Oxygen Therapy during Exercise in Patients with Interstitial Lung Diseases
Abstract
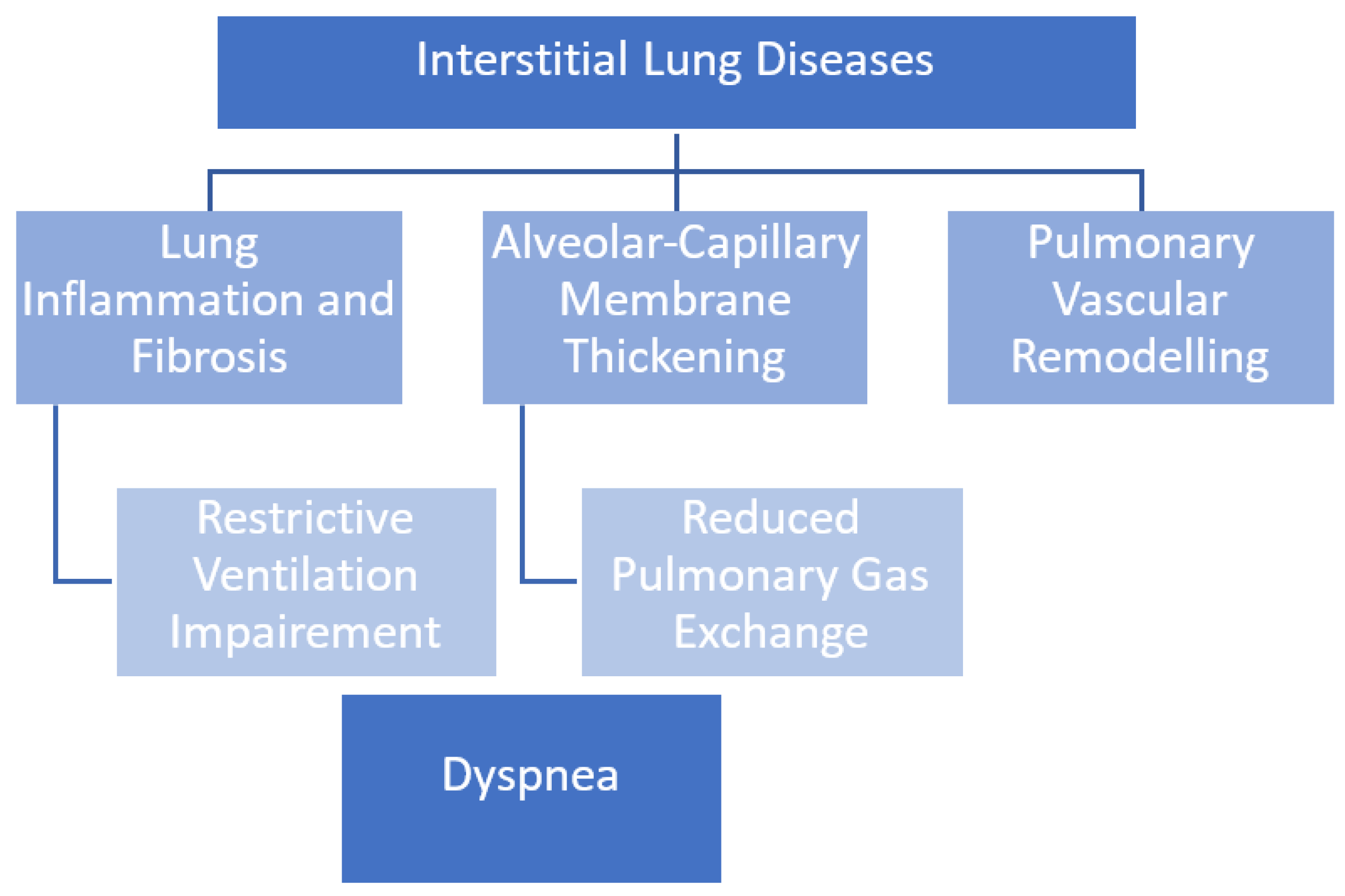
:1. Introduction
2. Ventilatory Mechanisms in ILDs
3. Oxygen Therapy in ILD
4. Ambulatory Oxygen in Daily Life
5. Safety Data of Ambulatory Oxygen in ILD’s Patients
6. Quality of Life and Psychological Implications
7. Cost-Effectiveness of Oxygen Therapy
8. Concluding Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Fischer, A.; Antoniou, K.M.; Brown, K.K.; Cadranel, J.; Corte, T.J.; Du Bois, R.M.; Lee, J.S.; Leslie, K.O.; Lynch, D.A.; Matteson, E.L.; et al. An official European Respiratory Socie-ty/American Thoracic Society research statement: Interstitial pneumonia with autoimmune features. “ERS/ATS Task Force on Undifferentiated Forms of CTD-ILD”. Eur. Respir. J. 2015, 46, 976–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Raghu, G.; Remy-Jardin, M.; Myers, J.L.; Richeldi, L.; Ryerson, C.J.; Lederer, D.J.; Behr, J.; Cottin, V.; Danoff, S.K.; Morell, F.; et al. Diagnosis of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. An Official ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT Clinical Practice Guideline. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2018, 198, e44–e68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- d’Alessandro, M.; Carleo, A.; Cameli, P.; Bergantini, L.; Perrone, A.; Vietri, L.; Lanzarone, N.; Vagaggini, C.; Sestini, P.; Bargagli, E. BAL biomarkers’ panel for differential diagnosis of interstitial lung diseases. Clin. Exp. Med. 2020, 20, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergantini, L.; D’Alessandro, M.; Cameli, P.; Perrone, A.; Cekorja, B.; Boncompagni, B.; Mazzei, M.A.; Sestini, P.; Bargagli, E. Integrated approach to bronchoalveolar lavage cytology to distinguish interstitial lung diseases. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2021, 89, 76–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flaherty, K.R.; Wells, A.U.; Cottin, V.; Devaraj, A.; Walsh, S.L.; Inoue, Y.; Richeldi, L.; Kolb, M.; Tetzlaff, K.; Stowasser, S.; et al. Nintedanib in Progressive Fibrosing Interstitial Lung Diseases. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 1718–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Richeldi, L.; Du Bois, R.M.; Raghu, G.; Azuma, A.; Brown, K.K.; Costabel, U.; Cottin, V.; Flaherty, K.R.; Hansell, D.M.; Inoue, Y.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Nintedanib in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 2071–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tarpy, S.P.; Celli, B.R. Long-Term Oxygen Therapy. N. Engl. J. Med. 1995, 333, 710–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holland, A.E. Review series: Aspects of interstitial lung disease: Exercise limitation in interstitial lung disease—Mechanisms, significance and therapeutic options. Chronic Respir. Dis. 2010, 7, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Plantier, L.; Cazes, A.; Dinh-Xuan, A.-T.; Bancal, C.; Marchand-Adam, S.; Crestani, B. Physiology of the lung in idiopathic pul-monary fibrosis. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2018, 27, 170062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Flaherty, K.R.; Andrei, A.-C.; Murray, S.; Fraley, C.; Colby, T.V.; Travis, W.D.; Lama, V.; Kazerooni, E.A.; Gross, B.H.; Toews, G.B.; et al. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: Prognostic value of changes in physiology and six-minute-walk test. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2006, 174, 803–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jacobs, S.S.; Krishnan, J.A.; Lederer, D.J.; Ghazipura, M.; Hossain, T.; Tan, A.Y.M.; Carlin, B.; Drummond, M.B.; Ekström, M.; Garvey, C.; et al. An Official American Thoracic Society Clinical Practice Guideline. Home Oxygen Therapy for Adults with Chronic Lung Disease. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2020, 202, e121–e141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bye, P.T.; Anderson, S.D.; Woolcock, A.J.; Young, I.H.; Alison, J.A. Bicycle endurance performance of patients with interstitial lung disease breathing air and oxygen. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1982, 126, 1005–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frank, R.C.; Hicks, S.; Duck, A.M.; Spencer, L.; Leonard, C.T.; Barnett, E. Ambulatory oxygen in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: Of what benefit? Eur. Respir. J. 2012, 40, 269–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Visca, D.; Montgomery, A.; De Lauretis, A.; Sestini, P.; Soteriou, H.; Maher, T.; Wells, A.U.; Renzoni, E.A. Ambulatory oxygen in interstitial lung disease. Eur. Respir. J. 2011, 38, 987–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishiyama, O.; Miyajima, H.; Fukai, Y.; Yamazaki, R.; Satoh, R.; Yamagata, T.; Sano, H.; Iwanaga, T.; Higashimoto, Y.; Nakajima, H.; et al. Effect of ambulatory oxygen on exertional dyspnea in IPF patients without resting hypoxemia. Respir. Med. 2013, 107, 1241–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ora, J.; Coppola, A.; Perduno, A.; Manzetti, G.M.; Puxeddu, E.; Rogliani, P. Acute effect of oxygen therapy on exercise tolerance and dyspnea perception in ILD patients. Monaldi Arch. Chest Dis. 2021, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visca, D.; Tsipouri, V.; Mori, L.; Firouzi, A.; Fleming, S.; Farquhar, M.; Leung, E.; Maher, T.; Cullinan, P.; Hopkinson, N.; et al. Ambulatory oxygen in fibrotic lung disease (AmbOx): Study protocol for a randomised controlled trial. Trials 2017, 18, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Parshall, M.B.; Schwartzstein, R.M.; Adams, L.; Banzett, R.B.; Manning, H.L.; Bourbeau, J.; Calverley, P.M.; Gift, A.G.; Harver, A.; Lareau, S.C.; et al. An Official American Thoracic Society Statement: Update on the Mechanisms, Assessment, and Management of Dyspnea. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2012, 185, 435–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Whitty, J.A.; Rankin, J.; Visca, D.; Tsipouri, V.; Mori, L.; Spencer, L.; Adamali, H.; Maher, T.; Hopkinson, N.S.; Birring, S.S.; et al. Cost-effectiveness of ambulatory oxygen in improving quality of life in fibrotic lung disease: Preliminary evidence from the AmbOx Trial. Eur. Respir. J. 2019, 55, 1901157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Continuous Oxygen |
|---|
|
| Non-continuous oxygen (oxygen flow rate and number of hours per day must be specified) |
|
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Viani, M.; Ventura, V.; Bianchi, F.; d’Alessandro, M.; Bergantini, L.; Sestini, P.; Bargagli, E. Oxygen Therapy during Exercise in Patients with Interstitial Lung Diseases. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 717. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12050717
Viani M, Ventura V, Bianchi F, d’Alessandro M, Bergantini L, Sestini P, Bargagli E. Oxygen Therapy during Exercise in Patients with Interstitial Lung Diseases. Biomolecules. 2022; 12(5):717. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12050717
Chicago/Turabian StyleViani, Magda, Vittoria Ventura, Francesco Bianchi, Miriana d’Alessandro, Laura Bergantini, Piersante Sestini, and Elena Bargagli. 2022. "Oxygen Therapy during Exercise in Patients with Interstitial Lung Diseases" Biomolecules 12, no. 5: 717. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12050717
APA StyleViani, M., Ventura, V., Bianchi, F., d’Alessandro, M., Bergantini, L., Sestini, P., & Bargagli, E. (2022). Oxygen Therapy during Exercise in Patients with Interstitial Lung Diseases. Biomolecules, 12(5), 717. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12050717









