Biological Effects of Human Exposure to Environmental Cadmium
Abstract
1. Introduction
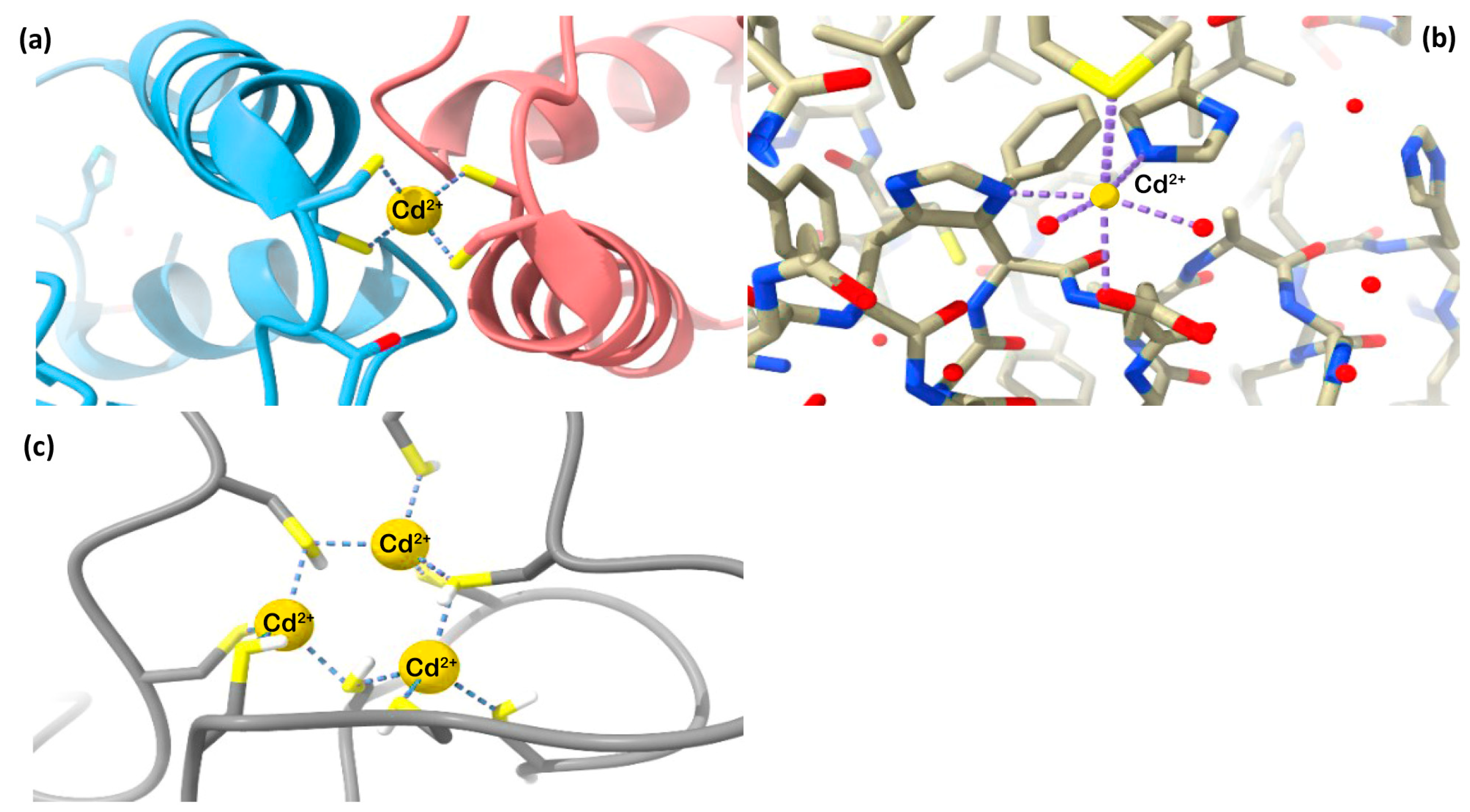
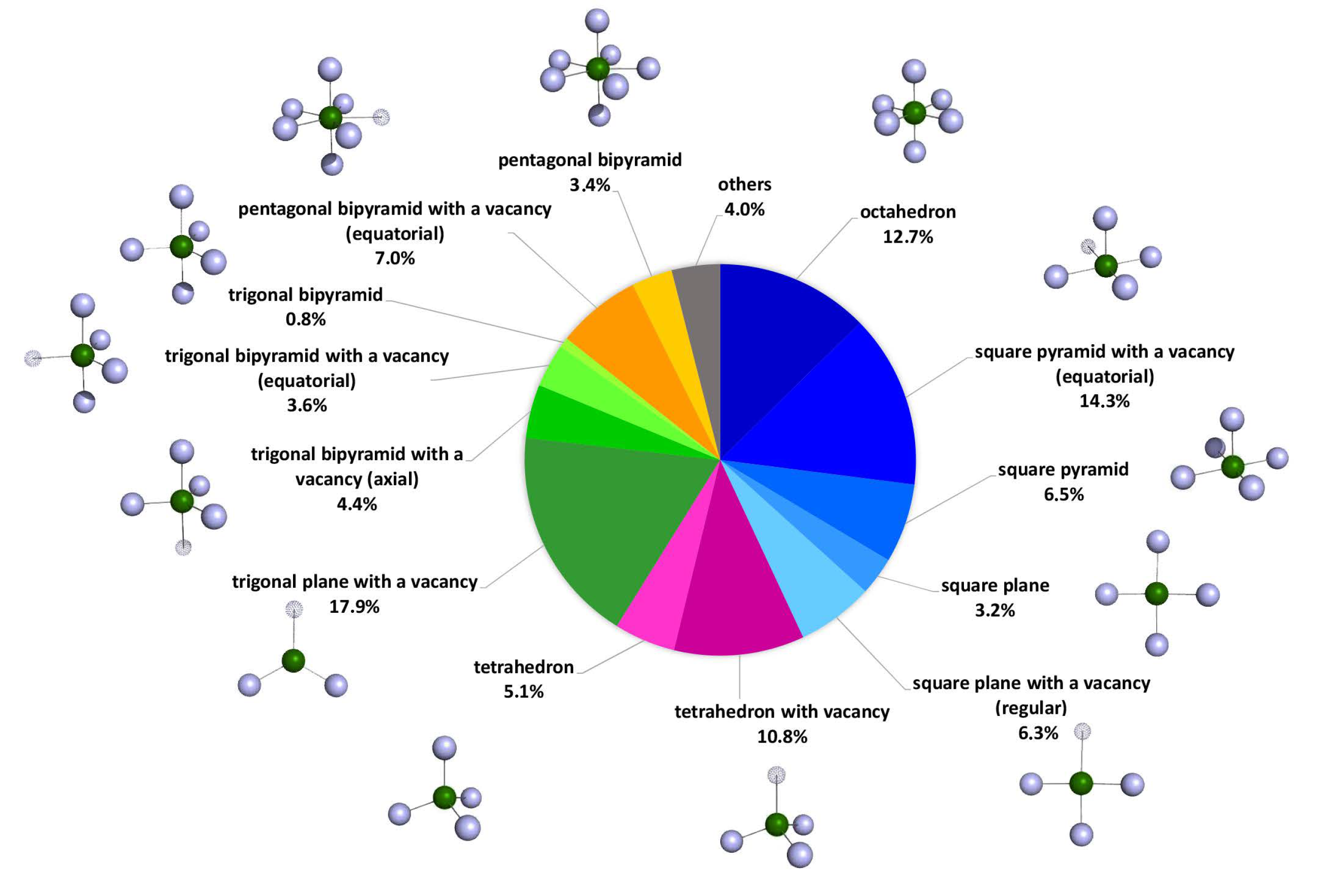
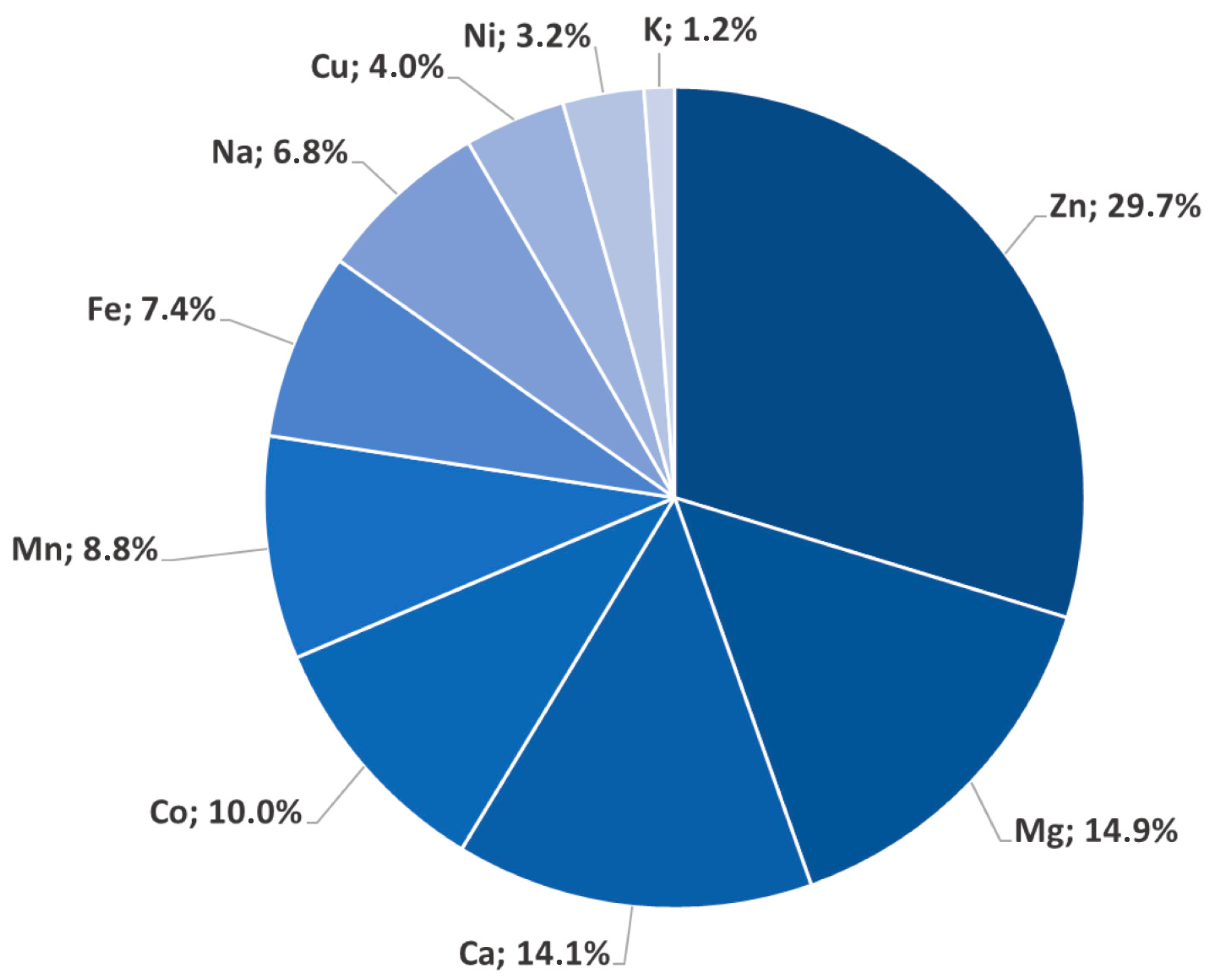
2. The Bioinorganic Chemistry of Cadmium
3. Uses and Environmental Dispersion of Cadmium
4. Human Exposure to Cadmium
4.1. Ingestion
4.2. Inhalation
4.3. Permeation
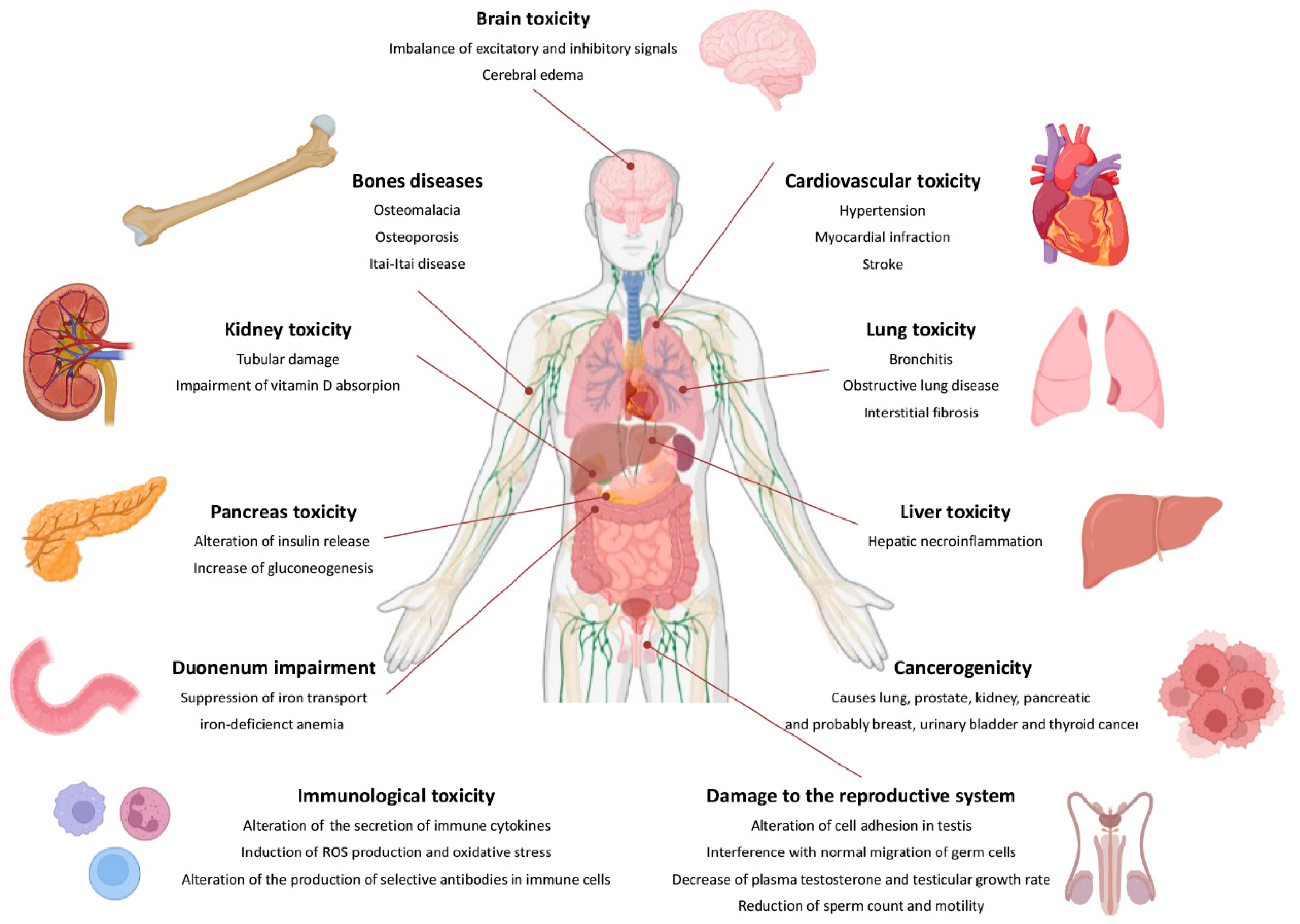
5. Effect of Human Exposure to Cadmium
5.1. General Effects That Are Harmful to Health
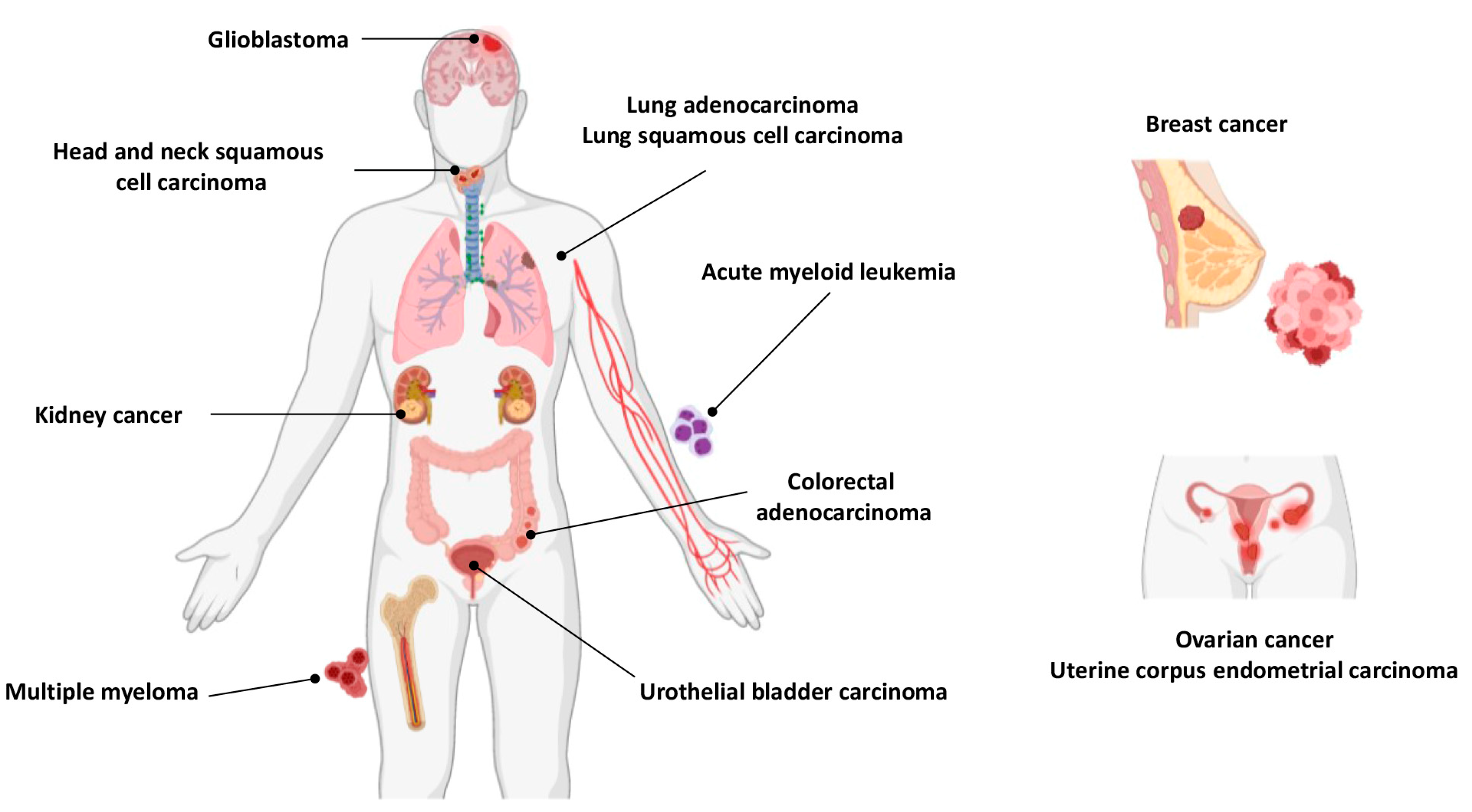
5.2. Carcinogenicity of Cadmium
5.3. Cd-Metalloproteins with Relevance to Carcinogenesis
6. Environmental Remediation of Cadmium
7. Detoxifying Agents and Chelating Agents for the Prevention and Treatment of Cadmium Toxicity
8. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sharma, H.; Rawal, N.; Mathew, B.B. The characteristics, toxicity and effects of cadmium. Int. J. Nanotechnol. 2015, 3, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Zoroddu, M.A.; Aaseth, J.; Crisponi, G.; Medici, S.; Peana, M.; Nurchi, V.M. The essential metals for humans: A brief overview. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2019, 195, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maret, W.; Moulis, J.M. The bioinorganic chemistry of cadmium in the context of its toxicity. In Metal ions in life sciences; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; Volume 11, pp. 1–29. [Google Scholar]
- Mason, R.P. Trace Metals in Aquatic Systems, 1st ed.; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Nordberg, M.; Nordberg, G.F. Metallothionein and Cadmium Toxicology-Historical Review and Commentary. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krezel, A.; Maret, W. The Bioinorganic Chemistry of Mammalian Metallothioneins. Chem. Rev. 2021, 121, 14594–14648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klaassen, C.D.; Liu, J.; Diwan, B.A. Metallothionein protection of cadmium toxicity. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2009, 238, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egli, D.; Domenech, J.; Selvaraj, A.; Balamurugan, K.; Hua, H.; Capdevila, M.; Georgiev, O.; Schaffner, W.; Atrian, S. The four members of the Drosophila metallothionein family exhibit distinct yet overlapping roles in heavy metal homeostasis and detoxification. Genes Cells 2006, 11, 647–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinicropi, M.S.; Amantea, D.; Caruso, A.; Saturnino, C. Chemical and biological properties of toxic metals and use of chelating agents for the pharmacological treatment of metal poisoning. Arch. Toxicol. 2010, 84, 501–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernhoft, R.A. Cadmium toxicity and treatment. Sci. World J. 2013, 2013, 394652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarup, L.; Rogenfelt, A.; Elinder, C.G.; Nogawa, K.; Kjellstrom, T. Biological half-time of cadmium in the blood of workers after cessation of exposure. Scand J. Work Environ. Health 1983, 9, 327–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, A.; Kumar, A.; Lal, A.; Pant, M. Cellular mechanisms of cadmium-induced toxicity: A review. Int. J. Environ. Health Res. 2014, 24, 378–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branca, J.J.V.; Pacini, A.; Gulisano, M.; Taddei, N.; Fiorillo, C.; Becatti, M. Cadmium-Induced Cytotoxicity: Effects on Mitochondrial Electron Transport Chain. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 604377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gasmi, A.; Peana, M.; Arshad, M.; Butnariu, M.; Menzel, A.; Bjørklund, G. Krebs cycle: Activators, inhibitors and their roles in the modulation of carcinogenesis. Arch. Toxicol. 2021, 95, 1161–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koedrith, P.; Seo, Y.R. Advances in carcinogenic metal toxicity and potential molecular markers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2011, 12, 9576–9595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beyersmann, D.; Hartwig, A. Carcinogenic metal compounds: Recent insight into molecular and cellular mechanisms. Arch. Toxicol. 2008, 82, 493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bjørklund, G.; Zou, L.; Peana, M.; Chasapis, C.T.; Hangan, T.; Lu, J.; Maes, M. The Role of the Thioredoxin System in Brain Diseases. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, R.G. Chemical hardness and density functional theory. J. Chem. Sci. 2005, 117, 369–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peana, M.; Pelucelli, A.; Medici, S.; Cappai, R.; Nurchi, V.M.; Zoroddu, M.A. Metal Toxicity and Speciation: A Review. Curr. Med. Chem. 2021, 28, 7190–7208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remelli, M.; Nurchi, V.M.; Lachowicz, J.I.; Medici, S.; Zoroddu, M.A.; Peana, M. Competition between Cd(II) and other divalent transition metal ions during complex formation with amino acids, peptides, and chelating agents. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2016, 327-328, 55–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wernimont, A.K.; Huffman, D.L.; Lamb, A.L.; O’Halloran, T.V.; Rosenzweig, A.C. Structural basis for copper transfer by the metallochaperone for the Menkes/Wilson disease proteins. Nat. Struct. Biol. 2000, 7, 766–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muramoto, K.; Hirata, K.; Shinzawa-Itoh, K.; Yoko-o, S.; Yamashita, E.; Aoyama, H.; Tsukihara, T.; Yoshikawa, S. A histidine residue acting as a controlling site for dioxygen reduction and proton pumping by cytochrome <em>c</em> oxidase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 7881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zangger, K.; Oz, G.; Otvos, J.D.; Armitage, I.M. Three-dimensional solution structure of mouse [Cd7]-metallothionein-1 by homonuclear and heteronuclear NMR spectroscopy. Protein Sci. 1999, 8, 2630–2638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Putignano, V.; Rosato, A.; Banci, L.; Andreini, C. MetalPDB in 2018: A database of metal sites in biological macromolecular structures. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D459–D464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valasatava, Y.; Rosato, A.; Cavallaro, G.; Andreini, C. MetalS(3), a database-mining tool for the identification of structurally similar metal sites. J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 2014, 19, 937–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bulat, Z.; Dukic-Cosic, D.; Antonijevic, B.; Bulat, P.; Vujanovic, D.; Buha, A.; Matovic, V. Effect of magnesium supplementation on the distribution patterns of zinc, copper, and magnesium in rabbits exposed to prolonged cadmium intoxication. Sci. World J. 2012, 2012, 572514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulat, Z.P.; Djukic-Cosic, D.; Malicevic, Z.; Bulat, P.; Matovic, V. Zinc or magnesium supplementation modulates cd intoxication in blood, kidney, spleen, and bone of rabbits. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2008, 124, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekiari, V.; Lianos, P. High-Yield Luminescence from Cadmium Sulfide Nanoclusters Supported in a Poly(ethylene glycol) Oligomer. Langmuir 2000, 16, 3561–3563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobiech, M.; Bujak, P.; Luliński, P.; Pron, A. Semiconductor nanocrystal–polymer hybrid nanomaterials and their application in molecular imprinting. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 12030–12074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Parliament. Directive (EU) 2017/2102 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 15 November 2017 amending Directive 2011/65/EU on the restriction of the use of certain hazardous substances in electrical and electronic equipment (Text with EEA relevance.). Off. J. Eur. Union 2017, L305. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, L.; Huo, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Qin, Q.; Xu, X. Hearing loss risk and DNA methylation signatures in preschool children following lead and cadmium exposure from an electronic waste recycling area. Chemosphere 2020, 246, 125829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baloch, S.; Kazi, T.G.; Baig, J.A.; Afridi, H.I.; Arain, M.B. Occupational exposure of lead and cadmium on adolescent and adult workers of battery recycling and welding workshops: Adverse impact on health. Sci. Total. Environ. 2020, 720, 137549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayat, M.T.; Nauman, M.; Nazir, N.; Ali, S.; Bangash, N. Chapter 7—Environmental Hazards of Cadmium: Past, Present, and Future. In Cadmium Toxicity and Tolerance in Plants; Hasanuzzaman, M., Prasad, M.N.V., Fujita, M., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 163–183. [Google Scholar]
- Chavez, E.; He, Z.L.; Stoffella, P.J.; Mylavarapu, R.S.; Li, Y.C.; Moyano, B.; Baligar, V.C. Concentration of cadmium in cacao beans and its relationship with soil cadmium in southern Ecuador. Sci. Total. Environ. 2015, 533, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.; Melough, M.M.; Vance, T.M.; Noh, H.; Koo, S.I.; Chun, O.K. Dietary Cadmium Intake and Sources in the US. Nutrients 2018, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, T.; Zhang, Z.W.; Moon, C.S.; Shimbo, S.; Nakatsuka, H.; Matsuda-Inoguchi, N.; Higashikawa, K.; Ikeda, M. Cadmium exposure of women in general populations in Japan during 1991-1997 compared with 1977-1981. Int. Arch. Occup. Environ. Health 2000, 73, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Wang, Y.; Mao, W.; Sui, H.; Yong, L.; Yang, D.; Jiang, D.; Zhang, L.; Gong, Y. Dietary cadmium exposure assessment among the Chinese population. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0177978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satarug, S.; Baker, J.R.; Urbenjapol, S.; Haswell-Elkins, M.; Reilly, P.E.; Williams, D.J.; Moore, M.R. A global perspective on cadmium pollution and toxicity in non-occupationally exposed population. Toxicol. Lett. 2003, 137, 65–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horiguchi, H.; Oguma, E.; Sasaki, S.; Miyamoto, K.; Ikeda, Y.; Machida, M.; Kayama, F. Dietary exposure to cadmium at close to the current provisional tolerable weekly intake does not affect renal function among female Japanese farmers. Environ. Res. 2004, 95, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogawa, K.; Suwazono, Y.; Nishijo, M.; Sakurai, M.; Ishizaki, M.; Morikawa, Y.; Watanabe, Y.; Kido, T.; Nakagawa, H. Increase of lifetime cadmium intake dose-dependently increased all cause of mortality in female inhabitants of the cadmium-polluted Jinzu River basin, Toyama, Japan. Environ. Res. 2018, 164, 379–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishijo, M.; Nogawa, K.; Suwazono, Y.; Kido, T.; Sakurai, M.; Nakagawa, H. Lifetime Cadmium Exposure and Mortality for Renal Diseases in Residents of the Cadmium-Polluted Kakehashi River Basin in Japan. Toxics 2020, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uetani, M.; Kobayashi, E.; Suwazono, Y.; Kido, T.; Nogawa, K. Cadmium exposure aggravates mortality more in women than in men. Int. J. Environ. Health Res. 2006, 16, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duggan, R.E.; Lipscomb, G.Q. Dietary intake of pesticide chicals in the United States (II), June 1966—April 1968. Pestic. Monit. J. 1969, 2, 153–162. [Google Scholar]
- Choudhury, H.; Harvey, T.; Thayer, W.C.; Lockwood, T.F.; Stiteler, W.M.; Goodrum, P.E.; Hassett, J.M.; Diamond, G.L. Urinary cadmium elimination as a biomarker of exposure for evaluating a cadmium dietary exposure--biokinetics model. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health A 2001, 63, 321–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahjoub, M.; Fadlaoui, S.; El Maadoudi, M.; Smiri, Y. Mercury, Lead, and Cadmium in the Muscles of Five Fish Species from the Mechraa-Hammadi Dam in Morocco and Health Risks for Their Consumers. J. Toxicol. 2021, 2021, 8865869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mok, J.S.; Yoo, H.D.; Kim, P.H.; Yoon, H.D.; Park, Y.C.; Lee, T.S.; Kwon, J.Y.; Son, K.T.; Lee, H.J.; Ha, K.S.; et al. Bioaccumulation of heavy metals in oysters from the southern coast of Korea: Assessment of potential risk to human health. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2015, 94, 749–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mok, J.S.; Kwon, J.Y.; Son, K.T.; Choi, W.S.; Shim, K.B.; Lee, T.S.; Kim, J.H. Distribution of heavy metals in muscles and internal organs of Korean cephalopods and crustaceans: Risk assessment for human health. J. Food Prot. 2014, 77, 2168–2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, W.; Zhao, X.; Han, Y.; Che, Z.; Chai, X.; Liu, G. Ocean acidification increases cadmium accumulation in marine bivalves: A potential threat to seafood safety. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 20197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conterato, G.M.; Bulcao, R.P.; Sobieski, R.; Moro, A.M.; Charao, M.F.; de Freitas, F.A.; de Almeida, F.L.; Moreira, A.P.; Roehrs, M.; Tonello, R.; et al. Blood thioredoxin reductase activity, oxidative stress and hematological parameters in painters and battery workers: Relationship with lead and cadmium levels in blood. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2013, 33, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberdorster, G. Airborne cadmium and carcinogenesis of the respiratory tract. Scand J. Work Environ. Health 1986, 12, 523–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannino, D.M.; Holguin, F.; Greves, H.M.; Savage-Brown, A.; Stock, A.L.; Jones, R.L. Urinary cadmium levels predict lower lung function in current and former smokers: Data from the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Thorax 2004, 59, 194–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satarug, S.; Moore, M.R. Adverse health effects of chronic exposure to low-level cadmium in foodstuffs and cigarette smoke. Environ. Health Perspect 2004, 112, 1099–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barregard, L.; Fabricius-Lagging, E.; Lundh, T.; Molne, J.; Wallin, M.; Olausson, M.; Modigh, C.; Sallsten, G. Cadmium, mercury, and lead in kidney cortex of living kidney donors: Impact of different exposure sources. Environ. Res. 2010, 110, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjørklund, G.; Oliinyk, P.; Lysiuk, R.; Rahaman, M.S.; Antonyak, H.; Lozynska, I.; Lenchyk, L.; Peana, M. Arsenic intoxication: General aspects and chelating agents. Arch. Toxicol. 2020, 94, 1879–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Gao, H.; Long, M.; Fu, H.; Alvarez, P.J.J.; Li, Q.; Zheng, S.; Qu, X.; Zhu, D. Sunlight Promotes Fast Release of Hazardous Cadmium from Widely-Used Commercial Cadmium Pigment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 6877–6886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chavatte, L.; Juan, M.; Mounicou, S.; Leblanc Noblesse, E.; Pays, K.; Nizard, C.; Bulteau, A.L. Elemental and molecular imaging of human full thickness skin after exposure to heavy metals. Metallomics 2020, 12, 1555–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akesson, A.; Lundh, T.; Vahter, M.; Bjellerup, P.; Lidfeldt, J.; Nerbrand, C.; Samsioe, G.; Stromberg, U.; Skerfving, S. Tubular and glomerular kidney effects in Swedish women with low environmental cadmium exposure. Environ. Health Perspect 2005, 113, 1627–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kjellstrom, T. Mechanism and epidemiology of bone effects of cadmium. IARC Sci. Publ. 1992, 301–310. [Google Scholar]
- Pizent, A.; Tariba, B.; Zivkovic, T. Reproductive toxicity of metals in men. Arh. Hig. Rada Toksikol. 2012, 63 (Suppl. 1), 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, J.; Bannigan, J. Cadmium: Toxic effects on the reproductive system and the embryo. Reprod. Toxicol. 2008, 25, 304–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eum, K.D.; Lee, M.S.; Paek, D. Cadmium in blood and hypertension. Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 407, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallagher, C.M.; Meliker, J.R. Blood and urine cadmium, blood pressure, and hypertension: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Environ. Health Perspect 2010, 118, 1676–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, J.R.; Prozialeck, W.C. Cadmium, diabetes and chronic kidney disease. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2009, 238, 289–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horiguchi, H.; Teranishi, H.; Niiya, K.; Aoshima, K.; Katoh, T.; Sakuragawa, N.; Kasuya, M. Hypoproduction of erythropoietin contributes to anemia in chronic cadmium intoxication: Clinical study on Itai-itai disease in Japan. Arch. Toxicol. 1994, 68, 632–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujiwara, Y.; Lee, J.Y.; Banno, H.; Imai, S.; Tokumoto, M.; Hasegawa, T.; Seko, Y.; Nagase, H.; Satoh, M. Cadmium induces iron deficiency anemia through the suppression of iron transport in the duodenum. Toxicol. Lett. 2020, 332, 130–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.J.; Surolia, R.; Singh, P.; Dsouza, K.G.; Stephens, C.T.; Wang, Z.; Liu, R.M.; Bae, S.; Kim, Y.I.; Athar, M.; et al. Fibrinogen mediates cadmium-induced macrophage activation and serves as a predictor of cadmium exposure in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2022, 322, L593–L606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.J.; Surolia, R.; Li, H.; Wang, Z.; Liu, G.; Liu, R.M.; Mirov, S.B.; Athar, M.; Thannickal, V.J.; Antony, V.B. Low-dose cadmium exposure induces peribronchiolar fibrosis through site-specific phosphorylation of vimentin. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2017, 313, L80–L91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinaldi, M.; Micali, A.; Marini, H.; Adamo, E.B.; Puzzolo, D.; Pisani, A.; Trichilo, V.; Altavilla, D.; Squadrito, F.; Minutoli, L. Cadmium, Organ Toxicity and Therapeutic Approaches: A Review on Brain, Kidney and Testis Damage. Curr. Med. Chem. 2017, 24, 3879–3893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branca, J.J.V.; Morucci, G.; Pacini, A. Cadmium-induced neurotoxicity: Still much ado. Neural. Regen. Res. 2018, 13, 1879–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filipic, M.; Fatur, T.; Vudrag, M. Molecular mechanisms of cadmium induced mutagenicity. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2006, 25, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, P.; Muchnok, T.K.; Klishis, M.L.; Roberts, J.R.; Antonini, J.M.; Whong, W.-Z.; Ong, T.-m. Cadmium-Induced Cell Transformation and Tumorigenesis Are Associated with Transcriptional Activation of c-fos, c-jun, and c-myc Proto-Oncogenes: Role of Cellular Calcium and Reactive Oxygen Species. Toxicol. Sci. 2001, 61, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Qu, W.; Kadiiska, M.B. Role of oxidative stress in cadmium toxicity and carcinogenesis. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2009, 238, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogasawara, Y.; Takeda, Y.; Takayama, H.; Nishimoto, S.; Ichikawa, K.; Ueki, M.; Suzuki, T.; Ishii, K. Significance of the rapid increase in GSH levels in the protective response to cadmium exposure through phosphorylated Nrf2 signaling in Jurkat T-cells. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2014, 69, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwerdtle, T.; Ebert, F.; Thuy, C.; Richter, C.; Mullenders, L.H.F.; Hartwig, A. Genotoxicity of Soluble and Particulate Cadmium Compounds: Impact on Oxidative DNA Damage and Nucleotide Excision Repair. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2010, 23, 432–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birkou, M.; Chasapis, C.T.; Marousis, K.D.; Loutsidou, A.K.; Bentrop, D.; Lelli, M.; Herrmann, T.; Carthy, J.M.; Episkopou, V.; Spyroulias, G.A. A Residue Specific Insight into the Arkadia E3 Ubiquitin Ligase Activity and Conformational Plasticity. J. Mol. Biol. 2017, 429, 2373–2386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chasapis, C.T.; Kandias, N.G.; Episkopou, V.; Bentrop, D.; Spyroulias, G.A. NMR-based insights into the conformational and interaction properties of Arkadia RING-H2 E3 Ub ligase. Proteins Struct. Funct. Bioinform. 2012, 80, 1484–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fatur, T.; Lah, T.T.; Filipic, M. Cadmium inhibits repair of UV-, methyl methanesulfonate- and N-methyl-N-nitrosourea-induced DNA damage in Chinese hamster ovary cells. Mutat. Res. 2003, 529, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, P.; Yamane, K. DNA mismatch repair: Molecular mechanism, cancer, and ageing. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2008, 129, 391–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.H.; Clark, A.B.; Slebos, R.J.C.; Al-Refai, H.; Taylor, J.A.; Kunkel, T.A.; Resnick, M.A.; Gordenin, D.A. Cadmium is a mutagen that acts by inhibiting mismatch repair. Nat. Genet. 2003, 34, 326–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieland, M.; Levin, M.K.; Hingorani, K.S.; Biro, F.N.; Hingorani, M.M. Mechanism of Cadmium-Mediated Inhibition of Msh2-Msh6 Function in DNA Mismatch Repair. Biochemistry 2009, 48, 9492–9502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lützen, A.; Liberti, S.E.; Rasmussen, L.J. Cadmium inhibits human DNA mismatch repair in vivo. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2004, 321, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Ren, X.; Hu, X.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, M. Cadmium-induced apoptosis through reactive oxygen species-mediated mitochondrial oxidative stress and the JNK signaling pathway in TM3 cells, a model of mouse Leydig cells. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2019, 368, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, S.; Chen, J.; Yang, J.; Wang, T.; Zou, H.; Wang, Y.; Gu, J.; Liu, X.; et al. Cadmium-induced apoptosis in neuronal cells is mediated by Fas/FasL-mediated mitochondrial apoptotic signaling pathway. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 8837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghajari, H.; Hosseini, S.A.; Farsi, S. The Effect of Endurance Training Along with Cadmium Consumption on Bcl-2 and Bax Gene Expressions in Heart Tissue of Rats. Ann. Mil. Health Sci. Res. 2019, 17, e86795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, S.H.; Lee, C.M.; Nam, M.J. Cytoprotective effects of taxifolin against cadmium-induced apoptosis in human keratinocytes. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2019, 38, 992–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Shi, M.; Yin, L.; Hou, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Chu Wong, C.K.; Chen, D.; Guo, Z.; et al. Inhibition of Autophagy Alleviates Cadmium-Induced Mouse Spleen and Human B Cells Apoptosis. Toxicol. Sci. 2019, 170, 109–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiarelli, R.; Roccheri, M.C. Heavy Metals and Metalloids as Autophagy Inducing Agents: Focus on Cadmium and Arsenic. Cells 2012, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Dong, X.; Zhao, R.; Zhang, R.; Xu, C.; Wang, X.; Liu, C.; Hu, X.; Huang, S.; Chen, L. Cadmium results in accumulation of autophagosomes-dependent apoptosis through activating Akt-impaired autophagic flux in neuronal cells. Cell. Signal. 2019, 55, 26–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, T.; Zhang, H.; Yu, Q.; Liu, G.; Long, M.; Zhang, K.; Liu, W.; Song, R.; Bian, J.; Gu, J.; et al. ERK1/2 MAPK promotes autophagy to suppress ER stress-mediated apoptosis induced by cadmium in rat proximal tubular cells. Toxicol. Vitr. 2018, 52, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Mandal, A.K.; Son, Y.-O.K.; Pratheeshkumar, P.; Wise, J.T.F.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Shi, X.; Chen, Z. Roles of ROS, Nrf2, and autophagy in cadmium-carcinogenesis and its prevention by sulforaphane. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2018, 353, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vilahur, N.; Vahter, M.; Broberg, K. The Epigenetic Effects of Prenatal Cadmium Exposure. Curr. Environ. Health Rep. 2015, 2, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Li, Y.; Shao, C.; Tan, Y.; Cai, L. Cadmium and its epigenetic effects. Curr. Med. Chem. 2012, 19, 2611–2620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chasapis, C.T. Shared gene-network signatures between the human heavy metal proteome and neurological disorders and cancer types. Metallomics 2018, 10, 1678–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinstein, J.N.; Collisson, E.A.; Mills, G.B.; Shaw, K.R.; Ozenberger, B.A.; Ellrott, K.; Shmulevich, I.; Sander, C.; Stuart, J.M. The Cancer Genome Atlas Pan-Cancer analysis project. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 1113–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petersen, D.L.; Krejsgaard, T.; Berthelsen, J.; Fredholm, S.; Willerslev-Olsen, A.; Sibbesen, N.A.; Bonefeld, C.M.; Andersen, M.H.; Francavilla, C.; Olsen, J.V.; et al. B-lymphoid tyrosine kinase (Blk) is an oncogene and a potential target for therapy with dasatinib in cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL). Leukemia 2014, 28, 2109–2112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Montero-Ruiz, O.; Alcantara-Ortigoza, M.A.; Betancourt, M.; Juarez-Velazquez, R.; Gonzalez-Marquez, H.; Perez-Vera, P. Expression of RUNX1 isoforms and its target gene BLK in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leuk Res. 2012, 36, 1105–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, M.R.; Hoessli, D.C.; Fang, M. N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferases in cancer. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 54067–54081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sapio, L.; Di Maiolo, F.; Illiano, M.; Esposito, A.; Chiosi, E.; Spina, A.; Naviglio, S. Targeting protein kinase A in cancer therapy: An update. Excli. J. 2014, 13, 843–855. [Google Scholar]
- Busch, S.; Acar, A.; Magnusson, Y.; Gregersson, P.; Rydén, L.; Landberg, G. TGF-beta receptor type-2 expression in cancer-associated fibroblasts regulates breast cancer cell growth and survival and is a prognostic marker in pre-menopausal breast cancer. Oncogene 2015, 34, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, S.; Chytil, A.; Washington, K.; Romero-Gallo, J.; Gorska, A.E.; Wirth, P.S.; Gautam, S.; Moses, H.L.; Grady, W.M. Transforming growth factor beta receptor type II inactivation promotes the establishment and progression of colon cancer. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 4687–4692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Herrmann, C.J.; Simonovic, M.; Szklarczyk, D.; von Mering, C. Version 4.0 of PaxDb: Protein abundance data, integrated across model organisms, tissues, and cell-lines. PROTEOMICS 2015, 15, 3163–3168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Den, R.B.; Lu, B. Heat shock protein 90 inhibition: Rationale and clinical potential. Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2012, 4, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moser, C.; Lang, S.A.; Stoeltzing, O. Heat-shock Protein 90 (Hsp90) as a Molecular Target for Therapy of Gastrointestinal Cancer. Anticancer Res. 2009, 29, 2031. [Google Scholar]
- Mahalingam, D.; Swords, R.; Carew, J.S.; Nawrocki, S.T.; Bhalla, K.; Giles, F.J. Targeting HSP90 for cancer therapy. Br. J. Cancer 2009, 100, 1523–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neckers, L. Heat shock protein 90: The cancer chaperone. J. Biosci. 2007, 32, 517–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, T.; Schwartz, S.J.; Sun, D. New developments in Hsp90 inhibitors as anti-cancer therapeutics: Mechanisms, clinical perspective and more potential. Drug Resist. Updat. 2009, 12, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahajan, P.; Kaushal, J. Role of Phytoremediation in Reducing Cadmium Toxicity in Soil and Water. J. Toxicol. 2018, 2018, 4864365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chellaiah, E.R. Cadmium (heavy metals) bioremediation by Pseudomonas aeruginosa: A minireview. Appl. Water Sci. 2018, 8, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Subrahmanyam, G.; Mondal, R.; Cabral-Pinto, M.M.S.; Shabnam, A.A.; Jigyasu, D.K.; Malyan, S.K.; Fagodiya, R.K.; Khan, S.A.; Yu, Z.G. Bio-remediation approaches for alleviation of cadmium contamination in natural resources. Chemosphere 2021, 268, 128855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakhar, A.; Gul, B.; Gurmani, A.R.; Khan, S.M.; Ali, S.; Sultan, T.; Chaudhary, H.J.; Rafique, M.; Rizwan, M. Heavy metal remediation and resistance mechanism of Aeromonas, Bacillus, and Pseudomonas: A review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 52, 1868–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chasapis, C.T.; Peana, M.; Bekiari, V. Structural Identification of Metalloproteomes in Marine Diatoms, an Efficient Algae Model in Toxic Metals Bioremediation. Molecules 2022, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, V.; Daverey, A. Phytoremediation: A multidisciplinary approach to clean up heavy metal contaminated soil. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2020, 18, 100774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, A.; Habib, M.; Kakavand, S.N.; Zahid, Z.; Zahra, N.; Sharif, R.; Hasanuzzaman, M. Phytoremediation of Cadmium: Physiological, Biochemical, and Molecular Mechanisms. Biology (Basel) 2020, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidalgo, J.; Aschner, M.; Zatta, P.; Vasak, M. Roles of the metallothionein family of proteins in the central nervous system. Brain Res. Bull. 2001, 55, 133–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bjørklund, G.; Shanaida, M.; Lysiuk, R.; Antonyak, H.; Klishch, I.; Shanaida, V.; Peana, M. Selenium: An Antioxidant with a Critical Role in Anti-Aging. Molecules 2022, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardoso, B.R.; Roberts, B.R.; Bush, A.I.; Hare, D.J. Selenium, selenoproteins and neurodegenerative diseases. Metallomics 2015, 7, 1213–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.C.; Xu, Y.; Chen, Y.M.; Li, J.; Zhao, F.; Zheng, G.; Jing, J.F.; Ke, T.; Chen, J.Y.; Luo, W.J. The effect of sodium selenite on lead induced cognitive dysfunction. Neurotoxicology 2013, 36, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitek, A.; Kozlowska, L. The role of well-known antioxidant vitamins in the prevention of cadmium-induced toxicity. Int. J. Occup. Med. Environ. Health 2022, 35, 367–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halttunen, T.; Collado, M.C.; El-Nezami, H.; Meriluoto, J.; Salminen, S. Combining strains of lactic acid bacteria may reduce their toxin and heavy metal removal efficiency from aqueous solution. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2008, 46, 160–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forsyth, C.B.; Farhadi, A.; Jakate, S.M.; Tang, Y.; Shaikh, M.; Keshavarzian, A. Lactobacillus GG treatment ameliorates alcohol-induced intestinal oxidative stress, gut leakiness, and liver injury in a rat model of alcoholic steatohepatitis. Alcohol 2009, 43, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhai, Q.; Wang, G.; Zhao, J.; Liu, X.; Tian, F.; Zhang, H.; Chen, W. Protective effects of Lactobacillus plantarum CCFM8610 against acute cadmium toxicity in mice. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 1508–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Yu, L.; Shen, X.; Tian, F.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Chen, W.; Zhai, Q. Protective Effects of Lactobacillus plantarum CCFM8610 against Acute Toxicity Caused by Different Food-Derived Forms of Cadmium in Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Q.; Wang, G.; Zhao, J.; Liu, X.; Narbad, A.; Chen, Y.Q.; Zhang, H.; Tian, F.; Chen, W. Protective effects of Lactobacillus plantarum CCFM8610 against chronic cadmium toxicity in mice indicate routes of protection besides intestinal sequestration. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 4063–4071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Xia, Y.; Hu, W.; Zhang, H.; Shen, Z. Cadmium-induced oxidative damage and protective effects of N-acetyl-L-cysteine against cadmium toxicity in Solanum nigrum L. J. Hazard. Mater 2010, 180, 722–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gil, H.W.; Kang, E.J.; Lee, K.H.; Yang, J.O.; Lee, E.Y.; Hong, S.Y. Effect of glutathione on the cadmium chelation of EDTA in a patient with cadmium intoxication. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2011, 30, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Su, S.; Zhai, R.; Chen, K.; Jin, T.; Huang, B.; Zhou, Y.; Ge, X.; Wei, G.; Liao, R. Lack of reversal effect of EDTA treatment on cadmium induced renal dysfunction: A fourteen-year follow-up. Biometals 2004, 17, 435–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonick, H.C. Nephrotoxicity of cadmium & lead. Indian J. Med. Res. 2008, 128, 335–352. [Google Scholar]
- Jalilehvand, F.; Leung, B.O.; Mah, V. Cadmium(II) complex formation with cysteine and penicillamine. Inorg. Chem. 2009, 48, 5758–5771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patrick, L. Toxic metals and antioxidants: Part II. The role of antioxidants in arsenic and cadmium toxicity. Altern. Med. Rev. A J. Clin. Ther. 2003, 8, 106–128. [Google Scholar]
- Flora, S.J.; Pachauri, V. Chelation in metal intoxication. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2010, 7, 2745–2788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafati Rahimzadeh, M.; Kazemi, S.; Moghadamnia, A.A. Cadmium toxicity and treatment: An update. Caspian J. Intern. Med. 2017, 8, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Routzomani, A.; Lada, Z.G.; Angelidou, V.; C, P.R.; Psycharis, V.; Konidaris, K.F.; Chasapis, C.T.; Perlepes, S.P. Confirming the Molecular Basis of the Solvent Extraction of Cadmium(II) Using 2-Pyridyl Oximes through a Synthetic Inorganic Chemistry Approach and a Proposal for More Efficient Extractants. Molecules 2022, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazarakioti, E.C.; Beobide, A.S.; Angelidou, V.; Efthymiou, C.G.; Terzis, A.; Psycharis, V.; Voyiatzis, G.A.; Perlepes, S.P. Modeling the Solvent Extraction of Cadmium(II) from Aqueous Chloride Solutions by 2-pyridyl Ketoximes: A Coordination Chemistry Approach. Molecules 2019, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| A/A | Gene | UniProt ID | Abundance (ppm) | Protein Name | High Expression Level |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | GALNT10 | Q86SR1 | 161 | Polypeptide N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase 10 | Lung, gall bladder, kidney |
| 2 | NOTCH4 | Q99466 | 47 | Neurogenic locus notch homolog protein 4 | Adipose, lung |
| 3 | GZMB | P10144 | 288 | Granzyme B | Dendritic cells |
| 4 | BLK | P51451 | 36 | Tyrosine-protein kinase Blk | Spleen, bone marrow |
| 5 | AXL | P30530 | 681 | Tyrosine-protein kinase receptor UFO | Testis, skeletal muscle |
| 6 | TGFBR2 | P37173 | 182 | TGF-beta receptor type-2 | Adipose, breast |
| 7 | IL2RG | P31785 | 105 | Cytokine receptor common subunit gamma | Spleen, tonsil |
| 8 | LCK | P06239 | 941 | Tyrosine-protein kinase Lck | Thymus, T-cells |
| 9 | ESR1 | P03372 | 35 | Estrogen receptor | Endometrium, cervix, uterine |
| 10 | PRKACA | P17612 | 697 | cAMP-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit alpha | Cerebral cortex, testis |
| 11 | SHC | P29353 | 200 | SHC-transforming protein 1 | Cerebellum, thyroid gland |
| 12 | HSP90AB1 | P08238 | 16962 | Heat shock protein HSP 90-beta | Cerebellum, adrenal gland |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Peana, M.; Pelucelli, A.; Chasapis, C.T.; Perlepes, S.P.; Bekiari, V.; Medici, S.; Zoroddu, M.A. Biological Effects of Human Exposure to Environmental Cadmium. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13010036
Peana M, Pelucelli A, Chasapis CT, Perlepes SP, Bekiari V, Medici S, Zoroddu MA. Biological Effects of Human Exposure to Environmental Cadmium. Biomolecules. 2023; 13(1):36. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13010036
Chicago/Turabian StylePeana, Massimiliano, Alessio Pelucelli, Christos T. Chasapis, Spyros P. Perlepes, Vlasoula Bekiari, Serenella Medici, and Maria Antonietta Zoroddu. 2023. "Biological Effects of Human Exposure to Environmental Cadmium" Biomolecules 13, no. 1: 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13010036
APA StylePeana, M., Pelucelli, A., Chasapis, C. T., Perlepes, S. P., Bekiari, V., Medici, S., & Zoroddu, M. A. (2023). Biological Effects of Human Exposure to Environmental Cadmium. Biomolecules, 13(1), 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13010036









