A Novel High-Throughput Assay Reveals That the Temperature Induced Increases in Transphosphatidylation of Phospholipase D Are Dependent on the Alcohol Acceptor Concentration
Abstract
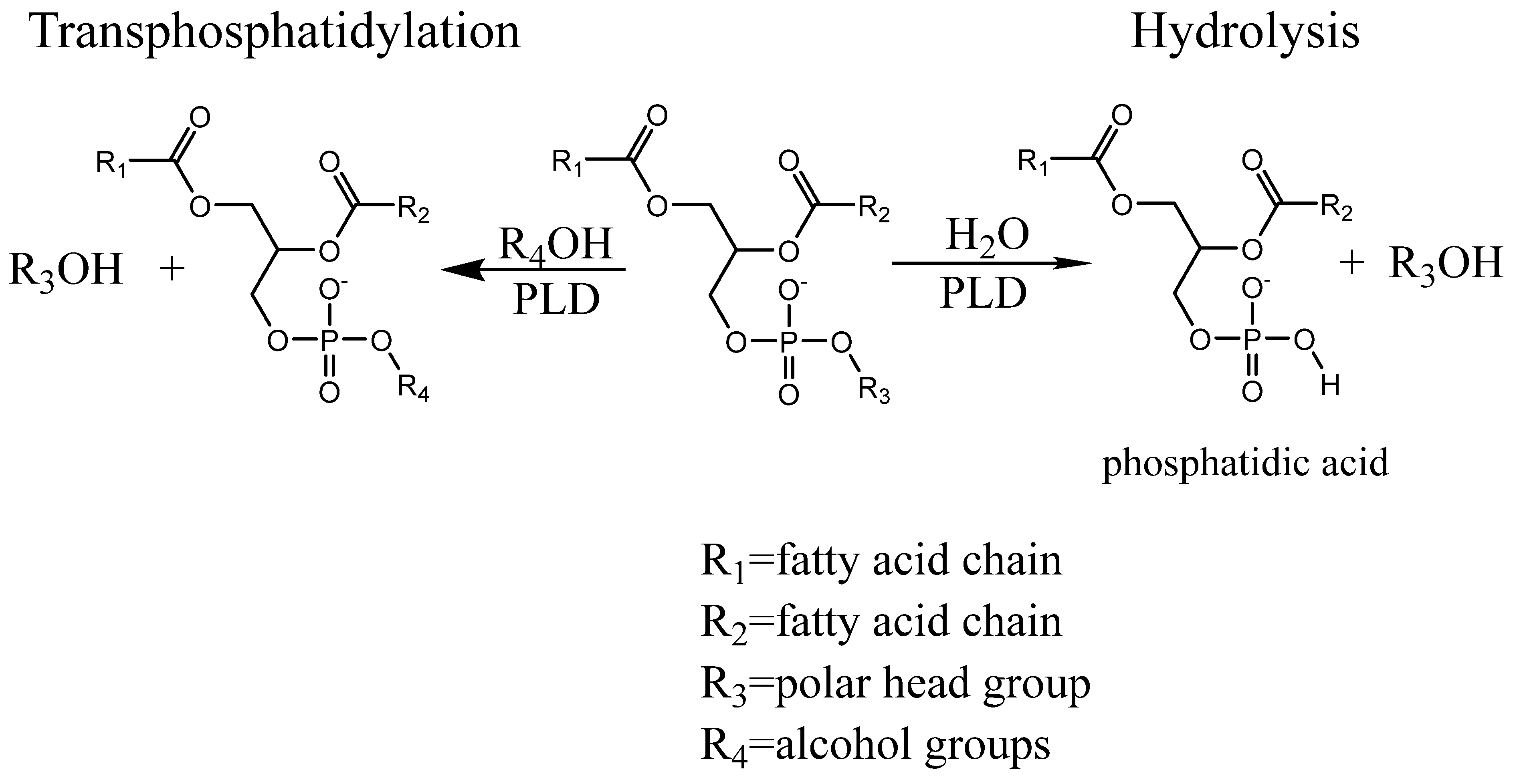
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Transphosphatidylation
2.2. Hydrolysis
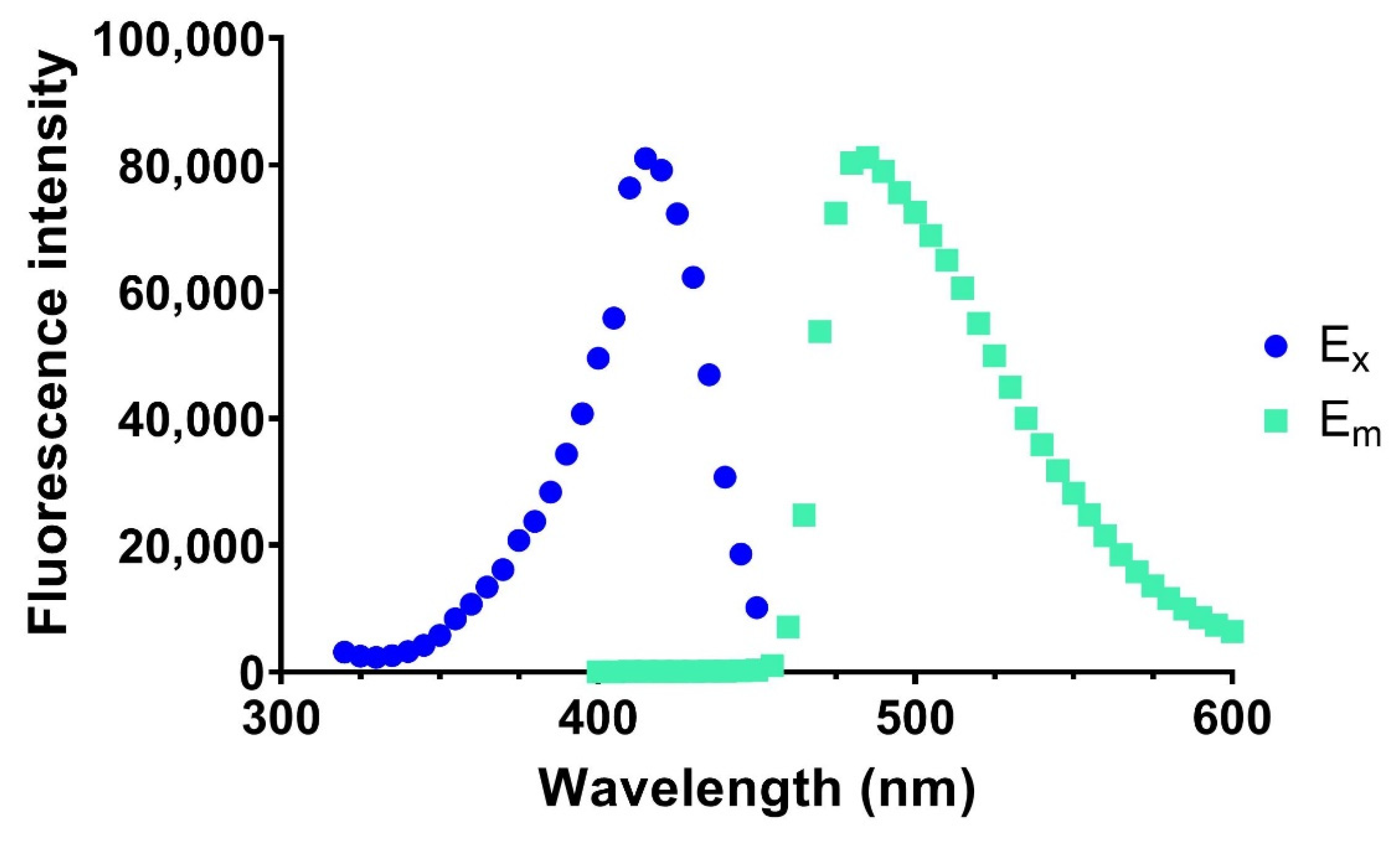
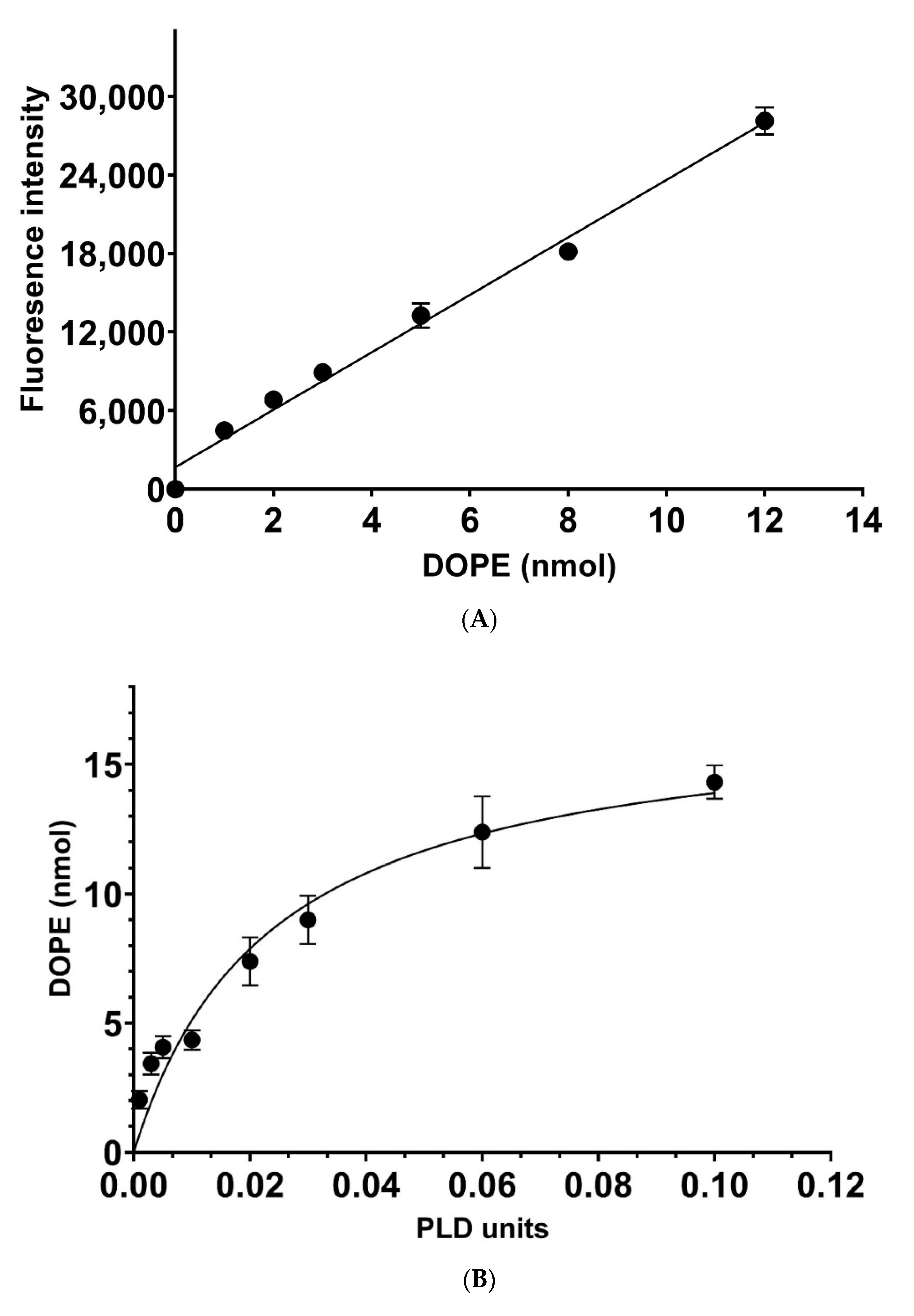
2.3. Determination of Catalytic Rates
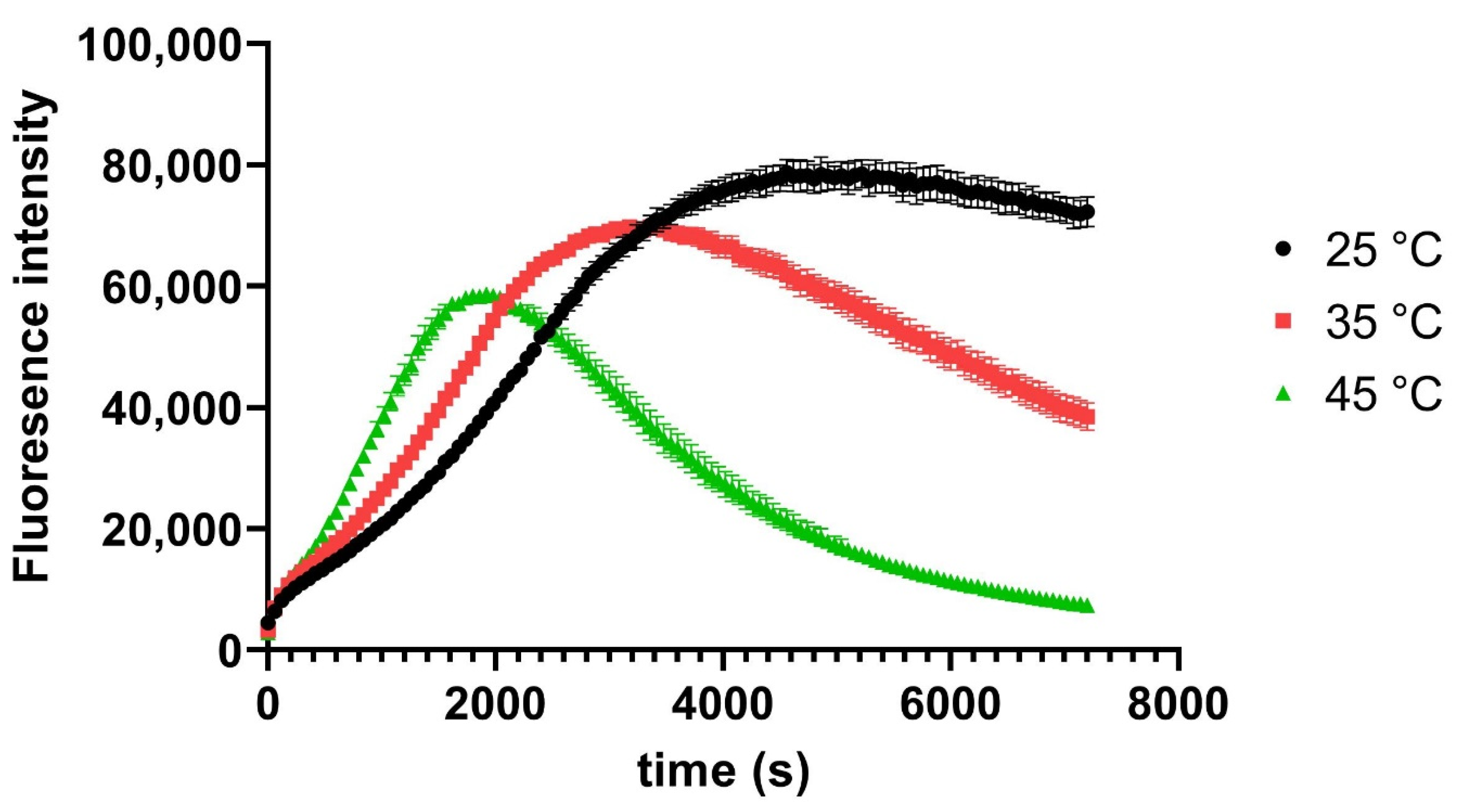
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chapman, J.; Ismail, A.E.; Dinu, C.Z. Industrial Applications of Enzymes: Recent Advances, Techniques, and Outlooks. Catalysts 2018, 8, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gotor, V.; Flitsch, S. Increasing the diversity of biocatalytic reactions. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2011, 15, 185–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Truppo, M.D. Biocatalysis in the Pharmaceutical Industry: The Need for Speed. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2017, 8, 476–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Selvy, P.E.; Lavieri, R.R.; Lindsley, C.W.; Brown, H.A. Phospholipase D: Enzymology, functionality, and chemical modulation. Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 6064–6119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yu, C.H.; Liu, S.Y.; Panagia, V. The transphosphatidylation activity of phospholipase D. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 1996, 157, 101–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damnjanovic, J.; Iwasaki, Y. Phospholipase D as a catalyst: Application in phospholipid synthesis, molecular structure and protein engineering. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2013, 116, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allegretti, C.; Denuccio, F.; Rossato, L.; D’Arrigo, P. Polar Head Modified Phospholipids by Phospholipase D-Catalyzed Transformations of Natural Phosphatidylcholine for Targeted Applications: An Overview. Catalysts 2020, 10, 997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirche, F.; Ulbrich-Hofmann, R. The Interdependence of Solvent, Acceptor Alcohol and Enzyme Source in Transphosphatidylation by Phospholipase D. Biocatal. Biotransformation 2000, 18, 343–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuto, S.; Itoh, H.; Sakai, A.; Nakagami, K.; Imamura, S.; Matsuda, A. Nucleosides and nucleotides—CXXXVII. Antitumor phospholipids with 5-fluorouridine as a cytotoxic polar-head: Synthesis of 5’-phosphatidyl-5-fluorouridines by phospholipase D-catalyzed transphosphatidylation. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 1995, 3, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takami, M.; Suzuki, Y. Transphosphatidylation reaction of phosphatidylcholine to 4-methoxyphenol in water-immiscible organic solvents with immobilized phospholipase D. J. Ferment. Bioeng. 1995, 79, 313–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuto, S.; Matsuda, A. Synthesis of Pseudo-Phospholipids by Phospholipase D-Catalyzed Transphosphatidylation. J. Synth. Org. Chem. 1997, 55, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zumbuehl, A. Artificial Phospholipids and Their Vesicles. Langmuir 2019, 35, 10223–10232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mak, L.H.; Woscholski, R. Targeting PTEN using small molecule inhibitors. Methods 2015, 77–78, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aurich, I.; Hirche, F.; Ulbrich-Hofmann, R. The determination of phospholipase D activity in emulsion systems. Anal. Biochem. 1999, 268, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosokawa, M.; Shimatani, T.; Kanada, T.; Inoue, Y.; Takahashi, K. Conversion to docosahexaenoic acid-containing phosphatidylserine from squid skin lecithin by phospholipase D-mediated transphosphatidylation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2000, 48, 4550–4554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dittrich, N.; Ulbrich-Hofmann, R. Transphosphatidylation by immobilized phospholipase D in aqueous media. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 2001, 34, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santra, M.; Luthra-Guptasarma, M. Assaying Collagenase Activity by Specific Labeling of Freshly Generated N-Termini with Fluorescamine at Mildly Acidic pH. Int. J. Pept. Res. Ther. 2020, 26, 775–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, S.F.; DeBlanc, R.L.; Hergenrother, P.J. Determination of the substrate specificity of the phospholipase D from Streptomyces chromofuscus via an inorganic phosphate quantitation assay. Anal. Biochem. 2000, 278, 106–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geladopoulos, T.P.; Sotiroudis, T.G.; Evangelopoulos, A.E. A malachite green colorimetric assay for protein phosphatase activity. Anal. Biochem. 1991, 192, 112–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baykov, A.A.; Evtushenko, O.A.; Avaeva, S.M. A malachite green procedure for orthophosphate determination and its use in alkaline phosphatase-based enzyme immunoassay. Anal. Biochem. 1988, 171, 266–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brennan, J.C.; Tillitt, D.E. Development of a dual luciferase activity and fluorescamine protein assay adapted to a 384 micro-well plate format: Reducing variability in human luciferase transactivation cell lines aimed at endocrine active substances. Toxicol. Vitr. Int. J. Publ. Assoc. BIBRA 2018, 47, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashby, J.; Duan, Y.; Ligans, E.; Tamsi, M.; Zhong, W. High-throughput profiling of nanoparticle-protein interactions by fluorescamine labeling. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 2213–2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rawyler, A.; Roelofsen, B.; Op den Kamp, J.A. The use of fluorescamine as a permeant probe to localize phosphatidylethanolamine in intact friend erythroleukaemic cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1984, 769, 330–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeda, N.; Akiyama, Y. Rapid determination of sulphonamides in milk using liquid chromatographic separation and fluorescamine derivatization. J. Chromatogr. 1992, 607, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, C.H.; Ridella, J.D. An evaluation of fluorometric proteinase assays which employ fluorescamine. Anal. Biochem. 1984, 142, 411–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mak, L.H.; Georgiades, S.N.; Rosivatz, E.; Whyte, G.F.; Mirabelli, M.; Vilar, R.; Woscholski, R. A small molecule mimicking a phosphatidylinositol (4,5)-bisphosphate binding pleckstrin homology domain. ACS Chem. Biol. 2011, 6, 1382–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Omar, M.A.; Hammad, M.A.; Salman, B.I.; Derayea, S.M. Highly sensitive spectrofluorimetric method for determination of doxazosin through derivatization with fluorescamine; Application to content uniformity testing. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2016, 157, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrea, G.; D’Arrigo, P.; Piergianni, V.; Roncaglio, S.; Secundo, F.; Servi, S. Purification and properties of two phospholipases D from Streptomyces sp. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1995, 1255, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.-B.; Gong, J.-S.; Hou, H.-J.; Li, H.; Lu, Z.-M.; Xu, H.-Y.; Xu, Z.-H.; Shi, J.-S. Mining of a phospholipase D and its application in enzymatic preparation of phosphatidylserine. Bioengineered 2018, 9, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, H.; Roberts, M.F. Phosphohydrolase and transphosphatidylation reactions of two Streptomyces phospholipase D enzymes: Covalent versus noncovalent catalysis. Protein Sci. 2003, 12, 2087–2098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sato, R.; Itabashi, Y.; Suzuki, A.; Hatanaka, T.; Kuksis, A. Effect of temperature on the stereoselectivity of phospholipase D toward glycerol in the transphosphatidylation of phosphatidylcholine to phosphatidylglycerol. Lipids 2004, 39, 1019–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, K.; Liu, Y.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Cong, P.; Li, H.; Xu, J.; Li, Z.; Wang, J.; Mao, X.; et al. Reaction Specificity of Phospholipase D Prepared from Acinetobacter radioresistens a2 in Transphosphatidylation. Lipids 2018, 53, 517–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
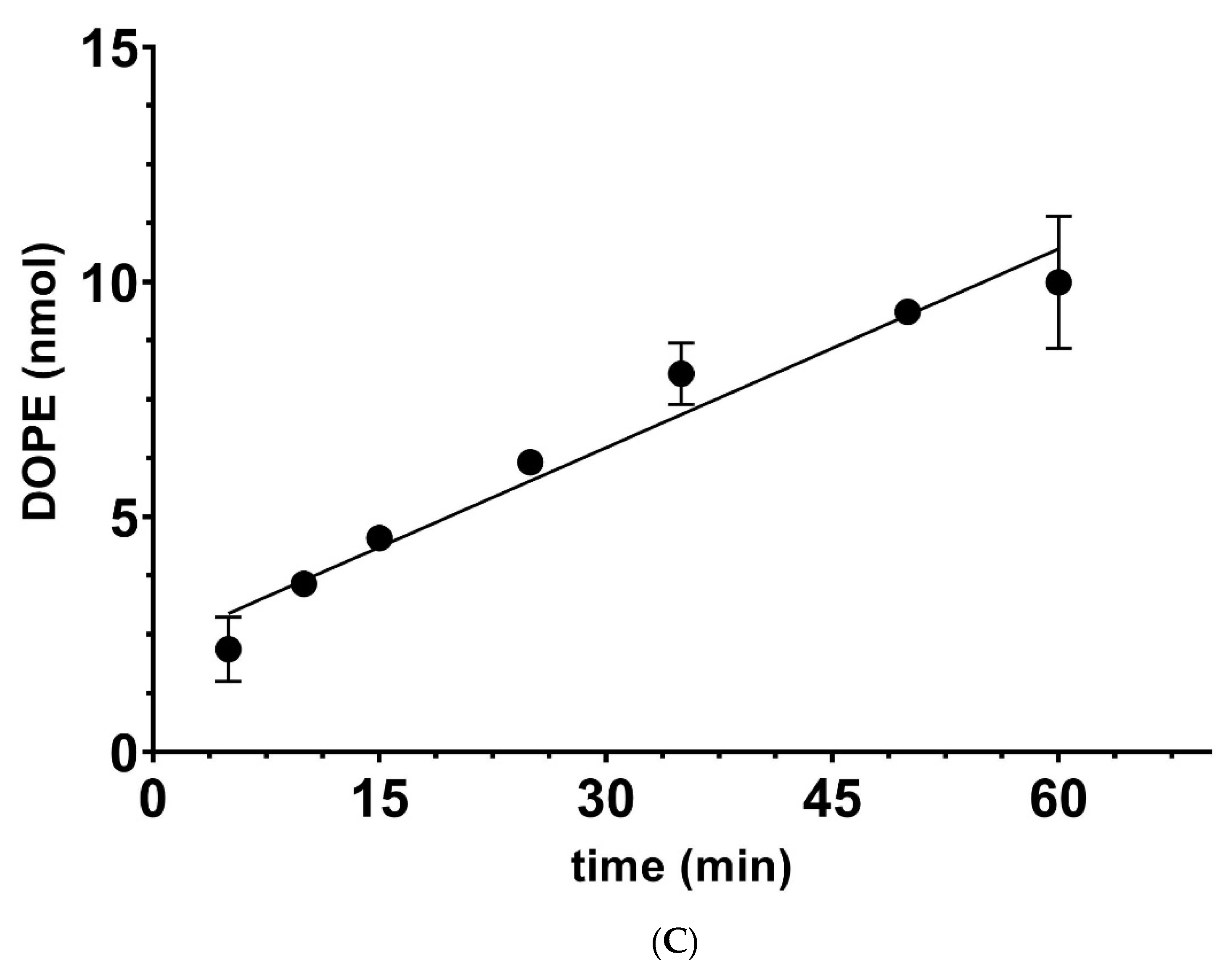

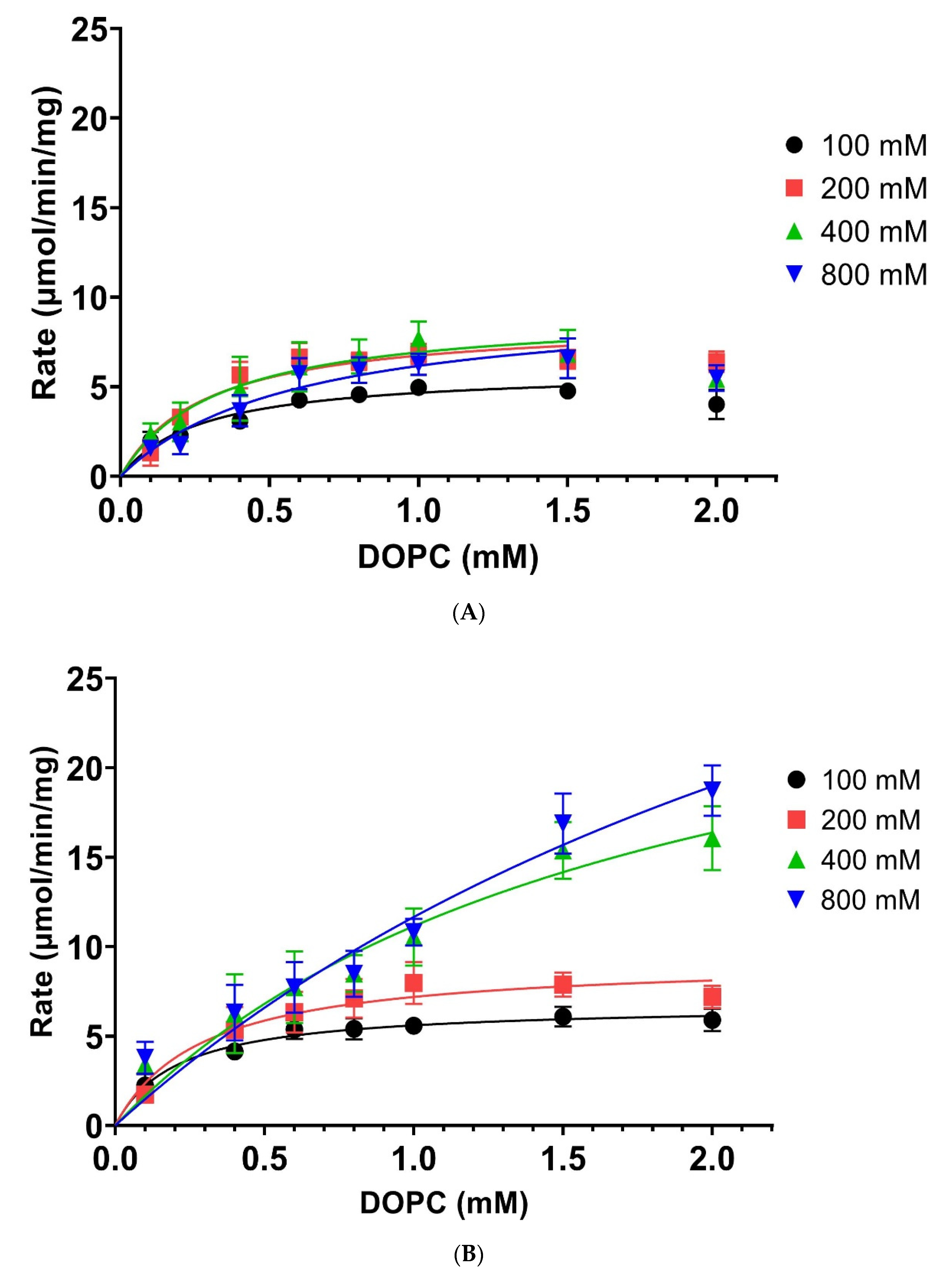
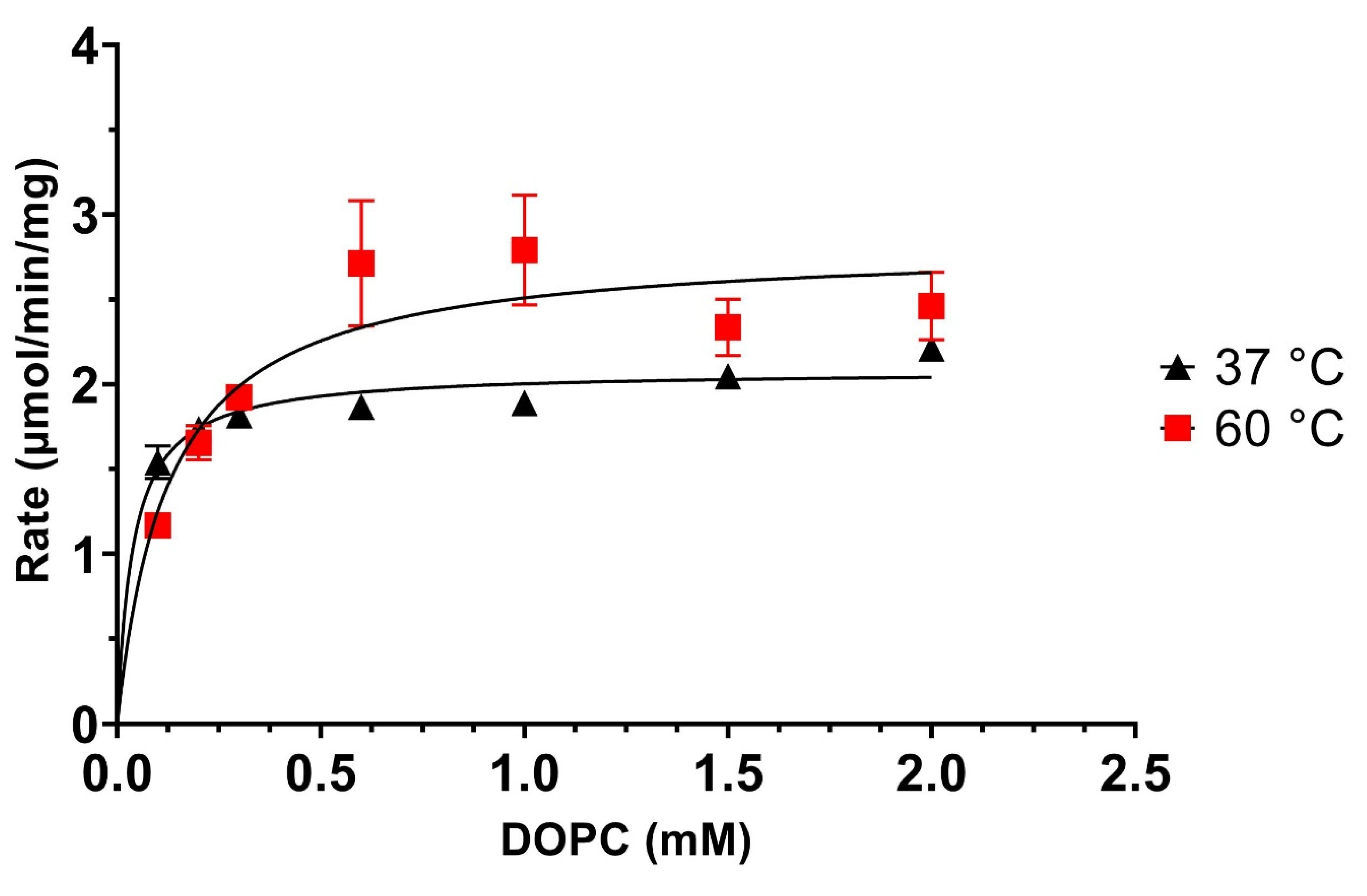
| [Ethanolamine] mM | 100 | 200 | 400 | 800 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature (°C) | 37 | 60 | 37 | 60 | 37 | 60 | 37 | 60 |
| Vmax (µmol/min/mg) | 5.9 ± 0.48 | 6.76 ± 0.25 | 8.68 ± 1.0 | 9.29 ± 0.79 | 9.19 ± 0.84 | 30.87 ± 6.93 | 9.85 ± 1.49 | 50.88 ± 20.59 |
| KM (mM) | 0.28 ± 0.07 | 0.21 ± 0.03 | 0.29 ± 0.11 | 0.29 ± 0.09 | 0.33 ± 0.09 | 1.77 ± 0.67 | 0.6 ± 0.21 | 3.36 ± 1.91 |
| Significance for Vmax against 200 mM of same temperature | S | S | NA | NA | NS | S | NS | S |
| Significance for Vmax against 37 °C of same concentration | NA | S | NA | NS | NA | S | NA | S |
| Significance for KM against 200 mM of same temperature | NS | NS | NA | NA | NS | S | S | S |
| Significance for KM against 37 °C of same concentration | NA | S | NA | NS | NA | S | NA | S |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, H.; Woscholski, R. A Novel High-Throughput Assay Reveals That the Temperature Induced Increases in Transphosphatidylation of Phospholipase D Are Dependent on the Alcohol Acceptor Concentration. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 632. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12050632
Yang H, Woscholski R. A Novel High-Throughput Assay Reveals That the Temperature Induced Increases in Transphosphatidylation of Phospholipase D Are Dependent on the Alcohol Acceptor Concentration. Biomolecules. 2022; 12(5):632. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12050632
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Hengzhang, and Rüdiger Woscholski. 2022. "A Novel High-Throughput Assay Reveals That the Temperature Induced Increases in Transphosphatidylation of Phospholipase D Are Dependent on the Alcohol Acceptor Concentration" Biomolecules 12, no. 5: 632. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12050632
APA StyleYang, H., & Woscholski, R. (2022). A Novel High-Throughput Assay Reveals That the Temperature Induced Increases in Transphosphatidylation of Phospholipase D Are Dependent on the Alcohol Acceptor Concentration. Biomolecules, 12(5), 632. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12050632






