Advances in the Pathogenesis of Steroid-Associated Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. The Dose and Time Effect Relationship of SANFH
3. Relative Mechanisms of SANFH
3.1. Endothelial Cell Damage, Coagulation Abnormalities, and Tendency for Thrombosis
3.2. Oxidative Stress and Reactive Oxygen Species Mechanism
3.3. Lipid Metabolism Disorder and Fat Embolism Mechanism
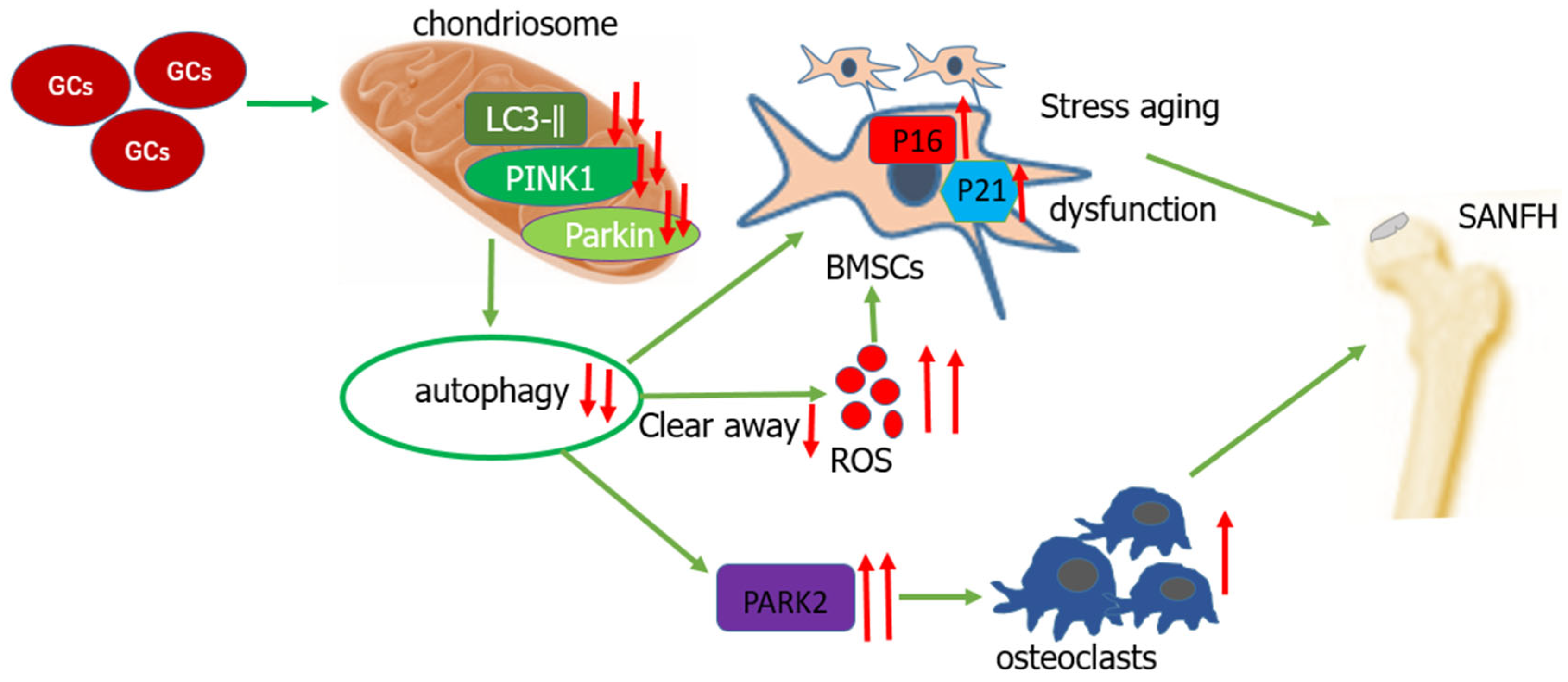
3.4. Mechanisms of Apoptosis and Autophagy
3.5. Mechanism of Non-Coding RNAs
3.6. Mechanisms of Genetic Susceptibility and Epigenetics
3.7. Mechanism of Immune Imbalance
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Larson, E.; Jones, L.C.; Goodman, S.B.; Koo, K.H.; Cui, Q. Early-stage osteonecrosis of the femoral head: Where are we and where are we going in year 2018? Int. Orthop. 2018, 42, 1723–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, R.; Ando, W.; Fukushima, W.; Sakai, T.; Hamada, H.; Takao, M.; Ito, K.; Sugano, N. Epidemiological study of osteonecrosis of the femoral head using the national registry of designated intractable diseases in Japan. Mod. Rheumatol. 2022, 32, 808–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Yan, Y.; Peng, W.; Wang, L.; Wang, T.; Xie, Z.; Luo, H.; Zhang, J.; Dong, W. PARK7 promotes repair in early steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head by enhancing resistance to stress-induced apoptosis in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells via regulation of the Nrf2 signaling pathway. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, K.H.; Kim, R.; Kim, Y.S.; Ahn, I.O.; Cho, S.H.; Song, H.R.; Park, Y.S.; Kim, H.; Wang, G.J. Risk period for developing osteonecrosis of the femoral head in patients on steroid treatment. Clin. Rheumatol. 2002, 21, 299–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, K.; Liu, Y.; He, J.; Pavlos, N.; Wang, C.; Kenny, J.; Yuan, J.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, J.; He, W. Steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head reveals enhanced reactive oxygen species and hyperactive osteoclasts. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2020, 16, 1888–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, B.H.; Jones, L.C.; Chen, C.H.; Cheng, E.Y.; Cui, Q.; Drescher, W.; Fukushima, W.; Gangji, V.; Goodman, S.B.; Ha, Y.C.; et al. Etiologic Classification Criteria of ARCO on Femoral Head Osteonecrosis Part 1: Glucocorticoid-Associated Osteonecrosis. J. Arthroplast. 2019, 34, 163–168.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Géraud, C.; Koch, P.S.; Goerdt, S. Vascular niches: Endothelial cells as tissue- and site-specific multifunctional team players in health and disease. J. Ger. Soc. Dermatol. JDDG 2014, 12, 685–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Wen, Z.; Niu, J.; Lin, S.; Wang, W. Steroid-Induced Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head: Novel Insight into the Roles of Bone Endothelial Cells in Pathogenesis and Treatment. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 777697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liverani, E.; Banerjee, S.; Roberts, W.; Naseem, K.M.; Perretti, M. Prednisolone exerts exquisite inhibitory properties on platelet functions. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2012, 83, 1364–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezus, E.; Tamba, B.I.; Badescu, M.C.; Popescu, D.; Bratoiu, I.; Rezus, C. Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head in Patients with Hypercoagulability-From Pathophysiology to Therapeutic Implications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, K.; Okamoto, T.; Okumoto, K.; Takafuji, Y.; Ishida, M.; Kawao, N.; Matsuo, O.; Kaji, H. PAI-1 is involved in delayed bone repair induced by glucocorticoids in mice. Bone 2020, 134, 115310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramacciotti, E.; Hawley, A.E.; Wrobleski, S.K.; Myers, D.D., Jr.; Strahler, J.R.; Andrews, P.C.; Guire, K.E.; Henke, P.K.; Wakefield, T.W. Proteomics of microparticles after deep venous thrombosis. Thromb. Res. 2010, 125, e269–e274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, S.C.; Yuan, T.; Rui, B.Y.; Zhu, Z.Z.; Guo, S.C.; Zhang, C.Q. Exosomes derived from human platelet-rich plasma prevent apoptosis induced by glucocorticoid-associated endoplasmic reticulum stress in rat osteonecrosis of the femoral head via the Akt/Bad/Bcl-2 signal pathway. Theranostics 2017, 7, 733–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, M.S. Prostacyclin: A major prostaglandin in the regulation of adipose tissue development. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 3254–3262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, W.; Guo, W.S.; Yu, H.C.; Liu, P.; Zhang, Q.D. Role of Junction-Mediating and Regulatory Protein in the Pathogenesis of Glucocorticoid-Induced Endothelial Cell Lesions. Orthop. Surg. 2020, 12, 964–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Zong, Y.; Shan, H.; Liu, P.; Zhang, Q.D.; Lin, Y.; Xia, W.; Wang, N.; Zhou, L.; Gao, Y.; et al. MicroRNA-23b-3p participates in steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head by suppressing ZNF667 expression. Steroids 2020, 163, 108709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, J.; Wang, L.; Wang, K.; Su, H.; Luo, D.; Yang, H.; Wen, Y.; Wu, Q.; Li, X. Tauroursodeoxycholic Acid Inhibited Apoptosis and Oxidative Stress in H(2)O(2)-Induced BMSC Death via Modulating the Nrf-2 Signaling Pathway: The Therapeutic Implications in a Rat Model of Spinal Cord Injury. Mol. Neurobiol. 2023, 11, 893–7648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, L.Z.; Teng, X.; Zhang, Z.B.; Zheng, C.J.; Chen, S.H. Mangiferin inhibits apoptosis and oxidative stress via BMP2/Smad-1 signaling in dexamethasone-induced MC3T3-E1 cells. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2018, 41, 2517–2526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, N.; Sun, H.; Xue, Y.; Zhang, W.; Wang, H.; Tao, H.; Liang, X.; Li, M.; Xu, Y.; Chen, L.; et al. Inhibition of MAGL activates the Keap1/Nrf2 pathway to attenuate glucocorticoid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Clin. Transl. Med. 2021, 11, e447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, J.; Wang, Y.; Anwar, N.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, D.; Ma, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Xiao, L.; et al. The role of autophagy in bone metabolism and clinical significance. Autophagy 2023, 19, 2409–2427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubo, Y.; Drescher, W.; Fragoulis, A.; Tohidnezhad, M.; Jahr, H.; Gatz, M.; Driessen, A.; Eschweiler, J.; Tingart, M.; Wruck, C.J.; et al. Adverse Effects of Oxidative Stress on Bone and Vasculature in Corticosteroid-Associated Osteonecrosis: Potential Role of Nuclear Factor Erythroid 2-Related Factor 2 in Cytoprotection. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2021, 35, 357–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, H.; Li, Z.; Hu, S.; Chen, X.; Cong, X. Apoptosis of mesenchymal stem cells induced by hydrogen peroxide concerns both endoplasmic reticulum stress and mitochondrial death pathway through regulation of caspases, p38 and JNK. J. Cell. Biochem. 2010, 111, 967–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.Y.; Pang, C.Y.; Li, D.K.; Liao, C.H.; Huang, W.C.; Wu, C.C.; Chou, Y.Y.; Li, W.W.; Chen, S.Y.; Liu, H.W.; et al. Antioxidants cause rapid expansion of human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells via CDK and CDK inhibitor regulation. J. Biomed. Sci. 2013, 20, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okada, H.; Okabe, K.; Tanaka, S. Finely-Tuned Calcium Oscillations in Osteoclast Differentiation and Bone Resorption. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 22, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, H.; Ge, G.; Liang, X.; Zhang, W.; Sun, H.; Li, M.; Geng, D. ROS signaling cascades: Dual regulations for osteoclast and osteoblast. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2020, 52, 1055–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nie, Z.; Deng, S.; Zhang, L.; Chen, S.; Lu, Q.; Peng, H. Crocin protects against dexamethasone-induced osteoblast apoptosis by inhibiting the ROS/Ca2+-mediated mitochondrial pathway. Mol. Med. Rep. 2019, 20, 401–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Yang, X.; Yang, S.; Ren, G.; Ferreri, M.; Su, Y.; Chen, L.; Han, B. Sodium fluoride suppress proliferation and induce apoptosis through decreased insulin-like growth factor-I expression and oxidative stress in primary cultured mouse osteoblasts. Arch. Toxicol. 2011, 85, 1407–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, P.; Nie, Z.; Sun, F.; Peng, H. Glucocorticoids induce femoral head necrosis in rats through the ROS/JNK/c-Jun pathway. FEBS Open Bio 2021, 11, 312–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, J.H. Activation of the PI3K/Akt pathway by oxidative stress mediates high glucose-induced increase of adipogenic differentiation in primary rat osteoblasts. J. Cell. Biochem. 2013, 114, 2595–2602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Zhang, X.Y.; Zhen, Y.F.; Chen, C.; Tan, H.; Hu, J.; Tan, M.S. PGK1 depletion activates Nrf2 signaling to protect human osteoblasts from dexamethasone. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Compton, J.T.; Lee, F.Y. A review of osteocyte function and the emerging importance of sclerostin. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. Vol. 2014, 96, 1659–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domazetovic, V.; Marcucci, G.; Iantomasi, T.; Brandi, M.L.; Vincenzini, M.T. Oxidative stress in bone remodeling: Role of antioxidants. Clin. Cases Miner. Bone Metab. 2017, 14, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kar, R.; Riquelme, M.A.; Hua, R.; Jiang, J.X. Glucocorticoid-Induced Autophagy Protects Osteocytes Against Oxidative Stress Through Activation of MAPK/ERK Signaling. JBMR Plus 2019, 3, e10077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Han, C.; Tian, P.; Li, P.F.; Ma, X.L. Role of Teriparatide in Glucocorticoid-induced Osteoporosis through Regulating Cellular Reactive Oxygen Species. Orthop. Surg. 2018, 10, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henriksen, K.; Neutzsky-Wulff, A.V.; Bonewald, L.F.; Karsdal, M.A. Local communication on and within bone controls bone remodeling. Bone 2009, 44, 1026–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sithole, C.; Pieterse, C.; Howard, K.; Kasonga, A. GPR120 Inhibits RANKL-Induced Osteoclast Formation and Resorption by Attenuating Reactive Oxygen Species Production in RAW264.7 Murine Macrophages. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, J.; Hao, D.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, B.; Zhang, R.; Wang, Y.; Yang, H. Natural products for treatment of bone erosive diseases: The effects and mechanisms on inhibiting osteoclastogenesis and bone resorption. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2016, 36, 118–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Pan, C.; Wang, N.; Zhou, L.; Shan, H.; Gao, Y.; Yu, X. A high-fat diet aggravates osteonecrosis through a macrophage-derived IL-6 pathway. Int. Immunol. 2019, 31, 263–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baek, S.H.; Kim, K.H.; Lee, W.K.; Hong, W.; Won, H.; Kim, S.Y. Abnormal Lipid Profiles in Nontraumatic Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head: A Comparison with Osteoarthritis Using Propensity Score Matching. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2022, 104 (Suppl. 2), 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.Y.; Zhang, L.L.; Jiang, C.; Hua, B.X.; Ji, Z.F.; Fan, W.S.; Gong, L.J.; Zhu, L.; Wang, X.D.; Yan, Z.Q. Altered lipidomic profiles in patients with and without osteonecrosis of the femoral head after 1-month glucocorticoid treatment. Clin. Transl. Med. 2021, 11, e298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Li, H.Y.; Wu, Y.F.; Mi, R.J.; Liu, W.Z.; Shen, X.; Lu, Y.X.; Jiang, Y.H.; Ma, M.J.; Shen, H.Y. ac4C acetylation of RUNX2 catalyzed by NAT10 spurs osteogenesis of BMSCs and prevents ovariectomy-induced bone loss. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2021, 26, 135–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schepper, J.D.; Collins, F.; Rios-Arce, N.D.; Kang, H.J.; Schaefer, L.; Gardinier, J.D.; Raghuvanshi, R.; Quinn, R.A.; Britton, R.; Parameswaran, N.; et al. Involvement of the Gut Microbiota and Barrier Function in Glucocorticoid-Induced Osteoporosis. J. Bone Min. Res. 2020, 35, 801–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Zhu, H.; Wang, Q.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, C. Inhibition of PERK Signaling Prevents Against Glucocorticoid-induced Endotheliocyte Apoptosis and Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2020, 16, 543–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Lu, Y.; Jiang, X.; Hu, J.; Li, R.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, G.; Rong, X. Glucocorticoids induce osteoporosis mediated by glucocorticoid receptor-dependent and -independent pathways. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 125, 109979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, S.; Dai, G.; Chen, S.; Nie, Z.; Zhou, J.; Fang, H.; Peng, H. Dexamethasone induces osteoblast apoptosis through ROS-PI3K/AKT/GSK3β signaling pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 110, 602–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, X.; Yu, S.; Jing, X.; Guo, J.; Sun, K.; Guo, F.; Ye, Y. PTEN inhibitor VO-OHpic attenuates GC-associated endothelial progenitor cell dysfunction and osteonecrosis of the femoral head via activating Nrf2 signaling and inhibiting mitochondrial apoptosis pathway. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2020, 11, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhan, J.; Yan, Z.; Zhao, M.; Qi, W.; Lin, J.; Lin, Z.; Huang, Y.; Pan, X.; Xue, X. Allicin inhibits osteoblast apoptosis and steroid-induced necrosis of femoral head progression by activating the PI3K/AKT pathway. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 7830–7841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.Y.; Rao, S.S.; Yue, T.; Tan, Y.J.; Yin, H.; Chen, L.J.; Luo, M.J.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.Y.; Hong, C.G.; et al. Glucocorticoid-induced loss of beneficial gut bacterial extracellular vesicles is associated with the pathogenesis of osteonecrosis. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eabg8335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimasaki, M.; Ueda, S.; Ichiseki, T.; Hirata, H.; Kawahara, N.; Ueda, Y. Resistance of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in a stressed environment—Comparison with osteocyte cells. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2021, 18, 1375–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knowles, H.J. The Adenosine A(2B) Receptor Drives Osteoclast-Mediated Bone Resorption in Hypoxic Microenvironments. Cells 2019, 8, 624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrington, J.S.; Ryter, S.W.; Plataki, M.; Price, D.R.; Choi, A.M.K. Mitochondria in health, disease, and aging. Physiol. Rev. 2023, 103, 2349–2422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Peng, W.; Zhang, J.; Dong, W.; Wu, J.; Wang, T.; Xie, Z. P53 and Parkin co-regulate mitophagy in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells to promote the repair of early steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Shi, X.; Weng, S.J.; Xie, J.; Tang, J.H.; Yan, D.Y.; Wang, B.Z.; Xie, Z.J.; Wu, Z.Y.; Yang, L.; et al. Vitamin K2 Can Rescue the Dexamethasone-Induced Downregulation of Osteoblast Autophagy and Mitophagy Thereby Restoring Osteoblast Function In Vitro and In Vivo. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, S.J.; Jung, S.; Jang, J.S.; Mo, S.; Kwon, J.O.; Kim, M.K.; Kim, H.H. PARK2 Induces Osteoclastogenesis through Activation of the NF-κB Pathway. Mol. Cells 2022, 45, 749–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, R.; Zhang, H.L.; Huang, J.H.; Cai, R.Z.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.H.; Hu, B.X.; Ye, Z.P.; Li, Z.L.; Mai, J.; et al. MAPK1/3 kinase-dependent ULK1 degradation attenuates mitophagy and promotes breast cancer bone metastasis. Autophagy 2021, 17, 3011–3029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, X.; Ma, H.; Xiong, Y.; Zou, L.; Yuan, Z.; Xiao, Y. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes mediate nuclear receptor coactivator-3 expression in osteoblasts by delivering miR-532-5p to influence osteonecrosis of the femoral head development. Cell Biol. Int. 2022, 46, 2185–2197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Z.J.; Liu, B.Y.; Zhang, Y.T.; Chen, X.Z.; Qiao, G.Y.; Wang, S.; Ma, Z.L. MiR-145 silencing promotes steroid-induced avascular necrosis of the femoral head repair via upregulating VEGF. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2017, 21, 3763–3769. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Statement of Retraction: Down-regulated microRNA-141 facilitates osteoblast activity and inhibits osteoclast activity to ameliorate osteonecrosis of the femoral head via up-regulating TGF-β2. Cell Cycle 2022, 21, 1892. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, W.; Ning, Y.; Xu, H.J.; Zou, W.Z.; Hu, J.; Liu, X.Z.; Yang, Y.; Li, Z.H. BMSC-derived exosomes carrying microRNA-122-5p promote proliferation of osteoblasts in osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Clin. Sci. 2019, 133, 1955–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.B.; Liu, W.; Zhu, X.H.; Yi, H.; Cui, S.Y.; Zhao, J.N.; Cui, Z.M. microRNA-25 targets PKCζ and protects osteoblastic cells from dexamethasone via activating AMPK signaling. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 3226–3236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nan, K.; Pei, J.P.; Fan, L.H.; Zhang, Y.K.; Zhang, X.; Liu, K.; Shi, Z.B.; Dang, X.Q.; Wang, K.Z. Resveratrol prevents steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head via miR-146a modulation. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2021, 1503, 23–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mondal, J.; Pillarisetti, S.; Junnuthula, V.; Saha, M.; Hwang, S.R.; Park, I.K.; Lee, Y.K. Hybrid exosomes, exosome-like nanovesicles and engineered exosomes for therapeutic applications. J. Control. Release 2023, 353, 1127–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krylova, S.V.; Feng, D. The Machinery of Exosomes: Biogenesis, Release, and Uptake. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nan, K.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, D.; Zhao, Y.; Jing, Z.; Liu, K.; Shang, D.; Geng, Z.; Fan, L. Exosomes from miRNA-378-modified adipose-derived stem cells prevent glucocorticoid-in duced osteonecrosis of the femoral head by enhancing angiogenesis and osteogenesis via targeting miR-378 negatively regulated suppressor of fused (Sufu). Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2021, 12, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuo, R.; Kong, L.; Wang, M.; Wang, W.; Xu, J.; Chai, Y.; Guan, J.; Kang, Q. Exosomes derived from human CD34 stem cells transfected with miR-26a prevent glucocorticoid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head by promoting angiogenesis and osteogenesis. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2019, 10, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, F.; Huang, W.; Yang, Y.; Liu, F.; Chen, J.; Wang, G.; Sun, Z. miR-155-5p regulates mesenchymal stem cell osteogenesis and proliferation by targeting GSK3B in steroid-associated osteonecrosis. Cell Biol. Int. 2021, 45, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.L.; Chi, C.T.; Meng, X.H.; Liang, S.D. miRNA-15a-5p facilitates the bone marrow stem cell apoptosis of femoral head necrosis through the Wnt/β-catenin/PPARγ signaling pathway. Mol. Med. Rep. 2019, 19, 4779–4787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Y.; Jiang, C.; Wang, X.; Wang, H.; Yan, Z.; Yuan, H. Reciprocal effect of microRNA-224 on osteogenesis and adipogenesis in steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Bone 2021, 145, 115844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, L.; Zuo, R.; Wang, M.; Wang, W.; Xu, J.; Chai, Y.; Guan, J.; Kang, Q. Silencing MicroRNA-137-3p, which Targets RUNX2 and CXCL12 Prevents Steroid-induced Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head by Facilitating Osteogenesis and Angiogenesis. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2020, 16, 655–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, D.Y.; Tang, J.; Tian, H.T.; Shi, Y.Y.; Jia, J. Adipocyte-secreted microvesicle-derived miR-148a regulates adipogenic and osteogenic differentiation by targeting Wnt5a/Ror2 pathway. Life Sci. 2021, 278, 119548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Wang, Q.; Li, Z.; Yang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Du, Z.; Zhang, G.; Song, Y. Circular RNA CDR1as promotes adipogenic and suppresses osteogenic differentiation of BMSCs in steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Bone 2020, 133, 115258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palumbo, T.; Poultsides, G.A.; Kouraklis, G.; Liakakos, T.; Drakaki, A.; Peros, G.; Hatziapostolou, M.; Iliopoulos, D. A functional microRNA library screen reveals miR-410 as a novel anti-apoptotic regulator of cholangiocarcinoma. BMC Cancer 2016, 16, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Peng, W.; Wang, T.; Zhang, J.; Dong, W.; Wang, C.; Xie, Z.; Luo, H.; Liu, G. Lnc Tmem235 promotes repair of early steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head by inhibiting hypoxia-induced apoptosis of BMSCs. Exp. Mol. Med. 2022, 54, 1991–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.Y.; Shan, H.J.; Zhang, P.; She, C.; Zhou, X.Z. LncRNA EPIC1 protects human osteoblasts from dexamethasone-induced cell death. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 503, 2255–2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.; Luo, S.; Lei, Y.; Jiao, M.; Cao, R.; Guan, H.; Tian, R.; Wang, K.; Yang, P. Osteogenesis-Related Long Noncoding RNA GAS5 as a Novel Biomarker for Osteonecrosis of Femoral Head. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 857612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chao, P.C.; Cui, M.Y.; Li, X.A.; Jiang, Y.; Lin, B.C.; Li, Z.B. Correlation between miR-1207-5p expression with steroid-induced necrosis of femoral head and VEGF expression. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2019, 23, 2710–2718. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Peng, P.; He, W.; Zhang, Y.X.; Liu, X.H.; Chen, Z.Q.; Mao, J.G. CircHIPK3 promotes bone microvascular endothelial cell proliferation, migration and angiogenesis by targeting miR-7 and KLF4/VEGF signaling in steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Adv. Clin. Exp. Med. Off. Organ Wroc. Med. Univ. 2023, 32, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; Zhang, L.; Kang, X.; Zheng, J.; Tian, B. Association Between Genetic Polymorphisms of Gene and the Risk of Steroid-Induced Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head in the Chinese Han Male Population. Genet. Test. Mol. Biomark. 2020, 24, 460–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Y.; An, F.; Wang, J.; Liu, C.; Wu, H.; Cao, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, G.; Wang, G. MMP2 and MMP10 Polymorphisms Are Related to Steroid-Induced Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head among Chinese Han Population. BioMed Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 8298193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishiyama, A.; Nakanishi, M. Navigating the DNA methylation landscape of cancer. Trends Genet. TIG 2021, 37, 1012–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poduval, D.B.; Ognedal, E.; Sichmanova, Z.; Valen, E.; Iversen, G.T.; Minsaas, L.; Lønning, P.E.; Knappskog, S. Assessment of tumor suppressor promoter methylation in healthy individuals. Clin. Epigenet. 2020, 12, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, M.; Cao, Y.; Yang, X.; An, F.; Wu, H.; Wang, J. DNA methylation in the OPG/RANK/RANKL pathway is associated with steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2021, 22, 599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walsh, M.C.; Choi, Y. Biology of the RANKL-RANK-OPG System in Immunity, Bone, and Beyond. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, M.C.; Zhang, J.; Chen, X.J.; Shen, Y.S.; Fang, B.; Qin, Y.X.; He, W.; Wei, Q.S. Osteoclastic activity was associated with the development of steroid-induced osteonecrosis of femoral head. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2020, 48, 1036–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, L.; Lu, J.; Cheng, J.; Rao, Q.; Li, Z.; Hou, H.; Lou, Z.; Zhang, L.; Li, W.; Gong, W.; et al. Structural insight into substrate preference for TET-mediated oxidation. Nature 2015, 527, 118–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.G.; Cai, Q.; Zheng, J.; Dong, Y.S.; Li, J.J.; Li, J.C.; Hao, G.Z.; Wang, C.; Wang, J.L. Epigenetic Suppression of GADs Expression is Involved in Temporal Lobe Epilepsy and Pilocarpine-Induced Mice Epilepsy. Neurochem. Res. 2016, 41, 1751–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Q.J.; Zhang, T.N.; Chen, H.H.; Yu, X.F.; Lv, J.L.; Liu, Y.Y.; Liu, Y.S.; Zheng, G.; Zhao, J.Q.; Wei, Y.F.; et al. The sirtuin family in health and disease. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 402. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Y.; Du, Z.; Ren, M.; Yang, Q.; Wang, Q.; Chen, G.; Zhao, H.; Li, Z.; Wang, J.; Zhang, G. Association of gene variants of transcription factors PPARγ, RUNX2, Osterix genes and COL2A1, IGFBP3 genes with the development of osteonecrosis of the femoral head in Chinese population. Bone 2017, 101, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, P.; Wang, H.; Yi, X.; Zhang, H.; Chen, H.; Pan, Z. C/EBPα regulates the fate of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and steroid-induced avascular necrosis of the femoral head by targeting the PPARγ signalling pathway. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2022, 13, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Wang, B.Z.; Xie, J.; Zhang, R.Y.; Jin, C.; Chen, W.K.; Fang, K.H.; Hong, C.X.; Xu, T.H.; Huang, C.B.; et al. Therapeutic effect of SIRT3 on glucocorticoid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head via intracellular oxidative suppression. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2021, 176, 228–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.; Raut, N.A.; Lawal, T.O.; Patel, S.R.; Lee, S.M.; Mahady, G.B. Peonidin-3-O-glucoside and cyanidin increase osteoblast differentiation and reduce RANKL-induced bone resorption in transgenic medaka. Phytother. Res. PTR 2021, 35, 6255–6269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, L.; Zhang, G.; Wu, Y.; Li, Z.; Gao, S.; Zhou, L. SIRT6 Prevents Glucocorticoid-Induced Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head in Rats. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2022, 2022, 6360133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Gong, S.; Han, L.; Shao, W.; Li, Z.; Xu, J.; Lv, X.; Xiao, B.; Feng, Y. Knockdown of HDAC9 Inhibits Osteogenic Differentiation of Human Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells Partially by Suppressing the MAPK Signaling Pathway. Clin. Interv. Aging 2022, 17, 777–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Tan, Z.; Li, W.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Y.; Yue, C. Osteoimmunology and osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Bone Jt. Res. 2022, 11, 26–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruyama, M.; Rhee, C.; Utsunomiya, T.; Zhang, N.; Ueno, M.; Yao, Z.; Goodman, S.B. Modulation of the Inflammatory Response and Bone Healing. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.T.; Xiao, F.; Li, N.; Shan, S.; Qi, M.; Wang, Z.Y.; Zhang, S.N.; Wei, W.; Sun, W.Y. Inflammasome as an Effective Platform for Fibrosis Therapy. J. Inflamm. Res. 2021, 14, 1575–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.; Wen, Q.; Dang, X.; You, W.; Fan, L.; Wang, K. Immune response associated with Toll-like receptor 4 signaling pathway leads to steroid-induced femoral head osteonecrosis. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2014, 15, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Z.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Y.; Ma, M.; Ma, Z.; Wang, C.; Zeng, H.; Xue, L.; Yue, C.; et al. The Dynamic Feature of Macrophage M1/M2 Imbalance Facilitates the Progression of Non-Traumatic Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 912133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Yue, J.; Wang, W.; Liu, P.; Zuo, W.; Guo, W.; Zhang, Q. Icariin promotes angiogenesis in glucocorticoid-induced osteonecrosis of femoral heads: In vitro and in vivo studies. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2019, 23, 7320–7330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, J.; Yu, H.; Liu, P.; Wen, P.; Zhang, H.; Guo, W.; Zhang, Q. Preliminary study of icariin indicating prevention of steroid-induced osteonecrosis of femoral head by regulating abnormal expression of miRNA-335 and protecting the functions of bone microvascular endothelial cells in rats. Gene 2021, 766, 145128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, B.; Wang, W.; Liu, X.; Xu, C.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Xu, J.; Guan, J.; Zhou, P.; Mao, Y. Gelatin methacrylate hydrogel scaffold carrying resveratrol-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles for enhancement of osteogenic differentiation of BMSCs and effective bone regeneration. Regen. Biomater. 2021, 8, rbab044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Zheng, J.; Yang, Y.; Ni, L.; Chen, H.; Yu, D. Hesperetin alleviated glucocorticoid-induced inhibition of osteogenic differentiation of BMSCs through regulating the ERK signaling pathway. Med. Mol. Morphol. 2021, 54, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, J.J.; Chau, Z.L.; Chen, S.Y.; Hill, J.J.; Korpany, K.V.; Liang, N.W.; Lin, L.H.; Lin, Y.H.; Liu, J.K.; Liu, Y.C.; et al. Exosome Processing and Characterization Approaches for Research and Technology Development. Adv. Sci. 2022, 9, e2103222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.; Wang, F.; Hu, Y.; Luo, Y.; Wei, Y.; Xu, K.; Zhang, H.; Liu, H.; Bo, L.; Lv, S.; et al. Exosome-based bone-targeting drug delivery alleviates impaired osteoblastic bone formation and bone loss in inflammatory bowel diseases. Cell Rep. Med. 2023, 4, 100881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.X.; Liu, P.; Ding, W.; Meng, Q.B.; Su, D.H.; Zhang, Q.C.; Lian, R.X.; Yu, B.Q.; Zhao, M.D.; Dong, J.; et al. Injectable Mussel-Inspired highly adhesive hydrogel with exosomes for endogenous cell recruitment and cartilage defect regeneration. Biomaterials 2021, 278, 121169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Cai, Z.; Ma, W.; Bai, L.; Luo, E.; Lin, Y. A DNA tetrahedron-based ferroptosis-suppressing nanoparticle: Superior delivery of curcumin and alleviation of diabetic osteoporosis. Bone Res. 2024, 12, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, J.; Cao, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, H. Advances in the Pathogenesis of Steroid-Associated Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 667. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14060667
Zhang J, Cao J, Liu Y, Zhao H. Advances in the Pathogenesis of Steroid-Associated Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head. Biomolecules. 2024; 14(6):667. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14060667
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Jie, Jianze Cao, Yongfei Liu, and Haiyan Zhao. 2024. "Advances in the Pathogenesis of Steroid-Associated Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head" Biomolecules 14, no. 6: 667. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14060667
APA StyleZhang, J., Cao, J., Liu, Y., & Zhao, H. (2024). Advances in the Pathogenesis of Steroid-Associated Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head. Biomolecules, 14(6), 667. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14060667




