Activation of the Rat α1β2ε GABAA Receptor by Orthosteric and Allosteric Agonists
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Receptors and Expression
2.2. Electrophysiology
2.3. Data Analysis
2.4. Cysteine Modification Experiments
2.5. Materials
3. Results
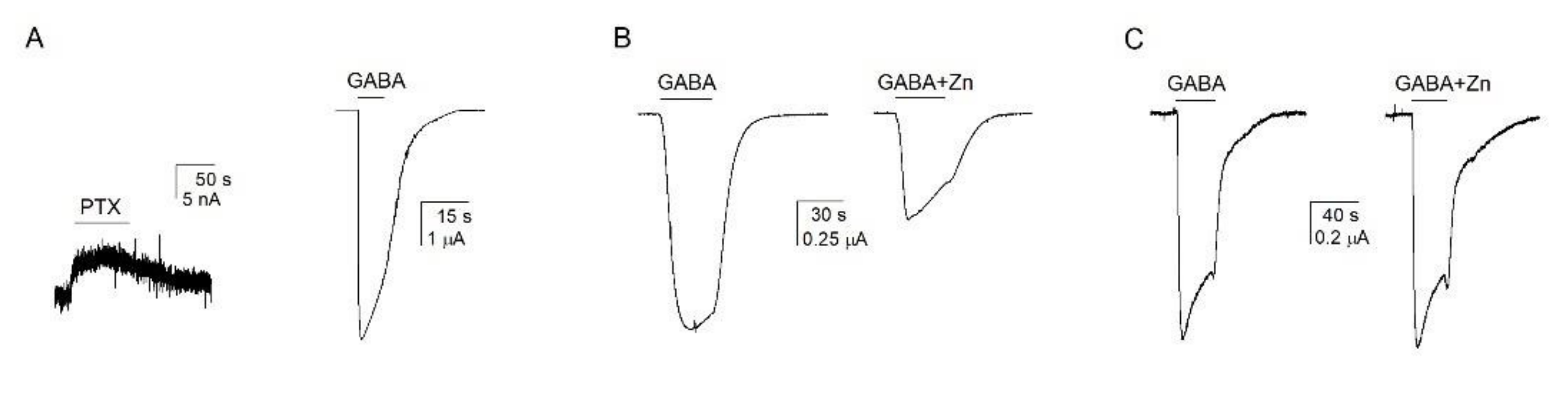
3.1. GABA Is a Weak Agonist of the α1β2ε GABAA Receptor
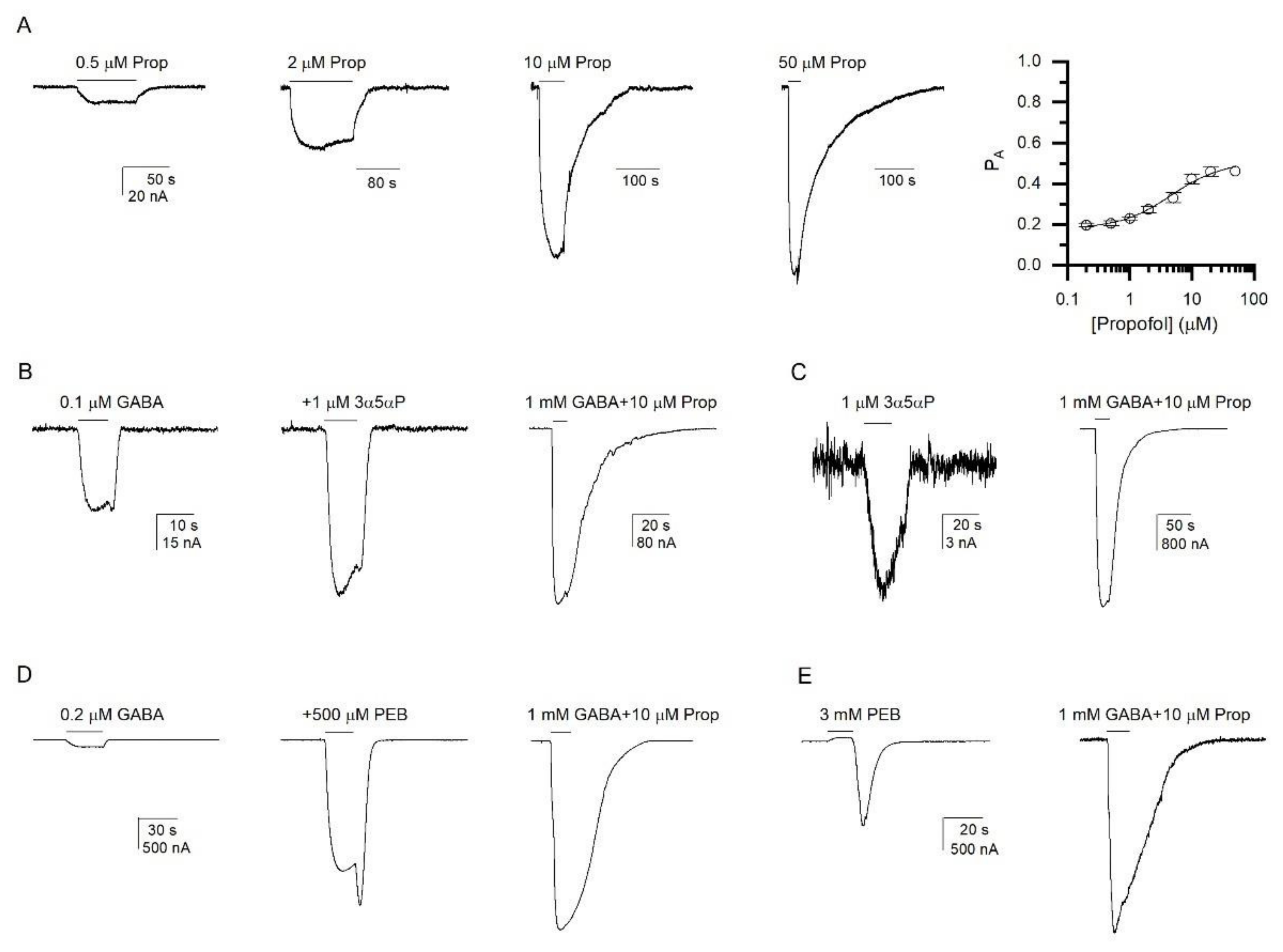
3.2. Activation of the α1β2ε GABAA Receptor by Allosteric Agonists
3.3. Changes in the Expression of ε Subunit Have Minor Effect on Receptor Function
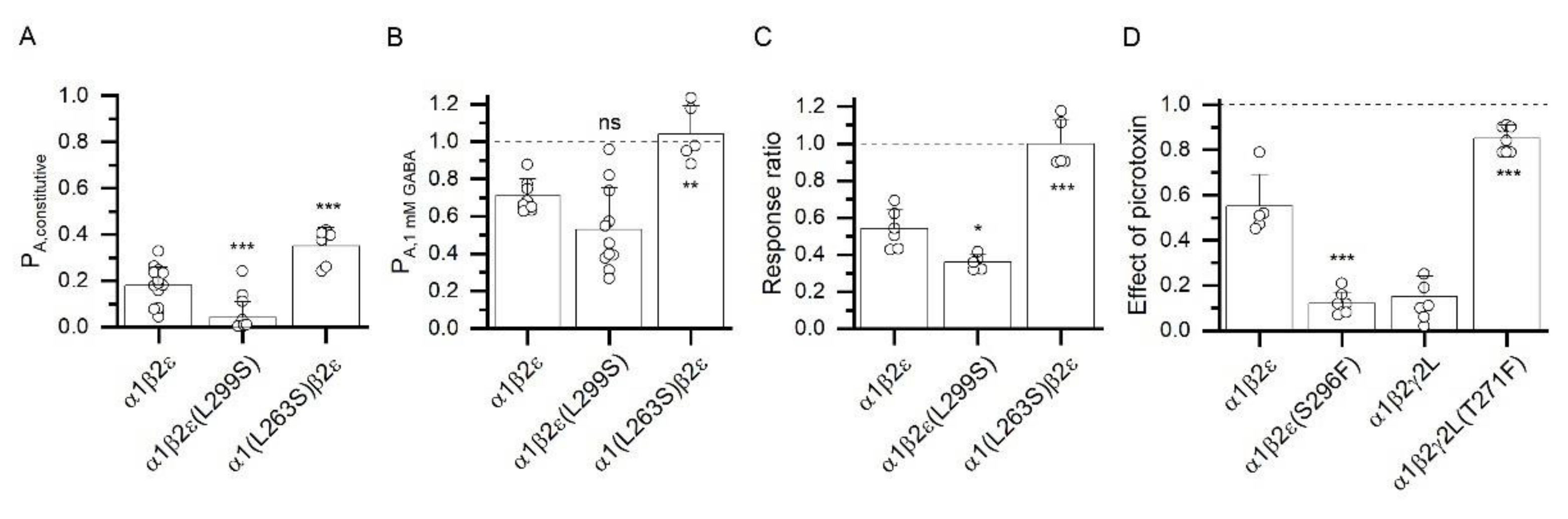
3.4. Atypical Properties of the α1β2ε Receptor
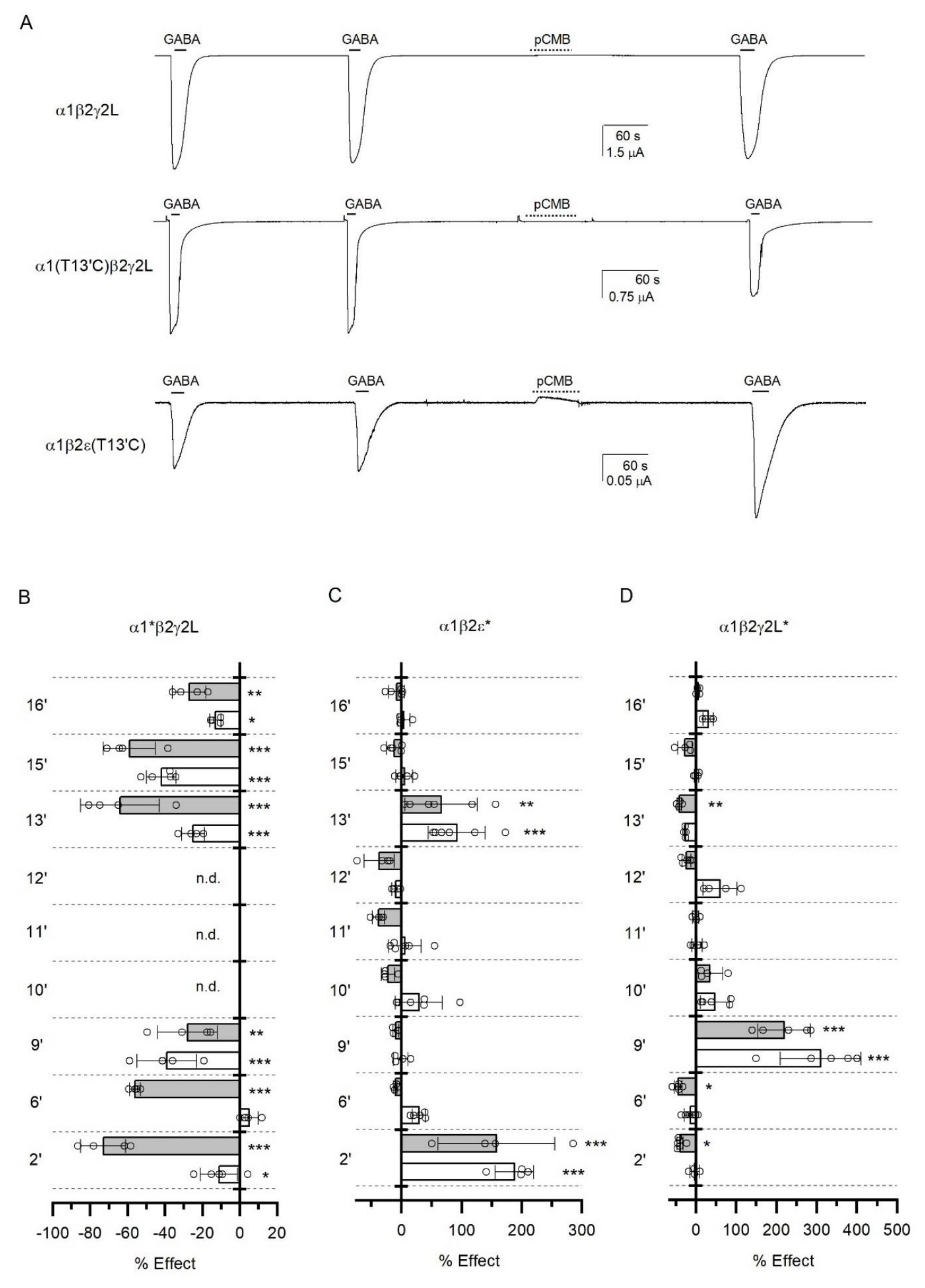
3.5. Accessibility of TM2 Residues in the ε Subunit
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Chua, H.C.; Chebib, M. GABAA Receptors and the Diversity in their Structure and Pharmacology. Adv. Pharmacol. 2017, 79, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Davies, P.A.; Hanna, M.C.; Hales, T.G.; Kirkness, E.F. Insensitivity to anaesthetic agents conferred by a class of GABAA receptor subunit. Nature 1997, 385, 820–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whiting, P.J.; McAllister, G.; Vassilatis, D.; Bonnert, T.P.; Heavens, R.P.; Smith, D.W.; Hewson, L.; O’Donnell, R.; Rigby, M.R.; Sirinathsinghji, D.J.; et al. Neuronally restricted RNA splicing regulates the expression of a novel GABAA receptor subunit conferring atypical functional properties [corrected; erratum to be published]. J. Neurosci. 1997, 17, 5027–5037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sinkkonen, S.T.; Hanna, M.C.; Kirkness, E.F.; Korpi, E.R. GABAA receptor ε and θ subunits display unusual structural variation between species and are enriched in the rat locus ceruleus. J. Neurosci. 2000, 20, 3588–3595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moragues, N.; Ciofi, P.; Lafon, P.; Odessa, M.F.; Tramu, G.; Garret, M. cDNA cloning and expression of a γ-aminobutyric acid A receptor ε-subunit in rat brain. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2000, 12, 4318–4330. [Google Scholar]
- Markus, F.; Angelini, C.; Trimouille, A.; Rudolf, G.; Lesca, G.; Goizet, C.; Lasseaux, E.; Arveiler, B.; van Slegtenhorst, M.; Brooks, A.S.; et al. Rare variants in the GABAA receptor subunit ε identified in patients with a wide spectrum of epileptic phenotypes. Mol. Genet. Genomic Med. 2020, 8, e1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neelands, T.R.; Fisher, J.L.; Bianchi, M.; Macdonald, R.L. Spontaneous and γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA)-activated GABAA receptor channels formed by ε subunit-containing isoforms. Mol. Pharmacol. 1999, 55, 168–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, B.L.; Henderson, L.P. Trafficking and potential assembly patterns of ε-containing GABAA receptors. J. Neurochem. 2007, 103, 1258–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortensen, M.; Wafford, K.A.; Wingrove, P.; Ebert, B. Pharmacology of GABAA receptors exhibiting different levels of spontaneous activity. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2003, 476, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranna, M.; Sinkkonen, S.T.; Moykkynen, T.; Uusi-Oukari, M.; Korpi, E.R. Impact of ε and θ subunits on pharmacological properties of α3β1 GABAA receptors expressed in Xenopus oocytes. BMC Pharmacol. 2006, 6, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wagner, D.A.; Goldschen-Ohm, M.P.; Hales, T.G.; Jones, M.V. Kinetics and spontaneous open probability conferred by the ε subunit of the GABAA receptor. J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 10462–10468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irnaten, M.; Walwyn, W.M.; Wang, J.; Venkatesan, P.; Evans, C.; Chang, K.S.; Andresen, M.C.; Hales, T.G.; Mendelowitz, D. Pentobarbital enhances GABAergic neurotransmission to cardiac parasympathetic neurons, which is prevented by expression of GABAA ε subunit. Anesthesiology 2002, 97, 717–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thompson, S.A.; Bonnert, T.P.; Cagetti, E.; Whiting, P.J.; Wafford, K.A. Overexpression of the GABAA receptor ε subunit results in insensitivity to anaesthetics. Neuropharmacology 2002, 43, 662–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, P.A.; McCartney, M.R.; Wang, W.; Hales, T.G.; Kirkness, E.F. Alternative transcripts of the GABAA receptor ε subunit in human and rat. Neuropharmacology 2002, 43, 467–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinbach, J.H.; Akk, G. Applying the Monod-Wyman-Changeux Allosteric Activation Model to Pseudo-Steady-State Responses from GABAA Receptors. Mol. Pharmacol. 2019, 95, 106–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Forman, S.A. Monod-Wyman-Changeux allosteric mechanisms of action and the pharmacology of etomidate. Curr. Opin. Anaesthesiol. 2012, 25, 411–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eaton, M.M.; Germann, A.L.; Arora, R.; Cao, L.Q.; Gao, X.; Shin, D.J.; Wu, A.; Chiara, D.C.; Cohen, J.B.; Steinbach, J.H.; et al. Multiple Non-Equivalent Interfaces Mediate Direct Activation of GABAA Receptors by Propofol. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2016, 14, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Akabas, M.H.; Stauffer, D.A.; Xu, M.; Karlin, A. Acetylcholine receptor channel structure probed in cysteine-substitution mutants. Science 1992, 258, 307–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Akabas, M.H. Identification of channel-lining residues in the M2 membrane-spanning segment of the GABAA receptor α1 subunit. J. Gen. Physiol. 1996, 107, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Germann, A.L.; Shin, D.J.; Manion, B.D.; Edge, C.J.; Smith, E.H.; Franks, N.P.; Evers, A.S.; Akk, G. Activation and modulation of recombinant glycine and GABAA receptors by 4-halogenated analogues of propofol. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 173, 3110–3120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Germann, A.L.; Pierce, S.R.; Senneff, T.C.; Burbridge, A.B.; Steinbach, J.H.; Akk, G. Steady-state activation and modulation of the synaptic-type α1β2γ2L GABAA receptor by combinations of physiological and clinical ligands. Physiol. Rep. 2019, 7, e14230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Akk, G.; Shin, D.J.; Germann, A.L.; Steinbach, J.H. GABA Type A Receptor Activation in the Allosteric Coagonist Model Framework: Relationship between EC50 and Basal Activity. Mol. Pharmacol. 2018, 93, 90–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rusch, D.; Zhong, H.; Forman, S.A. Gating allosterism at a single class of etomidate sites on α1β2γ2L GABAA receptors accounts for both direct activation and agonist modulation. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 20982–20992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lolait, S.J.; O’Carroll, A.M.; Kusano, K.; Muller, J.M.; Brownstein, M.J.; Mahan, L.C. Cloning and expression of a novel rat GABAA receptor. FEBS Lett. 1989, 246, 145–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smart, T.G.; Moss, S.J.; Xie, X.; Huganir, R.L. GABAA receptors are differentially sensitive to zinc: Dependence on subunit composition. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1991, 103, 1837–1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shin, D.J.; Germann, A.L.; Johnson, A.D.; Forman, S.A.; Steinbach, J.H.; Akk, G. Propofol is an allosteric agonist with multiple binding sites on concatemeric ternary GABAA receptors. Mol. Pharmacol. 2018, 93, 178–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ruesch, D.; Neumann, E.; Wulf, H.; Forman, S.A. An allosteric coagonist model for propofol effects on α1β2γ2L γ-aminobutyric acid type A receptors. Anesthesiology 2012, 116, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Germann, A.L.; Shin, D.J.; Kuhrau, C.R.; Johnson, A.D.; Evers, A.S.; Akk, G. High Constitutive Activity Accounts for the Combination of Enhanced Direct Activation and Reduced Potentiation in Mutated GABAA Receptors. Mol. Pharmacol. 2018, 93, 468–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hosie, A.M.; Wilkins, M.E.; da Silva, H.M.; Smart, T.G. Endogenous neurosteroids regulate GABAA receptors through two discrete transmembrane sites. Nature 2006, 444, 486–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bracamontes, J.; McCollum, M.; Esch, C.; Li, P.; Ann, J.; Steinbach, J.H.; Akk, G. Occupation of Either Site for the Neurosteroid Allopregnanolone Potentiates the Opening of the GABAA Receptor Induced from Either Transmitter Binding Site. Mol. Pharmacol. 2011, 80, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shin, D.J.; Germann, A.L.; Covey, D.F.; Steinbach, J.H.; Akk, G. Analysis of GABAA receptor activation by combinations of agonists acting at the same or distinct binding sites. Mol. Pharmacol. 2019, 95, 70–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Germann, A.L.; Pierce, S.R.; Tateiwa, H.; Sugasawa, Y.; Reichert, D.E.; Evers, A.S.; Steinbach, J.H.; Akk, G. Intrasubunit and Intersubunit Steroid Binding Sites Independently and Additively Mediate α1β2γ2L GABAA Receptor Potentiation by the Endogenous Neurosteroid Allopregnanolone. Mol. Pharmacol. 2021, 100, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziemba, A.M.; Forman, S.A. Correction for Inhibition Leads to an Allosteric Co-Agonist Model for Pentobarbital Modulation and Activation of α1β3γ2L GABAA Receptors. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0154031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chang, Y.; Wang, R.; Barot, S.; Weiss, D.S. Stoichiometry of a recombinant GABAA receptor. J. Neurosci. 1996, 16, 5415–5424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Patel, B.; Mortensen, M.; Smart, T.G. Stoichiometry of δ subunit containing GABAA receptors. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 171, 985–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, Y.; Weiss, D.S. Allosteric activation mechanism of the α1β2γ2 γ-aminobutyric acid type A receptor revealed by mutation of the conserved M2 leucine. Biophys. J. 1999, 77, 2542–2551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gurley, D.; Amin, J.; Ross, P.C.; Weiss, D.S.; White, G. Point mutations in the M2 region of the α, β, or γ subunit of the GABAA channel that abolish block by picrotoxin. Recept. Channels 1995, 3, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sedelnikova, A.; Erkkila, B.E.; Harris, H.; Zakharkin, S.O.; Weiss, D.S. Stoichiometry of a pore mutation that abolishes picrotoxin-mediated antagonism of the GABAA receptor. J. Physiol. 2006, 577, 569–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akk, G.; Eaton, M.; Li, P.; Zheng, S.; Lo, J.; Steinbach, J.H. Energetic contributions to channel gating of residues in the muscle nicotinic receptor β1 subunit. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e78539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Backstrom, T.; Andersson, A.; Andree, L.; Birzniece, V.; Bixo, M.; Bjorn, I.; Haage, D.; Isaksson, M.; Johansson, I.M.; Lindblad, C.; et al. Pathogenesis in menstrual cycle-linked CNS disorders. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2003, 1007, 42–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hengen, K.B.; Nelson, N.R.; Stang, K.M.; Johnson, S.M.; Crader, S.M.; Watters, J.J.; Mitchell, G.S.; Behan, M. Increased GABAA receptor ε-subunit expression on ventral respiratory column neurons protects breathing during pregnancy. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e30608. [Google Scholar]
- Belujon, P.; Baufreton, J.; Grandoso, L.; Boue-Grabot, E.; Batten, T.F.; Ugedo, L.; Garret, M.; Taupignon, A.I. Inhibitory transmission in locus coeruleus neurons expressing GABAA receptor ε subunit has a number of unique properties. J. Neurophysiol. 2009, 102, 2312–2325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sergeeva, O.A.; Andreeva, N.; Garret, M.; Scherer, A.; Haas, H.L. Pharmacological properties of GABAA receptors in rat hypothalamic neurons expressing the ε-subunit. J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hengen, K.B.; Behan, M.; Carey, H.V.; Jones, M.V.; Johnson, S.M. Hibernation induces pentobarbital insensitivity in medulla but not cortex. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2009, 297, R1028–R1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hengen, K.B.; Gomez, T.M.; Stang, K.M.; Johnson, S.M.; Behan, M. Changes in ventral respiratory column GABAaR ε- and δ-subunits during hibernation mediate resistance to depression by EtOH and pentobarbital. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2011, 300, R272–R283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pape, J.R.; Bertrand, S.S.; Lafon, P.; Odessa, M.F.; Chaigniau, M.; Stiles, J.K.; Garret, M. Expression of GABAA receptor α3-, θ-, and ε-subunit mRNAs during rat CNS development and immunolocalization of the ε subunit in developing postnatal spinal cord. Neuroscience 2009, 160, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moragues, N.; Ciofi, P.; Tramu, G.; Garret, M. Localisation of GABAA receptor ε-subunit in cholinergic and aminergic neurones and evidence for co-distribution with the θ-subunit in rat brain. Neuroscience 2002, 111, 657–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, P.A.; Kirkness, E.F.; Hales, T.G. Evidence for the formation of functionally distinct αβγε GABAA receptors. J. Physiol. 2001, 537, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boileau, A.J.; Pearce, R.A.; Czajkowski, C. The short splice variant of the γ2 subunit acts as an external modulator of GABAA receptor function. J. Neurosci 2010, 30, 4895–4903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Germann, A.L.; Burbridge, A.B.; Pierce, S.R.; Akk, G. Activation of the Rat α1β2ε GABAA Receptor by Orthosteric and Allosteric Agonists. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 868. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12070868
Germann AL, Burbridge AB, Pierce SR, Akk G. Activation of the Rat α1β2ε GABAA Receptor by Orthosteric and Allosteric Agonists. Biomolecules. 2022; 12(7):868. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12070868
Chicago/Turabian StyleGermann, Allison L., Ariel B. Burbridge, Spencer R. Pierce, and Gustav Akk. 2022. "Activation of the Rat α1β2ε GABAA Receptor by Orthosteric and Allosteric Agonists" Biomolecules 12, no. 7: 868. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12070868
APA StyleGermann, A. L., Burbridge, A. B., Pierce, S. R., & Akk, G. (2022). Activation of the Rat α1β2ε GABAA Receptor by Orthosteric and Allosteric Agonists. Biomolecules, 12(7), 868. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12070868





