TRAF1 from a Structural Perspective
Abstract
1. Introduction
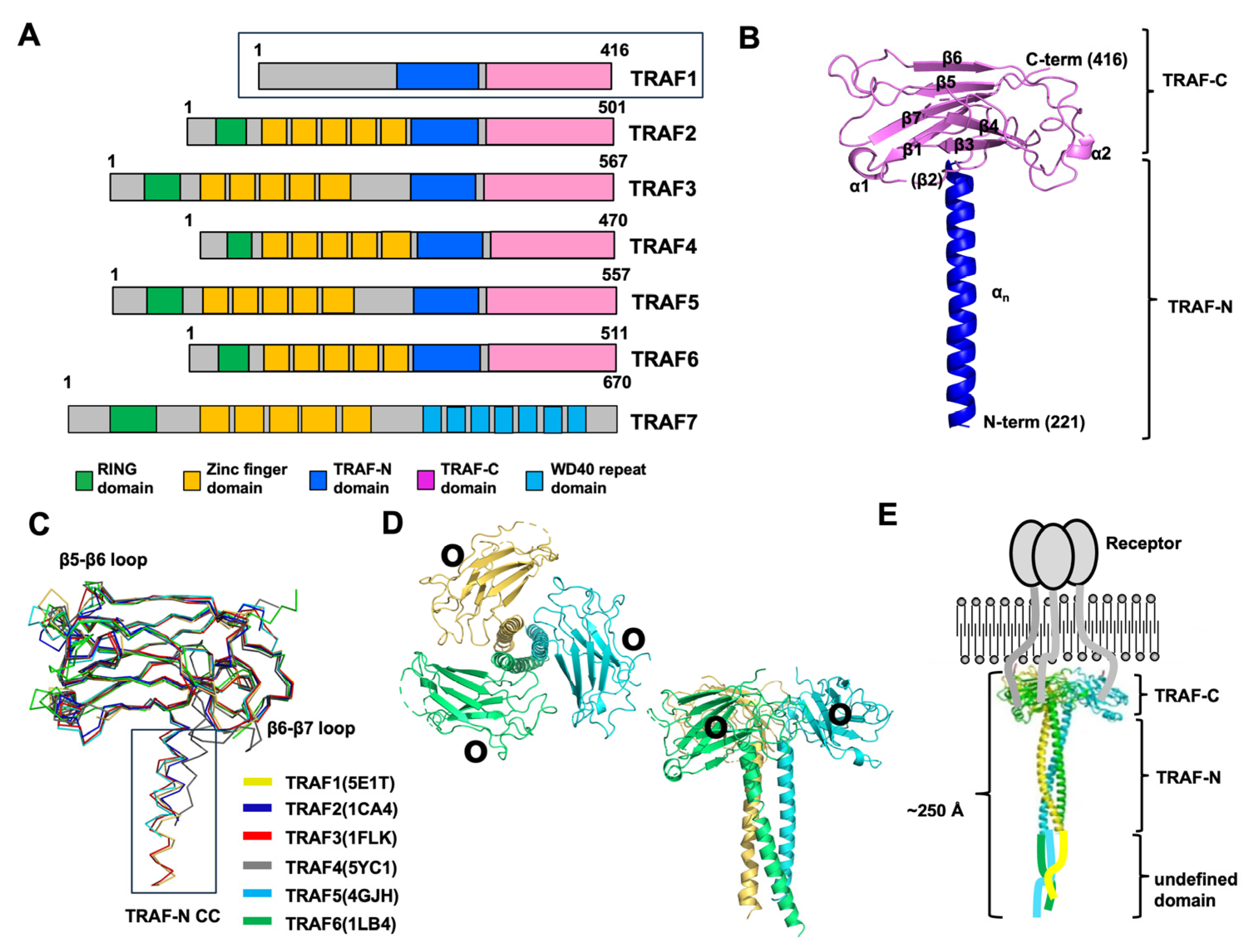
2. TRAF Domains and Structure
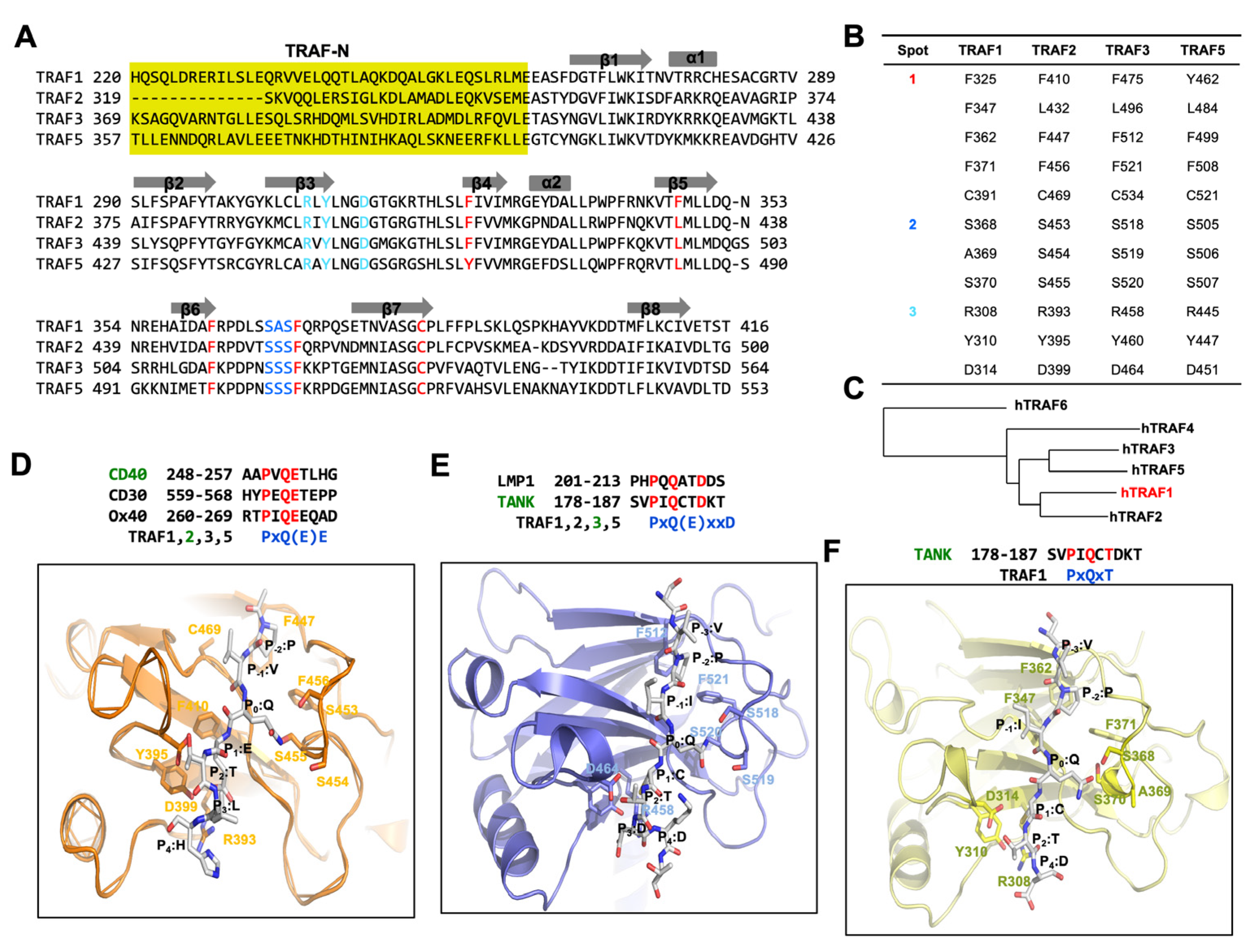
3. Understanding Receptor Interaction with TRAF Proteins
4. TRAF1 and Its Receptor Recognition
5. Concluding Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Arkee, T.; Bishop, G.A. TRAF family molecules in T cells: Multiple receptors and functions. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2020, 107, 907–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bishop, G.A. The multifaceted roles of TRAFs in the regulation of B-cell function. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2004, 4, 775–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wajant, H.; Henkler, F.; Scheurich, P. The TNF-receptor-associated factor family: Scaffold molecules for cytokine receptors, kinases and their regulators. Cell Signal 2001, 13, 389–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradley, J.R.; Pober, J.S. Tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factors (TRAFs). Oncogene 2001, 20, 6482–6491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deshaies, R.J.; Joazeiro, C.A. RING domain E3 ubiquitin ligases. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2009, 78, 399–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.D.; Sun, S.C. Targeting signaling factors for degradation, an emerging mechanism for TRAF functions. Immunol. Rev. 2015, 266, 56–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rothe, M.; Wong, S.C.; Henzel, W.J.; Goeddel, D.V. A novel family of putative signal transducers associated with the cytoplasmic domain of the 75 kDa tumor necrosis factor receptor. Cell 1994, 78, 681–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zapata, J.M.; Pawlowski, K.; Haas, E.; Ware, C.F.; Godzik, A.; Reed, J.C. TEFs: A diverse family of proteins containing TRAF domains. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 24242–24252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arch, R.H.; Gedrich, R.W.; Thompson, C.B. Tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factors (TRAFs)—A family of adapter proteins that regulates life and death. Genes Dev. 1998, 12, 2821–2830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, H.; Huang, J.; Shu, H.B.; Baichwal, V.; Goeddel, D.V. TNF-dependent recruitment of the protein kinase RIP to the TNF receptor-1 signaling complex. Immunity 1996, 4, 387–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.Y.; Regnier, C.H.; Kirschning, C.J.; Goeddel, D.V.; Rothe, M. Tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-mediated kinase cascades: Bifurcation of nuclear factor-kappaB and c-jun N-terminal kinase (JNK/SAPK) pathways at TNF receptor-associated factor 2. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 9792–9796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoeflich, K.P.; Yeh, W.C.; Yao, Z.; Mak, T.W.; Woodgett, J.R. Mediation of TNF receptor-associated factor effector functions by apoptosis signal-regulating kinase-1 (ASK1). Oncogene 1999, 18, 5814–5820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hacker, H.; Tseng, P.H.; Karin, M. Expanding TRAF function: TRAF3 as a tri-faced immune regulator. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 11, 457–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mu, Y.; Sundar, R.; Thakur, N.; Ekman, M.; Gudey, S.K.; Yakymovych, M.; Hermansson, A.; Dimitriou, H.; Bengoechea-Alonso, M.T.; Ericsson, J.; et al. TRAF6 ubiquitinates TGFbeta type I receptor to promote its cleavage and nuclear translocation in cancer. Nat. Commun. 2011, 2, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarez, S.E.; Harikumar, K.B.; Hait, N.C.; Allegood, J.; Strub, G.M.; Kim, E.Y.; Maceyka, M.; Jiang, H.; Luo, C.; Kordula, T.; et al. Sphingosine-1-phosphate is a missing cofactor for the E3 ubiquitin ligase TRAF2. Nature 2010, 465, 1084–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallabhapurapu, S.; Matsuzawa, A.; Zhang, W.; Tseng, P.H.; Keats, J.J.; Wang, H.; Vignali, D.A.; Bergsagel, P.L.; Karin, M. Nonredundant and complementary functions of TRAF2 and TRAF3 in a ubiquitination cascade that activates NIK-dependent alternative NF-kappaB signaling. Nat. Immunol. 2008, 9, 1364–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zapata, J.M.; Reed, J.C. TRAF1: Lord without a RING. Sci. STKE 2002, 2002, PE27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duckett, C.S.; Gedrich, R.W.; Gilfillan, M.C.; Thompson, C.B. Induction of nuclear factor kappaB by the CD30 receptor is mediated by TRAF1 and TRAF2. Mol. Cell Biol. 1997, 17, 1535–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.Y.; Mayo, M.W.; Korneluk, R.G.; Goeddel, D.V.; Baldwin, A.S., Jr. NF-kappaB antiapoptosis: Induction of TRAF1 and TRAF2 and c-IAP1 and c- IAP2 to suppress caspase-8 activation. Science 1998, 281, 1680–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.; Kabaleeswaran, V.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, G.; Wu, H. Crystal structures of the TRAF2: cIAP2 and the TRAF1: TRAF2: cIAP2 complexes: Affinity, specificity, and regulation. Mol. Cell 2010, 38, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.Y.; Li, Z.Z.; Jiang, D.S.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, K.; Zhang, X.F.; Liu, Y.; Fan, G.C.; Chen, Y.; et al. TRAF1 is a critical regulator of cerebral ischaemia-reperfusion injury and neuronal death. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, M.; Wang, P.X.; Wang, A.B.; Zhang, X.J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, P.; Mei, F.H.; Chen, M.H.; Li, H. Targeting hepatic TRAF1-ASK1 signaling to improve inflammation, insulin resistance, and hepatic steatosis. J. Hepatol. 2016, 64, 1365–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zapata, J.M.; Lefebvre, S.; Reed, J.C. Targeting TRAfs for therapeutic intervention. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2007, 597, 188–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arthur, J.F.; Shen, Y.; Gardiner, E.E.; Coleman, L.; Murphy, D.; Kenny, D.; Andrews, R.K.; Berndt, M.C. TNF receptor-associated factor 4 (TRAF4) is a novel binding partner of glycoprotein Ib and glycoprotein VI in human platelets. J. Thromb. Haemost. JTH 2011, 9, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhou, F.; Garcia de Vinuesa, A.; de Kruijf, E.M.; Mesker, W.E.; Hui, L.; Drabsch, Y.; Li, Y.; Bauer, A.; Rousseau, A.; et al. TRAF4 promotes TGF-beta receptor signaling and drives breast cancer metastasis. Mol. Cell 2013, 51, 559–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Starczynowski, D.T.; Lockwood, W.W.; Delehouzee, S.; Chari, R.; Wegrzyn, J.; Fuller, M.; Tsao, M.S.; Lam, S.; Gazdar, A.F.; Lam, W.L.; et al. TRAF6 is an amplified oncogene bridging the RAS and NF-kappaB pathways in human lung cancer. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 4095–4105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, P. TRAF molecules in cell signaling and in human diseases. J. Mol. Signal. 2013, 8, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, Y.C.; Burkitt, V.; Villa, A.R.; Tong, L.; Wu, H. Structural basis for self-association and receptor recognition of human TRAF2. Nature 1999, 398, 533–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, H.; Arron, J.R.; Lamothe, B.; Cirilli, M.; Kobayashi, T.; Shevde, N.K.; Segal, D.; Dzivenu, O.K.; Vologodskaia, M.; Yim, M.; et al. Distinct molecular mechanism for initiating TRAF6 signalling. Nature 2002, 418, 443–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, C.Z.; Welsh, K.; Leo, E.; Chiou, C.K.; Wu, H.; Reed, J.C.; Ely, K.R. Molecular basis for CD40 signaling mediated by TRAF3. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 10395–10399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.M.; Choi, J.Y.; Bhat, E.A.; Jeong, J.H.; Son, Y.J.; Kim, S.; Park, H.H. Crystal structure of TRAF1 TRAF domain and its implications in the TRAF1-mediated intracellular signaling pathway. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 25526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rousseau, A.; McEwen, A.G.; Poussin-Courmontagne, P.; Rognan, D.; Nomine, Y.; Rio, M.C.; Tomasetto, C.; Alpy, F. TRAF4 is a novel phosphoinositide-binding protein modulating tight junctions and favoring cell migration. PLoS Biol. 2013, 11, e1001726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, J.H.; Cho, Y.J.; Park, H.H. Structure of the TRAF4 TRAF domain with a coiled-coil domain and its implications for the TRAF4 signalling pathway. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2014, 70, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, F.; Ru, H.; Ding, W.; Ouyang, S.; Liu, Z.J. Structural biology study of human TNF receptor associated factor 4 TRAF domain. Protein Cell 2013, 4, 687–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Zhang, P.; Reichardt, A.; Liang, H.H.; Aliyari, R.; Cheng, D.; Wang, Y.Y.; Xu, F.; Cheng, G.H.; Liu, Y.F. Single Amino Acid Substitutions Confer the Antiviral Activity of the TRAF3 Adaptor Protein onto TRAF5. Sci. Signal 2012, 5, ra81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, C.M.; Son, Y.J.; Kim, S.; Kim, S.Y.; Park, H.H. Molecular basis for unique specificity of human TRAF4 for platelets GPIbbeta and GPVI. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 11422–11427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, J.Y.; Park, Y.C.; Ye, H.; Wu, H. All TRAFs are not created equal: Common and distinct molecular mechanisms of TRAF-mediated signal transduction. J. Cell Sci. 2002, 115, 679–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.H. Structure of TRAF Family: Current Understanding of Receptor Recognition. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, H.; Park, Y.C.; Kreishman, M.; Kieff, E.; Wu, H. The structural basis for the recognition of diverse receptor sequences by TRAF2. Mol. Cell 1999, 4, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.C.; Ye, H.; Hsia, C.; Segal, D.; Rich, R.L.; Liou, H.-L.; Myszka, D.G.; Wu, H. A novel mechanism of TRAF signaling revealed by structural and functional analyses of the TRADD-TRAF2 interaction. Cell 2000, 101, 777–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Ni, C.Z.; Havert, M.L.; Cabezas, E.; He, J.; Kaiser, D.; Reed, J.C.; Satterthwait, A.C.; Cheng, G.; Ely, K.R. Downstream regulator TANK binds to the CD40 recognition site on TRAF3. Structure 2002, 10, 403–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, C.M.; Jeong, J.H.; Son, Y.J.; Choi, J.H.; Kim, S.; Park, H.H. Molecular basis for TANK recognition by TRAF1 revealed by the crystal structure of TRAF1/TANK complex. FEBS Lett. 2017, 591, 810–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carpentier, I.; Beyaert, R. TRAF1 is a TNF inducible regulator of NF-kappaB activation. FEBS Lett. 1999, 460, 246–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.Y.; Choi, Y. TRAF1 and its biological functions. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2007, 597, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenfeld, H.; Takasaki, K.; Walsh, M.J.; Ersing, I.; Bernhardt, K.; Ma, Y.; Fu, B.; Ashbaugh, C.W.; Cabo, J.; Mollo, S.B.; et al. TRAF1 Coordinates Polyubiquitin Signaling to Enhance Epstein-Barr Virus LMP1-Mediated Growth and Survival Pathway Activation. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1004890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabbagh, L.; Pulle, G.; Liu, Y.; Tsitsikov, E.N.; Watts, T.H. ERK-dependent Bim modulation downstream of the 4-1BB-TRAF1 signaling axis is a critical mediator of CD8 T cell survival in vivo. J. Immunol. 2008, 180, 8093–8101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nocentini, G.; Riccardi, C. GITR: A modulator of immune response and inflammation. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2009, 647, 156–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.F.; Zhang, R.; Huang, L.; Wang, P.X.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, D.S.; Zhu, L.H.; Tian, S.; Zhang, X.D.; Li, H. TRAF1 is a key mediator for hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury. Cell Death Dis. 2014, 5, e1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abate, F.; Todaro, M.; van der Krogt, J.A.; Boi, M.; Landra, I.; Machiorlatti, R.; Tabbo, F.; Messana, K.; Abele, C.; Barreca, A.; et al. A novel patient-derived tumorgraft model with TRAF1-ALK anaplastic large-cell lymphoma translocation. Leukemia 2015, 29, 1390–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Xie, P.; Welsh, K.; Li, C.; Ni, C.Z.; Zhu, X.; Reed, J.C.; Satterthwait, A.C.; Bishop, G.A.; Ely, K.R. LMP1 protein from the Epstein-Barr virus is a structural CD40 decoy in B lymphocytes for binding to TRAF3. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 33620–33626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Li, C.; Wang, X.; He, F.; Sun, L.; Jiao, S.; Shi, W.; et al. Structural Insights into mitochondrial antiviral signaling protein (MAVS)-tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 6 (TRAF6) signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 26811–26820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jang, H.; Kim, S.; Kim, D.Y.; Han, J.H.; Park, H.H. TRAF1 from a Structural Perspective. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 510. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14050510
Jang H, Kim S, Kim DY, Han JH, Park HH. TRAF1 from a Structural Perspective. Biomolecules. 2024; 14(5):510. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14050510
Chicago/Turabian StyleJang, Hyunseok, Subin Kim, Do Yeon Kim, Ju Hee Han, and Hyun Ho Park. 2024. "TRAF1 from a Structural Perspective" Biomolecules 14, no. 5: 510. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14050510
APA StyleJang, H., Kim, S., Kim, D. Y., Han, J. H., & Park, H. H. (2024). TRAF1 from a Structural Perspective. Biomolecules, 14(5), 510. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14050510






