Abstract
This study identified a salt-tolerant GH11 xylanase, Xynst, which was isolated from a soil bacterium Bacillus sp. SC1 and can resist as high as 4 M NaCl. After rational design and high-throughput screening of site-directed mutant libraries, a double mutant W6F/Q7H with a 244% increase in catalytic activity and a 10 °C increment in optimal temperature was obtained. Both Xynst and W6F/Q7H xylanases were stimulated by high concentrations of salts. In particular, the activity of W6F/Q7H was more than eight times that of Xynst in the presence of 2 M NaCl at 65 °C. Kinetic parameters indicated they have the highest affinity for beechwood xylan (Km = 0.30 mg mL−1 for Xynst and 0.18 mg mL−1 for W6F/Q7H), and W6F/Q7H has very high catalytic efficiency (Kcat/Km = 15483.33 mL mg−1 s−1). Molecular dynamic simulation suggested that W6F/Q7H has a more compact overall structure, improved rigidity of the active pocket edge, and a flexible upper-end alpha helix. Hydrolysis of different xylans by W6F/Q7H released more xylooligosaccharides and yielded higher proportions of xylobiose and xylotriose than Xynst did. The conversion efficiencies of Xynst and W6F/Q7H on all tested xylans exceeded 20%, suggesting potential applications in the agricultural and food industries.
1. Introduction
Xylanases (EC 3.2.1.8) are a kind of enzyme that degrades xylan to xylooligosaccharides (XOS) and a small amount of xylose [1]. They are classified into a number of glycoside hydrolase (GH) families, with the vast majority of characterized xylanases belonging to the GH10 and GH11 families [2]. The GH11 xylanases are the most typical and true xylanases due to their substrate specificity toward xylan and only contain one catalytic domain [3]. These enzymes are conserved in structural domains, e.g., resembling a partially closed right hand and comprising two twisted β-sheets as well as a single α-helix. Stable Fingers and Palm structures are formed when the hydrophobic surfaces of two β-sheets accumulate together. Both the activation and binding sites are hidden in cracks in the Palm structure [4]. Amino acid residues at binding sites participate in substrate binding and recognition through hydrogen bonding or hydrophobic stacking interactions [5]. Between the two β-chains of the β-fold layer, there is an 11-amino acid-long ring shaped like a right-handed “thumb”. The binding of the substrate causes a change in the conformation of the thumb, and the exact position of the “thumb” determines the width of the catalytic crack, which plays a key role in substrate selectivity [6]. Currently, GH11 xylanases with different characters are required to satisfy industrial applications. In particular, salt-tolerant xylanases became a demand for many industrial applications, e.g., high-salt and marine food processing, aquatic feed production, industrial wastewater treatment, saline–alkali soil improvement, and global carbon cycling [7].
Catalytic activity and stability are the two most critical characteristics for xylanases [8]. Improving the catalytic properties and thermostability of GH11 xylanases on the basis of salt tolerance appears to have more practical value. The engineering of GH11 xylanases by directed evolution and rational design is gaining increasing attention [9]. Many directed evolution methods, including DNA shuffling, error-prone polymerase chain reactions, saturation mutagenesis, and disparity mutagenesis, were used in the irrational design of xylanases. Though robust and effective, these strategies are time-consuming and labor-intensive due to the heavy workload during screening [10]. On the other hand, rational design based on structure and function is somewhat more efficient for molecular modification of xylanase [11]. The replacement of some key amino acids often greatly changes the function of the protein [12]. Site-directed mutagenesis (SDM) of these key amino acids is an effective method to improve GH11 xylanase performance [13].
As proved through experimental validation, Bacillus sp. have greater and vital xylanolytic exertion with thermophilic advantage [14]. According to the CAZy database, there are already 28 xylanases cloned from Bacillus sp. that have been characterized (http://www.cazy.org/GH11_characterized.html, accessed on 7 September 2024). Among them, B. subtilis, B. pumilus, B. licheniformis, and B. amyloliquefaciens are widely recognized hosts. Notably, the majority structures in the Protein Data Bank (PDB) come from unclassified Bacillus sp. xylanases. B. subtilis XynA, one of the representative GH11 xylanases, has a relative constant activity at 40 °C and peaks at pH 7.0 [15]. In contrast, the optimal pH of B. amyloliquefaciens XynA is 4, and the optimal temperature is 25 °C [16]. In addition, the optimal pH of XynA from B. subtilis VSDB5 and B. licheniformis KBFB4 is 6, and the optimal temperature is 50 °C [17]. Other xylanases, like XynBYG from B. pumilus BYG, Bcx from B. circulans, and BaxA from B. amyloliquefaciens, were also reported with different properties [11,18,19]. From a review, the activities of most Bacillus wide-type xylanases are generally low [20]. Some of them have also been muted to improve catalytic activity and stability via protein engineering based on sequence and structure [12,13]. Although Bacillus are major industrial workhorses and enzymes cloned from them share about 50% of the enzyme market, Bacillus xylanases face limitations such as structural destabilization and lower activation energy at extreme temperatures [21,22].
In this study, we aimed to improve the catalytic performance and thermostability of a salt-tolerant GH11 xylanase. Firstly, we cloned and expressed the salt-tolerant GH11 xylanase gene from Bacillus sp. SC1. Secondly, we screened mutant enzymes with improved catalytic activity and thermostability by SDM under sequential and structural guidance. Thirdly, the differences between wild-type and mutant enzymes in catalytic activity, thermostability, substrate binding performance, kinetic parameters, and salt tolerance were analyzed. Finally, we analyzed possible reasons for these improved characters by molecular dynamic simulation and tested their applicability for producing XOS using different xylan resources.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Strains and Reagents
The salt-tolerant xylanases gene was obtained from Bacillus sp. SC1 (a strain isolated from the soil in 2017 and stored in our laboratory). Bacterial cells of Escherichia coli DH5α (E. coli DH5α) were used for cloning, and E. coli BL21 (DE3) cells were used for protein expression. Taq polymerase, a DNA gel extraction kit, isopropyl-β-D-thiogalactopyranoside (IPTG), and high-fidelity DNA polymerase were purchased from Takara (Takara Biomedical Technology Co., Ltd. Beijing, China). The one-step cloning DNA ligase was ordered from Vazyme (Vazyme International LLC, Nanjing, China). Beechwood xylan, bagasse xylan and corncob xylan were purchased from a commercial provider (Yuanye Co. Ltd., Shanghai, China). Wheat straw xylan was prepared from wheat straw by alkaline extraction, as described elsewhere [23]. Standards of xylose (X), xylobiose (X2), xylotriose (X3), xylotetraose (X4), and xylopentaose (X5) with purity ≥ 98% were purchased from Aladdin (Aladdin Biochemical Tech. Ltd., Shanghai, China). Kanamycin (Kan) sulfate powder was ordered from Sigma (Sigma-Aldrich, Shanghai, China).
2.2. Xylanase Activity Assay
Xylanase activity was analyzed according to the method reported elsewhere [24]. The reaction mixture containing 0.1 mL of a diluted enzyme solution (either crude extract or purified protein) and 0.9 mL of 10 mg/mL xylan substrate in 50 mM Gly-NaOH buffer (pH 9.0) was incubated at 55 °C for 10 min. The released reducing sugar content was evaluated by the 3,5-dinitrosalicylic acid (DNS) method using xylose as the standard [25]. One unit (U) of enzyme activity was defined as the amount that released 1 μmol reducing sugar equivalents per minute from the substrate under the above-described standard assay conditions. The absorbance at 540 nm was monitored by a Multimode Reader Spark® (Tecan, Groedig, Austria). For each assay, triplicate measurements were conducted to obtain the mean activity value.
2.3. Isolation and Identification of a Salt-Resistant Xylanase
The 19 isolates showing obvious degradation of xylan on agar were inoculated into LB broth for fermentation. Overnight culture supernatants were collected as crude enzyme extracts and used for xylanase activity assay. One isolate, Bacillus sp. SC1 with the highest xylanase activity, was inoculated into 200 mL LB, agitating at 37 °C for 24 h. A volume of 50 mL saturated ammonium sulphate solution was added into the overnight culture supernatants with stirring, and the mixture was left for 30 min to precipitate large fragments. Then, the supernatant was collected after centrifugation at 1000 RCF for 10 min. A volume of 80 mL saturated ammonium sulphate solution was added into the collected supernatant for further precipitation. After a second-round centrifugation at 1000 RCF for 10 min, the pellet was resuspended in 5 mL 50 mM Gly-NaOH buffer (pH 9.0). The resolved solution containing the target enzyme was used for sodium dodecyl-sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) analysis and further identification by liquid chromatography coupled with mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS).
2.4. Cloning of Xynst and Its Heterologous Overexpression
The mature form of the Xynst gene was amplified by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) using high-fidelity DNA polymerase and primers P-XF/PX-R (Table S1), with the genomic DNA extracted from Bacillus sp. SC1 as a template. The specific fragment with a size of 558 bp and the expression plasmid pET-28a(+) were digested with XhoI and HindIII, respectively. Then, the ligate was transformed into E. coli DH5α for cyclization with the ClonExpress II One Step Cloning Kit and subcloned into E. coli BL21 for expression. To facilitate purification via affinity chromatography, Xynst was fused to a hexa-histidine (6×His) tag at the C terminus. The positive transformants grown on antibiotic agar (50 μg/mL Kan) were screened by colony PCR. After sequencing validation, a single clone with correct ORF was propagated in LB medium containing 50 μg/mL Kan, until OD600 reached 0.6 (37 °C, 180 rpm). Expression was induced by the addition of 0.8 mM IPTG for 16 h at 25 °C [26].
2.5. Rational Designing and Xylanase Mutant Library Construction
To improve the thermostability and hydrolysis characteristics of Xynst, SDM libraries were constructed at eight sites (Y5, W6, Q7, W9, Y65, R49, R112, and W129) by computer docking between xylanase and xylohexaose/xylotriose using Autodock software (version: 4.2.6). Eight pairs of primers (Table S1) were used for PCR, using the plasmid pET-28a-Xynst as a template. The complete plasmid was amplified and then digested by restriction enzyme DpnI. The mutant plasmids were introduced into E. coli BL21 as in a previous report [12]. In order to enhance mutants further, the mutation sites determined in the first round were subjected to a second-round construction for combinatorial mutagenesis. The xylanase genes in all colonies with improved activities were amplified by PCR. The PCR fragments were sent out for nucleotide sequencing (General Biol. Co. Ltd., Chuzhou, China) to confirm the mutations and potential changes in corresponding amino acids.
2.6. High-Throughput Screen of Mutant Library
To screen the SDM libraries, a high-throughput method was developed. Briefly, all colonies were picked into deep-well microtiters that were filled with 0.6 mL sterile LB broth containing 50 μg/mL Kan in each well. After agitating at 180 r/min at 37 °C, IPTG solution was added to a final concentration of 0.8 mM when optical density at 600 nm (OD600) reached 0.6. Then, the temperature was shifted to 25 °C for protein expression induction (16 h). A volume of 0.2 mL bacterial culture from each well was transferred to a new 96-well microtiter plate for the collection of cell pellets. After rinsing twice, the cell pellets were resuspended in 0.2 mL 50 mM Gly-NaOH buffer and disrupted by a Non-Contact Ultrasonic Crusher (Jingxin XM08-II, Shanghai, China) at 4 °C for 30 min (Capacity 100%, Turn on 10 s, Pause 10 s). After centrifugation at 8000 RCF for 5 min, 50 µL supernatants were transferred into a 96-well PCR microtiter, and supplemented with 100 µL bagasse xylan solution (10 mg/mL). The microtiter was placed into a vibrated pre-heated Dry Bath Incubator (FOUR E’S Mixer, Guangzhou, China) for enzymatic reaction. Ten minutes later, 50 µL DNS solution was added immediately and heated at 99 °C in a Thermal Cycler (Eppendorf ®nexus, Hamburg, Germany) for 15 min. On each microplate, E. coli BL21/pET-Xynst was inoculated as a control during library screening. After detection, colonies with significantly improved absorbance were propagated for three consecutive generations.
2.7. Recombinant Xylanases Purification, Quantification, and Electrophoresis
The crude enzyme solution was collected through the following steps. Bacterial cells were collected by centrifugation (8000 RCF, 5 min, 4 °C) and suspended in 50 mM Gly-NaOH buffer (pH 9.0). Then, they were ultrasonicated at 4 °C to disrupt cells completely (10 s on and 10 s off, lasting for 30 min). Subsequently, the ultrasonicated supernatant and insoluble fraction were separated by centrifugation at 8000 RCF for 5 min. The supernatant was mixed with high-affinity Ni2+-charged resin (L00223, GenScript Corporation, Nanjing, China) and then incubated for 1 h by gently inverting it in an ice bath to allow the protein to bind to the resin. The slurry was transferred into a column, and the column was washed with 8 bed volumes of wash buffer (20 mM Tris, 500 mM NaCl, 40 mM imidazole, adjust pH to 7.4 using HCl) and 10 bed volumes of elution buffer (20 mM Tris, 500 mM NaCl, 250 mM imidazole, adjust pH to 7.4 using HCl). The eluate was collected step by step for subsequent analysis [27]. The enzyme concentration was measured using the Bradford Protein Assay Kit with bovine serum albumin as the standard. The purity of the enzymes was determined by electrophoresis using 15% SDS-PAGE gels [28].
2.8. Biochemical Characterization of Xynst and Its Mutant W6F/Q7H
The optimal pH of xylanases was measured at 55 °C using 50 mM Na2HPO4-C6H8O7 buffer (pH 3.0–8.0), 50 mM Gly-NaOH buffer (pH 9.0–10.0), and 50 mM Na2HPO4-NaOH buffer (pH 11.0–12.0). The pH stability of xylanases was determined by incubating it in buffers from pH 3.0 to 12.0 at 25 °C for 8 h and then measuring the residual enzyme activity under standard assay conditions [29].
The optimal temperature of xylanases was measured under temperatures ranging from 30 °C to 90 °C at the optimal pH. The thermostability of xylanase was determined by incubating the enzyme at temperatures ranging from 55 °C to 65 °C for 0–360 min and then measuring the residual enzyme activity [30].
The effect of ions (NaCl, NH4Cl, KCl, ZnCl2, NiCl2, CuSO4, MnCl2, CaCl2, CoCl2, LiCl, and MgCl2) and additive SDS on enzyme activity was tested as described elsewhere [31]. All chemicals were separately added to a final concentration of 10 mM, and the mixtures were incubated at 25 °C for 1 h. The residual activities were detected under the standard conditions. All experiments were performed in triplicate and non-preincubated enzymes were used as controls.
2.9. Test of Substrate Specificity and Kinetic Parameters
The substrate specificity of xylanases was measured using different substrates (beechwood xylan, bagasse xylan, corncob xylan, wheat straw xylan, arabinoxylan, cellulose, starch, 1% w/v) in 50 mM Gly-NaOH buffer (pH 9.0) at 55 °C [32]. Released reducing sugar content was determined by the DNS method. The kinetic parameters of xylanases were measured with different concentrations (0–10 mg/mL) of xylans under optimal reaction conditions [33]. The constants of Vmax, Km, and Kcat of these enzymes were calculated according to the Michaelis–Menten equation using Origin 2018.
2.10. Effect of Salts on Xynst and Its Mutant W6F/Q7H
The effect of salts on xylanase activity was studied under standard assay conditions with different concentrations of NaCl (0–4 M) or KCl (0–3 M). Relative activities were calculated by setting the activity in the absence of salts as 100%. The effect of salts on xylanase stability were also evaluated. After keeping enzymes in 50 mM Gly-NaOH buffer (pH 9.0) containing 2 M NaCl for 1–6 h, the residual enzyme activity was determined under standard assay conditions. Residual activities were calculated by setting the initial activity of Xynst as 100%. All experiments were performed in triplicate.
2.11. Molecular Dynamics Simulations of Xynst and Its Mutant W6F/Q7H
Using xylanase (PDB ID: 2dcy) as the template, homology modeling was performed to obtain a three-dimensional structure of Xynst. The structure images of mutant W6F/Q7H were prepared using Pymol (version: 2.5, Schrodinger, LLC, New York, NY, USA). Molecular dynamics (MD) simulations were performed to further assess the global stability of wild-type Xynst and mutant W6F/Q7H using GROMACS (version: 2019.6 release) at 333 K (60 °C) for 50 ns. Moreover, MD simulations of W6F/Q7H in 0 M and 2 M NaCl ware performed at 65 °C for 50 ns. The AMBER99SB force field was used, and the treated protein was placed inside an SPC water model in a cubic box. Solvent molecule modeling was performed using the TIP3P water model. Na+ and Cl− were used for the neutralization of the simulation system. Minimizations were executed with the steepest descent integrator until the maximum force was below 1000 kJ mol−1 nm−1 on each atom. The bonds linked with hydrogen atoms were restrained with a linear constraint solver. The pressure during simulation was fixed at 1.0 atm using a Parrinello–Rahman barostat with a coupling constant of 2 ps. Simulations were performed with a 2 fs time step. All MD simulations were firstly equilibrated under a constant-volume ensemble for 100 ps and then under a constant-pressure ensemble for 100 ps, and the MD simulation procedures were carried on for 50 ns. The Root Mean Square Deviation (RMSD) and Root Mean Square Fluctuation (RMSF) were calculated using the standard tools of the GROMACS package [34,35].
2.12. Hydrolysis Characteristics of Xynst and W6F/Q7H
Xylose (X) and standards of XOS with different polymerization degrees (X2–X5) were dissolved in pure water and used for analysis by thin-layer chromatography (TLC) and high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) separately. The hydrolysis characteristics of Xynst and W6F/Q7H were evaluated, as described previously [34]. In brief, 0.01 mg/mL xylanase was mixed with 10 mg/mL of substrates (wheat straw xylan or bagasse xylan) and incubated in 50 mM Gly-NaOH buffer (pH 9.0) at 55 °C for specific intervals. The hydrolysis products were analyzed qualitatively by TLC and quantitatively by HPLC [36]. For HPLC analysis, 10 µL hydrolysate was injected into a ZORBAX Carbohydrate Analysis column (4.6 mm ID × 150 mm, 5 µm) with a differential refractive index detector (RID). The temperatures of the chromatographic column and RID were 30 and 40 °C, using 75% acetonitrile as the mobile phase (1 mL/min). All experiments were performed in triplicate.
2.13. Data Analysis and Statistics
All original data were expressed as mean ± standard deviation (SD) obtained from at least triplicated experiments. Statistical analysis was performed by using SPSS 19.0 (IBM Corporation, Somers, NY, USA). Significant differences were analyzed by t-test and Tukey’s one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) when necessary. Values of p < 0.05 were considered as statistically significant.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Identification and Expression of the Salt-Tolerant GH11 Family Xylanase Xynst
In order to effectively convert xylan into more value-added products, more xylanases with different properties are needed for versatile applications [37]. In a preliminary screen, the highest xylanase activity (45.94 U/mL) was demonstrated in the culture supernatant of a soil isolate, Bacillus sp. SC1 (Figure S1). As only xylanases belonging to the GH11 family are considered true xylanases, we need to confirm the classification of this enzyme. The purification of culture supernatants by ammonium sulfate precipitation (65%) obtained active fractions. Loading these fractions on SDS-PAGE showed a band with an MW of ~25 kDa (Figure 1A). Further LC-MS/MS analysis suggested the protein has the highest identity to B. halotolerans glycoside hydrolase family 11 protein (sequence coverage 41%, Figure 1B and Figure S2). In fact, xylanase activity in B. halotolerans has been reported recently [38]. However, there was no sequence released in the report, and the activity is low (e.g., 23.47 U/mL after fermentation optimization).
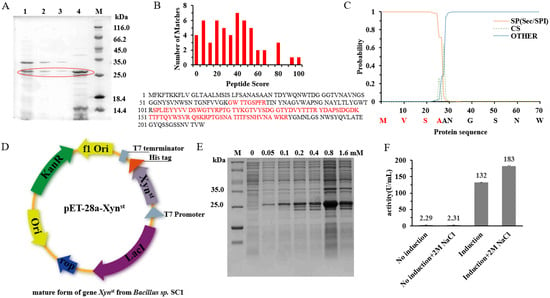
Figure 1.
The cloning and identification of a GH11 xylanase from Bacillus sp. SC1: (A) SDS-PAGE of Bacillus sp. SC1 cell free supernatant; (B) LC-MS/MS identification of the secreted xylanase; (C) prediction of the signal peptide and the cleavage site by SignalP; (D) cloning of the mature form of xylanase gene; (E) SDS-PAGE of the xylanase expression in recombinant E. coli BL21/pET-28a-Xyn at different concentrations of IPTG; (F) xylanase activity assay of the cell crude extract of E. coli BL21/pET-28a-Xyn. In (A), the red cycle indicates the protein bands of the potential target enzyme.
Analysis of the reference protein sequence (Accession: WP_101863413) indicates it has a Sec/SPI type signal peptide and a cleavage site at AA28/29 (Figure 1C). According to computational prediction, the protein is relatively stable and hydrophilic (Table S2). Based on the reference gene, we cloned its mature form into pET-28a and sequenced the corresponding nucleotide sequence (Figure 1D). The BLASTn analysis indicates the cloned gene has more than 95% identity to B. halotolerans xylanase (Figure S3). However, the gene is different from XynA, which is one of the most widely studied GH11 xylanases that has been frequently cloned from different genera of Bacillus [17]. Heterologous overexpression in recombinant E. coli BL21 obtained pure protein (Figure 1E), and 1,4-beta-xylanase activity can be detected in the crude extracts under both normal and high-salt conditions (Figure 1F). Interestingly, the activity is higher under 2 M NaCl, which suggests the enzyme we named Xynst is a salt-tolerant xylanase. Xynst is more tolerant to salt than Xyn40, a previously reported salt-tolerant xylanase from marine isolate that has the highest activity at 0.5 M NaCl [39]. In soils and marine sediments, salt can accumulate to high concentrations. To keep replication, microorganisms may need to have enzymes that can resist such extreme conditions. Taken together, these data indicate that Xynst isolated from strain SC1 is a salt-tolerant GH11 family xylanase.
3.2. Molecular Modification, Mutant Screen, and Characterization
Though the activity of Xynst is higher than many genes cloned from bacteria, it is much lower than a xylanase cloned from Aspergillus niger VTCC 017 [40]. To improve the enzyme performance, we constructed SDM libraries based on rational design. As the active and substrate binding sites are crucial for enzymes, we selected eight amino acids (Y5, W6, Q7, W9, Y65, R49, R112, and W129) as targets for saturation mutation based on protein structure and molecular docking results by Autodock. Facilitated by a newly developed high-throughput screening method, we obtained five positive mutants that possessed improved activity after the screening of 1520 colonies in the SDM library and reaction at 65, 75, and 80 °C, respectively (Figure 2A,B and Figure S4). The increase in the specific activity of these mutants was further confirmed using purified proteins (Figure S5). Among them, two adjacent mutations of W6F and Q7H significantly improve enzyme activity. Combination mutation of them increases activity to 6926 U/mg, which is 3.28-fold that of the wide-type enzyme (Figure 2C). The sequencing of the plasmid validates the mutation of two amino acids as designed (Figure 2D).
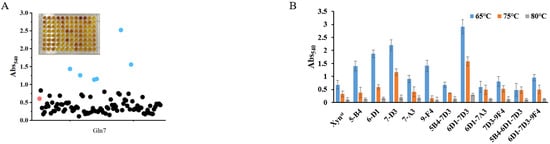
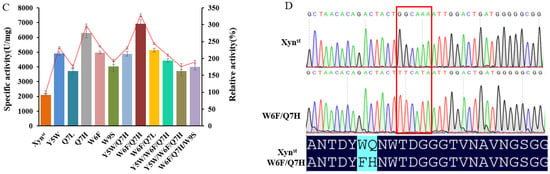
Figure 2.
High-throughput screening of SDM libraries for highly active mutants: (A) a representative screen of the SDM libraries using 96-well microtiter plate at 65 °C and dot scatter of the absorbance; (B) bar chart display of some mutants using cell crude extracts; (C) specific activity and relative activity of some mutants using cell crude extracts; (D) sequencing of the mutant W6F/Q7H to confirm changes in amino acids. In (A), the red dot represents the wide-type strain that is used as control on each microtiter plate. The blue dots are positive mutants that have significantly higher activities, while black dots are negative or nonsense mutants that have activities that are lower than or comparable with the control. In (C), the fold line indicates the relative activity. In (D), the red box indicates muted nucleotides.
Further characterization of these two enzymes was conducted with heterologous overexpressed pure proteins (Figure S5). As demonstrated, the optimal temperature of W6F/Q7H is 65 °C, which is 10 °C higher than that of the wide-type Xynst (Figure 3A). This value of optimal temperature was the same as that exhibited by xylanases from B. subtilis and Orpinomyces sp. PC-2, but lower than Thermotoga thermarum Xyn10B which has an optimum temperature of 80 °C [41,42,43]. W6F/Q7H also obtained improved thermostability as it is relatively stable after incubation at 60 °C (93% residual activity), compared to only less than 65% residual activity for Xynst after incubation at 55 °C for 360 min (Figure 3B,C). In addition, Xynst and W6F/Q7H displayed the same optimal pH, with the maximum activity at pH 9.0 (Figure 3D). These two enzymes are relatively stable within 4 h under pH 9, while W6F/Q7H possessed higher residual activity after incubation for 8 h (Figure 3E).
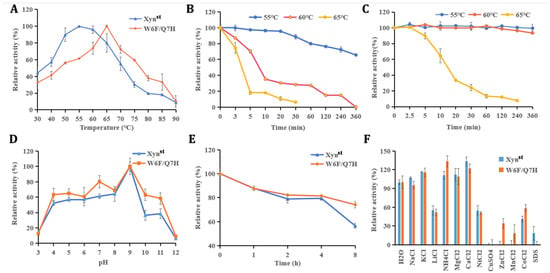
Figure 3.
Biochemical characters of Xynst and W6F/Q7H: (A) optimal temperature; (B) thermostability of Xynst; (C) thermostability of W6F/Q7H; (D) optical pH; (E) pH stability; (F) effects of different chemicals on enzyme activity. The optimum temperature was measured in 50 mM Gly-NaOH buffer at different temperatures (30–90 °C), and the highest enzyme activity was normalized as 100%. The thermostability was tested by incubation of enzymes at 55 °C, 60 °C, and 65 °C for 6 h, respectively. The pH stability was measured at pH 9 for 8 h under 55 °C. For all stability assays, enzyme activities at the beginning before incubation were normalized as 100%, respectively. Data represent the mean ± standard deviation of triplicate measurements.
Positively charged ions, including 10 mM K+, NH4+, Mg2+, and Ca2+, had a stimulating effect on the enzyme activity of Xynst and W6F/Q7H (Figure 3F). These ions might bind to enzymes directly or indirectly by changing the water activity of the solvent [44]. Conversely, other ions or compounds have inhibitory effects on enzyme activity, which may be due to the complexation of these metal ions with the reaction groups of enzymes [45]. Similar to the previous report of xylanase, Cu2+ completely inactivated Xynst and W6F/Q7H [46]. The inhibition may be due to the interaction of Cu2+ with the SH or carboxyl group of the protein, which leads to conformation changes and, subsequently, results in the inactivation of the enzyme [47]. Noticeably, it seems W6F/Q7H is more resistant to Zn2+, Mn2+, and Co2+ but more sensitive to SDS.
Regarding substrate preference, both Xynst and W6F/Q7H effectively degraded beechwood xylan, bagasse xylan, corncob xylan, and wheat straw xylan, but not arabinoxylan, cellulose, or starch (Figure S6). Further enzyme kinetic analysis with different amounts of substrates confirmed that both enzymes have relatively high affinity, as all Km constants are less than 1 mg/mL, with the highest being beechwood xylan. For all substrates, W6F/Q7H has higher Vmax and Kcat values but lower constants of Km (Table 1). In particular, site mutations led to a significant increase in Kcat/Km values (2.03~4.78-fold) compared to that of Xynst. The data demonstrated that our enzymes have higher catalytic efficiencies than other thermophilic xylanases [48]. However, they are lower than a xylanase and its derivatives cloned from Orpinomyces sp. PC-2 that had extremely higher Kcat/Km values [49]. Anyhow, these dynamic parameters clearly showed the superiority of W6F/Q7H over Xynst.

Table 1.
Kinetic values and specific activity of Xynst and W6F/Q7H.
3.3. Evaluation of Enzyme Activity and Stability in the Presence of Salt
As Xynst is a salt-tolerant xylanase, we further evaluated the effects of different salts on catalytic activity and thermostability. NaCl and KCl have no impact on enzyme activity at low concentrations (0–0.1 M), but they remarkably stimulate activity when salt concentrations exceed 0.25 M. As demonstrated, Xynst and W6F/Q7H exhibit maximal activity in 2 M NaCl (relative activity of 396% and 810%, respectively) (Figure 4A,B). The specific activity reached 16,854.4 U/mg for W6F/Q7H, which is far higher than a salt-tolerant GH11 xylanase derived from Phoma sp. MF13, e.g., a maximal activity of 1322.8 U/mg [49]. When the salt concentration exceeded 2 M, the specific activity decreased, agreeing with XynA which is derived from Zunongwangia profunda [50]. Increased enzyme activity in a high-salt environment may be due to a low proportion of hydrophobic amino acid residues that are concentrated only in the “palm” to balance the hydrophobic interaction [10]. In addition, 2 M NaCl enhanced the thermostability of Xynst. As demonstrated, the residual activity remained constant in the presence of NaCl, contrasting with a steady decline in the absence of NaCl after incubation at 55 °C for 30 min (Figure 4C). This is helpful for applications when substrates are mixed with salt and need long-term degradation.
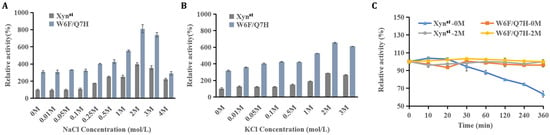
Figure 4.
The effects of salts on activity and thermostability of Xynst and W6F/Q7H: (A) effects of NaCl on enzyme activity at different concentrations; (B) effects of KCl on enzyme activity at different concentrations; (C) effects of NaCl on enzyme thermostability. Relative activities were calculated by setting the activity of Xynst as 100% in the absence of salts. For enzyme thermostability assays at 55 °C, activities at the beginning before incubation were normalized as 100%, respectively. Data represent the mean ± standard deviation of triplicate measurements.
3.4. Molecular Dynamic Simulations in the Presence and Absence of Salt
According to a molecular modeling analysis of five Bacillus GH11 xylanases, Bacillus sp. NCL 87-6-10 (sp_NCL 87-6-10) exhibited high thermal stability and achieved a transition state with minimal energy requirements [51]. To explore the possible molecular basis that led to the improved catalytic efficiency and thermostability, MD simulations were performed. Over 90% of residues in the favorable region of the Ramachandran plot indicated that the predicted models are of good quality and suitable for molecular docking and MD simulations (Figure S7). Notably, the RMSD curves of Xynst exhibit fluctuations within 30 ns but become stable after 40 ns. In contrast, W6F/Q7H displays lower RMSD values and is relatively stable (Figure 5A). For RMSF values, residues 11–18 and 85–90 of W6F/Q7H are significantly lower, suggesting improved rigidity in this region. Oppositely, residues 155–160 of W6F/Q7H are significantly higher, suggesting improved flexibility in this region (Figure 5B). According to Rg analysis, the value after mutation was slightly lower than that of the wild enzyme, which also indicated that the overall structure of the mutant enzyme protein was more compact (Figure S7E). The average RMSDs of W6F/Q7H reduced by 0.013 nm (11.6%) under 2 M NaCl, indicating conformational changes (Figure 5C). However, the average RMSF is reduced by 10.4%, indicating enhanced rigidity of the overall structure of W6F/Q7H in the presence of 2 M NaCl (Figure 5D). The 155–160 sites are located at the hinge at the upper end of the alpha helix (Figure 5E). As reported in Bacillus circulans GH11 xylanase, increasing the flexibility of the upper hinge of the alpha helix may result in higher collision probability and, therefore, higher catalytic efficiency [11]. The two sites (residues 11–18 and 85–90) with increased rigidity are at the very edge of the enzyme binding pocket, which may account for the improved thermostability of the mutant enzyme (Figure 5E). For example, enhanced thermostability of GH11 xylanase from Streptomyces rameus L2001 has been reported due to enhanced N-terminal rigidity and a more compact overall structure [34]. In addition, the grand average hydropathy value (GRAVY) of W6F/Q7H is a bit higher than Xynst (−0.436 vs. −0.454), suggesting a slight decrease in hydrophilicity [52].
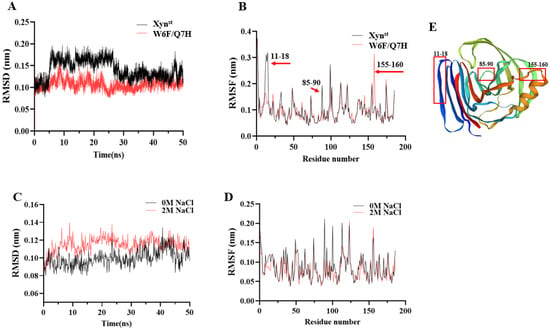
Figure 5.
Molecular dynamic simulation of Xynst and W6F/Q7H: (A) the RMSD values of Xynst and W6F/Q7H within the foremost 50 ns; (B) the RMSF values of whole Xynst and W6F/Q7H residues; (C) the RMSD values of Xynst and W6F/Q7H within the foremost 50 ns at 2 M NaCl; (D) the RMSF values of Xynst and W6F/Q7H residues at 2M NaCl; (E) predicted molecular structure of W6F/Q7H. RMSD, root mean square deviation, RMSF, root mean square fluctuation.
3.5. Degradation of Xylans and Production of XOS
To evaluate the applicability of these two enzymes, we performed degradation assays using two kinds of xylan, namely commercial bagasse xylan and self-prepared wheat straw xylan. As demonstrated by TLC, W6F/Q7H always yielded more XOS than Xynst did (Figure 6A,B). This can also be confirmed by hydrolysate quantification using HPLC (Figure 6C–F). For example, W6F/Q7H released 2.945 mg/mL XOS when using bagasse xylan, and 2.293 mg/mL XOS when using wheat straw xylan as substrate, which is 28.8% and 19.9% higher than that released by Xynst, respectively (Table S3). Notably, the ratios of X2 released by W6F/Q7H increased along with degradation time, while they turned steady after 2 h for Xynst. Further hydrolysis of standards with different polymerization degrees suggests both Xynst and W6F/Q7H cannot degrade X2, as no X was detected (Figure S8). In line with the previous report, both Xynst and W6F/Q7H can degrade X4 and X5 to smaller oligomers but not xylose [53]. Anyhow, in all cases, X2 and X3 are the main hydrolysis products (Table S3). In particular, X3 has the largest proportion (>50%) in all resulting XOS, which has been reported as one of the most effective bifidogenic components [54]. Within 0.5 h, the conversion rate of W6F/Q7H to XOS can reach 23.1% for wheat straw xylan and 29.5% for bagasse xylan. The data mean W6F/Q7H is superior in the enzymatic production of XOS, comparing the maximum yield of 20.71% from corncob xylan using an acidic xylanase assisted by ultrasound [55]. A small amount of xylose was produced by the hydrolysis of xylan from wheat straw, while no xylose was produced by the hydrolysis of bagasse xylan, which may be due to the different structural characteristics of xylans from different sources [56].
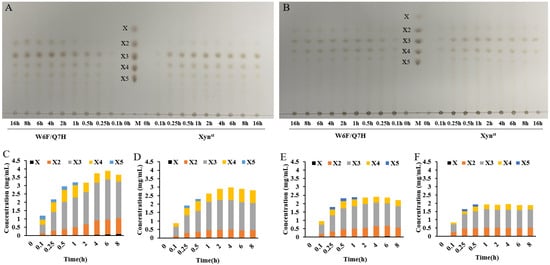
Figure 6.
Production of XOS by hydrolysis of xylan using Xynst and W6F/Q7H: (A) TLC analysis of hydrolysate of bagasse xylan after degradation for different hours; (B) TLC analysis of hydrolysate of wheat straw xylan after degradation for different hours; (C) HPLC quantification of different fractions of XOS after degradation of bagasse xylan by W6F/Q7H for different hours; (D) HPLC quantification of different fractions of XOS after degradation of bagasse xylan by Xynst for different hours; (E) HPLC quantification of different fractions of XOS after degradation of wheat straw xylan by W6F/Q7H for different hours; (F) HPLC quantification of different fractions of XOS after degradation of wheat straw xylan by Xynst for different hours. Lane M, xylose and xylooligosaccharides (XOS) standards with different polymerization degrees; X, xylose; X2, xylobiose; X3, xylotriose; X4, xylotetraose; X5, xylopentaose.
4. Conclusions
As the global focus shifts toward using renewable resources like xylan, more effective xylanase are required. The study identified a salt-tolerant GH11 xylanase, Xynst, from a soil bacterium Bacillus sp. SC1. A double mutant W6F/Q7H with increased catalytic activity and optimal temperature was obtained by rational designing and high-throughput screening. Both Xynst and W6F/Q7H xylanases were stimulated by high concentrations of salts. The salt-resistant property of xylanase from Bacillus sp. is a novel feature. These enzymes are efficient at degrading different xylans and have substrate specificity. The mutant enzyme W6F/Q7H released more xylooligosaccharides and yielded higher proportions of xylobiose and xylotriose than Xynst did. In short, the study identified and engineered a novel GH11 xylanase, which shows promising potential in the agricultural and food industries, especially under high-salt conditions.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/biom14091188/s1, Figure S1. Preliminary screen of of xylanase secretion by different isolates. Figure S2. Xylanase protein identification by LC-MS/MS. Figure S3. Phylogenetic tree of Xynst gene from Bacillus sp. SC1. Figure S4. High throughput screen of SDM library for highly active and thermo-stable mutants. Figure S5. SDS-PAGE analysis of xylanase expression and purification. Figure S6. Substrate preference of xylanase Xynst and W6F/Q7H. Figure S7. Molecular dynamics simulations. Figure S8. TLC analysis of the enzymatic degradation by W6F/Q7H. Table S1. PCR primers used for amplification of the target genes. Table S2. Predicted properties of the novel GH11 xylanase Xynst. Table S3. Hydrolysis products of xylan analyzed by HPLC.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Z.S.; Methodology, J.M. and Z.N.; Software, Z.N.; Validation, Q.S.; Formal analysis, Y.Q.; Investigation, J.M.; Resources, Y.H.; Data curation, Z.N. and Y.Q.; Writing—original draft, J.M.; Writing—review & editing, Z.S. and Y.H.; Visualization, Q.S.; Supervision, Z.S. and C.L.; Project administration, C.L.; Funding acquisition, Z.S. and C.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by the National Key R&D Project (No. 2022YFD2101405) and a Major Special Science and Technology Project of Henan Province (No. 231100110300).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article and Supplementary Materials, further inquires can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Nakamichi, Y.; Fouquet, T.; Ito, S.; Watanabe, M.; Matsushika, A.; Inoue, H. Structural and functional characterization of a bifunctional GH30-7 xylanase B from the filamentous fungus. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 4065–4078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramaniyan, S.; Prema, P. Biotechnology of microbial xylanases: Enzymology, molecular biology, and application. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2002, 22, 33–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Xu, Y.; Yu, X.W. Rational engineering a xylanase hyper-producing system in Trichoderma reesei for efficient biomass degradation. Biotechnol. Biofuels Bioprod. 2021, 14, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Törrönen, A.; Harkki, A.; Rouvinen, J. Three-dimensional structure of endo-1,4-beta-xylanase II from Trichoderma reesei: Two conformational states in the active site. EMBO J. 1994, 13, 2493–2501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, G.J.; Wilson, K.S.; Henrissat, B. Nomenclature for sugar-binding subsites in glycosyl hydrolases. Biochem. J. 1997, 321, 557–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paës, G.; Tran, V.; Takahashi, M.; Boukari, I.; O’Donohue, M.J. New insights into the role of the thumb-like loop in GH-11 xylanases. Protein Eng. Des. Sel. 2007, 20, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, D. Extremophilic prokaryotic endoxylanases: Diversity, applicability, and molecular insights. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 728475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motta, L.P.; Andrade, C.C.P.; Santana, M.H.A. A Review of Xylanase Production by the Fermentation of Xylan: Classification, Characterization and Applications; InTech: London, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acevedo, J.P.; Reetz, M.T.; Asenjo, J.A.; Parra, L.P. One-step combined focused epPCR and saturation mutagenesis for thermostability evolution of a new cold-active xylanase. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2017, 100, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Zhang, R.; Zhou, J.; Huang, Z. Biotechnological aspects of salt-tolerant xylanases: A review. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 8610–8624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Min, K.; Kim, H.; Park, H.J.; Lee, S.; Jung, Y.J.; Yoon, J.H.; Lee, J.S.; Park, K.; Yoo, Y.J.; Joo, J.C. Improving the catalytic performance of xylanase from Bacillus circulans through structure-based rational design. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 340, 125737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Cao, K.; Pedroso, M.M.; Wu, B.; Gao, Z.; He, B.; Schenk, G. Sequence- and structure-guided improvement of the catalytic performance of a GH11 family xylanase from Bacillus subtilis. J. Biol. Chem. 2021, 297, 101262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Qin, L.; Xu, Y.; Lu, H.; Wu, Q.; Li, W.; Zhang, C.; Li, X. Three molecular modification strategies to improve the thermostability of xylanase XynA from Streptomyces rameus L2001. Foods 2023, 12, 879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakry, M.M.; Salem, S.S.; Atta, H.M.; El-Gamal, M.S.; Fouda, A. Xylanase from thermotolerant Bacillus haynesii strain, synthesis, characterization, optimization using Box-Behnken Design, and biobleaching activity. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2022, 14, 9779–9792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beliën, T.; Joye, I.J.; Delcour, J.A.; Courtin, C.M. Computational design-based molecular engineering of the glycosyl hydrolase family 11 B. subtilis XynA endoxylanase improves its acid stability. Protein Eng. Des. Sel. 2009, 22, 587–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, C.U.; Lee, S.G.; Chung, Y.R.; Cho, I.; Kim, J.H. Cloning of a family 11 xylanase gene from Bacillus amyloliquefaciens CH51 isolated from Cheonggukjang. Indian J. Microbiol. 2012, 52, 695–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, J.B.; Priyadharshini, R.; Uthandi, S. Glycosyl hydrolase 11 (xynA) gene with xylanase activity from thermophilic bacteria isolated from thermal springs. Microb. Cell Factories 2022, 21, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Yang, M.; Yang, Y.; Zhan, J.; Zhou, Y.; Zhao, X. Optimal secretion of alkali-tolerant xylanase in Bacillus subtilis by signal peptide screening. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 100, 8745–8756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Li, J.; Rehman, A.U.; Luo, S.; Wang, Y.; Wei, H.; Zhang, K. Sensitivity of family GH11 Bacillus amyloliquefaciens xylanase A (BaxA) and the T33I mutant to Oryza sativa xylanase inhibitor protein (OsXIP): An experimental and computational study. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2022, 156, 109998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, R.; Sohail, M. Xylanolytic Bacillus species for xylooligosaccharides production: A critical review. Bioresour. Bioprocess. 2021, 8, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schallmey, M.; Singh, A.; Ward, O.P. Developments in the use of Bacillus species for industrial production. Can. J. Microbiol. 2004, 50, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walia, A.; Guleria, S.; Mehta, P.; Chauhan, A.; Parkash, J. Microbial xylanases and their industrial application in pulp and paper biobleaching: A review. Biotech 2017, 7, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dafchahi, M.N.; Acharya, B. Green extraction of xylan hemicellulose from wheat straw. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2024, 14, 21229–21243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, M.J.; Biely, P.; Poutanen, K. Interlaboratory testing of methods for assay of xylanase activity. J. Biotechnol. 1992, 23, 257–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Liu, H.; Yang, S.; Yan, Q. Biochemical characterization of a novel xylanase from Paenibacillus barengoltzii and its application in xylooligosaccharides production from corncobs. Food Chem. 2018, 264, 310–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, W.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, C.; Li, P.; Xiao, J.; Wang, R.; Du, P.; Li, N.; Wang, J. Engineering mesophilic GH11 xylanase from Cellulomonas flavigena by rational design of N-terminus substitution. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 3, 1044291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Liu, M.Q.; Huo, W.K.; Dai, X.J. Obtaining a mutant of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens xylanase A with improved catalytic activity by directed evolution. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2016, 86, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laemmli, U.K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 1970, 227, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Wei, X.; Wang, Y.; Liu, H.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Li, J.; Wang, J.; Guo, C.; Sui, S.; et al. Improvement of optimum pH and specific activity of pectate lyase from Bacillus RN.1 using loop replacement. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2023, 11, 1242123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.; Guo, Y.; Wu, B.; He, B. Extracellular expression of alkali tolerant xylanase from Bacillus subtilis Lucky9 in E. coli and application for xylooligosaccharides production from agro-industrial waste. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 96, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Xu, H.; Guo, X.; Yang, X.; Dong, B.; Cao, Y. Improved thermostability of an acidic xylanase from Aspergillus sulphureus by combined disulphide bridge introduction and proline residue substitution. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; She, Y.; Sun, B.; Song, H.; Zhu, Y.; Lv, Y.; Song, H. Purification and characterization of a cellulase-free, thermostable xylanase from Streptomyces rameus L2001 and its biobleaching effect on wheat straw pulp. Biochem. Eng. J. 2010, 52, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheladiya, P.; Kapadia, C.; Prajapati, V.; Ali El Enshasy, H.; Abd Malek, R.; Marraiki, N.; Zaghloul, N.S.S.; Sayyed, R.Z. Production, statistical optimization, and functional characterization of alkali stable pectate lyase of Paenibacillus lactis PKC5 for use in juice clarification. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 7564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Zhang, C.; Zhu, W.; Lu, H.; Li, X.; Yang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Li, W. Improved thermostability, acid tolerance as well as catalytic efficiency of Streptomyces rameus L2001 GH11 xylanase by N-terminal replacement. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2023, 126, 110143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.H.; Chen, Y.Y.; Zhuang, X.Y.; Xiao, Q.; Chen, J.; Chen, F.Q.; Yang, Q.M.; Weng, H.F.; Fang, B.S.; Xiao, A.F. A novel κ-Carrageenase from marine bacterium Rhodopirellula sallentina SM41: Heterologous expression, biochemical characterization and salt-tolerance mechanism investigation. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Liu, X.; Ma, J.; Li, X.; Jiang, Z.; Yan, Q.; Yang, S. Heterologous expression and enzymatic properties of xylanase of GH11 family from Trichoderma asperellum. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 38, 29–38. [Google Scholar]
- Chakdar, H.; Kumar, M.; Pandiyan, K.; Singh, A.; Nanjappan, K.; Kashyap, P.L.; Srivastava, A.K. Bacterial xylanases: Biology to biotechnology. 3 Biotech 2016, 6, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güler, F.; Özcelik, F. Screening of xylanase producing Bacillus species and optimization of xylanase process parameters in submerged fermentation. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2023, 51, 102801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khandeparker, R.; Verma, P.; Deobagkar, D. A novel halotolerant xylanase from marine isolate Bacillus subtilis cho40: Gene cloning and sequencing. New Biotechnol. 2011, 28, 814–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dao, T.M.A.; Cuong, N.T.; Nguyen, T.T.; Nguyen, N.P.D.; Tuyen, D.T. Purification, identification, and characterization of a glycoside hydrolase family 11-xylanase with high activity from Aspergillus niger VTCC 017. Mol. Biotechnol. 2022, 64, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleem, M.; Aslam, F.; Akhtar, M.S.; Tariq, M.; Rajoka, M.I. Characterization of a thermostable and alkaline xylanase from Bacillus sp. and its bleaching impact on wheat straw pulp. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 28, 513–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ventorim, R.Z.; de Oliveira Mendes, T.A.; Trevizano, L.M.; Dos Santos Camargos, A.M.; Guimarães, V.M. Impact of the removal of N-terminal non-structured amino acids on activity and stability of xylanases from Orpinomyces sp. PC-2. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 106, 312–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhong, H.; Huang, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, F. Cloning, over-expression and characterization of a thermo-tolerant xylanase from Thermotoga thermarum. Biotechnol. Lett. 2014, 36, 587–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azouz, R.A.M.; Hegazy, U.M.; Said, M.M.; Bassuiny, R.I.; Salem, A.M.; Fahmy, A.S. Improving the catalytic efficiency of thermostable Geobacillus stearothermophilus xylanase XT6 by single-amino acid substitution. J. Biochem. 2020, 167, 203–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinen, P.R.; Henn, C.; Peralt, R.M.; Bracht, A.; Simão, R.C.G.; Silva, J.L.C.; Polizelo, M.L.T.M.; Kadowaki, M.K. Xylanase from Fusarium heterosporum: Properties and influence of thiol compounds on xylanase activity. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2014, 13, 1047–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, G.Q.; Zhao, P.X.; Zhao, J.; Wang, M.J.; Huo, S.H.; Cui, F.J.; Jiang, J.X. Production and partial characterization of an alkaline xylanase from a novel fungus Cladosporium oxysporum. BioMed Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 4575024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Haq, I.; Prakash, J.; Singh, S.K.; Mishra, S.; Raj, A. Purification, characterization and thermostability improvement of xylanase from Bacillus amyloliquefaciens and its application in pre-bleaching of kraft pulp. 3 Biotech 2017, 7, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salzano, F.; Aulitto, M.; Fiorentino, G.; Cannella, D.; Peeters, E.; Limauro, D. A novel endo-1,4-β-xylanase from Alicyclobacillus mali FL18: Biochemical characterization and its synergistic action with β-xylosidase in hemicellulose deconstruction. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 264 Pt 1, 130550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Qiu, C.; Ren, Y.; Yan, R.; Ye, X.; Wang, G. Novel salt-tolerant xylanase from a mangrove-isolated fungus Phoma sp. MF13 and its application in chinese steamed bread. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 3708–3716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Shao, Z.; Liu, Z. Cloning, expression and characterization of a novel cold-active and halophilic xylanase from Zunongwangia profunda. Extremophiles 2014, 18, 441–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sree Agash, S.G.; Rajasekaran, R. Exploring Bacillus species xylanases for industrial applications: Screening via thermostability and reaction modelling. J. Mol. Model. 2024, 30, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyte, J.; Doolittle, R.F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J. Mol. Biol. 1982, 157, 105–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdella, A.; Ramadan, S.; Hamouda, R.A.; Saddiq, A.A.; Alhazmi, N.M.; Al-Saman, M.A. Paecilomyces variotii xylanase production, purification and characterization with antioxidant xylooligosaccharides production. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 16468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Yue, Z.; Liu, E.; Li, X.; Li, C. Assessment of the bifidogenic and antibacterial activities of xylooligosaccharide. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 858949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Fan, G.; Xia, H.; Zhang, X.; Teng, C.; Li, X. Ultrasound-assisted production of xylooligosaccharides from alkali-solubilized corncob bran using Penicillium janthinellum XAF01 acidic xylanase. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 755003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puițel, A.C.; Suditu, G.D.; Danu, M.; Ailiesei, G.L.; Nechita, M.T. An experimental study on the hot alkali extraction of xylan-based hemicelluloses from wheat straw and corn stalks and optimization methods. Agriculture 2022, 14, 1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).