Benzodiazepine Modulation of GABAA Receptors: A Mechanistic Perspective
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. A Brief History
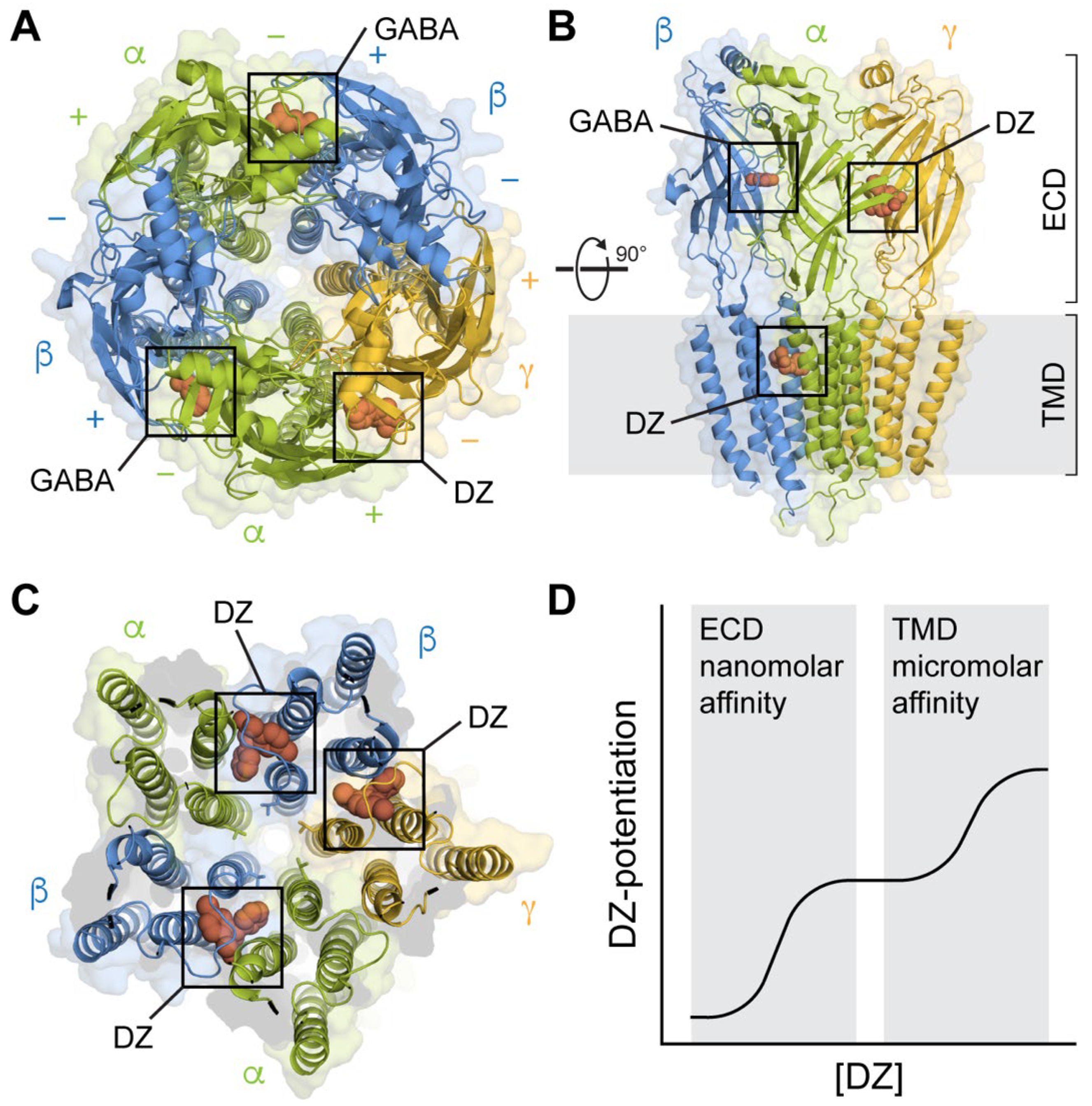
3. Canonical Extracellular High-Affinity Binding Site
4. Transmembrane Binding Sites
5. Other Binding Sites
6. BZD Modulation of GABA Binding
7. BZD Modulation of Pore Gating
8. BZD Modulation of Closed-Channel Pre-Activation
9. Structural Mechanism for BZD Modulation in the ECD
10. Structural Mechanism for BZD Modulation in the TMD
11. BZD-to-Pore Coupling
12. Conclusions and Perspectives
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Milani, S.A.; Raji, M.A.; Chen, L.; Kuo, Y.-F. Trends in the Use of Benzodiazepines, Z-Hypnotics, and Serotonergic Drugs Among US Women and Men Before and During the COVID-19 Pandemic. JAMA Netw. Open 2021, 4, e2131012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Möhler, H.; Fritschy, J.-M.; Rudolph, U. A New Benzodiazepine Pharmacology. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2002, 300, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fluyau, D.; Revadigar, N.; Manobianco, B.E. Challenges of the pharmacological management of benzodiazepine withdrawal, dependence, and discontinuation. Ther. Adv. Psychopharmacol. 2018, 8, 147–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schmitz, A. Benzodiazepine Use, Misuse, and Abuse: A Review. Ment. Health Clin. 2016, 6, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, C.M.; McAninch, J.K. Emergency Department Visits and Overdose Deaths from Combined Use of Opioids and Benzodiazepines. Am. J. Prev. Med. 2015, 49, 493–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jann, M.; Kennedy, W.K.; Lopez, G. Benzodiazepines: A major component in unintentional prescription drug overdoses with opioid analgesics. J. Pharm. Pr. 2014, 27, 5–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smart, T.G.; Stephenson, F.A. A half century of γ-aminobutyric acid. Brain Neurosci. Adv. 2019, 3, 2398212819858249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Olsen, R.W. GABAA receptor: Positive and negative allosteric modulators. Neuropharmacology 2018, 136, 10–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozrzymas, J.; Wójtowicz, T.; Piast, M.; Lebida, K.; Wyrembek, P.; Mercik, K. GABA transient sets the susceptibility of mIPSCs to modulation by benzodiazepine receptor agonists in rat hippocampal neurons. J. Physiol. 2007, 585, 29–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karayannis, T.; Elfant, D.; Huerta-Ocampo, I.; Teki, S.; Scott, R.S.; Rusakov, D.A.; Jones, M.V.; Capogna, M. Slow GABA Transient and Receptor Desensitization Shape Synaptic Responses Evoked by Hippocampal Neurogliaform Cells. J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 9898–9909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sternbach, L.H. The benzodiazepine story. J. Med. Chem. 1979, 22, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castellano, D.; Shepard, R.D.; Lu, W. Looking for Novelty in an “Old” Receptor: Recent Advances Toward Our Understanding of GABAARs and Their Implications in Receptor Pharmacology. Front. Neurosci. 2021, 14, 616298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wick, J.Y. The History of Benzodiazepines. Consult. Pharm. 2013, 28, 538–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Möhler, H.; Okada, T. Benzodiazepine Receptor: Demonstration in the Central Nervous System. Science 1977, 198, 849–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Möhler, H.; Okada, T. Properties of 3H-diazepam binding to benzodiazepine receptors in rat cerebral cortex. Life Sci. 1977, 20, 2101–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braestrup, C.; Squires, R.F. Specific benzodiazepine receptors in rat brain characterized by high-affinity (3H)diazepam binding. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1977, 74, 3805–3809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Braestrup, C.; Albrechtsen, R.; Squires, R.F. High densities of benzodiazepine receptors in human cortical areas. Nature 1977, 269, 702–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, R.W. GABA-Benzodiazepine-Barbiturate Receptor Interactions. J. Neurochem. 1981, 37, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigel, E.; Mamalaki, C.; Barnard, E.A. Isolation of a GABA receptor from bovine brain using a benzodiazepine affinity column. FEBS Lett. 1982, 147, 45–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sigel, E.; Stephenson, F.A.; Mamalaki, C.; Barnard, E.A. A gamma-aminobutyric acid/benzodiazepine receptor complex of bovine cerebral cortex. J. Biol. Chem. 1983, 258, 6965–6971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigel, E.; Barnard, E.A. A gamma-aminobutyric acid/benzodiazepine receptor complex from bovine cerebral cortex. Improved purification with preservation of regulatory sites and their interactions. J. Biol. Chem. 1984, 259, 7219–7223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Häring, P.; Stähli, C.; Schoch, P.; Takács, B.; Staehelin, T.; Möhler, H. Monoclonal antibodies reveal structural homogeneity of gamma-aminobutyric acid/benzodiazepine receptors in different brain areas. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1985, 82, 4837–4841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mamalaki, C.; Stephenson, F.; Barnard, E. The GABAA/benzodiazepine receptor is a heterotetramer of homologous alpha and beta subunits. EMBO J. 1987, 6, 561–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schofield, P.R.; Darlison, M.G.; Fujita, N.; Burt, D.R.; Stephenson, F.A.; Rodriguez, H.; Rhee, L.M.; Ramachandran, J.; Reale, V.; Glencorse, T.A.; et al. Sequence and functional expression of the GABAA receptor shows a ligand-gated receptor super-family. Nature 1987, 328, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnard, E.A.; Darlison, M.G.; Fujita, N.; Glencorse, T.A.; Levitan, E.S.; Reale, V.; Schofield, P.R.; Seeburg, P.H.; Squire, M.D.; Stephenson, F.A. Molecular Biology of the GABAA Receptor. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 1988, 236, 31–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seeburg, P.; Wisden, W.; Verdoorn, T.; Pritchett, D.; Werner, P.; Herb, A.; Luddens, H.; Sprengel, R.; Sakmann, B. The GABAA Receptor Family: Molecular and Functional Diversity. Cold Spring Harb. Symp. Quant. Biol. 1990, 55, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pritchett, D.B.; Sontheimer, H.; Shivers, B.D.; Ymer, S.; Kettenmann, H.; Schofield, P.R.; Seeburg, P.H. Importance of a novel GABAA receptor subunit for benzodiazepine pharmacology. Nature 1989, 338, 582–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, R.W.; Sieghart, W. International Union of Pharmacology. LXX. Subtypes of γ-Aminobutyric AcidA Receptors: Classification on the Basis of Subunit Composition, Pharmacology, and Function. Update. Pharmacol. Rev. 2008, 60, 243–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rudolph, U.; Crestani, F.; Benke, D.; Brünig, I.; Benson, J.A.; Fritschy, J.-M.; Martin, J.R.; Bluethmann, H.; Möhler, H. Benzodiazepine actions mediated by specific γ-aminobutyric acidA receptor subtypes. Nature 1999, 401, 796–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löw, K.; Crestani, F.; Keist, R.; Benke, D.; Brünig, I.; Benson, J.A.; Fritschy, J.-M.; Rülicke, T.; Bluethmann, H.; Möhler, H.; et al. Molecular and Neuronal Substrate for the Selective Attenuation of Anxiety. Science 2000, 290, 131–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKernan, R.M.; Rosahl, T.W.; Reynolds, D.S.; Sur, C.; Wafford, K.A.; Atack, J.; Farrar, S.; Myers, J.; Cook, G.; Ferris, P.; et al. Sedative but not anxiolytic properties of benzodiazepines are mediated by the GABAA receptor α1 subtype. Nat. Neurosci. 2000, 3, 587–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reynolds, D.S.; McKernan, R.M.; Dawson, G.R. Anxiolytic-like action of diazepam: Which GABAA receptor subtype is involved? Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2001, 22, 402–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rowlett, J.K.; Platt, D.M.; Lelas, S.; Atack, J.R.; Dawson, G.R. Different GABA A receptor subtypes mediate the anxiolytic, abuse-related, and motor effects of benzodiazepine-like drugs in primates. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 915–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moody, O.A.; Jenkins, A. The role of loops B and C in determining the potentiation of GABA A receptors by midazolam. Pharmacol. Res. Perspect. 2018, 6, e00433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Botta, P.; Demmou, L.; Kasugai, Y.; Markovic, M.; Xu, C.; Fadok, J.P.; Lu, T.; Poe, M.; Xu, L.; Cook, J.M.; et al. Regulating anxiety with extrasynaptic inhibition. Nat. Neurosci. 2015, 18, 1493–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Behlke, L.M.; Foster, R.A.; Liu, J.; Benke, D.; Benham, R.S.; Nathanson, A.J.; Yee, B.K.; Zeilhofer, H.U.; Engin, E.; Rudolph, U. A Pharmacogenetic ‘Restriction-of-Function’ Approach Reveals Evidence for Anxiolytic-Like Actions Mediated by α5-Containing GABAA Receptors in Mice. Neuropsychopharmacology 2016, 41, 2492–2501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tan, K.R.; Rudolph, U.; Lüscher, C. Hooked on benzodiazepines: GABAA receptor subtypes and addiction. Trends Neurosci. 2011, 34, 188–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Knoflach, F.; Benke, D.; Wang, Y.; Scheurer, L.; Lüddens, H.; Hamilton, B.J.; Carter, D.B.; Mohler, H.; Benson, J.A. Pharmacological modulation of the diazepam-insensitive recombinant gamma-aminobutyric acidA receptors alpha 4 beta 2 gamma 2 and alpha 6 beta 2 gamma 2. Mol. Pharmacol. 1996, 50, 1253–1261. [Google Scholar]
- Farrant, M.; Nusser, Z. Variations on an inhibitory theme: Phasic and tonic activation of GABAA receptors. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2005, 6, 215–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minier, F.; Sigel, E. Positioning of the α-subunit isoforms confers a functional signature to γ-aminobutyric acid type A receptors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 7769–7774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sieghart, W.; Savić, M.M. International Union of Basic and Clinical Pharmacology. CVI: GABAA Receptor Subtype- and Function-selective Ligands: Key Issues in Translation to Humans. Pharmacol. Rev. 2018, 70, 836–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, S.; Noviello, C.M.; Teng, J.; Walsh, R.M., Jr.; Kim, J.J.; Hibbs, R.E. Structure of a human synaptic GABAA receptor. Nature 2018, 559, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phulera, S.; Zhu, H.; Yu, J.; Claxton, D.P.; Yoder, N.; Yoshioka, C.; Gouaux, E. Cryo-EM structure of the benzodiazepine-sensitive α1β1γ2S tri-heteromeric GABAA receptor in complex with GABA. eLife 2018, 7, 39383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laverty, D.; Desai, R.; Uchański, T.; Masiulis, S.; Stec, W.J.; Malinauskas, T.; Zivanov, J.; Pardon, E.; Steyaert, J.; Miller, K.W.; et al. Cryo-EM structure of the human α1β3γ2 GABAA receptor in a lipid bilayer. Nature 2019, 565, 516–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masiulis, S.; Desai, R.; Uchański, T.; Martin, I.S.; Laverty, D.; Karia, D.; Malinauskas, T.; Zivanov, J.; Pardon, E.; Kotecha, A.; et al. GABAA receptor signalling mechanisms revealed by structural pharmacology. Nature 2019, 565, 454–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.J.; Gharpure, A.; Teng, J.; Zhuang, Y.; Howard, R.J.; Zhu, S.; Noviello, C.M.; Walsh, R.M., Jr.; Lindahl, E.; Hibbs, R.E. Shared structural mechanisms of general anaesthetics and benzodiazepines. Nature 2020, 585, 303–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sente, A.; Desai, R.; Naydenova, K.; Malinauskas, T.; Jounaidi, Y.; Miehling, J.; Zhou, X.; Masiulis, S.; Hardwick, S.W.; Chirgadze, D.Y.; et al. Differential assembly diversifies GABAA receptor structures and signalling. Nature 2022, 604, 190–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Sridhar, A.; Teng, J.; Howard, R.J.; Lindahl, E.; Hibbs, R.E. Structural and dynamic mechanisms of GABAA receptor modulators with opposing activities. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 4582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sieghart, W.; Sperk, G. Subunit Composition, Distribution and Function of GABA-A Receptor Subtypes. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2002, 2, 795–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieland, H.A.; Lüddens, H.; Seeburg, P.H. A single histidine in GABAA receptors is essential for benzodiazepine agonist binding. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 1426–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benson, J.A.; Löw, K.; Keist, R.; Mohler, H.; Rudolph, U. Pharmacology of recombinant γ-aminobutyric acidA receptors rendered diazepam-insensitive by point-mutated α-subunits. FEBS Lett. 1998, 431, 400–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudolph, U.; Möhler, H. Analysis of GABAA Receptor Function and Dissection of the Pharmacology of Benzodiazepines and General Anesthetics Through Mouse Genetics. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2004, 44, 475–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amin, J.; Brooks-Kayal, A.; Weiss, D.S. Two Tyrosine Residues on the α Subunit Are Crucial for Benzodiazepine Binding and Allosteric Modulation of γ-Aminobutyric AcidA Receptors. Mol. Pharmacol. 1997, 51, 833–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKernan, R.M.; Farrar, S.; Collins, I.; Emms, F.; Asuni, A.; Quirk, K.; Broughton, H. Photoaffinity Labeling of the Benzodiazepine Binding Site of α1β3γ2 γ-Aminobutyric AcidA Receptors with Flunitrazepam Identifies a Subset of Ligands that Interact Directly with His102 of the α Subunit and Predicts Orientation of These within the Benzodiazepine Pharmacophore. Mol. Pharmacol. 1998, 54, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigel, E.; Lüscher, B.P. A Closer Look at the High Affinity Benzodiazepine Binding Site on GABAA Receptors. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2011, 11, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foucaud, B.; Perret, P.; Grutter, T.; Goeldner, M. Cysteine mutants as chemical sensors for ligand–receptor interactions. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2001, 22, 170–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morlock, E.V.; Czajkowski, C. Different Residues in the GABAA Receptor Benzodiazepine Binding Pocket Mediate Benzodiazepine Efficacy and Binding. Mol. Pharmacol. 2011, 80, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wingrove, P.B.; Thompson, S.A.; Wafford, K.A.; Whiting, P.J. Key Amino Acids in the γ Subunit of the γ-Aminobutyric AcidA Receptor that Determine Ligand Binding and Modulation at the Benzodiazepine Site. Mol. Pharmacol. 1997, 52, 874–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middendorp, S.J.; Hurni, E.; Schönberger, M.; Stein, M.; Pangerl, M.; Trauner, D.; Sigel, E. Relative Positioning of Classical Benzodiazepines to the γ2-Subunit of GABAA Receptors. ACS Chem. Biol. 2014, 9, 1846–1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sancar, F.; Ericksen, S.; Kucken, A.M.; Teissére, J.A.; Czajkowski, C. Structural Determinants for High-Affinity Zolpidem Binding to GABA-A receptors. Mol. Pharmacol. 2006, 71, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Walters, R.J.; Hadley, S.H.; Morris, K.D.; Amin, J. Benzodiazepines act on GABAA receptors via two distinct and separable mechanisms. Nat. Neurosci. 2000, 3, 1274–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szabo, A.; Nourmahnad, A.; Halpin, E.; Forman, S.A. Monod-Wyman-Changeux Allosteric Shift Analysis in Mutant α1β3γ2L GABAA Receptors Indicates Selectivity and Crosstalk among Intersubunit Transmembrane Anesthetic Sites. Mol. Pharmacol. 2019, 95, 408–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McGrath, M.; Hoyt, H.; Pence, A.; Forman, S.A.; Raines, D.E. Selective actions of benzodiazepines at the transmembrane anaesthetic binding sites of the GABAA receptor: In vitro and in vivo studies. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2021, 178, 4842–4858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Y.; Yan, H.; Yu, G.; Su, R. Flumazenil-insensitive benzodiazepine binding sites in GABAA receptors contribute to benzodiazepine-induced immobility in zebrafish larvae. Life Sci. 2019, 239, 117033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baur, R.; Tan, K.R.; Lüscher, B.P.; Gonthier, A.; Goeldner, M.; Sigel, E. Covalent modification of GABAA receptor isoforms by a diazepam analogue provides evidence for a novel benzodiazepine binding site that prevents modulation by these drugs. J. Neurochem. 2008, 106, 2353–2363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wongsamitkul, N.; Maldifassi, M.C.; Simeone, X.; Baur, R.; Ernst, M.; Sigel, E. α subunits in GABAA receptors are dispensable for GABA and diazepam action. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 15498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramerstorfer, J.; Furtmüller, R.; Sarto-Jackson, I.; Varagic, Z.; Sieghart, W.; Ernst, M. The GABAA receptor α+β- interface: A novel target for subtype selective drugs. J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 870–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sigel, E.; Ernst, M. The Benzodiazepine Binding Sites of GABAA Receptors. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2018, 39, 659–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, J.-J.; Cao, Y.-Q.; Li, Y.-L.; Yu, G.; Su, R.-B. Flumazenil-Insensitive Benzodiazepine Effects in Recombinant αβ and Neuronal GABAA Receptors. Brain Sci. 2020, 10, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Twyman, R.E.; Rogers, C.J.; Macdonald, R.L. Differential regulation of γ-aminobutyric acid receptor channels by diazepam and phenobarbital. Ann. Neurol. 1989, 25, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lavoie, A.; Twyman, R. Direct Evidence For Diazepam Modulation of GABAA Receptor Microscopic Affinity. Neuropharmacology 1996, 35, 1383–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogers, C.J.; Twyman, R.E.; Macdonald, R.L. Benzodiazepine and beta-carboline regulation of single GABAA receptor channels of mouse spinal neurones in culture. J. Physiol. 1994, 475, 69–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perrais, D.; Ropert, N. Effect of zolpidem on miniature IPSCs and occupancy of postsynaptic GABAA receptors in central synapses. J. Neurosci. 1999, 19, 578–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vicini, S.; Mienville, J.M.; Costa, E. Actions of benzodiazepine and beta-carboline derivatives on gamma-aminobutyric acid-activated Cl- channels recorded from membrane patches of neonatal rat cortical neurons in culture. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1987, 243, 1195–1201. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.P.; Eaton, M.M.M.; Steinbach, J.H.; Akk, G. The Benzodiazepine Diazepam Potentiates Responses of α1β2γ2L γ-Aminobutyric Acid Type A Receptors Activated by either γ-Aminobutyric Acid or Allosteric Agonists. Anesthesiology 2013, 118, 1417–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tallman, J.F.; Thomas, J.W.; Gallager, D.W. GABAergic modulation of benzodiazepine binding site sensitivity. Nature 1978, 274, 383–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karobath, M.; Sperk, G. Stimulation of benzodiazepine receptor binding by gamma-aminobutyric acid. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1979, 76, 1004–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sharkey, L.M.; Czajkowski, C. Individually Monitoring Ligand-Induced Changes in the Structure of the GABAA Receptor at Benzodiazepine Binding Site and Non-Binding-Site Interfaces. Mol. Pharmacol. 2008, 74, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sancar, F.; Czajkowski, C. Allosteric modulators induce distinct movements at the GABA-binding site interface of the GABA-A receptor. Neuropharmacology 2011, 60, 520–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Middendorf, T.R.; Goldschen-Ohm, M.P. The surprising difficulty of “simple” equilibrium binding measurements on ligand-gated ion channels. J. Gen. Physiol. 2022, 154, e202213177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middendorf, T.R.; Aldrich, R.W. Structural identifiability of equilibrium ligand-binding parameters. J. Gen. Physiol. 2016, 149, 105–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mellor, J.R.; Randall, A.D. Frequency-Dependent Actions of Benzodiazepines on GABAA Receptors in Cultured Murine Cerebellar Granule Cells. J. Physiol. 1997, 503, 353–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercik, K.; Piast, M.; Mozrzymas, J. Benzodiazepine receptor agonists affect both binding and gating of recombinant α1β2γ2 gamma-aminobutyric acid-A receptors. NeuroReport 2007, 18, 781–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rüsch, D.; Forman, S.A. Classic Benzodiazepines Modulate the Open–Close Equilibrium in α1β2γ2Lγ-Aminobutyric Acid Type A Receptors. Anesthesiology 2005, 102, 783–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campo-Soria, C.; Chang, Y.; Weiss, D.S. Mechanism of action of benzodiazepines on GABAA receptors. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2006, 148, 984–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Downing, S.S.; Lee, Y.T.; Farb, D.H.; Gibbs, T.T. Benzodiazepine modulation of partial agonist efficacy and spontaneously active GABAA receptors supports an allosteric model of modulation. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2005, 145, 894–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Findlay, G.S.; Ueno, S.; Harrison, N.L.; Harris, R. Allosteric modulation in spontaneously active mutant γ-aminobutyric acidA receptors. Neurosci. Lett. 2001, 305, 77–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nors, J.W.; Gupta, S.; Goldschen-Ohm, M.P. A critical residue in the α1M2–M3 linker regulating mammalian GABAA receptor pore gating by diazepam. eLife 2021, 10, 64400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, Y.; Weiss, D.S. Allosteric Activation Mechanism of the α1β2γ2 γ-Aminobutyric Acid Type A Receptor Revealed by Mutation of the Conserved M2 Leucine. Biophys. J. 1999, 77, 2542–2551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scheller, M.; Forman, S.A. Coupled and uncoupled gating and desensitization effects by pore domain mutations in GABA(A) receptors. J. Neurosci. 2002, 22, 8411–8421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Purohit, P.; Auerbach, A. Unliganded gating of acetylcholine receptor channels. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lape, R.; Colquhoun, D.; Sivilotti, L.G. On the nature of partial agonism in the nicotinic receptor superfamily. Nature 2008, 454, 722–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colquhoun, D.; Lape, R. Perspectives on: Conformational coupling in ion channels: Allosteric coupling in ligand-gated ion channels. J. Gen. Physiol. 2012, 140, 599–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jadey, S.; Auerbach, A. An integrated catch-and-hold mechanism activates nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. J. Gen. Physiol. 2012, 140, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mukhtasimova, N.; Dacosta, C.J.; Sine, S.M. Improved resolution of single channel dwell times reveals mechanisms of binding, priming, and gating in muscle AChR. J. Gen. Physiol. 2016, 148, 43–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Szczot, M.; Kisiel, M.; Czyzewska, M.M.; Mozrzymas, J.W. α1F64 Residue at GABAA Receptor Binding Site Is Involved in Gating by Influencing the Receptor Flipping Transitions. J. Neurosci. 2014, 34, 3193–3209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gielen, M.C.; Lumb, M.J.; Smart, T.G. Benzodiazepines Modulate GABAA Receptors by Regulating the Preactivation Step after GABA Binding. J. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 5707–5715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goldschen-Ohm, M.P.; Haroldson, A.; Jones, M.V.; Pearce, R.A. A nonequilibrium binary elements-based kinetic model for benzodiazepine regulation of GABAA receptors. J. Gen. Physiol. 2014, 144, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jatczak-Śliwa, M.; Terejko, K.; Brodzki, M.; Michalowski, M.A.; Czyzewska, M.M.; Nowicka, J.M.; Andrzejczak, A.; Srinivasan, R.; Mozrzymas, J.W. Distinct Modulation of Spontaneous and GABA-Evoked Gating by Flurazepam Shapes Cross-Talk Between Agonist-Free and Liganded GABAA Receptor Activity. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, C.L.; Harrison, N.L.; Lynch, J.W.; Keramidas, A. Zolpidem and eszopiclone prime α1β2γ2 GABAA receptors for longer duration of activity. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2015, 172, 3522–3536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mortensen, M.; Kristiansen, U.; Ebert, B.; Frølund, B.; Krogsgaard-Larsen, P.; Smart, T.G. Activation of single heteromeric GABAA receptor ion channels by full and partial agonists. J. Physiol. 2004, 557, 389–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemecz, Á.; Prevost, M.S.; Menny, A.; Corringer, P.-J. Emerging Molecular Mechanisms of Signal Transduction in Pentameric Ligand-Gated Ion Channels. Neuron 2016, 90, 452–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.J.; Hibbs, R.E. Direct Structural Insights into GABAA Receptor Pharmacology. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2021, 46, 502–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pflanz, N.C.; Daszkowski, A.W.; Cornelison, G.L.; Trudell, J.R.; Mihic, S.J. An intersubunit electrostatic interaction in the GABAA receptor facilitates its responses to benzodiazepines. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 8264–8274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Venkatachalan, S.P.; Czajkowski, C. Structural Link between γ-Aminobutyric Acid Type A (GABAA) Receptor Agonist Binding Site and Inner β-Sheet Governs Channel Activation and Allosteric Drug Modulation. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 6714–6724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Terejko, K.; Michałowski, M.A.; Dominik, A.; Andrzejczak, A.; Mozrzymas, J.W. Interaction between GABAA receptor α1 and β2 subunits at the N-terminal peripheral regions is crucial for receptor binding and gating. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2020, 183, 114338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baur, R.; Sigel, E. Benzodiazepines Affect Channel Opening of GABAA Receptors Induced by Either Agonist Binding Site. Mol. Pharmacol. 2005, 67, 1005–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goldschen-Ohm, M.P.; Wagner, D.A.; Petrou, S.; Jones, M.V. An Epilepsy-Related Region in the GABAA Receptor Mediates Long-Distance Effects on GABA and Benzodiazepine Binding Sites. Mol. Pharmacol. 2009, 77, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, J.; Zhu, H.; Lape, R.; Greiner, T.; Du, J.; Lü, W.; Sivilotti, L.; Gouaux, E. Mechanism of gating and partial agonist action in the glycine receptor. Cell 2021, 184, 957–968.e21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hibbs, R.E.; Sulzenbacher, G.; Shi, J.; Talley, T.; Conrod, S.; Kem, W.R.; Taylor, P.; Marchot, P.; Bourne, Y. Structural determinants for interaction of partial agonists with acetylcholine binding protein and neuronal α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor. EMBO J. 2009, 28, 3040–3051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stewart, D.S.; Pierce, D.W.; Hotta, M.; Stern, A.T.; Forman, S.A. Mutations at Beta N265 in γ-Aminobutyric Acid Type A Receptors Alter Both Binding Affinity and Efficacy of Potent Anesthetics. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e111470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, D.B.; Akabas, M.H. Benzodiazepines Induce a Conformational Change in the Region of the γ-Aminobutyric Acid Type A Receptor α1-Subunit M3 Membrane-Spanning Segment. Mol. Pharmacol. 2000, 58, 1129–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, D.B.; Akabas, M.H. Evidence for distinct conformations of the two α1 subunits in diazepam-bound GABAA receptors. Neuropharmacology 2001, 41, 539–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanson, S.M.; Czajkowski, C. Disulphide trapping of the GABAA receptor reveals the importance of the coupling interface in the action of benzodiazepines. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2011, 162, 673–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kash, T.L.; Jenkins, A.; Kelley, J.C.; Trudell, J.R.; Harrison, N.L. Coupling of agonist binding to channel gating in the GABAA receptor. Nature 2003, 421, 272–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kash, T.L.; Dizon, M.-J.F.; Trudell, J.R.; Harrison, N.L. Charged Residues in the β2 Subunit Involved in GABAA Receptor Activation. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 4887–4893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hanson, S.M.; Czajkowski, C. Structural Mechanisms Underlying Benzodiazepine Modulation of the GABAA Receptor. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 3490–3499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Padgett, C.L.; Lummis, S.C.R. The F-loop of the GABAA Receptor γ2 Subunit Contributes to Benzodiazepine Modulation. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 2702–2708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baur, R.; Lüscher, B.P.; Richter, L.; Sigel, E. A residue close to α1 loop F disrupts modulation of GABAA receptors by benzodiazepines while their binding is maintained. J. Neurochem. 2010, 115, 1478–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatri, A.; Weiss, D.S. The role of Loop F in the activation of the GABA receptor. J. Physiol. 2010, 588, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dellisanti, C.D.; Ghosh, B.; Hanson, S.M.; Raspanti, J.M.; Grant, V.A.; Diarra, G.M.; Schuh, A.M.; Satyshur, K.; Klug, C.S.; Czajkowski, C. Site-Directed Spin Labeling Reveals Pentameric Ligand-Gated Ion Channel Gating Motions. PLoS Biol. 2013, 11, e1001714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gielen, M.; Corringer, P.-J. The dual-gate model for pentameric ligand-gated ion channels activation and desensitization. J. Physiol. 2018, 596, 1873–1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gielen, M.C.; Thomas, P.; Smart, T.G. The desensitization gate of inhibitory Cys-loop receptors. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Goldschen-Ohm, M.P. Benzodiazepine Modulation of GABAA Receptors: A Mechanistic Perspective. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 1784. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12121784
Goldschen-Ohm MP. Benzodiazepine Modulation of GABAA Receptors: A Mechanistic Perspective. Biomolecules. 2022; 12(12):1784. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12121784
Chicago/Turabian StyleGoldschen-Ohm, Marcel P. 2022. "Benzodiazepine Modulation of GABAA Receptors: A Mechanistic Perspective" Biomolecules 12, no. 12: 1784. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12121784
APA StyleGoldschen-Ohm, M. P. (2022). Benzodiazepine Modulation of GABAA Receptors: A Mechanistic Perspective. Biomolecules, 12(12), 1784. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12121784





