Epibrassinolide Regulates Lhcb5 Expression Though the Transcription Factor of MYBR17 in Maize
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Material and Treatments
2.2. RNA Isolation, Gene Cloning, and Expression Analysis
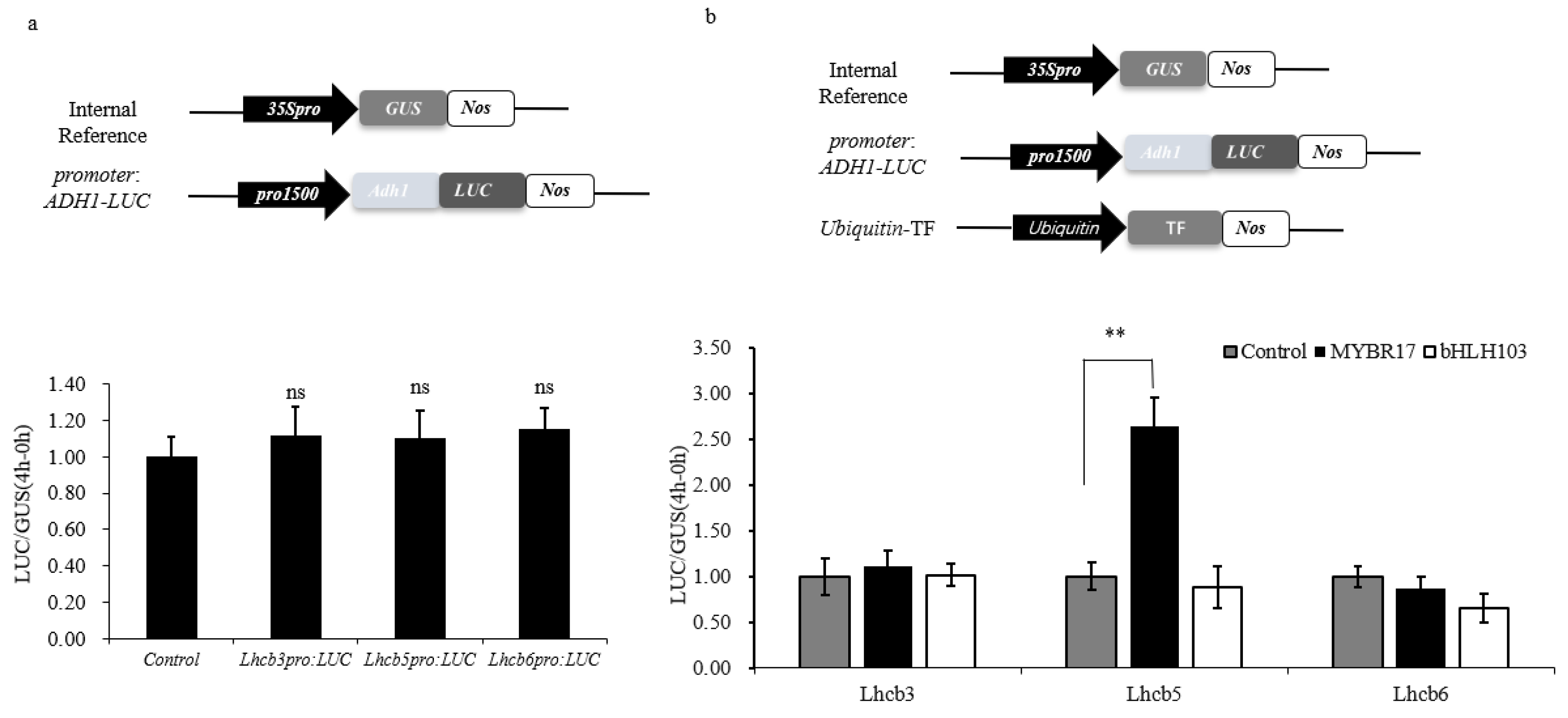
2.3. Promoter Activation Assays
2.4. Analysis of MYBR17 Transactivation
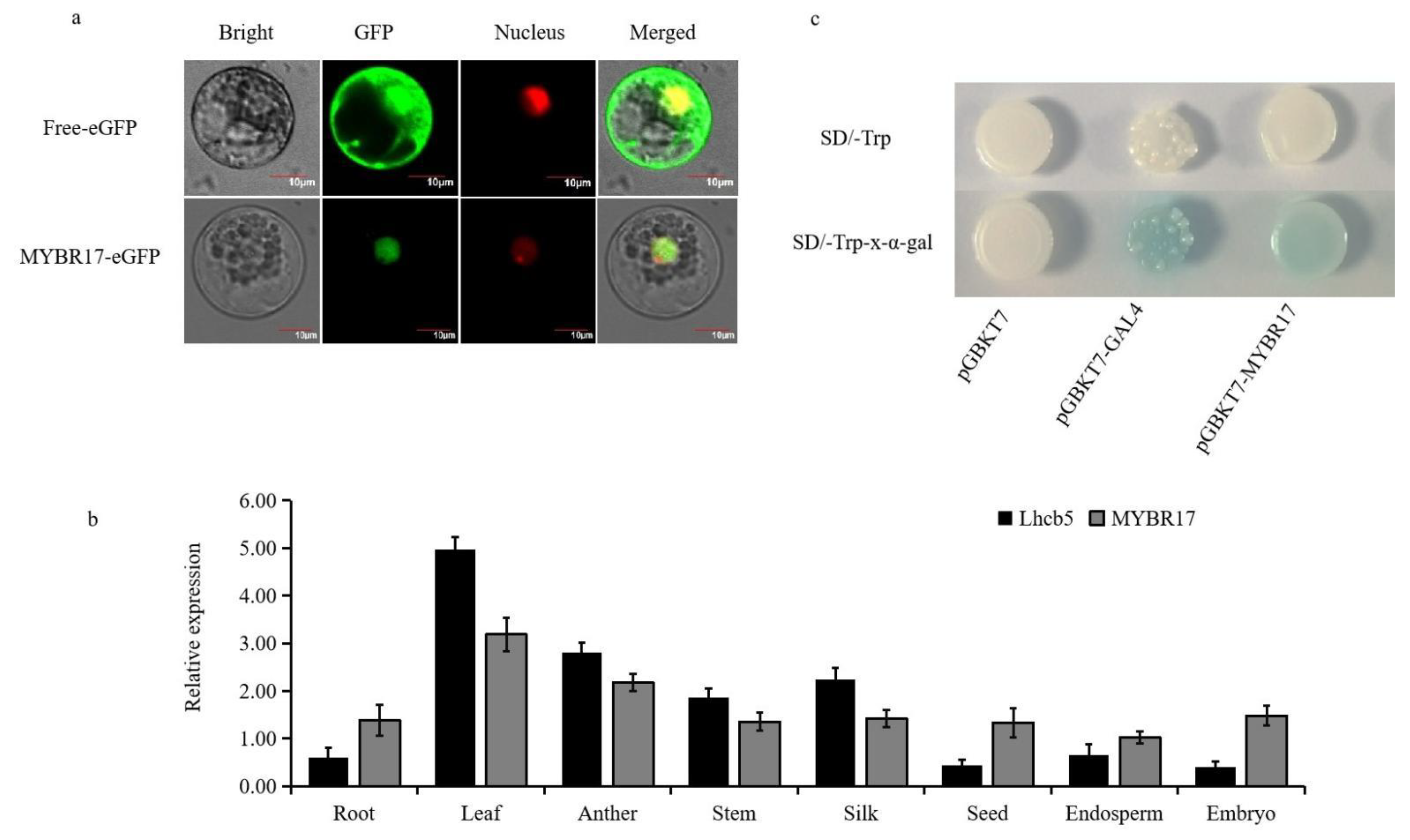
2.5. Subcellular Localization of MYBR17
2.6. Yeast One-Hybrid Analysis
2.7. Analysis of Photosynthetic Parameters and Chlorophyll Content
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Differential Gene Expression Analysis of Photosynthetic Antenna Protein RNA-Seq
3.2. Identification of Candidate TFs That Bind to the Lhcb5 Promoter
3.3. Analysis of the Expression Patterns of Candidate Transcription Factors and Target Genes
3.4. MYBR17 Activated the Promoters of Lhcb5
3.5. MYBR17 Deficiency Reduces Photosynthesis in Arabidopsis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bajguz, A.; Tretyn, A. The chemical characteristic and distribution of brassinosteroids in plants. Phytochemistry 2003, 62, 1027–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchel, J.W.; Mandava, N.; Worley, J.F.; Plimmer, J.R.; Smith, M.V. Brassins—A new family of plant hormones from rape pollen. Nature 1970, 225, 1065–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sirhindi, G.; Kumar, S.; Bhardwaj, R.; Kumar, M. Effects of 24-epibrassinolide and 28-homobrassinolide on the growth and antioxidant enzyme activities in the seedlings of Brassica juncea L. Physiol. Mol. Biol. Plants 2009, 15, 335–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mu, D.W.; Feng, N.J.; Zheng, D.F.; Zhou, H.; Liu, L.; Chen, G.J.; Mu, B. Physiological mechanism of exogenous brassinolide alleviating salt stress injury in rice seedlings. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 20439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobrikova, A.G.; Vladkova, R.S.; Rashkov, G.D.; Todinova, S.J.; Krumova, S.B.; Apostolova, E.L. Effects of exogenous 24-epibrassinolide on the photosynthetic membranes under non-stress conditions. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2014, 80, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swamy, K.; Rao, S. Effect of 24-epibrassinolide on growth, photosynthesis, and essential oil content of Pelargonium graveolens (L.) Herit. Russ. J. Plant Physiol. 2009, 56, 616–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, H.; Chu, C. Brassinosteroid signaling and application in rice. J. Genet. Genom. 2012, 39, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazir, F.; Fariduddin, Q.; Hussain, A.; Khan, T.A. Brassinosteroid and hydrogen peroxide improve photosynthetic machinery, stomatal movement, root morphology and cell viability and reduce Cu- triggered oxidative burst in tomato. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 207, 111081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogweno, J.O.; Song, X.S.; Shi, K.; Hu, W.H.; Mao, W.H.; Zhou, Y.H.; Yu, J.Q.; Nogués, S. Brassinosteroids alleviate heat-induced inhibition of photosynthesis by increasing carboxylation efficiency and enhancing antioxidant systems in Lycopersicon esculentum. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2008, 27, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Feng, Z.; Zhou, C.; Ren, Y.; Mou, C.; Wu, T.; Yang, C.; Liu, S.; Jiang, L.; Wan, J. Brassinosteroid (BR) biosynthetic gene lhdd10 controls late heading and plant height in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Cell Rep. 2016, 35, 357–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braun, P.; Wild, A. The influence of brassinosteroid on growth and parameters of photosynthesis of wheat and mustard plants. J. Plant Physiol. 1984, 116, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chollet, R.; Anderson, L.L. Regulation of ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase-oxygenase activities by temperature pretreatment and chloroplast metabolites. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1976, 176, 344–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.Y.; Trieu, A.; Radhakrishnan, P.; Kwok, S.F.; Harris, S.; Zhang, K.; Wang, J.; Wan, J.; Zhai, H.; Takatsuto, S.; et al. Brassinosteroids regulate grain filling in rice. Plant Cell 2008, 20, 2130–2145. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, J.Q.; Huang, L.F.; Hu, W.H.; Zhou, Y.H.; Mao, W.H.; Ye, S.F.; Nogués, S. A role for brassinosteroids in the regulation of photosynthesis in Cucumis sativus. J. Exp. Bot. 2004, 55, 1135–1143. [Google Scholar]
- Gruszka, D. The brassinosteroid signaling pathway-new key players and interconnections with other signaling networks crucial for plant development and stress tolerance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 8740–8774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ort, D.R.; Merchant, S.S.; Alric, J.; Barkan, A.; Blankenship, R.E.; Croce, R.; Hanson, M.R.; Hibberd, J.M.; Long, S.P.; Moore, T.A.; et al. Redesigning photosynthesis to sustainably meet global food and bioenergy demand. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 8529–8536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santarius, K.A.; Heber, U. Changes in the intracellular levels of ATP, ADP, AMP and P1 and regulatory function of the adenylate system in leaf cells during photosynthesis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1965, 102, 39–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dekker, J.P.; Boekema, E.J. Supramolecular organization of thylakoid membrane proteins in green plants. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2005, 1706, 12–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jansson, S. A guide to the Lhc genes and their relatives in Arabidopsis. Trends Plant Sci. 1999, 4, 236–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakushevska, A.E.; Keegstra, W.; Boekema, E.J.; Dekker, J.P.; Andersson, J.; Jansson, S.; Ruban, A.V.; Horton, P. The structure of photosystem II in Arabidopsis: Localization of the CP26 and CP29 antenna complexes. Biochemistry 2003, 42, 608–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grimm, B.; Kloppstech, K. The early light-inducible proteins of barley. Characterization of two families of 2-h-specific nuclear-coded chloroplast proteins. Eur. J. Biochem. 1987, 167, 493–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adamska, I.; Ohad, I.; Kloppstech, K. Synthesis of the early light-inducible protein is controlled by blue light and related to light stress. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 2610–2613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krauss, N. Mechanisms for photosystems I and II. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2003, 7, 540–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boekema, E.J.; Van Roon, H.; Van Breemen, J.F.; Dekker, J.P. Supramolecular organization of photosystem II and its light-harvesting antenna in partially solubilized photosystem II membranes. Eur. J. Biochem. 1999, 266, 444–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crimi, M.; Dorra, D.; Bösinger, C.S.; Giuffra, E.; Holzwarth, A.R.; Bassi, R. Time-resolved fluorescence analysis of the recombinant photosystem II antenna complex CP29. Effects of zeaxanthin, pH and phosphorylation. Eur. J. Biochem. 2001, 268, 260–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dall’Osto, L.; Caffarri, S.; Bassi, R. A mechanism of nonphotochemical energy dissipation, independent from PsbS, revealed by a conformational change in the antenna protein CP26. Plant Cell 2005, 17, 1217–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morosinotto, T.; Baronio, R.; Bassi, R. Dynamics of chromophore binding to Lhc proteins in vivo and in vitro during operation of the xanthophyll cycle. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 36913–36920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Oort, B.; Alberts, M.; de Bianchi, S.; Dall’Osto, L.; Bassi, R.; Trinkunas, G.; Croce, R.; van Amerongen, H. Effect of antenna-depletion in Photosystem II on excitation energy transfer in Arabidopsis thaliana. Biophys. J. 2010, 98, 922–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovács, L.; Damkjaer, J.; Kereïche, S.; Ilioaia, C.; Ruban, A.V.; Boekema, E.J.; Jansson, S.; Horton, P. Lack of the light-harvesting complex CP24 affects the structure and function of the grana membranes of higher plant chloroplasts. Plant Cell 2006, 18, 3106–3120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albanese, P.; Manfredi, M.; Meneghesso, A.; Marengo, E.; Saracco, G.; Barber, J.; Morosinotto, T.; Pagliano, C. Dynamic reorganization of photosystem II supercomplexes in response to variations in light intensities. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2016, 1857, 1651–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; He, X.; Lv, H.; Liu, H.; Li, Y.; Hu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, J. Epi-Brassinolide Regulates ZmC4 NADP-ME Expression through the Transcription Factors ZmbHLH157 and ZmNF-YC2. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 4614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajayo, B.S.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Dai, C.; Gao, L.; Liu, H.; Yu, G.; Zhang, J.; Huang, Y.; Hu, Y. The novel ZmTCP7 transcription factor targets AGPase-encoding gene ZmBt2 to regulate storage starch accumulation in maize. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 943050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, P.; Ma, W.; Hu, J.; Cai, W. The nitrate-inducible NAC transcription factor NAC056 controls nitrate assimilation and promotes lateral root growth in Arabidopsis thaliana. PLoS Genet. 2022, 18, e1010090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Fang, S.; Liu, Y.; Shang, X. Metabolome and Transcriptome Analyses Unravel the Molecular Regulatory Mechanisms Involved in Photosynthesis of Cyclocarya paliurus under Salt Stress. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, P.; Cai, W. Nitrate-responsive OBP4-XTH9 regulatory module controls lateral root development in Arabidopsis thaliana. PLoS Genet. 2019, 15, e1008465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, T.; Guo, L.; Ji, C.; Wang, H.; Wang, J.; Zheng, X.; Xiao, Q.; Wu, Y. The B3 domain-containing transcription factor ZmABI19 coordinates expression of key factors required for maize seed development and grain filling. Plant Cell 2021, 33, 104–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.F.; Li, Y.P.; Zhang, J.; Liu, H.; Chen, Z.; Huang, Y. PzsS3a, a novel endosperm specific promoter from maize (Zea mays L.) induced by ABA. Biotechnol. Lett. 2011, 33, 1465–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Liu, Q.; Wang, C.; Liang, J.; Liu, L.; Wang, Q. ZmWRKY79 positively regulates maize phytoalexin biosynthetic gene expression and is involved in stress response. J. Exp. Bot. 2018, 69, 497–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yu, G.; Lv, Y.; Long, T.; Li, P.; Hu, Y.; Liu, H.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Y.; Li, W.C.; et al. Combinatorial interaction of two adjacent cis-active promoter regions mediates the synergistic induction of Bt2 gene by sucrose and ABA in maize endosperm. Plant Sci. 2018, 274, 332–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, J.; Ren, F.; Lu, X.; Mao, H.; Xu, M.; Degenhardt, J.; Peters, R.J.; Wang, Q. A Tandem Array of ent-Kaurene Synthases in Maize with Roles in Gibberellin and More Specialized Metabolism. Plant Physiol. 2016, 170, 42–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogorad, L. Porphyrin synthesis. In Methods in Enzymology; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1962; Volume 5, pp. 885–895. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, Y.; Liu, X.; Ge, S.; Zhang, H.; Che, X.; Liu, S.; Liu, D.; Li, H.; Gu, X.; He, L.; et al. Involvement of Phospholipase C in Photosynthesis and Growth of Maize Seedlings. Genes 2022, 13, 1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.; Guyer, L.; Hörtensteiner, S. Chlorophyll and chlorophyll catabolite analysis by HPLC. Plant Senescence Methods Protoc. 2018, 1744, 223–235. [Google Scholar]
- Siddiqui, H.; Hayat, S.; Bajguz, A. Regulation of photosynthesis by brassinosteroids in plants. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2018, 40, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lescot, M.; Déhais, P.; Thijs, G.; Marchal, K.; Moreau, Y.; Van de Peer, Y.; Rouzé, P.; Rombauts, S. PlantCARE, a database of plant cis-acting regulatory elements and a portal to tools for in silico analysis of promoter sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, 325–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, H.; Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K.; Urao, T.; Iwasaki, T.; Hosokawa, D.; Shinozaki, K. Role of arabidopsis MYC and MYB homologs in drought-and abscisic acid-regulated gene expression. Plant Cell 1997, 9, 1859–1868. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Klessig, D.F. Isolation and characterization of a tobacco mosaic virus-inducible myb oncogene homolog from tobacco. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 14972–14977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, S.S.; Kayani, M.A.; Amjad, M. Transcription factors as tools to engineer enhanced drought stress tolerance in plants. Biotechnol. Prog. 2011, 27, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zhai, Z.; Tian, X.; Duan, L.; Li, Z. Brassinolide alleviated the adverse effect of water deficits on photosynthesis and the antioxidant of soybean (Glycine max L.). Plant Growth Regul. 2008, 56, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, H.; Zhang, L.S.; Zhang, G.Q.; Zheng, B.Q.; Liu, Z.J.; Wang, Y. Evolutionary history of PEPC genes in green plants: Implications for the evolution of CAM in orchids. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2016, 94, 559–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, J.C.; Sheen, J. Sugar sensing in higher plants. Plant Cell 1994, 6, 1665–1679. [Google Scholar]
- Carré, I.A.; Kim, J.Y. MYB transcription factors in the Arabidopsis circadian clock. J. Exp. Bot. 2002, 53, 1551–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.Y.; Kenigsbuch, D.; Sun, L.; Harel, E.; Ong, M.S.; Tobin, E.M. A Myb-related transcription factor is involved in the phytochrome regulation of an Arabidopsis Lhcb gene. Plant Cell 1997, 9, 491–507. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.Y.; Tobin, E.M. Constitutive expression of the CIRCADIAN CLOCK ASSOCIATED 1 (CCA1) gene disrupts circadian rhythms and suppresses its own expression. Cell 1998, 93, 1207–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Churin, Y.; Adam, E.; Kozma-Bognar, L.; Nagy, F.; Börner, T. Characterization of two Myb-like transcription factors binding to CAB promoters in wheat and barley. Plant Mol. Biol. 2003, 52, 447–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, B.; Chen, H.; Zheng, L.; Su, L.; Cui, X.; Ge, F.; Liu, D. An MYB Transcription Factor Modulates Panax notoginseng Resistance Against the Root Rot Pathogen Fusarium solani by Regulating the Jasmonate Acid Signaling Pathway and Photosynthesis. Phytopathology 2022, 112, 1323–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, C.; Li, C. A Novel R2R3-MYB Transcription Factor BpMYB106 of Birch (Betula platyphylla) Confers Increased Photosynthesis and Growth Rate through Up-regulating Photosynthetic Gene Expression. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Tan, B.; Cheng, Z.; Zhu, D.; Jiang, T.; Chen, S. Overexpression of McHB7 Transcription Factor from Mesembryanthemum crystallinum Improves Plant Salt Tolerance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 7879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubos, C.; Stracke, R.; Grotewold, E.; Weisshaar, B.; Martin, C.; Lepiniec, L. MYB transcription factors in Arabidopsis. Trends Plant Sci. 2010, 15, 573–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stracke, R.; Werber, M.; Weisshaar, B. The R2R3-MYB gene family in Arabidopsis thaliana. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2001, 4, 447–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Gene ID | Gene Name | Down- or Upregulated | log2 Fold-Change |
|---|---|---|---|
| Zm00001d009589 | Lhcb3 | Up | 0.903876796 |
| Zm00001d007267 | Lhcb5 | Up | 1.437698745 |
| Zm00001d433540 | Lhcb6 | Up | 0.696991975 |
| Zm00001d033957 | bHLH103 | Up | 1.007641981 |
| Zm00001d014698 | Sbp25 | Up | 0.839243932 |
| Zm00001d044409 | MYBR17 | Up | 1.706390574 |
| Zm00001d036736 | bZIP76 | Up | 1.020292463 |
| Zm00001d030108 | JMJ14 | Up | 1.109304348 |
| Cis-Element | Position | Signal Sequence | Putative Function |
|---|---|---|---|
| CAAT-box | CAAT/CCAAT/CAAAT | +146, −256, +495, +856, −125, +1800 | Common cis-acting element in promoter and enhancer regions |
| MYB | CAACCA/TAACCA | −485, −582, −885, +1290 | Myb-binding site |
| BRRE | CGTGCG | +445, +846 | Brassinolide responsive element |
| GARE-motif | TCTGTTG | +1820 | Gibberellin-responsive element |
| Parameter | WT | mybr17 |
|---|---|---|
| Total chlorophyll (mg/g FW) | 2.11 | 1.52 |
| Chlorophyll a/b | 3.59 | 3.56 |
| Fv/Fm | 0.81 | 0.75 |
| ΦPSII | 0.28 | 0.25 |
| NPQ | 1.13 | 0.95 |
| qP | 0.52 | 0.47 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, H.; He, X.; Lv, H.; Zhang, H.; Peng, F.; Song, J.; Liu, W.; Zhang, J. Epibrassinolide Regulates Lhcb5 Expression Though the Transcription Factor of MYBR17 in Maize. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 94. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15010094
Li H, He X, Lv H, Zhang H, Peng F, Song J, Liu W, Zhang J. Epibrassinolide Regulates Lhcb5 Expression Though the Transcription Factor of MYBR17 in Maize. Biomolecules. 2025; 15(1):94. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15010094
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Hui, Xuewu He, Huayang Lv, Hongyu Zhang, Fuhai Peng, Jun Song, Wenjuan Liu, and Junjie Zhang. 2025. "Epibrassinolide Regulates Lhcb5 Expression Though the Transcription Factor of MYBR17 in Maize" Biomolecules 15, no. 1: 94. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15010094
APA StyleLi, H., He, X., Lv, H., Zhang, H., Peng, F., Song, J., Liu, W., & Zhang, J. (2025). Epibrassinolide Regulates Lhcb5 Expression Though the Transcription Factor of MYBR17 in Maize. Biomolecules, 15(1), 94. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15010094






