Alleviating Heavy Metal Toxicity in Milk and Water through a Synergistic Approach of Absorption Technique and High Voltage Atmospheric Cold Plasma and Probable Rheological Changes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Preparation
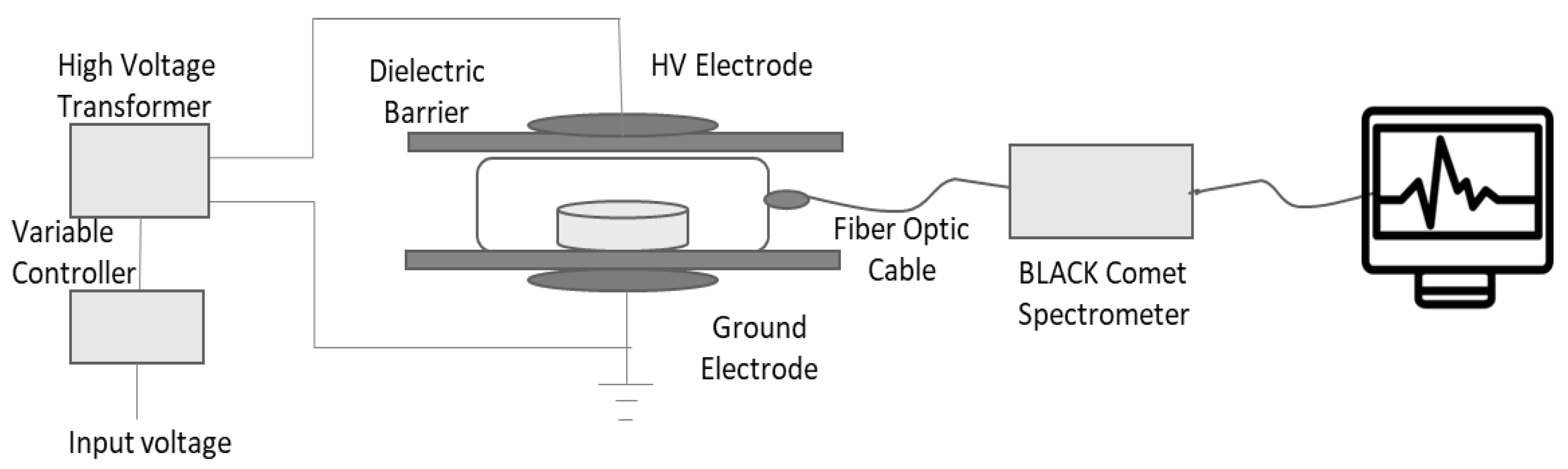
2.2. Cold Plasma Treatment
2.3. pH and Ozone Concentration Test
2.4. Optical Emission Spectroscopy (OES) Analysis
2.5. Colorimeter Test
2.6. Rheological Analysis (Frequency Sweep)
2.7. Sample Digestion and Metal Analysis
2.8. Fourier-Transform Infrared (FTIR) Analysis
2.9. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Optical Emission Spectroscopy (OES) Analysis
3.2. Ozone and pH Assay
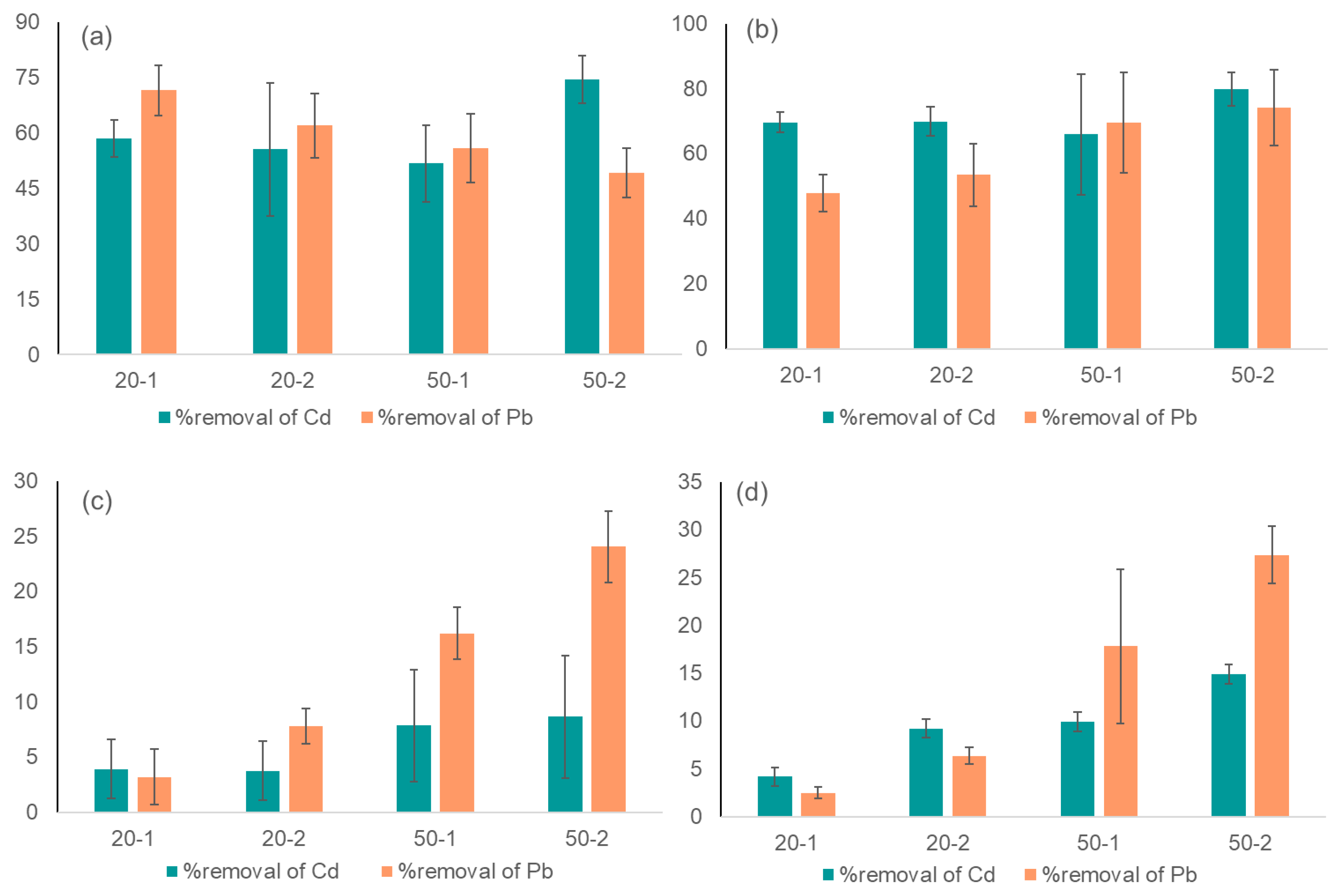
3.3. Heavy Metal Concentration
3.4. Changes in Color of the Milk Samples
3.5. Rheological Properties
3.6. FTIR Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Martinez-Finley, E.; Chakraborty, S.; Fretham, S.J.B.; Aschner, M. Cellular transport and homeostasis of essential and nonessential metals. Met. Integr. Biometal Sci. 2012, 4, 593–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anyanwu, B.O.; Ezejiofor, A.N.; Igweze, Z.N.; Orisakwe, O.E. Heavy Metal Mixture Exposure and Effects in Developing Nations: An Update. Toxics 2018, 6, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rai, P.K.; Lee, S.S.; Zhang, M.; Tsang, Y.F.; Kim, K. Heavy metals in food crops: Health risks, fate, mechanisms, and management. Environ. Int. 2019, 125, 365–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morais, S. Heavy Metals and Human Health; Garcia e Costa, F., Ed.; Environmental Health, IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2012; 10p. [Google Scholar]
- Jolly, Y.N.; Surovi, S.A.; Rahman, S.M.M.; Kabir, J.; Akter, S.; Mamun, K.M.; Rahman, A. A Probabilistic-Deterministic Approach towards Human Health Risk Assessment and Source Apportionment of Potentially Toxic Elements (PTEs) in Some Contaminated Fish Species. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2022, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habib, M.R.; Hoque, M.M.; Kabir, J.; Akhter, S.; Rahman, M.S.; Moore, J.; Jolly, Y.N. A comparative study of heavy metal exposure risk from the consumption of some common species of cultured and captured fishes of Bangladesh. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2022, 108, 104455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Hwang, J.; Lee, H.; Kim, T.; Choi, J.; Gang, G. Effects of food processing methods on migration of heavy metals to food. Appl. Biol. Chem. 2019, 62, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, J.N. Effects of processing of heavy metal content of foods. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 1999, 459, 195–211. [Google Scholar]
- Hussain, A. Removal of Heavy Metals from Wastewater by Adsorption; Heavy Metals; Madan, S., Ed.; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2021; 10p. [Google Scholar]
- WHO (World Health Organization). Mercury and Health. 2017. Available online: https://www.who.int/ipcs/assessment/public_health/chemicals_phc/en/ (accessed on 12 March 2021).
- Islam, G.M.; Habib, M.R.; Waid, J.L.; Rahman, M.S.; Kabir, J.; Akter, S.; Jolly, Y.N. Heavy metal contamination of freshwater prawn (Macrobrachium rosenbergii) and prawn feed in Bangladesh: A market-based study to highlight probable health risks. Chemosphere 2017, 170, 282–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolly, Y.N.; Iqbal, S.; Rahman, M.S.; Kabir, J.; Akter, S.; Ahmad, I. Energy dispersive X-ray fluorescence detection of heavy metals in Bangladesh cows’ milk. Heliyon 2017, 3, e00403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junejo, S.H.; Baig, J.A.; Kazi, T.G.; Afridi, H.I. Cadmium and Lead Hazardous Impact Assessment of Pond Fish Species. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2019, 191, 502–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USDA (United States Department of Agriculture). Soybean Productions by Year, US. United States Department of Agriculture-National Agricultural Statistics Service (USDA-NASS). 2019. Available online: https://www.nass.usda.gov/Charts_and_Maps/Field_Crops/soyprod.php (accessed on 19 January 2020).
- Liu, K. Chemistry and Nutritional Value of Soybean Components. In Soybeans: Chemistry, Technology, and Utilization; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1997; pp. 25–113. [Google Scholar]
- Sheng-quan, Y.; Si-yuan, G.; Yi-gang, Y.; Hui, W. Han-Rui Removal of the heavy metal ion Cr(VI) by soybean hulls in dyehouse wastewater treatment. Null 2012, 42, 197–201. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, U. Agricultural products and by-products as a low cost adsorbent for heavy metal removal from water and wastewater: A review. Sci. Res. Essay 2006, 1, 33. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, F.; Zhang, B.; Han, D.; Wu, L.; Hou, W. Preparation of composite soybean straw-based materials by LDHs modifying as a solid sorbent for removal of Pb(ii) from water samples. Open Chem. 2021, 19, 726–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaur, N.; Kukreja, A.; Yadav, M.; Tiwari, A. Adsorptive removal of lead and arsenic from aqueous solution using soya bean as a novel biosorbent: Equilibrium isotherm and thermal stability studies. Appl. Water Sci. 2018, 8, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arjunan, K.P.; Sharma, V.K.; Ptasinska, S. Effects of Atmospheric Pressure Plasmas on Isolated and Cellular DNA—A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 2971–3016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misra, N.N.; Yepez, X.; Xu, L.; Keener, K. In-package cold plasma technologies. J. Food Eng. 2019, 244, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chizoba Ekezie, F.; Sun, D.; Cheng, J. A review on recent advances in cold plasma technology for the food industry: Current applications and future trends. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 69, 46–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahanta, S.; Habib, M.R.; Moore, J.M. Effect of High-Voltage Atmospheric Cold Plasma Treatment on Germination and Heavy Metal Uptake by Soybeans (Glycine max). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misra, N.N.; Schlüter, O.; Cullen, P.J. Chapter 1—Plasma in Food and Agriculture. In Cold Plasma in Food and Agriculture; Misra, N.N., Schlüter, O., Cullen, P.J., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2016; pp. 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Mohamed, A.H.; Al Shariff, S.M.; Ouf, S.A.; Benghanem, M. Atmospheric pressure plasma jet for bacterial decontamination and property improvement of fruit and vegetable processing wastewater. J. Phys. D 2016, 49, 195401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yepez, X.V.; Keener, K.M. High-voltage Atmospheric Cold Plasma (HVACP) hydrogenation of soybean oil without trans-fatty acids. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2016, 38, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klockow, P.A.; Keener, K.M. Safety and quality assessment of packaged spinach treated with a novel ozone-generation system. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2009, 42, 1047–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connolly, J.; Valdramidis, V.P.; Byrne, E.; Karatzas, K.A.; Cullen, P.J.; Keener, K.M.; Mosnier, J.P. Characterization and antimicrobial efficacy againstE. coliof a helium/air plasma at atmospheric pressure created in a plastic package. J. Phys. D 2012, 46, 035401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herron, J.T.; Green, D.S. Chemical Kinetics Database and Predictive Schemes for Nonthermal Humid Air Plasma Chemistry. Part II. Neutral Species Reactions. Plasma Chem. Plasma Process. 2001, 21, 459–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadjistamov, D. Oscillatory measurements of silicone oils—Loss and storage modulus master curves. Rheol. Acta 1996, 35, 364–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weitz, D.; Wyss, H.; Larsen, R. Oscillatory Rheology Measuring the Viscoelastic Behaviour of Soft Materials. I.T. Lab. J. 2007, 111, 68–70. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Dan, Y.; Shi, H.; Ma, X. Elucidating the mechanisms for plant uptake and in-planta speciation of cerium in radish (Raphanus sativus L.) treated with cerium oxide nanoparticles. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 572–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Sun, W.; Zhang, S.; Sharifan, H.; Ma, X. Elucidating the Effects of Cerium Oxide Nanoparticles and Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles on Arsenic Uptake and Speciation in Rice (Oryza sativa) in a Hydroponic System. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 10040–10047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misra, N.N.; Keener, K.M.; Bourke, P.; Mosnier, J.; Cullen, P.J. In-package atmospheric pressure cold plasma treatment of cherry tomatoes. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2014, 118, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, L.; Hinkle, K. An Infrared Line List for C i. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 2007, 169, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Battino, R.; Rettich, T.R.; Tominaga, T. The Solubility of Oxygen and Ozone in Liquids. J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data 1983, 12, 163–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cataldo, F. On the action of ozone on proteins. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2003, 82, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Luo, Y.; Zhao, F.; Mu, G. Influence of dielectric barrier discharge cold plasma on physicochemical property of milk for sterilization. Plasma Process. Polym. 2021, 18, 1900219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, H.; Dong, S.; Han, F.; Li, Y.; Chen, G.; Li, L.; Chen, Y. Effects of Dielectric Barrier Discharge (DBD) Cold Plasma Treatment on Physicochemical and Functional Properties of Peanut Protein. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2018, 11, 344–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikari, B.; Adhikari, M.; Ghimire, B.; Park, G.; Choi, E.H. Cold Atmospheric Plasma-Activated Water Irrigation Induces Defense Hormone and Gene expression in Tomato seedlings. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinaga, H.; Bansal, N.; Bhandari, B. Effects of milk pH alteration on casein micelle size and gelation properties of milk. Int. J. Food Prop. 2017, 20, 179–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubino, F.M. Toxicity of Glutathione-Binding Metals: A Review of Targets and Mechanisms. Toxics 2015, 3, 20–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobbett, C.S. Phytochelatins and Their Roles in Heavy Metal Detoxification. Plant Physiol. 2000, 123, 825–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matzapetakis, M.; Ghosh, D.; Weng, T.; Penner-Hahn, J.; Pecoraro, V.L. Peptidic models for the binding of Pb(II), Bi(III) and Cd(II) to mononuclear thiolate binding sites. JBIC J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 2006, 11, 876–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, C.T.; Boulanger, Y.; Fesik, S.W.; Armitage, I.M. NMR analysis of the structure and metal sequestering properties of metallothioneins. Environ. Health Perspect. 1984, 54, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juan, C.A.; Pérez de la Lastra, J.M.; Plou, F.J.; Pérez-Lebeña, E. The Chemistry of Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) Revisited: Outlining Their Role in Biological Macromolecules (DNA, Lipids and Proteins) and Induced Pathologies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brzóska, M.M.; Moniuszko-Jakoniuk, J. Interactions between cadmium and zinc in the organism. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2001, 39, 967–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schelkopf, C.S.; Rice, E.A.; Swenson, J.K.; Hess, A.M.; Geornaras, I.; Belk, K.E.; Nair, M.N. Nix Pro Color Sensor provides comparable color measurements to HunterLab colorimeter for fresh beef. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 58, 3661–3665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurol, C.; Ekinci, F.Y.; Aslan, N.; Korachi, M. Low Temperature Plasma for decontamination of E. coli in milk. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2012, 157, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikmaram, N.; Keener, K.M. The effects of cold plasma technology on physical, nutritional, and sensory properties of milk and milk products. LWT 2022, 154, 112729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, N.; Barbano, D.M.; Drake, M.A. Hunter versus CIE color measurement systems for analysis of milk-based beverages. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 4891–4905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Yong, H.I.; Park, S.; Kim, K.; Choe, W.; Jo, C. Microbial safety and quality attributes of milk following treatment with atmospheric pressure encapsulated dielectric barrier discharge plasma. Food Control 2015, 47, 451–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milovanovic, B.; Djekic, I.; Miocinovic, J.; Djordjevic, V.; Lorenzo, J.M.; Barba, F.J.; Mörlein, D.; Tomasevic, I. What Is the Color of Milk and Dairy Products and How Is It Measured? Foods 2020, 9, 1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manoharan, D.; Stephen, J.; Radhakrishnan, M. Study on low-pressure plasma system for continuous decontamination of milk and its quality evaluation. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2021, 45, e15138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagoner, T.B.; Çakır-Fuller, E.; Shingleton, R.; Drake, M.; Foegeding, E.A. Viscosity drives texture perception of protein beverages more than hydrocolloid type. J. Texture Stud. 2020, 51, 78–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, W. Use of Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) Spectroscopy to Determine the Health-Promoting Index (HPI) of Cow’s Milk; Iowa State University: Ames, IA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Inon, F.A.; Garrigues, S.; de la Guardia, M. Nutritional parameters of commercially available milk samples by FTIR and chemometric techniques. Anal. Chim. Acta 2004, 513, 401–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salleh, N.A.; Selamat, J.; Meng, G.Y.; Abas, F.; Jambari, N.N.; Khatib, A. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy and multivariate analysis of milk from different goat breeds. Int. J. Food Prop. 2019, 22, 1673–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lingegowda, D.C.; Kumar, J.; Prasad, A.G.; Zarei, M.; Gopal, S. Ftir spectroscopic studies on cleome gynandra—Comparative analysis of functional group before and after extraction. Rom. J. Biophys. 2012, 22, 137–143. [Google Scholar]
- Abd-Elghany, S.M.; Zaher, H.A.; Elgazzar, M.M.; Sallam, K.I. Effect of boiling and grilling on some heavy metal residues in crabs and shrimps from the Mediterranean Coast at Damietta region with their probabilistic health risk assessment. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2020, 93, 103606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharafi, K.; Yunesian, M.; Mahvi, A.H.; Pirsaheb, M.; Nazmara, S.; Nabizadeh Nodehi, R. Advantages and disadvantages of different pre-cooking and cooking methods in removal of essential and toxic metals from various rice types-human health risk assessment in Tehran households, Iran. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 175, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, Z.; Goli, M. The effect of chelating agents including potassium tartrate and citrate on the maximum reduction of lead and cadmium during soaking and cooking from some different varieties of rice available in Iran. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 9, 5112–5118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, F. Potential Use of Agro/Food Wastes as Biosorbents in the Removal of Heavy Metals. In Emerging Contaminants; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2020; 8p. [Google Scholar]





| Parameters | Treatment Matrix * | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50 kV | 20 kV | Control ** | Total | |||||||
| Duration (min) | 1 min | 2 min | 1 min | 2min | ||||||
| Time (h) before Analysis | 0 | 24 | 0 | 24 | 0 | 24 | 0 | 24 | ||
| HM in water | 0 | 0 | 3 | 3 | ||||||
| HM in Milk | 0 | 0 | 3 | 3 | ||||||
| HM + SB + Water | 3 | 3 | 6 | 30 | ||||||
| HM + SB + Milk | 3 | 3 | 6 | 30 | ||||||
| Milk | Water | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| kV-min | Ozone (ppm) * | pH * | Ozone (ppm) * | pH * |
| Control | 0 | 6.6 | 0 | 6.3 |
| 20-1 | 10 ± 10 | 6.5 ± 0.1 | 10 ± 10 | 6.2 ± 0.1 |
| 20-2 | 20 ± 10 | 6.5 ± 0.1 | 20 ± 10 | 6.2 ± 0.1 |
| 50-1 | 320 ± 70 | 6.3 ± 0.1 | 300 ± 30 | 6.1 ± 0.1 |
| 50-2 | 500 ± 100 | 6.3 ± 0.1 | 520 ± 50 | 6.1 ± 0.1 |
| Samples ** | L * | a * | b * | ΔE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 77.88 | −1.91 | 4.79 | - |
| 50-2-24 | 71.89 | −1.67 | 2.00 | 6.61 |
| 50-1-24 | 73.25 | −1.71 | 2.58 | 5.13 |
| 20-2-24 | 71.58 | −1.56 | 2.54 | 6.70 |
| 20-1-24 | 73.54 | −1.60 | 3.31 | 4.60 |
| 50-2-0 | 73.85 | −1.89 | 2.21 | 4.79 |
| 50-1-0 | 73.16 | −1.87 | 1.89 | 5.54 |
| 20-2-0 | 74.08 | −1.85 | 2.09 | 4.66 |
| 20-1-0 | 73.86 | −1.84 | 1.92 | 4.94 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Habib, M.R.; Mahanta, S.; Jolly, Y.N.; Moore, J.M. Alleviating Heavy Metal Toxicity in Milk and Water through a Synergistic Approach of Absorption Technique and High Voltage Atmospheric Cold Plasma and Probable Rheological Changes. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 913. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12070913
Habib MR, Mahanta S, Jolly YN, Moore JM. Alleviating Heavy Metal Toxicity in Milk and Water through a Synergistic Approach of Absorption Technique and High Voltage Atmospheric Cold Plasma and Probable Rheological Changes. Biomolecules. 2022; 12(7):913. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12070913
Chicago/Turabian StyleHabib, Mohammad Ruzlan, Shikhadri Mahanta, Yeasmin Nahar Jolly, and Janie McClurkin Moore. 2022. "Alleviating Heavy Metal Toxicity in Milk and Water through a Synergistic Approach of Absorption Technique and High Voltage Atmospheric Cold Plasma and Probable Rheological Changes" Biomolecules 12, no. 7: 913. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12070913
APA StyleHabib, M. R., Mahanta, S., Jolly, Y. N., & Moore, J. M. (2022). Alleviating Heavy Metal Toxicity in Milk and Water through a Synergistic Approach of Absorption Technique and High Voltage Atmospheric Cold Plasma and Probable Rheological Changes. Biomolecules, 12(7), 913. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12070913






