Evaluation of Plasma E-Selectin Concentration as a Risk Marker for Atherosclerotic Vascular Damage in Patients with Early CAD
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Groups
2.2. Clinical Data Collection
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
5.1. Is There an Association Between Plasma E-Selectin Levels and Stable CAD or the Presence of Known Biochemical and Clinical Risk Factors for Cardiovascular Disease?
5.2. Could Plasma Measurement of E-Selectin Replace Classical Cardiac or Radiological Examination of Vascular Status?
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mangoni, A.A.; Zinellu, A. Circulating cell adhesion molecules in systemic sclerosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1438302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vitale, C.; Cornoldi, A.; Gebara, O.; Silvestri, A.; Wajngarten, M.; Cerquetani, E.; Fini, M.; Ramires, J.A.F.; Rosano, G.M.C. Interleukin-6 and flow-mediated dilatation as markers of increased vascular inflammation in women receiving hormone therapy. Menopause 2005, 12, 552–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zakynthinos, E.; Pappa, N. Inflammatory biomarkers in coronary artery disease. J. Cardiol. 2009, 53, 317–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoke, M.; Winter, M.P.; Wagner, O.; Exner, M.; Schillinger, M.; Arnold, Z.; Mlekusch, W.; Maurer, G.; Koppensteiner, R.; Minar, E.; et al. The impact of selectins on mortality in stable carotid atherosclerosis. Thromb. Haemost. 2015, 114, 632–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stachowiak, G.; Stetkiewicz, T.; Połać, I.; Sobczuk, A.; Jędrzejczyk, S.; Pertyński, T. The role of E-selectin in inflammatory and atherogenic processes—The impact of hormonal therapy of the menopausal period. Przegląd Menopauzalny 2006, 3, 153–158. [Google Scholar]
- Lind, L. Circulating markers of inflammation and atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis 2003, 169, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Rux, A.H.; Ma, P.; Bdeir, K.; Sachais, B.S. Endothelial expression of E-selectin is induced by the platelet-specific chemokine platelet factor 4 through LRP in an NF-κB-dependent manner. Blood 2005, 105, 3545–3551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, M.; Videira, P.A.; Sackstein, R. E-Selectin Ligands in the Human Mononuclear Phagocyte System: Implications for Infection, Inflammation, and Immunotherapy. Front. Immunol. 2018, 8, 1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roldán, V.; Marín, F.; Lip, G.Y.H.; Blann, A.D. Soluble E-selectin in cardiovascular disease and its risk factors. A review of the literature. Thromb. Haemost. 2003, 90, 1007–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Shaikh, F.; Zamzam, A.; Raphael, R.; Syed, M.H.; Younes, H.K.; Abdin, R.; Qadura, M. Prediction of Peripheral Artery Disease Prognosis Using Clinical and Inflammatory Biomarker Data. J. Inflamm. Res. 2024, 17, 4865–4879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.D.; Cao, Y.; Mu, J.Y.; Liu, Y.M.; Gao, F.; Han, F.; Zhai, F.F.; Zhou, L.X.; Ni, J.; Yao, M.; et al. Inflammatory biomarkers and cerebral small vessel disease: A community-based cohort study. Stroke Vasc. Neurol. 2022, 7, 302–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasad, K.; Mishra, M. Mechanism of Hypercholesterolemia-Induced Atherosclerosis. Rev. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 23, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wünnemann, F.; Tadjo, T.F.; Beaudoin, M.; Lalonde, S.; Lo, K.S.; Kleinstiver, B.P.; Lettre, G. Multimodal CRISPR perturbations of GWAS loci associated with coronary artery disease in vascular endothelial cells. PLoS Genet. 2023, 19, e1010680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, L.Q.; Ghareeb, R.M. E-selectin is associated with stable angina and myocardial infarction in a sample of Kurdish population. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2024, 70, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nartowicz, S.A.; Szczepaniak-Chicheł, L.; Lipski, D.; Miechowicz, I.; Bartczak-Rutkowska, A.; Gabriel, M.; Lesiak, M.; Trojnarska, O. E-Selectin and Asymmetric Dimethylarginine Levels in Adult Cyanotic Congenital Heart Disease: Their Relation to Biochemical Parameters, Vascular Function, and Clinical Status. Cells 2024, 13, 1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safonova, J.; Kozhevnikova, M.; Danilogorskaya, J.; Zheleznykh, E.; Zektser, V.; Ilgisonis, I.; Popova, L.; Khabarova, N.; Privalova, E.; Belenkov, Y. Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitor Therapy Effects in Patients With Heart Failure With Preserved and Mid-Range Ejection Fraction. Cardiol. Res. 2021, 12, 363–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J. Biomarkers of endothelial activation and dysfunction in cardiovascular diseases. Rev. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 23, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichman-Warmusz, E.; Kaczmarek, K.; Badziński, A.; Warmusz, O.; Wojnicz, R. The presence of E-selectin in the myocardium indicates a sustained inflammatory reaction in patients with dilated cardiomyopathy. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2022, 232, 153845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semaan, H.B.; Gurbel, P.A.; Anderson, J.L.; Muhlestein, J.B.; Carlquist, J.F.; Horne, B.D.; Serebruany, V.L. Soluble VCAM-1 and E-selectin, but not ICAM-1 discriminate endothelial injury in patients with documented coronary artery disease. Comp. Study Cardiol. 2000, 93, 7–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cwikiel, J.; Seljeflot, I.; Berge, E.; Njerve, I.U.; Ulsaker, H.; Arnesen, H.; Flaa, A. Effect of strenuous exercise on mediators of inflammation in patients with coronary artery disease. Cytokine 2018, 105, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.H.; Sheng, Z.Q.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, L. Levels of soluble adhesion molecules in patients with various clinical presentations of coronary atherosclerosis. Chin. Med. J. 2010, 123, 3123–3126. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Boos, C.J.; Balakrishnan, B.; Blann, A.D.; Lip, G.Y.H. The relationship of circulating endothelial cells to plasma indices of endothelial damage/dysfunction and apoptosis in acute coronary syndromes: Implications for prognosis. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2008, 6, 1841–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, R.B.; Colangelo, L.A.; Reiner, A.P.; Gross, M.D.; Jacobs, D.R., Jr.; Launer, L.J.; Lima, J.A.C.; Lloyd-Jones, D.M.; Shah, S.J. Cellular Adhesion Molecules in Young Adulthood and Cardiac Function in Later Life. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020, 75, 2156–2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blankenberg, S.; Rupprecht, H.J.; Bickel, C.; Peetz, D.; Hafner, G.; Tiret, L.; Meyer, J. Circulating cell adhesion molecules and death in patients with coronary artery disease. Circulation 2001, 104, 1336–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vargas-Alarcon, G.; Perez-Mendez, O.; Herrera-Maya, G.; Posadas-Romero, C.; Posadas-Sanchez, R.; Ramirez-Bello, J.; Escobedo, G.; Fragoso, J.M. The rs1805193, rs5361, and rs5355 single nucleotide polymorphisms in the E-selectin gene (SEL-E) are associated with subclinical atherosclerosis: The Genetics of Atherosclerotic Disease (GEA) Mexican study. Immunobiology 2019, 224, 10–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoshbin, M.; Ahmadi, S.A.Y.; Cheraghi, M.; Nouryazdan, N.; Birjandi, M.; Shahsavari, G. Association of E-Selectin gene polymorphisms and serum E-Selectin level with risk of coronary artery disease in lur population of Iran. Arch. Physiol. Biochem. 2023, 129, 387–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zak, I.; Sarecka, B.; Krauze, J. Synergistic effects between 561A > C and 98G > T polymorphisms of E-selectin gene and hypercholesterolemia in determining the susceptibility to coronary artery disease. Heart Vessels 2008, 23, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorący, J.; Kaczmarczyk, M.; Ciechanowicz, A.; Safranow, K.; Gorący, J.; Jakubowska, K.; Chlubek, D.; Gorący, I. E-selectin gene haplotypes are associated with the risk of myocardial infarction. Arch. Med. Sci. 2019, 15, 1223–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wei, Y.S.; Wang, M.; Zhang, P.A.; Jiang, X.J.; Huang, C.X. Association between the Ser128Arg variant of the E-selectin and risk of coronary artery disease in the central China. Int. J. Cardiol. 2005, 103, 33–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, C.; Wang, D.; Huang, W.; Song, Y.; Ge, L.; Zhang, X.; Yang, L.; Lu, J.; Tu, X.; Chen, Q.; et al. Feedback regulation of coronary artery disease susceptibility gene ADTRP and LDL receptors LDLR/CD36/LOX-1 in endothelia cell functions involved in atherosclerosis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2021, 1867, 166130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponasenko, A.; Sinitskaya, A.; Sinitsky, M.; Khutornaya, M.; Barbarash, O. The Role of Polymorphism in the Endothelial Homeostasis and Vitamin D Metabolism Genes in the Severity of Coronary Artery Disease. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 2382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galvani, M.; Ferrini, D.; Ottani, F.; Nanni, C.; Ramberti, A.; Amboni, P.; Iamele, L.; Vernocchi, A.; Nicolini, F.A. Soluble E-selectin is not a marker of unstable coronary plaque in serum of patients with ischemic heart disease. J. Thromb. Thrombolysis 2000, 9, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, L.; Wei, H.; Mak, K.H.; Xiong, Z.; Song, J.; Wang, D.; Lim, Y.L.; Chatterjee, S. Markers of low-grade inflammation and soluble cell adhesion molecules in Chinese patients with coronary artery disease. Can. J. Cardiol. 2004, 20, 1433–1438. [Google Scholar]
- Marschang, P.; Friedrich, G.J.; Ditlbacher, H.; Stoeger, A.; Nedden, D.Z.; Kirchmair, R.; Dienstl, A.; Pachinger, O.; Patsch, J.R. Reduction of soluble P-selectin by statins is inversely correlated with the progression of coronary artery disease. Int. J. Cardiol. 2006, 106, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linhartova, K.; Sterbakova, G.; Racek, J.; Cerbak, R.; Porazikova, K.; Rokyta, R. Linking soluble vascular adhesion molecule-1 level to calcific aortic stenosis in patients with coronary artery disease. Exp. Clin. Cardiol. 2009, 14, e80–e83. [Google Scholar]
- Paiker, J.E.; Raal, F.J.; Veller, M.; von Arb, M.; Chetty, N.; Naran, N.H. Cell adhesion molecules—Can they be used to predict coronary artery disease in patients with familial hypercholesterolaemia? Clin. Chim. Acta 2000, 293, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alen, N.V.; Parenteau, A.M.; Sloan, R.P.; Hostinar, C.E. Heart Rate Variability and Circulating Inflammatory Markers in Midlife. Brain Behav. Immun. Health 2021, 15, 100273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bialecka, M.; Rac, M.; Dziedziejko, V.; Safranow, K.; Chlubek, D.; Rac, M. An Evaluation of Plasma TNF, VEGF-A, and IL-6 Determination as a Risk Marker of Atherosclerotic Vascular Damage in Early-Onset CAD Patients. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puchałowicz, K.; Kłoda, K.; Dziedziejko, V.; Rac, M.; Wojtarowicz, A.; Chlubek, D.; Safranow, K. Association of Adiponectin, Leptin and Resistin Plasma Concentrations with Echocardiographic Parameters in Patients with Coronary Artery Disease. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauli, N.; Kuligowska, A.; Krzystolik, A.; Dziedziejko, V.; Safranow, K.; Rac, M.; Chlubek, D.; Rac, M. The circulating vascular endothelial growth factor is only marginally associated with an increased risk for atherosclerosis. Minerva Cardioangiol. 2020, 68, 332–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauli, N.; Puchałowicz, K.; Kuligowska, A.; Krzystolik, A.; Dziedziejko, V.; Safranow, K.; Rac, M.; Chlubek, D.; Rac, M. Associations between IL-6 and Echo-Parameters in Patients with Early Onset Coronary Artery Disease. Diagnostics 2019, 9, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Białecka, M.; Dziedziejko, V.; Safranow, K.; Krzystolik, A.; Marcinowska, Z.; Chlubek, D.; Rać, M. Could Tumor Necrosis Factor Serve as a Marker for Cardiovascular Risk Factors and Left Ventricular Hypertrophy in Patients with Early-Onset Coronary Artery Disease? Diagnostics 2024, 14, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang, R.M.; Bierig, M.; Devereux, R.B.; Flachskampf, F.A.; Foster, E.; Pellikka, P.A.; Picard, M.H.; Roman, M.J.; Seward, J.; Shanewise, J.; et al. Recommendations for chamber quantification. Eur. J. Echocardiogr. 2006, 7, 79–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devereux, R.B.; Alonso, D.R.; Lutas, E.M.; Gottlieb, G.J.; Campo, E.; Sachs, I.; Reichek, N. Echocardiographic assessment of left ventricular hypertrophy: Comparison to necropsy findings. Am. J. Cardiol. 1986, 57, 450–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Simone, G.; Daniels, S.R.; Devereux, R.B.; Meyer, R.A.; Roman, M.J.; de Divitiis, O.; Alderman, M.H. Left ventricular mass and body size in normotensive children and adults: Assessment of allometric relations and impact of overweight. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 1992, 20, 1251–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, M.P.; Azam, I.; Yousuf, F.A.; Kazmi, K. Relationship of adhesion molecules (ICAM-1 and E-selectin) with ABO blood groups in patients hospitalized with acute myocardial infarction. Pak. J. Med. Sci. 2024, 40, 1551–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antwi-Boasiako, C.; Donkor, E.S.; Sey, F.; Dzudzor, B.; Dankwah, G.B.; Otu, K.H.; Doku, A.; Dale, C.A.; Ekem, I. Levels of Soluble Endothelium Adhesion Molecules and Complications among Sickle Cell Disease Patients in Ghana. Diseases 2018, 6, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zdanowska, N.; Owczarczyk-Saczonek, A.; Czerwińska, J.; Nowakowski, J.J.; Kozera-Żywczyk, A.; Owczarek, W.; Zdanowski, W.; Placek, W. Methotrexate and Adalimumab Decrease the Serum Levels of Cardiovascular Disease Biomarkers (VCAM-1 and E-Selectin) in Plaque Psoriasis. Medicina 2020, 56, 473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.H.; Kuo, F.C.; Tang, W.H.; Lu, C.H.; Su, S.C.; Liu, J.S.; Hsieh, C.H.; Hung, Y.J.; Lin, F.H. Serum E-selectin concentration is associated with risk of metabolic syndrome in females. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0222815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osmancik, P.; Kvasnicka, J.; Widimsky, P.; Tarnok, A. Diurnal variation of soluble E- and P-selectin, and intercellular adhesion molecule-1 in patients with and without coronary artery disease. Cardiology 2004, 102, 194–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilgic, M.A.; Yilmaz, H.; Bozkurt, A.; Celik, H.T.; Bilgic, I.C.; Gurel, O.M.; Kirbas, I.; Bavbek, N.; Akcay, A. Relationship of late arteriovenous fistula stenosis with soluble E-selectin and soluble EPCR in chronic hemodialysis patients with arteriovenous fistula. Clin. Exp. Nephrol. 2015, 19, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turhan, H.; Erbay, A.R.; Yasar, A.S.; Aksoy, Y.; Bicer, A.; Yetkin, G.; Yetkin, G. Plasma soluble adhesion molecules; intercellular adhesion molecule-1, vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 and E-selectin levels in patients with isolated coronary artery ectasia. Coron. Artery Dis. 2005, 16, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rość, D.; Ogorzeja, W.; Kotschy, M.; Missima, M.; Jurkowski, P. Selectins E and P in the plasma of patients suffering from ischaemic heart disease undergoing surgery with cardiopulmonary bypass. Folia Cardiol. 2004, 11, 733–740. [Google Scholar]
- Yamada, H.; Hirose, Y.; Toyoshima, M.; Kobayashi, H.; Kurahashi, K.; Kudoh, I. Activation of endothelium in cardiac surgery: The circulating level of soluble E selectin as maker of the activation of endothelium. Masui 1997, 46, 478–483. [Google Scholar]
- Nordestgaard, B.; Varbo, A. Triglycerides and cardiovascular disease. Lancet 2014, 384, 626–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kącka, A.; Charemska, A.; Jarocka-Cyrta, E.; Głowińska-Olszewska, B. Comparison of novel markers of metabolic complications and cardiovascular risk factors between obese non-diabetic and obese type 1 diabetic children and young adults. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 1036109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Peng, H.; Xu, T.; Wang, A.; Wang, G.; Tong, W.; Zhang, Y. Association of biomarkers of inflammation with dyslipidemia and its components among Mongolians in China. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e89023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanojević, N.B.; Jelić-Ivanović, Z.; Djurovic, S.; Spasojević-Kalimanovska, V.; Spasić, S.; Kalimanovska-Ostrić, D.; Memon, L. Lack of association between low HDL-cholesterol and elevated circulating cellular adhesion molecules in normolipidemic CAD patients and healthy subjects. Int. Heart J. 2005, 46, 593–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babar, G.; Clements, M.; Dai, H.; Raghuveer, G. Assessment of biomarkers of inflammation and premature atherosclerosis in adolescents with type-1 diabetes mellitus. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2019, 32, 109–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasza, M.; Meleg, J.; Vardai, J.; Nagy, B., Jr.; Szalai, E.; Damjanovich, J.; Csutak, A.; Ujhelyi, B.; Nagy, V. Plasma E-selectin levels can play a role in the development of diabetic retinopathy. Graefes Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2017, 255, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conger, A.K.; Tomasek, T.; Riedmann, K.J.; Douglas, J.S.; Berkey, L.E.; Ware, L.B.; Bastarache, J.A.; Meegan, J.E. Hemoglobin increases leukocyte adhesion and initiates lung microvascular endothelial activation via Toll-like receptor 4 signaling. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2023, 324, C665–C673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nader, E.; Skinner, S.; Romana, M.; Fort, R.; Lemonne, N.; Guillot, N.; Gauthier, A.; Antoine-Jonville, S.; Renoux, C.; Hardy-Dessources, M.D.; et al. Blood Rheology: Key Parameters, Impact on Blood Flow, Role in Sickle Cell Disease and Effects of Exercise. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tokgözoglu, L.; Can, I.; Korkusuz, P.; Asan, E.; Ozer, N.; Demircin, M. Correlation of tissue selectin expression and hemodynamic parameters in rheumatic mitral valve disease. J. Heart Valve Dis. 2006, 15, 671–678. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Konstam, M.A.; Kiernan, M.S.; Bernstein, D.; Bozkurt, B.; Jacob, M.; Kapur, N.K.; Kociol, R.D.; Lewis, E.F.; Mehra, M.R.; Pagani, F.D.; et al. Evaluation and Management of Right-Sided Heart Failure: A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association. Circulation 2018, 137, e578–e622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remmelzwaal, S.; Beulens, J.W.J.; Elders, P.J.M.; Stehouwer, C.D.A.; Zhang, Z.; Handoko, M.L.; Appelman, J.; van Empel, V.; Heymans, S.R.B.; Thijs, L.; et al. Sex differences in the longitudinal relationship of low-grade inflammation and echocardiographic measures in the Hoorn and FLEMENGHO Study. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0251148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.J.; Park, C.S.; Lee, S.; Park, J.B.; Kim, H.K.; Park, S.J.; Kim, Y.J.; Lee, S.P. Systemic proinflammatory-profibrotic response in aortic stenosis patients with diabetes and its relationship with myocardial remodeling and clinical outcome. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2023, 22, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarząbek, K.; Sobczyk, A.; Sobczyk, W.; Łabuzek, K.; Belowski, D.; Gabryel, B. The concept of unstable atherosclerotic plaque and pharmacological therapeutic strategies. Chir. Pol. 2015, 17, 49–68. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, J.; Maehara, A.; Mintz, G.S.; Margolis, M.P.; Biro, S.; Stone, G.W.; Leon, M.B. Relation between individual plaque components and overall plaque burden in the prospective, multicenter virtual histology intravascular ultrasound registry. Am. J. Cardiol. 2009, 104, 501–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okulla, T.; Gass, S.; Böhme, K.; Tiemann, K.; Harbrecht, U.; Klockgether, T.; Pohl, C. Circulating adhesion molecules in patients with internal carotid artery stenosis. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2002, 14, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, N.L.; Hunt, K.J.; Stevens, D.R.; Jarai, G.; Rosen, G.D.; Klein, R.L.; Virella, G.; Lopes-Virella, M.F. Association Between Inflammatory Markers and Progression to Kidney Dysfunction: Examining Different Assessment Windows in Patients with Type 1 Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2018, 41, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Lou, Y.; Lu, L.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Q.; Chen, X.; Jin, W. Heterogeneous effect of two selectin gene polymorphisms on coronary artery disease risk: A meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e88152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, G.; Wang, J.; Liu, K.; Huang, B.; Deng, W.; He, T. Association of E-Selectin gene rs5361 polymorphism with ischemic stroke susceptibility: A systematic review and Meta-analysis. Int. J. Neurosci. 2021, 131, 511–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zinellu, A.; Mangoni, A.A. Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of the Effect of Statins on Circulating E-Selectin, L-Selectin, and P-Selectin. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Huang, S.; Zhu, Z.; Gatt, A.; Liu, J. E-selectin in vascular pathophysiology. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1401399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Parameter in CAD Group | Value |
|---|---|
| Past MI | 70% |
| Time since diagnosis of MI to joining the program (years) | 3.20 ± 0.74 |
| Age of the first MI (years) | 44.0 ± 5.6 |
| Age of patient (years) | 49.9 ± 5.91 |
| Gender (% males) | 75% |
| Weight (kg) | 83.4 ± 17.0 |
| Waist (cm) | 98.3 ± 12.5 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 28.1 ± 3.98 |
| WHR | 0.96 ± 0.09 |
| Systolic BP (mmHg) | 127 ± 14.2 |
| Diastolic BP (mmHg) | 77.0 ± 9.01 |
| Heart rate (1/min) | 70.7 ± 12.1 |
| MAP (mmHg) | 93.8 ± 9.35 |
| History of hypertension | 66% |
| Age at diagnosis of hypertension (years) | 42.6 ± 8.6 |
| Cigarette smokers | 89% |
| Years smoking | 18.9 ± 9.8 |
| Past CABG | 37% |
| Past PTCA | 71% |
| Diabetes type 2 | 13% |
| Glucose (mg/dL) | 107 ± 24.8 |
| Statins | 96% |
| Total cholesterol (mg/dL) | 173 ± 40.4 |
| LDL-cholesterol (mg/dL) | 102 ± 36.2 |
| HDL-cholesterol (mg/dL) | 48.4 ± 11.5 |
| ApoA1 (mg/dL) | 154 ± 38.4 |
| ApoB/ApoA1 | 0.53 ± 0.15 |
| Lp(a) (mg/dL) | 40.3 ± 49.3 |
| Triacylglycerols (mg/dL) | 136 ± 57.1 |
| Anti-platelet drugs (Aspirin) | 90% |
| Beta-blockers | 88% |
| ACEI | 80% |
| Diuretics | 31% |
| Calcium channel blockers | 18% |
| ARB | 17% |
| LVEF (%) | 53.6 ± 11.1 |
| LVMI (g/m2) | 183 ± 62.3 |
| Left ventricular end–diastolic diameter (mm) | 51.3 ± 7.17 |
| Left ventricular end–diastolic volume (mL) | 121 ± 43.4 |
| Left atrium diameter (mm) | 38.6 ± 5.71 |
| LVDF normal | 38% |
| LVDF impaired | 54% |
| LVDF pseudonormal | 8% |
| Right ventricular end–diastolic diameter (mm) | 32.9 ± 5.60 |
| Right ventricular mean systolic pressure (mmHg) | 22.0 ± 6.27 |
| DT (ms) | 221 ± 69.5 |
| E/A ratio | 1.12 ± 0.37 |
| TNF (pg/mL) | 1.33 ± 0.36 |
| IL-6 (pg/mL) | 1.69 ± 2.77 |
| VEGF (pg/mL) | 236 ± 17.2 |
| hsCRP (mg/L) | 1.82 ± 2.7 |
| Platelets (G/L) | 218 ± 44.6 |
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | 14.8 ± 1.14 |
| Hematocrit (%) | 43.9 ± 3.17 |
| RBC (T/L) | 4.91 ± 0.42 |
| MCV (fL) | 89.6 ± 4.40 |
| MPV (fl) | 10.6 ± 0.09 |
| WBC (G/L) | 6.80 ± 0.22 |
| ABI | 1.16 ± 0.03 |
| IMC cca (mm) | 0.81 ± 0.01 |
| IMC ba (mm) | 0.57 ± 0.01 |
| PLA present (%) | 76% |
| PLA thickness (mm) | 1.41 ± 0.08 |
| PLA length (mm) | 7.71 ± 0.33 |
| PLA density (AU) | 70.0 ± 3.20 |
| Parameter in Control Group | Value |
|---|---|
| Age of patient (years) | 48 ± 3.20 |
| Gender (% males) | 74% |
| Glucose (mg/dL) | 96.0 ± 4.07 |
| Total cholesterol (mg/dL) | 217 ± 6.36 |
| LDL-cholesterol (mg/dL) | 126 ± 5.74 |
| HDL-cholesterol (mg/dL) | 66.0 ± 2.15 |
| ApoA1 (mg/dL) | 177 ± 5.16 |
| ApoB/ApoA1 | 0.51 ± 0.03 |
| Lp(a) (mg/dL) | 23.2 ± 9.83 |
| Triacylglycerols (mg/dL) | 110 ± 8.52 |
| TNF (pg/mL) | 1.51 ± 0.005 |
| IL-6 (pg/mL) | 1.47 ± 0.33 |
| VEGF (pg/mL) | 220 ± 77.5 |
| hsCRP (mg/L) | 2.10 ± 0.26 |
| Platelets (G/L) | 223 ± 11.2 |
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | 13.7 ± 0.15 |
| Hematocrit (%) | 41.4 ± 0.43 |
| RBC (T/L) | 4.64 ± 0.06 |
| MCV (fL) | 90.0 ± 0.72 |
| MPV (fL) | 10.3 ± 0.14 |
| WBC (G/L) | 5.50 ± 0.16 |
| E-Selectin | ng/mL | p-Value * |
|---|---|---|
| CAD group | 35.58 ± 1.21 | 0.11 |
| control group | 41.17 ± 1.99 | |
| CAD male subgroup | 38.11 ± 1.48 | 0.011 |
| CAD female subgroup | 31.22 ± 2.01 |
| Parameter | Correlations for CAD Patients (n = 100) | Correlations for Control Group (n = 50) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rs | p-Value | Rs | p-Value | |
| RBC (T/L) | 0.19 | 0.067 | 0.37 | 0.0069 |
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | 0.31 | 0.0027 | 0.50 | 0.00015 |
| Hematocrit (%) | 0.30 | 0.0040 | 0.50 | 0.00032 |
| HDL-cholesterol (mg/dL) | −0.24 | 0.018 | −0.28 | 0.042 |
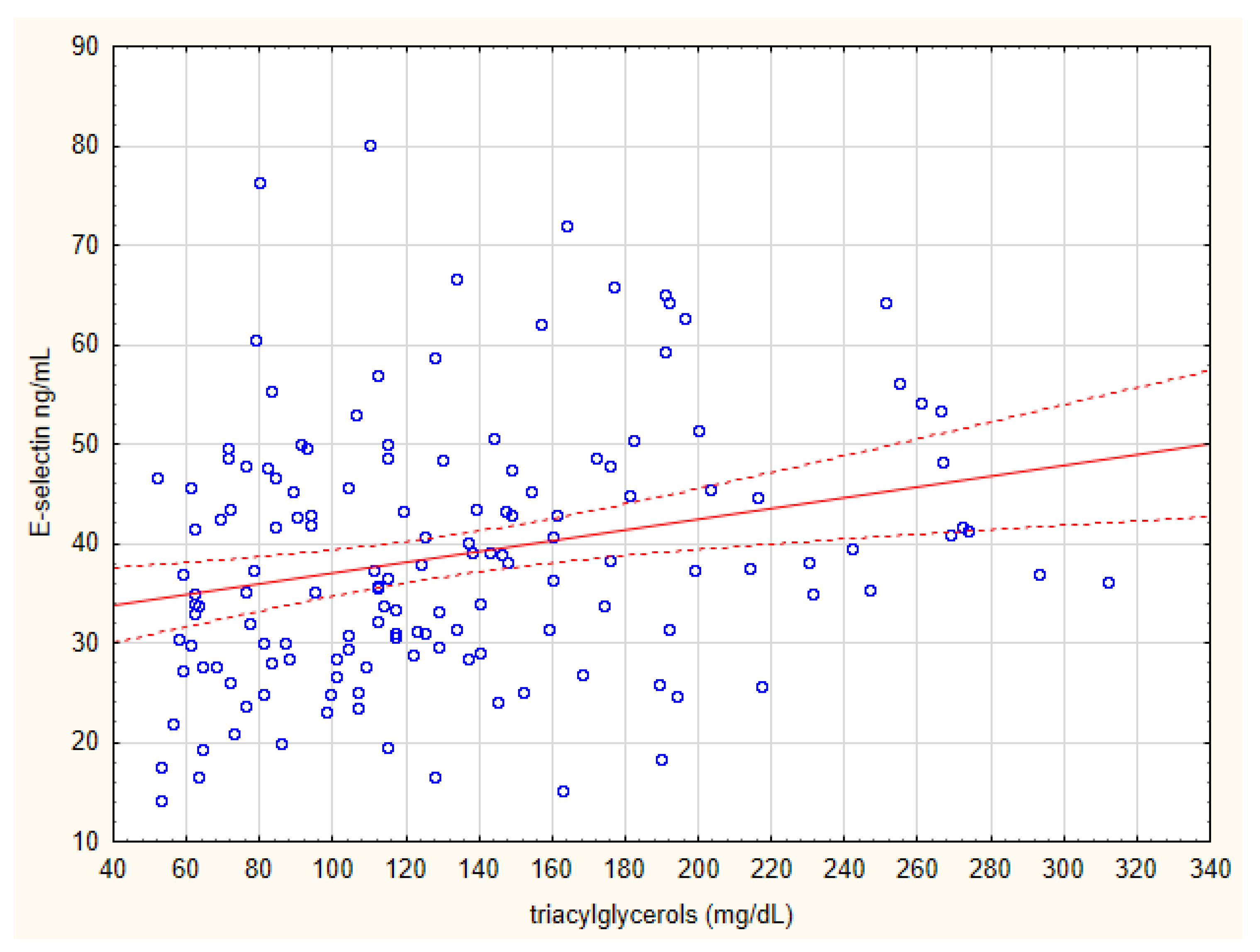
| Triacylglycerols (mg/dL) | 0.38 | 0.00018 | 0.24 | 0.093 |
| ApoB/ApoA1 | 0.26 | 0.012 | - | - |
| Glucose (mg/dL) | 0.10 | 0.33 | 0.314 | 0.025 |
| Parameter | Correlations for CAD Patients (n = 100) | |
|---|---|---|
| Rs | p-Value | |
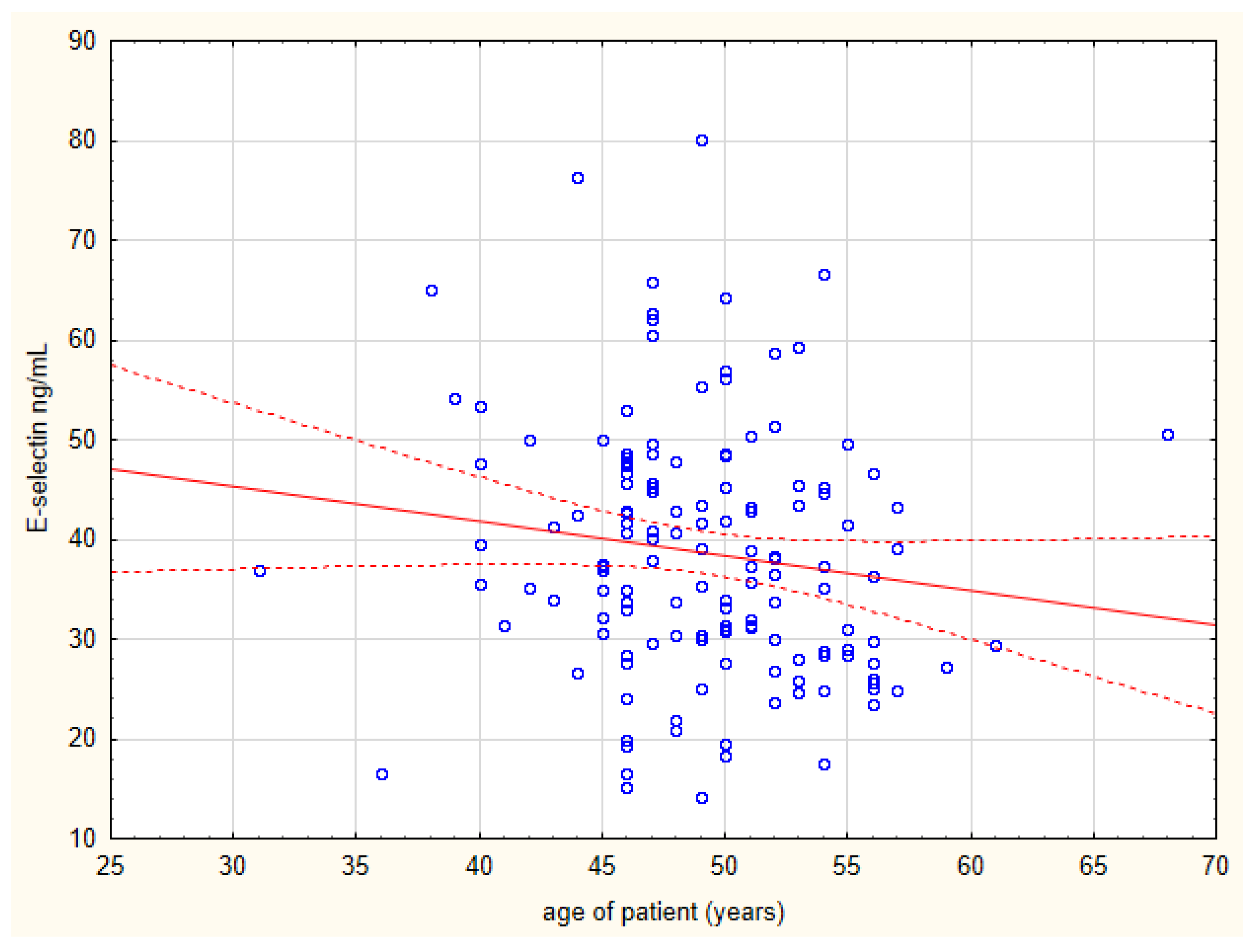
| Age of patient (years) | −0.34 | 0.00087 |
| Right ventricular end–diastolic diameter (mm) | 0.21 | 0.046 |
| PLA length (mm) | −0.43 | 0.0064 |
| Independent Variables | Standardized β Coefficient (95%CI) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|
| Triacylglycerols (mg/dL) | +0.37 | 0.00025 |
| Age of patient (years) | −0.22 | 0.023 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rac, M.; Rac, M.; Krzystolik, A.; Safranow, K.; Chlubek, D.; Dziedziejko, V. Evaluation of Plasma E-Selectin Concentration as a Risk Marker for Atherosclerotic Vascular Damage in Patients with Early CAD. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15010022
Rac M, Rac M, Krzystolik A, Safranow K, Chlubek D, Dziedziejko V. Evaluation of Plasma E-Selectin Concentration as a Risk Marker for Atherosclerotic Vascular Damage in Patients with Early CAD. Biomolecules. 2025; 15(1):22. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15010022
Chicago/Turabian StyleRac, Monika, Michal Rac, Andrzej Krzystolik, Krzysztof Safranow, Dariusz Chlubek, and Violetta Dziedziejko. 2025. "Evaluation of Plasma E-Selectin Concentration as a Risk Marker for Atherosclerotic Vascular Damage in Patients with Early CAD" Biomolecules 15, no. 1: 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15010022
APA StyleRac, M., Rac, M., Krzystolik, A., Safranow, K., Chlubek, D., & Dziedziejko, V. (2025). Evaluation of Plasma E-Selectin Concentration as a Risk Marker for Atherosclerotic Vascular Damage in Patients with Early CAD. Biomolecules, 15(1), 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15010022








