Long- and Short-Term Glucosphingosine (lyso-Gb1) Dynamics in Gaucher Patients Undergoing Enzyme Replacement Therapy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Sample Processing and DBS Analysis
2.3. Statistical and Quantitative Analysis
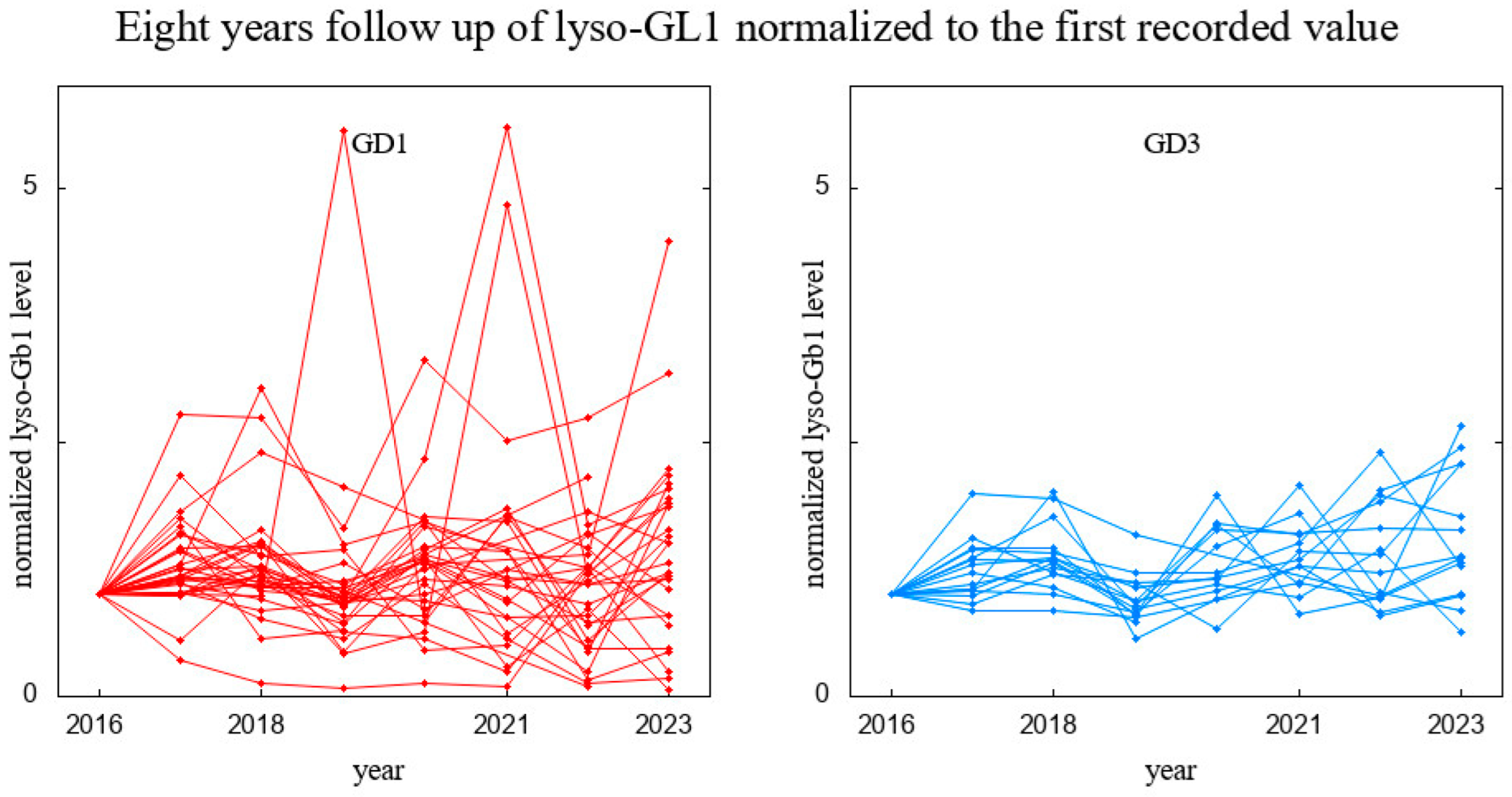
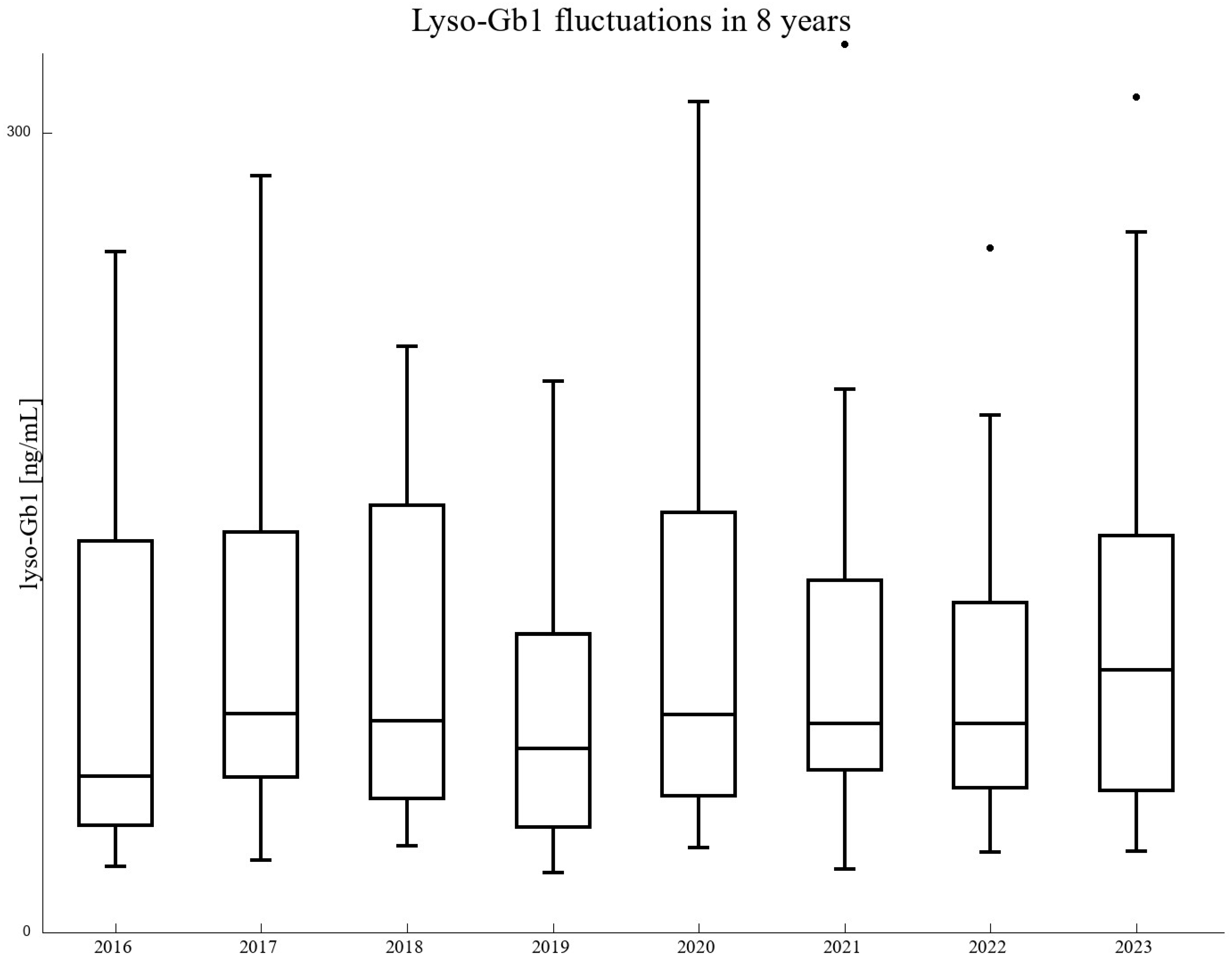
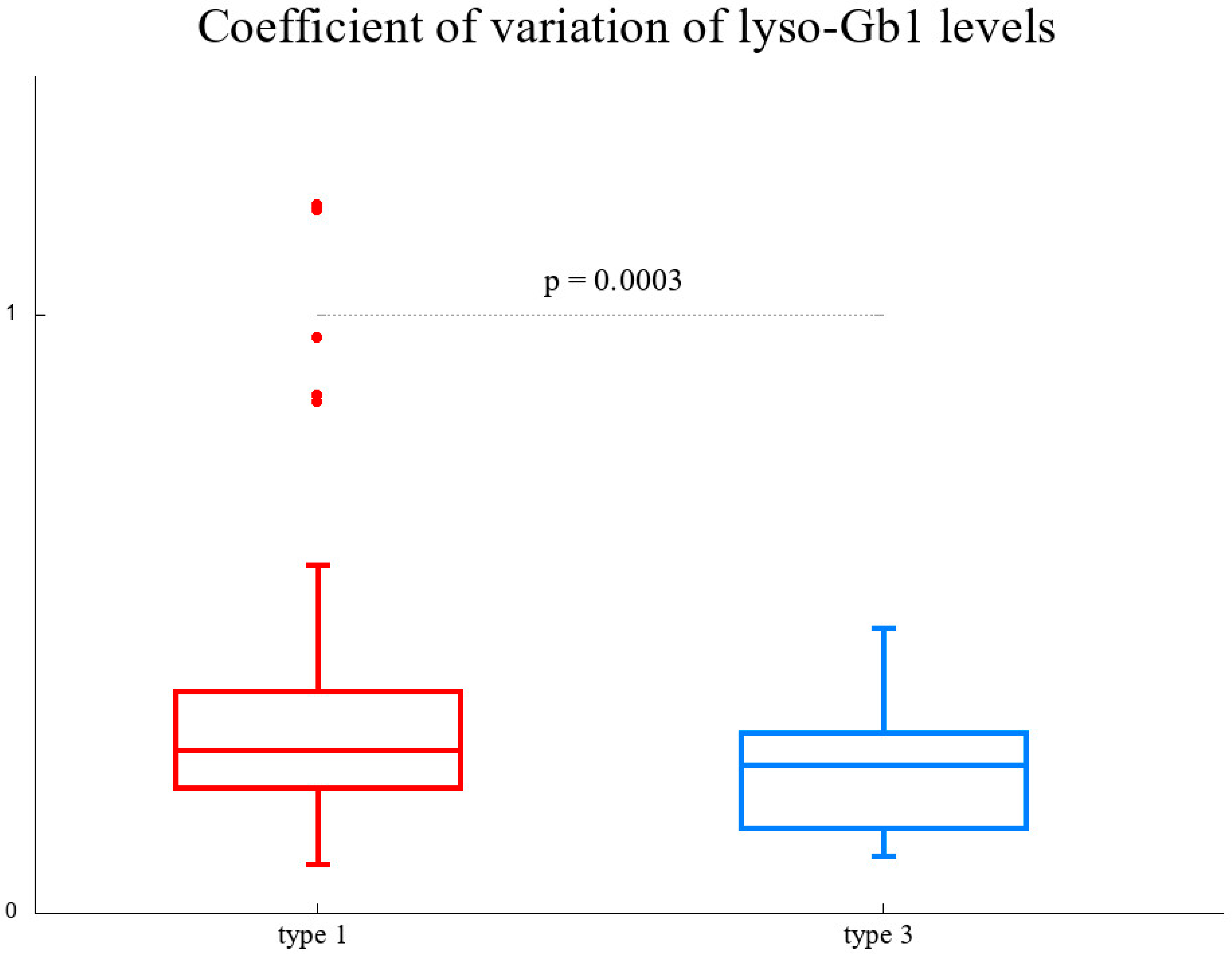
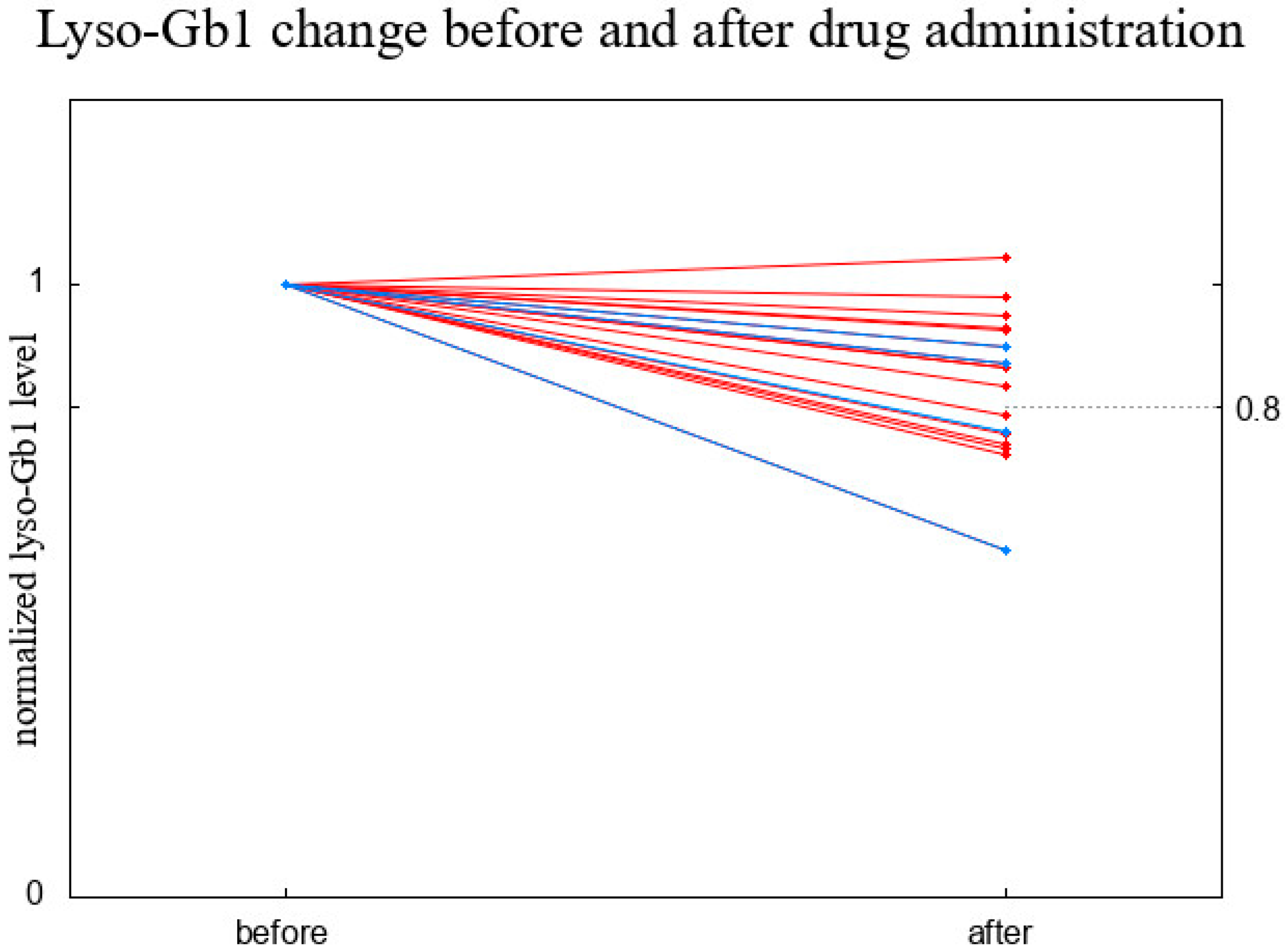
3. Results
3.1. Patients’ Characteristics and Long-Term Analysis
3.2. Short-Term Observation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hruska, K.S.; LaMarca, M.E.; Scott, C.R.; Sidransky, E. Gaucher disease: Mutation and polymorphism spectrum in the glucocerebrosidase gene (GBA). Hum. Mutat. 2008, 29, 567–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, M.K.; Grabowski, G.A. Immunological cells and functions in Gaucher disease. Crit. Rev. Oncog. 2013, 18, 197–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sidransky, E. Gaucher disease: Insights from a rare Mendelian disorder. Discov. Med. 2012, 14, 273–281. [Google Scholar]
- Schiffmann, R.; Sevigny, J.; Rolfs, A.; Davies, E.H.; Goker-Alpan, O.; Abdelwahab, M.; Vellodi, A.; Mengel, E.; Lukina, E.; Yoo, H.; et al. The definition of neuronopathic Gaucher disease. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2020, 43, 1056–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grabowski, G.A. Gaucher disease: Gene frequencies and genotype/phenotype correlations. Genet. Test. 1997, 1, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fairley, C.; Zimran, A.; Phillips, M.; Cizmarik, M.; Yee, J.; Weinreb, N.; Packman, S. Phenotype heterogeneity of N370S homozygotes with type 1 Gaucher disease: An analysis of 798 patients from the ICGG Gaucher registry. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2008, 31, 738–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuji, S.; Choudary, P.V.; Martin, B.M.; Stubblefield, B.K.; Mayor, J.A.; Barranger, J.A.; Ginns, E.I. A mutation in the human glucocerebrosidase gene in neuronopathic Gaucher’s disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 1987, 316, 570–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tylki-Szymańska, A.; Vellodi, A.; El-Beshlawy, A.; Cole, J.A.; Kolodny, E. Neuronopathic Gaucher disease: Demographic and clinical features of 131 patients enrolled in the International Collaborative Gaucher Group Neurological Outcomes Subregistry. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2010, 33, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinur, T.; Bauer, P.; Beetz, C.; Kramp, G.; Cozma, C.; Iurașcu, M.I.; Becker-Cohen, M.; Istaiti, M.; Rolfs, A.; Zimran, A.; et al. Gaucher Disease Diagnosis Using Lyso-Gb1 on Dry Blood Spot Samples: Time to Change the Paradigm? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edelbroek, P.M.; van der Heijden, J.; Stolk, L.M. Dried blood spot methods in tabletatherapeutic drug monitoring: Methods, assays, and pitfalls. Ther. Drug Monit. 2009, 31, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, J.; Thomas, D.C.; Kasper, D.C.; Sharma, S.; Puri, R.D.; Bijarnia-Mahay, S.; Mistry, P.K.; Verma, I.C. Inherited Metabolic Disorders: Efficacy of Enzyme Assays on Dried Blood Spots for the Diagnosis of Lysosomal Storage Disorders. JIMD Rep. 2017, 31, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Available online: https://www.centogene.com/fileadmin/resources/news/centogene_gaucher_P2_20180201_V2_CCN_ARO_MEA.pdf (accessed on 1 June 2024).
- Available online: https://www.archimedlife.com/#about (accessed on 1 June 2024).
- Hollak, C.E.; van Weely, S.; van Oers, M.H.; Aerts, J.M. Marked elevation of plasma chitotriosidase activity. A novel hallmark of Gaucher disease. J. Clin. Investig. 1994, 93, 1288–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Dussen, L.; Hendriks, E.J.; Groener, J.E.M.; Boot, R.G.; Hollak, C.E.M.; Aerts, J.M.F.G. Value of plasma chitotriosidase to assess non-neuronopathic Gaucher disease severity and progression in the era of enzyme replacement therapy. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2014, 37, 991–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bussink, A.P.; Verhoek, M.; Vreede, J.; der Vlugt, K.G.; Donker-Koopman, W.E.; Sprenger, R.R.; Hollak, C.E.; Aerts, J.M.F.G.; Boot, R.G. Common G102S polymorphism in chitotriosidase differentially affects activity towards 4-methylumbelliferyl substrates. FEBS J. 2009, 276, 5678–5688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szymańska-Rożek, P.; Czartoryska, B.; Kleinotiene, G.; Lipiński, P.; Tylki-Szymańska, A.; Ługowska, A. A 20-Year Longitudinal Study of Plasma Chitotriosidase Activity in Treated Gaucher Disease Type 1 and 3 Patients—A Qualitative and Quantitative Approach. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rolfs, A.; Giese, A.K.; Grittner, U.; Mascher, D.; Elstein, D.; Zimran, A.; Bottcher, T.; Lukas, J.; Hubner, R.; Golnitz, U.; et al. Glucosylsphingosine is a highly sensitive and specific biomarker for primary diagnostic and follow-up monitoring in Gaucher disease in a non-Jewish, Caucasian cohort of Gaucher disease patients. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e79732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Available online: https://www.archimedlife.com/gaucher-disease-enzyme-biomarker-genetic-testing/ (accessed on 1 June 2024).
- Hurvitz, N.; Dinur, T.; Becker-Cohen, M.; Cozma, C.; Hovakimyan, M.; Oppermann, S.; Demuth, L.; Rolfs, A.; Abramov, A.; Zimran, A.; et al. Glucosylsphingosine (lyso-Gb1) as a Biomarker for Monitoring Treated and Untreated Children with Gaucher Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Revel-Vilk, S.; Fuller, M.; Zimran, A. Value of Glucosylsphingosine (Lyso-Gb1) as a Biomarker in Gaucher Disease: A Systematic Literature Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saville, J.T.; McDermott, B.K.; Chin, S.J.; Fletcher, J.M.; Fuller, M. Expanding the clinical utility of glucosylsphingosine for Gaucher disease. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2020, 43, 558–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stiles, A.R.; Huggins, E.; Fierro, L.; Jung, S.H.; Balwani, M.; Kishnani, P.S. The role of glucosylsphingosine as an early indicator of disease progression in early symptomatic type 1 Gaucher disease. Mol. Genet. Metab. Rep. 2021, 27, 100729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rappold, B.A. Review of the Use of Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry in Clinical Laboratories: Part II–Operations. Ann. Lab. Med. 2022, 42, 531–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, I.R.; Linden, G.; Charão, M.F.; Antunes, M.V.; Linden, R. Dried blood spot sampling for therapeutic drug monitoring: Challenges and opportunities. Expert Rev. Clin. Pharmacol. 2023, 16, 691–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sidhu, R.; Mondjinou, Y.; Qian, M.; Song, H.; Kumar, A.B.; Hong, X.; Hsu, F.-F.; Dietzen, D.J.; Yanjanin, N.M.; Porter, F.D.; et al. N-acyl-O-phosphocholineserines: Structures of a novel class of lipids that are biomarkers for Niemann-Pick C1 disease. J. Lipid Res. 2019, 60, 1410–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Patient ID | GD1/3 | Genotype | Lyso-Gb1 before [ng/mL] | Lyso-Gb1 after [ng/mL] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7 | 1 | D438H/R87W | 42 | 41.4 |
| 31.2 | 34.9 | |||
| 20 | 1 | N370S/c.1085C>T | 50.6 | 47.9 |
| 28 | 1 | D448G/R202X | 54.3 | 51.2 |
| 55 | 50 | |||
| 32 | 1 | Unknown | 45.7 | 39.8 |
| 35 | 1 | N370S/L444P | 33.3 | 24.6 |
| NEW PATIENT ID1 | 1 | N370S/N370S | 63 | 49.4 |
| NEW PATIENT ID2 | 1 | N370S/L444P | 47.6 | 42.7 |
| NEW PATIENT ID3 | 1 | N370S/ R202X | 43.9 | 33.2 |
| NEW PATIENT ID4 | 1 | N370S/L444P | 47.8 | 27.1 |
| NEW PATIENT ID5 | 1 | N370S/L444P | 546 | 471 |
| NEW PATIENT ID6 | 1 | N370S/L444P | 563 | 469 |
| NEW PATIENT ID7 | 1 | N370S/N370S | 44.6 | 38.5 |
| NEW PATIENT ID8 | 1 | N370S/L444P | 34.4 | 25.1 |
| NEW PATIENT ID9 | 1 | N370S/c.1085C>T | 47.9 | 46.9 |
| 26 | 1 | N370S/ R202X | 42.4 | 30.6 |
| NEW PATIENT ID10 | 1 | N370S/c.1085C>T | 37.3 | 34.6 |
| NEW PATIENT ID11 | 3 | L444P/L444P | 52.3 | 39.6 |
| 59 | 3 | L444P/L444P | 59.7 | 33.7 |
| 71 | 3 | L444P/L444P | 145 | 148 |
| 96.3 | 67.4 | |||
| 71.4 | 65 | |||
| 72 | 3 | L444P/L444P | 53.9 | 48.5 |
| 49.6 | 41.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dubiela, P.; Szymanska-Rozek, P.; Hasinski, P.; Lipinski, P.; Kleinotiene, G.; Giersz, D.; Tylki-Szymanska, A. Long- and Short-Term Glucosphingosine (lyso-Gb1) Dynamics in Gaucher Patients Undergoing Enzyme Replacement Therapy. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 842. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14070842
Dubiela P, Szymanska-Rozek P, Hasinski P, Lipinski P, Kleinotiene G, Giersz D, Tylki-Szymanska A. Long- and Short-Term Glucosphingosine (lyso-Gb1) Dynamics in Gaucher Patients Undergoing Enzyme Replacement Therapy. Biomolecules. 2024; 14(7):842. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14070842
Chicago/Turabian StyleDubiela, Pawel, Paulina Szymanska-Rozek, Piotr Hasinski, Patryk Lipinski, Grazina Kleinotiene, Dorota Giersz, and Anna Tylki-Szymanska. 2024. "Long- and Short-Term Glucosphingosine (lyso-Gb1) Dynamics in Gaucher Patients Undergoing Enzyme Replacement Therapy" Biomolecules 14, no. 7: 842. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14070842
APA StyleDubiela, P., Szymanska-Rozek, P., Hasinski, P., Lipinski, P., Kleinotiene, G., Giersz, D., & Tylki-Szymanska, A. (2024). Long- and Short-Term Glucosphingosine (lyso-Gb1) Dynamics in Gaucher Patients Undergoing Enzyme Replacement Therapy. Biomolecules, 14(7), 842. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14070842








