Where Electrostatics Matter: Bacterial Surface Neutralization and Membrane Disruption by Antimicrobial Peptides SAAP-148 and OP-145
Abstract
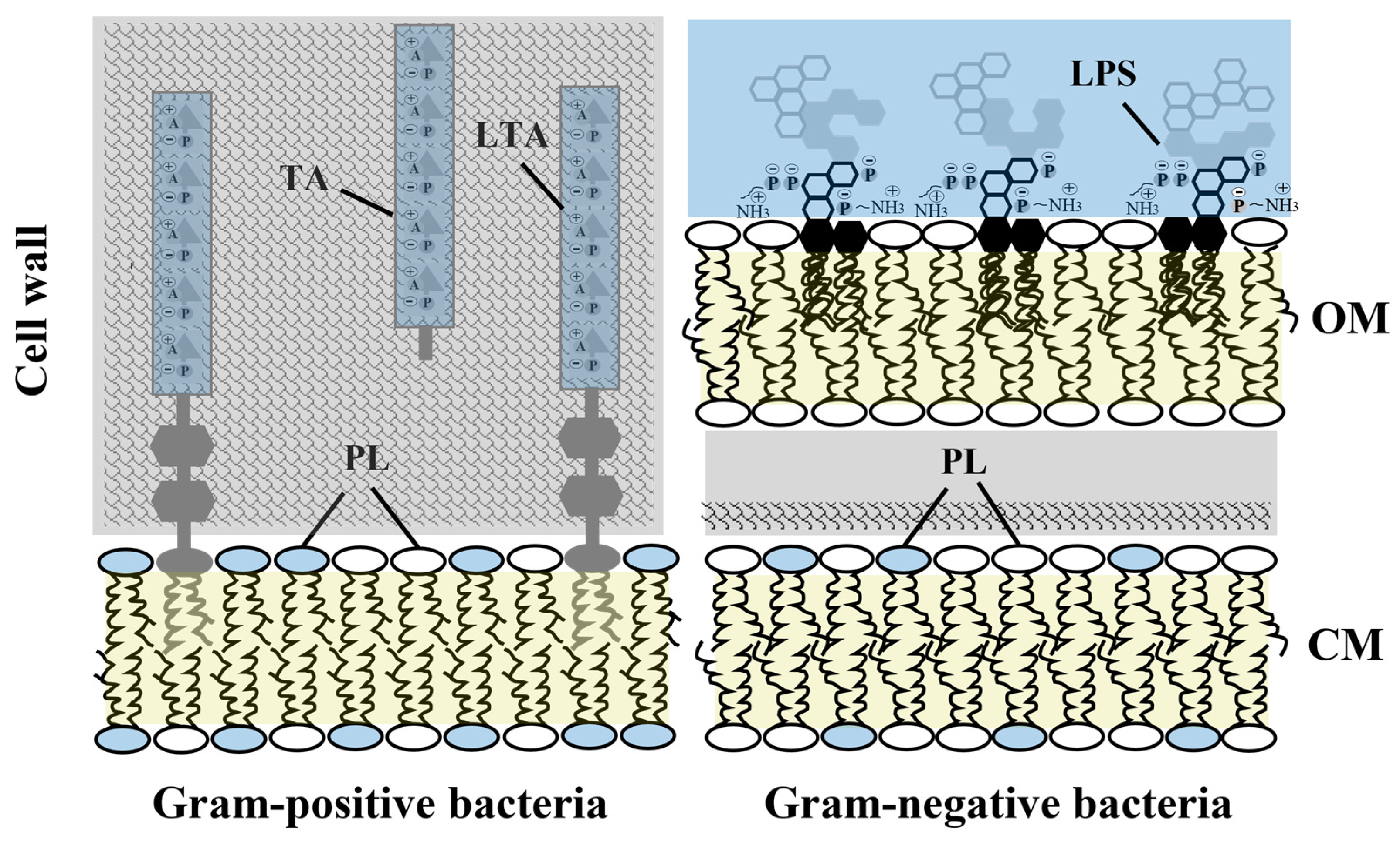
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Bacterial Strains
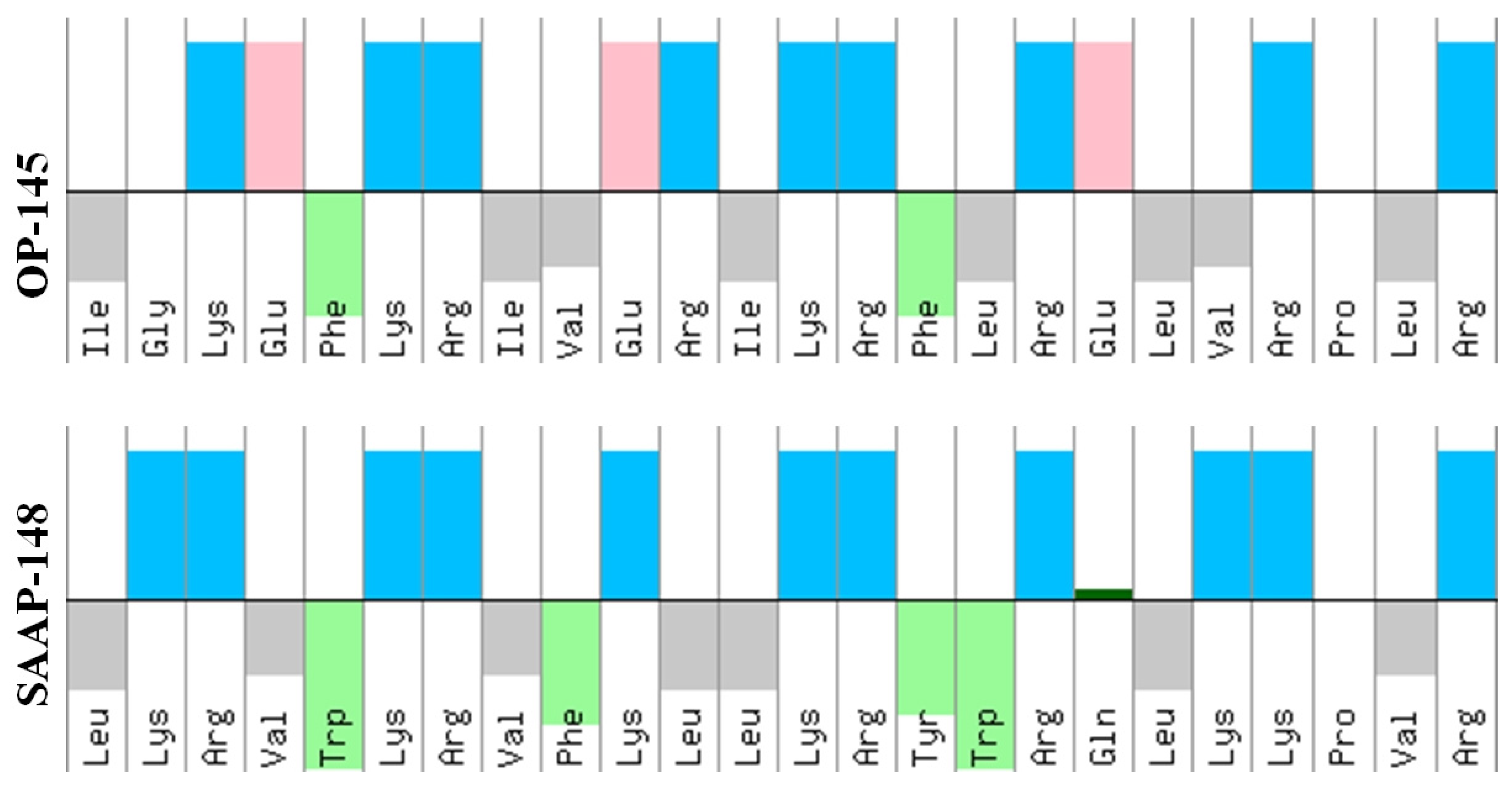
2.3. Antimicrobial Peptides
2.4. Growing Conditions of Bacterial Strains E. coli and E. hirae
2.5. Antimicrobial Activity of OP-145 and SAAP-148
2.6. Permeabilization of Bacterial Membranes
2.7. Measurement of Zeta Potential of LUVs and Bacterial Strains
2.8. Preparation of Liposomes
2.9. Permeabilization of Model Membranes/Vesicle Leakage Assay
3. Results
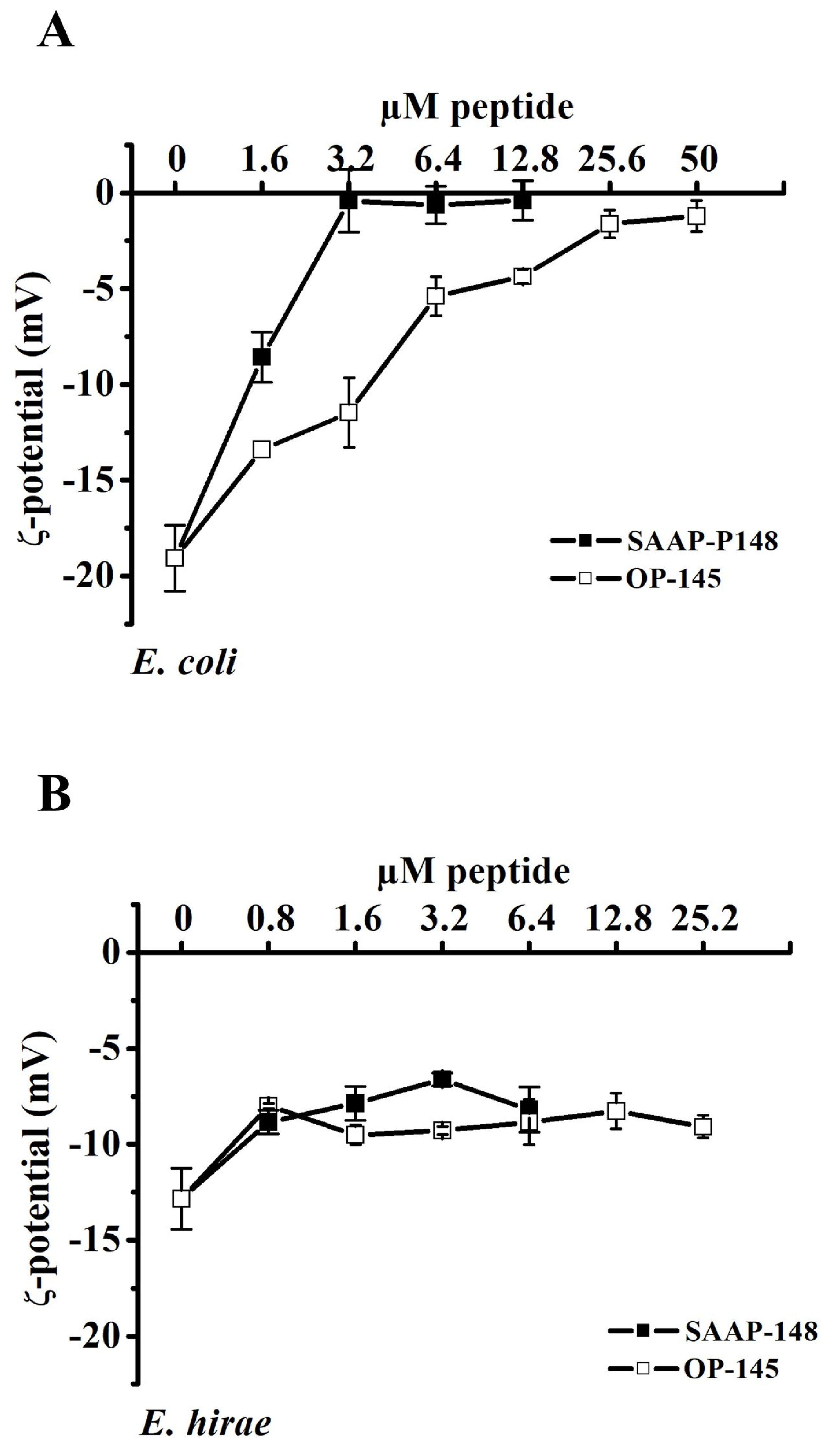
3.1. Antimicrobial Peptides Neutralize the Surface Charge of E. coli but Not of E. hirae
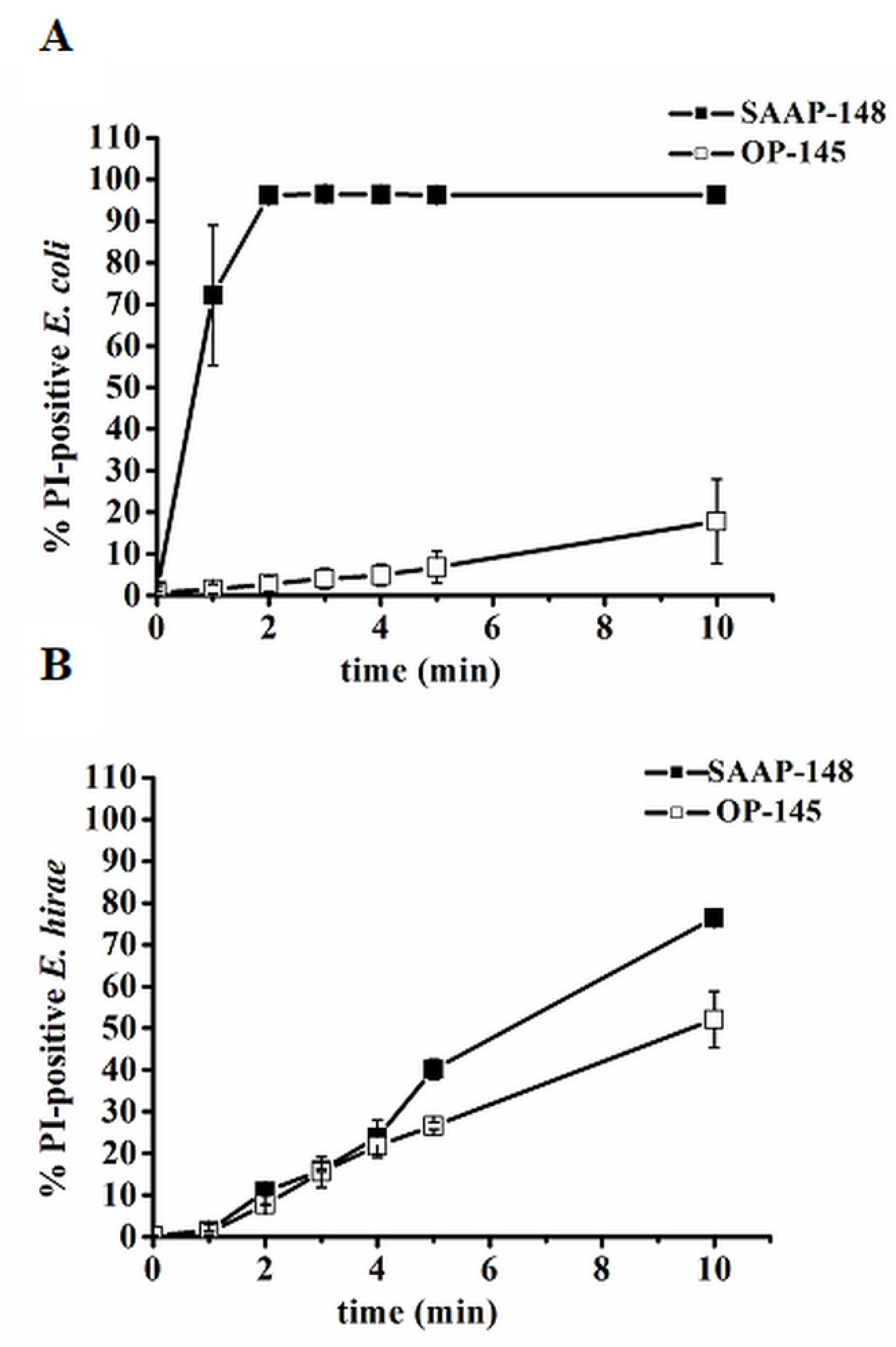
3.2. The Cytoplasmic Membrane Is Not Always a Direct Target Related to Cell Death
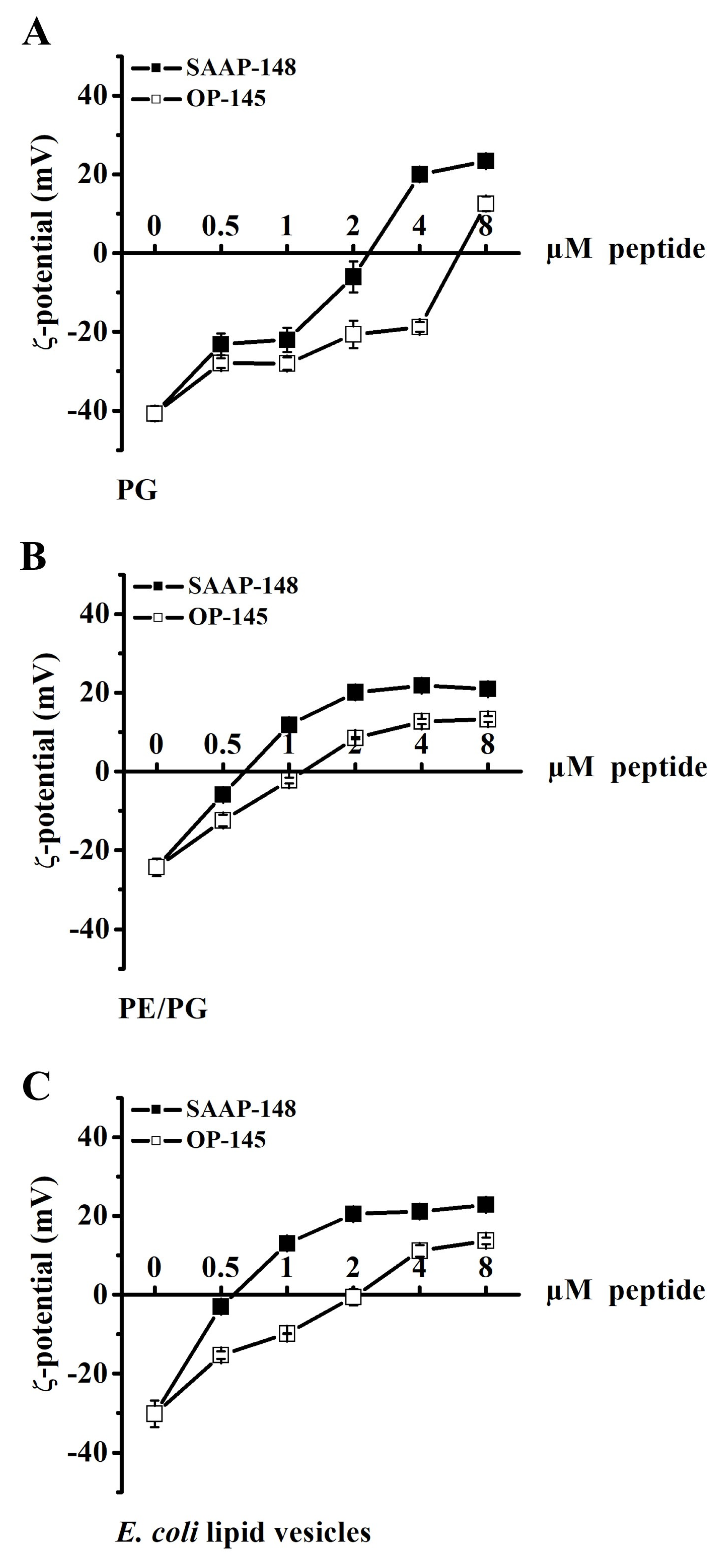
3.3. Antimicrobial Peptides Neutralize the Surface Charge of Model Membranes
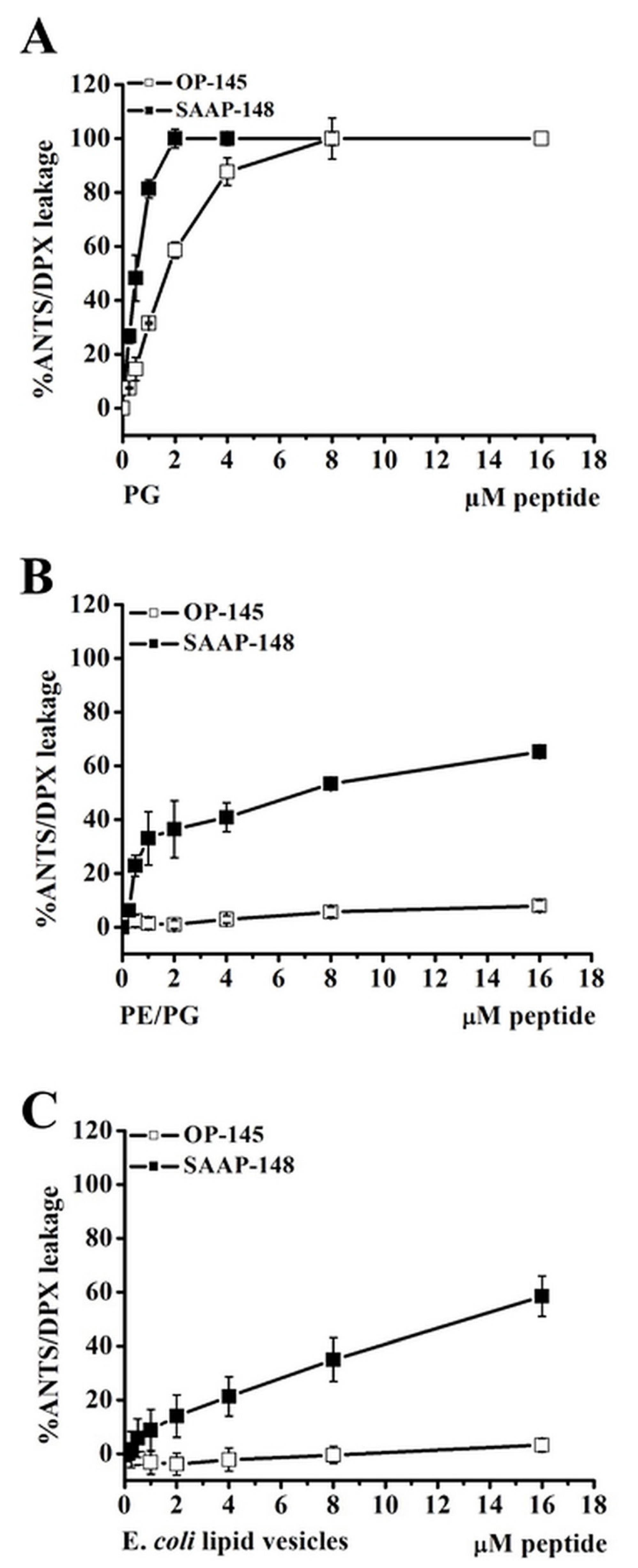
3.4. Antimicrobial Peptides Disrupt Efficiently Anionic Membranes, but Not Less Anionic Membranes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Murray, C.J.L.; Ikuta, K.S.; Sharara, F.; Swetschinski, L.; Robles Aguilar, G.; Gray, A.; Han, C.; Bisignano, C.; Rao, P.; Wool, E.; et al. Global burden of bacterial antimicrobial resistance in 2019: A systematic analysis. Lancet 2022, 399, 629–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Sun, J.; Zhou, M.; Zhou, J.; Lao, X.; Zheng, H.; Xu, H. DRAMP: A comprehensive data repository of antimicrobial peptides. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hancock, R.E.; Patrzykat, A. Clinical development of cationic antimicrobial peptides: From natural to novel antibiotics. Curr. Drug Targets. Infect. Disord. 2002, 2, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hancock, R.E. Collateral damage. Nat. Biotechnol. 2014, 32, 66–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohner, K. Development of Novel Antimicrobial Agents: Emerging Strategies; Horizon Scientific Press: Norfold, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelova, A.; Ionov, R.; Koch, M.H.; Rapp, G. Interaction of the peptide antibiotic alamethicin with bilayer- and non-bilayer-forming lipids: Influence of increasing alamethicin concentration on the lipids supramolecular structures. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2005, 378, 93–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, J.; Sun, L.; Huang, S.; Zhu, C.; Li, P.; He, J.; Mackey, V.; Coy, D.H.; He, Q. The antimicrobial peptides and their potential clinical applications. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2019, 11, 3919–3931. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- De Breij, A.; Riool, M.; Cordfunke, R.A.; Malanovic, N.; de Boer, L.; Koning, R.I.; Ravensbergen, E.; Franken, M.; van der Heijde, T.; Boekema, B.K.; et al. The antimicrobial peptide SAAP-148 combats drug-resistant bacteria and biofilms. Sci. Transl. Med. 2018, 10, eaan4044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malanovic, N.; Lohner, K. Gram-positive bacterial cell envelopes: The impact on the activity of antimicrobial peptides. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2016, 1858, 936–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheinpflug, K.; Krylova, O.; Nikolenko, H.; Thurm, C.; Dathe, M. Evidence for a novel mechanism of antimicrobial action of a cyclic R-,W-rich hexapeptide. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0125056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avdulov, N.A.; Chochina, S.V.; Igbavboa, U.; Warden, C.S.; Vassiliev, A.V.; Wood, W.G. Lipid binding to amyloid beta-peptide aggregates: Preferential binding of cholesterol as compared with phosphatidylcholine and fatty acids. J. Neurochem. 2005, 69, 1746–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Koh, J.-J.; Liu, S.; Lakshminarayanan, R.; Verma, C.S.; Beuerman, R.W. Membrane Active Antimicrobial Peptides: Translating Mechanistic Insights to Design. Front. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malanovic, N.; Lohner, K. Antimicrobial Peptides Targeting Gram-Positive Bacteria. Pharmaceuticals 2016, 9, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres, M.D.T.; Sothiselvam, S.; Lu, T.K.; La Fuente-Nunez, C.d. Peptide Design Principles for Antimicrobial Applications. J. Mol. Biol. 2019, 431, 3547–3567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melo, M.N.; Ferre, R.; Castanho, M.A.R.B. Antimicrobial peptides: Linking partition, activity and high membrane-bound concentrations. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2009, 7, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melo, M.N.; Castanho, M.A. The Mechanism of Action of Antimicrobial Peptides: Lipid Vesicles vs. Bacteria. Front. Immunol. 2012, 3, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lohner, K. Membrane-active Antimicrobial Peptides as Template Structures for Novel Antibiotic Agents. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2017, 17, 508–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nell, M.J.; Tjabringa, G.S.; Wafelman, A.R.; Verrijk, R.; Hiemstra, P.S.; Drijfhout, J.W.; Grote, J.J. Development of novel LL-37 derived antimicrobial peptides with LPS and LTA neutralizing and antimicrobial activities for therapeutic application. Peptides 2006, 27, 649–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piller, P.; Wolinski, H.; Cordfunke, R.A.; Drijfhout, J.W.; Keller, S.; Lohner, K.; Malanovic, N. Membrane Activity of LL-37 Derived Antimicrobial Peptides against Enterococcus hirae: Superiority of SAAP-148 over OP-145. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malanovic, N.; Leber, R.; Schmuck, M.; Kriechbaum, M.; Cordfunke, R.A.; Drijfhout, J.W.; de Breij, A.; Nibbering, P.H.; Kolb, D.; Lohner, K. Phospholipid-driven differences determine the action of the synthetic antimicrobial peptide OP-145 on Gram-positive bacterial and mammalian membrane model systems. Biochim. Biophyica Acta 2015, 1848, 2437–2447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ridyard, K.E.; Overhage, J. The Potential of Human Peptide LL-37 as an Antimicrobial and Anti-Biofilm Agent. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagaoka, I.; Tamura, H.; Reich, J. Therapeutic Potential of Cathelicidin Peptide LL-37, an Antimicrobial Agent, in a Murine Sepsis Model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sevcsik, E.; Pabst, G.; Jilek, A.; Lohner, K. How lipids influence the mode of action of membrane-active peptides. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2007, 1768, 2586–2595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevcsik, E.; Pabst, G.; Richter, W.; Danner, S.; Amenitsch, H.; Lohner, K. Interaction of LL-37 with model membrane systems of different complexity: Influence of the lipid matrix. Biophys. J. 2008, 94, 4688–4699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boaretti, M.; Canepari, P. Identification of daptomycin-binding proteins in the membrane of Enterococcus hirae. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1995, 39, 2068–2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snider, C.; Jayasinghe, S.; Hristova, K.; White, S.H. MPEx: A tool for exploring membrane proteins. Protein Sci. 2009, 18, 2624–2628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Leary, W.M.; Wilkinson, D.A. Gram-positive bacteria. In Microbial Lipids; Ratledge, C., Wilkinson, S.G., Eds.; Academic Press: London, UK, 1988; Volume 1, pp. 117–201. [Google Scholar]
- Malanovic, N.; Marx, L.; Blondelle, S.E.; Pabst, G.; Semeraro, E.F. Experimental concepts for linking the biological activities of antimicrobial peptides to their molecular modes of action. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Biomembr. 2020, 1862, 183275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clejan, S.; Krulwich, T.A.; Mondrus, K.R.; Seto-Young, D. Membrane lipid composition of obligately and facultatively alkalophilic strains of Bacillus spp. J. Bacteriol. 1986, 168, 334–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marx, L.; Semeraro, E.F.; Mandl, J.; Kremser, J.; Frewein, M.P.; Malanovic, N.; Lohner, K.; Pabst, G. Bridging the Antimicrobial Activity of Two Lactoferricin Derivatives in E. coli and Lipid-Only Membranes. Front. Med. Technol. 2021, 3, 625975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malanovic, N.; Ön, A.; Pabst, G.; Zellner, A.; Lohner, K. Octenidine: Novel insights into the detailed killing mechanism of Gram-negative bacteria at a cellular and molecular level. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2020, 56, 106146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leitgeb, B.; Szekeres, A.; Manczinger, L.; Vagvolgyi, C.; Kredics, L. The history of alamethicin: A review of the most extensively studied peptaibol. Chem. Biodivers. 2007, 4, 1027–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peek, N.F.A.W.; Nell, M.J.; Brand, R.; Jansen-Werkhoven, T.; Van Hoogdalem, E.J.; Verrijk, R.; Vonk, M.J.; Wafelman, A.R.; Valentijn, A.R.P.M.; Frijns, J.H.M.; et al. Ototopical drops containing a novel antibacterial synthetic peptide: Safety and efficacy in adults with chronic suppurative otitis media. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0231573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yau, W.M.; Wimley, W.C.; Gawrisch, K.; White, S.H. The preference of tryptophan for membrane interfaces. Biochemistry 1998, 37, 14713–14718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
| Antimicrobial Activity LC99.9% | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (106 CFU/mL, Napi) | (107 CFU/mL, Hepes) | |||
| Peptide | E. coli | E. hirae | E. coli | E. hirae |
| OP-145 | 6.4 µM | 3.2 µM | >51.2 µM | 51.2 µM |
| SAAP-148 | 1.6 µM | 0.4 µM | 6.4 µM | 12.8 µM |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vejzovic, D.; Piller, P.; Cordfunke, R.A.; Drijfhout, J.W.; Eisenberg, T.; Lohner, K.; Malanovic, N. Where Electrostatics Matter: Bacterial Surface Neutralization and Membrane Disruption by Antimicrobial Peptides SAAP-148 and OP-145. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 1252. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12091252
Vejzovic D, Piller P, Cordfunke RA, Drijfhout JW, Eisenberg T, Lohner K, Malanovic N. Where Electrostatics Matter: Bacterial Surface Neutralization and Membrane Disruption by Antimicrobial Peptides SAAP-148 and OP-145. Biomolecules. 2022; 12(9):1252. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12091252
Chicago/Turabian StyleVejzovic, Djenana, Paulina Piller, Robert A. Cordfunke, Jan W. Drijfhout, Tobias Eisenberg, Karl Lohner, and Nermina Malanovic. 2022. "Where Electrostatics Matter: Bacterial Surface Neutralization and Membrane Disruption by Antimicrobial Peptides SAAP-148 and OP-145" Biomolecules 12, no. 9: 1252. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12091252
APA StyleVejzovic, D., Piller, P., Cordfunke, R. A., Drijfhout, J. W., Eisenberg, T., Lohner, K., & Malanovic, N. (2022). Where Electrostatics Matter: Bacterial Surface Neutralization and Membrane Disruption by Antimicrobial Peptides SAAP-148 and OP-145. Biomolecules, 12(9), 1252. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12091252








