Deregulation of Plasma microRNA Expression in a TARDBP-ALS Family
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Cohorts and Ethics Statements
2.2. RNA Isolation
2.3. Reverse Transcription and Quantitative PCR
2.4. Statistical Analysis
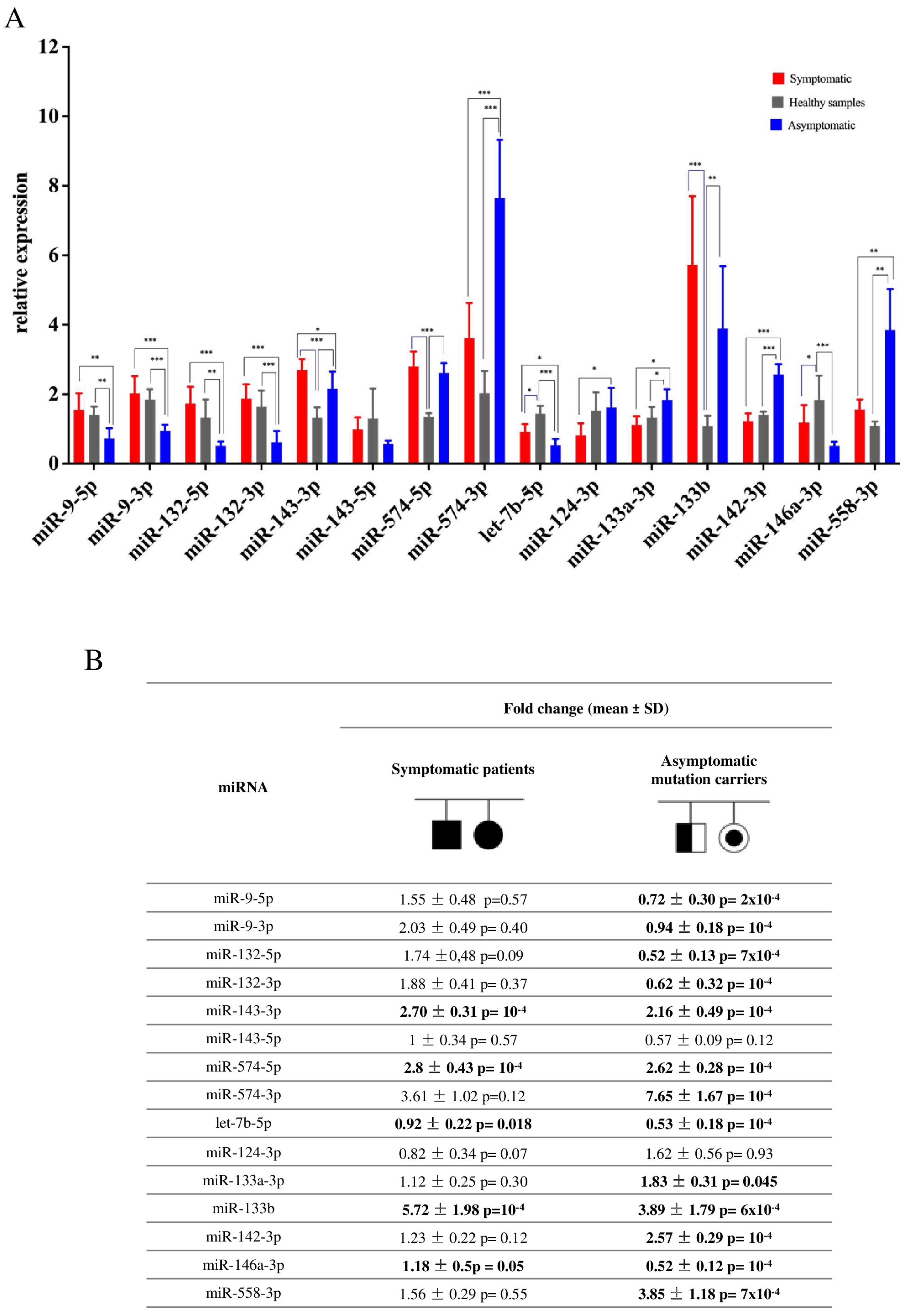
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mejzini, R.; Flynn, L.L.; Pitout, I.L.; Fletcher, S.; Wilton, S.D.; Akkari, P.A. ALS Genetics, Mechanisms, and Therapeutics: Where Are We Now? Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mead, R.J.; Shan, N.; Reiser, H.J.; Marshall, F.; Shaw, P.J. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: A neurodegenerative disorder poised for successful therapeutic translation. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2023, 22, 185–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ungaro, C.; Sprovieri, T.; Morello, G.; Perrone, B.; Spampinato, A.G.; Simone, I.L.; Trojsi, F.; Monsurro, M.R.; Spataro, R.; La Bella, V.; et al. Genetic investigation of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis patients in south Italy: A two-decade analysis. Neurobiol. Aging 2021, 99, 99.e7–99.e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goyal, N.A.; Berry, J.D.; Windebank, A.; Staff, N.P.; Maragakis, N.J.; van den Berg, L.H.; Genge, A.; Miller, R.; Baloh, R.H.; Kern, R.; et al. Addressing heterogeneity in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis CLINICAL TRIALS. Muscle Nerve 2020, 62, 156–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gros-Louis, F.; Gaspar, C.; Rouleau, G.A. Genetics of familial and sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2006, 1762, 956–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosen, D.R.; Siddique, T.; Patterson, D.; Figlewicz, D.A.; Sapp, P.; Hentati, A.; Donaldson, D.; Goto, J.; O′Regan, J.P.; Deng, H.X.; et al. Mutations in Cu/Zn superoxide dismutase gene are associated with familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Nature 1993, 362, 59–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwiatkowski, T.J., Jr.; Bosco, D.A.; Leclerc, A.L.; Tamrazian, E.; Vanderburg, C.R.; Russ, C.; Davis, A.; Gilchrist, J.; Kasarskis, E.J.; Munsat, T.; et al. Mutations in the FUS/TLS gene on chromosome 16 cause familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Science 2009, 323, 1205–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreedharan, J.; Blair, I.P.; Tripathi, V.B.; Hu, X.; Vance, C.; Rogelj, B.; Ackerley, S.; Durnall, J.C.; Williams, K.L.; Buratti, E.; et al. TDP-43 mutations in familial and sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Science 2008, 319, 1668–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrne, S.; Elamin, M.; Bede, P.; Shatunov, A.; Walsh, C.; Corr, B.; Heverin, M.; Jordan, N.; Kenna, K.; Lynch, C.; et al. Cognitive and clinical characteristics of patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis carrying a C9orf72 repeat expansion: A population-based cohort study. Lancet Neurol. 2012, 11, 232–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawahara, Y.; Mieda-Sato, A. TDP-43 promotes microRNA biogenesis as a component of the Drosha and Dicer complexes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 3347–3352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, B.R.; Miller, R.G.; Swash, M.; Munsat, T.L.; World Federation of Neurology Research Group on Motor Neuron Diseases. El Escorial revisited: Revised criteria for the diagnosis of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Amyotroph. Lateral Scler. Other Mot. Neuron Disord. 2000, 1, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvalho, M.D.; Swash, M. Awaji diagnostic algorithm increases sensitivity of El Escorial criteria for ALS diagnosis. Amyotroph. Lateral Scler. 2009, 10, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannaford, A.; Pavey, N.; van den Bos, M.; Geevasinga, N.; Menon, P.; Shefner, J.M.; Kiernan, M.C.; Vucic, S. Diagnostic Utility of Gold Coast Criteria in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Ann. Neurol. 2021, 89, 979–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sturmey, E.; Malaspina, A. Blood biomarkers in ALS: Challenges, applications and novel frontiers. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2022, 146, 375–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benatar, M.; Granit, V.; Andersen, P.M.; Grignon, A.L.; McHutchison, C.; Cosentino, S.; Malaspina, A.; Wuu, J. Mild motor impairment as prodromal state in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: A new diagnostic entity. Brain 2022, 145, 3500–3508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, B.; Lee, E.; Li, T.; Rampersaud, M. Role of miRNAs in Neurodegeneration: From Disease Cause to Tools of Biomarker Discovery and Therapeutics. Genes 2022, 13, 425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentile, G.; Morello, G.; La Cognata, V.; Guarnaccia, M.; Conforti, F.L.; Cavallaro, S. Dysregulated miRNAs as Biomarkers and Therapeutical Targets in Neurodegenerative Diseases. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panio, A.; Cava, C.; D′Antona, S.; Bertoli, G.; Porro, D. Diagnostic Circulating miRNAs in Sporadic Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 861960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Getz, G.; Miska, E.A.; Alvarez-Saavedra, E.; Lamb, J.; Peck, D.; Sweet-Cordero, A.; Ebert, B.L.; Mak, R.H.; Ferrando, A.A.; et al. MicroRNA expression profiles classify human cancers. Nature 2005, 435, 834–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, J.A.; Baxter, D.H.; Zhang, S.; Huang, D.Y.; Huang, K.H.; Lee, M.J.; Galas, D.J.; Wang, K. The microRNA spectrum in 12 body fluids. Clin. Chem. 2010, 56, 1733–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruffo, P.; Strafella, C.; Cascella, R.; Caputo, V.; Conforti, F.L.; Ando, S.; Giardina, E. Deregulation of ncRNA in Neurodegenerative Disease: Focus on circRNA, lncRNA and miRNA in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 784996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conforti, F.L.; Sproviero, W.; Simone, I.L.; Mazzei, R.; Valentino, P.; Ungaro, C.; Magariello, A.; Patitucci, A.; La Bella, V.; Sprovieri, T.; et al. TARDBP gene mutations in south Italian patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2011, 82, 587–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czell, D.; Andersen, P.M.; Morita, M.; Neuwirth, C.; Perren, F.; Weber, M. Phenotypes in Swiss patients with familial ALS carrying TARDBP mutations. Neurodegener. Dis. 2013, 12, 150–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsuzawa, S.; Akiyama, T.; Nishiyama, A.; Suzuki, N.; Kato, M.; Warita, H.; Izumi, R.; Osana, S.; Koyama, S.; Kato, T.; et al. TARDBP p.G376D mutation, found in rapid progressive familial ALS, induces mislocalization of TDP-43. eNeurologicalSci 2018, 11, 20–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfaffl, M.W. A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001, 29, e45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ingre, C.; Roos, P.M.; Piehl, F.; Kamel, F.; Fang, F. Risk factors for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Clin. Epidemiol. 2015, 7, 181–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buratti, E.; De Conti, L.; Stuani, C.; Romano, M.; Baralle, M.; Baralle, F. Nuclear factor TDP-43 can affect selected microRNA levels. FEBS J. 2010, 277, 2268–2281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freischmidt, A.; Muller, K.; Ludolph, A.C.; Weishaupt, J.H. Systemic dysregulation of TDP-43 binding microRNAs in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2013, 1, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karagkouni, D.; Paraskevopoulou, M.D.; Chatzopoulos, S.; Vlachos, I.S.; Tastsoglou, S.; Kanellos, I.; Papadimitriou, D.; Kavakiotis, I.; Maniou, S.; Skoufos, G.; et al. DIANA-TarBase v8: A decade-long collection of experimentally supported miRNA-gene interactions. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D239–D245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freischmidt, A.; Muller, K.; Zondler, L.; Weydt, P.; Volk, A.E.; Bozic, A.L.; Walter, M.; Bonin, M.; Mayer, B.; von Arnim, C.A.; et al. Serum microRNAs in patients with genetic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and pre-manifest mutation carriers. Brain 2014, 137, 2938–2950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freischmidt, A.; Muller, K.; Zondler, L.; Weydt, P.; Mayer, B.; von Arnim, C.A.; Hubers, A.; Dorst, J.; Otto, M.; Holzmann, K.; et al. Serum microRNAs in sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Neurobiol. Aging 2015, 36, 2660.e15–2660.e20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanet, A.; Tacheny, A.; Arnould, T.; Renard, P. miR-212/132 expression and functions: Within and beyond the neuronal compartment. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, 4742–4753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, B.P.; Burge, C.B.; Bartel, D.P. Conserved seed pairing, often flanked by adenosines, indicates that thousands of human genes are microRNA targets. Cell 2005, 120, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vacchiano, V.; Mastrangelo, A.; Zenesini, C.; Masullo, M.; Quadalti, C.; Avoni, P.; Polischi, B.; Cherici, A.; Capellari, S.; Salvi, F.; et al. Plasma and CSF Neurofilament Light Chain in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: A Cross-Sectional and Longitudinal Study. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2021, 13, 753242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poesen, K.; Van Damme, P. Diagnostic and Prognostic Performance of Neurofilaments in ALS. Front. Neurol. 2018, 9, 1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morlando, M.; Dini Modigliani, S.; Torrelli, G.; Rosa, A.; Di Carlo, V.; Caffarelli, E.; Bozzoni, I. FUS stimulates microRNA biogenesis by facilitating co-transcriptional Drosha recruitment. EMBO J. 2012, 31, 4502–4510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waller, R.; Wyles, M.; Heath, P.R.; Kazoka, M.; Wollff, H.; Shaw, P.J.; Kirby, J. Small RNA Sequencing of Sporadic Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Cerebrospinal Fluid Reveals Differentially Expressed miRNAs Related to Neural and Glial Activity. Front. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lagos-Quintana, M.; Rauhut, R.; Yalcin, A.; Meyer, J.; Lendeckel, W.; Tuschl, T. Identification of tissue-specific microRNAs from mouse. Curr. Biol. 2002, 12, 735–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sim, S.E.; Lim, C.S.; Kim, J.I.; Seo, D.; Chun, H.; Yu, N.K.; Lee, J.; Kang, S.J.; Ko, H.G.; Choi, J.H.; et al. The Brain-Enriched MicroRNA miR-9-3p Regulates Synaptic Plasticity and Memory. J. Neurosci. 2016, 36, 8641–8652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, X. Systematic identification of microRNA functions by combining target prediction and expression profiling. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, 1646–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.; Dong, X.; Zheng, D.; Nao, J. MiR-124 and the Underlying Therapeutic Promise of Neurodegenerative Disorders. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaz, A.R.; Vizinha, D.; Morais, H.; Colaco, A.R.; Loch-Neckel, G.; Barbosa, M.; Brites, D. Overexpression of miR-124 in Motor Neurons Plays a Key Role in ALS Pathological Processes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matamala, J.M.; Arias-Carrasco, R.; Sanchez, C.; Uhrig, M.; Bargsted, L.; Matus, S.; Maracaja-Coutinho, V.; Abarzua, S.; van Zundert, B.; Verdugo, R.; et al. Genome-wide circulating microRNA expression profiling reveals potential biomarkers for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Neurobiol. Aging 2018, 64, 123–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Pi, J.; Zou, D.; Wang, X.; Xu, J.; Yu, S.; Zhang, T.; Li, F.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, H.; et al. microRNA arm-imbalance in part from complementary targets mediated decay promotes gastric cancer progression. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhang, R.; Xu, R.; Shang, J.; He, H.; Yang, Q. MicroRNA-574-5p in gastric cancer cells promotes angiogenesis by targeting protein tyrosine phosphatase non-receptor type 3 (PTPN3). Gene 2020, 733, 144383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mackenzie, I.R.; Bigio, E.H.; Ince, P.G.; Geser, F.; Neumann, M.; Cairns, N.J.; Kwong, L.K.; Forman, M.S.; Ravits, J.; Stewart, H.; et al. Pathological TDP-43 distinguishes sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis from amyotrophic lateral sclerosis with SOD1 mutations. Ann. Neurol. 2007, 61, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boudreau, R.L.; Jiang, P.; Gilmore, B.L.; Spengler, R.M.; Tirabassi, R.; Nelson, J.A.; Ross, C.A.; Xing, Y.; Davidson, B.L. Transcriptome-wide discovery of microRNA binding sites in human brain. Neuron. 2014, 81, 294–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variable | SC (n = 7) | AC (n = 7) | HC (n = 13) | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age $ at blood drawing | 52 (42–60) | 42 (33–73) | 52 (44–76) | 0.47 * |
| Age $ at onset | 50 (37–57) | N.A. | N.A. | |
| Sex (M/F) | 1.33 | 2.5 | 0.85 | 0.19 ** |
| Onset Spinal, n (%) Bulbar, n (%) | 5 (71) 2(29) | N.A. | N.A. | |
| ALSFRS-R a | 44 (41–45) | N.A. | N.A. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ruffo, P.; Catalano, S.; La Bella, V.; Conforti, F.L. Deregulation of Plasma microRNA Expression in a TARDBP-ALS Family. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 706. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13040706
Ruffo P, Catalano S, La Bella V, Conforti FL. Deregulation of Plasma microRNA Expression in a TARDBP-ALS Family. Biomolecules. 2023; 13(4):706. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13040706
Chicago/Turabian StyleRuffo, Paola, Stefania Catalano, Vincenzo La Bella, and Francesca Luisa Conforti. 2023. "Deregulation of Plasma microRNA Expression in a TARDBP-ALS Family" Biomolecules 13, no. 4: 706. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13040706
APA StyleRuffo, P., Catalano, S., La Bella, V., & Conforti, F. L. (2023). Deregulation of Plasma microRNA Expression in a TARDBP-ALS Family. Biomolecules, 13(4), 706. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13040706







