain Reaction |
| SCID | Severe Combined Immunodeficiency |
| SE | Standard Error |
| STAT3 | Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3 |
| STR | Short Tandem Repeat |
| TME | Tumor Microenvironment |
References
- Bowtell, D.D.; Bohm, S.; Ahmed, A.A.; Aspuria, P.J.; Bast, R.C., Jr.; Beral, V.; Berek, J.S.; Birrer, M.J.; Blagden, S.; Bookman, M.A.; et al. Rethinking ovarian cancer II: Reducing mortality from high-grade serous ovarian cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2015, 15, 668–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bast, R.C., Jr.; Matulonis, U.A.; Sood, A.K.; Ahmed, A.A.; Amobi, A.E.; Balkwill, F.R.; Wielgos-Bonvallet, M.; Bowtell, D.D.L.; Brenton, J.D.; Brugge, J.S.; et al. Critical questions in ovarian cancer research and treatment: Report of an American Association for Cancer Research Special Conference. Cancer 2019, 125, 1963–1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prat, J. Ovarian carcinomas: Five distinct diseases with different origins, genetic alterations, and clinicopathological features. Virchows Arch. 2012, 460, 237–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Y.; Yang, Q. Targeting KRAS in gynecological malignancies. FASEB J. 2024, 38, e70089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakayama, N.; Nakayama, K.; Yeasmin, S.; Ishibashi, M.; Katagiri, A.; Iida, K.; Fukumoto, M.; Miyazaki, K. KRAS or BRAF mutation status is a useful predictor of sensitivity to MEK inhibition in ovarian cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2008, 99, 2020–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gershenson, D.M.; Miller, A.; Brady, W.E.; Paul, J.; Carty, K.; Rodgers, W.; Millan, D.; Coleman, R.L.; Moore, K.N.; Banerjee, S.; et al. Trametinib versus standard of care in patients with recurrent low-grade serous ovarian cancer (GOG 281/LOGS): An international, randomised, open-label, multicentre, phase 2/3 trial. Lancet 2022, 399, 541–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicola, N.A.; Babon, J.J. Leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF). Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2015, 26, 533–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stahl, N.; Boulton, T.G.; Farruggella, T.; Ip, N.Y.; Davis, S.; Witthuhn, B.A.; Quelle, F.W.; Silvennoinen, O.; Barbieri, G.; Pellegrini, S.; et al. Association and activation of Jak-Tyk kinases by CNTF-LIF-OSM-IL-6 beta receptor components. Science 1994, 263, 92–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yang, Q.; Yu, H.; Wu, L.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, C.; Yue, X.; Liu, Z.; Wu, H.; Haffty, B.G.; et al. LIF promotes tumorigenesis and metastasis of breast cancer through the AKT-mTOR pathway. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 788–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.C.; Tsang, N.M.; Chiang, W.C.; Chang, K.P.; Hsueh, C.; Liang, Y.; Juang, J.L.; Chow, K.P.; Chang, Y.S. Leukemia inhibitory factor promotes nasopharyngeal carcinoma progression and radioresistance. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 5269–5283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Gao, W.; Lytle, N.K.; Huang, P.; Yuan, X.; Dann, A.M.; Ridinger-Saison, M.; DelGiorno, K.E.; Antal, C.E.; Liang, G.; et al. Targeting LIF-mediated paracrine interaction for pancreatic cancer therapy and monitoring. Nature 2019, 569, 131–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.T.; Fer, N.; Galeas, J.; Collisson, E.A.; Kim, S.E.; Sharib, J.; McCormick, F. Blockade of leukemia inhibitory factor as a therapeutic approach to KRAS driven pancreatic cancer. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viswanadhapalli, S.; Luo, Y.; Sareddy, G.R.; Santhamma, B.; Zhou, M.; Li, M.; Ma, S.; Sonavane, R.; Pratap, U.P.; Altwegg, K.A.; et al. EC359: A First-in-Class Small-Molecule Inhibitor for Targeting Oncogenic LIFR Signaling in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2019, 18, 1341–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Ramasamy, K.; Pillai, S.M.A.; Santhamma, B.; Konda, S.; Venkata, P.P.; Blankenship, L.; Liu, J.; Liu, Z.; Altwegg, K.A.; et al. LIF/LIFR oncogenic signaling is a novel therapeutic target in endometrial cancer. Cell Death Discov. 2021, 7, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blankenship, L.; Pratap, U.P.; Yang, X.; Liu, Z.; Altwegg, K.A.; Santhamma, B.; Ramasamy, K.; Konda, S.; Chen, Y.; Lai, Z.; et al. Inhibition of LIFR Blocks Adiposity-Driven Endometrioid Endometrial Cancer Growth. Cancers 2022, 14, 5400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, B.R.; Cannon, A.; Thompson, C.; Santhamma, B.; Chavez-Riveros, A.; Bhatia, R.; Nair, H.B.; Nickisch, K.; Batra, S.K.; Kumar, S. Utilizing cell line-derived organoids to evaluate the efficacy of a novel LIFR-inhibitor, EC359 in targeting pancreatic tumor stroma. Genes. Cancer 2019, 10, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Giorgio, C.; Lupia, A.; Marchiano, S.; Bordoni, M.; Bellini, R.; Massa, C.; Urbani, G.; Roselli, R.; Moraca, F.; Sepe, V.; et al. Repositioning Mifepristone as a Leukaemia Inhibitory Factor Receptor Antagonist for the Treatment of Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma. Cells 2022, 11, 3482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, C.-Z.; Li, N.-Z.; Hu, X.-B.; Xie, Y.-Y.; Huang, Q.-H.; Zhang, J.; Chen, Z.; Chen, S.-J.; Wang, F.; Sun, X.-J. The LIFR-targeting small molecules EC330/EC359 are potent ferroptosis inducers. Genes Dis. 2023, 10, 735–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimi, B.; Viswanadhapalli, S.; Pratap, U.P.; Rahul, G.; Yang, X.; Venkata, P.P.; Drel, V.; Santhamma, B.; Konda, S.; Li, X.; et al. Pharmacological inhibition of the LIF/LIFR autocrine loop reveals vulnerability of ovarian cancer cells to ferroptosis. NPJ Precis. Oncol. 2024, 8, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walters, D.M.; Lindberg, J.M.; Adair, S.J.; Newhook, T.E.; Cowan, C.R.; Stokes, J.B.; Borgman, C.A.; Stelow, E.B.; Lowrey, B.T.; Chopivsky, M.E.; et al. Inhibition of the growth of patient-derived pancreatic cancer xenografts with the MEK inhibitor trametinib is augmented by combined treatment with the epidermal growth factor receptor/HER2 inhibitor lapatinib. Neoplasia 2013, 15, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malpica, A.; Wong, K.K. The molecular pathology of ovarian serous borderline tumors. Ann. Oncol. 2016, 27 (Suppl. 1), i16–i19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasaki, N.; Hirano, K.; Shichi, Y.; Gomi, F.; Yoshimura, H.; Matsushita, A.; Toyoda, M.; Ishiwata, T. Gp130-Mediated STAT3 Activation Contributes to the Aggressiveness of Pancreatic Cancer through H19 Long Non-Coding RNA Expression. Cancers 2022, 14, 2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanahan, D. Hallmarks of Cancer: New Dimensions. Cancer Discov. 2022, 12, 31–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorgensen, M.M.; de la Puente, P. Leukemia Inhibitory Factor: An Important Cytokine in Pathologies and Cancer. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Liu, J.; Wang, J.; Hu, W.; Feng, Z. The emerging role of leukemia inhibitory factor in cancer and therapy. Pharmacol. Ther. 2021, 221, 107754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kun, E.; Tsang, Y.T.M.; Ng, C.W.; Gershenson, D.M.; Wong, K.K. MEK inhibitor resistance mechanisms and recent developments in combination trials. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2021, 92, 102137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakadia, S.; Yarlagadda, N.; Awad, R.; Kundranda, M.; Niu, J.; Naraev, B.; Mina, L.; Dragovich, T.; Gimbel, M.; Mahmoud, F. Mechanisms of resistance to BRAF and MEK inhibitors and clinical update of US Food and Drug Administration-approved targeted therapy in advanced melanoma. OncoTargets Ther. 2018, 11, 7095–7107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez, J.N.; Wang, T.; Cohen, M.S. BRAF and MEK Inhibitors: Use and Resistance in BRAF-Mutated Cancers. Drugs 2018, 78, 549–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Arnold, W.C.; Panneerdoss, D.M.; Subramani, B.; Mahajan, M.; Ebrahimi, B.; Ramirez, P.; Santhamma, B.; Viswanadhapalli, S.; Kost, E.R.; Chen, Y.; et al. EC359 Enhances Trametinib Efficacy in Ras/Raf-Driven Ovarian Cancer by Suppressing LIFR Signaling. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 1396. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15101396
Arnold WC, Panneerdoss DM, Subramani B, Mahajan M, Ebrahimi B, Ramirez P, Santhamma B, Viswanadhapalli S, Kost ER, Chen Y, et al. EC359 Enhances Trametinib Efficacy in Ras/Raf-Driven Ovarian Cancer by Suppressing LIFR Signaling. Biomolecules. 2025; 15(10):1396. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15101396
Chicago/Turabian StyleArnold, William C., Durga Meenakshi Panneerdoss, Baskaran Subramani, Megharani Mahajan, Behnam Ebrahimi, Paulina Ramirez, Bindu Santhamma, Suryavathi Viswanadhapalli, Edward R. Kost, Yidong Chen, and et al. 2025. "EC359 Enhances Trametinib Efficacy in Ras/Raf-Driven Ovarian Cancer by Suppressing LIFR Signaling" Biomolecules 15, no. 10: 1396. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15101396
APA StyleArnold, W. C., Panneerdoss, D. M., Subramani, B., Mahajan, M., Ebrahimi, B., Ramirez, P., Santhamma, B., Viswanadhapalli, S., Kost, E. R., Chen, Y., Lai, Z., Nair, H. B., Vadlamudi, R. K., & Lyons, Y. A. (2025). EC359 Enhances Trametinib Efficacy in Ras/Raf-Driven Ovarian Cancer by Suppressing LIFR Signaling. Biomolecules, 15(10), 1396. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15101396





