A Flavonoid Glycoside Compound from Siraitia grosvenorii with Anti-Inflammatory and Hepatoprotective Effects In Vitro
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
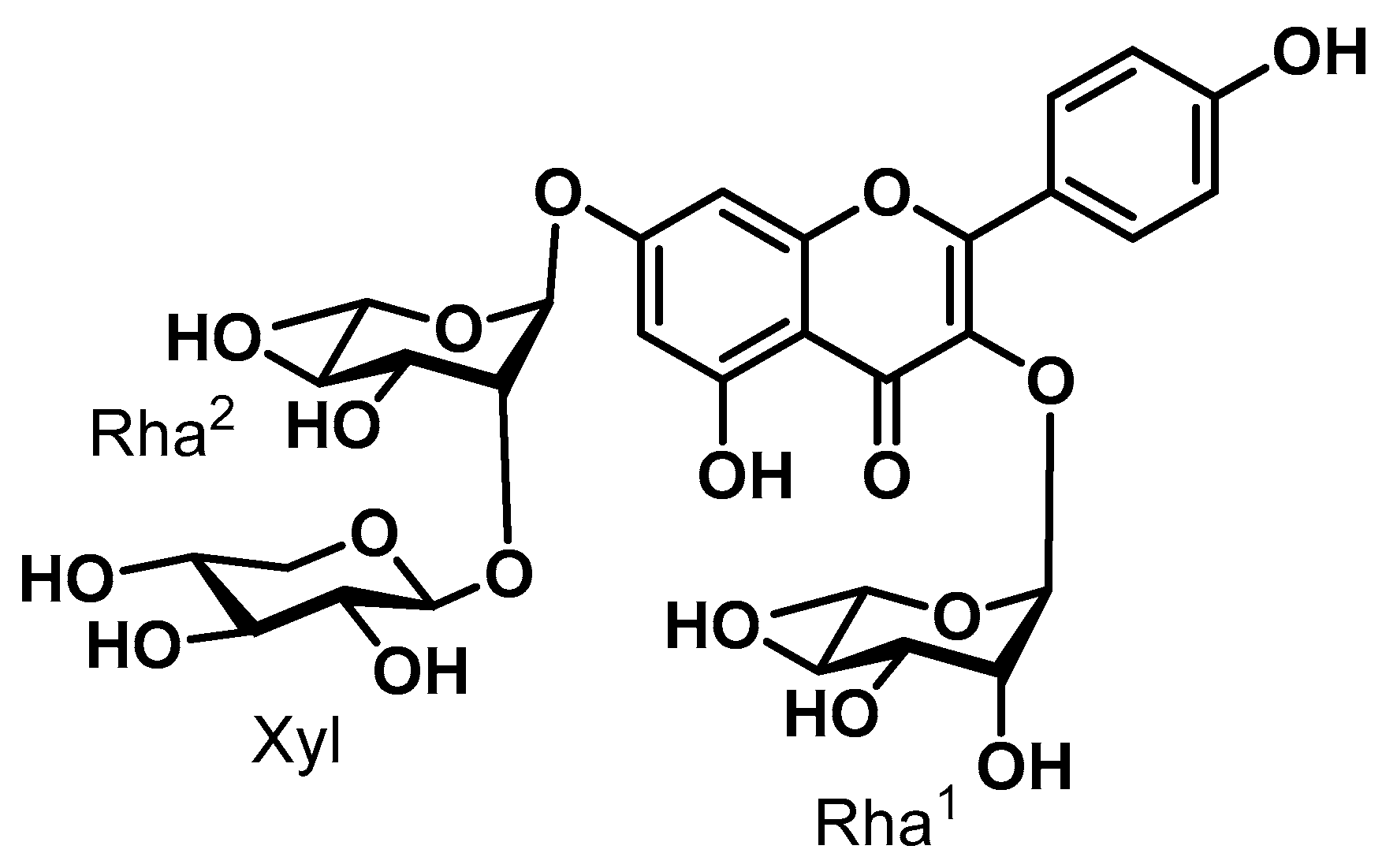
2.2. Isolation and Purification of SGPF
2.3. Cell Culture
2.4. Inhibited Proliferation Activity against MH-S and HepG2: Bioassay Cytotoxicity Analysis
2.5. Cytokine Analysis with ELISA Kits
2.6. Oil Red O Staining
2.7. Total Cholesterol and Total Triglyceride Levels in Cells
2.8. Intracellular GPx and SOD Content Test
2.9. Intracellular MDA Content Test
2.10. Intracellular Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) Level
2.11. Western Blot Analysis
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Results of CCK-8 Assay
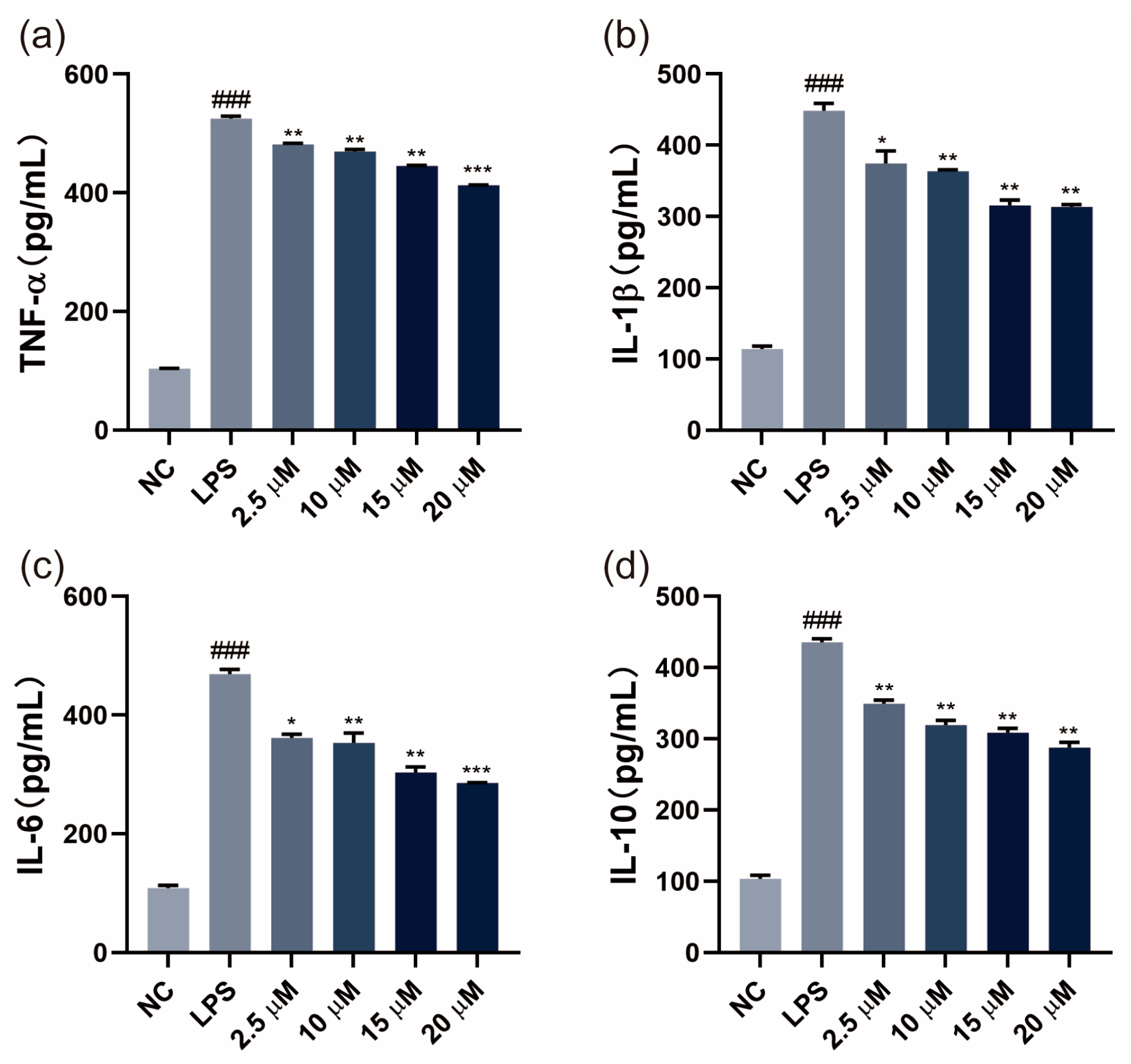
3.2. SGPF Inhibited LPS-Induced Inflammatory Cytokine Levels
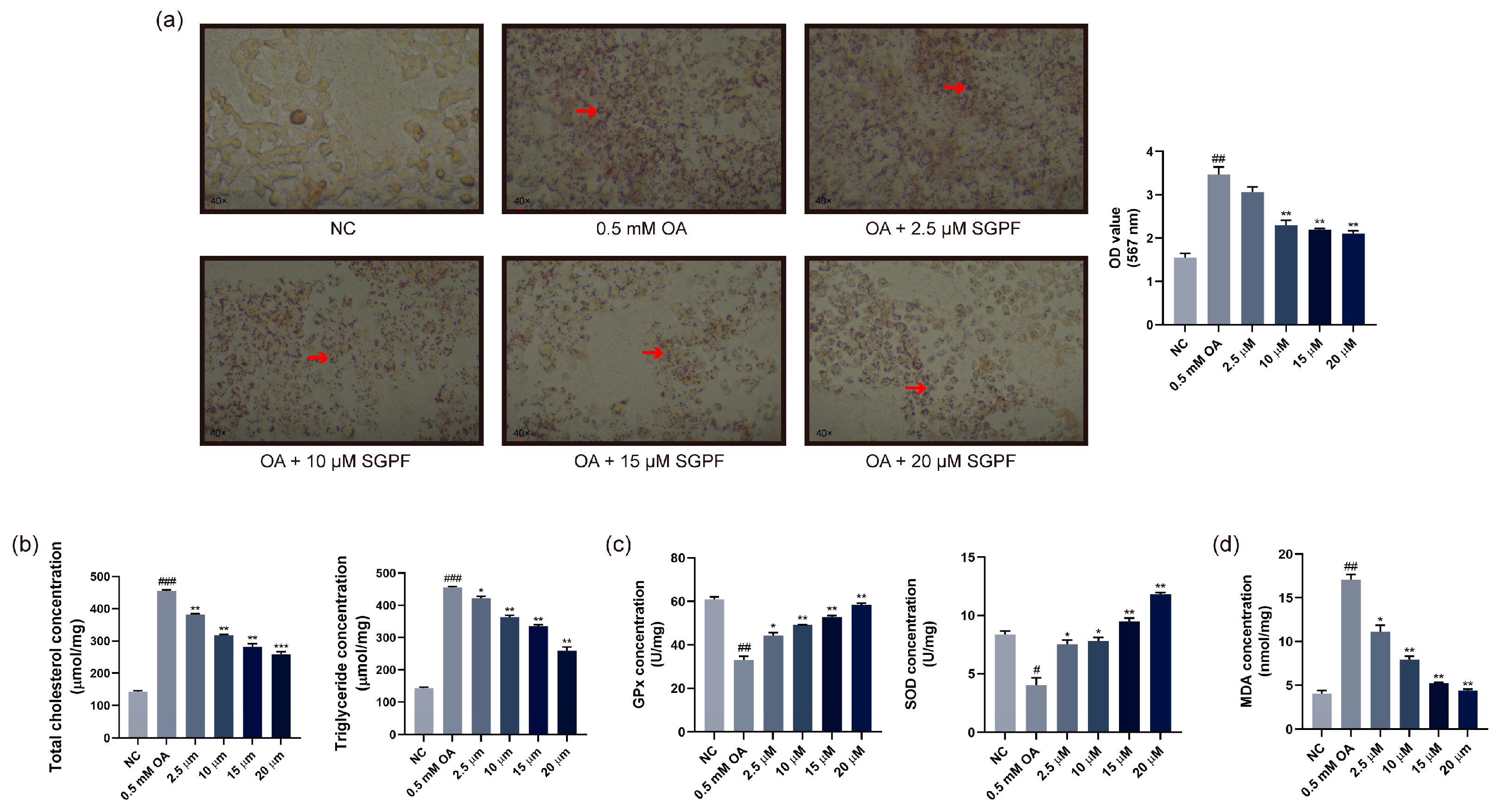
3.3. Lipid Droplet Accumulation in OA-Induced HepG2 Cells
3.4. Effect of SGPF on TC, TG, and Antioxidant Agent Levels in Cells
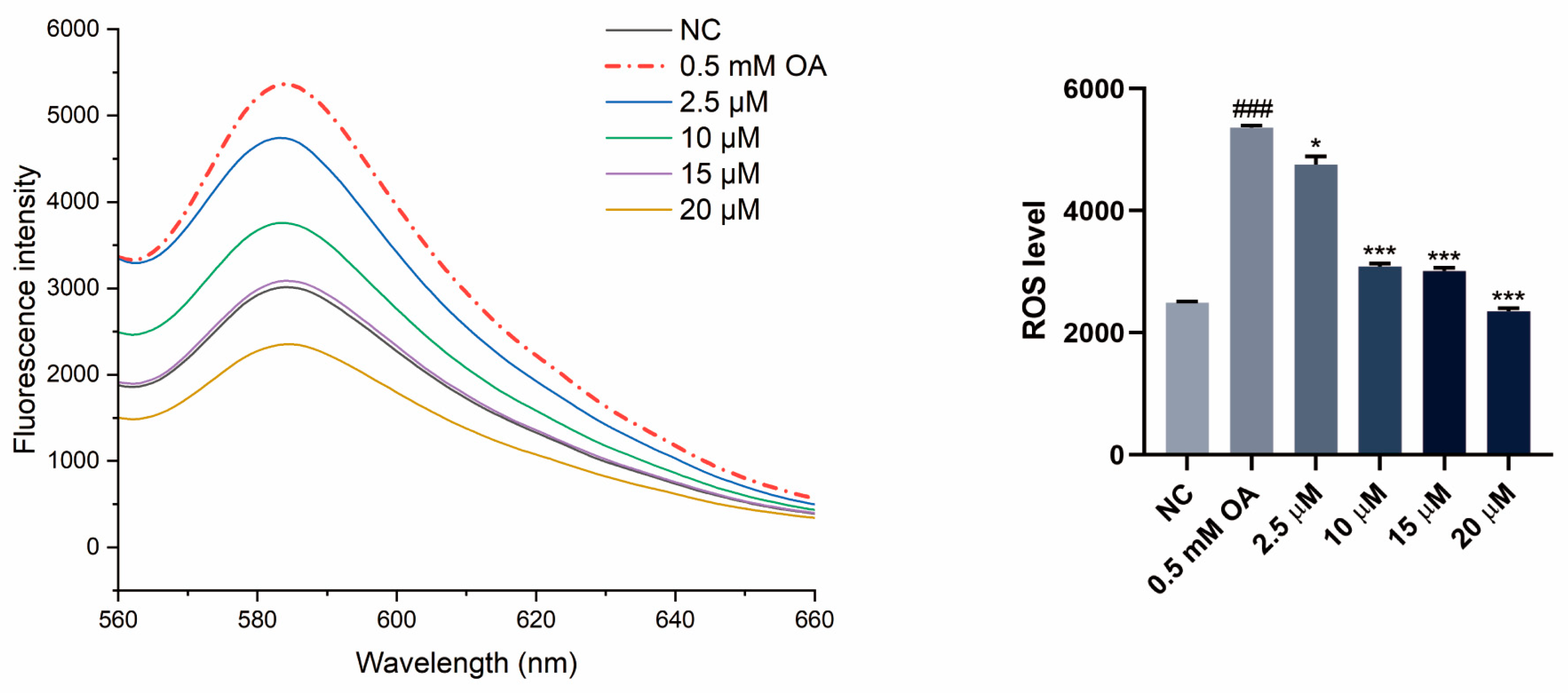
3.5. SGPF Inhibited OA-Induced Oxidative Stress in HepG2 Cells
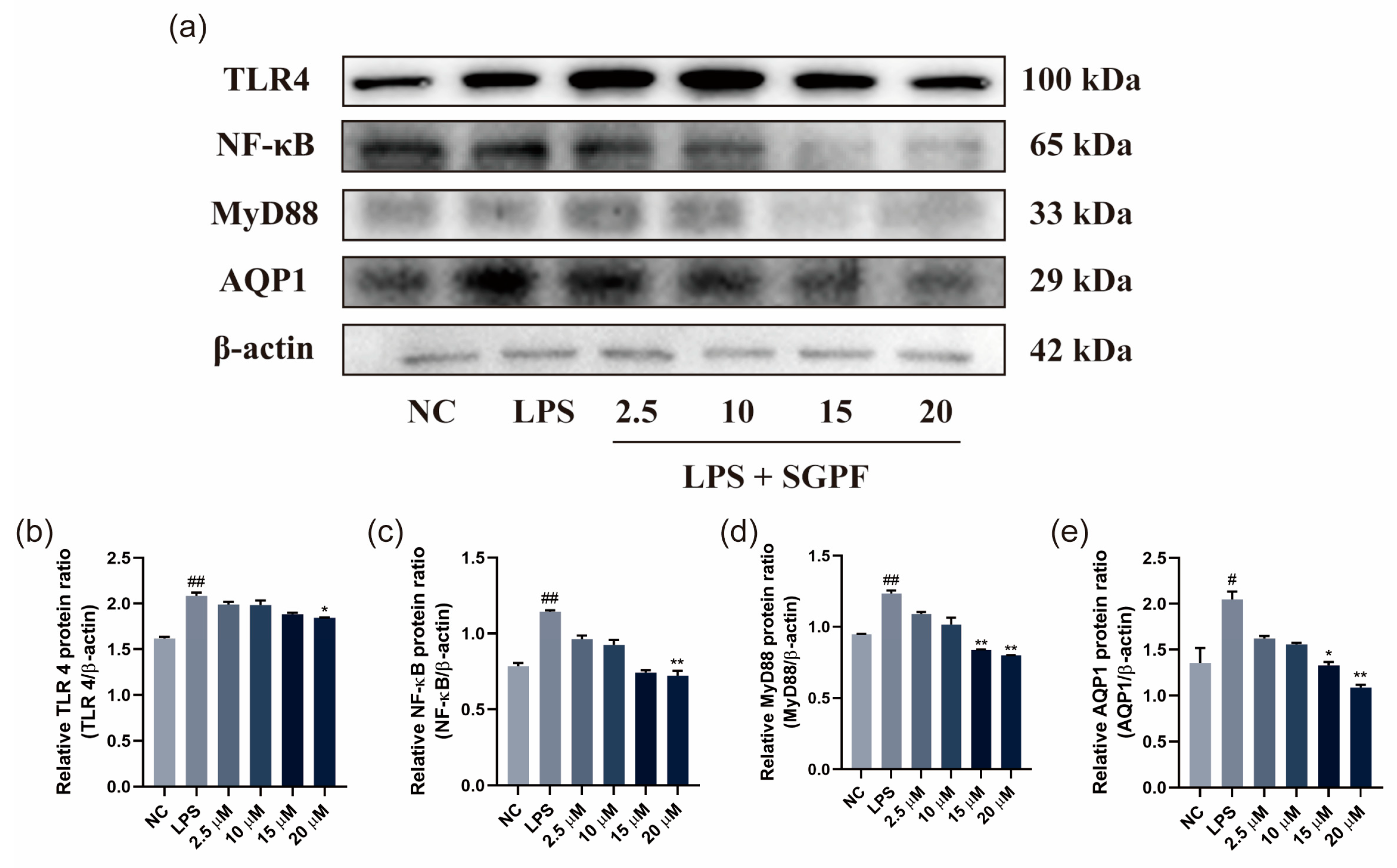
3.6. SGPF Treatment Suppressed TLR4/NF-κB/MyD88 Pathway Activation in LPS-Induced MH-S Cells
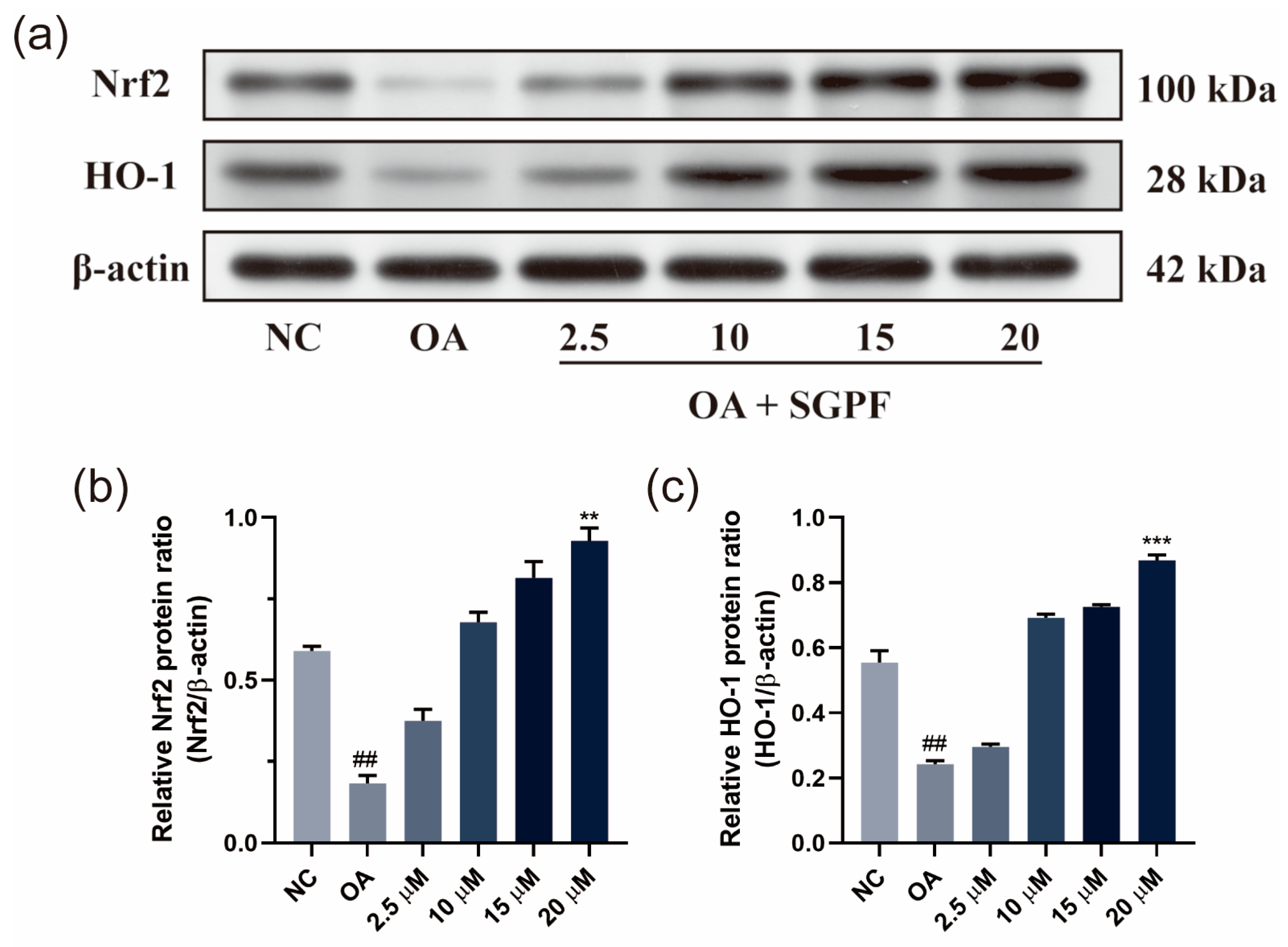
3.7. SGPF Treatment Increased Nrf2/HO-1 Pathway Activation in OA-Induced HepG2 Cells
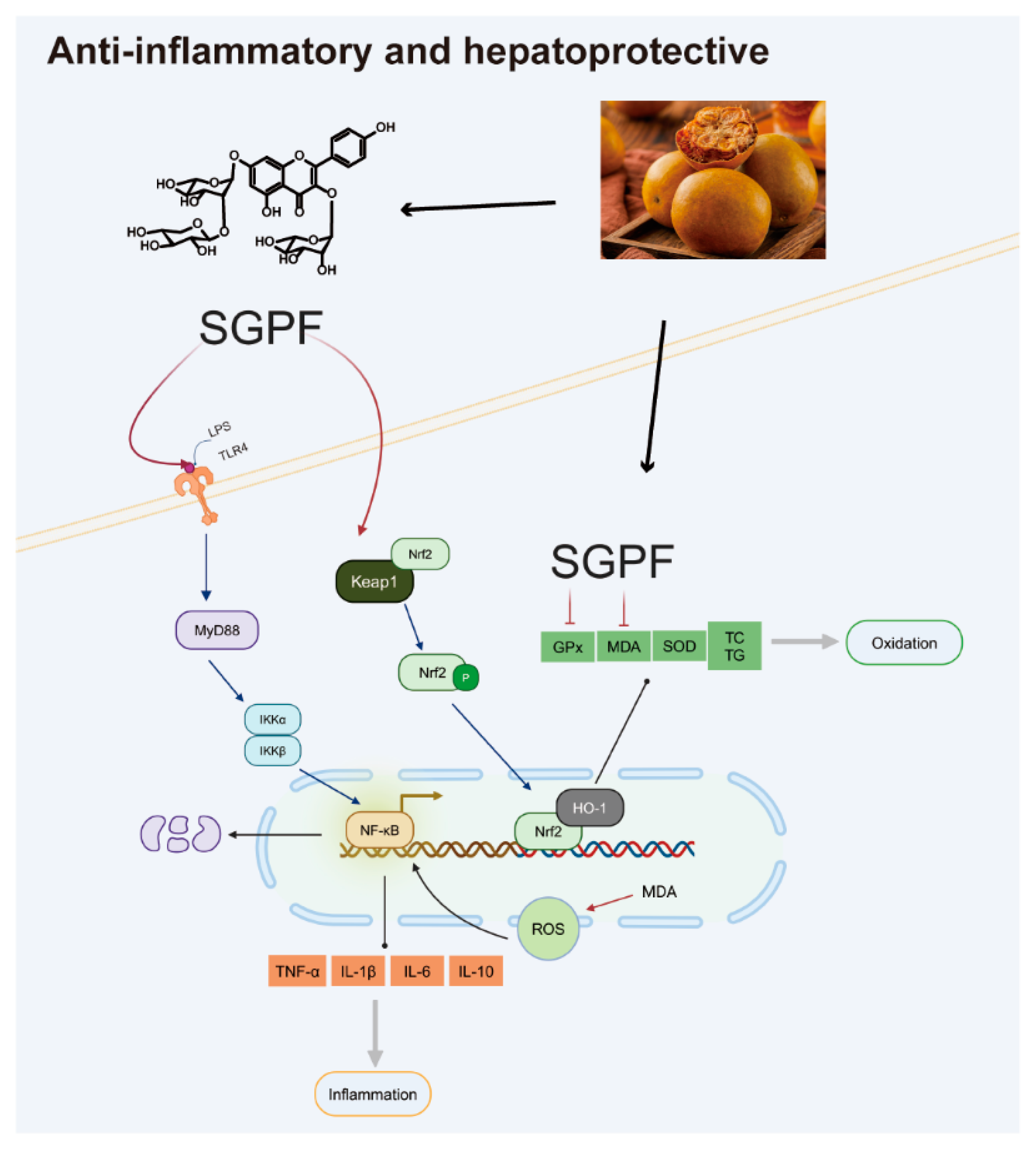
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
Abbreviations
| DCM | Dichloromethane | MDA | Malondialdehyde | RPMI | Roswell Park Memorial Institute |
| EA | Ethyl acetate | NAFLD | Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease | SGPF | Siraitia. grosvenorii pomace flavonoid |
| FBS | Fetal bovine serum | n-BuOH | n-Butanol | SOD | Superoxide dismutase |
| HO-1 | Heme oxygenase-1 | NC | Negative control | TLC | Thin-layer chromatography |
| IL-1β | Interleukin-1β | NHGR | S. grosvenorii residual extract | TNF-α | Tumor necrosis factor-α |
| IL-6 | Interleukin-6 | Nrf2 | Nuclear factor erythroid-2-related factor-2 | VEGF | Vascular endothelial growth factor |
| LPSs | Lipopolysaccharides | OA | Oil acid | ||
| MeOH | Methanol | PE | Petroleum benzin |
References
- Dinarello, C.A. Anti-Inflammatory Agents: Present and Future. Cell 2010, 140, 935–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berclaz, P.-Y.; Carey, B.; Fillipi, M.-D.; Wernke-Dollries, K.; Geraci, N.; Cush, S.; Richardson, T.; Kitzmiller, J.; O’Connor, M.; Hermoyian, C.; et al. GM-CSF Regulates a PU.1-Dependent Transcriptional Program Determining the Pulmonary Response to LPS. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2007, 36, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobbina, E.; Akhlaghi, F. Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)- Pathogenesis, Classification, and Effect on Drug Metabolizing Enzymes and Transporters. Drug Metab. Rev. 2017, 49, 197–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulet, B.; Staines, K.A. New Developments in Osteoarthritis and Cartilage Biology. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2016, 28, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchev, A.S.; Dimitrova, P.A.; Burns, A.J.; Kostov, R.V.; Dinkova-Kostova, A.T.; Georgiev, M.I. Oxidative Stress and Chronic Inflammation in Osteoarthritis: Can NRF2 Counteract These Partners in Crime?: The Regulatory Role of NRF2 in Osteoarthritis. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2017, 1401, 114–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yan, J.; Sun, C.; Li, G.; Li, S.; Zhang, L.; Di, C.; Gan, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, R.; et al. Ameliorating Mitochondrial Dysfunction Restores Carbon Ion-Induced Cognitive Deficits via Co-Activation of NRF2 and PINK1 Signaling Pathway. Redox Biol. 2018, 17, 143–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, X.; He, B.; Ning, Q.; Liu, Y.; Guo, J.; Niu, G.; Chen, M. Alantolactone Suppresses Inflammation, Apoptosis and Oxidative Stress in Cigarette Smoke-Induced Human Bronchial Epithelial Cells through Activation of Nrf2/HO-1 and Inhibition of the NF-κB Pathways. Respir. Res. 2020, 21, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Q.; Wang, T.; Wang, X.; Xu, H.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Shi, Q.; Liang, Q. Astragalin Suppresses Inflammatory Responses and Bone Destruction in Mice with Collagen-Induced Arthritis and in Human Fibroblast-like Synoviocytes. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, A.M.; Zhang, Z.Y. The Genus Siraitia Merr. in China. Guihaia 1984, 4, 27–33. [Google Scholar]
- Li, D.P.; Zhang, H.R. Studies and Uses of Chinese Medicine Luohanguo-a Special Local Product of Guangxi. Guihaia 2000, 20, 270–276. [Google Scholar]
- Sung, Y.Y.; Yuk, H.J.; Yang, W.K.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, D.S. Siraitia grosvenorii Residual Extract Attenuates Atopic Dermatitis by Regulating Immune Dysfunction and Skin Barrier Abnormality. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.J.; Jian, Y.Q.; Wang, H.Z.; Huang, H.X.; Gong, L.M.; Liu, G.G.; Yang, Y.P.; Wang, W. A Review of the Phytochemistry and Pharmacology of the Fruit of Siraitia grosvenorii (Swingle): A Traditional Chinese Medicinal Food. Molecules 2022, 27, 6618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, W.; Mao, J.H.; Chen, Q.J.; Ling, W.D.; Sun, Y.Q. Mogroside IIIE Alleviates High Glucose-Induced Inflammation, Oxidative Stress and Apoptosis of Podocytes by the Activation of AMPK/SIRT1 Signaling Pathway. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. Targets Ther. 2020, 13, 3821–3830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wei, M.; Wei, C. Preclinical In Silico Evidence Indicates the Pharmacological Targets and Mechanisms of Mogroside V in Patients With Ovarian Cancer and Coronavirus Disease 2019. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 845404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.H.; Zheng, W.F.; Wang, C.; Qi, J.M.; Li, H.B. Mogroside V Protects against Hepatic Steatosis in Mice on a High-Fat Diet and LO2 Cells Treated with Free Fatty Acids via AMPK Activation. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2020, 2020, 7826874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.B.; Zhuang, J.J.; Liu, J.H.; Lei, M.; Ma, L.; Chen, J.; Shen, X.; Hu, L.H. Potential AMPK Activators of Cucurbitane Triterpenoids from Siraitia grosvenorii Swingle. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2011, 19, 5776–5781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banno, A.; Reddy, A.T.; Lakshmi, S.P.; Reddy, R.C. Bidirectional Interaction of Airway Epithelial Remodeling and Inflammation in Asthma. Clin. Sci. 2020, 134, 1063–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Yao, Q.; Teng, F.; Cui, J.; Dong, J.; Wei, Y. Active Ingredients from Chinese Medicine Plants as Therapeutic Strategies for Asthma: Overview and Challenges. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 137, 111383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Qian, B.; Pan, C.; Lv, F.; Wang, H.; Gao, Y.; Zhou, Y. Protective Activity of Mogroside V against Ovalbumin-induced Experimental Allergic Asthma in Kunming Mice. J. Food Biochem. 2019, 43, e12973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Y.; Li, X.; Xu, F.; Zhao, S.; Wu, X.; Wang, Y.; Xie, J. Kaempferol Alleviates Murine Experimental Colitis by Restoring Gut Microbiota and Inhibiting the LPS-TLR4-NF-κB Axis. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 679897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maleki, S.J.; Crespo, J.F.; Cabanillas, B. Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Flavonoids. Food Chem. 2019, 299, 125124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbawuike, I.N.; Herscowitz, H.B. MH-S, a Murine Alveolar Macrophage Cell Line: Morphological, Cytochemical, and Functional Characteristics. J. Leukoc. Biol. 1989, 46, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, Y.; Liu, H.; Wang, D.; Liu, T.; Zhang, R.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Han, J.; Liu, M. Antioxidant Activity, Stability, in Vitro Digestion and Cytotoxicity of Two Dietary Polyphenols Co-Loaded by β-Lactoglobulin. Food Chem. 2022, 371, 131385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, J.; Dai, W.; Zheng, Y.; Zhao, S. miR-122 Promotes Hepatic Lipogenesis via Inhibiting the LKB1/AMPK Pathway by Targeting Sirt1 in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Mol. Med. 2019, 25, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, D.; Zheng, M.; Wang, Y.; Liu, C.; Chen, S. Protective Effects and Mechanisms of Mogroside V on LPS-Induced Acute Lung Injury in Mice. Pharm. Biol. 2014, 52, 729–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, C.L.; Zhang, Q.Q.; Zhang, S.H. Mogroside IIIE Attenuates Gestational Diabetes Mellitus through Activating of AMPK Signaling Pathway in Mice. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2018, 138, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, J.R. TNF-Mediated Inflammatory Disease. J. Pathol. 2008, 214, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Cong, M.; Li, J.; He, D.; Wu, Q.; Tian, P.; Wang, Y.; Yang, S.; Liang, C.; Liang, Y.; et al. Cathepsin C Promotes Breast Cancer Lung Metastasis by Modulating Neutrophil Infiltration and Neutrophil Extracellular Trap Formation. Cancer Cell 2021, 39, 423–437.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Liu, Y.; Wang, C.; Guo, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Qian, H.; Zhao, Y. Lycopene-Loaded Bilosomes Ameliorate High-Fat Diet-Induced Chronic Nephritis in Mice through the TLR4/MyD88 Inflammatory Pathway. Foods 2022, 11, 3042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Zeng, M.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, R.; Jia, J.; Cao, B.; Liu, M.; Guo, P.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, X.; et al. Ephedrae Herba Polysaccharides Inhibit the Inflammation of Ovalbumin Induced Asthma by Regulating Th1/Th2 and Th17/Treg Cell Immune Imbalance. Mol. Immunol. 2022, 152, 14–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Park, J.; Roh, Y. Molecular Insights into the Role of Mitochondria in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2019, 42, 935–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Wang, T.; Liu, P.; Yang, F.; Wang, X.; Zheng, W.; Sun, W. Hesperetin Ameliorates Hepatic Oxidative Stress and Inflammation via the PI3K/AKT-Nrf2-ARE Pathway in Oleic Acid-Induced HepG2 Cells and a Rat Model of High-Fat Diet-Induced NAFLD. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 3898–3918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arab, J.P.; Arrese, M.; Trauner, M. Recent Insights into the Pathogenesis of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Annu. Rev. Pathol. Mech. Dis. 2018, 13, 321–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, Y.; Pan, X.; Luo, J.; Xiao, X.; Li, J.; Bestman, P.L.; Luo, M. Association of Inflammatory Cytokines with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 880298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, G.; Xie, Z.; Li, E.; Yuan, Y.; Fu, Y.; Wang, P.; Zhang, X.; Qiao, Y.; Xu, J.; Hölscher, C.; et al. Dehydroabietic Acid Improves Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease through Activating the Keap1/Nrf2-ARE Signaling Pathway to Reduce Ferroptosis. J. Nat. Med. 2021, 75, 540–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.; Jiang, Z.; Li, C.; Zhu, Y.; Li, Z.; Tang, Y.; Ni, C. Apigenin Prevents Metabolic Syndrome in High-Fructose Diet-Fed Mice by Keap1-Nrf2 Pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 105, 1283–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biao, Y.; Chen, J.; Liu, C.; Wang, R.; Han, X.; Li, L.; Zhang, Y. Protective Effect of Danshen Zexie Decoction against Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease through Inhibition of ROS/NLRP3/IL-1β Pathway by Nrf2 Signaling Activation. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 877924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iida, K.; Itoh, K.; Kumagai, Y.; Oyasu, R.; Hattori, K.; Kawai, K.; Shimazui, T.; Akaza, H.; Yamamoto, M. Nrf2 Is Essential for the Chemopreventive Efficacy of Oltipraz against Urinary Bladder Carcinogenesis. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 6424–6431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, E.; Sato, Y.; Minagawa, A.; Okuyama, R. Pathogenesis of Psoriasis and Development of Treatment. J. Dermatol. 2018, 45, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, J.; Huang, H.; Gong, L.; Tian, X.; Peng, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, W. A Flavonoid Glycoside Compound from Siraitia grosvenorii with Anti-Inflammatory and Hepatoprotective Effects In Vitro. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 450. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14040450
Wu J, Huang H, Gong L, Tian X, Peng Z, Zhu Y, Wang W. A Flavonoid Glycoside Compound from Siraitia grosvenorii with Anti-Inflammatory and Hepatoprotective Effects In Vitro. Biomolecules. 2024; 14(4):450. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14040450
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Juanjiang, Huaxue Huang, Limin Gong, Xing Tian, Zhi Peng, Yizhun Zhu, and Wei Wang. 2024. "A Flavonoid Glycoside Compound from Siraitia grosvenorii with Anti-Inflammatory and Hepatoprotective Effects In Vitro" Biomolecules 14, no. 4: 450. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14040450
APA StyleWu, J., Huang, H., Gong, L., Tian, X., Peng, Z., Zhu, Y., & Wang, W. (2024). A Flavonoid Glycoside Compound from Siraitia grosvenorii with Anti-Inflammatory and Hepatoprotective Effects In Vitro. Biomolecules, 14(4), 450. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14040450






