t6A and ms2t6A Modified Nucleosides in Serum and Urine as Strong Candidate Biomarkers of COVID-19 Infection and Severity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture and Viral Infection
2.2. Sample Preparation and LC-MS Analysis of Modified RNA Nucleosides
2.3. Automatic Sample Preparation and LC-MS Analysis for t6A and ms2t6A in Serum and Urine Samples
2.4. Patients and Severity Assessment
2.5. Statistical Analysis
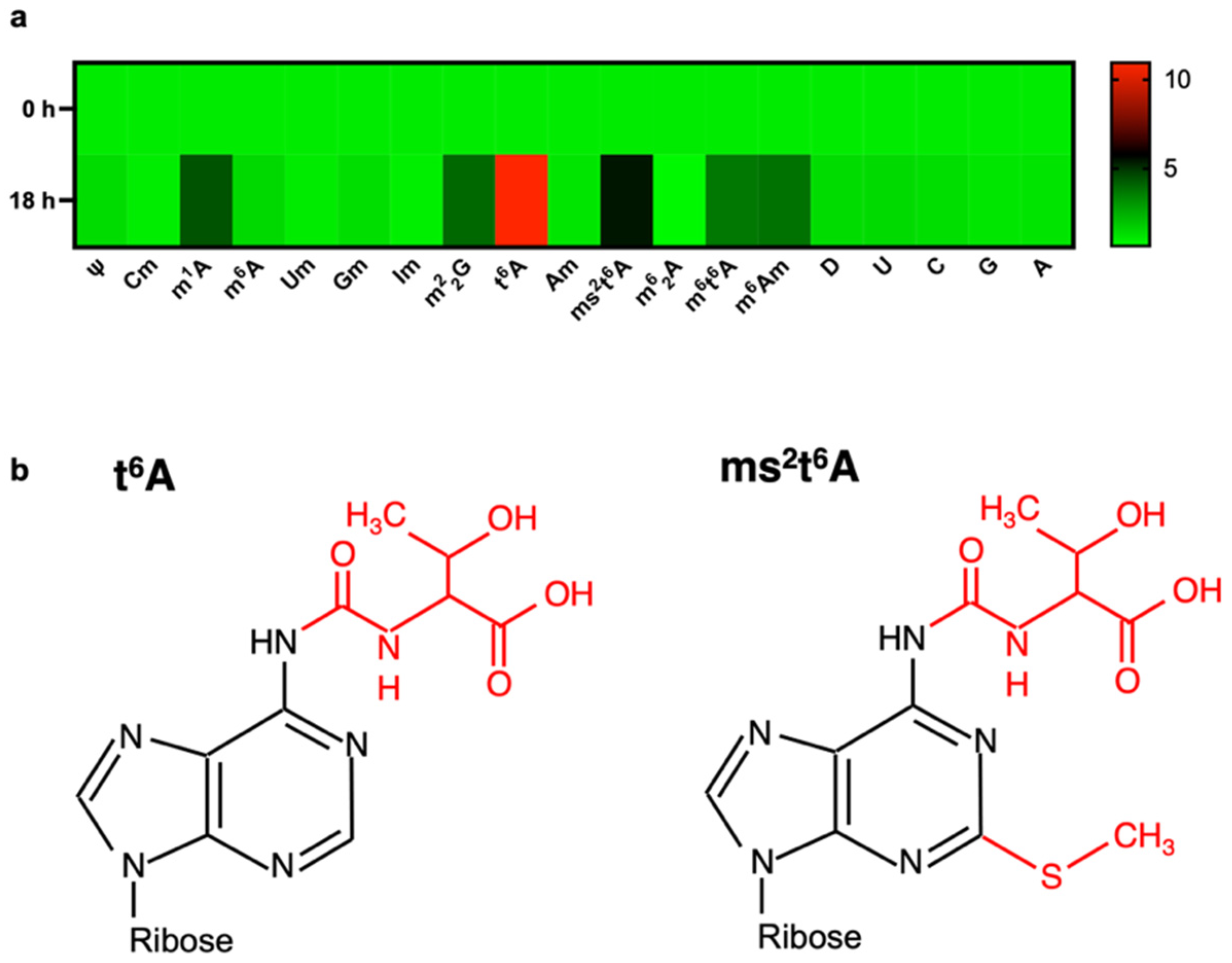
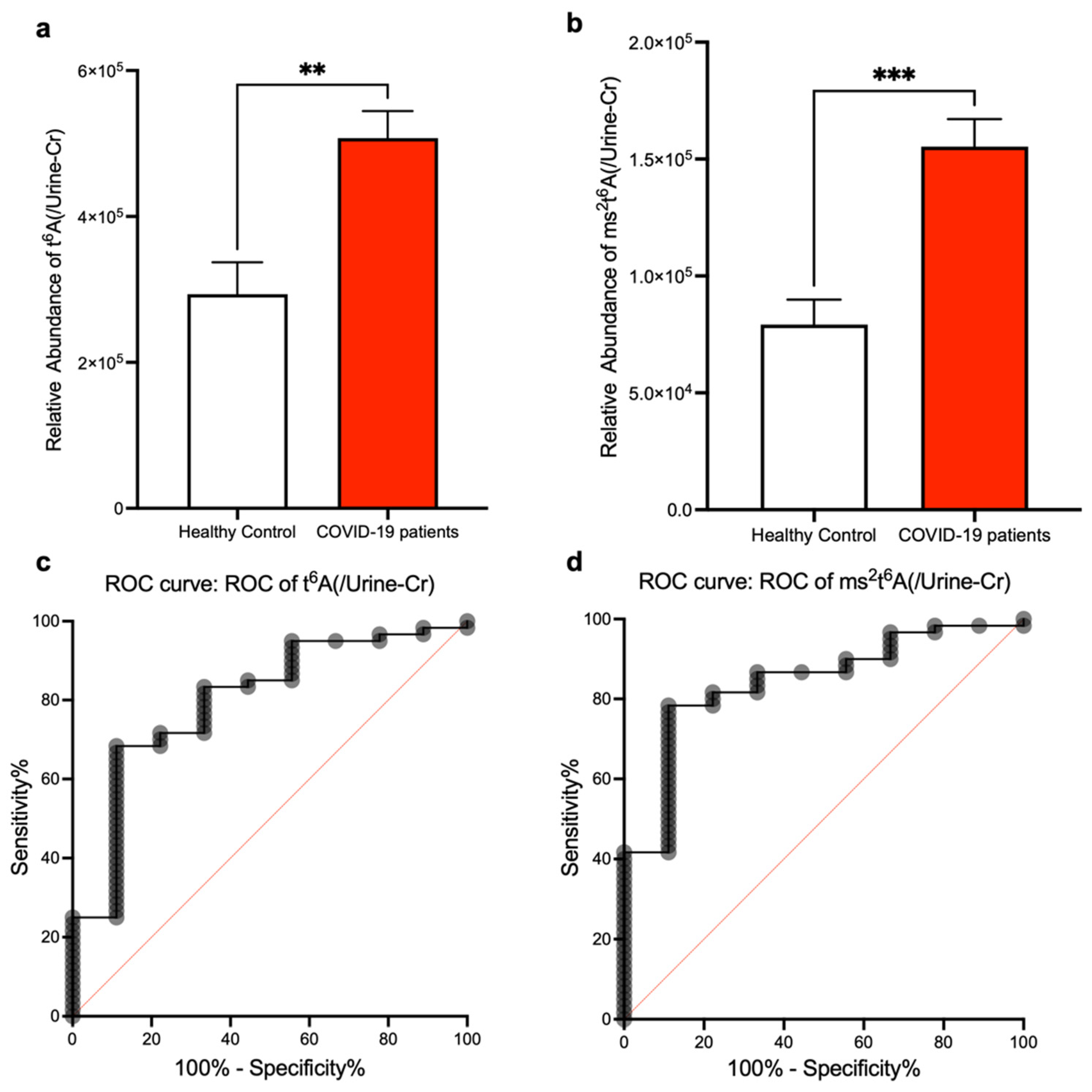
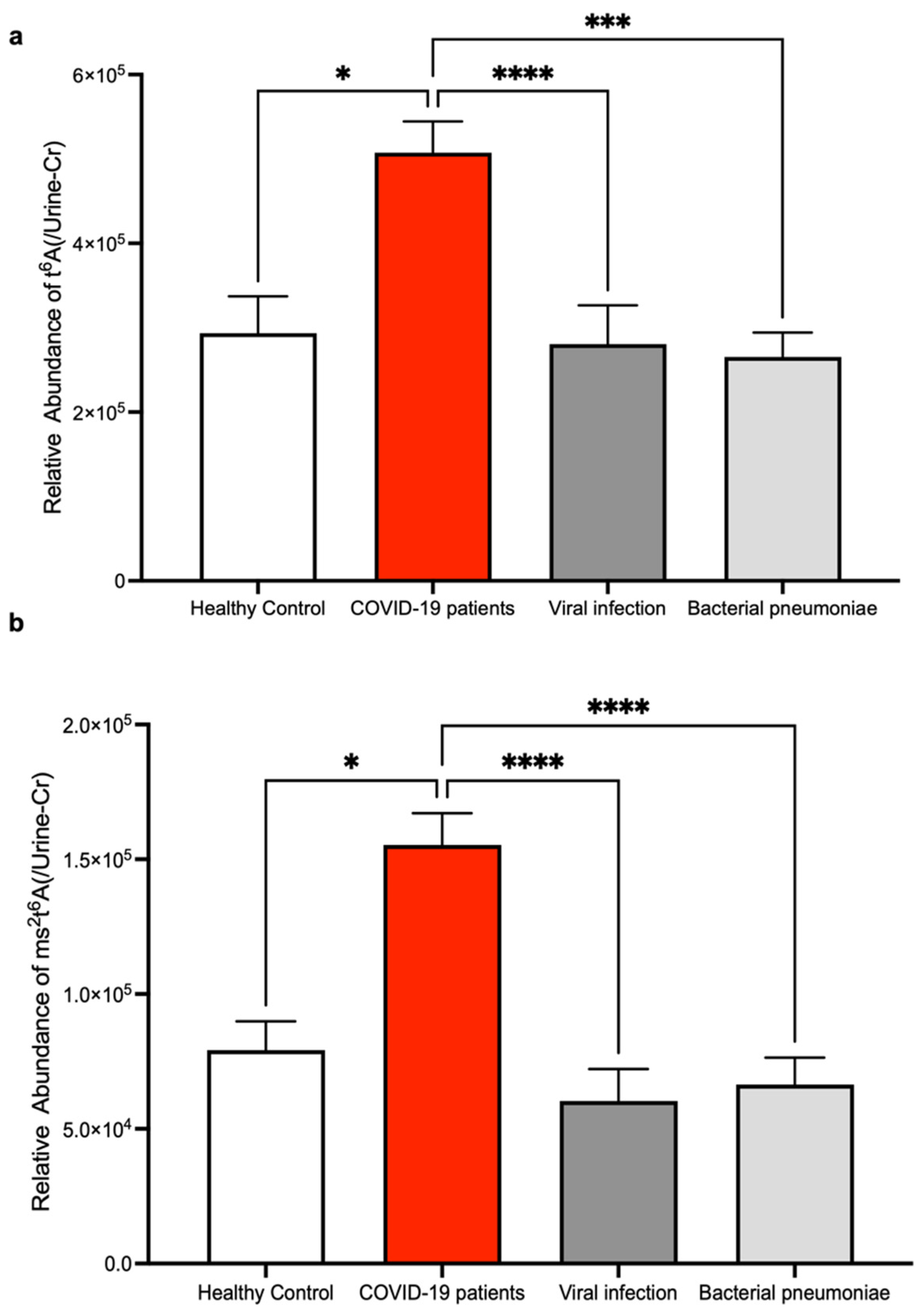
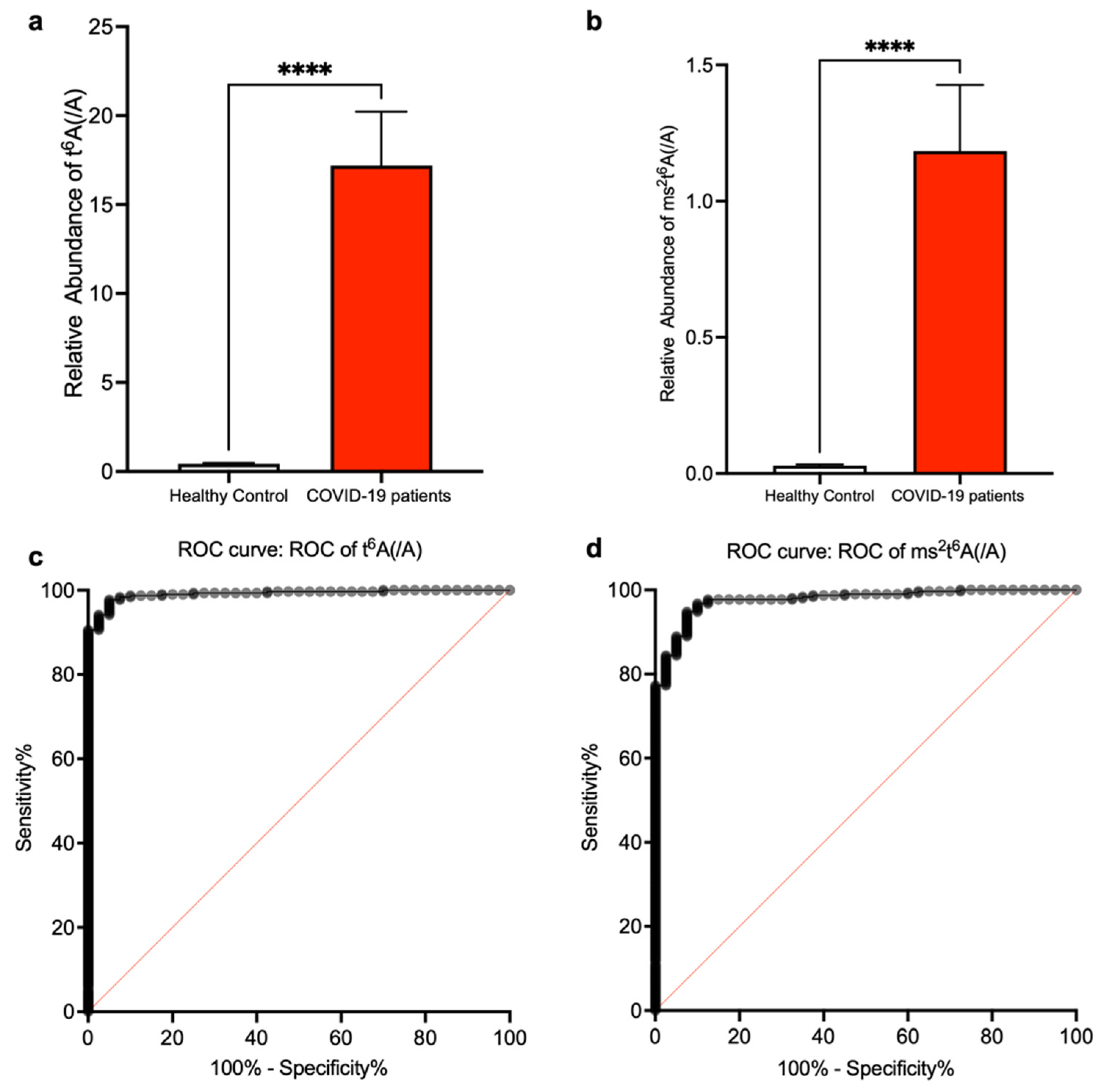
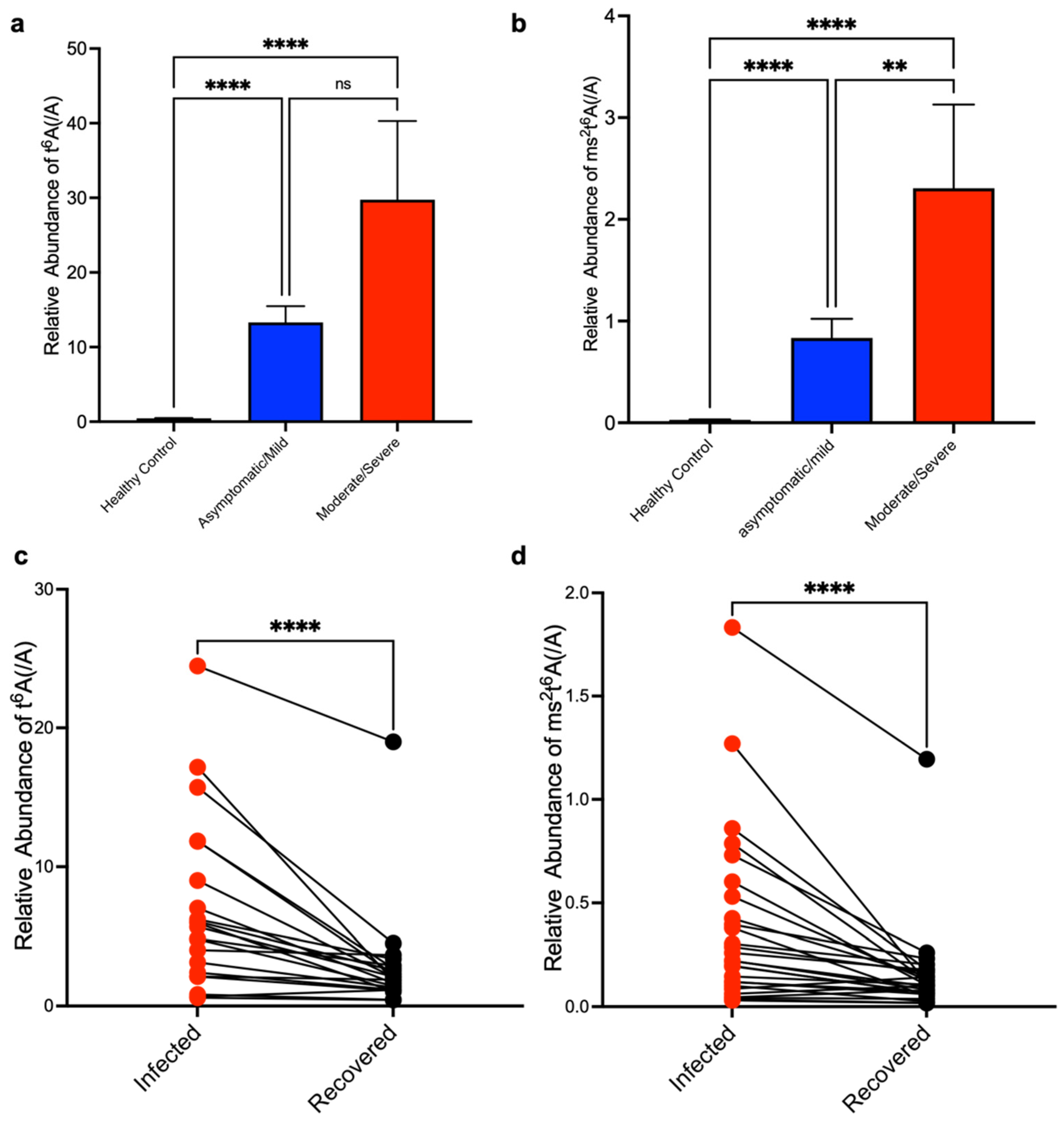
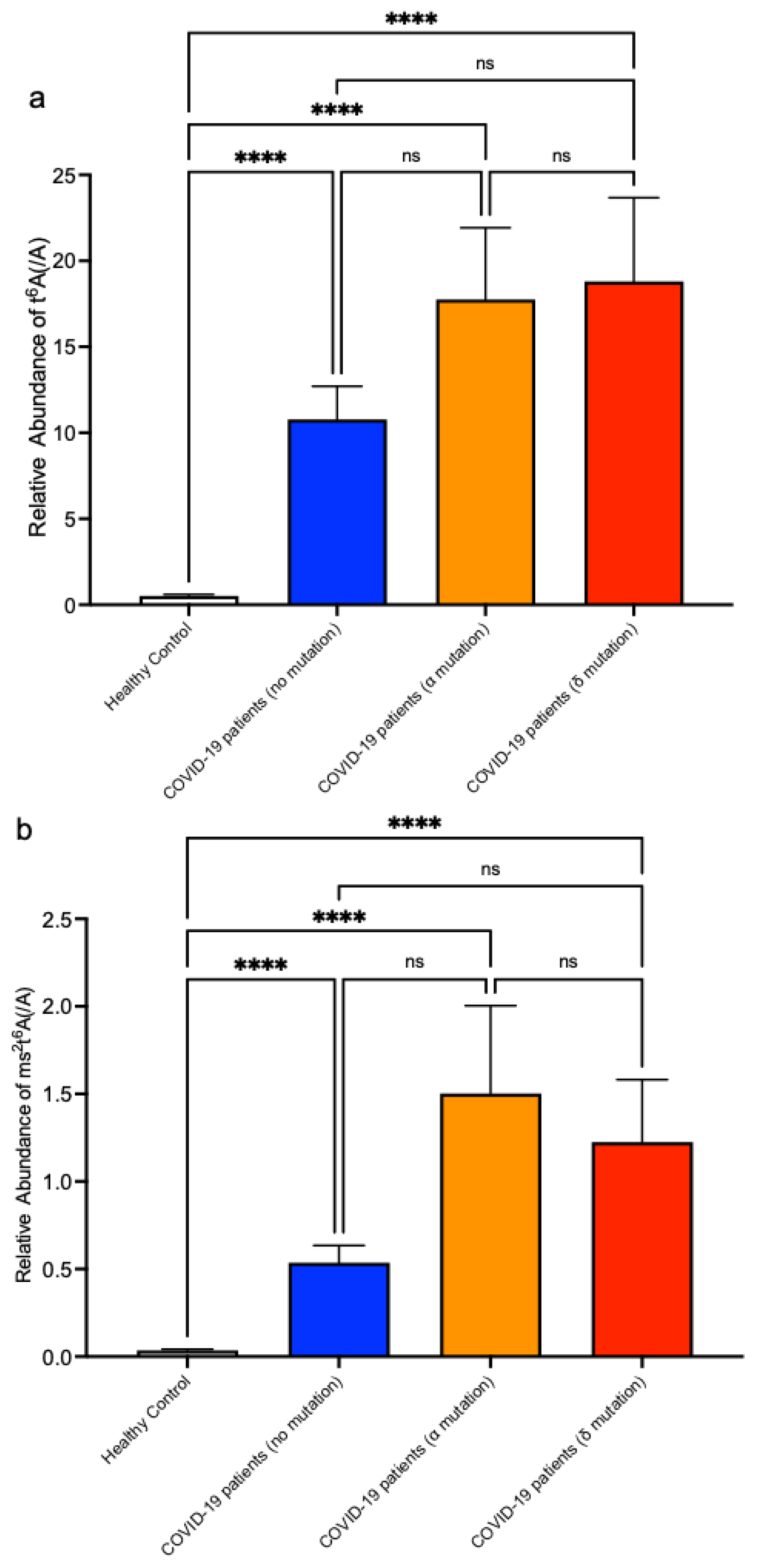
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhu, N.; Zhang, D.; Wang, W.; Li, X.; Yang, B.; Song, J.; Zhao, X.; Huang, B.; Shi, W.; Lu, R.; et al. A novel coronavirus from patients with pneumonia in China, 2019. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 727–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, P.; Yang, X.L.; Wang, X.G.; Hu, B.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, W.; Si, H.R.; Zhu, Y.; Li, B.; Huang, C.L.; et al. A pneumonia outbreak associated with a new coronavirus of probable bat origin. Nature 2020, 579, 270–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugiyama, M.; Kinoshita, N.; Ide, S.; Nomoto, H.; Nakamoto, T.; Saito, S.; Ishikane, M.; Kutsuna, S.; Hayakawa, K.; Hashimoto, M.; et al. Serum CCL17 level becomes a predictive marker to distinguish between mild/moderate and severe/critical disease in patients with COVID-19. Gene 2021, 766, 145145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renert-Yuval, Y.; Thyssen, J.P.; Bissonnette, R.; Bieber, T.; Kabashima, K.; Hijnen, D.; Guttman-Yassky, E. Biomarkers in atopic dermatitis-a review on behalf of the International Eczema Council. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2021, 147, 1174–1190.e1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, Y.; Hu, B.; Liu, Z.; Liu, K.; Jiang, H.; Li, H.; Li, R.; Luan, Y.; Liu, X.; Yu, G.; et al. No detection of SARS-CoV-2 from urine, expressed prostatic secretions, and semen in 74 recovered COVID-19 male patients: A perspective and urogenital evaluation. Andrology 2021, 9, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, X.D.; Li, Y.; Song, Y.S.; Yang, Z.Z.; Wang, P.; Wei, T.T.; Fan, T.L. Progress in research on the detection of the novel coronavirus in human samples of different groups. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2020, 24, 10879–10884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Lee, J.Y.; Yang, J.S.; Kim, J.W.; Kim, V.N.; Chang, H. The Architecture of SARS-CoV-2 Transcriptome. Cell 2020, 181, 914–921.e910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nencka, R.; Silhan, J.; Klima, M.; Otava, T.; Kocek, H.; Krafcikova, P.; Boura, E. Coronaviral RNA-methyltransferases: Function, structure and inhibition. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, 635–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boccaletto, P.; Machnicka, M.A.; Purta, E.; Piatkowski, P.; Baginski, B.; Wirecki, T.K.; de Crecy-Lagard, V.; Ross, R.; Limbach, P.A.; Kotter, A.; et al. MODOMICS: A database of RNA modification pathways. 2017 update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D303–D307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phelps, S.S.; Malkiewicz, A.; Agris, P.F.; Joseph, S. Modified nucleotides in tRNA(Lys) and tRNA(Val) are important for translocation. J. Mol. Biol. 2004, 338, 439–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrochia, L.; Guetta, D.; Hecker, A.; Forterre, P.; Basta, T. Functional assignment of KEOPS/EKC complex subunits in the biosynthesis of the universal t6A tRNA modification. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, 9484–9499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braun, D.A.; Rao, J.; Mollet, G.; Schapiro, D.; Daugeron, M.C.; Tan, W.; Gribouval, O.; Boyer, O.; Revy, P.; Jobst-Schwan, T.; et al. Mutations in KEOPS-complex genes cause nephrotic syndrome with primary microcephaly. Nat. Genet. 2017, 49, 1529–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arragain, S.; Handelman, S.K.; Forouhar, F.; Wei, F.Y.; Tomizawa, K.; Hunt, J.F.; Douki, T.; Fontecave, M.; Mulliez, E.; Atta, M. Identification of eukaryotic and prokaryotic methylthiotransferase for biosynthesis of 2-methylthio-N6-threonylcarbamoyladenosine in tRNA. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 28425–28433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, F.Y.; Suzuki, T.; Watanabe, S.; Kimura, S.; Kaitsuka, T.; Fujimura, A.; Matsui, H.; Atta, M.; Michiue, H.; Fontecave, M.; et al. Deficit of tRNA(Lys) modification by Cdkal1 causes the development of type 2 diabetes in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 3598–3608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, F.Y.; Zhou, B.; Suzuki, T.; Miyata, K.; Ujihara, Y.; Horiguchi, H.; Takahashi, N.; Xie, P.; Michiue, H.; Fujimura, A.; et al. Cdk5rap1-mediated 2-methylthio modification of mitochondrial tRNAs governs protein translation and contributes to myopathy in mice and humans. Cell Metab. 2015, 21, 428–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagayoshi, Y.; Chujo, T.; Hirata, S.; Nakatsuka, H.; Chen, C.W.; Takakura, M.; Miyauchi, K.; Ikeuchi, Y.; Carlyle, B.C.; Kitchen, R.R.; et al. Loss of Ftsj1 perturbs codon-specific translation efficiency in the brain and is associated with X-linked intellectual disability. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabf3072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chujo, T.; Tomizawa, K. Human transfer RNA modopathies: Diseases caused by aberrations in transfer RNA modifications. FEBS J. 2021, 288, 7096–7122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.L.; Fukuda, H.; Chujo, T.; Kouwaki, T.; Oshiumi, H.; Tomizawa, K.; Wei, F.Y. Export of RNA-derived modified nucleosides by equilibrative nucleoside transporters defines the magnitude of autophagy response and Zika virus replication. RNA Biol. 2021, 18, 478–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, A.; Nagiri, C.; Shihoya, W.; Inoue, A.; Kawakami, K.; Hiratsuka, S.; Aoki, J.; Ito, Y.; Suzuki, T.; Suzuki, T.; et al. N6-methyladenosine (m6A) is an endogenous A3 adenosine receptor ligand. Mol. Cell 2021, 81, 659–674.e657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, K.; Tzou, P.L.; Nouhin, J.; Gupta, R.K.; de Oliveira, T.; Kosakovsky Pond, S.L.; Fera, D.; Shafer, R.W. The biological and clinical significance of emerging SARS-CoV-2 variants. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2021, 22, 757–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fajnzylber, J.; Regan, J.; Coxen, K.; Corry, H.; Wong, C.; Rosenthal, A.; Worrall, D.; Giguel, F.; Piechocka-Trocha, A.; Atyeo, C.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 viral load is associated with increased disease severity and mortality. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singanayagam, A.; Patel, M.; Charlett, A.; Lopez Bernal, J.; Saliba, V.; Ellis, J.; Ladhani, S.; Zambon, M.; Gopal, R. Duration of infectiousness and correlation with RT-PCR cycle threshold values in cases of COVID-19, England, January to May 2020. Eurosurveill 2020, 25, 2001483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cantini, F.; Niccoli, L.; Matarrese, D.; Nicastri, E.; Stobbione, P.; Goletti, D. Baricitinib therapy in COVID-19: A pilot study on safety and clinical impact. J. Infect. 2020, 81, 318–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yokoyama, R.; Kurano, M.; Nakano, Y.; Morita, Y.; Ohmiya, H.; Kishi, Y.; Okada, J.; Qian, C.; Xia, F.; He, F.; et al. Association of the Serum Levels of the Nucleocapsid Antigen of SARS-CoV-2 with the Diagnosis, Disease Severity, and Antibody Titers in Patients with COVID-19: A Retrospective Cross-Sectional Study. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 791489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Crecy-Lagard, V.; Boccaletto, P.; Mangleburg, C.G.; Sharma, P.; Lowe, T.M.; Leidel, S.A.; Bujnicki, J.M. Matching tRNA modifications in humans to their known and predicted enzymes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, 2143–2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ringeard, M.; Marchand, V.; Decroly, E.; Motorin, Y.; Bennasser, Y. FTSJ3 is an RNA 2′-O-methyltransferase recruited by HIV to avoid innate immune sensing. Nature 2019, 565, 500–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Healthy Volunteers (N = 40) | COVID-19 Patients (N = 308) | Bacterial Infection Patients (N = 18) | Viral Infection Patients (N = 24) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age at inclusion (year 95% CI) | 28.1 (31.3–24.9) | 50.7 (52.9–48.5) | 73.2 (77.9–68.4) | 66.7 (71.9–61.4) |
| Sex | ||||
| Male (n, %) | 24 (60) | 178 (57.8) | 14 (77.8) | 13 (54.1) |
| Female (n, %) | 16 (40) | 130 (42.2) | 4 (22.2) | 11 (45.8) |
| Serum collection | 40 | 308 | - | - |
| Urine collection | 10 | 60 | 18 | 24 |
| Race | ||||
| East Asian (%) | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| COVID-19 Severity | ||||
| Asymptomatic/mild (n, %) | - | 235 (76.2) | - | - |
| Moderate/severe (n, %) | - | 73 (23.8) | - | - |
| Mutation of SARS-CoV-2 | ||||
| No mutation (n, %) | - | 51 (16.6) | - | - |
| α-mutation (n, %) | - | 80 (26) | - | - |
| δ-mutation (n, %) | - | 177 (57.4) | - | - |
| CKD patients (eGFR < 60) (n, %) | - | 69 (20.6) | 9 (50) | 9 (37.5) |
| WBC (/μL) (95% CI) | - | 5675.1 (5318.7–6033.2) | 10.375 (3570–26,980) | 6314.1 (3110–9660) |
| Lymphocyte (%) (95% CI) | - | 22.8 (21.3–24.2) | ||
| LDH (U/L) (95% CI) | - | 247.8 (232.1–263.5) | - | - |
| CRP (mg/dL) (95% CI) | - | 2.979 (2.41–3.54) | 9.17 (0.19–23.02) | 1.17 (0.02–3.53) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nagayoshi, Y.; Nishiguchi, K.; Yamamura, R.; Chujo, T.; Oshiumi, H.; Nagata, H.; Kaneko, H.; Yamamoto, K.; Nakata, H.; Sakakida, K.; et al. t6A and ms2t6A Modified Nucleosides in Serum and Urine as Strong Candidate Biomarkers of COVID-19 Infection and Severity. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 1233. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12091233
Nagayoshi Y, Nishiguchi K, Yamamura R, Chujo T, Oshiumi H, Nagata H, Kaneko H, Yamamoto K, Nakata H, Sakakida K, et al. t6A and ms2t6A Modified Nucleosides in Serum and Urine as Strong Candidate Biomarkers of COVID-19 Infection and Severity. Biomolecules. 2022; 12(9):1233. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12091233
Chicago/Turabian StyleNagayoshi, Yu, Kayo Nishiguchi, Ryosuke Yamamura, Takeshi Chujo, Hiroyuki Oshiumi, Hiroko Nagata, Hitomi Kaneko, Keiichi Yamamoto, Hirotomo Nakata, Korin Sakakida, and et al. 2022. "t6A and ms2t6A Modified Nucleosides in Serum and Urine as Strong Candidate Biomarkers of COVID-19 Infection and Severity" Biomolecules 12, no. 9: 1233. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12091233
APA StyleNagayoshi, Y., Nishiguchi, K., Yamamura, R., Chujo, T., Oshiumi, H., Nagata, H., Kaneko, H., Yamamoto, K., Nakata, H., Sakakida, K., Kunisawa, A., Adachi, M., Kakizoe, Y., Mizobe, T., Kuratsu, J.-i., Shimada, S., Nakamori, Y., Matsuoka, M., Mukoyama, M., ... Tomizawa, K. (2022). t6A and ms2t6A Modified Nucleosides in Serum and Urine as Strong Candidate Biomarkers of COVID-19 Infection and Severity. Biomolecules, 12(9), 1233. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12091233






