Toxic Effects of Endocrine Disruptor Exposure on Collagen-Induced Arthritis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. CIA-Induced RA and Treatments
2.3. Experimental Groups
- −
- CIA: rats were subjected to CIA as described above;
- −
- CIA + CP: same as the CIA group, and CP (15 mg/kg) was administered;
- −
- CIA + DEP: same as the CIA group, and DEP (2 μg/mL) was administered;
- −
- CIA + VCZ: same as the CIA group, and VCZ (100 mg/kg) was administered;
- −
- CIA + EE: same as the CIA group, and EE (1 μg/kg) was administered;
- −
- CIA + PFOS: same as the CIA group, and PFOS (10 mg/kg) was administered;
- −
- CIA + ATR: same as the CIA group, and ATR (25 mg/kg) was administered;
- −
- Sham groups = mice received two injections of 100 uL of 0.01 M acetic acid instead of the emulsion. Then, animals were orally administered with either vehicle or CP, DEP, VLZ, EE, PFOS, or ATR every day, starting from day 21 to day 35.
2.4. Behavioral Tests
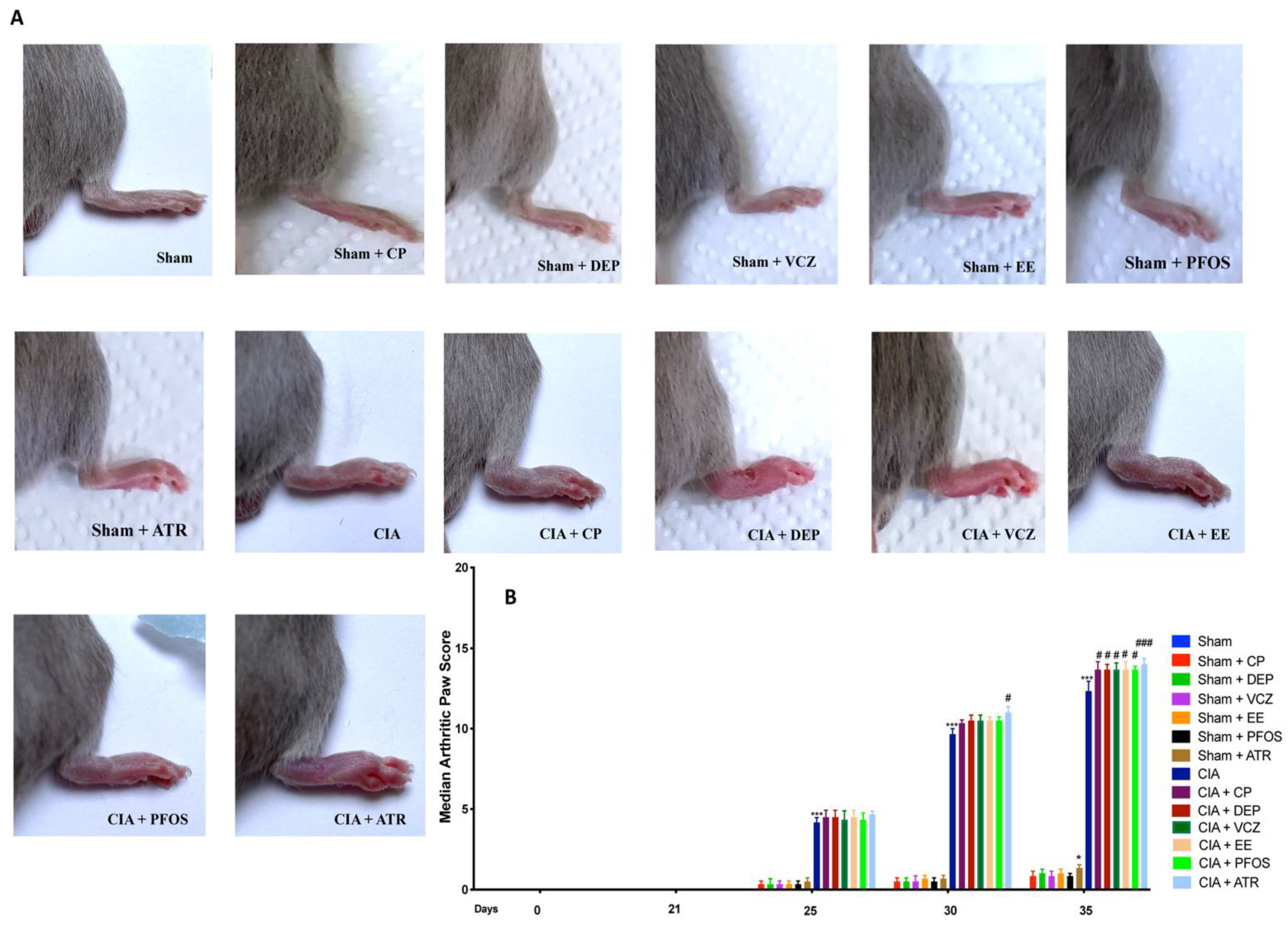
2.5. Clinical Severity of CIA
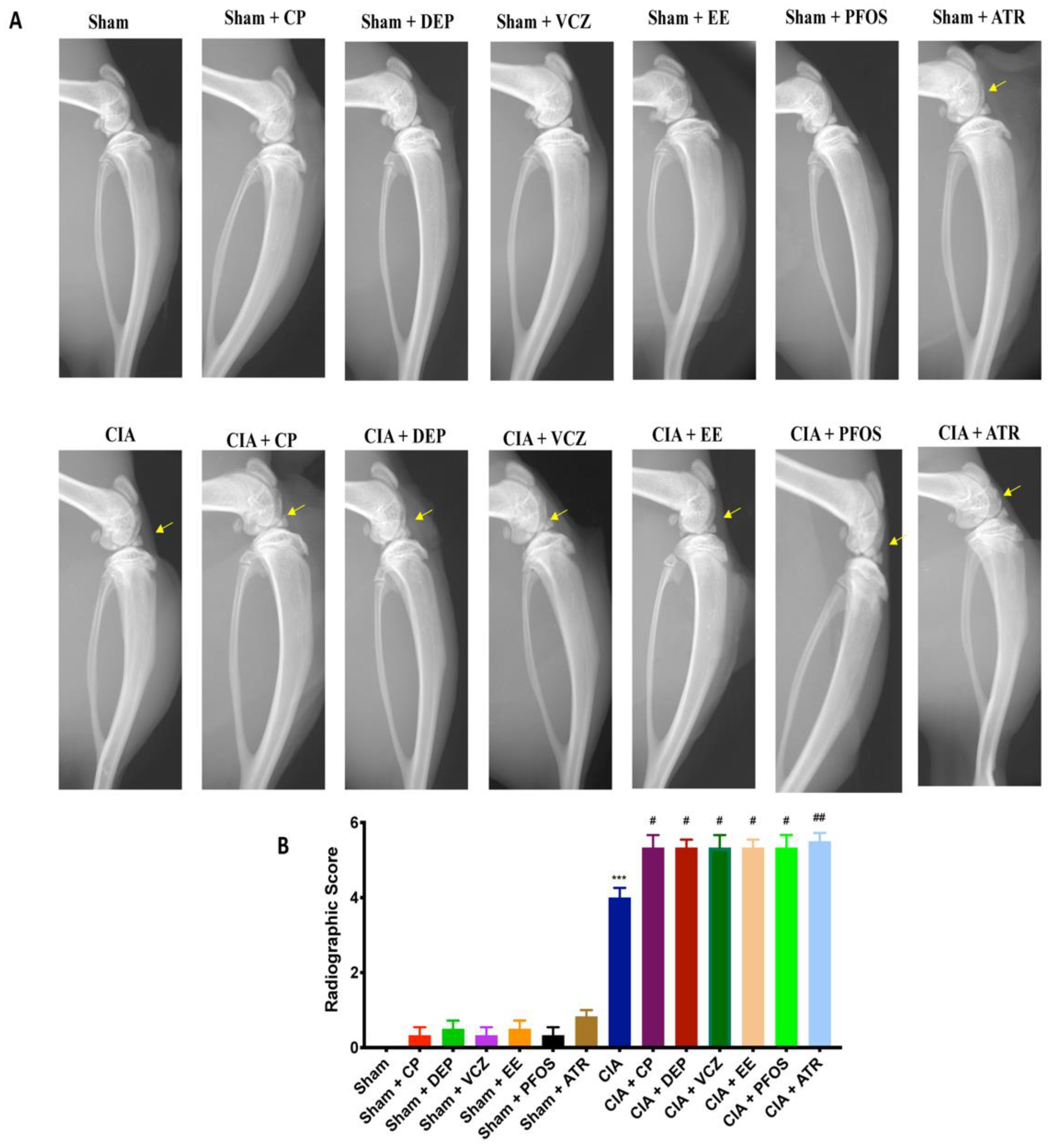
2.6. Radiographic Analysis
2.7. Haematoxylin/Eosin (H/E) and Toluidine Blue Staining
2.8. Staining of Mast Cells
2.9. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
2.10. Myeloperoxidase (MPO) Assay and Thiobarbituric Acid-Reactant Substances Measurement (MDA Levels)
2.11. Immunohistochemical Analysis of Cyclooxygenase (COX)-2
2.12. Materials
2.13. Statistical Evaluation
3. Results
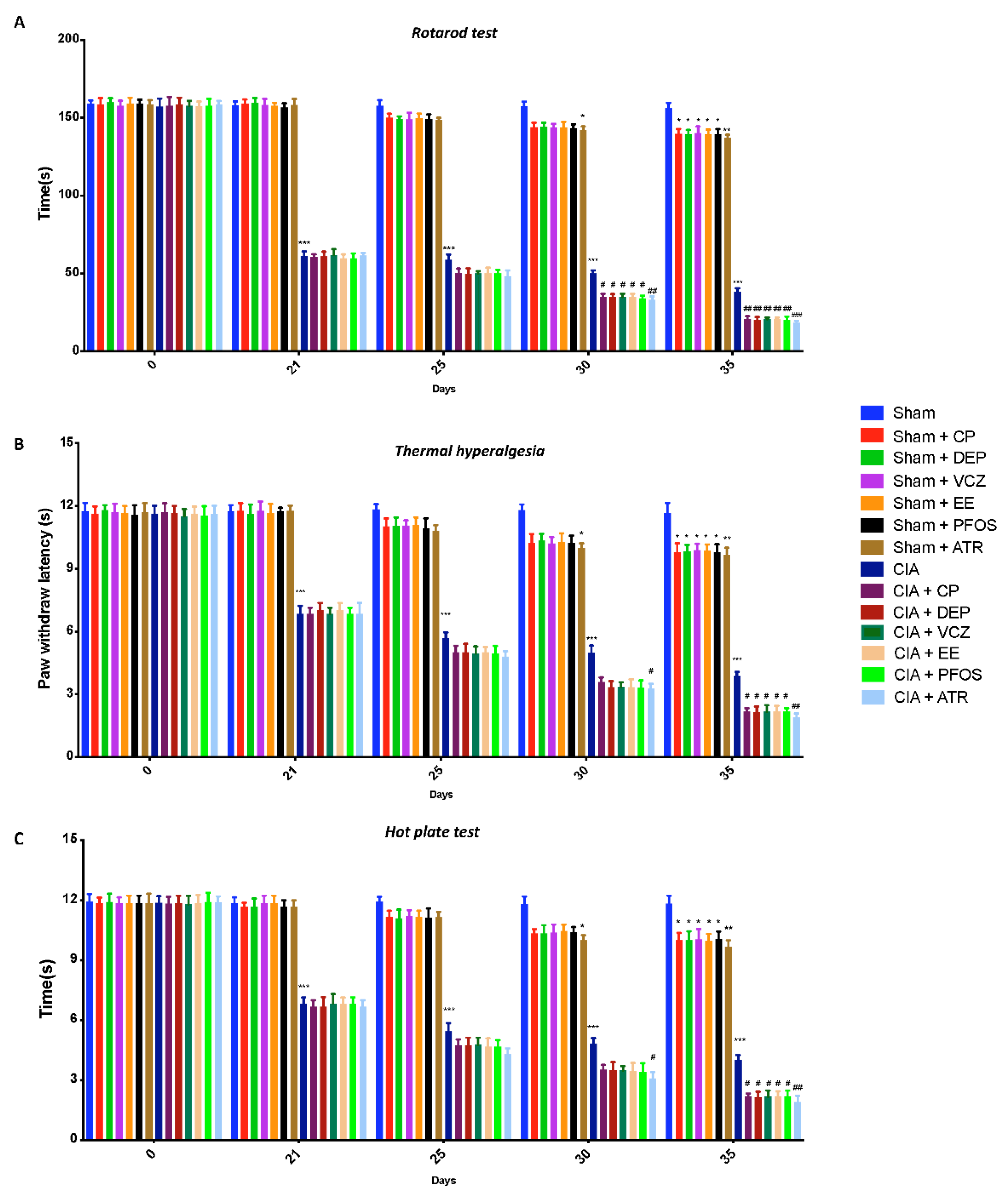
3.1. Impact of ED Exposure on Behavioral Function
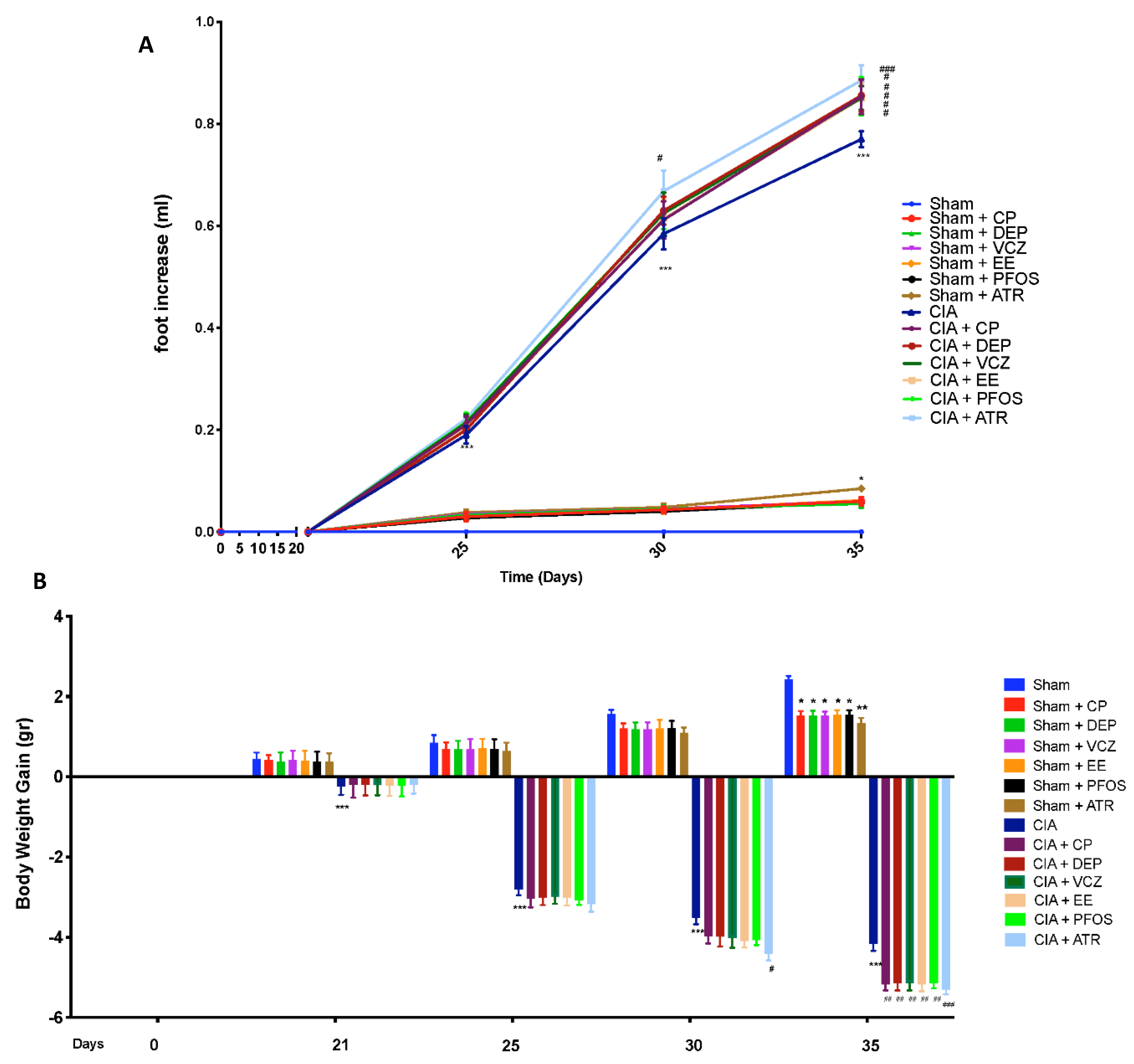
3.2. Impact of ED Exposure on Clinical Signs and Body Weight
3.3. Impact of ED Exposure on Radiographic Analysis
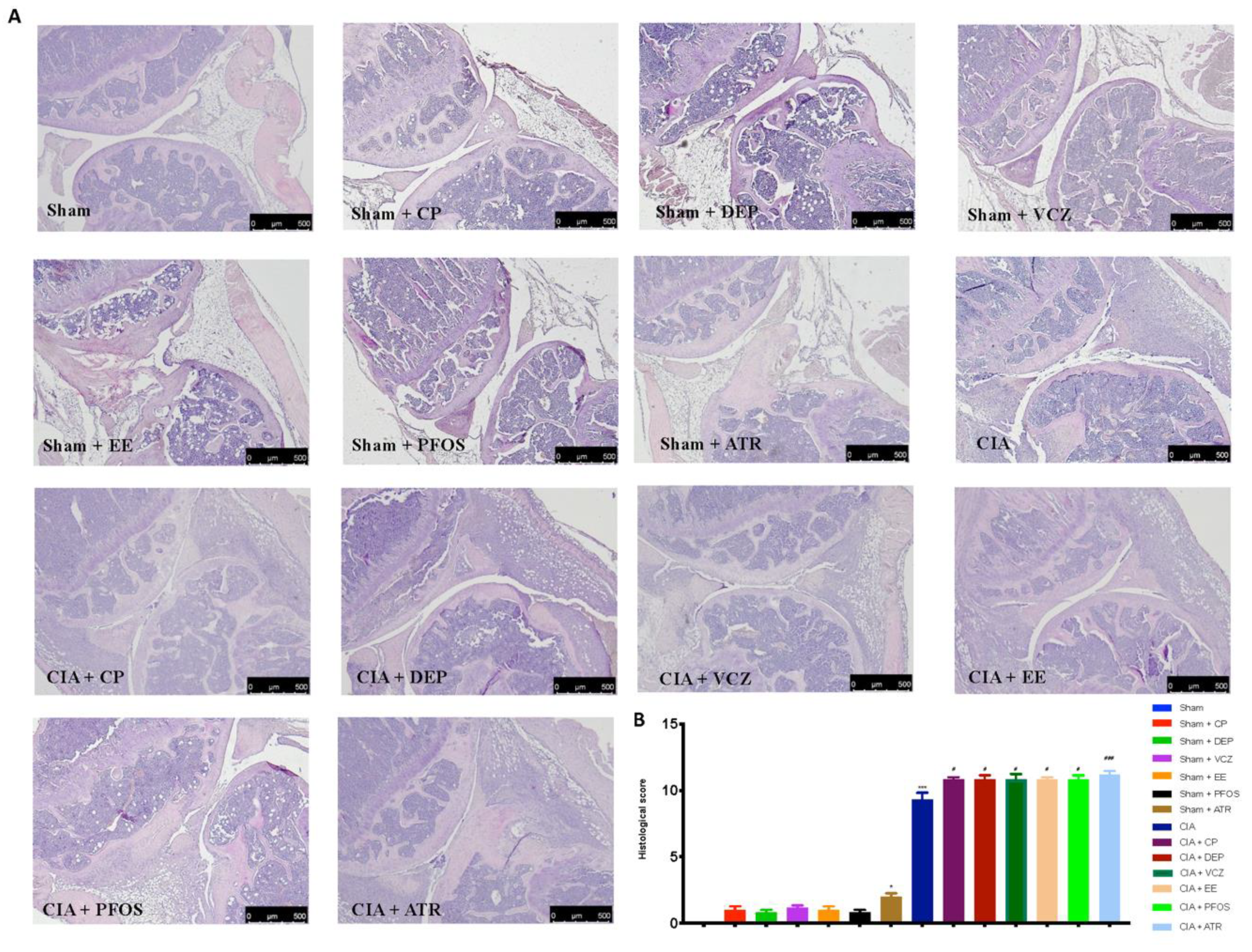
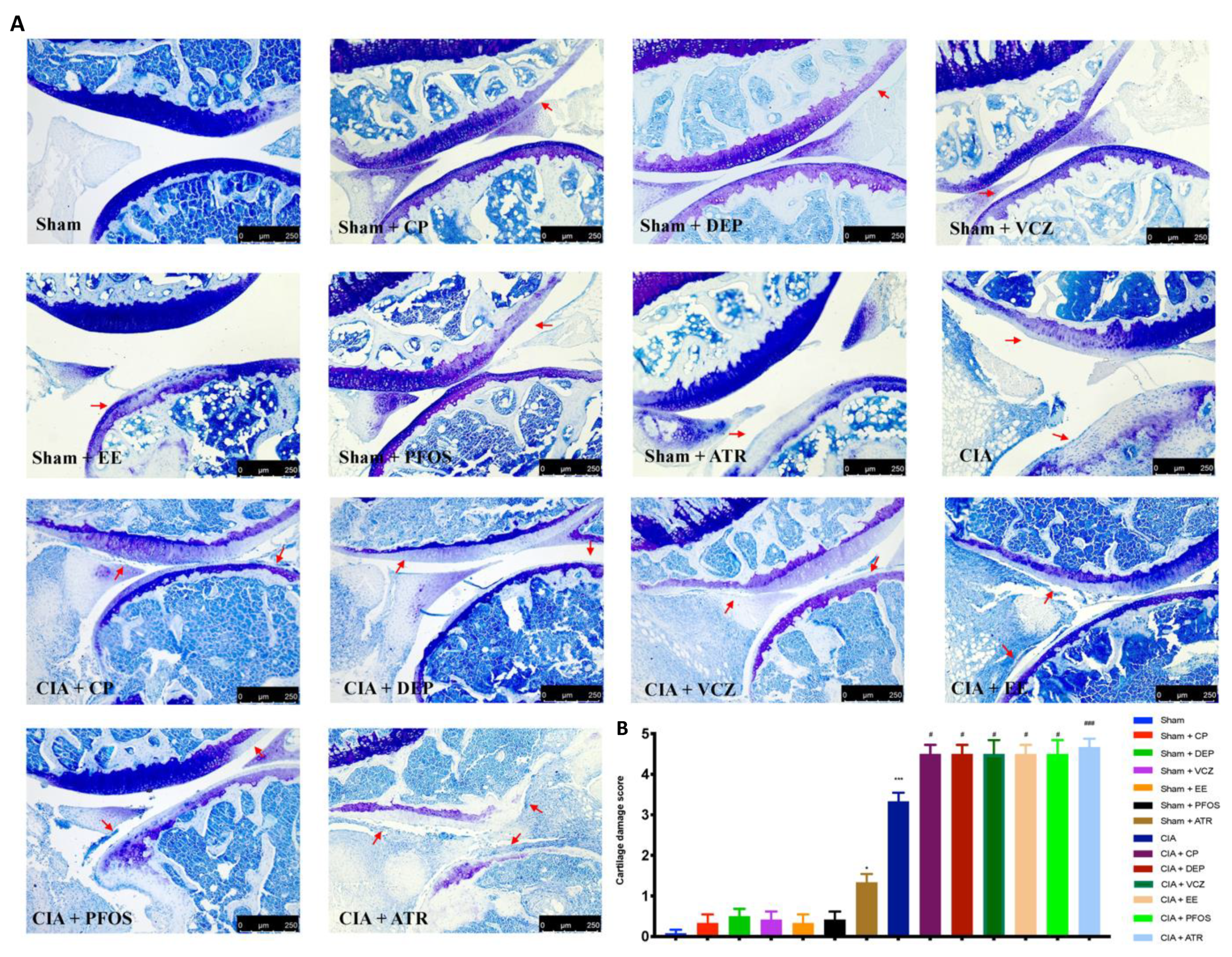
3.4. Impact of ED Exposure on Histopathological Analysis
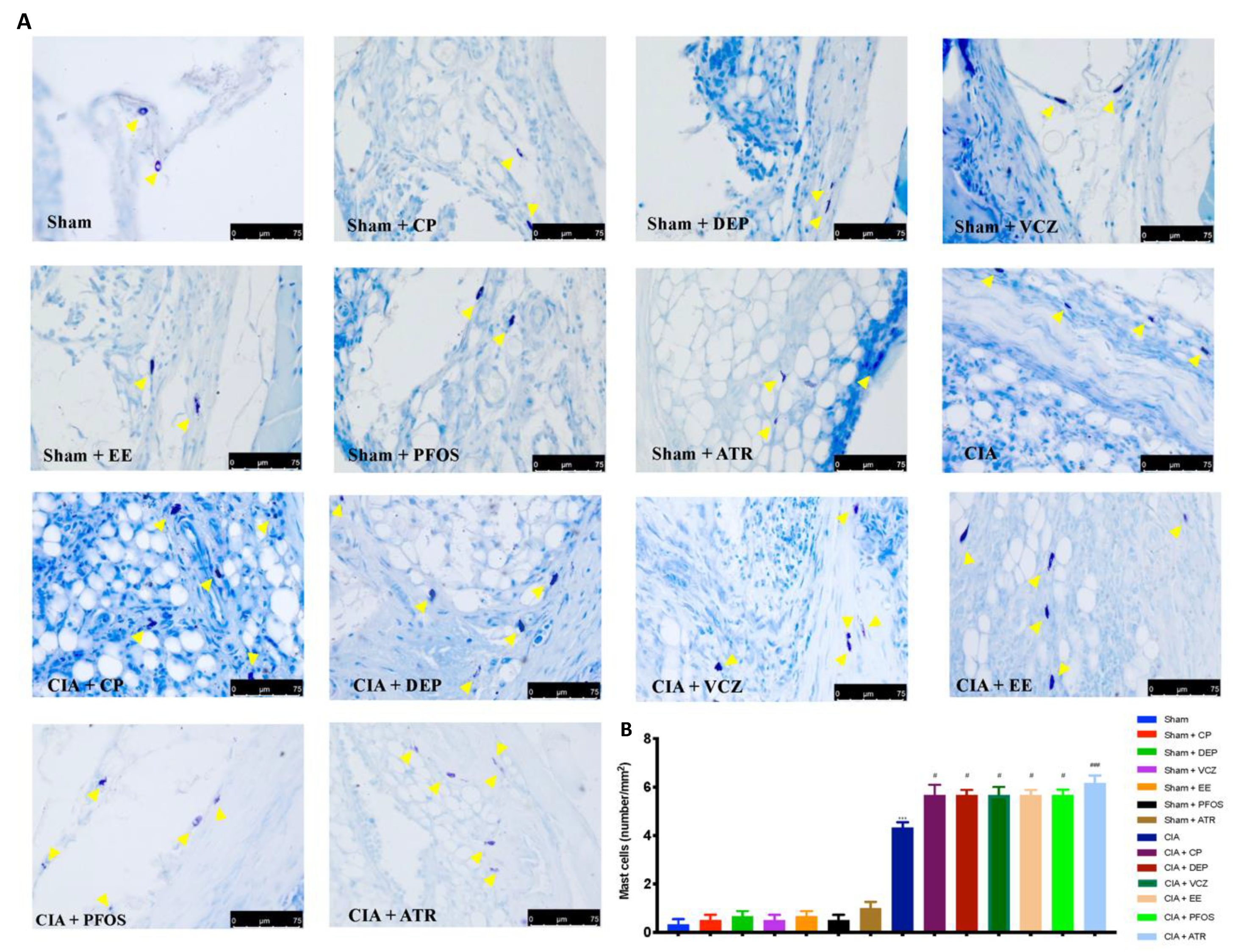
3.5. Impact of ED Exposure on Mast Cell Degranulation
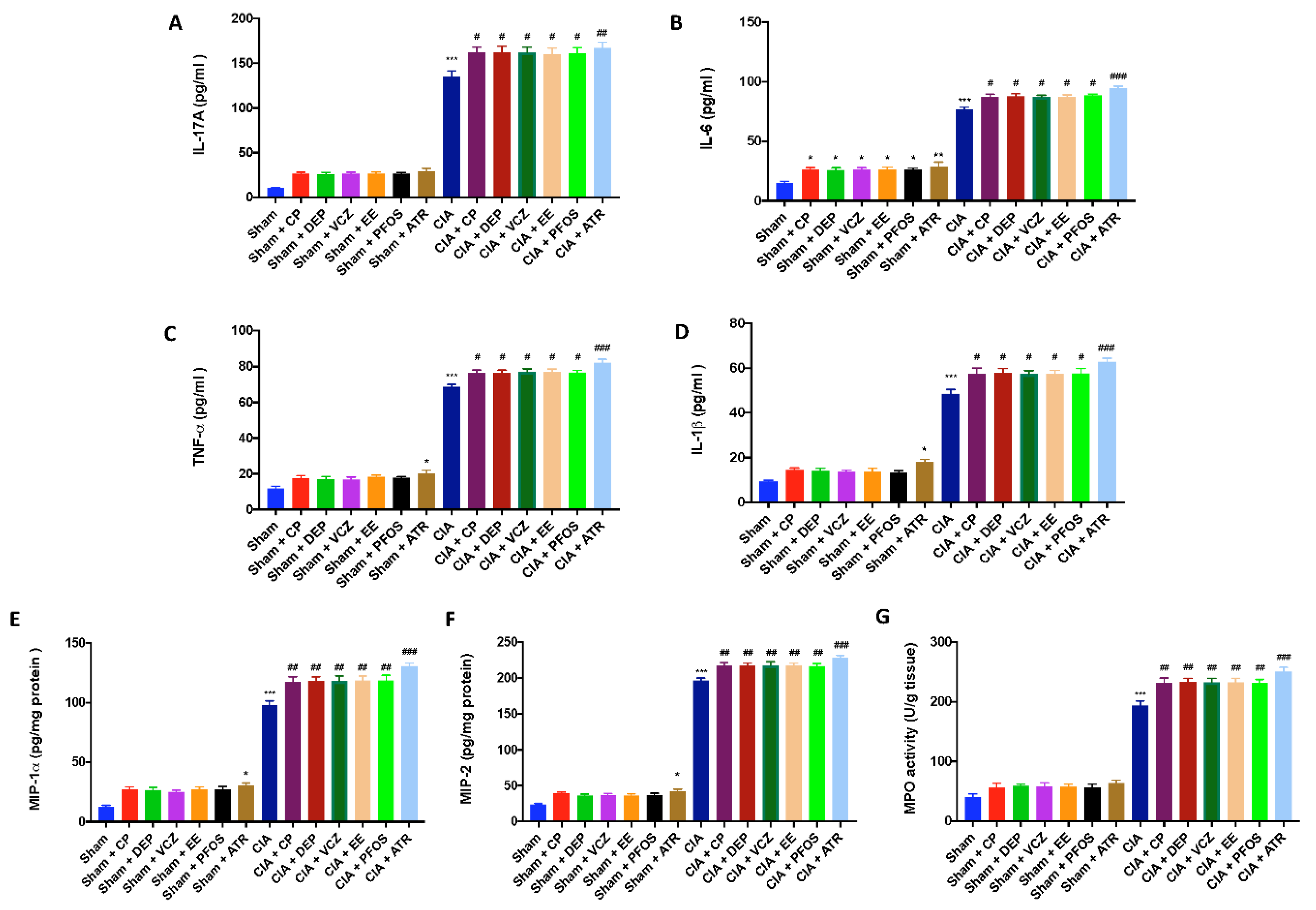
3.6. Impact of ED Exposure on Cytokine and Chemokine Levels and Neutrophil Infiltration
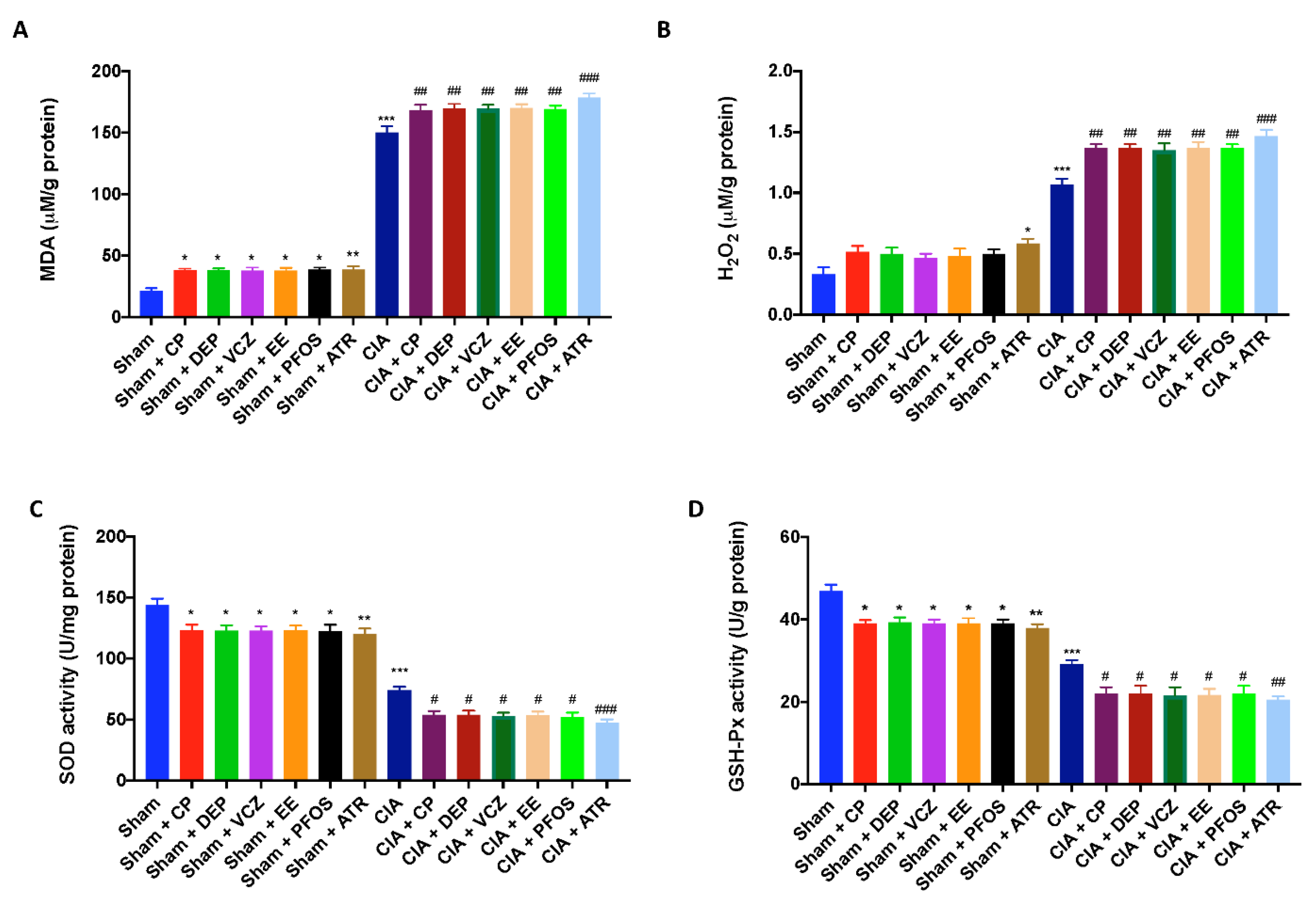
3.7. Impact of ED Exposure on Oxidative Stress and Lipid Peroxidation
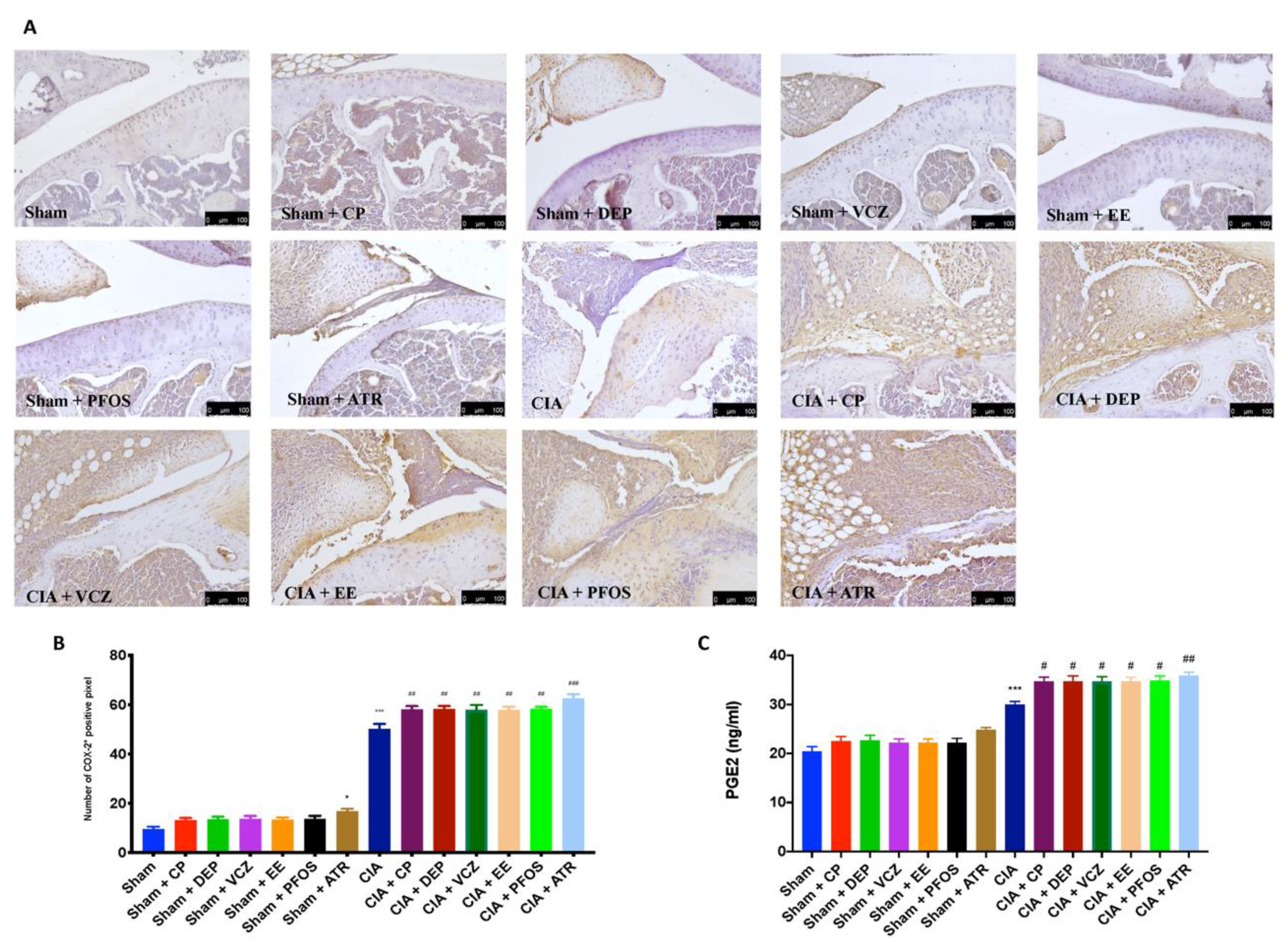
3.8. Impact of ED Exposure on COX-2 and PGE2 Expression
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yilmaz, B.; Terekeci, H.; Sandal, S.; Kelestimur, F. Endocrine disrupting chemicals: Exposure, effects on human health, mechanism of action, models for testing and strategies for prevention. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2020, 21, 127–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauretta, R.; Sansone, A.; Sansone, M.; Romanelli, F.; Appetecchia, M. Endocrine Disrupting Chemicals: Effects on Endocrine Glands. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De Coster, S.; van Larebeke, N. Endocrine-disrupting chemicals: Associated disorders and mechanisms of action. J. Environ. Public Health 2012, 2012, 713696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gore, A.C.; Chappell, V.A.; Fenton, S.E.; Flaws, J.A.; Nadal, A.; Prins, G.S.; Toppari, J.; Zoeller, R.T. EDC-2: The Endocrine Society’s Second Scientific Statement on Endocrine-Disrupting Chemicals. Endocr. Rev. 2015, 36, E1–E150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koch, C.A.; Diamanti-Kandarakis, E. Introduction to Endocrine Disrupting Chemicals—Is it time to act? Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2015, 16, 269–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- D’Amico, R.; Monaco, F.; Fusco, R.; Siracusa, R.; Impellizzeri, D.; Peritore, A.F.; Crupi, R.; Gugliandolo, E.; Cuzzocrea, S.; Di Paola, R.; et al. Atrazine Inhalation Worsen Pulmonary Fibrosis Regulating the Nuclear Factor-Erythroid 2-Related Factor (Nrf2) Pathways Inducing Brain Comorbidities. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2021, 55, 704–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, C.H.; Yang, S.N.; Kuo, P.L.; Hung, C.H. Immunomodulatory effects of environmental endocrine disrupting chemicals. Kaohsiung J. Med. Sci. 2012, 28, S37–S42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Popescu, M.; Feldman, T.B.; Chitnis, T. Interplay Between Endocrine Disruptors and Immunity: Implications for Diseases of Autoreactive Etiology. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 626107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalubinski, M.; Kowalski, M.L. Endocrine disrupters—Potential modulators of the immune system and allergic response. Allergy 2006, 61, 1326–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, M.W.; Garcia, S.; Gerlag, D.M.; Tak, P.P.; Reedquist, K.A. Insight into the Endocrine System and the Immune System: A Review of the Inflammatory Role of Prolactin in Rheumatoid Arthritis and Psoriatic Arthritis. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kelley, K.W.; Weigent, D.A.; Kooijman, R. Protein hormones and immunity. Brain Behav. Immun. 2007, 21, 384–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Al-Suhaimi, E.A.; Al-Jafary, M.A. Endocrine roles of vitamin K-dependent- osteocalcin in the relation between bone metabolism and metabolic disorders. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2020, 21, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yaglova, N.V.; Yaglov, V.V. Endocrine Disruptors as a New Etiologic Factor of Bone Tissue Diseases (Review). Sovrem Tekhnol. Med. 2021, 13, 84–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holmdahl, R.; Andersson, M.; Goldschmidt, T.J.; Gustafsson, K.; Jansson, L.; Mo, J.A. Type II collagen autoimmunity in animals and provocations leading to arthritis. Immunol. Rev. 1990, 118, 193–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Impellizzeri, D.; Siracusa, R.; Cordaro, M.; Peritore, A.F.; Gugliandolo, E.; D’Amico, R.; Fusco, R.; Crupi, R.; Rizzarelli, E.; Cuzzocrea, S.; et al. Protective effect of a new hyaluronic acid -carnosine conjugate on the modulation of the inflammatory response in mice subjected to collagen-induced arthritis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 125, 110023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, B.; Zou, W.; Hu, Z.; Liu, F.; Zhou, L.; Yang, S.; Kuang, H.; Wu, L.; Wei, J.; Wang, J.; et al. Involvement of oxidative stress and inflammation in liver injury caused by perfluorooctanoic acid exposure in mice. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 409837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coban, A.; Filipov, N.M. Dopaminergic toxicity associated with oral exposure to the herbicide atrazine in juvenile male C57BL/6 mice. J. Neurochem. 2007, 100, 1177–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero-Bosagna, C.; Covert, T.R.; Haque, M.M.; Settles, M.; Nilsson, E.E.; Anway, M.D.; Skinner, M.K. Epigenetic transgenerational inheritance of vinclozolin induced mouse adult onset disease and associated sperm epigenome biomarkers. Reprod. Toxicol. 2012, 34, 694–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- European Food Safety Authority. Statement on the impact of the harmonised classification on the conclusion on the peer review of the pesticide risk assessment of the active substance flutianil. EFSA J. 2018, 16, e05383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, D.; Irani, D.; Bhagat, S.; Vanage, G. Cypermethrin exposure during perinatal period affects fetal development and impairs reproductive functions of F1 female rats. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 707, 135945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saravanabhavan, G.; Walker, M.; Guay, M.; Aylward, L. Urinary excretion and daily intake rates of diethyl phthalate in the general Canadian population. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 500–501, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Leitz, J.; Kuballa, T.; Rehm, J.; Lachenmeier, D.W. Chemical analysis and risk assessment of diethyl phthalate in alcoholic beverages with special regard to unrecorded alcohol. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e8127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cleuren, A.C.; Van der Linden, I.K.; De Visser, Y.P.; Wagenaar, G.T.; Reitsma, P.H.; Van Vlijmen, B.J. 17alpha-Ethinylestradiol rapidly alters transcript levels of murine coagulation genes via estrogen receptor alpha. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2010, 8, 1838–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LaPlante, C.D.; Vandenberg, L.N. Data describing lack of effects of 17alpha-ethinyl estradiol on mammary gland morphology in female mice exposed during pregnancy and lactation. Data Brief 2017, 14, 337–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siracusa, R.; Fusco, R.; Cordaro, M.; Peritore, A.F.; D’Amico, R.; Gugliandolo, E.; Crupi, R.; Genovese, T.; Evangelista, M.; Di Paola, R.; et al. The Protective Effects of Pre- and Post-Administration of Micronized Palmitoylethanolamide Formulation on Postoperative Pain in Rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peritore, A.F.; Siracusa, R.; Fusco, R.; Gugliandolo, E.; D’Amico, R.; Cordaro, M.; Crupi, R.; Genovese, T.; Impellizzeri, D.; Cuzzocrea, S.; et al. Ultramicronized Palmitoylethanolamide and Paracetamol, a New Association to Relieve Hyperalgesia and Pain in a Sciatic Nerve Injury Model in Rat. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szabo, C.; Virag, L.; Cuzzocrea, S.; Scott, G.S.; Hake, P.; O’Connor, M.P.; Zingarelli, B.; Salzman, A.; Kun, E. Protection against peroxynitrite-induced fibroblast injury and arthritis development by inhibition of poly(ADP-ribose) synthase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 3867–3872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gugliandolo, E.; Peritore, A.F.; Impellizzeri, D.; Cordaro, M.; Siracusa, R.; Fusco, R.; D’Amico, R.; Paola, R.D.; Schievano, C.; Cuzzocrea, S.; et al. Dietary Supplementation with Palmitoyl-Glucosamine Co-Micronized with Curcumin Relieves Osteoarthritis Pain and Benefits Joint Mobility. Animals 2020, 10, 1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mausset-Bonnefont, A.L.; Cren, M.; Vicente, R.; Quentin, J.; Jorgensen, C.; Apparailly, F.; Louis-Plence, P. Arthritis sensory and motor scale: Predicting functional deficits from the clinical score in collagen-induced arthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2019, 21, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, D.Y.; Lin, C.C.; Chen, Y.M.; Chao, Y.H.; Yang, D.H. Dextromethorphan Exhibits Anti-inflammatory and Immunomodulatory Effects in a Murine Model of Collagen-Induced Arthritis and in Human Rheumatoid Arthritis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 11353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alavala, S.; Nalban, N.; Sangaraju, R.; Kuncha, M.; Jerald, M.K.; Kilari, E.K.; Sistla, R. Anti-inflammatory effect of stevioside abates Freund’s complete adjuvant (FCA)-induced adjuvant arthritis in rats. Inflammopharmacology 2020, 28, 1579–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Cao, C.; Sun, S.; Xu, Q. Selective spleen tyrosine kinase inhibition delays autoimmune arthritis in mice. Mol. Med. Rep. 2015, 12, 2902–2906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Min, S.Y.; Yan, M.; Kim, S.B.; Ravikumar, S.; Kwon, S.R.; Vanarsa, K.; Kim, H.Y.; Davis, L.S.; Mohan, C. Green Tea Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate Suppresses Autoimmune Arthritis Through Indoleamine-2,3-Dioxygenase Expressing Dendritic Cells and the Nuclear Factor, Erythroid 2-Like 2 Antioxidant Pathway. J. Inflamm. 2015, 12, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Impellizzeri, D.; Esposito, E.; Di Paola, R.; Ahmad, A.; Campolo, M.; Peli, A.; Morittu, V.M.; Britti, D.; Cuzzocrea, S. Erratum to: Palmitoylethanolamide and luteolin ameliorate development of arthritis caused by injection of collagen type II in mice. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2016, 18, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Impellizzeri, D.; Esposito, E.; Mazzon, E.; Paterniti, I.; Di Paola, R.; Morittu, V.M.; Procopio, A.; Britti, D.; Cuzzocrea, S. Oleuropein aglycone, an olive oil compound, ameliorates development of arthritis caused by injection of collagen type II in mice. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2011, 339, 859–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, K.T.; Lin, C.C.; Lin, S.C.; Wang, J.H.; Tsai, S.W. Kurarinone Attenuates Collagen-Induced Arthritis in Mice by Inhibiting Th1/Th17 Cell Responses and Oxidative Stress. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusco, R.; Cordaro, M.; Genovese, T.; Impellizzeri, D.; Siracusa, R.; Gugliandolo, E.; Peritore, A.F.; D’Amico, R.; Crupi, R.; Cuzzocrea, S.; et al. Adelmidrol: A New Promising Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Therapeutic Tool in Pulmonary Fibrosis. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordaro, M.; Siracusa, R.; Fusco, R.; D’Amico, R.; Peritore, A.F.; Gugliandolo, E.; Genovese, T.; Scuto, M.; Crupi, R.; Mandalari, G.; et al. Cashew (Anacardium occidentale L.) Nuts Counteract Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in an Acute Experimental Model of Carrageenan-Induced Paw Edema. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohkawa, H.; Ohishi, N.; Yagi, K. Assay for lipid peroxides in animal tissues by thiobarbituric acid reaction. Anal. Biochem. 1979, 95, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Amico, R.; Fusco, R.; Cordaro, M.; Siracusa, R.; Peritore, A.F.; Gugliandolo, E.; Crupi, R.; Scuto, M.; Cuzzocrea, S.; Di Paola, R.; et al. Modulation of NLRP3 Inflammasome through Formyl Peptide Receptor 1 (Fpr-1) Pathway as a New Therapeutic Target in Bronchiolitis Obliterans Syndrome. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zoeller, R.T.; Brown, T.R.; Doan, L.L.; Gore, A.C.; Skakkebaek, N.E.; Soto, A.M.; Woodruff, T.J.; Vom Saal, F.S. Endocrine-disrupting chemicals and public health protection: A statement of principles from The Endocrine Society. Endocrinology 2012, 153, 4097–4110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ying, G.G.; Toze, S.; Hanna, J.; Yu, X.Y.; Dillon, P.J.; Kookana, R.S. Decay of endocrine-disrupting chemicals in aerobic and anoxic groundwater. Water Res. 2008, 42, 1133–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, M.; Sarma, D.K.; Shubham, S.; Kumawat, M.; Verma, V.; Prakash, A.; Tiwari, R. Environmental Endocrine-Disrupting Chemical Exposure: Role in Non-Communicable Diseases. Front. Public Health 2020, 8, 553850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genovese, T.; Siracusa, R.; Fusco, R.; D’Amico, R.; Impellizzeri, D.; Peritore, A.F.; Crupi, R.; Gugliandolo, E.; Morabito, R.; Cuzzocrea, S.; et al. Atrazine Inhalation Causes Neuroinflammation, Apoptosis and Accelerating Brain Aging. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassotis, C.D.; Vandenberg, L.N.; Demeneix, B.A.; Porta, M.; Slama, R.; Trasande, L. Endocrine-disrupting chemicals: Economic, regulatory, and policy implications. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2020, 8, 719–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalofiri, P.; Balias, G.; Tekos, F. The EU endocrine disruptors’ regulation and the glyphosate controversy. Toxicol. Rep. 2021, 8, 1193–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alavian-Ghavanini, A.; Ruegg, J. Understanding Epigenetic Effects of Endocrine Disrupting Chemicals: From Mechanisms to Novel Test Methods. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2018, 122, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lite, C.; Raja, G.L.; Juliet, M.; Sridhar, V.V.; Subhashree, K.D.; Kumar, P.; Chakraborty, P.; Arockiaraj, J. In utero exposure to endocrine-disrupting chemicals, maternal factors and alterations in the epigenetic landscape underlying later-life health effects. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2022, 89, 103779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusco, R.; Siracusa, R.; Peritore, A.F.; Gugliandolo, E.; Genovese, T.; D’Amico, R.; Cordaro, M.; Crupi, R.; Mandalari, G.; Impellizzeri, D.; et al. The Role of Cashew (Anacardium occidentale L.) Nuts on an Experimental Model of Painful Degenerative Joint Disease. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimura, S.; Asano, K.; Nakane, A. Attenuation of collagen-induced arthritis in mice by salmon proteoglycan. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 406453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McInnes, I.B.; Schett, G. Cytokines in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Nat. Rev. Immunol 2007, 7, 429–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alunno, A.; Carubbi, F.; Giacomelli, R.; Gerli, R. Cytokines in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis: New players and therapeutic targets. BMC Rheumatol. 2017, 1, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Liu, F.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, D.; Dai, Q.; Liu, S. Anti-Arthritic Effect of Chebulanin on Collagen-Induced Arthritis in Mice. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0139052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esalatmanesh, K.; Jamali, A.; Esalatmanesh, R.; Soleimani, Z.; Khabbazi, A.; Malek Mahdavi, A. Effects of N-acetylcysteine supplementation on disease activity, oxidative stress, and inflammatory and metabolic parameters in rheumatoid arthritis patients: A randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trial. Amino Acids 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Liu, Y.; Pan, W.; Li, Y. Angiotensin-(1-7) attenuates collagen-induced arthritis via inhibiting oxidative stress in rats. Amino Acids 2021, 53, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salaffi, F.; Giacobazzi, G.; Di Carlo, M. Chronic Pain in Inflammatory Arthritis: Mechanisms, Metrology, and Emerging Targets-A Focus on the JAK-STAT Pathway. Pain Res. Manag. 2018, 2018, 8564215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kunisch, E.; Jansen, A.; Kojima, F.; Loffler, I.; Kapoor, M.; Kawai, S.; Rubio, I.; Crofford, L.J.; Kinne, R.W. Prostaglandin E2 differentially modulates proinflammatory/prodestructive effects of TNF-alpha on synovial fibroblasts via specific E prostanoid receptors/cAMP. J. Immunol. 2009, 183, 1328–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Villares, R.; Criado, G.; Juarranz, Y.; Lopez-Santalla, M.; Garcia-Cuesta, E.M.; Rodriguez-Frade, J.M.; Leceta, J.; Lucas, P.; Pablos, J.L.; Martinez, A.C.; et al. Inhibitory Role of Growth Hormone in the Induction and Progression Phases of Collagen-Induced Arthritis. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cutolo, M.; Seriolo, B.; Villaggio, B.; Pizzorni, C.; Craviotto, C.; Sulli, A. Androgens and estrogens modulate the immune and inflammatory responses in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2002, 966, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertoldo, E.; Adami, G.; Rossini, M.; Giollo, A.; Orsolini, G.; Viapiana, O.; Gatti, D.; Fassio, A. The Emerging Roles of Endocrine Hormones in Different Arthritic Disorders. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 620920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
D’Amico, R.; Gugliandolo, E.; Cordaro, M.; Fusco, R.; Genovese, T.; Peritore, A.F.; Crupi, R.; Interdonato, L.; Di Paola, D.; Cuzzocrea, S.; et al. Toxic Effects of Endocrine Disruptor Exposure on Collagen-Induced Arthritis. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 564. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12040564
D’Amico R, Gugliandolo E, Cordaro M, Fusco R, Genovese T, Peritore AF, Crupi R, Interdonato L, Di Paola D, Cuzzocrea S, et al. Toxic Effects of Endocrine Disruptor Exposure on Collagen-Induced Arthritis. Biomolecules. 2022; 12(4):564. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12040564
Chicago/Turabian StyleD’Amico, Ramona, Enrico Gugliandolo, Marika Cordaro, Roberta Fusco, Tiziana Genovese, Alessio Filippo Peritore, Rosalia Crupi, Livia Interdonato, Davide Di Paola, Salvatore Cuzzocrea, and et al. 2022. "Toxic Effects of Endocrine Disruptor Exposure on Collagen-Induced Arthritis" Biomolecules 12, no. 4: 564. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12040564
APA StyleD’Amico, R., Gugliandolo, E., Cordaro, M., Fusco, R., Genovese, T., Peritore, A. F., Crupi, R., Interdonato, L., Di Paola, D., Cuzzocrea, S., Impellizzeri, D., Siracusa, R., & Di Paola, R. (2022). Toxic Effects of Endocrine Disruptor Exposure on Collagen-Induced Arthritis. Biomolecules, 12(4), 564. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12040564












