Abstract
Dupilumab was first approved for the treatment of atopic dermatitis (AD) and blocks the signaling of interleukin (IL)-4 and -13. Several other chronic skin conditions share mechanistic overlaps with AD in their pathophysiology, i.e., are linked to type 2 inflammation. Most recently, dupilumab was approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for prurigo nodularis (PN). Given its relatively good safety profile, effective off-label use of dupilumab has been reported for a multitude of dermatologic diseases and several clinical trials for dermatologic skin conditions are currently ongoing. We conducted a systematic review of applications of dupilumab in dermatology other than AD and PN by searching the databases PubMed/Medline, Scopus, Web of Science and Cochrane Library as well as the clinical trial registry ClinicalTrials.gov. We found several reports for effective treatment of bullous autoimmune diseases, eczema, prurigo, alopecia areata, chronic spontaneous urticaria, Netherton syndrome and a variety of other chronic inflammatory skin diseases.
1. Introduction
Dupilumab is a human monoclonal IgG4 antibody directed against the interleukin (IL)-4 receptor alpha chain (IL4Rα) and inhibits signaling of both IL-4 and -13. These cytokines are key mediators of type 2 helper T cell (Th2)-related immune responses that drive atopic and many other inflammatory skin diseases. Th2-responses are associated with eosinophilia, basophil and mast cell recruitment and production of IgE. Dupilumab was first approved by the European Medicines Agency and the U.S. Food and Drug Administration in 2017 for the management of moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis (AD) in adults, and more recently, in adolescents and children from the age of 6 months. Clinical trials showed long-term improvement of AD-signs and symptoms including pruritus, size and severity of skin lesions and overall quality of life, as well as lower rates of skin infections compared with placebo treatment [1,2,3]. Patient skin samples revealed downregulation of Th2 molecular markers, reduction of cellular infiltrate and an improved skin barrier function [4,5]. Beyond dermatology, dupilumab is also effective and approved for moderate-to-severe asthma, chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyposis (CRSwNP) [6] and eosinophilic esophagitis. In addition, efficacy of dupilumab in prurigo nodularis (PN) and other forms of chronic prurigo was previously shown in several reports [7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32]. The phase 3 clinical trials LIBERTY-PN PRIME and PRIME2 showed significantly reduced itch, amelioration of skin lesions, sleep, pain and quality of life compared to placebo treatment in a total of 153 treated patients (NCT04202679, NCT04183335). These findings led to the approval of dupilumab for PN in adults in September of 2022 [33].
Adverse events reported most frequently are nasopharyngitis, upper respiratory tract infections, headache, injection-site reactions and conjunctivitis [2]; further, facial and neck erythema was rare but typically attributed to dupilumab [34]. As this indicates relatively high drug safety, dupilumab has been administered off-label in several other dermatologic disease entities known to be associated with Th2-responses, reviewed previously in [35,36,37] (Figure 1). A number of clinical trials are currently ongoing for chronic pruritus of unknown origin, chronic hand eczema, nummular eczema, bullous pemphigoid, alopecia areata, chronic spontaneous, cold or cholinergic urticaria, localized scleroderma, keloids, food allergies and Netherton syndrome.
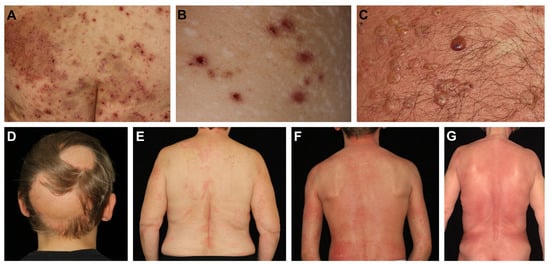
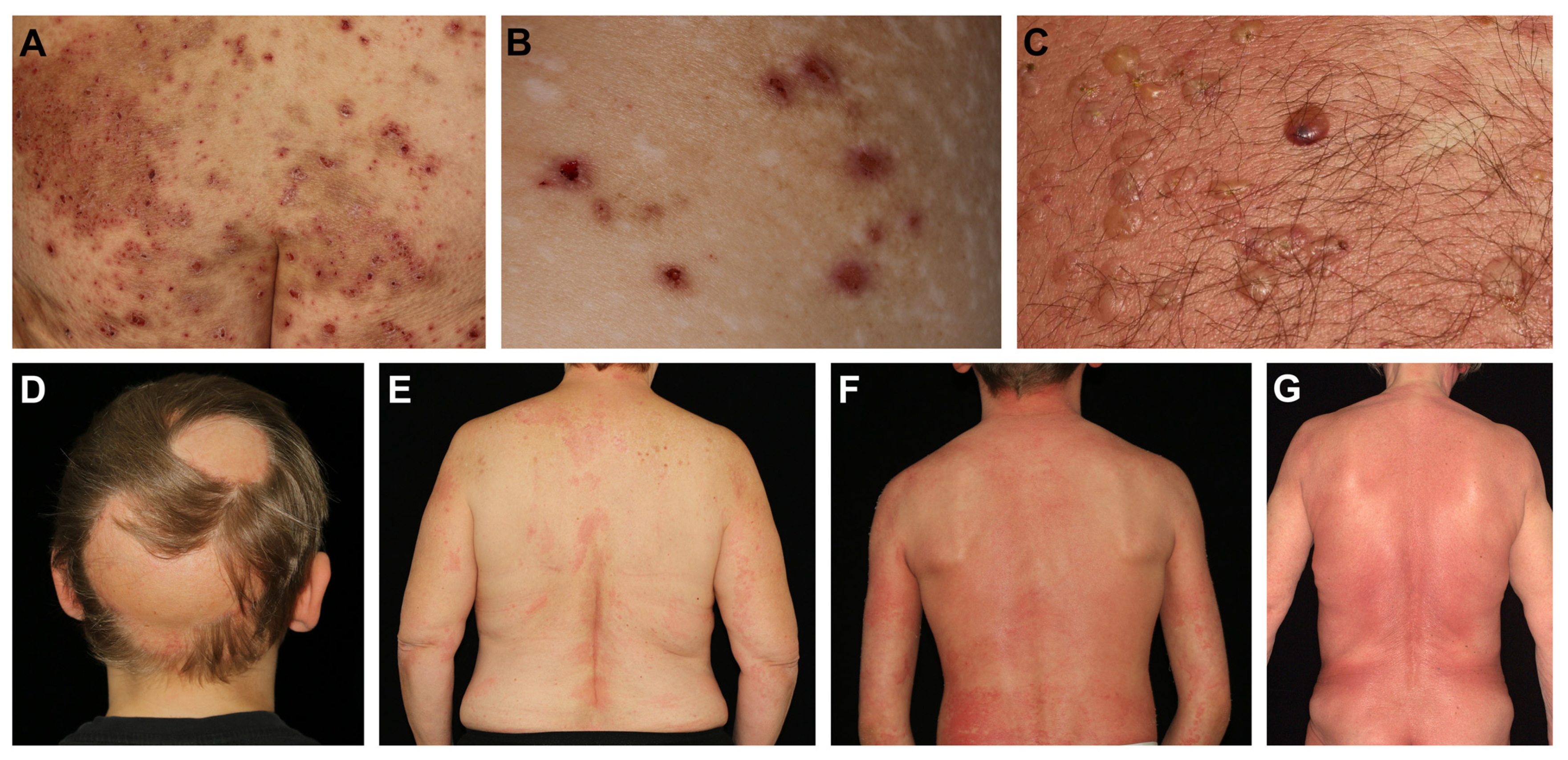
Figure 1.
Clinical presentations of chronic inflammatory skin diseases with reports of effective dupilumab treatment. (A) Severe nummular eczema with confluent itchy and scaly plaques showing superficial excoriations. (B) Chronic prurigo presenting with intensely pruritic nodules that are developed and sustained by pathognomonic itch-scratch cycles. Deep scratching results in visible scars. (C) Tense clear or hemorrhagic blisters on reddish and infiltrated skin typically seen in bullous pemphigoid. (D) Nonscarring patchy hair loss on the scalp in a patient with alopecia areata. Progression can lead to total hair loss of the head (alopecia totalis, AT) or even the entire body (alopecia universalis, AU). (E) Chronic urticaria presenting with recurrent wheals that form and fade in rapid succession and can be accompanied with itch. (F) A pediatric patient with Netherton syndrome presenting with severe itchy chronic infiltration, lichenification and papulation of the skin resembling atopic dermatitis. (G) Mycosis fungoides in an elderly patient with localized dark patches on the trunk that are highly pruritic.
This systematic review addresses clinical outcomes and potential future use of dupilumab in chronic inflammatory skin conditions.
2. Methods
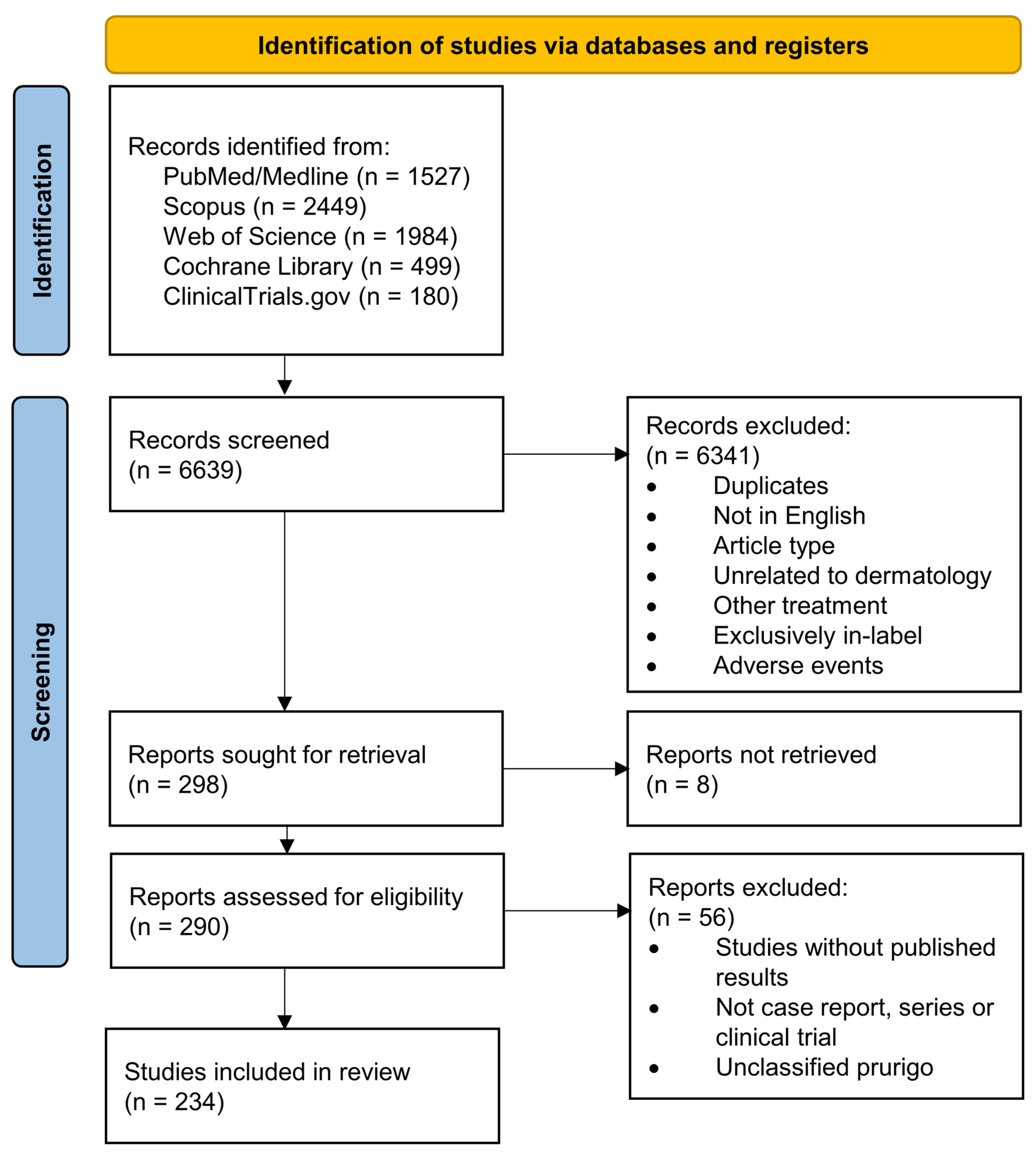
The databases PubMed/Medline, Scopus, Web of Science and Cochrane Library were queried for the terms (“dermatology” OR “skin” OR “dermatitis”) AND “dupilumab” and reports published before 15 January 2023 were collected. Spelling variants of the query terms were included. Further, the registry ClinicalTrials.gov was queried for “dupilumab” as specialty specifications were frequently not denoted. The search strategy was represented in a flow chart according to the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) [38] (Figure 2).
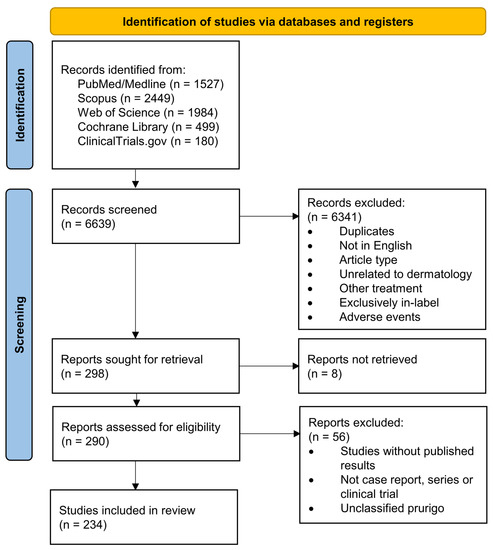
Figure 2.
PRISMA flow diagram depicting the different phases of this systematic review.
Duplicate reports were identified automatically by PubMed or ClinicalTrials.gov identifiers (PMID or NCT registry numbers) and excluded. By screening based on titles and abstracts performed by hand, we then excluded duplicate reports not identified previously, articles in languages other than English, all review articles and meeting abstracts. Further, we excluded reports unrelated to the field of dermatology, reports on other drugs than dupilumab, or reports of sole in-label treatment with dupilumab (including treatment for AD or PN in adults), as well as reports of adverse events of in-label dupilumab treatment.
The search was refined by full-text review after excluding articles that could not be retrieved. Here, we excluded reports other than case reports, case series, retrospective clinical studies or randomized controlled trials (RCT), reports that did not clarify clinical responses, and studies that had not yet reported. Further, reports of adult patients with chronic prurigo were excluded if the subtype of prurigo was not elucidated in order to avoid repeated reporting of PN. The levels of evidence were categorized for each report adapting the Oxford Centre for Evidence-Based Medicine (OCEBM) levels of evidence table [39]: Level 5—singular case reports; level 4—case series or uncontrolled retrospective studies; level 3—prospective and interventional studies as well as controlled retrospective studies; level 2—randomized controlled trials and level 1—meta-analyses.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Eczema
Pruritus is often a prime symptom of eczema and hence, eczematous skin lesions frequently show signs of scratching and excoriation (Figure 1A). A variety of eczema entities including atopic hand eczema (HE)/hand dermatitis or nummular eczema (NE) can have clinical and functional overlaps with AD. Still, hand and nummular eczema/dermatitis can develop in non-atopic individuals and without fulfilling diagnostic criteria for AD (e.g., Hanifin’s and Rajka’s criteria), thus, treatment with dupilumab in these conditions is currently off-label, or can be offered to patients with concomitant AD.
NE is characterized by coin-shaped eczematous plaques and was typically associated with skin microbial disbalance; yet, pathogenesis is highly heterogeneous. We identified retrospective case series with a total of 36 patients with NE treated with dupilumab. However, the majority of patients (30/36) had concomitant AD. Significant improvement of skin manifestations measured by the eczema area and severity index (EASI) or affected body surface area (BSA) as well as improvement in pruritus and quality of life was found in all treated patients, including 6 patients without AD. The responses were sustained in all but one patient during a follow-up period of up to 2 years (Table 1) [40,41]. The phase 2 placebo-controlled RCT DUPINUM (NCT04600362) investigating efficacy and safety of dupilumab in adults with NE is currently recruiting.
Contact dermatitis is frequently associated with the patient’s occupation and can be caused by irritants (irritant-toxic contact dermatitis, ICD) or type-IV allergens (allergic contact dermatitis, ACD). ACD is found more frequently in patients with AD, suggesting a susceptibility to type-IV sensitivities possibly by a defective skin barrier. ACD mechanisms are highly variable and allergen-specific with, e.g., a strong Th1/Th17-polarization found for nickel while fragrances and rubber showed a Th2-bias [42]. Records found for a total of 67 patients with or without concomitant AD that were refractory to topical and systemic steroids as well as other systemic immunosuppressants and subsequently treated with dupilumab showed complete or partial responses in 65/67 patients (Table 1) [43,44,45,46,47,48,49,50,51,52,53,54,55,56,57,58,59]. In two cases, no effects of dupilumab were reported [60,61]. Interestingly, some reports demonstrated clinical remissions under dupilumab when allergen or irritant avoidance was not feasible. Other studies performed patch-testing before and after treatment with dupilumab and found that for most type-IV allergens except for fragrance and balsam of Peru, testing results remained positive despite overall clinical improvement [62]. Thus, larger studies considering allergen specificities and concomitant atopy are needed. Currently, two open-label phase 4 clinical trials evaluating dupilumab in ACD are recruiting (NCT05535738, NCT03935971).

Table 1.
Eczema.
Table 1.
Eczema.
| Disease | Study Type | n | Sex/Age | Presentation | Medical History | Prior Therapies | Concomitant Therapy | Therapy | Response | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nummular dermatitis | retrospective study (4) | 30 | 38.2 (mean, 19–78 range), females: 12/30 | nummular eczema associated with AD (30/30) | AD (30/30) | topical (18/30) and systemic (28/30) steroids, topical calcineurin inhibitors (8/30), ciclosporin (22/30) | Dupilumab 600 mg s.c., then 300 mg q2w | Improvement in skin manifestations (EASI -32.87 mean), itch (NRS -7.17 mean) and quality of life (DLQI -14.57 mean) at 16 wk | [40] | |
| Nummular dermatitis | case series (4) | 6 | 73.5 (median, 45–90 range), females: 1/6 | nummular eczema without AD | no AD (0/6), allergic rhinitis (2/6), asthma (1/6), allergic contact dermatitis (2/6), CHE (1/6) Grover’s disease (1/6) | topical (6/6) and systemic (2/6) steroids, topical calcineurin inhibitor (4/6), topical Vitamin-D analogue (1/6), phototherapy (3/6), MTX (1/6), mycophenolic acid (2/6), ciclosporin (2/6) | ciclosporin (1/6) | Dupilumab 600 mg s.c., then 300 mg q2w | sustained complete response with BSA < 1% (5/6) at up to 2 years follow-up, temporary improvement (1/6) | [41] |
| Contact dermatitis | retrospective study (4) | 15 | 55 (median, 28–72 range), females: 9/15 | allergic contact dermatitis, hand involvement in 11/15 | various type-IV sensitivities (15/15, including cocamidoylpropyl betaine in 40%, nickel in 33%), AD (11/15) | systemic steroid (15/15), ciclosporin (13/15), mycophenolic acid (8/15), MTX (2/15), apremilast (1/15), azathioprin (2/15), ustekinumab (2/15), etanercept (1/15) | Dupilumab 600 mg s.c., then 300 mg q2w | 85% mean improvement in BSA (range 70–100%) | [43] | |
| Contact dermatitis | case report (5) | 1 | M/55 | allergic contact dermatitis | suspected type-IV sensitivity to chromate (no patch-testing performed), bronchitis, viral hepatitis C | topical steroids | Allergen exposure was continued. | Dupilumab 600 mg s.c. q2w | complete resolution of skin lesions at 8 wk | [44] |
| Contact dermatitis | case report (5) | 1 | M/61 | allergic contact dermatitis | type-IV sensitivity to isobornyl acrylate (patch-testing performed), AD, asthma, diabetes mellitus | azathioprin (100 mg/d), topical steroid, antihistamines | Allergen exposure was continued. | Dupilumab 600 mg s.c., then 300 mg q2w | partial resolution of skin manifestations and pruritus at 7 wk, complete resolution at 16 wk | [45] |
| Contact dermatitis | case series (4) | 2 | F/65, M/51 | allergic contact dermatitis | type-IV sensitivity to sesquiterpene lactones (patch-testing performed) (2/2), AD (1/2) | topical (2/2) and systemic (1/2) steroids, MMF (1/2), MTX (1/2), ciclosporin (1/2), azathioprin (150 mg/d, 2/2), ustekinumab (1/2) | Dupilumab 600 mg s.c., then 300 mg q2w | Partial improvement of skin lesions (2/2), dupilumab paused during winter without deterioration (2/2) | [46] | |
| Contact dermatitis | case report (5) | 1 | M/54 | allergic contact dermatitis, generalized eczema and hand/foot dermatitis | multiple type-IV sensitivities (including nickel, patch-testing performed), AD | topical steroid, phototherapy, acitretin | Dupilumab 600 mg s.c., then 300 mg q2w | Improvement of skin manifestations, repeated patch-testing remained positive | [47] | |
| Contact dermatitis | case series (4) | 3 | F/20, F/52, F/53 | allergic contact dermatitis, generalized (1/3), torso and extremities (2/3) | multiple type-IV sensitivities (3/3), type-I allergies (3/3), AD (1/3), allergic rhinitis (1/3) | systemic steroid (3/3), azathioprin (1/3), ciclosporin (1/3) | Dupilumab 600 mg s.c., then 300 mg q2w | ≥90% improvement in BSA (3/3) after 6–12 wk | [48] | |
| Contact dermatitis | case series (4) | 6 | 47.5 (median, 26–67 range), females: 5/6 | occupational irritant contact dermatitis (3/6), allergic contact dermatitis (3/6) | type-IV sensitivities (4/6), history of atopy (3/6) | topical (6/6) and systemic (1/6) steroids, phototherapy (3/6), alitretinoin (4/6), MTX (5/6) | Topical tacrolimus (1/6). Allergen/irritant exposure was continued (4/6). | Dupilumab 600 mg s.c., then 300 mg q2w | total clearance of skin lesions (5/6), partial remission (1/6) | [49] |
| Contact dermatitis | case report (5) | 1 | M/44 | disseminated spongiotic dermatitis | type-IV sensitivities (nickel), nickel-containing stent, antiphospholipid syndrome, no AD or atopy | topical and systemic steroids, antihistamines, MMF (1.5 g/d) | systemic steroid, tapered | Dupilumab 600 mg s.c., then 300 mg q2w | significant improvement after 8 wk | [50] |
| Contact dermatitis | case series (4) | 3 | F/52, F/54, F/54 | disseminated eczema including body and face | type-IV sensitivities (neomycin, fragrance and perfume (1/3); budesonide, limonene (1/3); shampoo (1/3)) AD (2/2) | Dupilumab 600 mg s.c., then 300 mg q2w | 75%-improvement after 10 wk (1/3), full clearance after 8 wk (2/3) | [51] | ||
| Contact dermatitis | case report (5) | 1 | F/42 | eczema on hands and arms | type-IV sensitivity (colophonium), AD | topical and systemic steroids, MTX, ciclosporin | Dupilumab 300 mg q2w | flare-up at former patch-testing sites (recall dermatitis), partial control at 10 wk | [52] | |
| Contact dermatitis | case series (4) | 2 | F/83, F/69 | disseminated eczema including body and extremitites | type-IV sensitivities (fragrance, propylene glycol (1/2); balsam of peru, propylene glycol (1/2)) | topical and systemic steroids (2/2), MTX (15 mg/wk, 1/2), MMF (2 g/d, 1/2) | topical steroids and calcineurin inhibitors | Dupilumab 300 mg q2w | Significant improvement, BSA 2% after 4 mo (1/2) or 5% after 6 mo (1/2) | [53] |
| Contact dermatitis | retrospective study (4) | 15 | 44 (mean, 18 SD), females: 12/17 | AD (17/17) | 4 modalities on average | Dupilumab | BSA improvement in 82%, 71%-reduction (mean, 42 SD), pruritus improved in 100% | [54] | ||
| Contact dermatitis | case report (4) | 5 | 54 (median, 29–69 range), females: 2/5 | AD or history of atopy (4/5), type-IV sensitivities (5/5, miscellaneous) | topical (5/5) and systemic (3/5) steroid, ciclosporin (4/5), mycophenolic acid (4/3), MTX (1/5), phototherapy (1/5) | 80–100% improvement within 10–12 wk (5/5) | [55] | |||
| Contact dermatitis | retrospective study (4) | 6 | 55.3 (mean, 4.9 SD), females: 4/6 | generalized eczema | AD (6/6), type-IV sensitivities (multiple personal care products) | topical steroids, phototherapy (1/6) | Dupilumab 600 mg s.c., then 300 mg q2w | complete clearance of dermatitis (4/6), residual hand dermatitis (1/6), flares (1/6) | [56] | |
| Contact dermatitis | case report (5) | 1 | F/43 | pruritic rash on face and upper trunk after hair dyeing | type-IV sensitivity (p-phenylenediamine), dermatomyositis | topical steroids, antihistamines | Dupilumab 600 mg s.c., then 300 mg q2w | complete resolution after 6 wk | [57] | |
| Contact dermatitis | case report (5) | 1 | M/52 | facial eczema | no AD; type-IV sensitivities (sesquiterpene lactone, artichoke) | systemic steroids, ciclosporin | Dupilumab 600 mg s.c., then 300 mg q2w | partial response after 8 wk | [58] | |
| Contact dermatitis | case report (5) | 1 | F/45 | eczema of hands and arms | AD, allergic conjuncitivitis, type-IV sensitivity (rubber) | topical and systemic steroids, ciclosporin | Dupilumab 600 mg s.c. q2w | complete resolution of skin lesions at 18 wk, resolution of pruritus | [59] | |
| Contact dermatitis | case report (5) | 1 | F/48 | pruritic fissured hand eczema, eyelid eczema | asthma, no AD, type-IV sensitivities (p-phenylenediamine and others) | topical steroids | Dupilumab 600 mg s.c., then 300 mg q2w | no efficacy, discontinued | [60] | |
| Contact dermatitis | case report (5) | 1 | M/54 | vesiculobullous lesions of hands and feet | no AD; type-IV sensitivities (thiuram mix and others) | systemic steroids, ciclosporin | Dupilumab | no efficacy, discontinued after 12 mo | [61] | |
| Dyshidrotic eczema | case series (5) | 15 | 56 (mean, 32–76 range), females: 33% | no AD (15/15) | topical steroids (15/15), systemic immunosuppressive (7/15), phototherapy (3/15), psoriasis biologic (7/15) | ustekinumab (1/15, for concomitant psoriasis) | Dupilumab | Partial response (15/15) with reduced itch and skin lesions, complete clearance (6/15). | [63] | |
| CHE | case report (5) | 1 | M/12 | vesicular eczema of hands and feet with pruritus and painful lesions | AD | topical and systemic steroid, phototherapy, MTX (10 mg/m2/wk), ciclosporin (5 mg/kg biweekly) | topical mometasone and systemic prednisolone, tapered | Dupilumab 600 mg s.c., then 300 mg q2w | Gradual resolution of skin lesions at 4 wk, complete stable remission at 4 mo. | [64] |
| CHE | retrospective study (4) | 19 | 55.9 (mean, 13.0 SD), females: 16/19 | hyperkeratotic CHE (10/19), atopic CHE (4/19), allergic contact dermatitis (2/19), irritant contact dermatitis (1/19), pulpitis (1/19), vesicular hand eczema (1/19) | AD (6/19) | topical (19/19) and systemic (6/19) steroid, MTX (12/19), acitretin (6/19), alitretinoin (12/19), ciclosporin (5/19), azathioprin (11/19), MMF (7/19), psoriasis biologicals (7/19) | Dupilumab 600 mg s.c., then 300 mg q2w | Improvement of skin lesions and quality of life (14/19); no effect or deterioration (5/19). Effects were worse in hyperkeratotic CHE (p = 0.033 compared with all others) | [65] | |
| CHE | prospective observational study (3) | 72 | 45.2 (mean, 13.0 SD), females: 33.3% | chronic fissured HE (72.2%), recurrent vesicular HE (27.8%) | AD (100%), type-IV sensitivity (38.9%, patch testing performed), irritant contact dermatitis (22.2%), asthma (61.1%), allergic rhinitis (70.8%), allergic conjunctivitis (55.6%) | topical (100%) and systemic (81.9%) steroid, ciclosporin (93.1%), MTX (36.1%), azathioprin (26.4%), alitretinoin (13.9%), MMF (6.9%), systemic tacrolimus (2.8%) | Topical steroids or calcineurin inhibitors. No systemic immunosuppressive drugs (various washout intervals). | Dupilumab 600 mg s.c., then 300 mg q2w | HECSI −89% (95%-CI: −93.1 to −84.5) at wk 52, HECSI-90 met by 62.9%, no difference between HE-subtype or concomitant irritant contact dermatitis, improved quality of life | [66] |
| CHE | case series (4) | 3 | M/65, M/47, F/65 | hyperceratotic HE (3/3) | no AD (3/3) | topical steroids (3/3), alitretinoin (3/3) | no topical treatment (2 wk washout) | Dupilumab 600 mg s.c., then 300 mg q2w | Improvement in itch and quality of life (3/3), complete clearance of skin lesions (2/3) at 16 wk, no effect on skin lesions (1/3) | [67] |
| CHE | case report (5) | 1 | M/43 | occupational irritant hand dermatitis (compulsive hand washing, cleaning agents, steering wheel, handling coins) | no AD, no type-IV sensitvity (patch-testing performed) | topical and systemic steroids, phototherapy, acitretin (25 mg/d), MTX (15–20 mg/wk), antibiotics | topical steroid | Dupilumab 600 mg s.c., then 300 mg q2w | Improvement of HECSI (33 to 10 at 4 wk, 0 at 5 mo) | [68] |
| CHE | case report (5) | 1 | M/67 | recurrent vesicular HE | no AD, no atopy, no type-IV sensitivity (patch-testing performed) | topical and systemic steroids, tar, phototherapy, MTX (25 mg/wk), azathioprine (150 mg/d), ciclosporin (200 mg/d) | Dupilumab 600 mg s.c., then 300 mg q2w | Improvement of skin lesions at 2 wk, complete clearance at 4 wk, sustained response for 3 mo follow-up | [69] | |
| CHE | prospective observational study (3) | 47 | 45.2 (mean, 20–69 range), females: 31.9% | chronic fissured HE (74.5%), recurrent vesicular HE (25.5%) | AD (100%), type-IV sensitivity (29.8%, patch testing performed) | Topical steroids or calcineurin inhibitors. No systemic immunosuppressive drugs (various washout intervals). | Dupilumab 600 mg s.c., then 300 mg q2w | Improvement of HECSI (in 45/47), HECSI-90 met by 32%, HECSI mean change −74.6% (95%-CI −67.9 to −81.2) at 16 wk. No difference between HE-types. No response in 2/45 | [70] | |
| CHE | retrospective study (4) | 38 | 42.2 (mean, 18.4 SD), females: 23/38 | various subtypes of HE including dyshidrotic eczema, atopic HE, contact dermatitis | systemic steroid (42%), MMF (32%), ciclosporin (16%) | Topical steroids | Dupilumab 600 mg s.c., then 300 mg q2w | Improvement in pruritus (96.7%, complete resolution in 26.7%), improvement in BSA (−15.9% mean) in ≥12 wk follow-up | [71] | |
| CHE | case report (5) | 1 | F/50s | atopic HE | AD, asthma, rhinitis, multiple type-IV sensitivities (including nickel, cobalt) | topical and systemic steroids, phototherapy, alitretinoin (10–30 mg/d), ciclosporin (5 mg/kg/d), azathioprin (2.5 mg/kg/d), mycophenolic acid (1140 mg/d), tacrolimus (0.1 mg/kg/d), MTX (10–20 mg/wk) | prednisolone (7.5 mg/d) | Dupilumab 600 mg s.c., then 300 mg q2w | Improvement in HECSI from 244 to 11 (“almost clear”) in 16 wk | [72] |
| CHE | case series (4) | 4 | F/72, F/65, M/48 | atopic HE (4/4) | AD (3/3), allergic rhinitis (2/3) multiple type-I sensitivities (1/3), no type-IV sensitvity (0/3, patch-testing performed) | topical (3/3) and systemic (2/3) steroids, topical (3/3) and systemic (1/3) calcineurin inhibitor, thalidomide (1/3), MTX (1/3), MMF (3/3), ciclosporin (2/3), apremilast (1/3), ustekinumab (1/3) | Dupilumab 600 mg s.c., then 300 mg q2w | Complete clearance (1/3), partial improvement (2/3) after 6–12 wk, sustained response at 3–8 mo follow-up | [73] | |
| CHE | case series (4) | 2 | M/63, M38 | dyshidrotic hand and foot eczema | asthma (1/2), no AD (0/2) | topical and systemic steroids (2/2), phototherapy (2/2), excimer laser (1/2), apremilast (2/2), MTX (2/2), efalizumab (1/2), etanercept (1/2), adalimumab (1/2), ixekizumab (1/2), ciclosporin (1/2), MMF (1/2) | ciclosporin (1/2) | Dupilumab 600 mg s.c., then 300 mg q2w | complete clearance after 8 wk (1/2) or 16 wk (1/2) | [74] |
| CHE | case report (5) | 1 | F/44 | dyshidrotic hand and foot eczema | asthma, no type-IV sensibilities (patch-testing performed) | topical and systemic steroids, topical calcineurin inhibitors, antihistamines, excimer laser therapy, | Dupilumab 600 mg s.c., then 300 mg q2w | complete clearance after 8 wk | [75] | |
| CHE | case report (5) | 1 | M/40s | dyshidrotic hand and foot eczema | no atopy | topical and systemic steroids, antifungals, ciclosporin | Dupilumab 600 mg s.c., then 300 mg q2w | Complete resolution after 3 wk | [76] | |
| CHE | case series (4) | 2 | M/38 (2/2) | dyshidrotic hand (2/2) and foot (2/2) eczema | type IV-sensibilities (1/2; multiple) | topical and systemic steroids (2/2), apremilast (1/2), acitretin (1/2), phototherapy (1/2) | topical steroids (2/2), phototherapy (1/2) | Dupilumab 600 mg s.c., then 300 mg q2w | Near complete resolution after 1 (1/2) or 6 wk (1/2) | [77] |
| CHF | case report (5) | 1 | F/29 | occupational irritant hand dermatitis | no atopy, no type-IV sensibilities (patch-testing performed) | topical seroids, topical calcineurin inhibitors, antihistamines | Dupilumab 600 mg s.c., then 300 mg q2w. Later q4w. | HECSI 116 to 15 after 4 wk | [78] | |
| Eczematous eruption (αIL17R-induced) | case report (5) | 1 | M/62 | generalized pruritic rash under brodalumab for psoriasis | psoriasis, AD, allergic rhinitis, latent tuberculosis infection | topical and systemic steroids, antihistamines | guselkumab; brodalumab discontinued | Dupilumab 600 mg s.c., then 300 mg q2w | Complete clearance of skin manifestations and itch at 8 wk | [79] |
| Eczematous eruption (αIL17 or -23 induced) | case series (4) | 3 | M/42, F/24, F/54 | localized AD-like eczema | psoriasis (2/3), Crohn’s disease (1/3) | topical (3/3) and systemic (1/3) steroids, topical calcineurin inhibitors (3/3) | ixekizumab (1/3), ustekinumab (1/3), tildrakizumab (1/3) (all continued) | Dupilumab 600 mg s.c., then 300 mg q2w | Complete resolution (EASI 0) after 4 wk (1/3), 6 (1/3) or 7 mo (1/3) | [80] |
| Eczematous eruption of aging | case series (4) | 15 | 75 (mean, SD: 8), females: 67% | no AD or atopy (15/15) | topical (15/15) and systemic steroids (11/15), topical calcineurin inhibitors (11/15), systemic immunosuppression (2/15), phototherapy (1/15) | Dupilumab 600 mg s.c., then 300 mg q2w | Improvement of skin lesions (15/15), BSA 20% (SD 15) to 2.6 (SD 4) in 2–8 wk. Sustained response in 7/15 after 8–12 mo follow-up | [81] | ||
| Eczematous eruption of aging | case report (5) | 1 | M/66 | 3-years history of generalized pruritic rash excluding head and neck | no atopy; type-IV allergy to ciprofloxacin | topical and systemic steroids, MTX (17.5 mg/wk), MMF (1 g/d), phototherapy | Dupilumab 600 mg s.c., then 300 mg q2w | Complete clearance of skin manifestations and itch at 8 wk, sustained at 4 mo follow-up | [82] | |
| Eczematous eruption (CVID) | case report (5) | 1 | F/59 | Recurrent generalized pruritic rash | CVID, type-IV sensitivity (chrome, nickel, colophonium, mercapto-mix, thiomersal) | topical and systemic steroids, ciclosporin (150 mg/d), IVIg | Dupilumab 600 mg s.c., then 300 mg q2w | Control of itch in 4 wk. Complete resolution of skin manifestations (EASI 41.10 to 1.20) in 8 wk. | [83] | |
| Autoeczema-tization in chronic stasis dermatitis | case report (5) | 1 | M/80 | generalized pruritic papules and eczematous patches, venous stasis dermatitis of lower extremity | no type-IV sensitivity (patch-testing performed) | topical and systemic steroids, compression therapy | compression therapy | Dupilumab 600 mg s.c., then 300 mg q2w | Improvement of itch (-7 NRS) and reduced lower extremity edema at 10 wk. New psoriasiform dermatitis, dupilumab discontinued. | [84] |
Reports of eczema other than AD treated with dupilumab were identified via database search. Evidence levels 1 through 5 were assigned to each report according to the Oxford Centre for Evidence Based Medicine and denoted in parentheses after the study type. AD, atopic dermatitis; BSA, body surface area; CHE, chronic hand eczema; CVID, common variable immunodeficiency; DLQI, dermatology life quality index; EASI, eczema area and severity index; HE, hand eczema; HECSI, hand eczema severity index; MMF, mycophenolate mofetil; mo, month; MTX, methotrexate; NRS, numerical rating scale; q2w, biweekly; s.c., subcutaneous; SD, standard deviation; wk, week.
Chronic hand eczema, also known as dermatitis (CHE), can be a clinical form of AD (atopic HE), ACD or ICD, but unrelated etiologies are found as well. Frequent clinical phenotypes include chronic hyperkeratotic/fissured and recurrent dyshidrotic/vesicular HE among others. Reports of a total of 162 patients demonstrated clinical effectiveness of dupilumab in various subtypes of CHE for patients that had failed various topical and systemic therapies including most frequently topical and systemic steroids, topical calcineurin inhibitors, retinoids, ciclosporin A and phototherapy (Table 1) [63,64,65,66,67,68,69,70,71,72,73,74,75,76,77,78]. A prospective study following 72 patients with chronic fissured or vesicular HE for 52 weeks showed a mean reduction of 89% of the hand eczema severity index (HECSI, 95%; confidence interval 93.1–84.5%) and a 90% improvement of HECSI met by 62.9% with no difference between clinical subtypes [66]. Another retrospective study of 19 patients indicated significantly smaller effects of dupilumab in patients with hyperkeratotic CHE compared to all other investigated subtypes (p = 0.033) [65]. Likewise, a lack of response to dupilumab or even deterioration was reported in a total of 6 cases, all of which had hyperkeratotic CHE [65,67]. Two phase 2 placebo-controlled RCTs evaluating effects of dupilumab were found with one being currently active with patients with severe CHE (DUPSHE, NCT04512339) and one currently recruiting patients with moderate to severe CHE (DUPECZEMAIN, NCT03861455).
Localized or generalized eczema can develop in response to drugs in the form of drug-induced eczematous eruption (EE) typically described for TNFα-inhibitors. Dupilumab treatment of EE induced by anti-IL-17 or -23 agents (tildrakizumab, brodalumab, ixekizumab and ustekinumab) given for underlying psoriasis or Crohn’s disease led to complete clearance within months in all 4 reported patients [79,80]. EE of aging is an exclusion diagnosis and was treated with dupilumab leading to sustained improvement of skin lesions and itch in a total of 16 patients without a history of AD or atopic diathesis (Table 1) [81,82]. Furthermore, one record of a patient with EE associated with a common variable immunodeficiency (CVID) demonstrated complete resolution of skin manifestations within 8 weeks [83]. Secondary generalized eczematization in a patient with underlying chronic venous stasis dermatitis was treated with dupilumab which led to significant improvement of itch; however, new psoriasiform lesions developed subsequently and dupilumab was discontinued [84].
3.2. Chronic Pruritus and Prurigo
Chronic pruritus imposes a high disease burden and can be refractory to multiple treatment regimens including topical and systemic steroids as well as systemic antipruritic medications such as antihistamines, antidepressants, antiemetics, opioid-antagonists, cannabinoids and anticonvulsants. Etiologies are diverse and include AD and atopy as well as other dermatologic, systemic/metabolic or mental diseases. Th2-mediated inflammation with complex interactions between neurons, keratinocytes and immune cells via chemokines, neuropeptides, alarmins and proteases are described. This includes direct effects on sensory neurons by IL-4 and -13 [85]. Itch-scratch cycles can sustain pruritus and induce skin lesions (Figure 1B). Most notably, dupilumab was approved for prurigo nodularis (PN) in adults. Additionally, two case reports showed efficient use of dupilumab in weight-adjusted dosing schemes in pediatric patients with PN (Table 2) [86,87].

Table 2.
Chronic pruritus and prurigo.
Chronic pruritus of unknown origin (CPUO) or chronic idiopathic pruritus refers to itch lasting more than 6 weeks without an underlying medical condition and can be accompanied by skin lesions. Opposed to skin lesions found in prurigo, CPUO manifestations are secondary. Several reports demonstrated efficient itch control by dupilumab measured by numerical scales, including a case series of 15 cases with a mean itch numerical rating scale (NRS)-reduction of 7 points (SD 1.9) as well as a series of 4 cases with a mean reduction of 8.75 points (SD 1.26). Notably, 26 out of 27 reported patients had no AD. In two cases, dupilumab was withdrawn after only 4 weeks and a sustained response was reported for a 20 weeks follow-up period (Table 2) [8,88,89,90]. Currently, the placebo-controlled RCT LIBERTY-CPUO-CHIC (NCT05263206) is ongoing and recruiting.
Dupilumab further demonstrated efficiency in pruritus with various defined etiologies. This included 6 cases with uremic pruritus [8,91] and one case with cholestatic pruritus (Table 2) [92]. A clinical exploratory study evaluating dupilumab in cholestatic pruritus is currently recruiting (NCT04256759). Efficient treatment of localized pruritus was reported for a case of neuropathic brachioradial pruritus [93] and a case of anal and genital pruritus (Table 2) [94].
Reactive perforating collagenosis (RPC) is characterized by umbilicated nodules with a central keratotic plug and is frequently associated with chronic kidney disease. Reports of six cases showed partial improvement of itch NRS as well as resolution of skin lesions under dupilumab treatment. Notably, three patients had no history of AD or atopy (Table 2) [95,96,97,98,99].
3.3. Bullous and Acantholytic Dermatoses
Dermatoses with sub- or intraepidermal cleft formation and blistering can be caused by autoantibody deposition and subsequent recruitment of effector cells [100], or by inherited defects of structural proteins of the dermoepidermal junction (DEJ) or the epidermis [101].
The most frequent acquired bullous dermatosis is bullous pemphigoid (BP) caused by IgG autoantibodies against BP180 and/or BP230 [102,103]. Autoantibody binding at the DEJ leads to complement fixation and, most prominently, the activation of neutrophils and eosinophils inducing itch and the formation of plaques and tense blisters (Figure 1C). IL-4 and -13 as well as other Th2-cytokines were found in higher concentrations in sera of patients with BP, as well as in blister fluid [103]. Peripheral eosinophilia is often seen in blood and in inflamed skin. Further, total IgE concentrations in BP sera are frequently increased and correlate with disease severity [104]. Thus, therapeutic efficacy of dupilumab was hypothesized due to inhibition of eosinophil chemotaxis and activation directed by Th2-associated chemokines as well as reduction of IgG and IgE synthesis by B cells stimulated by Th2-responses.
Several case reports showed successful treatment of BP-patients that were resistant to previous standard of care treatments or had contraindications for high-dose systemic steroids or immunosuppressants leading to complete clinical remissions defined by resolution of skin lesions and pruritus (Table 3) [105,106,107,108,109,110,111,112,113,114,115,116]. This included one pediatric patient [117]. Efficient dupilumab mono-therapy inducing clinical remission was reported in 3 cases [118,119,120]. However, some reports showed only partial or no response [114]. In addition, 4 cases of checkpoint inhibitor-induced BP were treated efficiently with dupilumab, a favorable medication as strong immunosuppression needs to be avoided due to the underlying malignancy [121,122,123,124]. Two patients with BP presumably triggered by COVID-19 vaccinations were also treated efficiently with dupilumab [120,125]. Most noticeably, two retrospective cohort studies compared co-therapy of dupilumab with conventional therapy against conventional therapy alone (comprised of systemic high-dose steroids and immunosuppressants) and found shorter median time to disease control, more rapid decline of itch measured by NRS and disease activity (measured by the BP disease activity index, BPDAI), higher quality of life (measured by the dermatology life quality index, DLQI) as well as lower cumulative doses of steroids and immunosuppressants in a total of 28 patients [126,127]. A large retrospective study (NCT05649579) and a placebo-controlled RCT evaluating dupilumab in BP (LIBERTY-BP, NCT04206553) are currently recruiting.
More rare subtypes of BP treated efficiently with dupilumab include pemphigoid gestationis [128], lichen planus pemphigoides [129,130], Brunsting–Perry cicatricial pemphigoid [131,132] and pemphigoid nodularis [133]. Additionally, a case of linear IgA-dermatosis was efficiently treated with dupilumab [134].
By contrast, pemphigus vulgaris (PV), the most frequent intraepidermal autoimmune blistering disease [135], is caused by autoantibodies against desmoglein-3 (Dsg-3), and eosinophilia is seen far less frequently than in BP. Two reports, however, showed efficiency of dupilumab as mono-therapy or as an add-on therapy to strong immunosuppression in a recalcitrant PV case (Table 3) [136,137]. This could be attributed to the finding of Dsg-3 reactive Th2-cells in PV-patients that might stimulate Dsg-3 autoantibody production by B lymphocytes [138]. However, data regarding dupilumab in pemphigus diseases is limited.

Table 3.
Bullous and acantholytic dermatoses.
Table 3.
Bullous and acantholytic dermatoses.
| Disease | Study Type | n | Sex/Age | Medical History | Prior Systemic Therapies | Concomitant Systemic Medication | Therapy | Response | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BP | case series (4) | 7 | 74 (median, 63–88 range) | hypertension (4/7), diabetes (2/7), MDS (1/7) | none (5/7), steroid + ciclosporin (1/7), tofacitinib + omalizumab (1/7) | none (1/7), methylprednisolone 0.5–0.6 mg/kg/d with reduction (5/7), prednisolone 0.5 mg/kg/d with reduction (1/7) | Dupilumab 600 mg s.c. initially, then 300 mg q2w for 16 wk | Total BPDAI reduced to 2 (median, IQR 6 to 0), p < 0.0001 at 16 wk, Reduction of BP180 and BP230 ab, also IgE. 4 stopped dupilumab, no relapse. 2 prolonged dosing with 300 mg q3-4w, no relapse. 1 relapse after taper of dupilumab, controlled again with 300 mg q2w. 1 relapse after glucocorticoid taper, controlled with dupilumab. | [105] |
| BP | case series (4) | 2 | F/53, M/78 | prednisolone 0.5–0.8 mg/kg/d | prednisolone 20 mg/d | Dupilumab 600 mg s.c. initially, then 300 mg q2w. Withdrawal after 2 months | Sustained clinical remission | [106] | |
| BP | case series (4) | 2 | M/72, M/88 | methylprednisolone (2/2), MTX (1/2) | Dupilumab 600 mg s.c. initially, then 300 mg q2w | Relief of pruritus, improvement of lesions at 2 wk follow-up | [107] | ||
| BP | case series (4) | 3 | 2F, 1M | psychiatric disorders (1/3), Hepatitis B (2/3), gastric ulcers (1/3) | steroids (max. equivalent to 2.5 mg/kg/d prednisone, 2/3), IVIG (2/3), cyclophosphamide (1/3), MTX (1/3), ciclosporin (1/3), none (1/3) | prednisone (0.75 mg/kg/d) + cyclophosphamide (1/3), methylprednisolone + MTX + ciclosporin (1/3), none (1/3) | Dupilumab 600 mg s.c. initially, then 300 mg q2w | Relief of pruritus (3/3), improvement of skin lesions (2/3), clinical remission (1/3) | [108] |
| Vesicular BP | case report (5) | 1 | M/32 | pulmonary tuberculosis | high-dose systemic steroids | prednisolone 30 mg/d, isoniazide, rifampicin, ethambutol | Dupilumab 600 mg s.c. initially, then 300 mg q2w | Clinical remission, no relapse of tuberculosis | [109] |
| BP (non-bullous) | case report (5) | 1 | M/74 | diabetes mellitus, hypertension | high-dose systemic steroids | Dupilumab 600 mg s.c. initially, then 300 mg q2w | Sustained clinical remission from 4 wk | [110] | |
| BP | case report (5) | 1 | F/61 | methylprednisolone (max. 0.5 mg/kg/d), azathioprine (100 mg/d) | methylprednisolone, azathioprine (100 mg/d) | Dupilumab 600 mg s.c. initially, then 300 mg q2w | Resolution of pruritus and cessation of blister development within 1 month. Sustained clinical remission. | [111] | |
| BP | case report (5) | 1 | M/80 | prednisone 40 mg/d, doxycycline 200 mg/d, mycophenolate mofetil 1.000 mg/d, niacinamide 1.500 mg/d | prednisone, doxycycline | Dupilumab 600 mg s.c. initially, then 300 mg q2w | Sustained clinical remission | [112] | |
| BP | case report (5) | 1 | M/70 | obesity, diabetes mellitus, hypertension | dapsone (150 mg/d), MTX (7.5 mg/wk s.c.), mycophenolate mofetil (2 g/d), omalizumab (300 mg s.c. q4w) | mycophenolate mofetil, omalizumab | Dupilumab 600 mg s.c. initially, then 300 mg q2w | Reduced itch NRS (0/10) and cessation of new lesions after 3 months, sustained clinical remission | [113] |
| BP | case series (4) | 13 | 78 (median, 53–91 range) | none (1/13), steroids (9/13), MMF (2/13), rituximab (2/13), IVIG (3/13), azathioprine (1/13), nicotinamide (3/13), doxycycline (4/13), MTX (4/13) | none (7/13), MTX (3/13), prednisone with taper (3/13) | Dupilumab 600 mg s.c. initially, then 300 mg q2w or qw | Sustained clinical remission (7/13), relief of pruritus (12/13), no response (1/13) | [114] | |
| BP | case report (5) | 1 | M/89 | diabetes mellitus | doxycycline (200 mg/d), nicotinamide (1000 mg/d), MMF (2 g/d), prednisone (10 mg/d), omalizumab | prednisone (2.5 mg/d), MMF, doxycycline, nicotinamide | Dupilumab 600 mg s.c. initially, then 300 mg q2w | Relief of pruritus at 2 wk, resolution of BP lesions at 7 wk. Sustained clinical remission at 1 year. | [115] |
| BP | case report (5) | 1 | M/86 | PN, type 2 diabetes mellitus | methylprednisolone, azathioprine, doxycycline | methylprednisolone, doxycycline; both discontinued after 4 mo | Dupilumab 600 mg s.c. initially, then 300 mg q2w | Complete remission after 4 mo, sustained under dupilumab-monotherapy for 10 mo follow-up | [116] |
| BP | case report (5) | 1 | F/17 | doxycycline, methylprednisolone 75 mg/d, prednisolone, rituximab (q2w, later q4w), plasmapheresis (13 sessions total), IVIG (2g/kg q4w) | steroids, rituximab, IVIG | Dupilumab 600 mg s.c. initially, then 300 mg q2w | Complete blister resolution, undetectable BP180 (initially 574 U/mL) | [117] | |
| BP | case report (5) | 1 | M/85 | suspected AD, asthma, ulcerative colitis | tofacitinib and omalizumab for suspected AD, ineffective | none | Dupilumab 600 mg s.c. initially, then 300 mg q2w | Sustained clinical remission at 6 mo | [118] |
| BP | case report (5) | 1 | M/80 | prednisone | none | Dupilumab 600 mg s.c. initially, then 300 mg q2w | Sustained clinical remission at 10 mo | [119] | |
| BP, COVID-vaccination induced | case report (5) | 1 | M/78 | diabetes mellitus, hypertension, hyperlipidemia | prednisone, doxycycline | none | Dupilumab 600 mg s.c. initially, then 300 mg q2w | Sustained clinical remission | [120] |
| BP (ICI-induced) | case report (5) | 1 | M/76 | Melanoma St. IV (adjuvant Nivolumab 480 mg i.v. q4w for 6 mo) | methylprednisolone (0.6 mg/kg/d), doxycycline (200 mg/d), nivolumab discontinuation | methylprednisolone, tapered | Dupilumab 300 mg s.c. q2w | Sustained clinical remission | [121] |
| BP (ICI-induced) | case report (5) | 1 | F/59 | Cervical cancer St. IIB (adjuvant Pembrolizumab for 5 wk prior) | methylprednisolone (1 mg/kg/d), doxycycline (200 mg/d), niacinamide (1 g/d), dapsone (75 mg/d), pembrolizumab discontinuation | methylprednisolone (0.75 mg/kg/d), tapered | Dupilumab 600 mg s.c. initially, then 300 mg q2w | Cessation of new blister formation at 2 mo, severe flare after discontinuation, sustained clinical remission after re-initiation of dupilumab | [122] |
| BP (ICI-induced) | case report (5) | 1 | F/79 | Melanoma St. II (adjuvant Nivolumab for 11 mo prior) | prednisone, doxycycline, dapsone | Dupilumab 600 mg s.c. initially, then 300 mg q2w | Sustained clinical remission reached at 4 wk | [123] | |
| BP and GD (ICI-induced) | case report (5) | 1 | M/73 | Metastatic renal cell carinoma (ipilimumab/nivolumab treatment), autoimmune thyreoiditis | steroids, doxycycline, dapsone | Dupilumab 600 mg s.c. initially, then 300 mg q2w | Complete resolution of skin lesions and pruritus of both BP and GD | [124] | |
| BP, COVID-vaccination induced | case report (5) | 1 | F/91 | hypertension, chronic kidney failure | prednisone, azathioprine, rituximab (1 cycle) | prednisone with tapering | Dupilumab 600 mg s.c. initially, then 300 mg q2w | Resolution of pruritus and BP lesions after 2 months | [125] |
| BP | Retrospective cohort study (3) | 20 vs. 20 | 72 (median, 54–86 range) | hypertension (30%), cardiovascular disease (15%), diabetes mellitus (20%), chronic renal insufficiency (15%), neurologic disorder (25%), interstitial lung disease (25%), tumor (5%) | no prior therapy (17/20 cases, 20/20 controls) | methylprednisolone (<0.4 mg/kg/d) | Dupilumab 600 mg s.c. initially, then 300 mg q2w vs. 0.4 mg/kg/d methylprednisolone | Shorter median time to disease control (14 vs. 19 days, p = 0.043), lower cumulative dose of steroid (p < 0.01) | [126] |
| BP | Retro-spective cohort study (3) | 8 vs. 16 | 64.5 (median, 22–90 range) | cardiovascular disease (3/8), neurologic disorder (1/8), hyperlipidemia (3/8), tumor (2/8) | methylprednisolone (0.6 mg/kg/d) + azathioprine (2 mg/kg/d) with reduction | Dupilumab 600 mg s.c. initially, then 300 mg q2w vs. methylprednisolone (0.6 mg/kg/d) + azathioprine (2 mg/kg/d) with reduction | More rapid decline of itch NRS (p = 0.034) and BPDAI (p = 0.0308), shorter median time to cessation of new blisters (8 vs. 12 days, p = 0.028), lower cumulative dose of methylprednisolone (p = 0.036), lower cumulative dose of azathioprine (p = 0.0048) | [127] | |
| Pemphigoid gestationis | case report (5) | 1 | F/37 | 20 wk of gestation, g5, p4 | prednisone (0.5 mg/kg/d) | prednisone, tapered | Dupilumab 600 mg s.c. initially, then 300 mg q2w | Decline of BP18 autoantibodies, clearance of skin lesions, sustained clinical remission postpartum. Newborn without skin lesions | [128] |
| LPP | case report (5) | 1 | M/69 | Lichen planus mucosae (20 years) | prednicolone (50 mg/d) | prednisolone, tapered | Dupilumab 600 mg s.c. initially, then 300 mg q2w | Sustained clinical remission reached at 2 wk, normal BP180 ab | [129] |
| LPP | case report (5) | 1 | M/18 | AD | dexamethasone (8 mg/d), MMF (1 g/d) | none | Dupilumab 600 mg s.c. initially, then 300 mg q2w | Partial remission at 4 wk, clinical remission reached at 15 wk and sustained after discontinuation of dupilumab | [130] |
| Brunsting-Perry Pemphigoid | case report (5) | 1 | M/71 | prednisone, MMF | none | Dupilumab 600 mg s.c. initially, then 300 mg q2w | Partial clearance of bullae and erosions after 6 wk, persistent occasional bullae, mild pruritus, scarring | [131] | |
| Brunsting-Perry Pemphigoid | case report (5) | 1 | F/63 | AD, allergic rhinitis | rituximab, steroids, MMF, MTX, dapsone, doxycycline, nicotinamide | Dupilumab 300 mg s.c. q2w | Partial remission | [132] | |
| Pemphigoid nodularis | case report (5) | 1 | F/76 | hypertension, diabetes, obesity, and atrial fibrillation | none | none | Dupilumab 600 mg s.c. initially, then 300 mg q2w | Sustained clinical remission reached at 4 mo | [133] |
| LAD | case report (5) | 1 | M/63 | AD, allergic rhino-conjunctivitis | methylprednisolone, azathioprine, dapsone (100 mg/d), colchicine (3 mg/d) | Dupilumab 600 mg s.c. initially, then 300 mg q2w | Sustained clinical remission reached at 4 wk | [134] | |
| Pemphigus vulgaris | case report (5) | 1 | F/41 | steroids | none | Dupilumab 600 mg s.c. initially, then 300 mg q2w | Clearance of oral lesions at 6 wk, sustained clinical remission | [136] | |
| Pemphigus vulgaris | case report (5) | 1 | M/35 | steroids, IVIG | steroids, IVIG | Dupilumab 600 mg s.c. initially, then 300 mg q2w | Partial remission with PDAI -55 at 6 wk | [137] | |
| DEB-Pr (COL7A1 mutation) | case report (5) | 1 | F/52 | no AD | antihistamines, promethazine, cannabis, St. John’s wort | none | Dupilumab 600 mg s.c. initially, then 300 mg q2w | Improvement of itch NAS and quality of life (measured by DLQI), improvement of skin lesions at 12 wk | [139] |
| DEB-Pr (COL7A1 mutation) | case series (4) | 2 | M/15, F/27 | asthma (1/2), ADHD (1/2) | steroids (1/2), antihistamines (2/2), ciclosporine (2/2), MMF (1/2), thalidomide (2/2), lenalidomide (1/2), omalizumab (1/2), tofacitinib (1/2), gabapentin (1/2), pregabalin (1/2), naltrexone (1/2), melatonine (1/2), clonidine (1/2), ondansetron (1/2), antidepressants (2/2), phototherapy (2/2), dermabrasio (1/2) | none | Dupilumab 600 mg s.c. initially, then 300 mg q2w (1/2) or qw (1/2) | Sustained improvement of itch (-3.5 and -7 NRS), improvement of skin findings, improvement of sleep | [140] |
| DEB-Pr (COL7A1 mutation) | case report (5) | 1 | M/39 | dapsone, cyproheptadine | none | Dupilumab 600 mg s.c. initially, then 300 mg q2w | Improvement of itch at 2 wk, cessation of new lesions at 4 wk, partial remission at 9 mo | [141] | |
| DEB-Pr (COL7A1 mutation) | case report (5) | 1 | F/10 | steroids | none | Dupilumab 600 mg s.c. initially, then 300 mg q2w | Improvement of itch NAS and quality of life (measured by DLQI) | [142] | |
| DEB-Pr (COL7A1 mutation) | case report (5) | 1 | F/43 | frequent bacterial skin infections | none | Dupilumab 600 mg s.c. initially, then 300 mg q2w | Improvement of itch, no more episodes of skin infections | [143] | |
| Hailey-Hailey | case report (5) | 1 | F/22 | ciclosporine (5 mg/kg/d) | none | Dupilumab 300 mg s.c. q2w | Resolution of skin lesions after 4 mo | [144] | |
| Hailey-Hailey | case series (4) | 3 | F/56, M/52, F/59 | antihistamines (3/3), acitretin (3/3), steroids (3/3), MTX (2/3), ciclosporine (2/3), hydroxychloroquine (2/3), naltrexone (2/3), apremilast (3/3), fluconazole (2/3), tetracyclines (3/3), dapsone (3/3), oxybutynin (2/3), MMF (1/3), local laser ablation (1/3) | none | Dupilumab 600 mg s.c. initially, then 300 mg q2w | Improvement in affected body surface area (BSA) and quality of life (2/3), no improvement (1/3) | [145] | |
| Hailey-Hailey | case series (4) | 3 | F/50s, M/50s, M/70s | antihistamines (3/3), isotretinoin (1/3), etanercept (1/3), steroids (1/3), acitretin (2/3), naltrexone (2/3), antibiotics (1/3), ciclosporine (1/3), local botulinum toxin (1/3) | none | Dupilumab 600 mg s.c. initially, then 300 mg q2w | Reduction of size and thickness of skin lesions | [146] | |
| GD | case report (5) | 1 | M/71 | Metastatic renal cell carinoma (ipilimumab/nivolumab treatment) | pulsed prednisone (60 mg/d max.), antihistamines, gabapentin, aprepitant, topical phototherapy | Dupilumab 600 mg s.c. initially, then 300 mg q2w | Complete resolution of skin lesions and pruritus at 3 mo; sustained after restart of ipilimumab/nivolumab | [147] | |
| GD | case series (4) | 3 | M/70s, F/50s, M/70s | steroids (3/3), azathioprine (1/3), MTX (2/3), gabapentin (1/3), topical phototherapy (1/3), acitretin (1/3) | Dupilumab 600 mg s.c. initially, then 300 mg q2w | Complete resolution of skin lesions and pruritus within 2 mo (3/3) | [148] | ||
| GD | case report (5) | 1 | M/77 | CRSwNP | steroids | pulsed steroid | Dupilumab 600 mg s.c. initially, then 300 mg q2w | Complete resolution of skin lesions and pruritus at 14 wk | [149] |
Reports of hereditary or autoimmune bullous and acantholytic dermatoses treated with dupilumab were collated after a database search. Evidence levels 1 through 5 were assigned to each report according to the Oxford Centre for Evidence Based Medicine and denoted in parentheses after the study type. ab, antibody; AD, atopic dermatitis; ADHD, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder; BP, bullous pemphigoid; BPDAI, bullous pemphigoid disease activity index; BSA, body surface area; CRSwNP, chronic sinusitis with nasal polyps; DEB-Pr, dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa, pruritic subtype/epidermolysis bullosa pruriginosa; GD, Grover’s disease; ICI, immune-checkpoint inhibitor; IQR, interquartile range; IVIG, intravenous immunoglobulins; LAD, linear IgA-dermatosis; LPP, lichen planus pemphigoides; MDS, myelodysplastic syndrome; MMF, mycophenolate mofetil; mo, month; MTX, methotrexate; NRS, numerical rating scale; PDAI, pemphigus disease activity index; PN, prurigo nodularis; q2w, biweekly; q3w, every 3 weeks; q4w, every 4 weeks; qw, weekly; s.c., subcutaneous; wk, weeks.
Dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa (DEB) is a hereditary subepidermal blistering disease caused by mutations in the gene for collagen 7 (COL7A1). DEB can be associated with intense pruritus highly refractory to anti-inflammatory (steroids, phototherapy) and antipruritic treatments and is termed epidermolysis bullosa pruriginosa (DEB-Pr). Dupilumab showed efficient reduction of itch measured by NAS and despite the hereditary origin of the disease also led to improvement of the skin findings in 6 patients with DEB-Pr that were resistant to extensive previous therapy regimes (Table 3) [139,140,141,142,143]. This reflects a putative Th2-mediated component of the disease and the role of itch–scratch cycles possibly similar to PN.
The most frequent hereditary intraepidermal blistering disease is Hailey–Hailey disease (HHD) often caused by mutations in ATP2C1 that lead to disrupted development of desmosomes of the epidermis and subsequent acantholysis. A total of seven patients were treated with dupilumab after extensive ineffective previous therapies including immunosuppressants, retinoids, antipruritic medications or dermabrasion with significant improvement of skin lesions, itch and quality of life in six patients (Table 3) [144,145,146]. One patient did not respond to dupilumab. HHD-caused skin barrier defects might give rise to secondary Th2-mediated local inflammation possibly inhibited by treatment with dupilumab.
Grover’s disease (GD) is characterized histologically by acantholysis; yet, no disease mechanism is known. A total of five patients were reported with complete resolution of skin lesions and pruritus by dupilumab, including one patient with concomitant BP [124,147,148,149].
3.4. Alopecia Areata
Despite being one of the most common forms of nonscarring hair loss, treatment options for alopecia areata (AA, Figure 1D) are still limited. Topical immunosuppression or immunomodulation (including topical steroids, diphenylcyclopropenone, squaric acid, photodynamic therapy), minoxidil as well as systemic immunosuppression, are used with varying effects. Recently, the JAK1/2-inhibitor baricitinib was approved for severe AA in adults. Disease mechanisms in AA are not fully elucidated and possibly heterogeneous: multiple studies suggested a major role of interferon (IFN)-γ-mediated Th1-responses, while others highlighted Th2-mediated effects and regulatory T cell (Treg) deficiency [150]. Notably, patients with AD have a high susceptibility to develop AA, with one study finding a 26-fold increased chance compared to healthy individuals [151], underlining the role of Th2-skewed responses in AA.
Several case reports and case series showed clinical efficiency of dupilumab in 51 patients with AA, including patients with alopecia totalis (AT) and universalis (AU). Most of the patients treated had AD and reported multiple failed previous therapies. One case of incontinentia pigmenti-associated scalp alopecia was reported. Clinical responses were mostly measured by the severity of alopecia tool (SALT) with a score < 10 defined as complete response (Table 4) [152,153,154,155,156,157,158,159,160,161,162,163,164,165,166,167,168,169,170,171]. Noticeably, 13 pediatric patients were treated effectively with dupilumab [172,173,174,175,176,177]. However, 15 of a total of 66 reported patients did not experience clinical improvement; notably, one case series with 10 patients found no significant improvements throughout the investigated cohort [178].

Table 4.
Alopecia areata.
Additionally, a phase 2 randomized clinical trial (NCT03359356) [179] compared weekly injections of 300 mg dupilumab versus placebo and showed improvement in SALT at week 24 (p = 0.049) and week 48 (p < 0.0001) as well as 30% improvement in SALT (SALT30) at week 48 reached by 32.5% versus 20% (p = 0.067) and a 50% improvement in SALT (SALT50) at week 48 reached by 22.5% versus 15% (p = 0.02). Interestingly, high serum levels of IgE (>200 U/mL) as well as a medical history of AD or family history of atopy predicted a better outcome.
Conversely, several reports showed novel development of AA after commencing therapy with dupilumab for AD (exemplarily, [180]). Possible predictors of clinical outcomes (IgE serum levels, disease severity, concomitant atopy, age at onset, sex) have to be considered. Currently, a multicenter RCT is registered and not yet recruiting (NCT05551793).
3.5. Chronic Urticaria
Urticaria that lasts for more than 6 weeks is defined as chronic urticaria and can have a broad spectrum of etiologies and provocation factors causing recurrent urticae and swellings (Figure 1E). Dupilumab may exert an inhibitory effect on mast cells by hindering IL-4 driven proliferation and chemotaxis, IL-4 regulated expression of FcεRI and by lowering IgE-production from B cells; also, IL-4 blockade can desensitize vascular structures towards histamine and decrease mast cell-mediated anaphylaxis [181].
Chronic spontaneous urticaria (CSU) entails the absence of identified causes of urticaria and can be highly debilitating and recalcitrant to standard treatments. A total of 14 patients were reported that had failed standard therapies with antihistamines, omalizumab and/or ciclosporin and were subsequently treated with dupilumab (12/14) or a combination of dupilumab and omalizumab (2/14) (Table 5) [182,183,184,185,186,187,188,189]. Complete sustained resolutions were reported in 10/14 patients by clinical evaluation and the 7-day urticaria activity score (UAS7) or urticaria control test (UCT); a UAS7 of 0 was reported in 5 of these cases. In total, 3/14 patients had a partial response; one patient ended therapy due to financial reasons. Notably, 9/14 patients had AD or other signs of atopy. The placebo-controlled phase 3 clinical trial LIBERTY-CSU CUPID Study A investigated 138 patients with antihistamine-refractory CSU and found an 8.5 points-higher reduction of UAS7 in the dupilumab-treated cohort (p = 0.0003) as well as significantly reduced itch and hives at week 24; strikingly, the effects of dupilumab were independent of baseline serum IgE (NCT04180488) [190,191]. The phase 3 LIBERTY-CSU CUPID Study B enrolled 83 omalizumab-refractory CSU patients and was closed after interim analysis due to the lack of significant differences (NCT04180488). The phase 2 clinical trial DUPICSU (NCT03749135) has not published results, yet.

Table 5.
Chronic urticaria.
Besides CSU, dupilumab treatment in cases with chronic inducible urticaria with identified triggers were reported. A patient with cold urticaria experienced complete remission and tolerance to cold water under therapy with dupilumab [192]; one patient with exercise-induced cholinergic urticaria had a complete remission after 8 weeks with dupilumab [193]; further, a patient with adrenergic urticaria was efficiently treated with a combination of propranolol and dupilumab [194]. Three placebo-controlled RCTs are registered for evaluation of dupilumab in chronic inducible urticaria: A phase 2 RCT is recruiting adults with cholinergic urticaria (CHED, NCT03749148) and a phase 3 RCT for adults with cold urticaria is currently active (LIBERTY-CINDU CUrIADS, NCT04681729). Furthermore, a phase 3 RCT is currently recruiting children (2–12 years) with cold urticaria or CSU (LIBERTY-CSU/CINDU CUPIDKids, NCT05526521).
3.6. Netherton Syndrome and Other Hereditary Skin Diseases
Mutations in the gene SPINK5 in patients with Netherton syndrome causes dysfunction of the skin-expressed serine protease LEKTI that can lead to severe pruritus, skin inflammation and increased IgE. Subsequent epidermal remodeling makes patients susceptible to atopic manifestations resembling AD (Figure 1F) as well as skin infections. Other typical findings are ichthyosis (type linearis circumflexa) and hair abnormalities (trichorrhexis invaginata). Dupilumab treatment for patients with Netherton syndrome was reported in a total of 16 cases (Table 6) [195,196,197,198,199,200,201,202,203,204,205]. All cases showed prompt resolution of itch measured by NRS and an improvement of skin lesions evaluated by EASI or BSA within 3 months. In patients with hair abnormalities, three cases reported improved hair growth while two reported no effect. The response was sustained in 14/16 cases for various follow-up periods, while two patients experienced a relapse after 8 or 20 weeks that was not sufficiently controlled by a dose increase and led to withdrawal of dupilumab [195,202]. Currently, a placebo-controlled RCT is recruiting (NS-DUPI, NCT04244006).Other congenital ichthyoses can lead to skin findings similar to AD by impaired skin barrier functions. Clinical improvement of ichthyosis in patients with concomitant AD treated with dupilumab was reported in a case of lamellar ichthyosis [206] and erythrodermic ichthyosis [207]. A partial response to dupilumab with improved skin findings but persistent itch was reported in one case of peeling skin syndrome 1 [208]. A case of ichthyosiform erythroderma caused by trichothiodystrophy with ERCC2-mutation experienced complete remission of skin lesions and pruritus with dupilumab [209]. An exploratory study in children with congenital ichthyoses compares effects of dupilumab and other biologicals to symptomatic treatment and is currently recruiting (NCT04996485).

Table 6.
Netherton syndrome and other hereditary skin diseases.
One report of a patient with neurofibromatosis type 1 treated with dupilumab for concomitant AD showed a size reduction of preexisting neurofibromas and stable size and number of neurofibromas for a follow-up of 1.5 years [210].
TTC7A deficiency is a rare congenital disease that leads to intestinal atresia and various immune defects; one patient with pruritic eczema and ichthyosis as well as immunologic findings suggesting vancomycin-induced linear IgA-dermatosis was treated efficiently with dupilumab and experienced complete sustained resolution of itch and skin findings [211].
Mutations in FOXP3 lead to dysfunction of Tregs and severe clinical findings termed IPEX syndrome often associated with various inflammatory skin diseases. One case of a patient with pruritic eczema due to IPEX syndrome was treated efficiently with dupilumab with sustained resolution of skin findings after a range of ineffective aggressive immunosuppressive therapies as well as bone marrow transplantation [212].
A patient with X-linked agammaglobulinemia that resulted in frequent skin infections and AD-like eczema experienced complete remission with dupilumab [213].
3.7. Eosinophilic Dermatoses
Peripheral and tissue eosinophilia is known to be promoted by IL-4, -5 and -13 by stimulating eosinophil trafficking and inducing other eosinophil chemoattractants [214]. Several dermatoses are specifically characterized by eosinophilic skin infiltrates or result from systemic eosinophilia.
Hypereosinophilic syndrome (HES) is a difficult to treat hematologic disease characterized by idiopathic blood eosinophilia that can present with pruritic eczema and other organ manifestations. A total of 11 patients with HES, 7 of which had skin manifestations, were treated with dupilumab after failure of systemic steroids. Of note, 2/7 patients reported a history of atopy. Improvement of skin lesions to various degrees was reported in 5/7 patients, one non-atopic individual experienced complete remission (Table 7) [215,216,217].

Table 7.
Eosinophilic dermatoses.
Hematologic malignancies can be associated with pruritic rashes with skin eosinophilia, a condition termed eosinophilic dermatosis of hematological malignancy (EDHM). We found records of four patients with EDHM treated with dupilumab after failure of systemic steroids, three of which had underlying chronic lymphatic leukemia and one small lymphocytic lymphoma. In two of the reported patients, strikingly, no eosinophilia was found in the blood. All four patients reported rapid complete clearance of skin manifestations within 4–6 weeks (Table 7) [8,218,219,220].
Hyper-IgE syndromes can be caused by a variety of mutations and patients typically present with generalized eczema and peripheral eosinophilia. Clinically and mechanistically, eczema in hyper-IgE syndromes have a large overlap with AD. We found records of a total of 12 patients with hyper-IgE syndrome presenting with generalized pruritic eczema that was treated with dupilumab. Of those, seven patients had a mutation of STAT3, three of DOCK8 and one of ZNF341. A complete remission of pruritus and skin findings were reported in 10/12 patients andtwo patients showed partial remissions (Table 7) [221,222,223,224,225,226,227,228,229,230,231].
Further reports were found for Kimura’s disease with 4 patients treated with dupilumab and 3/4 experiencing complete and one partial remission [232,233,234,235]. Four cases of steroid-refractory papuloerythroderma Ofuji treated with dupilumab all reported complete resolution of skin lesions and pruritus [236,237,238]. Two cases of highly steroid- and immunosuppressant-refractory Well’s syndrome reported complete resolutions [239,240], as did two cases of the related erythema annulare eosinophilicum [241,242]. One case of eosinophilic fasciitis reported resolution of skin induration clinically and in MRI-studies under dupilumab treatment [243]. Further, one case of angiolymphoid hyperplasia with eosinophilia refractory to IL-5 inhibitors treated with dupilumab reported sustained resolution of pruritic skin lesions even after discontinuation of the therapy [244].
3.8. Connective Tissue Disorders
Several systemic or localized connective tissue inflammatory diseases are accompanied by pruritus. Th2-associated inflammation has been found in some diseases, but Th1-pathways are more prominent in systemic collagenoses such as lupus erythematosus.
Dupilumab showed reduction of skin lesions and pruritus in one case of extragenital lichen sclerosus (Table 8) [245]; further, a phase 2 placebo-controlled study is recruiting patients for evaluating dupilumab in localized scleroderma (DupiMorph, NCT04200755).

Table 8.
Connective tissue disorders and other inflammatory skin diseases.
No effects have, however, been shown for systemic collagenoses, e.g., in a case of dermatomyositis with severe pruritus, dupilumab was ineffective [246]. Notably, some reports showed newly developed lupus erythematosus in AD patients treated with dupilumab. In contrast, a case of steroid-refractory IgG4-related disease and concomitant AD with retroperitoneal fibrosis and pruritic skin manifestations showed resolution of fibrosis and skin lesions on dupilumab [247].
One report showed increased expression of Th2-associated transcripts (IL-4 receptor, IL-13) in keloid tissue in an individual with severe AD. Dupilumab was evaluated in a total of 12 reported cases with keloids (Table 8). One case showed size reduction of the keloid [248], one case with a highly pruritic keloid reported reduction of itch [249]; however, the remaining 10 cases did not report any effects of dupilumab or deterioration [250,251]. Two clinical trials evaluating dupilumab in keloids are currently recruiting (NCT04988022, NCT05128383).
3.9. Other Inflammatory Skin Diseases
Chronic photodermatoses including chronic actinic dermatosis (CAD) and actinic prurigo are induced by exposure to UV-radiation and can resemble photosensitive AD. Reports showed efficacy of dupilumab in 16 cases of CAD (Table 8) [252,253,254,255,256,257,258] as well as in a pediatric patient with actinic prurigo [259], leading to higher minimal erythema doses in repeated UV-phototesting in some cases.
Graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation can show clinical and histologic features of AD; a case series of 4 pediatric patients showed complete resolution of GVHD under treatment with dupilumab, while one patient did not respond [260].
One case found complete resolution of a severe palmoplantar pustulosis with dupilumab after lacking disease control with secukinumab in a non-atopic individual [261]. Psoriasiform dermatoses, however, have been implicated as adverse effects of dupilumab in other reports.
Lichen planus was treated efficiently with dupilumab in three cases, leading to resolution of skin manifestations and pruritus (Table 8) [8,262,263]. Conversely, also lichenoid dermatoses were reported as adverse effects of dupilumab.
Three cases of patients with hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) and concomitant AD showed remission of the previously uncontrolled HS after having failed systemic antibiotics and in one case adalimumab (Table 8) [264,265,266]. High AD-disease activity might impose an additional trigger to flares of HS, however, HS itself is mainly associated with Th1/Th17-responses.
One case of generalized granuloma annulare refractory to adalimumab showed a sustained partial response [267], however, emergence of granulomatous drug reactions was also reported under dupilumab therapy.
Lichen amyloidosus is characterized by extracellular deposits of amyloid proteins in the dermis with often intense pruritus. Reports of 4 patients with lichen amyloidosus and concomitant AD treated with dupilumab showed flattening of dermal papules and reduction of itch (Table 8) [268,269], a partial resolution was also observed in one non-atopic individual after failure of therapy with benralizumab [270].
Food allergies can be associated with AD. One case report of a patient that had suffered an anaphylactic shock after ingestion of corn and had detection of specific IgE against corn extract showed no reaction in a later oral provocation after 12 weeks of dupilumab therapy for AD [271]. A phase 2 clinical trial evaluating dupilumab in 24 patients with peanut allergy showed a tolerance to oral challenge after 24 weeks of therapy in 8.3% (NCT03793608). Another phase 2 study in patients with peanut allergy is completed and has not yet reported (NCT03682770); one was terminated due to COVID-19 (NCT04462055). Currently, a phase 2 study for patients with milk allergy is recruiting (NCT04148352).
3.10. Cutaneous Lymphoma
Cutaneous T cell lymphoma (CTCL), including mycosis fungoides and Sézary syndrome, is frequently accompanied by highly refractory pruritus that drastically affects quality of life, especially in palliative settings (Figure 1G). Dupilumab showed reduction of itch as a supportive care treatment in 10 patients (Table 9) [272,273,274,275,276]. However, 7 of those experienced disease progression with two reported deaths; an average length of initial improvement of 1.9 months was reported for 6 patients. Other reports of 8 patients showed no response, primary worsening or new development of CTCL under dupilumab [274,275,276,277,278,279,280,281,282]. Possible mechanisms could be increased binding of IL-13 to IL-13RA2 expressed on lymphoma cells that is not inhibited by dupilumab. Thus, dupilumab could merely be considered a supportive care strategy for symptom control.

Table 9.
Cutaneous lymphoma.
One patient with cutaneous B cell pseudolymphoma showed complete remission with dupilumab [283].
Further, one patient with a treatment-refractory generalized lichenoid drug eruption associated with mogamulizumab given for treatment of underlying MF reported complete resolution of the drug rash with dupilumab [284].
4. Discussion
This systematic review summarizes the existing evidence for treatment with dupilumab in other dermatologic conditions than atopic dermatitis and prurigo nodularis.
A high level of evidence (level 2 according to the OCEBM) was found for alopecia areata with a phase 2 RCT reporting significant improvement of the disease score SALT at week 24 and 48; however, conflicting case reports showed paradoxical reactions or lack of effects (15/66 reported patients).
Further, a high level of evidence (level 2) was found for antihistamine-refractory chronic spontaneous urticaria with a phase 3 RCT showing a significantly higher reduction of the disease score UAS7 compared with placebo in 138 treated patients. Anecdotal evidence was found for other forms of chronic urticaria.
For bullous pemphigoid, a medium level of evidence (level 3) was found based on multiple cohort studies. Dupilumab could become more relevant in checkpoint inhibitor-induced BP for patients with underlying malignancy.
A medium level of evidence (level 3) was also found for chronic hand eczema with a large prospective study showing an average 89% reduction of the disease score HECSI at 52 weeks. Numerous reports also showed efficacy of dupilumab in allergic contact dermatitis; however, the culprit allergen seemed to affect responses.
Lower levels of evidence (level 4) were found for nummular eczema, chronic pruritus of unknown origin and Netherton syndrome. Anecdotal evidence (level 5) based on individual reports was shown for eczematous eruptions, cholestatic or uremic pruritus, perforating collagenosis, other pemphigoid diseases than BP and pemphigus diseases, epidermolysis bullosa dystrophica, Hailey–Hailey disease, Grover’s disease, congenital ichthyoses and other genodermatoses, eosinophilic dermatoses such as Kimura’s disease, chronic photodermatoses, graft-versus-host disease and food allergies.
For symptomatic treatment of cutaneous lymphoma, the reports were ambivalent and some showed progression or novel development of the underlying disease.
Strengths of this systemic review are the multifaceted comprehensive evaluation of dupilumab effects in a range of heterogeneous dermatologic conditions in order to give a broad overview. However, the evidence found was scarce or conflicting for many diseases and mainly based on individual reports; statistical meta-analysis was thus not feasible and larger cohort sizes are needed. In addition, many of the reported conditions can be considered multicausal with unidentified factors confounding the responses to dupilumab. In addition, dupilumab was frequently given as second- or third-line treatment in refractory patients.
As a drug with favorable safety profile as well as established and efficient clinical use for a broad range of patient populations [285], dupilumab holds significant promise for amending treatment options for a plethora of dermatologic conditions. With numerous clinical trials ongoing, we expect future expansion of the use of dupilumab in dermatology.
Author Contributions
H.O. and K.B. performed the data collection and analysis. D.T., C.D.S. and R.J.L. acquired funding. H.O. drafted the manuscript. D.T., C.D.S., R.J.L. and K.B. revised the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Clinician Scientist School Lübeck (CS01-2022), by the Cluster of Excellence Precision Medicine in Chronic Inflammation (DFG EXC 2167) and the Schleswig-Holstein Excellence-Chair Program from the State of Schleswig-Holstein.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
No new data were created or analyzed in this study. Data sharing is not applicable to this article.
Conflicts of Interest
All authors have read the journal’s policy and the authors of this manuscript have the following competing interests: D.T. received honoraria and lecture fees from AbbVie, Almirall, Amgen, Biogen Idec, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol Myers Squibb, Janssen, Leo Pharma, Novartis, Pfizer, Regeneron, Roche-Posay, Sanofi, Target-Solution and UCB. All other authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Beck, L.A.; Thaçi, D.; Hamilton, J.D.; Graham, N.M.; Bieber, T.; Rocklin, R.; Ming, J.E.; Ren, H.; Kao, R.; Simpson, E.; et al. Dupilumab Treatment in Adults with Moderate-to-Severe Atopic Dermatitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 130–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deleuran, M.; Thaçi, D.; Beck, L.A.; de Bruin-Weller, M.; Blauvelt, A.; Forman, S.; Bissonnette, R.; Reich, K.; Soong, W.; Hussain, I.; et al. Dupilumab shows long-term safety and efficacy in patients with moderate to severe atopic dermatitis enrolled in a phase 3 open-label extension study. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2020, 82, 377–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, L.A.; Thaçi, D.; Deleuran, M.; Blauvelt, A.; Bissonnette, R.; De Bruin-Weller, M.; Hide, M.; Sher, L.; Hussain, I.; Chen, Z.; et al. Dupilumab Provides Favorable Safety and Sustained Efficacy for up to 3 Years in an Open-Label Study of Adults with Moderate-to-Severe Atopic Dermatitis. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2020, 21, 567–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guttman-Yassky, E.; Bissonnette, R.; Ungar, B.; Suárez-Fariñas, M.; Ardeleanu, M.; Esaki, H.; Suprun, M.; Estrada, Y.; Xu, H.; Peng, X.; et al. Dupilumab progressively improves systemic and cutaneous abnormalities in patients with atopic dermatitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2019, 143, 155–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berdyshev, E.; Goleva, E.; Bissonnette, R.; Bronova, I.; Bronoff, A.S.; Richers, B.N.; Garcia, S.; Ramirez-Gama, M.; Taylor, P.; Praestgaard, A.; et al. Dupilumab significantly improves skin barrier function in patients with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis. Allergy 2022, 77, 3388–3397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Napolitano, M.; Maffei, M.; Patruno, C.; Leone, C.A.; Di Guida, A.; Potestio, L.; Scalvenzi, M.; Fabbrocini, G. Dupilumab effectiveness for the treatment of patients with concomitant atopic dermatitis and chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyposis. Dermatol. Ther. 2021, 34, e15120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rambhia, P.H.; Levitt, J.O. Recalcitrant prurigo nodularis treated successfully with dupilumab. JAAD Case Rep. 2019, 5, 471–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhai, L.L.; Savage, K.T.; Qiu, C.C.; Jin, A.; Valdes-Rodriguez, R.; Mollanazar, N.K. Chronic Pruritus Responding to Dupilumab—A Case Series. Medicines 2019, 6, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calugareanu, A.; Jachiet, M.; Lepelletier, C.; De Masson, A.; Rybojad, M.; Bagot, M.; Bouaziz, J. Dramatic improvement of generalized prurigo nodularis with dupilumab. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2019, 33, e303–e304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almustafa, Z.; Weller, K.; Autenrieth, J.; Maurer, M.; Metz, M. Dupilumab in Treatment of Chronic Prurigo: A Case Series and Literature Review. Acta Derm.-Venereol. 2019, 99, 905–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, K.M.; Yang, E.J.; Sekhon, S.; Bhutani, T.; Liao, W. Dupilumab Treatment for Generalized Prurigo Nodularis. JAMA Dermatol. 2019, 155, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanis, R.; Ferenczi, K.; Payette, M. Dupilumab Treatment for Prurigo Nodularis and Pruritis. J. Drugs Dermatol. 2019, 18, 940–942. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mollanazar, N.K.; Elgash, M.; Weaver, L.; Valdes-Rodriguez, R.; Hsu, S. Reduced Itch Associated with Dupilumab Treatment In 4 Patients with Prurigo Nodularis. JAMA Dermatol. 2019, 155, 121–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieser, J.K.; Mercurio, M.G.; Somers, K. Resolution of Treatment-Refractory Prurigo Nodularis with Dupilumab: A Case Series. Cureus 2020, 12, e8737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calugareanu, A.; Jachiet, M.; Tauber, M.; Nosbaum, A.; Aubin, F.; Misery, L.; Droitcourt, C.; Barbarot, S.; Debarbieux, S.; Saussine, A.; et al. Effectiveness and safety of dupilumab for the treatment of prurigo nodularis in a French multicenter adult cohort of 16 patients. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2020, 34, e74–e76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Napolitano, M.; Fabbrocini, G.; Scalvenzi, M.; Nisticò, S.P.; Dastoli, S.; Patruno, C. Effectiveness of Dupilumab for the Treatment of Generalized Prurigo Nodularis Phenotype of Adult Atopic Dermatitis. Dermatitis 2020, 31, 81–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovács, B.; Rose, E.; Kuznik, N.; Shimanovich, I.; Zillikens, D.; Ludwig, R.J.; Thaçi, D. Dupilumab for treatment-refractory prurigo nodularis. JDDG J. Dtsch. Dermatol. Ges. 2020, 18, 618–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Criado, P.; Pincelli, T.P.; Criado, R.F.J. Dupilumab as a useful treatment option for prurigo nodularis in an elderly patient with atopic diathesis. Int. J. Dermatol. 2020, 59, e358–e361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giura, M.T.; Viola, R.; Fierro, M.T.; Ribero, S.; Ortoncelli, M. Efficacy of dupilumab in prurigo nodularis in elderly patient. Dermatol. Ther. 2020, 33, e13201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, M.T.; Dinehart, S.M.; Anderson, K.R.; Gorelick, J. Treatment of Recalcitrant Prurigo Nodularis with Dupilumab. Ski. J. Cutan. Med. 2020, 4, 279–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holm, J.G.; Agner, T.; Sand, C.; Thomsen, S.F. Dupilumab for prurigo nodularis: Case series and review of the literature. Dermatol. Ther. 2020, 33, e13222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiricozzi, A.; Maurelli, M.; Gori, N.; Argenziano, G.; De Simone, C.; Calabrese, G.; Girolomoni, G.; Peris, K. Dupilumab improves clinical manifestations, symptoms, and quality of life in adult patients with chronic nodular prurigo. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2020, 83, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bloomstein, J.D.; Hawkes, J.E. Simultaneous treatment of Samter triad and prurigo nodularis with dupilumab. JAAD Case Rep. 2021, 18, 20–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Georgakopoulos, J.R.; Croitoru, D.; Felfeli, T.; Alhusayen, R.; Lansang, P.; Shear, N.H.; Yeung, J.; Walsh, S. Long-term dupilumab treatment for chronic refractory generalized prurigo nodularis: A retrospective cohort study. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2021, 85, 1049–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrucci, S.; Tavecchio, S.; Berti, E.; Angileri, L. Dupilumab and prurigo nodularis-like phenotype in atopic dermatitis: Our experience of efficacy. J. Dermatol. Treat. 2019, 32, 453–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Bai, J.; Wang, S.; Ying, S.; Li, S.; Qiao, J.; Fang, H. Effectiveness of Dupilumab for an Elderly Patient with Prurigo Nodularis Who Was Refractory and Contradicted to Traditional Therapy. J. Asthma Allergy 2021, 14, 175–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romano, C. Safety and Effectiveness of Dupilumab in Prurigo Nodularis. J. Investig. Allergol. Clin. Immunol. 2021, 31, 162–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilotta, G.; Pistone, G.; Caruso, P.; Gurreri, R.; Castelli, E.; Curiale, S.; Caputo, V.; Bongiorno, M. Our experience with prurigo nodularis treated with dupilumab. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2021, 35, e285–e287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkler, J.K.; Haenssle, H.A.; Enk, A.; Toberer, F.; Hartmann, M. Erfolgreiche Behandlung einer chronischen Prurigo mit Dupilumab. Der Hautarzt 2020, 72, 528–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, N.; Wang, Q.; Lei, M.; Li, T.; Hao, P. Dupilumab for Chronic Prurigo in Different Backgrounds: A Case Series. Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dermatol. 2022, 15, 1863–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lönndahl, L.; Lundqvist, M.; Bradley, M.; Johansson, E.K. Dupilumab Significantly Reduces Symptoms of Prurigo Nodularis and Depression: A Case Series. Acta Derm. Venereol. 2022, 102, adv00754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitsuyama, S.; Higuchi, T. Effectiveness of dupilumab for chronic prurigo in elderly patients with atopic dermatitis. An. Bras. Dermatol. 2022, 98, 86–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gade, A.; Ghani, H.; Rubenstein, R. Dupilumab; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK585114/ (accessed on 6 December 2022).
- Muzumdar, S.; Skudalski, L.; Sharp, K.; Waldman, R.A. Dupilumab Facial Redness/Dupilumab Facial Dermatitis: A Guide for Clinicians. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2022, 23, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hendricks, A.J.; Yosipovitch, G.; Shi, V.Y. Dupilumab use in dermatologic conditions beyond atopic dermatitis—A systematic review. J. Dermatol. Treat. 2021, 32, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maloney, N.J.; Tegtmeyer, K.; Zhao, J.; Worswick, S. Dupilumab in Dermatology: Potential for Uses Beyond Atopic Dermatitis. J. Drugs Dermatol. 2019, 18, S1545961619P1053X. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, F.; Zhao, Q.; Shi, P.; Liu, H.; Zhang, F. Dupilumab: Advances in the off-label usage of IL4 / IL13 antagonist in dermatoses. Dermatol. Ther. 2022, 35, e15924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 Statement: An Updated Guideline for Reporting Systematic Reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OCEBM Levels of Evidence Working Group. ‘The Oxford Levels of Evidence 2’. Oxford Centre for Evidence-Based Medicine. Available online: https://www.cebm.ox.ac.uk/resources/levels-of-evidence/ocebm-levels-of-evidence (accessed on 28 March 2023).
- Patruno, C.; Stingeni, L.; Hansel, K.; Ferrucci, S.M.; Tavecchio, S.; Fabbrocini, G.; Nisticò, S.P.; Foti, C.; De Prezzo, S.; Napolitano, M. Effectiveness of dupilumab for the treatment of nummular eczema phenotype of atopic dermatitis in adults. Dermatol. Ther. 2020, 33, e13290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.; Zhu, G.A.; Lewis, M.A.; Honari, G.; Chiou, A.S.; Ko, J.; Chen, J.K. Dupilumab treatment of nummular dermatitis: A retrospective cohort study. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2020, 82, 1252–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhingra, N.; Shemer, A.; da Rosa, J.C.; Rozenblit, M.; Fuentes-Duculan, J.; Gittler, J.K.; Finney, R.; Czarnowicki, T.; Zheng, X.; Xu, H.; et al. Molecular profiling of contact dermatitis skin identifies allergen-dependent differences in immune response. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2014, 134, 362–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machler, B.C.; Sung, C.T.; Darwin, E.; Jacob, S.E. Dupilumab use in allergic contact dermatitis. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2019, 80, 280–281.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, B.; Balogh, E.; Rayhan, D.; Shitabata, P.; Yousefzadeh, D.; Feldman, S. Chromate-Induced Allergic Contact Dermatitis Treated with Dupilumab. J. Drugs Dermatol. 2021, 20, 1340–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arasu, A.; Ross, G. Treatment of generalised isobornyl acrylate contact allergy from diabetes pump with Dupilumab. Australas. J. Dermatol. 2022, 63, e91–e93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruge, I.F.; Skov, L.; Zachariae, C.; Thyssen, J.P. Dupilumab treatment in two patients with severe allergic contact dermatitis caused by sesquiterpene lactones. Contact Dermat. 2020, 83, 137–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.A.; Chen, J.K.; Chiou, A.; Ko, J.; Honari, G. Repeat patch testing in a patient with allergic contact dermatitis improved on dupilumab. JAAD Case Rep. 2019, 5, 336–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldminz, A.M.; Scheinman, P.L. A case series of dupilumab-treated allergic contact dermatitis patients. Dermatol. Ther. 2018, 31, e12701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slodownik, D.; Levi, A.; Lapidoth, M.; Moshe, S. Occupational Chronic Contact Dermatitis Successfully Treated with Dupilumab: A Case Series. Dermatology 2022, 238, 1073–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, S.R.; Khan, D.A. Effective Use of Dupilumab in Managing Systemic Allergic Contact Dermatitis. Dermatitis® 2018, 29, 282–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suresh, R.; Murase, J.E. The role of expanded series patch testing in identifying causality of residual facial dermatitis following initiation of dupilumab therapy. JAAD Case Rep. 2018, 4, 899–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collantes-Rodríguez, C.; Jiménez-Gallo, D.; García, L.O.; Villegas-Romero, I.; Linares-Barrios, M. Recall dermatitis at patch test sites in an atopic dermatitis patient treated with dupilumab. Contact Dermat. 2019, 80, 69–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chipalkatti, N.; Lee, N.; Zancanaro, P.; Dumont, N.; Donovan, C.; Rosmarin, D. Dupilumab as a Treatment for Allergic Contact Dermatitis. Dermatitis® 2018, 29, 347–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chipalkatti, N.; Lee, N.; Zancanaro, P.; Dumont, N.; Kachuk, C.; Rosmarin, D. A retrospective review of dupilumab for atopic dermatitis patients with allergic contact dermatitis. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2019, 80, 1166–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, S.E.; Sung, C.T.; Machler, B.C. Dupilumab for Systemic Allergy Syndrome with Dermatitis. Dermatitis 2019, 30, 164–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stout, M.; Silverberg, J.I. Variable impact of dupilumab on patch testing results and allergic contact dermatitis in adults with atopic dermatitis. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2019, 81, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, P.; Yang, C.; Bai, J.; Dong, L.; Zhi, L. Successfully treatment with Dupilumab for systemic contact dermatitis following hair dye in a patient with dermatomyositis. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2022, 21, 6468–6469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallo, R.; Oddenino, G.; Trave, I.; Gasparini, G.; Guadagno, A.; Parodi, A. Contact sensitivity to sesquiterpene lactone mix and artichoke in a patient with severe recurrent dermatitis: A puzzling case. Contact Dermat. 2023, 88, 156–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, Y.; Park, J.; Shin, S.; Kim, B.; Yoo, K. Dupilumab for the treatment of refractory allergic contact dermatitis from rubber/latex concomitant with atopic dermatitis. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2022, 36, e640–e643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- E Koblinski, J.; Hamann, D. Mixed occupational and iatrogenic allergic contact dermatitis in a hairdresser. Occup. Med. 2020, 70, 523–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mainville, L.; Veillette, H.; Houle, M. Sequential patch testing in a patient treated with dupilumab then with upadacitinib: Differences in patch test results as well as in disease control. Contact Dermat. 2023, 1, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, C.E.; Mufti, A.; Sachdeva, M.; Pratt, M.; Yeung, J. Effect of dupilumab on allergic contact dermatitis and patch testing. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2021, 84, 1772–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldman, R.A.; DeWane, M.E.; Sloan, B.; Grant-Kels, J.M.; Lu, J. Dupilumab for the treatment of dyshidrotic eczema in 15 consecutive patients. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2020, 82, 1251–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weins, A.B.; Biedermann, T.; Eyerich, K.; Moeckel, S.; Schnopp, C. Successful treatment of recalcitrant dyshidrotic eczema with dupilumab in a child. JDDG J. Dtsch. Dermatol. Ges. 2019, 17, 1165–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olesen, C.M.; Yüksel, Y.T.; Zachariae, C.; Lund, T.T.; Agner, T.; Petersen, T.S.; Thyssen, J.P. Treatment of chronic hand eczema with dupilumab—A retrospective follow-up study. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2022, 37, e557–e559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voorberg, A.N.; Romeijn, G.L.E.; de Bruin-Weller, M.S.; Schuttelaar, M.L.A. The long-term effect of dupilumab on chronic hand eczema in patients with moderate to severe atopic dermatitis—52 week results from the Dutch BioDay Registry. Contact Dermat. 2022, 87, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loman, L.; Diercks, G.F.; Schuttelaar, M.L. Three cases of non-atopic hyperkeratotic hand eczema treated with dupilumab. Contact Dermat. 2021, 84, 124–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.A.; Honari, G.; Ko, J.M.; Chiou, A.S.; Chen, J.K. Dupilumab for occupational irritant hand dermatitis in a nonatopic individual: A case report. JAAD Case Rep. 2020, 6, 296–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halling, A.; Zachariae, C.; Thyssen, J.P. Severe treatment-resistant acute and recurrent vesicular chronic hand eczema successfully treated with dupilumab. Contact Dermat. 2020, 83, 37–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oosterhaven, J.A.; Voorberg, A.N.; Romeijn, G.L.; De Bruin-Weller, M.S.; Schuttelaar, M.L. Effect of dupilumab on hand eczema in patients with atopic dermatitis: An observational study. J. Dermatol. 2019, 46, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, N.; Chipalkatti, N.; Zancanaro, P.; Kachuk, C.; Dumont, N.; Rosmarin, D. A Retrospective Review of Dupilumab for Hand Dermatitis. Dermatology 2019, 235, 187–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oosterhaven, J.A.F.; Romeijn, G.L.E.; Schuttelaar, M.L.A. Dupilumab Treatment of Very Severe Refractory Atopic Hand Eczema. JAMA Dermatol. 2018, 154, 969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zirwas, M.J. Dupilumab for hand eczema. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2018, 79, 167–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weston, G.K.; Hooper, J.; E Strober, B. Dupilumab in the Treatment of Dyshidrosis: A Report of Two Cases. J. Drugs Dermatol. 2018, 17, 355–356. [Google Scholar]
- Nanda, S.; Nagrani, N.; MacQuhae, F.; Nichols, A. A Case of Complete Resolution of Severe Plantar Dyshidrotic Eczema With Dupilumab. J. Drugs Dermatol. 2019, 18, 211–212. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Xiao, J.; Sun, Y.; Fang, H.; Qiao, J. Quick Treatment of Very Severe Refractory Hand and Foot Eczema with Dupilumab: A Case Report and Literature Review. J. Asthma Allergy 2023, 16, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A Gall, R.; Peters, J.D.; Brinker, A.J. Two Cases of Recalcitrant Dyshidrotic Eczema Treated with Dupilumab. J. Drugs Dermatol. 2021, 20, 558–559. [Google Scholar]
- Gan, H.; Gao, Y.-D. Occupational Chronic Hand Dermatitis in Hospital Environment Successfully Treated with Dupilumab: A Case Report. Iran. J. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2022, 21, 484–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Megna, M.; Genco, L.; Noto, M.; Patruno, C.; Fabbrocini, G.; Napolitano, M. Eczematous eruption after brodalumab successfully treated with guselkumab and dupilumab. Dermatol. Ther. 2022, 35, e15839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koschitzky, M.; Tan, K.; Encarnacion, M.R.N.; Rivera-Oyola, R.; Khattri, S. Eczematous reactions to psoriasis biologics treated with dupilumab: A case series. JAAD Case Rep. 2021, 11, 29–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahriari, N.; Strober, B.; Shahriari, M. The role of dupilumab in the management of idiopathic chronic eczematous eruption of aging. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2020, 83, 1533–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brummer, G.C.; Wang, L.T.; Sontheimer, R.D. A possible role for dupilumab (Dupixent) in the management of idiopathic chronic eczematous eruption of aging. Dermatol. Online J. 2018, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Votquenne, N.; Dupire, G.; Michel, O.; Ben Said, B. Dupilumab for severe generalized eczematous eruption complicating common variable immunodeficiency. Eur. J. Dermatol. 2021, 31, 93–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrom, K.P.; Kobs, A.; Nedorost, S. Clinical Psoriasiform Dermatitis Following Dupilumab Use for Autoeczematization Secondary to Chronic Stasis Dermatitis. Cureus 2020, 12, e7831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oetjen, L.K.; Mack, M.R.; Feng, J.; Whelan, T.M.; Niu, H.; Guo, C.J.; Chen, S.; Trier, A.M.; Xu, A.Z.; Tripathi, S.V.; et al. Sensory Neurons Co-opt Classical Immune Signaling Pathways to Mediate Chronic Itch. Cell 2017, 171, 217–228.e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fachler, T.; Faitataziadou, S.M.; Molho-Pessach, V. Dupilumab for pediatric prurigo nodularis: A case report. Pediatr. Dermatol. 2021, 38, 334–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giovannini, M.; Mori, F.; Oranges, T.; Ricci, S.; Barni, S.; Canessa, C.; Liccioli, G.; Lodi, L.; Sarti, L.; Novembre, E.; et al. Dupilumab treatment of prurigo nodularis in an adolescent. Eur. J. Dermatol. 2021, 31, 104–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edmonds, N.; Noland, M.; Flowers, R.H. Six cases of refractory pruritus and histologic dermal hypersensitivity reaction successfully treated with dupilumab. JAAD Case Rep. 2022, 19, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, J.; Wang, F.; Badic, A.; Kim, B.S. Treatment of patients with chronic pruritus of unknown origin with dupilumab. J. Dermatol. Treat. 2022, 33, 1754–1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanger, R.; Rivera-Oyola, R.; Lebwohl, M. Dupilumab as a treatment for generalized idiopathic pruritus: A report of two cases. Br. J. Dermatol. 2020, 182, 1494–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silverberg, J.I.; Brieva, J. A successful case of dupilumab treatment for severe uremic pruritus. JAAD Case Rep. 2019, 5, 339–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chovatiya, R.; Brieva, J.; Hung, A. Dupilumab treatment for cholestatic pruritus. Dermatol. Ther. 2022, 35, e15296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abel, M.K.; Ashbaugh, A.G.; Stone, H.F.; Murase, J.E. The use of dupilumab for the treatment of recalcitrant brachioradial pruritus. JAAD Case Rep. 2021, 10, 69–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, E.; Murase, J. Recalcitrant anal and genital pruritus treated with dupilumab. Int. J. Womens Dermatol. 2018, 4, 223–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.J.; Lee, J.H.; Choi, J.E.; Han, T.Y. Treatment of acquired reactive perforating collagenosis with dupilumab in a patient with end-stage renal disease. Dermatol. Ther. 2022, 35, e15926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, L.; Zeng, Y.; Jin, H. Reactive perforating collagenosis treated with dupilumab: A case report and literature review. Dermatol. Ther. 2022, 35, e15916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsebayel, M.M.; Alzaid, T.; Alobaida, S.A. Dupilumab in acquired perforating dermatosis: A potential new treatment. JAAD Case Rep. 2022, 28, 34–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil-Lianes, J.; Loughlin, C.R.; Mascaró, J.M. Reactive perforating collagenosis successfully treated with dupilumab. Australas. J. Dermatol. 2022, 63, 398–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ying, Y.; Shuang, C.; Zhen-Ying, Z. Dupilumab may be an alternative option in the treatment of acquired reactive perforating collagenosis combined with AD. Immunity Inflamm. Dis. 2022, 10, e574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ludwig, R.J.; Vanhoorelbeke, K.; Leypoldt, F.; Kaya, Z.; Bieber, K.; McLachlan, S.M.; Komorowski, L.; Luo, J.; Cabral-Marques, O.; Hammers, C.M.; et al. Mechanisms of Autoantibody-Induced Pathology. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Has, C.; Bauer, J.W.; Bodemer, C.; Bolling, M.C.; Bruckner-Tuderman, L.; Diem, A.; Fine, J.-D.; Heagerty, A.; Hovnanian, A.; Marinkovich, M.P.; et al. Consensus reclassification of inherited epidermolysis bullosa and other disorders with skin fragility. Br. J. Dermatol. 2020, 183, 614–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kridin, K.; Ludwig, R. The Growing Incidence of Bullous Pemphigoid: Overview and Potential Explanations. Front. Med. 2018, 5, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, E.; Zillikens, D. Pemphigoid diseases. Lancet 2013, 381, 320–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Beek, N.; Lüttmann, N.; Huebner, F.; Recke, A.; Karl, I.; Schulze, F.S.; Zillikens, D.; Schmidt, E. Correlation of Serum Levels of IgE Autoantibodies Against BP180 With Bullous Pemphigoid Disease Activity. JAMA Dermatol. 2017, 153, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Man, X.; Tang, Z.; Dai, R.; Shen, Y. Dupilumab as a novel therapy for bullous pemphigoid. Int. J. Dermatol. 2022, 62, e263–e266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Song, W.; Cai, Y.; Huang, R.; Wei, J.; Liu, H.; Peng, X.; Zeng, K.; Li, C. Successful treatment of eczema-like bullous pemphigoid and typical bullous pemphigoid with dupilumab: Two case reports. Int. J. Dermatol. 2022, 62, e144–e146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Wang, J.; Shi, B. Case report: Dupilumab for the treatment of bullous pemphigoid. Dermatol. Ther. 2022, 35, e15541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Ma, J.; Qiu, X.; Hong, D.; Wang, L.; Shi, Z. Dupilumab, an emerging therapeutic choice for recalcitrant subepidermal autoimmune bullous diseases: A case series of three patients. Eur. J. Dermatol. 2021, 31, 846–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, Y.; Zuo, Y. A successful case of vesicular pemphigoid concurrent with pulmonary tuberculosis with dupilumab. Dermatol. Ther. 2022, 35, e15330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bal, A.; Sorensen, A.; Ondreyco, S.M. Nonbullous erythrodermic pemphigoid with florid lymphadenopathy, response to dupilumab. JAAD Case Rep. 2021, 17, 58–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Chen, J.; Lin, M.; Gong, T.; Cheng, B.; Ji, C. Dupilumab successfully treated refractory bullous pemphigoid with early clinical manifestations imitating atopic dermatitis: A case letter. Australas. J. Dermatol. 2021, 62, 525–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, M.; Reedy, M.; Torok, H.; Weaver, J. Successful treatment of bullous pemphigoid with dupilumab: A case and brief review of the literature. Dermatol. Online J. 2021, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari, S.M.S.; Feldmeyer, L.; Bossart, S.; Simon, D.; Schlapbach, C.; Borradori, L. Case Report: Combination of Omalizumab and Dupilumab for Recalcitrant Bullous Pemphigoid. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 611549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdat, R.; Waldman, R.A.; de Bedout, V.; Czernik, A.; Mcleod, M.; King, B.; Gordon, S.; Ahmed, R.; Nichols, A.; Rothe, M.; et al. Dupilumab as a novel therapy for bullous pemphigoid: A multicenter case series. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2020, 83, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidman, J.S.; Eichenfield, D.Z.; Orme, C.M. Dupilumab for bullous pemphigoid with intractable pruritus. Dermatol. Online J. 2019, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, H.-C.; Lai, P.-T. Refractory bullous pemphigoid with prurigo nodularis successfully treated with dupilumab monotherapy. Dermatol. Sin. 2022, 40, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, A.E.; Shao, K.; Ferenczi, K.; Adalsteinsson, J.A. Recalcitrant bullous pemphigoid responsive to dupilumab in an adolescent patient. JAAD Case Rep. 2022, 29, 149–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Cai, S.; Man, X. The treatment of refractory atypical bullous pemphigoid with generalized eczema and intense pruritus with dupilumab. Dermatol. Ther. 2022, 35, e15243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaye, A.; Gordon, S.C.; Deverapalli, S.C.; Her, M.J.; Rosmarin, D. Dupilumab for the Treatment of Recalcitrant Bullous Pemphigoid. JAMA Dermatol. 2018, 154, 1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savoldy, M.A.; Tadicherla, T.; Moureiden, Z.; Ayoubi, N.; Baldwin, B.T. The Successful Treatment of COVID-19-Induced Bullous Pemphigoid With Dupilumab. Cureus 2022, 14, e30541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruni, M.; Moar, A.; Schena, D.; Girolomoni, G. A case of nivolumab-induced bullous pemphigoid successfully treated with dupilumab. Dermatol. Online J. 2022, 28, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pop, S.R.; Strock, D.; Smith, R.J. Dupilumab for the treatment of pembrolizumab-induced bullous pemphigoid: A case report. Dermatol. Ther. 2022, 35, e15623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klepper, E.M.; Robinson, H.N. Dupilumab for the treatment of nivolumab-induced bullous pemphigoid: A case report and review of the literature. Dermatol. Online J. 2021, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khazaeli, M.; Grover, R.; Pei, S. Concomitant nivolumab associated Grover disease and bullous pemphigoid in a patient with metastatic renal cell carcinoma. J. Cutan. Pathol. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baffa, M.E.; Maglie, R.; Montefusco, F.; Pipitò, C.; Senatore, S.; Antiga, E. Severe bullous pemphigoid following COVID-19 vaccination resistant to rituximab and successfully treated with dupilumab. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2022, 37, e135–e137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Gao, H.; Zhang, Z.; Tang, C.; Chen, Z.; Wang, L.; Yang, F.; Chen, S.; He, S.; Liu, S.; et al. Dupilumab combined with low-dose systemic steroid therapy improves efficacy and safety for bullous pemphigoid. Dermatol. Ther. 2022, 35, e15648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xu, Q.; Chen, L.; Chen, J.; Zhang, J.; Zou, Y.; Gong, T.; Ji, C. Efficacy and Safety of Dupilumab in Moderate-to-Severe Bullous Pemphigoid. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 4144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loughlin, C.R.; Mascaró, J.M. Treatment of pemphigoid gestationis with dupilumab. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2021, 46, 1578–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.-Z.; Xie, Y.-H.; Wang, S.-H.; Fang, R.-Y.; Jin, H.-Z.; Zuo, Y.-G. Case report: Successful treatment of non-bullous lichen planus pemphigoides with dupilumab. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 3735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ch’en, P.Y.; Song, E.J. Lichen planus pemphigoides successfully treated with dupilumab. JAAD Case Rep. 2023, 31, 56–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blum, F.R.; Sigmon, J.R. Successful treatment of Brunsting-Perry pemphigoid with dupilumab. JAAD Case Rep. 2021, 10, 107–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raef, H.S.; Elmariah, S.B. Successful Treatment of Brunsting-Perry Cicatricial Pemphigoid With Dupilumab. J. Drugs Dermatol. JDD 2021, 20, 1113–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jendoubi, F.; Bost, C.; Tournier, E.; Paul, C.; Konstantinou, M.P. Severe pemphigoid nodularis successfully treated with dupilumab. Dermatol. Ther. 2022, 35, e15727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valenti, M.; De Giacomo, P.; Lavecchia, A.; Valenti, G. A severe case of IgA bullous pemphigoid successfully treated with dupilumab. Dermatol. Ther. 2022, 35, e15890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, E.; Kasperkiewicz, M.; Joly, P. Pemphigus. Lancet 2019, 394, 882–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, A.Y.; Hurley, K. Dupilumab monotherapy suppresses recalcitrant pemphigus vulgaris. JAAD Case Rep. 2023, 31, 16–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhan, S.; Hua, C.; Tang, Y.; Cheng, H. A Novel Combined Use of Dupilumab for Treatment of Aggressive Refractory Pemphigus Vulgaris Complicated with Pulmonary Tuberculosis: A Case Report and the RNA-seq Analysis. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasperkiewicz, M.; Ellebrecht, C.T.; Takahashi, H.; Yamagami, J.; Zillikens, D.; Payne, A.S.; Amagai, M. Pemphigus. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers. 2017, 3, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shehadeh, W.; Sarig, O.; Bar, J.; Sprecher, E.; Samuelov, L. Treatment of epidermolysis bullosa pruriginosa-associated pruritus with dupilumab. Br. J. Dermatol. 2020, 182, 1495–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bs, A.G.Z.; Little, A.J.; Antaya, R.J. Epidermolysis bullosa pruriginosa treated with dupilumab. Pediatr. Dermatol. 2021, 38, 526–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clawson, R.C.; Duran, S.F.; Pariser, R.J. Epidermolysis bullosa pruriginosa responding to dupilumab. JAAD Case Rep. 2021, 16, 69–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhou, M.; Zhang, L.; Zheng, S.; Hong, Y.; Gao, X. Amelioration of dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa pruriginosa symptoms with dupilumab: A case report. Dermatol. Ther. 2021, 34, e15130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caroppo, F.; Milan, E.; Giulioni, E.; Fortina, A.B. A case of dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa pruriginosa treated with dupilumab. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2022, 36, e365–e367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Licata, G.; Buononato, D.; Calabrese, G.; Gambardella, A.; Briatico, G.; Pagliuca, F.; Argenziano, G. A case of Hailey-Hailey disease successfully treated with dupilumab. Int. J. Dermatol. 2022, 61, 1427–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alamon-Reig, F.; Serra-García, L.; Bosch-Amate, X.; Loughlin, C.R.; Mascaró, J. Dupilumab in Hailey-Hailey disease: A case series. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2022, 36, e776–e779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzahrani, N.; Grossman-Kranseler, J.; Swali, R.; Fiumara, K.; Zancanaro, P.; Tyring, S.; Rosmarin, D. Hailey–Hailey disease treated with dupilumab: A case series. Br. J. Dermatol. 2021, 185, 680–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shelton, E.; Doolittle, C.; Shinohara, M.M.; Thompson, J.A.; Moshiri, A.S. Can’t handle the itch? Refractory immunotherapy-related transient acantholytic dermatosis: Prompt resolution with dupilumab. JAAD Case Rep. 2022, 22, 31–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, D.C.; Kollhoff, A.; Berger, T. Treatment of Grover Disease with Dupilumab. JAMA Dermatol. 2021, 157, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barei, F.; Torretta, S.; Morini, N.; Ferrucci, S. A case of Grover disease treated with Dupilumab: Just serendipity or a future perspective? Dermatol. Ther. 2022, 35, e15429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, T.; Kageyama, R.; Nakazawa, S.; Honda, T. Understanding the significance of cytokines and chemokines in the pathogenesis of alopecia areata. Exp. Dermatol. 2020, 29, 726–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, Y.M.; Egeberg, A.; Gislason, G.H.; Skov, L.; Thyssen, J.P. Autoimmune diseases in adults with atopic dermatitis. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2017, 76, 274–280.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alotaibi, L.; Alfawzan, A.; Alharthi, R.; Al Sheikh, A. Improvement of atopic dermatitis and alopecia universalis with dupilumab: A case report. Dermatol. Rep. 2022, 14, 9359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romagnuolo, M.; Barbareschi, M.; Tavecchio, S.; Angileri, L.; Ferrucci, S.M. Remission of Alopecia Universalis after 1 Year of Treatment with Dupilumab in a Patient with Severe Atopic Dermatitis. Ski. Appendage Disord. 2022, 8, 38–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Call, J.E.; Sahni, S.; Zug, K.A. Effectiveness of Dupilumab in the treatment of both atopic dermatitis and alopecia universalis. Clin. Case Rep. 2020, 8, 1337–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szekely, S.; Vaccari, D.; Salmaso, R.; Belloni-Fortina, A.; Alaibac, M. Onset of Schamberg Disease and Resolution of Alopecia Areata During Treatment of Atopic Dermatitis with Dupilumab. J. Investig. Allergol. Clin. Immunol. 2021, 31, 65–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babino, G.; Fulgione, E.; D’Ambra, I.; Calabrese, G.; Alfano, R.; Argenziano, G. Rapid hair regrowth induced by dupilumab in a patient affected by alopecia totalis of 28 years’ duration: Clinical and dermoscopic features. Dermatol. Ther. 2020, 33, e13582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ushida, M.; Ohshita, A.; Arakawa, Y.; Kanehisa, F.; Katoh, N.; Asai, J. Dupilumab therapy rapidly improved alopecia areata associated with trichotillomania in an atopic dermatitis patient. Allergol. Int. 2020, 69, 480–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harada, K.; Irisawa, R.; Ito, T.; Uchiyama, M.; Tsuboi, R. The effectiveness of dupilumab in patients with alopecia areata who have atopic dermatitis: A case series of seven patients. Br. J. Dermatol. 2020, 183, 396–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludriksone, L.; Elsner, P.; Schliemann, S. Simultaneous effectiveness of dupilumab in atopic dermatitis and alopecia areata in two patients. JDDG J. Dtsch. Dermatol. Ges. 2019, 17, 1278–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magdaleno-Tapial, J.; Valenzuela-Oñate, C.; García-Legaz-Martínez, M.; Martínez-Domenech, Á.; Pérez-Ferriols, A. Improvement of alopecia areata with Dupilumab in a patient with severe atopic dermatitis and review the literature. Australas. J. Dermatol. 2020, 61, e223–e225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchida, H.; Kamata, M.; Watanabe, A.; Agematsu, A.; Nagata, M.; Fukaya, S.; Hayashi, K.; Fukuyasu, A.; Tanaka, T.; Ishikawa, T.; et al. Dupilumab Improved Alopecia Areata in a Patient with Atopic Dermatitis: A Case Report. Acta Derm. Venereol. 2019, 99, 675–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smogorzewski, J.; Sierro, T.; Compoginis, G.; Kim, G. Remission of alopecia universalis in a patient with atopic dermatitis treated with dupilumab. JAAD Case Rep. 2019, 5, 116–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darrigade, A.-S.; Legrand, A.; Andreu, N.; Jacquemin, C.; Boniface, K.; Taïeb, A.; Seneschal, J. Dual efficacy of dupilumab in a patient with concomitant atopic dermatitis and alopecia areata. Br. J. Dermatol. 2018, 179, 534–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patruno, C.; Napolitano, M.; Ferrillo, M.; Fabbrocini, G. Dupilumab and alopecia: A Janus effect. Dermatol. Ther. 2019, 32, e13023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alniemi, D.T.; McGevna, L. Dupilumab treatment for atopic dermatitis leading to unexpected treatment for alopecia universalis. JAAD Case Rep. 2019, 5, 111–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flanagan, K.E.; Bs, I.M.P.W.; Ba, J.T.P.; Walker, C.J.; Senna, M.M. Dupilumab-induced psoriasis in a patient with atopic dermatitis and alopecia totalis: A case report and literature review. Dermatol. Ther. 2022, 35, e15255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muto, J.; Yoshida, S.; Doi, C.; Habu, M.; Sayama, K. Dupilumab treatment of atopic dermatitis leading to successful treatment of alopecia universalis: A Japanese case report. J. Dermatol. 2021, 48, e72–e73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevray, M.; Dupré, D.; Misery, L.; Abasq-Thomas, C. Hair regrowth and dissemination of molluscum contagiosum: Two unexpected effects with dupilumab. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2019, 33, e296–e298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visconti, M.J.; Richardson, A.; LaFond, A.A. Visconti Dupilumab as a Therapeutic Approach in Alopecia Universalis. Cutis 2022, 110, E7–E8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukuyama, M.; Kinoshita-Ise, M.; Mizukawa, Y.; Ohyama, M. Two-sided influence of dupilumab on alopecia areata co-existing with severe atopic dermatitis: A case series and literature review. J. Cutan. Immunol. Allergy 2023, 6, 13–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choe, S.; Newman, E.M. Time to loss of response for dupilumab in ophiasis-pattern alopecia areata. JAAD Case Rep. 2021, 15, 133–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zilberstein, A.T.; Teng, E.L.; Mancini, A.J. Dupilumab, incontinentia pigmenti, and alopecia: A serendipitous observation. JAAD Case Rep. 2022, 29, 121–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulkarni, M.; Rohan, C.A.; Travers, J.B.; Serrao, R. Long-Term Efficacy of Dupilumab in Alopecia Areata. Am. J. Case Rep. 2022, 23, e936488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.K.; Craiglow, B.G. Dupilumab for the treatment of alopecia areata in children with atopic dermatitis. JAAD Case Rep. 2021, 16, 82–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenzie, P.L.; Castelo-Soccio, L. Dupilumab therapy for alopecia areata in pediatric patients with concomitant atopic dermatitis. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2021, 84, 1691–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruenstein, D.; Malik, K.; Levitt, J. Full scalp hair regrowth in a 4-year-old girl with alopecia areata and atopic dermatitis treated with dupilumab. JAAD Case Rep. 2020, 6, 1286–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penzi, L.R.; Yasuda, M.; Manatis-Lornell, A.; Hagigeorges, D.; Senna, M.M. Hair Regrowth in a Patient With Long-standing Alopecia Totalis and Atopic Dermatitis Treated With Dupilumab. JAMA Dermatol. 2018, 154, 1358–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Napolitano, M.; Cantelli, M.; Potestio, L.; Ocampo-Garza, S.; Vastarella, M.; Nappa, P.; Scalvenzi, M.; Fabbrocini, G.; Patruno, C. Clinical, trichoscopic and in vivo reflectance confocal microscopy evaluation of alopecia areata in atopic dermatitis patients treated with dupilumab. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2022, 36, e561–e563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guttman-Yassky, E.; Renert-Yuval, Y.; Bares, J.; Chima, M.; Hawkes, J.E.; Gilleaudeau, P.; Sullivan-Whalen, M.; Singer, G.K.; Garcet, S.; Pavel, A.B.; et al. Phase 2a randomized clinical trial of dupilumab (anti-IL-4Rα) for alopecia areata patients. Allergy 2022, 77, 897–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ständer, S.; Trense, Y.; Thaçi, D.; Ludwig, R.J. Alopecia areata development in atopic dermatitis patients treated with dupilumab. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2020, 34, e612–e613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLeod, J.J.; Baker, B.; Ryan, J.J. Mast cell production and response to IL-4 and IL-13. Cytokine 2015, 75, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puxkandl, V.; Hoetzenecker, W.; Altrichter, S. Case report: Severe chronic spontaneous urticaria successfully treated with omalizumab and dupilumab. Allergol. Sel. 2023, 7, 17–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Lin, S.Y.; Lan, C.E. Dupilumab as a rescue therapy for a chronic urticaria patient who showed secondary failure to omalizumab. Kaohsiung J. Med. Sci. 2022, 38, 610–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holm, J.G.; Sørensen, J.A.; Thomsen, S.F. Concurrent use of omalizumab and dupilumab in a 47-year-old woman with chronic spontaneous urticaria and atopic dermatitis. Int. J. Dermatol. 2022, 61, e173–e174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Errichetti, E.; Stinco, G. Recalcitrant chronic urticaria treated with dupilumab: Report of two instances refractory to H1-antihistamines, omalizumab and cyclosporine and brief literature review. Dermatol. Ther. 2021, 34, e14821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.K.; Simpson, R.S. Dupilumab as a novel therapy for difficult to treat chronic spontaneous urticaria. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2019, 7, 1659–1661.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abadeh, A.; Lee, J.K. Long-term follow-up of patients treated with dupilumab for chronic spontaneous urticaria: A case report. SAGE Open Med. Case Rep. 2022, 10, 2050313X221117702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staubach, P.; Peveling-Oberhag, A.; Lang, B.M.; Zimmer, S.; Sohn, A.; Mann, C. Severe chronic spontaneous urticaria in children—Treatment options according to the guidelines and beyond—A 10 years review. J. Dermatol. Treat. 2022, 33, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Fok, J.S.; Lin, L.; Su, H.; Maurer, M. Complete response to dupilumab in a patient with chronic spontaneous urticaria who did not tolerate omalizumab. JAAD Case Rep. 2023, 32, 109–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurer, M.; Casale, T.; Saini, S.; Ben-Shoshan, M.; Amin, N.; Radin, A.; Akinlade, B.; Fan, C.; Bauer, D.; Laws, E.; et al. Dupilumab Significantly Reduces Itch and Hives in Patients with Chronic Spontaneous Urticaria: Results From a Phase 3 Trial (LIBERTY-CSU CUPID Study A). J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2022, 149, AB312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurer, M.; Casale, T.; Saini, S.; Ben-Shoshan, M.; Radin, A.; Akinlade, B.; Laws, E.; Mannent, L. DUPILUMAB EFFICACY IN PATIENTS WITH CHRONIC SPONTANEOUS URTICARIA BY IGE LEVEL: LIBERTY-CSU CUPID STUDY A. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2022, 129, S11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrucci, S.; Benzecry, V.; Berti, E.; Asero, R. Rapid disappearance of both severe atopic dermatitis and cold urticaria following dupilumab treatment. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2020, 45, 345–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirufo, M.N.; Catalogna, A.; Raggiunti, M.; De Pietro, F.; Ginaldi, L.; De Martinis, M. Cholinergic Urticaria, an Effective and Safe “Off Label” Use of Dupilumab: A Case Report with Literature Review. Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dermatol. 2022, 15, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodman, B.; Jariwala, S. Dupilumab as a novel therapy to treat adrenergic urticaria. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2021, 126, 205–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Wu, X.; Jiang, J.; Yu, S.; Fang, X.; Yang, H.; Bai, X.; Wang, H.; Luo, X. Dupilumab improves clinical symptoms in children with Netherton syndrome by suppressing Th2-mediated inflammation. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1054422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odorici, G.; Schenetti, C.; Marzola, E.; Monti, A.; Borghi, A.; Corazza, M. Treatment of Netherton syndrome with dupilumab. JDDG J. Dtsch. Dermatol. Ges. 2022, 20, 1636–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galdo, G.; Fania, L. A Netherton syndrome case report: Response to dupilumab treatment. Dermatol. Ther. 2022, 35, e15862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragamin, A.; Nouwen, A.E.; Dalm, V.A.; van Mierlo, M.M.; Lincke, C.R.; Pasmans, S.G. Treatment Experiences with Intravenous Immunoglobulins, Ixekizumab, Dupilumab, and Anakinra in Netherton Syndrome: A Case Series. Dermatology 2022, 239, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inaba, Y.; Kanazawa, N.; Muraoka, K.; Yariyama, A.; Kawaguchi, A.; Kunimoto, K.; Kaminaka, C.; Yamamoto, Y.; Tsujioka, K.; Yoshida, A.; et al. Dupilumab Improves Pruritus in Netherton Syndrome: A Case Study. Children 2022, 9, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yu, L.; Zhang, S.; Wang, C.; Li, Z.; Li, M.; Zhang, S. Successful treatment of Netherton syndrome with dupilumab: A case report and review of the literature. J. Dermatol. 2022, 49, 165–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murase, C.; Takeichi, T.; Taki, T.; Yoshikawa, T.; Suzuki, A.; Ogi, T.; Suga, Y.; Akiyama, M. Successful dupilumab treatment for ichthyotic and atopic features of Netherton syndrome. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2021, 102, 126–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aktas, M.; Salman, A.; Sengun, O.A.; Ozer, E.C.; Tekin, S.H.; Cakici, O.A.; Demir, G.; Ergun, T. Netherton syndrome: Temporary response to dupilumab. Pediatr. Dermatol. 2020, 37, 1210–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Süßmuth, K.; Traupe, H.; Loser, K.; Ständer, S.; Kessel, C.; Wittkowski, H.; Oji, V. Response to dupilumab in two children with Netherton syndrome: Improvement of pruritus and scaling. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2020, 35, e152–e155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andreasen, T.H.; Karstensen, H.G.; Duno, M.; Lei, U.; Zachariae, C.; Thyssen, J.P. Successful treatment with dupilumab of an adult with Netherton syndrome. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2020, 45, 915–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steuer, A.B.; Cohen, D.E. Treatment of Netherton Syndrome With Dupilumab. JAMA Dermatol. 2020, 156, 350–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binkhonain, F.K.; Aldokhayel, S.; BinJadeed, H.; Madani, A. Successful Treatment of an Adult with Atopic Dermatitis and Lamellar Ichthyosis Using Dupilumab. Biol. Targets Ther. 2022, 16, 85–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinhoff, M.; Al-Marri, F.; Al Chalabi, R.; Gieler, U.; Buddenkotte, J. Recalcitrant erythrodermic ichthyosis with atopic dermatitis successfully treated with Dupilumab in combination with Guselkumab. Ski. Health Dis. 2022, 2, e87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexis, B.; Nathalie, J.; Audrey, M.-B.; Pol-André, A.; Juliette, M.-H. Peeling Skin Syndrome Type 1: Dupilumab Reduces IgE, But Not Skin Anomalies. J. Clin. Immunol. 2022, 42, 873–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruber, R.; Zschocke, A.; Zellner, H.; Schmuth, M. Successful treatment of trichothiodystrophy with dupilumab. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2021, 46, 1381–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chello, C.; Sernicola, A.; Paolino, G.; Grieco, T. Effects of dupilumab in type 1 neurofibromatosis coexisting with severe atopic dermatitis. An. Bras. Dermatol. 2021, 96, 638–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tehrany, Y.A.; Marois, L.; Colmant, C.; Marchand, V.; Kokta, V.; Coulombe, J.; Marcoux, D.; Haddad, E.; McCuaig, C. Refractory pruritus responds to dupilumab in a patient with TTC7A mutation. JAAD Case Rep. 2021, 8, 9–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maher, M.C.; Hall, E.M.; Horii, K.A.; Maher, M.C. Generalized eczematous dermatitis and pruritus responsive to dupilumab in a patient with immune dysregulation, polyendocrinopathy, enteropathy, X-linked (IPEX) syndrome. Pediatr. Dermatol. 2021, 38, 1370–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atwal, S.; Ong, P.Y. Successful use of dupilumab to treat eczema in a child with X-linked agammaglobulinemia. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2022, 129, 384–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandhi, N.A.; Bennett, B.L.; Graham, N.M.H.; Pirozzi, G.; Stahl, N.; Yancopoulos, G.D. Targeting key proximal drivers of type 2 inflammation in disease. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2016, 15, 35–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wieser, J.K.; Kuehn, G.J.; Prezzano, J.C.; Cusick, E.H.; Stiegler, J.D.; Scott, G.A.; Liesveld, J.L.; Beck, L.A. Improvement in a patient with hypereosinophilic syndrome after initiation of dupilumab treatment. JAAD Case Rep. 2020, 6, 292–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.M.; Roufosse, F.; Wang, S.A.; Verstovsek, S.; Durrani, S.R.; Rothenberg, M.E.; Pongdee, T.; Butterfield, J.; Lax, T.; Wechsler, M.E.; et al. An International, Retrospective Study of Off-Label Biologic Use in the Treatment of Hypereosinophilic Syndromes. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2022, 10, 1217–1228.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Chen, Y.; Chang, J.; Sun, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Maurer, M.; Li, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Tong, X. Dupilumab as a novel steroid-sparing treatment for hypereosinophilic syndrome. JAAD Case Rep. 2022, 29, 106–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, A.; Pousti, B.T.; Savage, K.T.; Mollanazar, N.K.; Lee, J.B.; Hsu, S. Eosinophilic dermatosis of hematologic malignancy responding to dupilumab in a patient with chronic lymphocytic leukemia. JAAD Case Rep. 2019, 5, 815–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, A.; Lofgreen, S.; Mariash, E.; Bershow, A.; Gaddis, K.J. Targeted inhibition of IL -4/13 with dupilumab is an effective treatment for eosinophilic dermatosis of hematologic malignancy. Dermatol. Ther. 2020, 33, e13725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maglie, R.; Ugolini, F.; De Logu, F.; Simi, S.; Senatore, S.; Montefusco, F.; Nassini, R.; Massi, D.; Antiga, E. Dupilumab for the treatment of recalcitrant eosinophilic dermatosis of haematologic malignancy. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2021, 35, e501–e503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lévy, R.; Béziat, V.; Barbieux, C.; Puel, A.; Bourrat, E.; Casanova, J.-L.; Hovnanian, A. Efficacy of Dupilumab for Controlling Severe Atopic Dermatitis in a Patient with Hyper-IgE Syndrome. J. Clin. Immunol. 2020, 40, 418–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nihal, A.; Comstock, J.R.; Holland, K.E.; Singh, A.M.; Seroogy, C.M.; Arkin, L.M. Clearance of atypical cutaneous manifestations of hyper-IgE syndrome with dupilumab. Pediatr. Dermatol. 2022, 39, 940–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matucci-Cerinic, C.; Viglizzo, G.; Pastorino, C.; Corcione, A.; Prigione, I.; Bocca, P.; Bustaffa, M.; Cecconi, M.; Gattorno, M.; Volpi, S. Remission of eczema and recovery of Th1 polarization following treatment with Dupilumab in STAT3 hyper IgE syndrome. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 2022, 33, e13770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Yang, T.; Lan, C. Dupilumab treatment of eczema in a child with STAT3 hyper-immunoglobulin E syndrome. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2021, 36, e367–e369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gracia-Darder, I.; De Ves, J.P.; Cortina, M.R.; Martín-Santiago, A. Patient with atopic dermatitis, hyper IgE syndrome and ulcerative colitis, treated successfully with dupilumab during pregnancy. Dermatol. Ther. 2021, 35, e15237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, C.-W.; Lee, W.-I.; Chung, W.-H. Dupilumab for STAT3-Hyper-IgE Syndrome with Refractory Intestinal Complication. Pediatrics 2021, 148, e2021050351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixit, C.; Thatayatikom, A.; Pappa, H.; Knutsen, A.P. Treatment of severe atopic dermatitis and eosinophilic esophagitis with dupilumab in a 14-year-old boy with autosomal dominant hyper-IgE syndrome. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2021, 9, 4167–4169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, C.-J.; Tseng, H.-C. Treatment efficacy of dupilumab in a hyper-immunoglobulin E syndrome patient with severe atopic dermatitis. JAAD Case Rep. 2021, 11, 60–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sogkas, G.; Hirsch, S.; Jablonka, A.; Witte, T.; Schmidt, R.E.; Atschekzei, F. Dupilumab to treat severe atopic dermatitis in autosomal dominant hyper-IgE syndrome. Clin. Immunol. 2020, 215, 108452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joshi, T.P.; Anvari, S.; Gupta, M.R.; Davis, C.M.; Hajjar, J. Case Report: Dupilumab Successfully Controls Severe Eczema in a Child with Elevated IgE Levels and Recurrent Skin Infections. Front. Pediatr. 2021, 9, 646997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ollech, A.; Mashiah, J.; Lev, A.; Simon, A.J.; Somech, R.; Adam, E.; Barzilai, A.; Hagin, D.; Greenberger, S. Treatment options for DOCK8 deficiency-related severe dermatitis. J. Dermatol. 2021, 48, 1386–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teraki, Y.; Terao, A. Treatment of Kimura Disease with Dupilumab. JAMA Dermatol. 2022, 158, 329–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.-Y.; Yang, C.-Y.; Yao, W.-T.; Chen, Y.-F.; Yu, C.-M.; Tung, K.-Y.; Tsai, M.-F. Kimura Disease of the Thigh Treated with Surgical Excision and Dupilumab. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2022, 88, S110–S113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellinato, F.; Mastrosimini, M.G.; Querzoli, G.; Gisondi, P.; Girolomoni, G. Dupilumab for recalcitrant Kimura disease. Dermatol. Ther. 2022, 35, e15674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, B.; Yu, H.; Jia, M.; Yao, W.; Diao, R.; Li, B.; Wang, Y.; Li, T.; Ge, L.; Wang, H. Successful treatment of dupilumab in Kimura disease independent of IgE: A case report with literature review. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1084879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teraki, Y.; Taguchi, R.; Takamura, S.; Fukuda, T. Use of Dupilumab in the Treatment of Papuloerythroderma of Ofuji. JAMA Dermatol. 2019, 155, 979–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komatsu-Fujii, T.; Nonoyama, S.; Ogawa, M.; Fukumoto, T.; Tanabe, H. Rapid effects of dupilumab treatment on papuloerythroderma of Ofuji. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2020, 34, e739–e741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizuno, A.; Habe, K.; Matsushima, Y.; Kondo, M.; Yamanaka, K. A Case of Papuloerythroderma Successfully Treated with Dupilumab. Case Rep. Dermatol. 2022, 14, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traidl, S.; Angela, Y.; Kapp, A.; Suhling, H.; Schacht, V.; Werfel, T. Dupilumab in eosinophilic cellulitis (Wells’ syndrome)—Case report of a potential new treatment option. JDDG J. Dtsch. Dermatol. Ges. 2021, 19, 1653–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirven, R.M.; Plotner, A.N. Wells syndrome successfully treated with dupilumab. Int. J. Dermatol. 2022, 36349453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, S.C.; Robinson, S.N.; Abudu, M.; Her, M.; Deverapalli, S.; Levin, A.; Schmidt, B.A.R.; Gellis, S.E.; Rosmarin, D. Eosinophilic annular erythema treated with dupilumab. Pediatr. Dermatol. 2018, 35, e255–e256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maione, V.; Caravello, S.; Cozzi, C.; Venturini, M.; Incardona, P.; Frassi, M.; Pinton, P.C. Refractory eosinophilic annular erythema treated successfully with dupilumab. JDDG J. Dtsch. Dermatol. Ges. 2020, 18, 1031–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, R.; Liu, J.; Su, T.; Xia, J.; Yin, Z. Dupilumab for treatment of eosinophilic fasciitis. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2022, 47, 2298–2300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franke, K.; Notaro, E.; Moshiri, A.S.; Ayars, A.; Kalus, A. Use of Dupilumab and Eosinophil Targeted Therapy in Treating Angiolymphoid Hyperplasia with Eosinophilia. JAMA Dermatol. 2022, 158, 960–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, D.M.; Damsky, W.E.; Vesely, M.D. Treatment of lichen sclerosus and hypertrophic scars with dupilumab. JAAD Case Rep. 2022, 23, 76–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Brien, M.A.; Hsu, S.; Shevchenko, A.; Quartey, A. Dupilumab Failure in Treating Dermatomyositis-Associated Pruritus. Cureus 2022, 14, e28270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simpson, R.S.; Lau, S.; Lee, J.K. Dupilumab as a novel steroid-sparing treatment for IgG4-related disease. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2020, 79, 549–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaz, A.; Tan, K.; He, H.; Xu, H.; Cueto, I.; Pavel, A.B.; Krueger, J.G.; Guttman-Yassky, E. Keloid lesions show increased IL -4/ IL -13 signaling and respond to Th2-targeting dupilumab therapy. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2020, 34, e161–e164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, A.J.S.; Song, E.J. Dupilumab as an adjuvant treatment for keloid-associated symptoms. JAAD Case Rep. 2021, 13, 73–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tirgan, M.; Uitto, J. Lack of efficacy of dupilumab in the treatment of keloid disorder. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2022, 36, e120–e122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luk, K.; Fakhoury, J.; Ozog, D. Nonresponse and Progression of Diffuse Keloids to Dupilumab Therapy. J. Drugs Dermatol. 2022, 21, 197–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.P.; Ly, K.; Thibodeaux, Q.; Beck, K.; Berger, T.; Khodosh, R.; Liao, W.; Bhutani, T. Dupilumab for the treatment of severe photodermatitis. JAAD Case Rep. 2019, 5, 614–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, N.; Konda, S.; Lim, H.W. Dupilumab for the treatment of chronic actinic dermatitis. Photodermatol. Photoimmunol. Photomed. 2020, 36, 398–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Li, H.; Zhu, H. Successful Treatment of Chronic Actinic Dermatitis with Dupilumab: A Case Report and Review of the Literature. Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dermatol. 2021, 14, 1913–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Lian, C. Chronic actinic dermatitis in an old adult significantly improved by dupilumab. Photodermatol. Photoimmunol. Photomed. 2022, 38, 176–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McFeely, O.; Doyle, C.; Blasco, M.C.; Beatty, P.; Murphy, L.; O’Mahony, S.; Andrawis, M.; Salim, A. Chronic actinic dermatitis successfully treated with methotrexate and dupilumab. Photodermatol. Photoimmunol. Photomed. 2023, 39, 172–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, K.; Wu, L.; Lou, H.; Zhong, J.; Qiu, Y.; Da, J.; Shan, J.; Lu, K. Clearance of Chronic Actinic Dermatitis With Dupilumab Therapy in Chinese Patients: A Case Series. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 803692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, L.; Pratt, M. A case report of therapeutically challenging chronic actinic dermatitis. SAGE Open Med. Case Rep. 2019, 7, 2050313X19845235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eickstaedt, J.B.; Starke, S.; Krakora, D.; Hinshaw, M.; Arkin, L.M. Clearance of pediatric actinic prurigo with dupilumab. Pediatr. Dermatol. 2020, 37, 1176–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larijani, M.; Zarowin, D.; Wohlschlaeger, A.; Perman, M.J.; Treat, J.R. Atopic dermatitis-like graft-versus-host disease treated with dupilumab. Pediatr. Dermatol. 2022, 40, 320–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Zheng, M.; Cai, S. Successful treatment of secukinumab-resistant palmoplantar pustulosis by Dupilumab: A case report. Dermatol. Ther. 2022, 35, e15781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazemi, S.; Murphrey, M.; Hawkes, J.E. Rapid resolution of widespread cutaneous lichen planus and generalized pruritus in an elderly patient following treatment with dupilumab. JAAD Case Rep. 2022, 30, 108–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pousti, B. Dupilumab for the Treatment of Lichen Planus. Cutis 2021, 107, E8–E10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, M.K.; Shin, J.U.; Kim, D.H.; Lee, H.J. Severe atopic dermatitis and concurrent severe hidradenitis suppurativa successfully treated with dupilumab. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2022, 47, 2303–2305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molinelli, E.; Sapigni, C.; Simonetti, O.; Radi, G.; Gambini, D.; Maurizi, A.; Rizzetto, G.; D’Agostino, G.M.; Offidani, A. Successfully and safety use of dupilumab in the management of severe atopic dermatitis and concomitant moderate-to-severe hidradenitis suppurativa. Dermatol. Ther. 2022, 35, e15645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gambardella, A.; Calabrese, G.; Di Brizzi, E.V.; Alfano, R.; Argenziano, G. A case of Atopic dermatitis and Hidradenitis Suppurativa successfully treated with Dupilumab. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2020, 34, e284–e286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, E.J.; Bezecny, J.; Farrer, S. Recalcitrant generalized granuloma annulare treated successfully with dupilumab. JAAD Case Rep. 2021, 7, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aoki, K.; Ohyama, M.; Mizukawa, Y. A case of lichen amyloidosis associated with atopic dermatitis successfully treated with dupilumab: A case report and literature review. Dermatol. Ther. 2021, 34, e15005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zahid, S.; Saussine, A.; Calugareanu, A.; Jachiet, M.; Vignon-Pennamen, M.; Rybojad, M.; Bagot, M.; Bouaziz, J.; Mahévas, T. Dramatic response to dupilumab in papular amyloidosis. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2022, 36, e1071–e1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humeda, Y.; Beasley, J.; Calder, K. Clinical resolution of generalized lichen amyloidosis with dupilumab: A new alternative therapy. Dermatol. Online J. 2020, 26, 0513030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rial, M.J.; Barroso, B.; Sastre, J. Dupilumab for treatment of food allergy. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2019, 7, 673–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mollanazar, N.K.; Savage, K.T.; Pousti, B.T.; Jariwala, N.; Del Guzzo, C.; Haun, P.; Vittorio, C.C.; Rook, A.H.; Kim, E.J. Cutaneous T-cell Lymphoma and Concomitant Atopic Dermatitis Responding to Dupilumab. Cutis 2020, 106, 131–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steck, O.; Bertschi, N.L.; Luther, F.; Berg, J.V.D.; Winkel, D.J.; Holbro, A.; Schlapbach, C. Rapid and sustained control of itch and reduction in Th2 bias by dupilumab in a patient with Sézary syndrome. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2021, 35, 1331–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazaridou, I.; Ram-Wolff, C.; Bouaziz, J.; Bégon, E.; Battistella, M.; Rivet, J.; Jachiet, M.; Bagot, M.; Masson, A. Dupilumab Treatment in Two Patients with Cutaneous T-cell Lymphomas. Acta Derm. Venereol. 2020, 100, adv00271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyashiro, D.; Vivarelli, A.G.; Gonçalves, F.; Cury-Martins, J.; Sanches, J.A. Progression of mycosis fungoides after treatment with dupilumab: A case report. Dermatol. Ther. 2020, 33, e13880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinosa, M.L.; Nguyen, M.T.; Aguirre, A.S.; Martinez-Escala, M.E.; Kim, J.; Walker, C.J.; Pontes, D.S.; Silverberg, J.I.; Choi, J.; Pro, B.; et al. Progression of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma after dupilumab: Case review of 7 patients. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2020, 83, 197–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umemoto, N.; Demitsu, T.; Otaki, K.; Matsumoto, T.; Takazawa, M.; Yamada, A.; Kimura, S.; Kakurai, M. Dupilumab therapy in Sézary syndrome misdiagnosed as atopic dermatitis: A case report. J. Dermatol. 2020, 47, e356–e357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashimoto, M.; Miyagaki, T.; Komaki, R.; Takeuchi, S.; Kadono, T. Development of Nodular Lesions after Dupilumab Therapy in Erythrodermic Mycosis Fungoides with Interleukin-13 Receptor alpha2 Expression. Acta Derm. Venereol. 2022, 102, adv00766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiba, T.; Nagai, T.; Osada, S.; Manabe, M. Diagnosis of Mycosis Fungoides Following Administration of Dupilumab for Misdiagnosed Atopic Dermatitis. Acta Derm.-Venereol. 2019, 99, 818–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, A.; Wong, L.; Lang, A.; Kraus, C.; Anderson, N.; Elsensohn, A. Dupilumab-Associated Mycosis Fungoides with a CD8+ Immunophenotype. Dermatopathology 2022, 9, 385–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newsom, M.; Hrin, M.L.; Hamid, R.N.; Strowd, L.C.; Ahn, C.; Jorizzo, J.L.; Feldman, S.R. Two cases of mycosis fungoides diagnosed after treatment non-response to dupilumab. Dermatol. Online J. 2021, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, J.; Morris, L.; Vu, A.; Duvic, M. Development of Sézary syndrome following the administration of dupilumab. Dermatol. Online J. 2020, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, T.P.; Duvicy, M.; Torres-Cabala, C.A.; Tschen, J. Treatment with Dupilumab for Refractory Cutaneous B-Cell Pseudolymphoma. JAMA Dermatol. 2022, 158, 697–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trum, N.A.; Zain, J.; Abad, C.; Rosen, S.T.; Querfeld, C. Dupilumab as a therapy option for treatment refractory mogamulizumab-associated rash. JAAD Case Rep. 2021, 14, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patruno, C.; Potestio, L.; Scalvenzi, M.; Battista, T.; Raia, F.; Picone, V.; Fabbrocini, G.; Napolitano, M. Dupilumab for the treatment of adult atopic dermatitis in special populations. J. Dermatol. Treat. 2022, 33, 3028–3033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).