Role of the Unique Secreted Peptide Adropin in Various Physiological and Disease States
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Sex Hormones and Adropin
1.2. Adropin and Hypertensive Disorders Complicating Pregnancy and Gestational Diabetes Mellitus
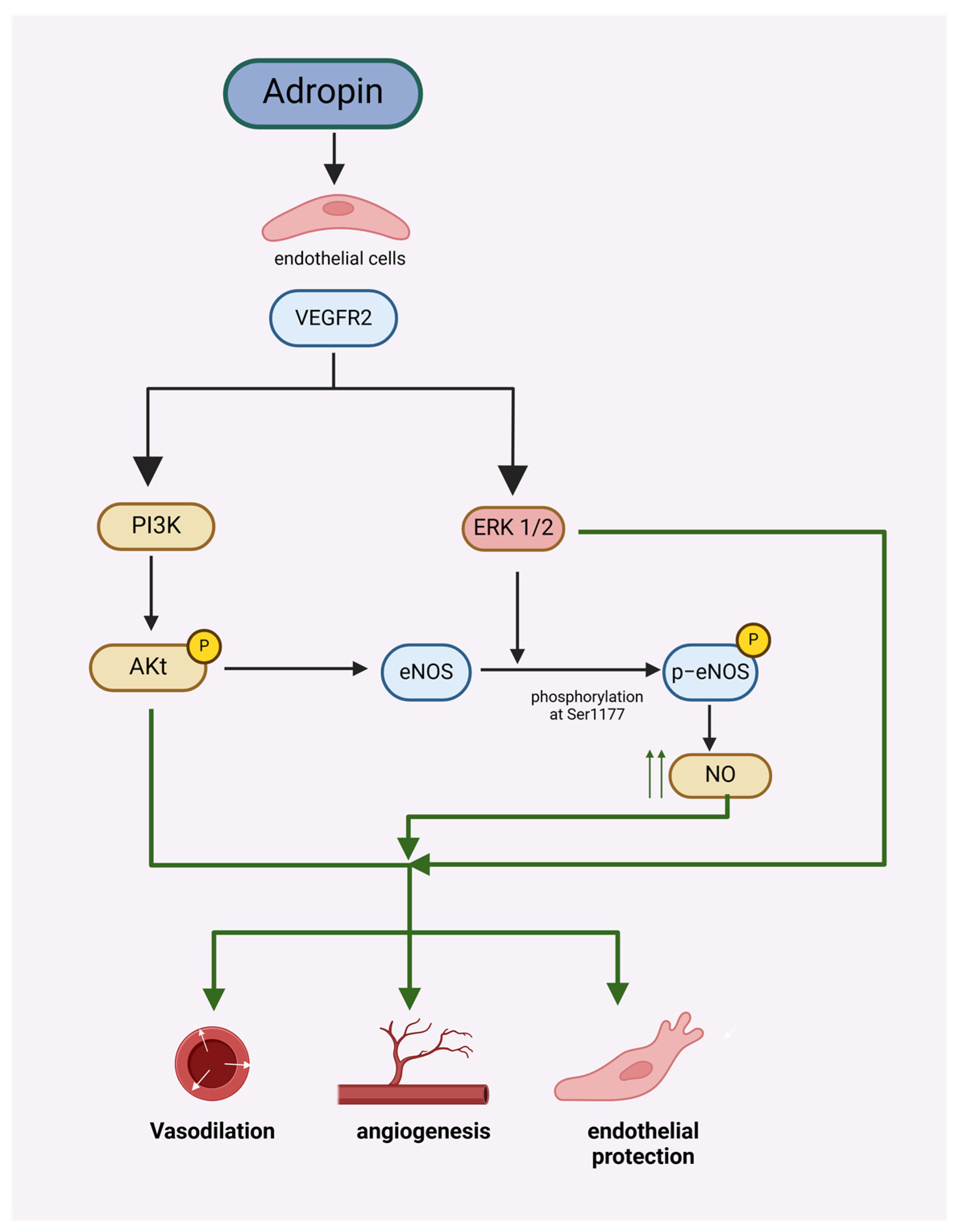
1.3. Adropin and Coronary Artery Diseases
1.4. Adropin’s Role in Hypertension
1.5. Adropin’s Role in Atherosclerosis
1.6. Adropin’s Role in Obesity
1.7. Adropin’s Role in Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA)
1.8. Adropin’s Role in DM
1.9. Endothelial Dysfunction in T2DM
1.10. DM Nephropathy and Retinopathy
1.11. Adropin and Hepatic Diseases
1.12. Adropin and Renal Diseases
1.13. Nutrition and Exercise Effects on Adropin
1.14. Adropin and Neurological Disorders
1.15. Adropin and Neurodegenerative Diseases
1.16. Adropin and Ischemic Stroke
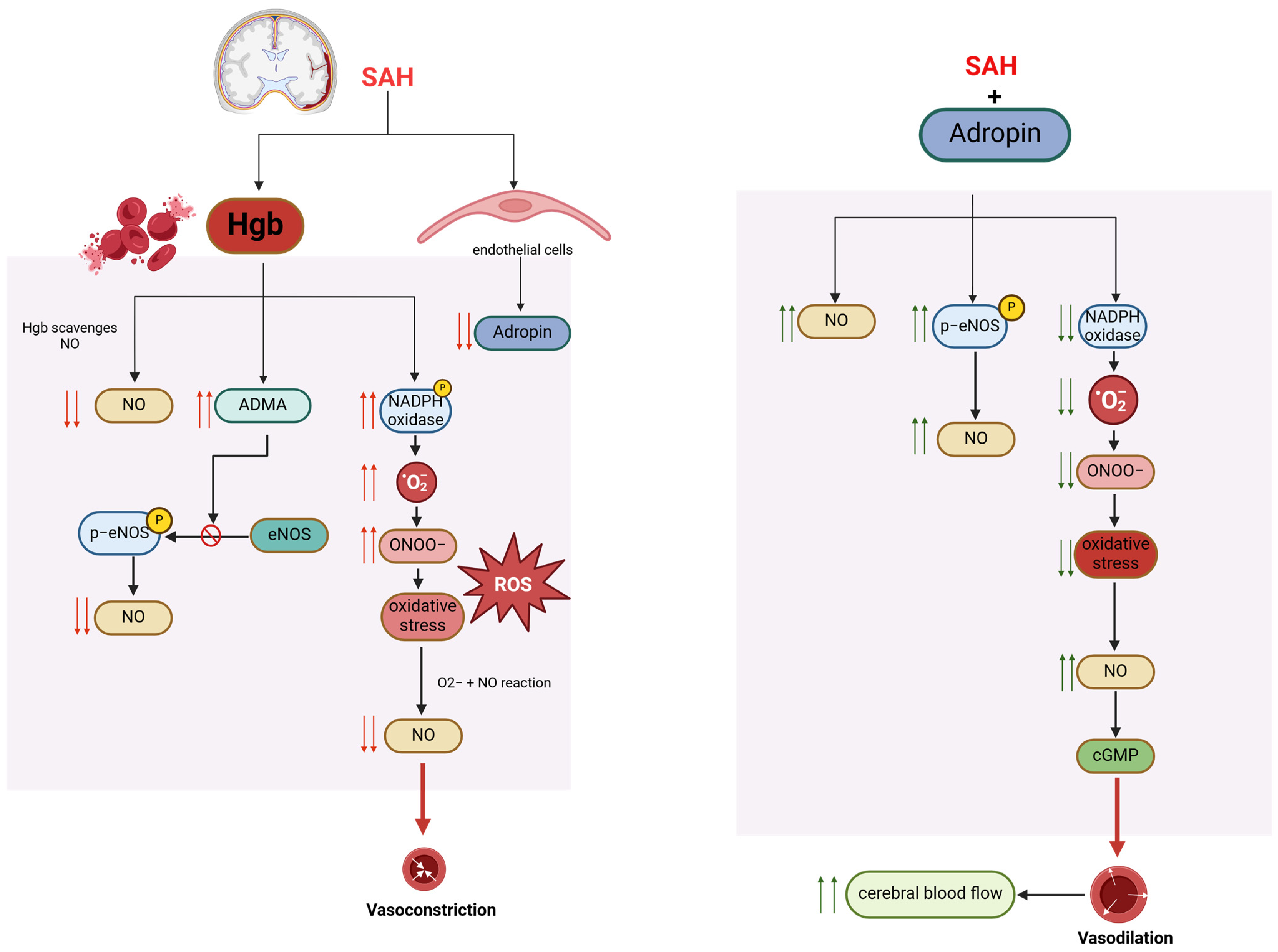
1.17. Adropin and Subarachnoid Hemorrhage
2. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kumar, K.G.; Trevaskis, J.L.; Lam, D.D.; Sutton, G.M.; Koza, R.A.; Chouljenko, V.N.; Kousoulas, K.G.; Rogers, P.M.; Kesterson, R.A.; Thearle, M.; et al. Identification of Adropin as a Secreted Factor Linking Dietary Macronutrient Intake with Energy Homeostasis and Lipid Metabolism. Cell Metab. 2008, 8, 468–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swarup, S.; Ahmed, I.; Grigorova, Y.; Zeltser, R. Metabolic Syndrome; StatPearls: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Mathers, C.D.; Loncar, D. Projections of Global Mortality and Burden of Disease from 2002 to 2030. PLoS Med. 2006, 3, e442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.; Guo, S.; Niu, Y.; Yang, L.; Liu, B.; Jiang, N.; Su, M.; Wang, L. Heat-shock protein 60 of Porphyromonas gingivalis may induce dysfunction of human umbilical endothelial cells via regulation of endothelial-nitric oxide synthase and vascular endothelial-cadherin. Biomed. Rep. 2016, 5, 243–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baron, A.D. Insulin resistance and vascular function. J. Diabetes Complicat. 2002, 16, 92–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mather, K.J.; Lteif, A.; Steinberg, H.O.; Baron, A.D. Interactions Between Endothelin and Nitric Oxide in the Regulation of Vascular Tone in Obesity and Diabetes. Diabetes 2004, 53, 2060–2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinberg, H.O.; Baron, A.D. Vascular function, insulin resistance and fatty acids. Diabetologia 2002, 45, 623–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lovren, F.; Pan, Y.; Quan, A.; Singh, K.K.; Shukla, P.C.; Gupta, M.; Al-Omran, M.; Teoh, H.; Verma, S. Adropin Is a Novel Regulator of Endothelial Function. Circulation 2010, 122, S185–S192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Wu, Q.; Ding, Q.; Wu, W.; Li, Q.; Zheng, Z. High Level of Adropin Promotes the Progression of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2024, 24, 629–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydin, S.; Kuloglu, T.; Aydin, S.; Eren, M.N.; Yilmaz, M.; Kalayci, M.; Sahin, I.; Kocaman, N.; Citil, C.; Kendir, Y. Expression of adropin in rat brain, cerebellum, kidneys, heart, liver, and pancreas in streptozotocin-induced diabetes. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2013, 380, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Price, C.A.; Stevens, J.R.; Graham, J.L.; Stanhope, K.L.; King, S.; Krauss, R.M.; Bremer, A.A.; Havel, P.J. Low plasma adropin concentrations increase risks of weight gain and metabolic dysregulation in response to a high-sugar diet in male nonhuman primates. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 9706–9719. [Google Scholar]
- Mierzwicka, A.; Bolanowski, M. New peptides players in metabolic disorders. Postepy Hig. Med. Dosw. 2016, 70, 881–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stokar, J.; Gurt, I.; Cohen-Kfir, E.; Yakubovsky, O.; Hallak, N.; Benyamini, H.; Lishinsky, N.; Offir, N.; Tam, J.; Dresner-Pollak, R. Hepatic adropin is regulated by estrogen and contributes to adverse metabolic phenotypes in ovariectomized mice. Mol. Metab. 2022, 60, 101482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meda, C.; Barone, M.; Mitro, N.; Lolli, F.; Pedretti, S.; Caruso, D.; Maggi, A.; Della Torre, S. Hepatic ERα accounts for sex differences in the ability to cope with an excess of dietary lipids. Mol. Metab. 2020, 32, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meda, C.; Dolce, A.; Vegeto, E.; Maggi, A.; Della Torre, S. ERα-Dependent Regulation of Adropin Predicts Sex Differences in Liver Homeostasis during High-Fat Diet. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shrivastava, S.; Conigliaro, R.L. Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome. Med. Clin. N. Am. 2023, 107, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kume, T.; Calan, M.; Yilmaz, O.; Kocabas, G.U.; Yesil, P.; Temur, M.; Bicer, M.; Calan, O.G. A possible connection between tumor necrosis factor alpha and adropin levels in polycystic ovary syndrome. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2016, 39, 747–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inal, Z.O.; Erdem, S.; Gederet, Y.; Duran, C.; Kucukaydin, Z.; Kurku, H.; Sakarya, D.K. The impact of serum adropin and ischemia modified albumin levels based on BMI in PCOS. Endokrynol. Pol. 2018, 69, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bousmpoula, A.; Kouskouni, E.; Benidis, E.; Demeridou, S.; Kapeta-Kourkouli, R.; Chasiakou, A.; Baka, S. Adropin levels in women with polycystic ovaries undergoing ovarian stimulation: Correlation with lipoprotein lipid profiles. Gynecol. Endocrinol. 2018, 34, 153–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuliczkowska-Płaksej, J.; Mierzwicka, A.; Jończyk, M.; Stachowska, B.; Urbanovych, A.; Bolanowski, M. Adropin in women with polycystic ovary syndrome. Endokrynol. Pol. 2019, 70, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziarniak, K.; Dudek, M.; Matuszewska, J.; Bijoch, Ł.; Skrzypski, M.; Celichowski, J.; Sliwowska, J.H. Two weeks of moderate intensity locomotor training increased corticosterone concentrations but did not alter the number of adropin-immunoreactive cells in the hippocampus of diabetic type 2 and control rats. Acta Histochem. 2021, 123, 151751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ke, Y.; Hu, J.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chen, S.; Liu, S. Correlation Between Circulating Adropin Levels and Patients with PCOS: An Updated Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Reprod. Sci. 2022, 29, 3295–3310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muter, J.; Alam, M.T.; Vrljicak, P.; Barros, F.S.V.; Ruane, P.T.; Ewington, L.J.; Aplin, J.D.; Westwood, M.; Brosens, J.J. The Glycosyltransferase EOGT Regulates Adropin Expression in Decidualizing Human Endometrium. Endocrinology 2018, 159, 994–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cakmak, B.D.; Dundar, B.; Acikgoz, A.S.; Ozgen, G.; Cift, T.; Ahmedian, R.; Altekin, Y. The relationship between maternal and umbilical cord adropin levels with the presence and severity of preeclampsia. J. Perinat. Med. 2017, 45, 879–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karaca, E.; Ercan, C.C.; Akdemir, C.; Sivrikoz, T.S.; Salmaslioglu, A.; Verit, F.F.; Gurdol, F.; Omer, B. The Evaluation of Adropin and Autotaxin as Potential Markers of Endothelial Dysfunction in Preeclampsia. Angiology 2023, 17, 33197231183228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Gao, B.; Wu, Z.; Wang, H.; Dong, M. Alteration of serum adropin level in preeclampsia. Pregnancy Hypertens. 2017, 8, 6–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aydin, H.I.; Eser, A.; Kaygusuz, I.; Yildirim, S.; Celik, T.; Gunduz, S.; Kalman, S. Adipokine, adropin and endothelin-1 levels in intrauterine growth restricted neonates and their mothers. J. Perinat. Med. 2016, 44, 669–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baka, S.; Malamitsi-Puchner, A.; Briana, D.D.; Boutsikou, M.; Marmarinos, A.; Gourgiotis, D.; Boutsikou, T. Adropin concentrations in term pregnancies with normal, restricted and increased fetal growth. J. Matern. Neonatal Med. 2016, 29, 2403–2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Z.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, J. Hepatokine levels during the first or early second trimester of pregnancy and the subsequent risk of gestational diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Biomarkers 2021, 26, 517–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vivek, K.; Reddy, E.P.; Thangappazham, B.; Raj, H.; Pérez-López, F.R.; Varikasuvu, S.R. Maternal adropin levels in patients with gestational diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Gynecol. Endocrinol. 2022, 38, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamczak, L.; Mantaj, U.; Gutaj, P.; Skrypnik, D.; Ozegowski, S.; Bogdanski, P.; Wender-Ozegowska, E. Adropin as a potential protective factor of metabolic complications in obese pregnant women with hyperglycaemia diagnosed in early pregnancy. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2023, 74, 11–19. [Google Scholar]
- Celik, E.; Yilmaz, E.; Celik, O.; Ulas, M.; Turkcuoglu, I.; Karaer, A.; Simsek, Y.; Minareci, Y.; Aydin, S. Maternal and fetal adropin levels in gestational diabetes mellitus. J. Perinat. Med. 2013, 41, 375–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beigi, A.; Shirzad, N.; Nikpour, F.; Esfahani, E.N.; Emamgholipour, S.; Bandarian, F. Association between serum adropin levels and gestational diabetes mellitus; a case–control study. Gynecol. Endocrinol. 2015, 31, 939–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dincer, E.; Topçuoğlu, S.; Arman, D.; Kaya, A.; Yavuz, T.; Karatekin, G. Inflammation Markers in Infants of Mothers with Gestational Diabetes. Fetal Pediatr. Pathol. 2022, 41, 616–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, X.; He, J.R.; Zhao, M.G.; Kuang, Y.S.; Xu, S.Q.; Zhang, H.Z.; Hu, S.P.; Chen, J.; Xia, H.M. Relationship between human cord blood adropin levels and fetal growth. Peptides 2014, 52, 19–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celik, A.; Balin, M.; Kobat, M.A.; Erdem, K.; Baydas, A.; Bulut, M.; Altas, Y.; Aydin, S.; Aydin, S. Deficiency of a new protein associated with cardiac syndrome X; called adropin. Cardiovasc. Ther. 2013, 31, 174–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.-Y.; Zhao, P.; Wu, M.-C.; Liu, J.; Yin, W. Serum adropin levels are decreased in patients with acute myocardial infarction. Regul. Pept. 2014, 190–191, 46–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Zhao, L.; Xu, W.; Li, J.; Wang, B.; Gu, X.; Chen, J. Correlation of serum adropin level with coronary artery disease. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi 2014, 94, 1255–1257. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Akkaya, H.; Güntürk, E.E.; Akkaya, F.; Karabıyık, U.; Güntürk, İ.; Yılmaz, S. Assessment of the Relationship Between the Adropin Levels and the Coronary Collateral Circulation in Patients wıth Chronic Coronary Syndrome. Arq. Bras. Cardiol. 2022, 119, 402–410. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gulen, B.; Eken, C.; Kucukdagli, O.T.; Serinken, M.; Kocyigit, A.; Kılıc, E.; Uyarel, H. Adropin levels and target organ damage secondary to high blood pressure in the ED. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2016, 34, 2061–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, X.; Cao, Y.; Han, W.; Guo, Y.; Yang, G.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, P. Association of polymorphisms of preptin, irisin and adropin genes with susceptibility to coronary artery disease and hypertension. Medicine 2020, 99, e19365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Hu, D.; Chen, G.; Zheng, D.; Li, S.; Lin, Y.; Hong, H.; Luo, Y.; Ke, Y.; Huang, Y.; et al. Adropin-based dual treatment enhances the therapeutic potential of mesenchymal stem cells in rat myocardial infarction. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uysal, B.A.; Kuyumcu, M.S. Serum irisin and adropin levels may be predictors for coronary artery ectasia. Clin. Exp. Hypertens. 2022, 44, 223–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özkan, B.; Örsçelik, Ö.; Yaroğlu, H.Y.; Balcı, Ş.; Özcaıı, M.K.; Çelik, A.; Özcaıı, İ.T. Association between serum adropin levels and isolated coronary artery ectasia in patients with stable angina pectoris. Anatol. J. Cardiol. 2019, 22, 250–255. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lian, W.; Gu, X.; Qin, Y.; Zheng, X. Elevated Plasma Levels of Adropin in Heart Failure Patients. Intern. Med. 2011, 50, 1523–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalkan, A.K.; Cakmak, H.A.; Erturk, M.; Kalkan, K.E.; Uzun, F.; Tasbulak, O.; Diker, V.O.; Aydin, S.; Celik, A. Adropin and Irisin in Patients with Cardiac Cachexia. Arq. Bras. de Cardiol. 2018, 111, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, W.; Qian, L.; Yuan, X.; Lu, Y. Combined effects of hydralazine and nitrate on serum biochemistry and left ventricular remodeling in chronic heart failure patients. Pak. J. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 34, 381–386. [Google Scholar]
- Thapa, D.; Stoner, M.W.; Zhang, M.; Xie, B.; Manning, J.R.; Guimaraes, D.; Shiva, S.; Jurczak, M.J.; Scott, I. Adropin regulates pyruvate dehydrogenase in cardiac cells via a novel GPCR-MAPK-PDK4 signaling pathway. Redox Biol. 2018, 18, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altamimi, T.R.; Gao, S.; Karwi, Q.G.; Fukushima, A.; Rawat, S.; Wagg, C.S.; Zhang, L.; Lopaschuk, G.D. Adropin regulates cardiac energy metabolism and improves cardiac function and efficiency. Metabolism 2019, 98, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Ai, J.; Shuai, Z.; Tang, K.; Li, Z.; Huang, Y. Adropin Alleviates Myocardial Fibrosis in Diabetic Cardiomyopathy Rats: A Preliminary Study. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 8, 688586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Pei, Q.; Zhang, J.; Weng, H.; Jing, F.; Yi, Q. Association between adropin and coronary artery lesions in children with Kawasaki disease. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2021, 180, 2253–2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallo, G.; Volpe, M.; Savoia, C. Endothelial Dysfunction in Hypertension: Current Concepts and Clinical Implications. Front. Med. 2022, 8, 798958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, X.; Li, H.; Zhu, X.; Gu, H.; Chen, J.; Wang, L.; Harding, P.; Xu, W. Inverse Correlation Between Plasma Adropin and ET-1 Levels in Essential Hypertension: A Cross-Sectional Study. Medicine 2015, 94, e1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Çelik, H.T.; Akkaya, N.; Erdamar, H.; Gok, S.; Kazanci, F.; Demircelik, B.; Cakmak, M.; Yigitoglu, R. The Effects of Valsartan and Amlodipine on the Levels of Irisin, Adropin, and Perilipin. Clin. Lab. 2015, 61, 1889–1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Xie, W. LncRNA HDAC11-AS1 Suppresses Atherosclerosis by Inhibiting HDAC11-Mediated Adropin Histone Deacetylation. J. Cardiovasc. Transl. Res. 2022, 15, 1256–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, K.; Yamashita, T.; Shirai, R.; Shibata, K.; Okano, T.; Yamaguchi, M.; Mori, Y.; Hirano, T.; Watanabe, T. Adropin Contributes to Anti-Atherosclerosis by Suppressing Monocyte-Endothelial Cell Adhesion and Smooth Muscle Cell Proliferation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, J.A.; Soares, R.N.; McMillan, N.J.; Jurrissen, T.J.; Martinez-Lemus, L.A.; Padilla, J.; Manrique-Acevedo, C. Young Women Are Protected Against Vascular Insulin Resistance Induced by Adoption of an Obesogenic Lifestyle. Endocrinology 2022, 163, bqac137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghoshal, S.; Stevens, J.R.; Billon, C.; Girardet, C.; Sitaula, S.; Leon, A.S.; Rao, D.C.; Skinner, J.S.; Rankinen, T.; Bouchard, C.; et al. Adropin: An endocrine link between the biological clock and cholesterol homeostasis. Mol. Metab. 2018, 8, 51–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, R.-M.; Yuan, X.; Ouyang, Q.; Lin, X.-Q.; Ai, Z.-Z.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, X.-H. Adropin and glucagon-like peptide-2 are associated with glucose metabolism in obese children. World J. Pediatr. 2019, 15, 565–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Chen, R.; Ouyang, Q.; Lin, X.; Ai, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, X. Novel associations of serum adropin and lipopolysaccharide-binding protein versus lipid profiles in childhood obesity. J. Pediatric. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 33, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, J.-B.; Chu, N.-F.; Lin, F.-H.; Hsu, J.-T.; Chen, P.-Y. Relationship between plasma adropin levels and body composition and lipid characteristics amongst young adolescents in Taiwan. Obes. Res. Clin. Pract. 2018, 12 (Suppl. S2), 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altincik, A.; Sayin, O. Evaluation of the relationship between serum adropin levels and blood pressure in obese children. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 28, 1095–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erman, H.; Ozdemir, A.; Sitar, M.E.; Cetin, S.I.; Boyuk, B. Role of serum adropin measurement in the assessment of insulin resistance in obesity. J. Investig. Med. 2021, 69, 1318–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrero, L.; de Dios, O.; Gavela-Pérez, T.; Riestra, P.; Jois, A.; Soriano-Guillén, L.; Garcés, C. Opposite Association of Adropin Concentrations with Obesity in Prepubertal Children Compared with Adolescents. Obesity 2020, 28, 1736–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, A.A.; Tam, C.S.; Stanhope, K.L.; Wolfe, B.M.; Ali, M.R.; O’Keeffe, M.; St-Onge, M.-P.; Ravussin, E.; Havel, P.J. Low Circulating Adropin Concentrations with Obesity and Aging Correlate with Risk Factors for Metabolic Disease and Increase after Gastric Bypass Surgery in Humans. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 97, 3783–3791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Jiang, L.; Yang, Y.-J.; Ge, R.-K.; Zhou, M.; Hu, H.; Liu, H.; Cui, J.; Li, L.-L.; Dong, Y.-F.; et al. Aerobic exercise improves endothelial function and serum adropin levels in obese adolescents independent of body weight loss. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 17717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faramia, J.; Ostinelli, G.; Drolet-Labelle, V.; Picard, F.; Tchernof, A. Metabolic adaptations after bariatric surgery: Adipokines, myokines and hepatokines. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2020, 52, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glück, M.; Glück, J.; Wiewióra, M.; Rogala, B.; Piecuch, J. Serum Irisin, Adropin, and Preptin in Obese Patients 6 Months After Bariatric Surgery. Obes. Surg. 2019, 29, 3334–3341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, C.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, M.; Xiao, Y. Adropin and apelin-12 efficiently predict metabolic syndrome in obese children. Pediatr. Diabetes 2020, 21, 1132–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orsso, C.E.; Butler, A.A.; Muehlbauer, M.J.; Cui, H.N.; Rubin, D.A. Obestatin and adropin in Prader-Willi syndrome and nonsyndromic obesity: Associations with weight, BMI-z, and HOMA-IR. Pediatr. Obes. 2019, 14, e12493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choe, S.S.; Huh, J.Y.; Hwang, I.J.; Kim, J.I.; Kim, J.B. Adipose Tissue Remodeling: Its Role in Energy Metabolism and Metabolic Disorders. Front. Endocrinol. 2016, 7, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimizu, H.; Mori, M. The brain–adipose axis: A review of involvement of molecules. Nutr. Neurosci. 2005, 8, 7–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jasaszwili, M.; Wojciechowicz, T.; Billert, M.; Strowski, M.Z.; Nowak, K.W.; Skrzypski, M. Effects of adropin on proliferation and differentiation of 3T3-L1 cells and rat primary preadipocytes. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2019, 496, 110532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozic, J.; Borovac, J.A.; Galic, T.; Kurir, T.T.; Supe-Domic, D.; Dogas, Z. Adropin and Inflammation Biomarker Levels in Male Patients With Obstructive Sleep Apnea: A Link With Glucose Metabolism and Sleep Parameters. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2018, 14, 1109–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Z.; Liu, Y. Soluble Vascular Adhesion Protein-1 Level Correlates With Adropin and Inflammatory Biomarkers in Patients With Obstructive Sleep Apnea. Ear Nose Throat J. 2022, 9, 1455613221074147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Celikhisar, H.; Ilkhan, G.D. Alterations in Serum Adropin, Adiponectin, and Proinflammatory Cytokine Levels in OSAS. Can. Respir. J. 2020, 2020, 2571283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zou, F.; Xu, T.; Pan, P.; Hu, C.; Su, X. Serum adropin level is associated with endothelial dysfunction in patients with obstructive sleep apnea and hypopnea syndrome. Sleep Breath. 2020, 25, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gozal, D.; Kheirandish-Gozal, L.; Bhattacharjee, R.; Molero-Ramirez, H.; Tan, H.-L.; Bandla, H.P. Circulating Adropin Concentrations in Pediatric Obstructive Sleep Apnea: Potential Relevance to Endothelial Function. J. Pediatr. 2013, 163, 1122–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kheirandish-Gozal, L.; Gileles-Hillel, A.; Alonso-Álvarez, M.L.; Peris, E.; Bhattacharjee, R.; Terán-Santos, J.; Duran-Cantolla, J.; Gozal, D. Effects of adenotonsillectomy on plasma inflammatory biomarkers in obese children with obstructive sleep apnea: A community-based study. Int. J. Obes. 2015, 39, 1094–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, S.; McMillan, R.P.; Zhu, Q.; Lopaschuk, G.D.; Hulver, M.W.; Butler, A.A. Therapeutic effects of adropin on glucose tolerance and substrate utilization in diet-induced obese mice with insulin resistance. Mol. Metab. 2015, 4, 310–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thapa, D.; Xie, B.; Manning, J.R.; Zhang, M.; Stoner, M.W.; Huckestein, B.R.; Edmunds, L.R.; Zhang, X.; Dedousis, N.L.; O’Doherty, R.M.; et al. Adropin reduces blood glucose levels in mice by limiting hepatic glucose production. Physiol. Rep. 2019, 7, e14043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, L.; Zhang, F.-J.; Li, H.-Y.; Li, L.; Song, L.-G.; Mao, Y.; Li, J.; Liu, H.-M.; Li, F.-L.; Xu, L.-Y.; et al. Anti-diabetic Role of Adropin in Streptozotocin Induced Diabetic Rats via Alteration of PI3K/Akt and Insulin Signaling Pathway. J. Oleo Sci. 2021, 70, 657–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.-X.; Cheng, K.-C.; Liu, I.-M.; Niu, H.-S. Myricetin Increases Circulating Adropin Level after Activation of Glucagon-like Peptide 1 (GLP-1) Receptor in Type-1 Diabetic Rats. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skrzypski, M.; Kołodziejski, P.A.; Pruszyńska-Oszmałek, E.; Wojciechowicz, T.; Janicka, P.; Krążek, M.; Małek, E.; Strowski, M.Z.; Nowak, K.W. Daily Treatment of Mice with Type 2 Diabetes with Adropin for Four Weeks Improves Glucolipid Profile, Reduces Hepatic Lipid Content and Restores Elevated Hepatic Enzymes in Serum. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 9807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jurrissen, T.J.; Ramirez-Perez, F.I.; Cabral-Amador, F.J.; Soares, R.N.; Pettit-Mee, R.J.; Betancourt-Cortes, E.E.; McMillan, N.J.; Sharma, N.; Rocha, H.N.M.; Fujie, S.; et al. Role of adropin in arterial stiffening associated with obesity and type 2 diabetes. Am. J. Physiol. Circ. Physiol. 2022, 323, H879–H891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizk, F.H.; El-Saka, M.H.; Ibrahim, R.R.; El-Deeb, O.S.; Ibrahim, H.A.; El Saadany, A.A.; Mashal, S.S.; Ammar, L.; Abdelsattar, A.M.; Barhoma, R.A. Possible mitigating effect of adropin on lung injury in diabetic rats: Targeting the role of Rho A/Rho-associated kinase pathway. Biofactors 2023, 49, 928–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, S.; Ghoshal, S.; Zhang, L.; Stevens, J.R.; McCommis, K.S.; Finck, B.N.; Lopaschuk, G.D.; Butler, A.A. The peptide hormone adropin regulates signal transduction pathways controlling hepatic glucose metabolism in a mouse model of diet-induced obesity. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 13366–13377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Chen, S.; Shen, T.; Yang, W.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, P.; You, Y.; Sun, X.; Xu, H.; Tang, Y.; et al. Adropin regulates hepatic glucose production via PP2A/AMPK pathway in insulin-resistant hepatocytes. FASEB J. 2020, 34, 10056–10072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palizban, A.-A.; Yazdani, A.-H.; Jahanbani-Ardakani, H. Role of rs7903146 polymorphism and adropin serum level in patients with diabetes mellitus; a case–control study from Isfahan, Iran. Arch. Physiol. Biochem. 2022, 128, 378–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; An, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, G.; Liu, J. Regulation of Adropin by Sitagliptin monotherapy in participants with newly diagnosed type 2 Diabetes. BMC Endocr. Disord. 2022, 22, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wu, X.; Li, X.; Chang, X.; Ding, X.; Wang, Q.; Jiang, T.; Wang, G.; Liu, J. Longitudinal changes in serum adropin levels and liver fat content during liraglutide treatment in newly diagnosed patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease. Acta Diabetol. 2023, 60, 971–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaeinezhad, N.; Alizadeh, R.; Ghanbari-Niaki, A. Short-term circuit resistance training improves insulin resistance probably via increasing circulating Adropin. J. Diabetes Metab. Disord. 2022, 21, 583–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davoodi, M.; Hesamabadi, B.K.; Ariabood, E.; Izadi, M.R.; Ghardashi-Afousi, A.; Bigi, M.A.B.; Asvadi-Fard, M.; Gaeini, A.A. Improved blood pressure and flow-mediated dilatation via increased plasma adropin and nitrate/nitrite induced by high-intensity interval training in patients with type 2 diabetes. Exp. Physiol. 2022, 107, 813–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nematbakhsh, R.; Hajhashemy, Z.; Lotfi, K.; Shahdadian, F.; Rouhani, P.; Saneei, P. Association between dietary insulin index and load with brain derived neurotrophic factor, adropin and metabolic health status in Iranian adults. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 20540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Fang, J.; Chen, L.; Zhao, Z.; Luo, Y.; Lin, C.; Fan, L. Low serum adropin is associated with coronary atherosclerosis in type 2 diabetic and non-diabetic patients. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2014, 52, 751–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oruc, C.U.; Akpinar, Y.E.; Dervisoglu, E.; Amikishiyev, S.; Salmaslıoglu, A.; Gurdol, F.; Omer, B. Low concentrations of adropin are associated with endothelial dysfunction as assessed by flow-mediated dilatation in patients with metabolic syndrome. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2017, 55, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topuz, M.; Celik, A.; Aslantas, T.; Demir, A.K.; Aydin, S.; Aydin, S. Plasma adropin levels predict endothelial dysfunction like flow-mediated dilatation in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. J. Investig. Med. 2013, 61, 1161–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, W.; Liu, H.; Qiu, X.; Zhang, J.; Huang, J.; Chen, H.; Qiu, S.; Lin, R.; Li, S.; Tu, M. The association between serum adropin and carotid atherosclerosis in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A cross-sectional study. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2022, 14, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makboul, K.M.; Elhalawany, S.H.; Mansour, H.K.; Marwan, D.A.; Ibrahim, B.E. A Study of the Assessment of Serum Adropin Level as a Risk Factor of Ischaemic Heart Disease in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Cases. Georgian Med. News 2022, 328–329, 115–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berezin, A.A.; Obradovic, Z.; Novikov, E.V.; Boxhammer, E.; Lichtenauer, M.; Berezin, A.E. Interplay between Myokine Profile and Glycemic Control in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients with Heart Failure. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 2940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berezin, A.A.; Obradovic, Z.; Fushtey, I.M.; Berezina, T.A.; Novikov, E.V.; Schmidbauer, L.; Lichtenauer, M.; Berezin, A.E. The Impact of SGLT2 Inhibitor Dapagliflozin on Adropin Serum Levels in Men and Women with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Chronic Heart Failure. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Chen, L. Association of Serum Adropin Concentrations with Diabetic Nephropathy. Mediat. Inflamm. 2016, 2016, 6038261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Tian, X.; Guo, S.; Zhang, M.; Li, J.; Zhai, N.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Y. Pentraxin-3 and adropin as inflammatory markers of early renal damage in type 2 diabetes patients. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2020, 52, 2145–2152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Es-Haghi, A.; Al-Abyadh, T.; Mehrad-Majd, H. The Clinical Value of Serum Adropin Level in Early Detection of Diabetic Nephropathy. Kidney Blood Press. Res. 2021, 46, 734–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Wang, D.; Zhong, D.; Xie, W.; Luo, J. Adropin Carried by Reactive Oxygen Species-Responsive Nanocapsules Ameliorates Renal Lipid Toxicity in Diabetic Mice. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 37330–37344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berezina, T.A.; Obradovic, Z.; Boxhammer, E.; Berezin, A.A.; Lichtenauer, M.; Berezin, A.E. Adropin Predicts Chronic Kidney Disease in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients with Chronic Heart Failure. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 2231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Sun, J.; Hu, W.; Liu, Y.; Lin, D.; Duan, H.; Liu, F. The association of serum and vitreous adropin concentrations with diabetic retinopathy. Ann. Clin. Biochem. Int. J. Biochem. Lab. Med. 2018, 56, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Li, N.; Guo, S.; Zhang, M.; Li, J.; Zhai, N.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Y. The changing features of serum adropin, copeptin, neprilysin and chitotriosidase which are associated with vascular endothelial function in type 2 diabetic retinopathy patients. J. Diabetes Its Complicat. 2020, 34, 107686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Kumar, N.; Solt, L.A.; Richardson, T.I.; Helvering, L.M.; Crumbley, C.; Garcia-Ordonez, R.D.; Stayrook, K.R.; Zhang, X.; Novick, S. Modulation of retinoic acid receptor-related orphan receptor alpha and gamma activity by 7-oxygenated sterol ligands. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 5013–5025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, J.L.; Stanhope, K.L.; Wong, S.; King, S.; Bremer, A.A.; Krauss, R.M.; Hamilton, J.; Havel, P.J. Role of angiopoietin-like protein 3 in sugar-induced dyslipidemia in rhesus macaques: Suppression by fish oil or RNAi. J. Lipid Res. 2020, 61, 376–386. [Google Scholar]
- Sayın, O.; Tokgöz, Y.; Arslan, N. Investigation of adropin and leptin levels in pediatric obesity-related nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 27, 479–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kutlu, O.; Altun, Ö.; Dikker, O.; Aktaş, Ö.; Özsoy, N.; Arman, Y.; Çil, E.; Özcan, M.; Yoldemir, A.; Akarsu, M.; et al. Serum Adropin Levels Are Reduced in Adult Patients with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Med. Princ. Pract. 2019, 28, 463–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Sun, X.; Shen, T.; Chen, Q.; Chen, S.; Pang, J.; Mi, J.; Tang, Y.; You, Y.; Xu, H.; et al. Lower adropin expression is associated with oxidative stress and severity of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2020, 160, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prystupa, A.; Kiciński, P.; Luchowska-Kocot, D.; Sak, J.; Prystupa, T.; Chen, K.-H.; Chen, Y.-C.; Panasiuk, L.; Załuska, W. Afamin and adropin in patients with alcohol-induced liver cirrhosis. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. 2018, 25, 527–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolben, Y.; Kenig, A.; Kessler, A.; Ishay, Y.; Weksler-Zangen, S.; Eisa, M.; Ilan, Y. Serum Levels of Adropin Improve the Predictability of MELD and Child-Pugh Score in Cirrhosis: Results of Proof-of-Concept Clinical Trial. Transpl. Int. 2023, 36, 11176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eser Karlidag, G.; Arslan Solmaz, O. Are adropin, apelin, elabela, asprosin and betatrophin biomarkers for chronic hepatitis and staging of fibrosis? Biotech. Histochem. 2020, 95, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, N.; Xie, G.; Zhou, B.; Qu, A.; Meng, H.; Liu, J.; Wang, G. Serum Adropin as a Potential Biomarker for Predicting the Development of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Individuals With Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 696163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Xue, H.; Fang, W.; Chen, K.; Chen, S.; Yang, W.; Shen, T.; Chen, X.; Zhang, P.; Ling, X.; et al. Adropin protects against liver injury in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis via the Nrf2 mediated antioxidant capacity. Redox Biol. 2019, 21, 101068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.; Liu, L.; Wei, Y.; Fang, C.; Liu, S.; Zhou, F.; Li, Y.; Zhao, G.; Guo, Z.; Luo, Y.; et al. Exercise suppresses NLRP3 inflammasome activation in mice with diet-induced NASH: A plausible role of adropin. Lab. Investig. 2021, 101, 369–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, N.R.; Fatoba, S.T.; Oke, J.L.; Hirst, J.A.; O’Callaghan, C.A.; Lasserson, D.S.; Hobbs, F.D.R. Global Prevalence of Chronic Kidney Disease—A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0158765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazgan, B.; Avcı, F.; Memi, G.; Tastekin, E. Inflammatory response and matrix metalloproteinases in chronic kidney failure: Modulation by adropin and spexin. Exp. Biol. Med. 2021, 246, 1917–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boric-Skaro, D.; Mizdrak, M.; Luketin, M.; Martinovic, D.; Tokic, D.; Vilovic, M.; Supe-Domic, D.; Kurir, T.T.; Bozic, J. Serum Adropin Levels in Patients on Hemodialysis. Life 2021, 11, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grzegorzewska, A.E.; Niepolski, L.; Mostowska, A.; Warchoł, W.; Jagodziński, P.P. Involvement of adropin and adropin-associated genes in metabolic abnormalities of hemodialysis patients. Life Sci. 2016, 160, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Cui, B.; Zhao, X.; Wu, Y.; Qin, H.; Guo, Y.; Wang, H.; Lu, M.; Zhang, S.; Shen, J.; et al. Correlation of Serum Adropin Levels with Risk Factors of Cardiovascular Disease in Hemodialysis Patients. Metab. Syndr. Relat. Disord. 2021, 19, 401–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grzegorzewska, A.E.; Niepolski, L.; Świderska, M.K.; Mostowska, A.; Stolarek, I.; Warchoł, W.; Figlerowicz, M.; Jagodziński, P.P. ENHO, RXRA, and LXRA polymorphisms and dyslipidaemia, related comorbidities and survival in haemodialysis patients. BMC Med. Genet. 2018, 19, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kałużna, M.; Hoppe, K.; Schwermer, K.; Ibrahim, A.Y.; Pawlaczyk, K.; Ziemnicka, K. Adropin and irisin levels in relation to nutrition, body composition, and insulin resistance in patients with end-stage renal disease on chronic hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis. Pol. Arch. Intern. Med. 2016, 126, 474–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Memi, G.; Yazgan, B. Adropin and spexin hormones regulate the systemic inflammation in adenine-induced chronic kidney failure in rat. Chin. J. Physiol. 2021, 64, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, R.; Krishan, P.; Kumari, P.; Singh, T.; Singh, V.; Singh, R.; Ahmad, S.F. Clinical Significance of Adropin and Afamin in Evaluating Renal Function and Cardiovascular Health in the Presence of CKD-MBD Biomarkers in Chronic Kidney Disease. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 3158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radić, J.; Lovrić Kojundžić, S.; Gelemanović, A.; Vučković, M.; Budimir Mršić, D.; Šupe Domić, D.; Novaković, M.D.; Radić, M. Serum Adropin Levels and Body Mass Composition in Kidney Transplant Recipients-Are There Sex Differences? Diagnostics 2023, 13, 2768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- St-Onge, M.; Shechter, A.; Shlisky, J.; Tam, C.S.; Gao, S.; Ravussin, E.; Butler, A.A. Fasting plasma adropin concentrations correlate with fat consumption in human females. Obesity 2014, 22, 1056–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydin, S. Presence of adropin, nesfatin-1, apelin-12, ghrelins and salusins peptides in the milk, cheese whey and plasma of dairy cows. Peptides 2013, 43, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, A.A.; St-Onge, M.-P.; Siebert, E.A.; Medici, V.; Stanhope, K.L.; Havel, P.J. Differential Responses of Plasma Adropin Concentrations To Dietary Glucose or Fructose Consumption In Humans. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 14691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevens, J.R.; Kearney, M.L.; St-Onge, M.P.; Stanhope, K.L.; Havel, P.J.; Kanaley, J.A.; Thyfault, J.P.; Weiss, E.P.; Butler, A.A. Inverse association between carbohydrate consumption and plasma adropin concentrations in humans. Obesity 2016, 24, 1731–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarrati, M.; Lahiji, M.R.; Salehi, E.; Yazdani, B.; Razmpoosh, E.; Shoormasti, R.S.; Shidfar, F. Effects of Probiotic Yogurt on Serum Omentin-1, Adropin, and Nesfatin-1 Concentrations in Overweight and Obese Participants Under Low-Calorie Diet. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2019, 11, 1202–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assi, M.J.; Poursalehi, D.; Tirani, S.A.; Shahdadian, F.; Hajhashemy, Z.; Mokhtari, E.; Mohammadi, S.; Saneei, P. Legumes and nuts intake in relation to metabolic health status, serum brain derived neurotrophic factor and adropin levels in adults. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 16455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasaszwili, M.; Pruszyńska-Oszmałek, E.; Wojciechowicz, T.; Strowski, M.Z.; Nowak, K.W.; Skrzypski, M. Adropin Slightly Modulates Lipolysis, Lipogenesis and Expression of Adipokines but Not Glucose Uptake in Rodent Adipocytes. Genes 2021, 12, 914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, S.; McMillan, R.P.; Jacas, J.; Zhu, Q.; Li, X.; Kumar, G.K.; Casals, N.; Hegardt, F.G.; Robbins, P.D.; Lopaschuk, G.D.; et al. Regulation of Substrate Oxidation Preferences in Muscle by the Peptide Hormone Adropin. Diabetes 2014, 63, 3242–3252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skugor, A.; Kjos, N.P.; Sundaram, A.Y.M.; Mydland, L.T.; Ånestad, R.; Tauson, A.-H.; Øverland, M. Effects of long-term feeding of rapeseed meal on skeletal muscle transcriptome, production efficiency and meat quality traits in Norwegian Landrace growing-finishing pigs. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0220441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujie, S.; Hasegawa, N.; Kurihara, T.; Sanada, K.; Hamaoka, T.; Iemitsu, M. Association between aerobic exercise training effects of serum adropin level, arterial stiffness, and adiposity in obese elderly adults. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2017, 42, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbasian, S.; Ravasi, A.A.; Soori, R.; Aydin, S.; Choobineh, S.; Aydin, S. High-intensity interval training ameliorates endothelial dysfunction through adropin, nitric oxide, MR-proADM, and copeptin changes in overweight subjects. Hormones 2022, 21, 707–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, T.C.; Huang, T.-H.; Tseng, W.-C.; Tseng, K.-W.; Hsieh, C.-C.; Chen, M.-Y.; Chou, T.-Y.; Huang, Y.-C.; Chen, H.-L.; Nosaka, K. Changes in plasma C1q, apelin and adropin concentrations in older adults after descending and ascending stair walking intervention. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 17644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, C.M.; Wang, Y.; Lee JT, H.; Huang, Z.; Wu, D.; Xu, A.; Lam, K.S.L. Adropin is a brain membrane-bound protein regulating physical activity via the NB-3/Notch signaling pathway in mice. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 25976–25986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, S.; Ghoshal, S.; Girardet, C.; De Mars, K.M.; Yang, C.; Niehoff, M.L.; Nguyen, A.D.; Jayanth, P.; Hoelscher, B.A.; Xu, F.; et al. Adropin correlates with aging-related neuropathology in humans and improves cognitive function in aging mice. NPJ Aging Mech. Dis. 2021, 7, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolben, Y.; Weksler-Zangen, S.; Ilan, Y. Adropin as a potential mediator of the metabolic system-autonomic nervous system-chronobiology axis: Implementing a personalized signature-based platform for chronotherapy. Obes. Rev. 2021, 22, e13108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Logan, R.W.; McClung, C.A. Rhythms of life: Circadian disruption and brain disorders across the lifespan. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2019, 20, 49–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cicek, M.A.; Tuygar Okutucu, F.; Ozturk, N. Irisin, adropin, and preptin as biomarkers of energy dysregulation in depressive disorder. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 2023, 39, 1263–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atwoli, L.; Baqui, A.H.; Benfield, T.; Bosurgi, R.; Godlee, F.; Hancocks, S.; Horton, R.; Laybourn-Langton, L.; Monteiro, C.A.; Norman, I. Call for Emergency Action to Limit Global Temperature Increases, Restore Biodiversity, and Protect Health. Alpha Psychiatry 2021, 22, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dogru, Y.Z.; Nacar, T.; Erat, M. Effect of adropin on seizure activity in rats with penicillin-induced epilepsy. Epilepsy Res. 2023, 194, 107170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirdöğen, F.; Akdağ, T.; Gündüz, Z.B.; Odabaş, F.Ö. Investigation of serum adropin levels and its relationship with hypothalamic atrophy in patients with multiple sclerosis. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2022, 66, 103948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cinkir, U.; Bir, L.S.; Topsakal, S.; Cicek, E.A.; Tekin, S. Investigation of blood leptin and adropin levels in patients with multiple sclerosis: A CONSORT-clinical study. Medicine 2021, 100, e27247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Algul, S.; Ozcelik, O. Evaluating the energy regulatory hormones of nesfatin-1, irisin, adropin and preptin in multiple sclerosis. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2022, 68, 104221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abulmeaty, M.M.; Almajwal, A.M.; Razak, S.; Al-Ramadhan, F.R.; Wahid, R.M. Energy Homeostasis-Associated (Enho) mRNA Expression and Energy Homeostasis in the Acute Stress Versus Chronic Unpredictable Mild Stress Rat Models. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loewen, S.P.; Ferguson, A.V. Adropin acts in the rat paraventricular nucleus to influence neuronal excitability. Am. J. Physiol. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2017, 312, R511–R519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, F.; Zhou, L.; Qian, X.; Wang, D.; He, W.J.; Tang, Z.W.; Yin, J.; Huang, Q. Adropin Is a Key Mediator of Hypoxia Induced Anti-Dipsogenic Effects via TRPV4-CamKK-AMPK Signaling in the Circumventricular Organs of Rats. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2017, 10, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Yang, P.; Zhang, Q.; Jiang, Q. Tilapia adropin: The localization and regulation of growth hormone gene expression in pituitary cells. Peptides 2017, 97, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghoshal, S.; Banerjee, S.; Zhang, J.; Niehoff, M.L.; Farr, S.A.; Butler, A.A. Adropin transgenesis improves recognition memory in diet-induced obese LDLR-deficient C57BL/6J mice. Peptides 2021, 146, 170678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozkan, A.; Aslan, M.A.; Sinen, O.; Munzuroglu, M.; Derin, N.; Parlak, H.; Bulbul, M.; Agar, A. Effects of adropin on learning and memory in rats tested in the Morris water maze. Hippocampus 2022, 32, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, G.; Morley, J.E.; Vellas, B.; Nguyen, A.D.; Butler, A.A. Low circulating adropin concentrations predict increased risk of cognitive decline in community-dwelling older adults. GeroScience 2024, 46, 897–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aggarwal, G.; Malmstrom, T.K.; Morley, J.E.; Miller, D.K.; Nguyen, A.D.; Butler, A.A. Low circulating adropin levels in late-middle aged African Americans with poor cognitive performance. NPJ Aging 2023, 9, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Gheit, R.E.A.; Atef, M.M.; El Deeb, O.S.; Badawi, G.A.; Alshenawy, H.A.; Elwan, W.M.; Arakeep, H.M.; Emam, M.N. Unique Novel Role of Adropin in a Gastric Ulcer in a Rotenone-Induced Rat Model of Parkinson’s Disease. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2020, 11, 3077–3088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saçmacı, H.; Çakır, M.; Özcan, S.S. Adropin and MOTS-c as new peptides: Do levels change in neurodegenerative diseases and ischemic stroke? J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2023, 37, e23246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; DeMars, K.M.; Hawkins, K.E.; Candelario-Jalil, E. Adropin reduces paracellular permeability of rat brain endothelial cells exposed to ischemia-like conditions. Peptides 2016, 81, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Liu, L.; Lavayen, B.P.; Larochelle, J.; Gunraj, R.E.; Butler, A.A.; Candelario-Jalil, E. Therapeutic Benefits of Adropin in Aged Mice After Transient Ischemic Stroke via Reduction of Blood-Brain Barrier Damage. Stroke 2023, 54, 234–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Lavayen, B.P.; Liu, L.; Sanz, B.D.; DeMars, K.M.; Larochelle, J.; Pompilus, M.; Febo, M.; Sun, Y.-Y.; Kuo, Y.-M.; et al. Neurovascular protection by adropin in experimental ischemic stroke through an endothelial nitric oxide synthase-dependent mechanism. Redox Biol. 2021, 48, 102197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadirhan, O.A.; Kucukdagli, O.T.; Gulen, B. The effectiveness of serum S100B, TRAIL, and adropin levels in predicting clinical outcome, final infarct core, and stroke subtypes of acute ischemic stroke patients. Biomédica 2022, 42, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; DeMars, K.M.; Candelario-Jalil, E. Age-Dependent Decrease in Adropin is Associated with Reduced Levels of Endothelial Nitric Oxide Synthase and Increased Oxidative Stress in the Rat Brain. Aging Dis. 2018, 9, 322–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siuta, M.; Zuckerman, S.L.; Mocco, J. Nitric Oxide in Cerebral Vasospasm: Theories, Measurement, and Treatment. Neurol. Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 972417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suhardja, A. Mechanisms of disease: Roles of nitric oxide and endothelin-1 in delayed cerebral vasospasm produced by aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. Nat. Clin. Pract. Cardiovasc. Med. 2004, 1, 110–116; quiz 2 p following 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pluta, R.M. Delayed cerebral vasospasm and nitric oxide: Review, new hypothesis, and proposed treatment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2005, 105, 23–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hänggi, D.; Steiger, H.-J. Nitric oxide in subarachnoid haemorrhage and its therapeutics implications. Acta Neurochir. 2006, 148, 605–613; discussion 613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pluta, R.M. Dysfunction of nitric oxide synthases as a cause and therapeutic target in delayed cerebral vasospasm after SAH. Acta Neurochir. Suppl. 2008, 104, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Chen, S.; Zhang, J.-M. The Updated Role of Oxidative Stress in Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2017, 14, 832–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dodd, W.S.; Patel, D.; Lucke-Wold, B.; Hosaka, K.; Chalouhi, N.; Hoh, B.L. Adropin decreases endothelial monolayer permeability after cell-free hemoglobin exposure and reduces MCP-1-induced macrophage transmigration. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2021, 582, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dodd, W.S.; Patel, D.; Laurent, D.; Lucke-Wold, B.; Hosaka, K.; Johnson, R.D.; Chalouhi, N.; Butler, A.A.; Candelario-Jalil, E.; Hoh, B.L. Subarachnoid hemorrhage-associated brain injury and neurobehavioral deficits are reversed with synthetic adropin treatment through sustained Ser1179 phosphorylation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase. Front. Stroke 2024, 3, 1371140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, L.; Lu, Z.; Burchell, S.; Nowrangi, D.; Manaenko, A.; Li, X.; Xu, Y.; Xu, N.; Tang, J.; Dai, H.; et al. Adropin preserves the blood-brain barrier through a Notch1/Hes1 pathway after intracerebral hemorrhage in mice. J. Neurochem. 2017, 143, 750–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hasanpour-Segherlou, Z.; Butler, A.A.; Candelario-Jalil, E.; Hoh, B.L. Role of the Unique Secreted Peptide Adropin in Various Physiological and Disease States. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 1613. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14121613
Hasanpour-Segherlou Z, Butler AA, Candelario-Jalil E, Hoh BL. Role of the Unique Secreted Peptide Adropin in Various Physiological and Disease States. Biomolecules. 2024; 14(12):1613. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14121613
Chicago/Turabian StyleHasanpour-Segherlou, Zahra, Andrew A. Butler, Eduardo Candelario-Jalil, and Brian L. Hoh. 2024. "Role of the Unique Secreted Peptide Adropin in Various Physiological and Disease States" Biomolecules 14, no. 12: 1613. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14121613
APA StyleHasanpour-Segherlou, Z., Butler, A. A., Candelario-Jalil, E., & Hoh, B. L. (2024). Role of the Unique Secreted Peptide Adropin in Various Physiological and Disease States. Biomolecules, 14(12), 1613. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14121613






