Abstract
Complex regional pain syndrome (CRPS) is a chronic pain that affects the extremities after a trauma or nerve injury with no definite established treatment. The mechanisms mediating CRPS are not completely elucidated. Thus, we conducted a bioinformatics analysis to identify hub genes and key pathways to determine strategies for more effective treatments of CRPS. Finally, there is only one expression profile of GSE47063 in terms of homo sapiens-based CRPS from the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database, which included four patients and five controls. We explored the differentially expressed genes (DEGs) in the dataset and conducted Gene Ontology (GO) functional and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) enrichment analysis of the potential hub genes. A protein–protein interaction (PPI) network was also established; then, according to the score of each hub genes, we used R software to draw the nomogram model to predict the rate of CRPS. Furthermore, GSEA analysis was estimated and assessed by the normalized enrichment score (NES). From the GO and KEGG analysis, we identified the top five hub genes (MMP9, PTGS2, CXCL8, OSM, TLN1); all of the selected DEGs were mainly enriched in their inflammatory response. In addition, the GSEA analysis showed complement and coagulation cascades also play an important role in CRPS. This study, to our knowledge, is the first to conduct further PPI network and GSEA analyses. Thus, targeting excessive inflammation could offer new therapeutic methods for CRPS and related physical and psychiatric disorders.
1. Introduction
Complex regional pain syndrome (CRPS) is a chronic and disabling pain, with a prevalence of approximately 5.4–26.2 per 100,000 person years, with females being affected 3–4 times more than males [1]. A longitudinal study including 1549 patients with fracture of carpal bones, the distal radius or ulna or both, showed a 3.8% incidence of CRPS [2]. There are some risk factors that have been identified currently: female gender; age over 70 years; upper limb involvement; and intraarticular, dislocated and high-energy fractures; however, the underlying pathophysiology seems to be complex and controversial; some potential mechanisms have been suggested, including cytokine imbalance and neuroinflammation [3,4]. Moreover, CRPS has a large impact on daily life, with people commonly presenting with allodynia, hyperalgesia, skin temperature changes, and oedema, which all bring a heavy financial burden to families [5].
At the moment, the attention we pay to CRPS is not enough; it is distinct from other pain syndromes by the presence of autonomic dysfunction and persistent regional inflammatory changes, with a lack of dermatomal distribution; the clinical diagnosis of CRPS was established using the “Budapest criteria”, published by the International Association for the Study of Pain (IASP) 2007 [6]. Recently, CRPS has been further divided into two subtypes, based on the absence (CRPS I, previously known as reflex sympathetic dystrophy) or presence (CRPS II, previously known as causalgia) of a major nerve injury [5]. Although rat models (chronic post ischemia pain or tibial fracture/casting rodent model) provide valuable evidence for different aspects of the pathophysiology of acute posttraumatic pain and inflammation, these models do not produce all the long-term symptoms that patients experience in some way [7].
The discovery of effective therapeutic targets for CRPS is vitally imperative because of the lack of effective treatments. Increased evidence suggests that inflammation, as characterized by an activation of glial cells and infiltration of leukocytes, has a critical role in the pathogenesis of CRPS [8]. Moreover, inflammatory processes have also been postulated to contribute to specific syndromes such as depression and other behavioral manifestations common to this syndrome in CRPS (sleep disorders, decreased activity, decreased social interaction). A growing body of evidence suggests that inflammatory mediators, including proinflammatory cytokines, chemokines, and growth factors in dorsal root ganglion and the spinal cord, contribute substantially to the genesis and maintenance of CRPS. Previous research found that HLA-A29.1, MMP9, ANPEP, HDC, G-CSF3R, and STAT3 were associated with CRPS patients, but they did not conduct further PPI network and GSEA analysis [9].
Microarray is a mature high-throughput method for genome-wide gene expression profiling. Bioinformatics can provide tools for the analysis of large amounts of information from the GEO database to identify hub genes and key pathways for new clinical treatment strategies [10]. Therefore, this study aimed to discuss the molecular mechanisms and pathogenesis of CRPS, thus providing a new foundation for the prevention of this life-altering condition.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Microarray Datasets of CRPS
The gene expression microarray GSE47063 (9 samples: 2 CRPS I, 2 CRPS II, and 5 controls) was downloaded from the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo, accessed on 5 November 2022), a subdataset of the National Center of Biotechnology Information (NCBI), which includes biological expression data of many species obtained via array, SNP array, and high-throughput sequencing [11]. All datasets in the present study were downloaded from public databases. These public databases allowed researchers to analyze for scientific purposes, and thus ethics approval was not required.
2.2. Differential Expression Analysis
We downloaded the gene expression series matrix, platform information, and clinical information from the GEO database. Then, the corresponding platform information was used to convert the probe IDs in the expression series matrix into gene symbols to obtain an international general expression series matrix with the row name of gene symbols and the column name of sample names. The mean value of multiple probe sets was calculated if they corresponded to the same gene. Next, we further used the tool of GEO2R (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/geo2r/, accessed on 5 November 2022) to analyze the differentially expressed genes (DEGs) in the CRPS group and the Control group. Results are presented in the browser as a table of the top 250 genes ranked by p-value, for RNA-seq; the table is the result of the Wald test when comparing 2 groups of samples. Highlighted genes are significantly differentially expressed at a default adjusted p-value cutoff of 0.05 (red = upregulated, blue = downregulated). The DEGs were defined as genes with a p-value < 0.05 and a |log (fold change (FC))| ≥ 1.
2.3. Gene Ontology and Pathway Enrichment Analysis
The gene enrichment analysis of the genes in the meaningful module was performed composed of Gene Ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway enrichment through the ClusterProfiler package using R Software (version 4.0.3). Afterward, the enrichment results were visualized with the R package “enrichplot” to further analyze the biological functions and pathways. At the same time, Metascape (https://metascape.org/, accessed on 7 November 2022) combines functional enrichment, interactome analysis, gene annotation, and membership search for experimental biologists to comprehensively analyze and interpret gene expression profiling [12].
2.4. Protein–Protein Interaction (PPI) Network Analysis
The STRING database (STRING: functional protein association networks (string-db.org, accessed on 8 November 2022)) is an online search for known and predicted protein interactions [13]. At present, it stores at least 14,094 kinds of organisms, 67.6 million kinds of proteins, and more than 20 billion interaction data. We uploaded 37 DEGs to the string database and visualized a PPI network map of the String database using Cytoscape software. In Cytoscape, each gene was considered as a node and experimentally determined interactions were used as edge attributes. The important modules were identified and visualized using Molecular Complex Detection (MCODE), which is a plugin in Cytoscape for discovering densely connected nodes in a given network. We further used the MCODE module to calculate the core interactions in the PPI network and the Clugo to further analyze the key pathways.
2.5. Gene Set Enrichment Analyses (GSEA)
In brief, GSEA (http://software.broadinstitute.org/gsea/index.jsp, accessed on 8 November 2022) is routinely used to analyze and interpret coordinate pathway-level changes in transcriptomics experiments with less than seven samples per condition. Since its initial application to microarray experiments, GSEA has demonstrated utility across many applications, including RNA-seq gene expression experiments, genome-wide associations studies, and proteomics and metabolomics studies. To further study the potential pathways associated with CRPS for biological processes enrichment, GSEA enrichments were estimated using the normalized enrichment score (NES). The significance of the enrichment was assessed at an FDR < 0.25 level and p-value < 0.05.
2.6. Establishment of Predictive Models
First of all, we use cytoHubba in Cytoscape to screen out the top hub genes. In order to simplify the predictive model, we converted the expression score of each hub gene into binary variables through logistic regression. To further determine the convenience for clinical application, in our study, the DynNom package of R software was used to draw the nomogram to preliminarily predict the rate of CRPS. All statistical analyses were performed using the R programming language and environment (http://www.r-project.org/, accessed on 9 November 2022).
2.7. Ethical Declaration
All of the data used in this study were obtained from public databases; thus, this study does not contain any intervention experiments associated with animals or humans.
3. Results
3.1. Identification of CRPS-Associated Genes
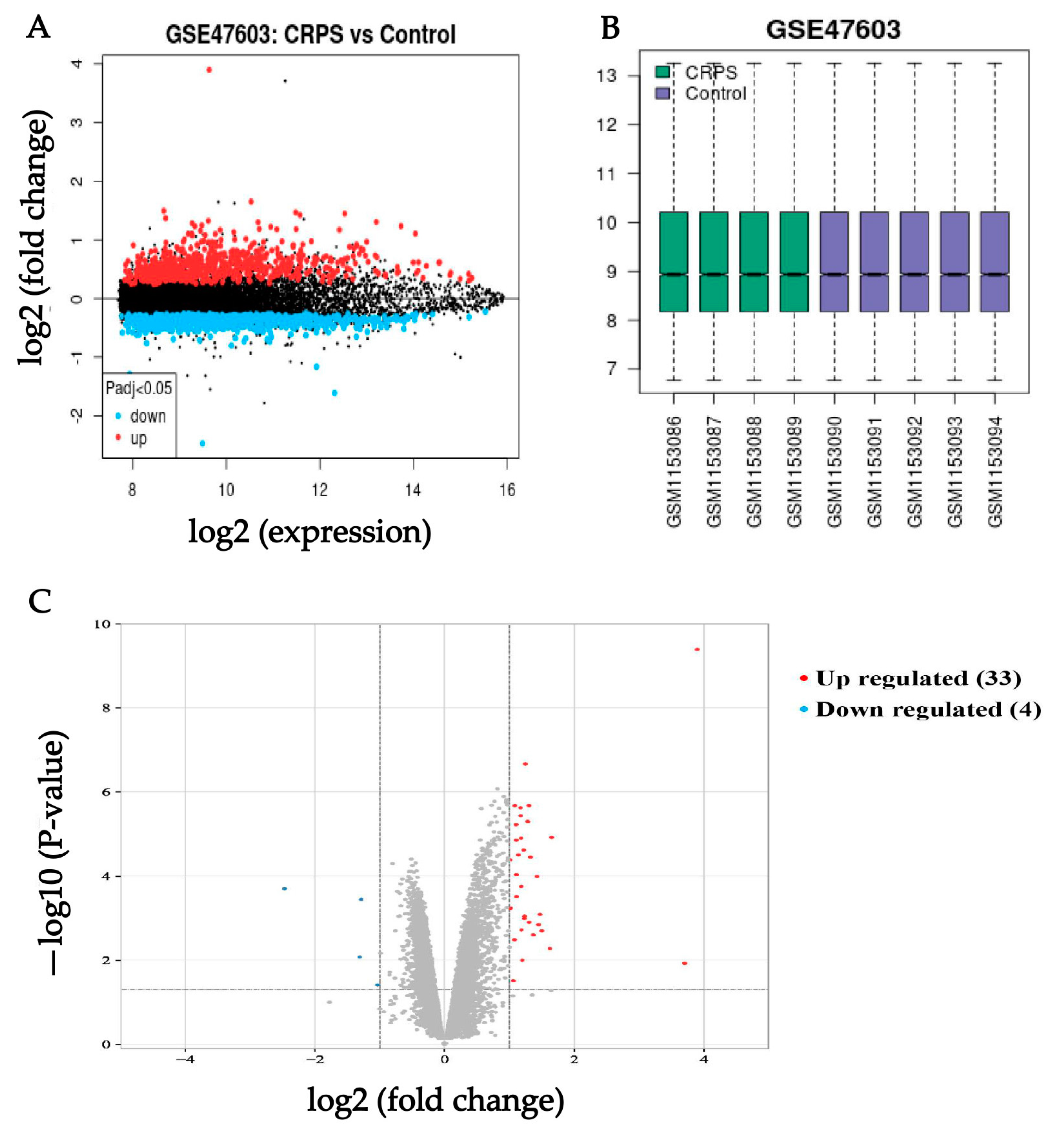
We downloaded series Metrix and corresponding platform information (GPL10558) and clinical information from the NCBI website which contains high-throughput gene expression data, chips, and microarrays under the accession number GSE47603. These nine samples (four in the CRPS group, five in the Control group) were selected for deep analysis in our study in accordance with our aims. To find the genes that were tightly correlated with CRPS, differential analysis was run for the genes in the GSE. DEGs of the dataset were found by using the GEO2R tool with the cutoff criteria of p < 0.05 and |log (fold change)| ≥ 1. The results revealed that a total of thirty-seven DEGs (thirty-three upregulated and four downregulated) were identified from the CRPS group versus the Control group (Figure 1); the details are shown in Table 1.
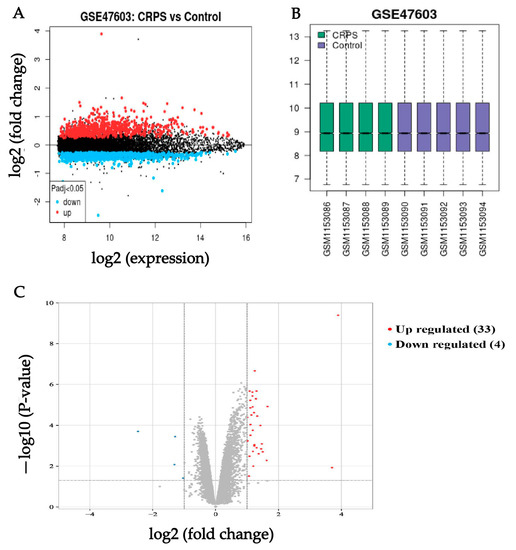
Figure 1.
(A) Volcano of original gene expression from GEO dataset. (B) Box diagram of original gene expression from GEO dataset. (C) Identification of DEGs between the CRPS group and Control group in the GSE 47,063 dataset. Highlighted genes are significantly differentially expressed at a default p-value cutoff of 0.05 (red = upregulated, blue = downregulated).

Table 1.
DEGs of the dataset between the CRPS and Control groups.
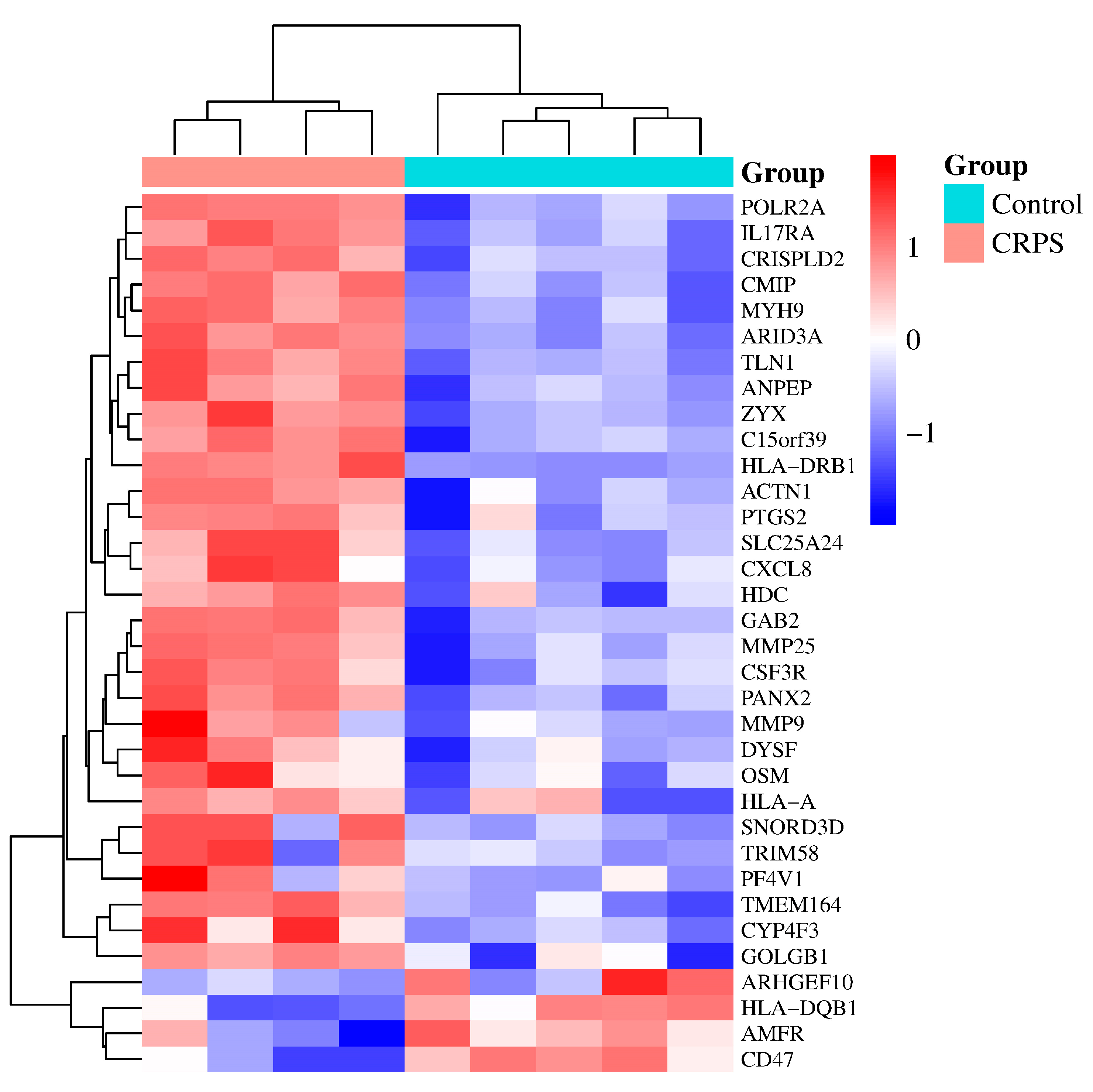
Next, according to the DEGs we have identified, we present a heatmap of the differentially expressed genes in the GEO dataset that colors the samples–groups (Figure 2).
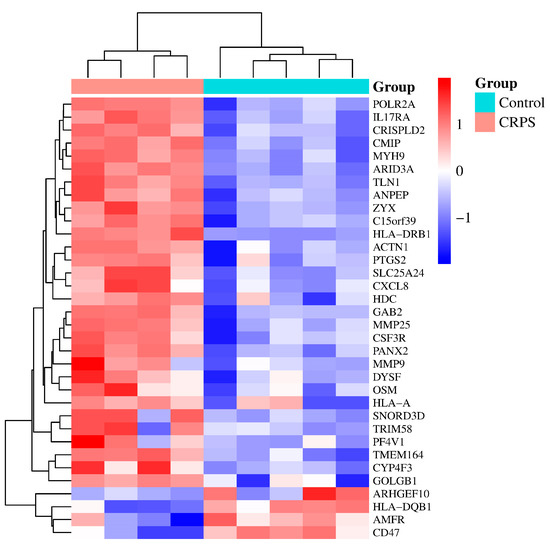
Figure 2.
A heatmap based on gene expression dataset. p < 0.05 and |log (fold change)| ≥ 1. From Table 1 above, we found 3 duplicate genes; they are ZYX (ILMN_2371169, ILMN_1701875), CXCL8 (ILMN_2184373, ILMN_1666733), and PTGS2 (ILMN_1677511, ILMN_2054297). Some of them were automatically deleted when we drew the heatmap.
3.2. Functional Annotation
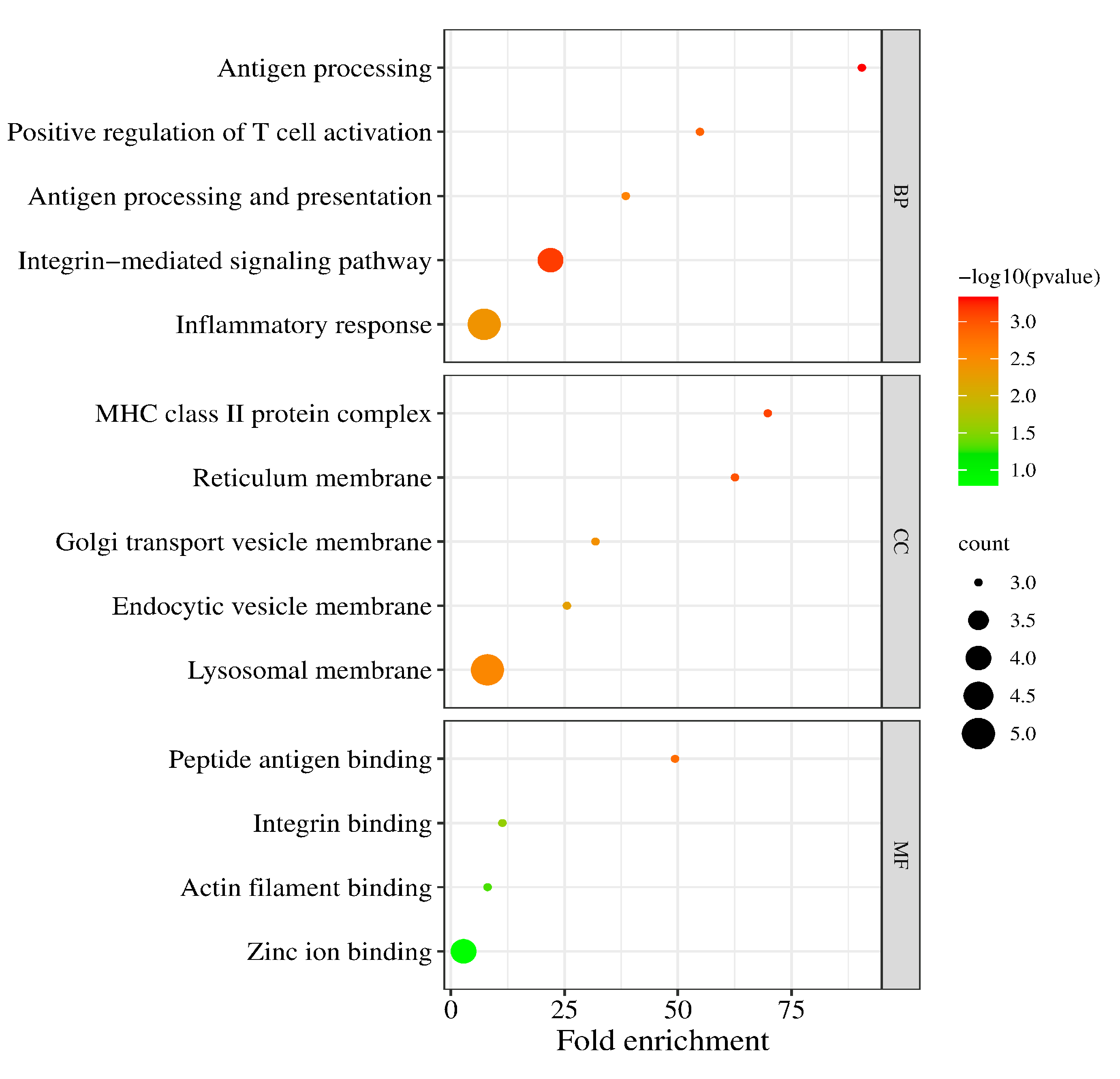
We performed the GO functional annotation and KEGG pathway enrichment analysis on the 37 DEGs. For biological processes (BPs), these DEGs mainly involved antigen processing, T cell activation, the integrin-mediated signaling pathway, and inflammatory response. For the cellular component (CC), the DEGs were associated with the MHC class II protein complex, reticulum membrane, golgi transport vesicle membrane, endocytic vesicle membrane, and lysosomal membrane (Figure 3).
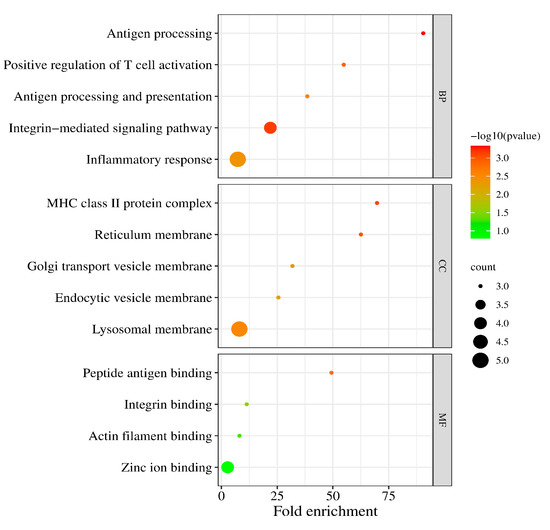
Figure 3.
The enriched biological (BP), cellular component (CC), and molecular function (MF) terms in the GO analysis.
In addition, the GO molecular function (MF) analysis revealed that the DEGs were principally involved in the peptide antigen binding, integrin binding, and actin filament binding (Table 2).

Table 2.
GO terms and enrichment analysis of DEGs.
Together, KEGG databases were also selected for preferred pathway sources and were used to explore the function of genes in biological systems. For simplicity, only the significant terms were recorded (Table 3).

Table 3.
KEGG pathway enrichment analysis of DEGs.
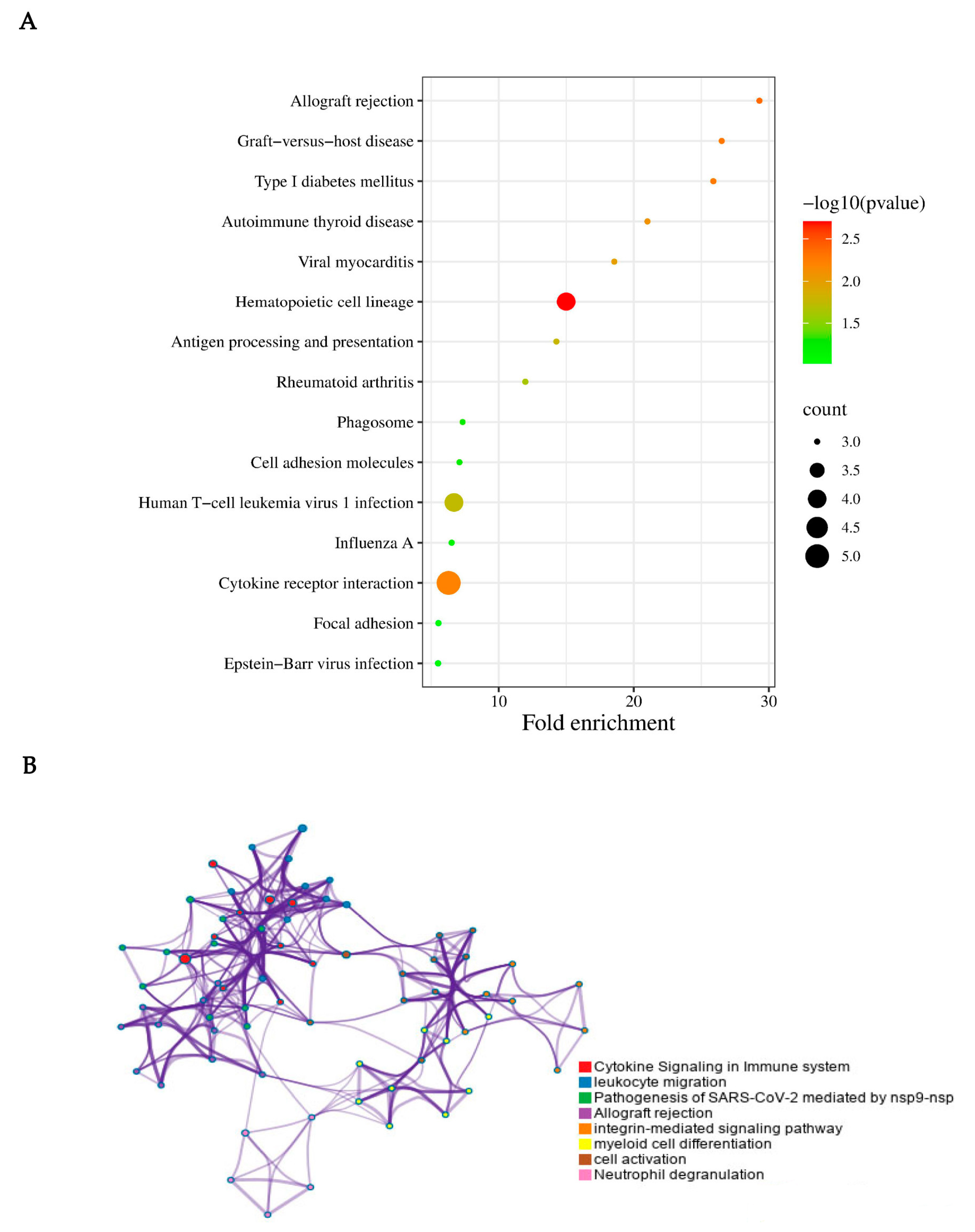
Finally, we used online software (http://www.bioinformatics.com.cn/, accessed on 8 November 2022) and Metascape to perform further visual analysis. In fact, Metascape was initially designed to support biologists, as we observed most gene-list analysis tools were bioinformatician-oriented rather than biologist-oriented. It enables users to apply popular bioinformatics analyses to gene and protein lists in order to make effective data-driven gene prioritization decisions (Figure 4).
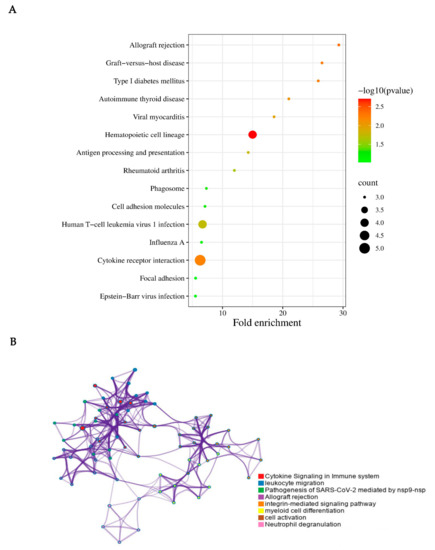
Figure 4.
KEGG pathway enrichment analysis of the integrated DEGs. (A) KEGG pathway enrichment analysis on the 37 DEGs. The cytokine receptor interaction, human T-cell leukemia virus 1 infection, and hematopoietic cell lineage may play important roles in CRPS. (B) Visual analysis was performed using Metascape. In consideration of the result performed via Metascape, the cytokine signaling in the immune system, leukocyte migration, pathogenesis of SARS-CoV-2, allograft rejection, integrin-mediated signaling pathway, myeloid cell differentiation, cell activation, and neutrophil degranulation were closely associated with CRPS.
3.3. PPI Network Analysis and GSEA Analysis
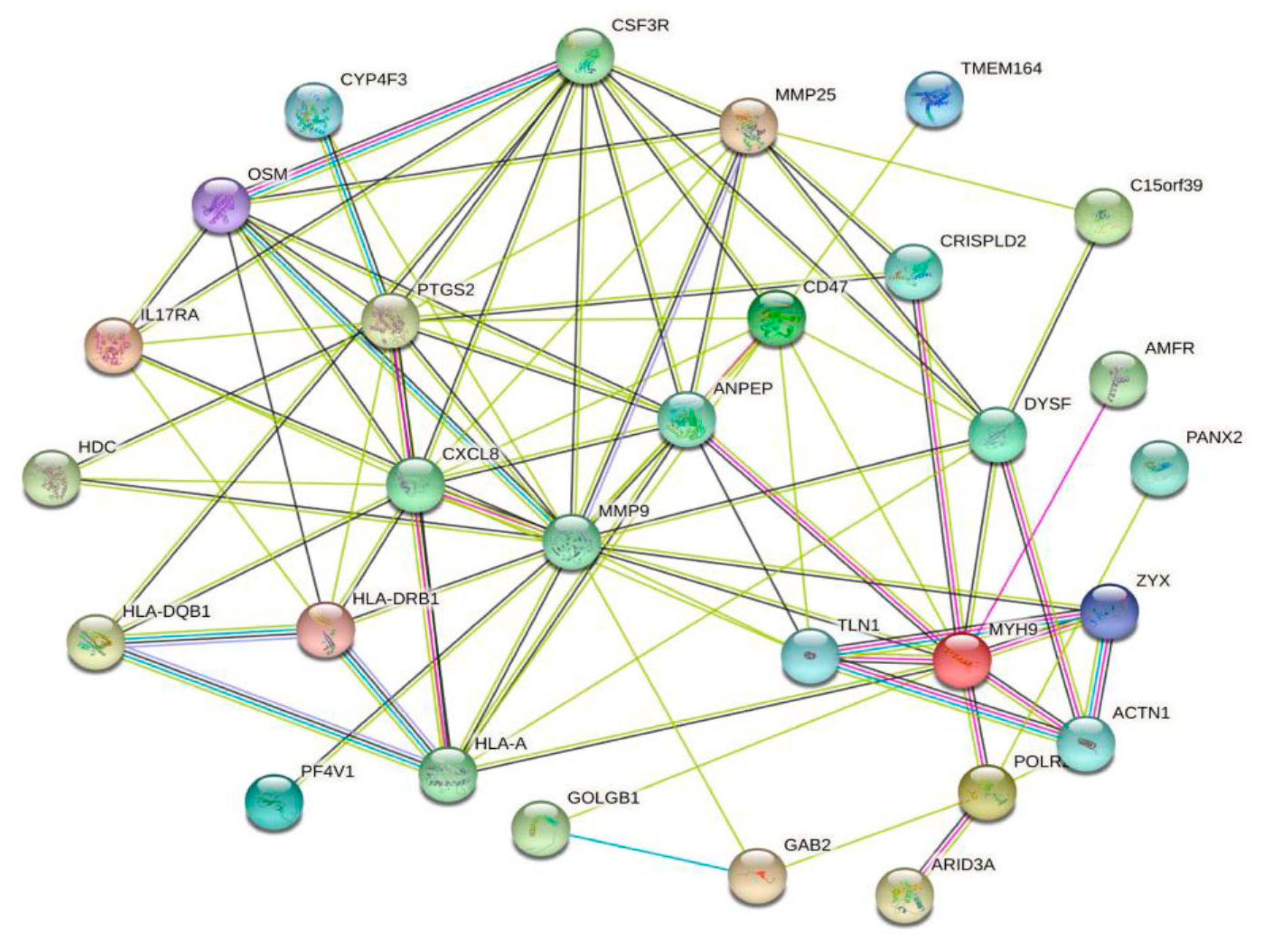
We used the String online database to analyze DEGs and construct a PPI network. Homo sapiens were used as the organism for subsequent analysis. Network visualization in String was transferred to Cytoscape software to explore target modules and hub genes (Figure 5).
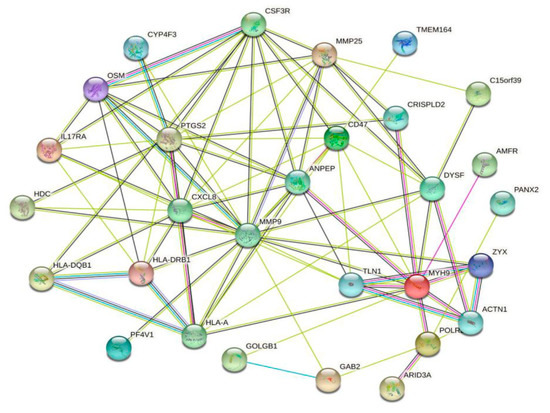
Figure 5.
The PPI network of the DEGs, constructed using the Cytoscape software.
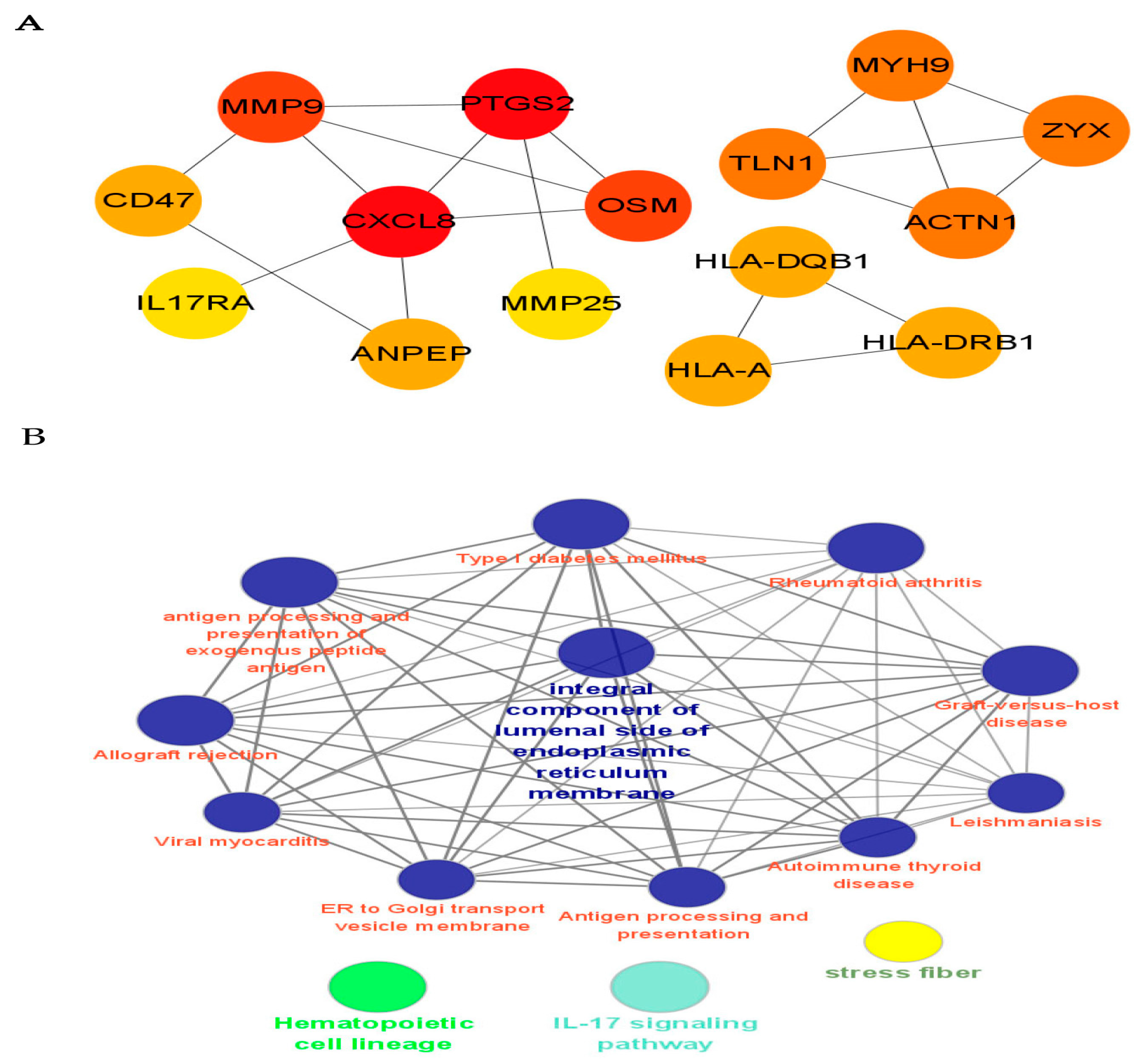
In order to further clarify the critical role of CRPS, we used the cytoHubba in Cytoscape to screen out the top hub genes, MMP9, PTGS2, CXCL8, OSM, and TLN1; additionally, we found that MYH9, ZYX, and ACTN1 also play an important role in CRPS (Figure 6).
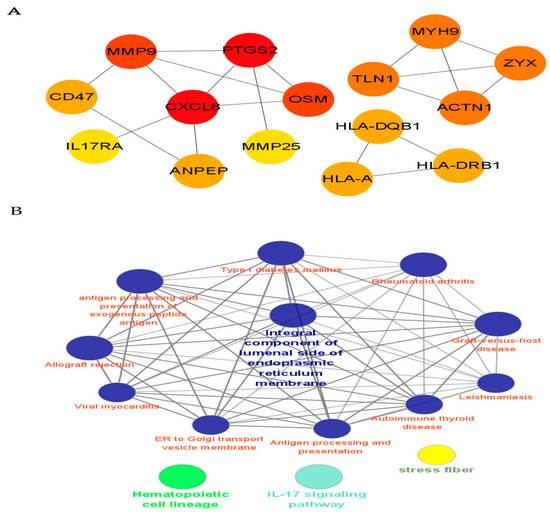
Figure 6.
PPI network analysis and identification of hub genes. (A) We identified the top hub genes (MMP9, PTGS2, CXCL8, OSM, TLN1) associated with CRPS. (B) Cytoscape provides basic functionality to lay out and query the network associated with CRPS; to visually integrate the network with expression profiles, phenotypes, and other molecular states; and to link the network to databases of functional annotations [14]. The potential mechanism of CRPS is analyzed via the PPI network.
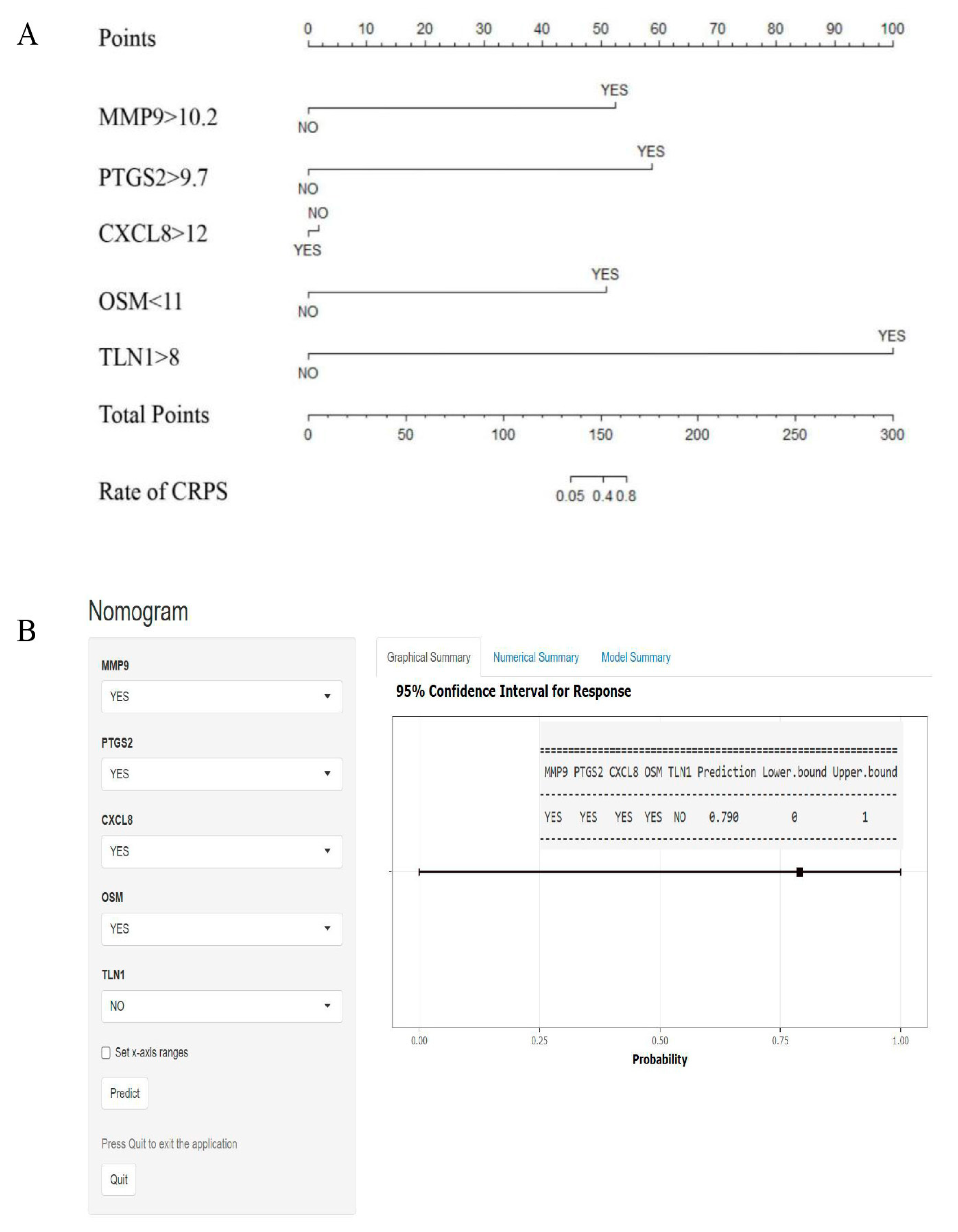
To simplify the predictive model, we converted the expression score of each hub gene into binary variables; then, we used R software to draw the nomogram to predict the rate of CRPS, in consideration of the convenience for clinical application; the dynamic nomogram has been plotted using the DynNom package (Figure 7).
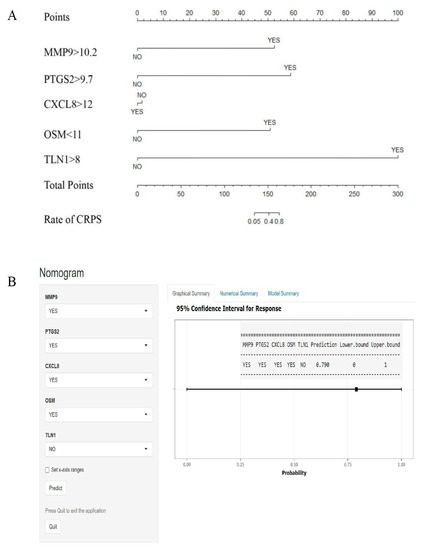
Figure 7.
Nomogram for predicting CRPS. (A) According to the score of each independent variable, the vertical projection to the uppermost points score axis can correspond to a score, and finally all 5 independent risk factor variables are scored and counted. (B) Based on the hub genes, dynamic nomograms are plotted. For example, patients with scores for MMP9 > 10.2, PTGS2 > 9.7, CXCL8 > 12, OSM < 11, and TLN1 < 8; the prediction rate of CRPS is about 79%.
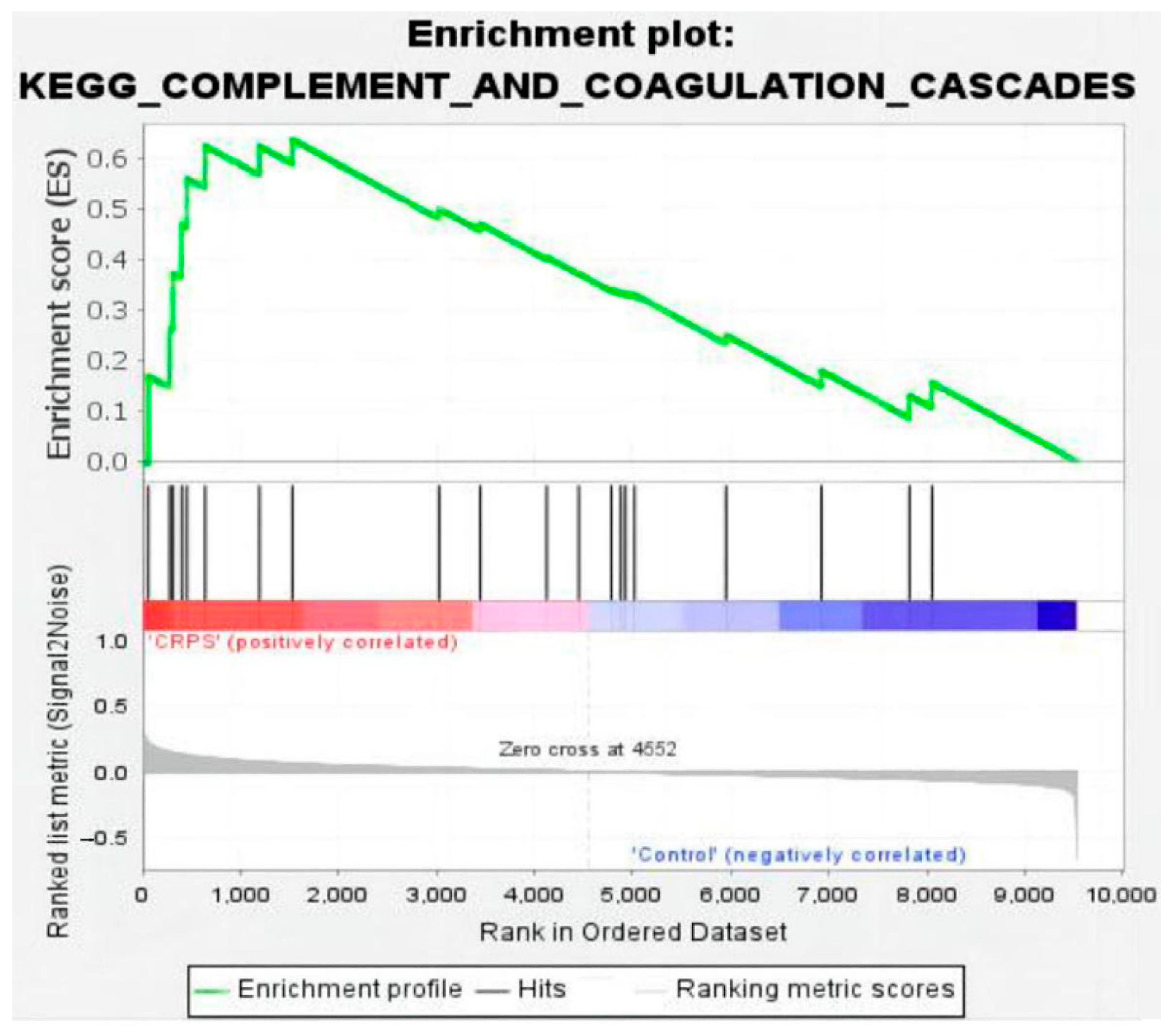
At the same time, GSEA employs a competitive null hypothesis to test significance; thus, we screened out one commonly significant enriched pathway through GSEA analysis (Version 4.3.2): the system of complement and coagulation cascade cascades affected by inflammation (Figure 8). Collectively, the complement and coagulation system is a part of the innate immune system, comprising more than 50 soluble and membrane-bound proteins that mediate inflammatory responses and defend against microbes [15]. Complement activation leads to the generation of C3a, C5a, and the membrane attack complex (C5b-9), which causes a release of pro-inflammatory and procoagulant cytokines such as TNF and in IL-6 associated with CRPS. In our study, the power of GSEA lies in its use of gene sets, which provide a more stable and interpretable measure of biological functions and can show greater experimental and technical variation.
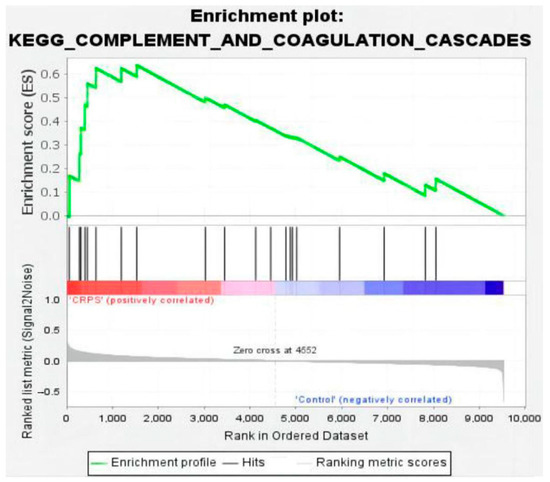
Figure 8.
Enrichment plot for complement and coagulation cascades (nominal p value < 0.01, FDR < 0.25, NES = 1.88).
4. Discussion
The discovery of effective therapeutic targets for CRPS is vitally imperative because of the lack of effective treatments. There is currently little research on the pathogenesis of CRPS, and about 10% of cases develop without a clear clinical symptom [4]. A recent study divided CRPS into two categories: ‘warm’ and ‘cold’ CRPS. The warm subtype is characterized by a warm, red, edematous, and sweaty extremity, whereas the cold type is typically indicated by a cold, blue, less edematous extremity [16]. Previous studies have shown that many targeting inflammatory genes are closely related to CRPS [9]; however, with the continuous research into CRPS undertaken over the past 10 years, and the updated methods of bioinformation analysis, we hope that this research can benefit patients to some extent. Moreover, some new studies have found that acute inflammation and edema due to tissue damage caused ischemia reperfusion through abnormal pathways and changes in the nerves system, including bones and muscles [17]. An increasing amount of evidence suggests that disturbances of body representation and body perception are important features of the CRPS phenotype with the impaired two-point discrimination threshold, but a recent review clarified that this phenomenon also occurs in various nonneuropathic pain conditions [18,19].
In this study, we searched the GEO dataset and only found one expression profile of GSE47063 in relation to homo sapiens-based CRPS. According to a prospective cohort study, the independent factors that were associated with the CRPS type I included high-energy injuries, severe fractures, and female sex [20]. GO functional and KEGG enrichment analysis demonstrated that most overlapped DEGs were mainly enriched in their inflammatory response. From the functional perspective, inflammation in traumatic or nerve injury induces peripheral and central sensitization to limit further injury. As a result, we identified that the top five hub genes (MMP9, PTGS2, CXCL8, OSM, TLN1) and complement system were associated with CRPS, and thus constructed a protein PPI network.
A recent study on CRPS showed inflammatory and anti-inflammatory serum cytokines are potential biomarkers for CRPS, which is consistent with our results [7,21]. Strikingly, Lenz M et al. found that bilaterally proinflammatory TNF-α and MIP-1β were increased and anti-inflammatory IL-1RA was decreased in CRPS [22]. Morellini N et al. demonstrated that an interaction between cutaneous nerves and mast cells may contribute to CRPS, and loss of dermal nerve fibers might attenuate chemotactic signals [23]. Heyn J et al. [24] found that the decrease in Th17 is regulated by CD39+ Tregs and that the anti-inflammatory T-cell shift may be a mechanism of CRPS. Therefore, targeting the processes and molecules that are involved in inflammation could lead to better treatments for CRPS.
Converging lines of evidence suggest that matrix metalloproteinase MMP9 plays an important role in inflammation as well as in pain processes [25]. As expected, from our PPI analysis, we found MMP9, a secreted zinc metallopeptidase, was the most important gene in the development of CRPS. Zinc is an essential nutrient for human health and has anti-oxidative stress and anti-inflammatory functions, and we found zinc ion binding may be one of the important mechanisms of CRPS. Notably, a recent study found that MMP-2 and MMP-9 are differently expressed depending on the clinical phenotype in CRPS; ipsilateral MMP-2 and contralateral MMP-9 were lower in CRPS with trophic changes [26]. Such data may support a process by which contralateral pain progresses to non-injury sites in CRPS. Hossaini et al. also found that one-sided inflammation may increase pain systems in the contralateral cord, the c-fos activation pattern of spinal Gly/GABA neurons [27,28]. At the same time, after nerve injury, activated Schwann cells mediate the breakdown of the blood–nerve barrier via MMP-9, which promotes the recruitment of immune cells from the vasculature and their subsequent release of more pro-inflammatory mediators [29].
In the study of Zhou [30], they found PTGS2 is upregulated in atherosclerosis, which illustrated that the factor is involved in the early inflammatory response of blood vessels in some way. Chemokines, a special class of cytokines with more than 50 members, are a family of small, secreted proteins. In our analysis, we found that CXCL8 (known as IL-8) was an important protein-coding gene in CRPS. The small cytokine CXCL8 is known to be one of the most potent chemoattractant molecules; among several other functions, it is responsible for guiding neutrophils through the tissue matrix until they reach sites of injury [31,32]. According to Huang [33], activation of CXCL8 exacerbated inflammatory reactions in trophoblast cells by inducing TNF-α and IL-1β, which can result in unexplained recurrent pregnancy loss.
Oncostatin M (OSM) has been proven to be an inflammatory factor with multiple regulatory effects. Recent studies have demonstrated that the OSM signal pathway is an important approach for tumor–microglia interaction [34]. Interestingly, OSM is elevated in human obesity, and its specific receptor (OSMRβ) is also induced in conditions of obesity and insulin resistance [35,36]. Our PPI analysis found that type 1 diabetes, graft-versus-host disease, and autoimmune thyroid disease may be related to CRPS. Thus, for obese diabetes patients with CRPS, we should pay attention to the expression of OSM.
There are some studies that found that the human leukocyte antigen (HLA) system is associated with the pathophysiology of CRPS [37,38]. According to de Rooij [39], the involvement of HLA-B62 and HLA-DQ8 in CRPS with dystonia may indicate that these HLAs are implicated in the susceptibility or expression of the disease. Similarly, our study found that HLA-A, HLA-DQB1, and HLA-DRB1 play important roles in the occurrence and development of CRPS. Immunologic influences are also fundamental to CRPS; the increase in neuropeptides such as substance P and calcitonin gene-related peptide leads to the release of pro-inflammatory mediators such as TNF-a, IL-1b, and IL-6 [7,21]. Some researchers also found that aminopeptidase N (ANPEP), histidine decarboxylase (HDC), granulocyte colony-stimulating factor 3 receptor (G-CSF3R), Talin1 (TLN1), signal transducer, and the activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) gene expression, were significantly increased in CRPS patients, and were also all involved in signal transduction, cell motility, and immunity [9]. Previous studies have shown that the complement and coagulation cascades play key roles in innate immunity and are involved in the pathogenesis of inflammatory-related diseases [40]. Moreover, the complement system is composed of a large number of proteases that react with each other via proteolytic cleavage to induce inflammatory responses, which is consistent with our GSEA analysis. To the best of our knowledge, no prior studies have evaluated associations between the complement system and CRPS.
The treatment for CRPS is mainly directed toward physical and psychological therapy, neuropathic pain medications, anti-inflammatory medications, and sympathetic nerve blocking [41,42]. Many studies demonstrated that no good therapeutic results were achieved in the use of NSAIDs in CRPS [43,44]. Hyperbaric oxygen and spinal cord or dorsal root ganglion stimulation can also be used to treat CRPS [45,46,47]. Recently, Vitamin C was thought to be a form of intervention that acts by inhibiting pro-inflammatory pathways mediated through antioxidant mechanisms, but the recent meta-analysis showed no statistical significance in preventing CRPS with distal radial fractures [48,49]. At the same time, mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) actively contribute to the microenvironment of injured tissues; given the plasticity of the immunoregulatory phenotype of MSCs, inflammatory status and concurrent use of immunosuppressants should be considered when administering MSCs for the treatment of inflammatory diseases [50]. Nevertheless, these divergent findings suggest that the long-term efficacy of the methods above is yet to be determined.
Our study also has some limitations. Firstly, our analysis was based on blood samples from homo sapiens and only included nine samples, since there are fewer clinical trials investigating CRPS, especially on the study of its mechanisms. Secondly, we did not conduct further experimental verification for ethical reasons and because of a lack of tissue samples. It is our hope that this bioinformatics analysis will promote further research on the interactions between central and peripheral inflammatory pathways that manifest in CRPS.
5. Conclusions
In summary, this study used integrated bioinformatics to detect these hub genes (MMP9, PTGS2, CXCL8, OSM, TLN1) and the complement system that are associated with CRPS. Obviously, a clearer understanding of the mechanism and pathological significance of the DEGs mainly enriched in their inflammatory response will provide new perspectives to design potential therapeutic targets to intervene in CRPS processes.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, H.Z.; methodology, B.W. and L.X.; software, H.Z. and Y.H.; validation, Y.H.; formal analysis, H.Z.; investigation, B.W.; resources, L.X.; data curation, Y.H.; writing—original draft preparation, H.Z.; writing—review and editing, H.Z.; visualization, B.W.; supervision, L.X.; project administration, Y.H.; funding acquisition, L.X. and Y.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (82271262 (Li Xu), 82071252 (Yuguang Huang)) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (3332022120 (Bei Wen)).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable. All of the data used in this study were obtained from public databases; thus, this study does not contain any intervention experiments associated with animals or humans.
Data Availability Statement
The gene expression microarray GSE47063 (9 samples, 2 CRPS I, 2 CRPS II and 5 controls) was downloaded from the GEO database.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Petersen, P.B.; Mikkelsen, K.L.; Lauritzen, J.B.; Krogsgaard, M.R. Risk Factors for Post-treatment Complex Regional Pain Syndrome (CRPS): An Analysis of 647 Cases of CRPS from the Danish Patient Compensation Association. Pain Pract. 2018, 18, 341–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moseley, G.L.; Herbert, R.D.; Parsons, T.; Lucas, S.; Van Hilten, J.J.; Marinus, J. Intense pain soon after wrist fracture strongly predicts who will develop complex regional pain syndrome: Prospective cohort study. J. Pain 2014, 15, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beerthuizen, A.; Stronks, D.L.; Van’t Spijker, A.; Yaksh, A.; Hanraets, B.M.; Klein, J.; Huygen, F.J.P.M. Demographic and medical parameters in the development of complex regional pain syndrome type 1 (CRPS1): Prospective study on 596 patients with a fracture. Pain 2012, 153, 1187–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ott, S.; Maihöfner, C. Signs and Symptoms in 1043 Patients with Complex Regional Pain Syndrome. J. Pain 2018, 19, 599–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shim, H.; Rose, J.; Halle, S.; Shekane, P. Complex regional pain syndrome: A narrative review for the practising clinician. Br. J. Anaesth. 2019, 123, e424–e433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harden, N.R.; Bruehl, S.; Perez, R.S.G.M.; Birklein, F.; Marinus, J.; Maihofner, C.; Lubenow, T.; Buvanendran, A.; Mackey, S.; Graciosa, J.; et al. Validation of proposed diagnostic criteria (the “Budapest Criteria”) for Complex Regional Pain Syndrome. Pain 2010, 150, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birklein, F.; Ajit, S.K.; Goebel, A.; Perez, R.S.G.M.; Sommer, C. Complex regional pain syndrome—Phenotypic characteristics and potential biomarkers. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2018, 14, 272–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharwani, K.D.; Dik, W.A.; Dirckx, M.; Huygen, F.J.P.M. Highlighting the Role of Biomarkers of Inflammation in the Diagnosis and Management of Complex Regional Pain Syndrome. Mol. Diagn. Ther. 2019, 23, 615–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, E.H.; Zhang, E.; Ko, Y.; Sim, W.S.; Moon, D.E.; Yoon, K.J.; Hong, J.H.; Lee, W.H. Genome-wide expression profiling of complex regional pain syndrome. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e79435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Yi, D.; Yu, Z.; Zhu, B.; Li, S.; Liu, X. Identification of the Hub Genes Related to Nerve Injury-Induced Neuropathic Pain. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, T.; Wilhite, S.E.; Ledoux, P.; Evangelista, C.; Kim, I.F.; Tomashevsky, M.; Marshall, K.A.; Phillippy, K.; Sherman, P.M.; Holko, M.; et al. NCBI GEO: Archive for functional genomics data sets–update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D991–D995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhou, B.; Pache, L.; Chang, M.; Khodabakhshi, A.H.; Tanaseichuk, O.; Benner, C.; Chanda, S.K. Metascape provides a biologist-oriented resource for the analysis of systems-level datasets. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szklarczyk, D.; Gable, A.L.; Nastou, K.C.; Lyon, D.; Kirsch, R.; Pyysalo, S.; Doncheva, N.T.; Legeay, M.; Fang, T.; Bork, P.; et al. The STRING database in 2021: Customizable protein-protein networks, and functional characterization of user-uploaded gene/measurement sets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D605–D612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shannon, P.; Markiel, A.; Ozier, O.; Baliga, N.S.; Wang, J.T.; Ramage, D.; Amin, N.; Schwikowski, B.; Ideker, T. Cytoscape: A software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 2498–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaturvedi, S.; Braunstein, E.M.; Brodsky, R.A. Antiphospholipid syndrome: Complement activation, complement gene mutations, and therapeutic implications. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2021, 19, 607–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruehl, S.; Maihöfner, C.; Stanton-Hicks, M.; Perez, R.S.; Vatine, J.J.; Brunner, F.; Birklein, F.; Schlereth, T.; Mackey, S.; Mailis-Gagnon, A.; et al. Complex regional pain syndrome: Evidence for warm and cold subtypes in a large prospective clinical sample. Pain 2016, 157, 1674–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, M.; Lee, K.H.; Kwon, M.; Lee, B. Possible Therapeutic Options for Complex Regional Pain Syndrome. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torta, D.M.; Legrain, V.; Rossetti, Y.; Mouraux, A. Prisms for pain. Can visuo-motor rehabilitation strategies alleviate chronic pain? Eur. J. Pain 2016, 20, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catley, M.J.; O’Connell, N.E.; Berryman, C.; Ayhan, F.F.; Moseley, G.L. Is tactile acuity altered in people with chronic pain? a systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Pain 2014, 15, 985–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roh, Y.H.; Lee, B.K.; Noh, J.H.; Baek, J.R.; Oh, J.H.; Gong, H.S.; Baek, G.H. Factors associated with complex regional pain syndrome type I in patients with surgically treated distal radius fracture. Arch. Orthop. Trauma Surg. 2014, 134, 1775–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David Clark, J.; Tawfik, V.L.; Tajerian, M.; Kingery, W.S. Autoinflammatory and autoimmune contributions to complex regional pain syndrome. Mol. Pain 2018, 14, 1744806918799127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lenz, M.; Üçeyler, N.; Frettlöh, J.; Höffken, O.; Krumova, E.K.; Lissek, S.; Reinersmann, A.; Sommer, C.; Stude, P.; Waaga-Gasser, A.M.; et al. Local cytokine changes in complex regional pain syndrome type I (CRPS I) resolve after 6 months. Pain 2013, 154, 2142–2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morellini, N.; Finch, P.M.; Goebel, A.; Drummond, P.D. Dermal nerve fibre and mast cell density, and proximity of mast cells to nerve fibres in the skin of patients with complex regional pain syndrome. Pain 2018, 159, 2021–2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heyn, J.; Azad, S.C.; Luchting, B. Altered regulation of the T-cell system in patients with CRPS. Inflamm. Res. 2019, 68, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, R.R.; Xu, Z.Z.; Gao, Y.J. Emerging targets in neuroinflammation-driven chronic pain. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2014, 13, 533–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escolano-Lozano, F.; Gries, E.; Schlereth, T.; Dimova, V.; Baka, P.; Vlckova, E.; König, S.; Birklein, F. Local and Systemic Expression Pattern of MMP-2 and MMP-9 in Complex Regional Pain Syndrome. J. Pain 2021, 22, 1294–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossaini, M.; Sarac, C.; Jongen, J.L.; Holstege, J.C. Spinal glycinergic and GABAergic neurons expressing C-fos after capsaicin stimulation are increased in rats with contralateral neuropathic pain. Neuroscience 2011, 196, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linnman, C.; Becerra, L.; Borsook, D. Inflaming the brain: CRPS a model disease to understand neuroimmune interactions in chronic pain. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2013, 8, 547–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, R.R.; Chamessian, A.; Zhang, Y.Q. Pain regulation by non-neuronal cells and inflammation. Science 2016, 354, 572–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhou, H.; Hua, L.; Hou, C.; Jia, Q.; Chen, J.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Y.; He, S.; Jia, E. Verification of ferroptosis and pyroptosis and identification of PTGS2 as the hub gene in human coronary artery atherosclerosis. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2021, 171, 55–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, S.; Reyes-Aldasoro, C.C.; Candel, S.; Renshaw, S.A.; Mulero, V.; Calado, A. Cxcl8 (IL-8) mediates neutrophil recruitment and behavior in the zebrafish inflammatory response. J. Immunol. 2013, 190, 4349–4359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liubomirski, Y.; Lerrer, S.; Meshel, T.; Rubinstein-Achiasaf, L.; Morein, D.; Wiemann, S.; Körner, C.; Ben-Baruch, A. Tumor-Stroma-Inflammation Networks Promote Pro-metastatic Chemokines and Aggressiveness Characteristics in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Front. Immunol. 2019, 12, 757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.; Du, G.; Huang, X.; Han, L.; Han, X.; Xu, B.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, M.; Qin, Y.; Xia, Y. The enhancer RNA lnc-SLC4A1-1 epigenetically regulates unexplained recurrent pregnancy loss (URPL) by activating CXCL8 and NF-kB pathway. EBioMedicine 2018, 38, 162–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Ren, R.; Lin, W.; Xiang, L.; Zhao, Z.; Shao, B. Exploring the oncostatin M (OSM) feed-forward signaling of glioblastoma via STAT3 in pan-cancer analysis. Cancer Cell Int. 2021, 21, 565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Infantes, D.; Stephens, J.M. Adipocyte Oncostatin Receptor Regulates Adipose Tissue Homeostasis and Inflammation. Front. Immunol. 2021, 29, 612013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elks, C.M.; Zhao, P.; Grant, R.W.; Hang, H.; Bailey, J.L.; Burk, D.H.; McNulty, M.A.; Mynatt, R.L.; Stephens, J.M. Loss of Oncostatin M Signaling in Adipocytes Induces Insulin Resistance and Adipose Tissue Inflammation In Vivo. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 17066–17076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Rooijen, D.E.; Roelen, D.L.; Verduijn, W.; Haasnoot, G.W.; Huygen, F.J.; Perez, R.S.; Claas, F.H.; Marinus, J.; van Hilten, J.J.; van den Maagdenberg, A.M. Genetic HLA associations in complex regional pain syndrome with and without dystonia. J. Pain 2012, 13, 784–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawcer, S. The complex genetics of multiple sclerosis: Pitfalls and prospects. Brain 2008, 131, 3118–3131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Rooij, A.M.; Florencia Gosso, M.; Haasnoot, G.W.; Marinus, J.; Verduijn, W.; Claas, F.H.; van den Maagdenberg, A.M.; van Hilten, J.J. HLA-B62 and HLA-DQ8 are associated with Complex Regional Pain Syndrome with fixed dystonia. Pain 2009, 145, 82–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.C.W.; You, W.H. Innate immunity in diabetic kidney disease. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2020, 16, 206–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harden, R.N.; Oaklander, A.L.; Burton, A.W.; Perez, R.S.; Richardson, K.; Swan, M.; Barthel, J.; Costa, B.; Graciosa, J.R.; Bruehl, S. Reflex Sympathetic Dystrophy Syndrome Association. Complex regional pain syndrome: Practical diagnostic and treatment guidelines, 4th edition. Pain Med. 2013, 14, 180–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urits, I.; Shen, A.H.; Jones, M.R.; Viswanath, O.; Kaye, A.D. Complex Regional Pain Syndrome, Current Concepts and Treatment Options. Curr. Pain Headache Rep. 2018, 22, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breuer, A.J.; Mainka, T.; Hansel, N.; Maier, C.; Krumova, E.K. Short-term treatment with parecoxib for complex regional pain syndrome: A randomized, placebo-controlled double-blind trial. Pain Physician 2014, 17, 127–137. [Google Scholar]
- Eckmann, M.S.; Ramamurthy, S.; Griffin, J.G. Intravenous regional ketorolac and lidocaine in the treatment of complex regional pain syndrome of the lower extremity: A randomized, double-blinded, crossover study. Clin. J. Pain 2011, 27, 203–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visnjevac, O.; Costandi, S.; Patel, B.A.; Azer, G.; Agarwal, P.; Bolash, R.; Mekhail, N.A. A Comprehensive Outcome-Specific Review of the Use of Spinal Cord Stimulation for Complex Regional Pain Syndrome. Pain Pract. 2017, 17, 533–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deer, T.R.; Levy, R.M.; Kramer, J.; Poree, L.; Amirdelfan, K.; Grigsby, E.; Staats, P.; Burton, A.W.; Burgher, A.H.; Obray, J.; et al. Dorsal root ganglion stimulation yielded higher treatment success rate for complex regional pain syndrome and causalgia at 3 and 12 months: A randomized comparative trial. Pain 2017, 158, 669–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Pan, Y.; Xu, H.; Song, X. Hyperbaric oxygen attenuates neuropathic pain and reverses inflammatory signaling likely via the Kindlin-1/Wnt-10a signaling pathway in the chronic pain injury model in rats. J. Headache Pain 2017, 18, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zollinger, P.E.; Tuinebreijer, W.E.; Kreis, R.W.; Breederveld, R.S. Effect of vitamin C on frequency of reflex sympathetic dystrophy in wrist fractures: A randomised trial. Lancet 1999, 354, 2025–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evaniew, N.; McCarthy, C.; Kleinlugtenbelt, Y.V.; Ghert, M.; Bhandari, M. Vitamin C to Prevent Complex Regional Pain Syndrome in Patients with Distal Radius Fractures: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. J. Orthop. Trauma 2015, 29, e235–e241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, Q.; Liu, K.; Hou, J.; Shao, C.; Wang, Y. Immunoregulatory mechanisms of mesenchymal stem and stromal cells in inflammatory diseases. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2018, 4, 493–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).