Comparison of the Accuracy of Epistasis and Haplotype Models for Genomic Prediction of Seven Human Phenotypes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Phenotypic and SNP Data
2.2. Mixed Model for GBLUP and GREML
2.3. Evaluation of Prediction Accuracy Using Cross-Validation
2.4. Initial Selection of Epistasis Effects for Prediction Models
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Initial Epistasis Models for Predicting Phenotypic Values
| Subscript in Equations (1) and (2) | HDL | LDL | TC | TG | HTo | WT | BMIo | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 1 | 0.241 | 0.284 | 0.331 | 0.221 | 0.648 | 0.424 | 0.320 |
| D | 2 | 0.055 | 0.034 | 0.085 | 0.079 | 0.134 | 0.071 | 0.012 |
| A × A | 3 | 0.356 | 0.423 | 0.145 | 0.135 | 0.192 | 0.106 | 0.219 |
| A × D | 4 | 0.111 | 0.000 | 0.003 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.057 | 0.126 |
| D × D | 5 | 0.001 | 0.000 | 0.001 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.015 | 0.008 |
| A × A × A | 6 | 0.002 | 0.000 | 0.004 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.017 | 0.000 |
| A × A × D | 7 | 0.002 | 0.000 | 0.001 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.014 | 0.000 |
| A × D × D | 8 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.001 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.008 | 0.000 |
| D × D × D | 9 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.004 | 0.000 |
| A × A × A × A | 10 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.001 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.004 | 0.000 |
| A × A × A × D | 11 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.003 | 0.000 |
| A × A × D × D | 12 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.002 | 0.000 |
| A × D × D × D | 13 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.001 | 0.000 |
| D × D × D × D | 14 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.001 | 0.000 |
| Total heritability | 0.768 | 0.742 | 0.573 | 0.437 | 0.974 | 0.728 | 0.686 | |
| Initial model | A + D + AA + AD | A + D + AA | A + D + AA | A + D + AA | A + D + AA | A + D + AA + AD + DD + AAA + AAD | A + D + AA + AD |
3.2. Accuracy of Epistasis Models for Predicting Phenotypic Values
3.3. Accuracy and Heritability Estimates of Integrated Models with Epistasis and Haplotype Effects
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Derbyshire, M.C.; Khentry, Y.; Severn-Ellis, A.; Mwape, V.; Saad, N.S.M.; Newman, T.E.; Taiwo, A.; Regmi, R.; Buchwaldt, L.; Denton-Giles, M. Modeling first order additive× additive epistasis improves accuracy of genomic prediction for sclerotinia stem rot resistance in canola. Plant Genome 2021, 14, e20088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Z.; Prakapenka, D.; Parker Gaddis, K.L.; VandeHaar, M.J.; Weigel, K.A.; Tempelman, R.J.; Koltes, J.E.; Santos, J.E.P.; White, H.M.; Peñagaricano, F. Impact of epistasis effects on the accuracy of predicting phenotypic values of residual feed intake in U. S Holstein cows. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 1017490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vojgani, E.; Pook, T.; Martini, J.W.; Hölker, A.C.; Mayer, M.; Schön, C.-C.; Simianer, H. Accounting for epistasis improves genomic prediction of phenotypes with univariate and bivariate models across environments. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2021, 134, 2913–2930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calleja-Rodriguez, A.; Chen, Z.; Suontama, M.; Pan, J.; Wu, H.X. Genomic predictions with nonadditive effects improved estimates of additive effects and predictions of total genetic values in Pinus sylvestris. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 666820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akdemir, D.; Jannink, J.-L. Locally epistatic genomic relationship matrices for genomic association and prediction. Genetics 2015, 199, 857–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Won, S.; Park, J.-E.; Son, J.-H.; Lee, S.-H.; Park, B.H.; Park, M.; Park, W.-C.; Chai, H.-H.; Kim, H.; Lee, J. Genomic Prediction Accuracy Using Haplotypes Defined by Size and Hierarchical Clustering Based on Linkage Disequilibrium. Front. Genet. 2020, 11, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, N.; Martini, J.W.; Zhang, Z.; Yuan, X.; Zhang, H.; Simianer, H.; Li, J. Incorporating gene annotation into genomic prediction of complex phenotypes. Genetics 2017, 207, 489–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Z.; Tan, C.; Prakapenka, D.; Ma, L.; Da, Y. Haplotype analysis of genomic prediction using structural and functional genomic information for seven human phenotypes. Front. Genet. 2020, 11, 588907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Difabachew, Y.F.; Frisch, M.; Langstroff, A.L.; Stahl, A.; Wittkop, B.; Snowdon, R.J.; Koch, M.; Kirchhoff, M.; Cselényi, L.; Wolf, M. Genomic prediction with haplotype blocks in wheat. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1168547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alemu, A.; Batista, L.; Singh, P.K.; Ceplitis, A.; Chawade, A. Haplotype-tagged SNPs improve genomic prediction accuracy for Fusarium head blight resistance and yield-related traits in wheat. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2023, 136, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da, Y.; Liang, Z.; Prakapenka, D. Multifactorial methods integrating haplotype and epistasis effects for genomic estimation and prediction of quantitative traits. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 922369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henderson, C. Best linear unbiased prediction of nonadditive genetic merits in noninbred populations. J. Anim. Sci. 1985, 60, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, G.; Christensen, O.F.; Ostersen, T.; Henryon, M.; Lund, M.S. Estimating additive and non-additive genetic variances and predicting genetic merits using genome-wide dense single nucleotide polymorphism markers. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e45293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muñoz, P.R.; Resende, M.F.; Gezan, S.A.; Resende, M.D.V.; de los Campos, G.; Kirst, M.; Huber, D.; Peter, G.F. Unraveling additive from nonadditive effects using genomic relationship matrices. Genetics 2014, 198, 1759–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vitezica, Z.G.; Legarra, A.; Toro, M.A.; Varona, L. Orthogonal estimates of variances for additive, dominance, and epistatic effects in populations. Genetics 2017, 206, 1297–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Reif, J.C. Efficient algorithms for calculating epistatic genomic relationship matrices. Genetics 2020, 216, 651–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Legarra, A.; Robert-Granié, C.; Manfredi, E.; Elsen, J.-M. Performance of genomic selection in mice. Genetics 2008, 180, 611–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
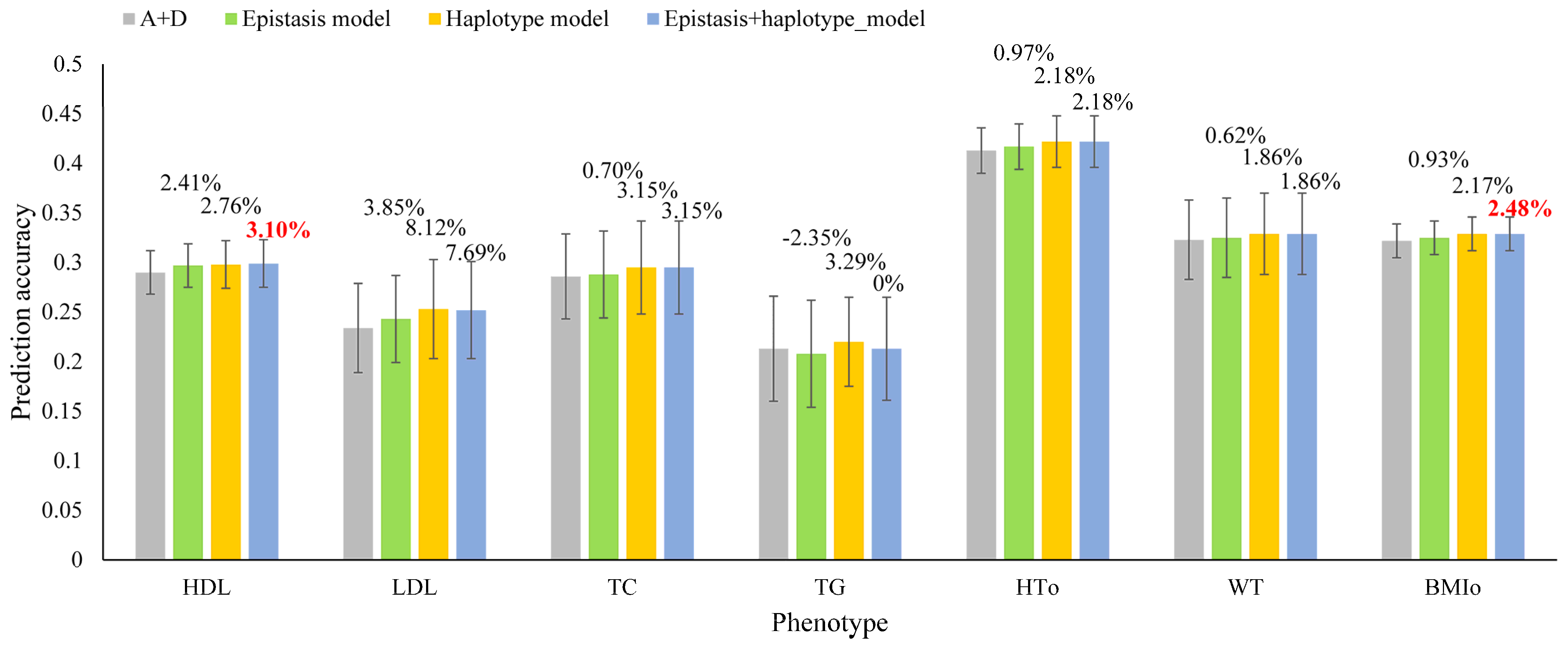
| HDL | LDL | TC | TG | HTO | WT | BMIO | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SNP model (A + D) | |||||||
| Prediction accuracy | 0.290 | 0.234 | 0.286 | 0.213 | 0.413 | 0.323 | 0.322 |
| Global epistasis model | |||||||
| Prediction model | A + D + AA + AD | A + D + AA | A + D + AA | A + D + AA | A + D + AA | A + D + AD | A + AD |
| Prediction accuracy | 0.297 | 0.243 | 0.288 | 0.208 | 0.417 | 0.325 | 0.325 |
| Accuracy increase over SNP model (%) | 2.41 | 3.85 | 0.70 | −2.35 | 0.97 | 0.62 | 0.93 |
| Haplotype model [8] | |||||||
| Prediction model | A + D + H | H | D + H | H | A + D + H | A + D + H | A + H |
| Haplotype blocking method | Genes | 12 SNPs | 50 Kb | 50 Kb | 200 Kb | 12 SNPs | 100 Kb |
| Prediction accuracy | 0.298 | 0.253 | 0.295 | 0.220 | 0.422 | 0.329 | 0.329 |
| Accuracy increase over SNP model (%) | 2.76 | 8.12 | 3.15 | 3.29 | 2.18 | 1.86 | 2.17 |
| Integrated model with epistasis and haplotype effects | |||||||
| Prediction model | A + D + AA + AD + H | A + D + AA + H | A + D + AA + H | A + D + AA + H | A + D + AA + H | A + D + AD + H | A + AD + H |
| Prediction accuracy | 0.299 | 0.252 | 0.295 | 0.213 | 0.422 | 0.329 | 0.330 |
| Accuracy increase over SNP model (%) | 3.10 | 7.69 | 3.15 | 0 | 2.18 | 1.86 | 2.48 |
| HDL | LDL | TC | TG | HTo | WT | BMIo | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SNP model (A + D) | |||||||
| A | 0.386 | 0.408 | 0.389 | 0.260 | 0.740 | 0.472 | 0.415 |
| D | 0.124 | 0.177 | 0.104 | 0.124 | 0.202 | 0.093 | 0.046 |
| Total | 0.510 | 0.585 | 0.493 | 0.383 | 0.942 | 0.565 | 0.462 |
| Global epistasis model | |||||||
| Model | A + D + AA + AD | A + D + AA | A + D + AA | A + D + AA | A + D + AA | A + D + AD | A + AD |
| A | 0.243 | 0.286 | 0.327 | 0.211 | 0.654 | 0.460 | 0.398 |
| D | 0.056 | 0.037 | 0.087 | 0.069 | 0.137 | 0.064 | - |
| A × A | 0.358 | 0.429 | 0.162 | 0.171 | 0.183 | - | - |
| A × D | 0.115 | - | - | - | - | 0.188 | 0.265 |
| Total | 0.771 | 0.752 | 0.576 | 0.451 | 0.975 | 0.712 | 0.663 |
| Integrated model with global epistasis effects and haplotype effects | |||||||
| Model | A + D + AA + AD + H | A + D + AA + H | A + D + AA + H | A + D + AA + H | A + D + AA + H | A + D + AD + H | A + AD + H |
| A | 0.102 | 0.010 | 0.010 | 0.072 | 0.361 | 0.010 | 0.119 |
| D | 0.041 | 0.040 | 0.078 | 0.062 | 0.145 | 0.043 | - |
| A × A | 0.042 | 0.134 | 0.017 | 0.082 | 0.001 | - | - |
| A × D | 0.264 | - | - | - | - | 0.105 | 0.135 |
| H | 0.332 | 0.517 | 0.403 | 0.206 | 0.494 | 0.427 | 0.356 |
| Total | 0.780 | 0.702 | 0.538 | 0.421 | 1.0 | 0.687 | 0.61 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liang, Z.; Prakapenka, D.; Da, Y. Comparison of the Accuracy of Epistasis and Haplotype Models for Genomic Prediction of Seven Human Phenotypes. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 1478. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13101478
Liang Z, Prakapenka D, Da Y. Comparison of the Accuracy of Epistasis and Haplotype Models for Genomic Prediction of Seven Human Phenotypes. Biomolecules. 2023; 13(10):1478. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13101478
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiang, Zuoxiang, Dzianis Prakapenka, and Yang Da. 2023. "Comparison of the Accuracy of Epistasis and Haplotype Models for Genomic Prediction of Seven Human Phenotypes" Biomolecules 13, no. 10: 1478. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13101478
APA StyleLiang, Z., Prakapenka, D., & Da, Y. (2023). Comparison of the Accuracy of Epistasis and Haplotype Models for Genomic Prediction of Seven Human Phenotypes. Biomolecules, 13(10), 1478. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13101478






