Ghrelin and Cancer: Examining the Roles of the Ghrelin Axis in Tumor Growth and Progression
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Ghrelin Structure and Function
3. Functional Role of Ghrelin Splice Variants across Tumor Types
4. Acylated Ghrelin (AG) and Unacylated Ghrelin (UAG)
5. GHSR-1a/1b
6. GOAT
7. Ghrelin-Related Signaling Pathways
8. Ghrelin in the Prevention of Cancer Cachexia
9. Ghrelin, Obesity, and Cancer Feedback Loop
10. Interactions between Ghrelin and Other Hormones: Implications for Cancer
11. Strengths and Limitations
12. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gahete, M.D.; Cordoba-Chacon, J.; Salvatori, R.; Castano, J.P.; Kineman, R.D.; Luque, R.M. Metabolic regulation of ghrelin O-acyl transferase (GOAT) expression in the mouse hypothalamus, pituitary, and stomach. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2010, 317, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.M.; Wang, G.; Englander, E.W.; Kojima, M.; Greeley, G.H., Jr. Ghrelin, a new gastrointestinal endocrine peptide that stimulates insulin secretion: Enteric distribution, ontogeny, influence of endocrine, and dietary manipulations. Endocrinology 2002, 143, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.S.; Wei, Q.; Wang, H.; Kim, D.M.; Balderas, M.; Wu, G.; Lawler, J.; Safe, S.; Guo, S.; Devaraj, S.; et al. Protective Effects of Ghrelin on Fasting-Induced Muscle Atrophy in Aging Mice. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2020, 75, 621–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seim, I.; Collet, C.; Herington, A.C.; Chopin, L.K. Revised genomic structure of the human ghrelin gene and identification of novel exons, alternative splice variants and natural antisense transcripts. BMC Genomics 2007, 8, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Lee, J.H.; Buras, E.D.; Yu, K.; Wang, R.; Smith, C.W.; Wu, H.; Sheikh-Hamad, D.; Sun, Y. Ghrelin receptor regulates adipose tissue inflammation in aging. Aging (Albany NY) 2016, 8, 178–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, A.H.; Rees, D.J.; Andrews, Z.B.; Davies, J.S. Ghrelin mediated neuroprotection - A possible therapy for Parkinson’s disease? Neuropharmacology 2018, 136, 317–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buntwal, L.; Sassi, M.; Morgan, A.H.; Andrews, Z.B.; Davies, J.S. Ghrelin-Mediated Hippocampal Neurogenesis: Implications for Health and Disease. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2019, 30, 844–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, C.; Xu, H.; Guo, S.; Mertens-Talcott, S.U.; Sun, Y. Ghrelin Signaling in Immunometabolism and Inflamm-Aging. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2018, 1090, 165–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, G.; Samson, S.L.; Sun, Y. Ghrelin: Much more than a hunger hormone. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2013, 16, 619–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Asnicar, M.; Smith, R.G. Central and peripheral roles of ghrelin on glucose homeostasis. Neuroendocrinology 2007, 86, 215–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R.G.; Jiang, H.; Sun, Y. Developments in ghrelin biology and potential clinical relevance. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2005, 16, 436–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delporte, C. Structure and physiological actions of ghrelin. Scientifica (Cairo) 2013, 2013, 518909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nass, R.; Gaylinn, B.D.; Thorner, M.O. The ghrelin axis in disease: Potential therapeutic indications. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2011, 340, 106–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stempniewicz, A.; Ceranowicz, P.; Warzecha, Z. Potential Therapeutic Effects of Gut Hormones, Ghrelin and Obestatin in Oral Mucositis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Kott, A.F.; Shati, A.A.; Al-Kahtani, M.A.; Alqahtani, S. Acylated Ghrelin Renders Chemosensitive Ovarian Cancer Cells Resistant to Cisplatin Chemotherapy via Activation of the PI3K/Akt/mTOR Survival Pathway. Anal. Cell Pathol. (Amst.) 2019, 2019, 9627810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonfili, L.; Cuccioloni, M.; Cecarini, V.; Mozzicafreddo, M.; Palermo, F.A.; Cocci, P.; Angeletti, M.; Eleuteri, A.M. Ghrelin induces apoptosis in colon adenocarcinoma cells via proteasome inhibition and autophagy induction. Apoptosis 2013, 18, 1188–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fung, J.N.; Seim, I.; Wang, D.; Obermair, A.; Chopin, L.K.; Chen, C. Expression and in vitro functions of the ghrelin axis in endometrial cancer. Horm. Cancer 2010, 1, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soleyman-Jahi, S.; Sadeghi, F.; Pastaki Khoshbin, A.; Khani, L.; Roosta, V.; Zendehdel, K. Attribution of Ghrelin to Cancer; Attempts to Unravel an Apparent Controversy. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Au, C.C.; Furness, J.B.; Brown, K.A. Ghrelin and Breast Cancer: Emerging Roles in Obesity, Estrogen Regulation, and Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2016, 6, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanfranco, F.; Baldi, M.; Cassoni, P.; Bosco, M.; Ghe, C.; Muccioli, G. Ghrelin and prostate cancer. Vitam. Horm. 2008, 77, 301–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginter, G.; Ceranowicz, P.; Warzecha, Z. Protective and Healing Effects of Ghrelin and Risk of Cancer in the Digestive System. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanagi, S.; Sato, T.; Kangawa, K.; Nakazato, M. The Homeostatic Force of Ghrelin. Cell Metab. 2018, 27, 786–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibanez-Costa, A.; Gahete, M.D.; Rivero-Cortes, E.; Rincon-Fernandez, D.; Nelson, R.; Beltran, M.; de la Riva, A.; Japon, M.A.; Venegas-Moreno, E.; Galvez, M.A.; et al. In1-ghrelin splicing variant is overexpressed in pituitary adenomas and increases their aggressive features. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gahete, M.D.; Cordoba-Chacon, J.; Hergueta-Redondo, M.; Martinez-Fuentes, A.J.; Kineman, R.D.; Moreno-Bueno, G.; Luque, R.M.; Castano, J.P. A novel human ghrelin variant (In1-ghrelin) and ghrelin-O-acyltransferase are overexpressed in breast cancer: Potential pathophysiological relevance. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e23302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patterson, M.; Murphy, K.G.; le Roux, C.W.; Ghatei, M.A.; Bloom, S.R. Characterization of ghrelin-like immunoreactivity in human plasma. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2005, 90, 2205–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blatnik, M.; Soderstrom, C.I.; Dysinger, M.; Fraser, S.A. Prandial ghrelin attenuation provides evidence that des-acyl ghrelin may be an artifact of sample handling in human plasma. Bioanalysis 2012, 4, 2447–2455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hormaechea-Agulla, D.; Gahete, M.D.; Jimenez-Vacas, J.M.; Gomez-Gomez, E.; Ibanez-Costa, A.; F, L.L.; Rivero-Cortes, E.; Sarmento-Cabral, A.; Valero-Rosa, J.; Carrasco-Valiente, J.; et al. The oncogenic role of the In1-ghrelin splicing variant in prostate cancer aggressiveness. Mol. Cancer 2017, 16, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luque, R.M.; Sampedro-Nunez, M.; Gahete, M.D.; Ramos-Levi, A.; Ibanez-Costa, A.; Rivero-Cortes, E.; Serrano-Somavilla, A.; Adrados, M.; Culler, M.D.; Castano, J.P.; et al. In1-ghrelin, a splice variant of ghrelin gene, is associated with the evolution and aggressiveness of human neuroendocrine tumors: Evidence from clinical, cellular and molecular parameters. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 19619–19633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rincon-Fernandez, D.; Culler, M.D.; Tsomaia, N.; Moreno-Bueno, G.; Luque, R.M.; Gahete, M.D.; Castano, J.P. In1-ghrelin splicing variant is associated with reduced disease-free survival of breast cancer patients and increases malignancy of breast cancer cells lines. Carcinogenesis 2018, 39, 447–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez-Vacas, J.M.; Montero-Hidalgo, A.J.; Gomez-Gomez, E.; Fuentes-Fayos, A.C.; Ruiz-Pino, F.; Guler, I.; Camargo, A.; Anglada, F.J.; Carrasco-Valiente, J.; Tena-Sempere, M.; et al. In1-Ghrelin Splicing Variant as a Key Element in the Pathophysiological Association Between Obesity and Prostate Cancer. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab 2021, 106, e4956–e4968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.J.; Pan, W.W.; Liu, S.B.; Shen, Z.F.; Xu, Y.; Hu, L.L. ERK/MAPK signalling pathway and tumorigenesis. Exp. Ther. Med. 2020, 19, 1997–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeffery, P.L.; Murray, R.E.; Yeh, A.H.; McNamara, J.F.; Duncan, R.P.; Francis, G.D.; Herington, A.C.; Chopin, L.K. Expression and function of the ghrelin axis, including a novel preproghrelin isoform, in human breast cancer tissues and cell lines. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2005, 12, 839–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, A.H.; Jeffery, P.L.; Duncan, R.P.; Herington, A.C.; Chopin, L.K. Ghrelin and a novel preproghrelin isoform are highly expressed in prostate cancer and ghrelin activates mitogen-activated protein kinase in prostate cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2005, 11, 8295–8303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karimi, M.; Heshmati, M.; Fattahi, S.; Bagheri, N.; Alibeigi, F.M.; Taheri, F.; Anjomshoa, M.; Jami, M.S.; Ghatreh Samani, M. The relation between the ghrelin receptor and FOXP3 in bladder cancer. Biotech. Histochem 2021, 96, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, R.X.; Wang, W.P.; Zhao, P.W.; Li, C.B. Ghrelin attenuates the growth of HO-8910 ovarian cancer cells through the ERK pathway. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2016, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fooladi, S.; Akbari, H.; Abolhassani, M.; Sadeghi, E.; Fallah, H. Can Estradiol and Ghrelin Play a Protective Role in Epithelial Ovarian Cancer Incidence in Postmenopausal Women? Arch. Med. Res. 2021, 52, 324–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pritchett, N.R.; Maziarz, M.; Shu, X.O.; Kamangar, F.; Dawsey, S.M.; Fan, J.H.; Ji, B.T.; Gao, Y.T.; Xiang, Y.B.; Qiao, Y.L.; et al. Serum ghrelin and esophageal and gastric cancer in two cohorts in China. Int. J. Cancer 2020, 146, 2728–2735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.L.; Zhu, Y.J.; Hu, C.H.; You, L.; Wu, J.; He, X.Y.; Huang, W.J.; Wu, Z.H. Ghrelin Affects Gastric Cancer Progression by Activating AMPK Signaling Pathway. Biochem. Genet. 2021, 59, 652–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, C.; Zhang, L.; Hu, D.; Ji, J. Ghrelin induces gastric cancer cell proliferation, migration, and invasion through GHS-R/NF-kappaB signaling pathway. Mol. Cell Biochem. 2013, 382, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Au, C.C.; Furness, J.B.; Britt, K.; Oshchepkova, S.; Ladumor, H.; Soo, K.Y.; Callaghan, B.; Gerard, C.; Inghirami, G.; Mittal, V.; et al. Three-dimensional growth of breast cancer cells potentiates the anti-tumor effects of unacylated ghrelin and AZP-531. Elife 2020, 9, e56913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konturek, P.C.; Burnat, G.; Rau, T.; Hahn, E.G.; Konturek, S. Effect of adiponectin and ghrelin on apoptosis of Barrett adenocarcinoma cell line. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2008, 53, 597–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeffery, P.L.; Herington, A.C.; Chopin, L.K. Expression and action of the growth hormone releasing peptide ghrelin and its receptor in prostate cancer cell lines. J. Endocrinol. 2002, 172, R7–R11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Lawnicka, H.; Melen-Mucha, G.; Motylewska, E.; Mucha, S.; Stepien, H. Modulation of ghrelin axis influences the growth of colonic and prostatic cancer cells in vitro. Pharmacol. Rep. 2012, 64, 951–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhang, X.; Feng, L. Ghrelin Regulates Cyclooxygenase-2 Expression and Promotes Gastric Cancer Cell Progression. Comput. Math. Methods Med. 2021, 2021, 5576808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lien, G.S.; Lin, C.H.; Yang, Y.L.; Wu, M.S.; Chen, B.C. Ghrelin induces colon cancer cell proliferation through the GHS-R, Ras, PI3K, Akt, and mTOR signaling pathways. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 776, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waseem, T.; Duxbury, M.; Ashley, S.W.; Robinson, M.K. Ghrelin promotes intestinal epithelial cell proliferation through PI3K/Akt pathway and EGFR trans-activation both converging to ERK 1/2 phosphorylation. Peptides 2014, 52, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waseem, T.; Javaid Ur, R.; Ahmad, F.; Azam, M.; Qureshi, M.A. Role of ghrelin axis in colorectal cancer: A novel association. Peptides 2008, 29, 1369–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barzon, L.; Pacenti, M.; Masi, G.; Stefani, A.L.; Fincati, K.; Palu, G. Loss of growth hormone secretagogue receptor 1a and overexpression of type 1b receptor transcripts in human adrenocortical tumors. Oncology 2005, 68, 414–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Brown, M.S.; Liang, G.; Grishin, N.V.; Goldstein, J.L. Identification of the acyltransferase that octanoylates ghrelin, an appetite-stimulating peptide hormone. Cell 2008, 132, 387–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera-Martinez, A.D.; Gahete, M.D.; Sanchez-Sanchez, R.; Alors-Perez, E.; Pedraza-Arevalo, S.; Serrano-Blanch, R.; Martinez-Fuentes, A.J.; Galvez-Moreno, M.A.; Castano, J.P.; Luque, R.M. Ghrelin-O-Acyltransferase (GOAT) Enzyme as a Novel Potential Biomarker in Gastroenteropancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2018, 9, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Gomez, E.; Jimenez-Vacas, J.M.; Carrasco-Valiente, J.; Herrero-Aguayo, V.; Blanca-Pedregosa, A.M.; Leon-Gonzalez, A.J.; Valero-Rosa, J.; Fernandez-Rueda, J.L.; Gonzalez-Serrano, T.; Lopez-Miranda, J.; et al. Plasma ghrelin O-acyltransferase (GOAT) enzyme levels: A novel non-invasive diagnosis tool for patients with significant prostate cancer. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2018, 22, 5688–5697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hormaechea-Agulla, D.; Gomez-Gomez, E.; Ibanez-Costa, A.; Carrasco-Valiente, J.; Rivero-Cortes, E.; F, L.L.; Pedraza-Arevalo, S.; Valero-Rosa, J.; Sanchez-Sanchez, R.; Ortega-Salas, R.; et al. Ghrelin O-acyltransferase (GOAT) enzyme is overexpressed in prostate cancer, and its levels are associated with patient’s metabolic status: Potential value as a non-invasive biomarker. Cancer Lett. 2016, 383, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jimenez-Vacas, J.M.; Gomez-Gomez, E.; Montero-Hidalgo, A.J.; Herrero-Aguayo, V.; F, L.L.; Sanchez-Sanchez, R.; Guler, I.; Blanca, A.; Mendez-Vidal, M.J.; Carrasco, J.; et al. Clinical Utility of Ghrelin-O-Acyltransferase (GOAT) Enzyme as a Diagnostic Tool and Potential Therapeutic Target in Prostate Cancer. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, P.Y.; Fan, X.M. The proliferative effects of ghrelin on human gastric cancer AGS cells. J. Dig. Dis. 2012, 13, 453–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Xie, T. Ghrelin inhibits cisplatin-induced MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cell apoptosis via PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling. Exp. Ther. Med. 2020, 19, 1633–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Yao, J.; Huang, R.; Wang, Y.; Jia, M.; Huang, Y. Ghrelin promotes human non-small cell lung cancer A549 cell proliferation through PI3K/Akt/mTOR/P70S6K and ERK signaling pathways. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 498, 616–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duxbury, M.S.; Waseem, T.; Ito, H.; Robinson, M.K.; Zinner, M.J.; Ashley, S.W.; Whang, E.E. Ghrelin promotes pancreatic adenocarcinoma cellular proliferation and invasiveness. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2003, 309, 464–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza, M.C.; Er, E.E.; Blenis, J. The Ras-ERK and PI3K-mTOR pathways: Cross-talk and compensation. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2011, 36, 320–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, F.; Lee, J.T.; Navolanic, P.M.; Steelman, L.S.; Shelton, J.G.; Blalock, W.L.; Franklin, R.A.; McCubrey, J.A. Involvement of PI3K/Akt pathway in cell cycle progression, apoptosis, and neoplastic transformation: A target for cancer chemotherapy. Leukemia 2003, 17, 590–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoxhaj, G.; Manning, B.D. The PI3K-AKT network at the interface of oncogenic signalling and cancer metabolism. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2020, 20, 74–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granata, R.; Settanni, F.; Biancone, L.; Trovato, L.; Nano, R.; Bertuzzi, F.; Destefanis, S.; Annunziata, M.; Martinetti, M.; Catapano, F.; et al. Acylated and unacylated ghrelin promote proliferation and inhibit apoptosis of pancreatic beta-cells and human islets: Involvement of 3’,5’-cyclic adenosine monophosphate/protein kinase A, extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2, and phosphatidyl inositol 3-Kinase/Akt signaling. Endocrinology 2007, 148, 512–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uddin, S.; Ahmed, M.; Hussain, A.; Assad, L.; Al-Dayel, F.; Bavi, P.; Al-Kuraya, K.S.; Munkarah, A. Cyclooxygenase-2 inhibition inhibits PI3K/AKT kinase activity in epithelial ovarian cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2010, 126, 382–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misra, S.; Sharma, K. COX-2 signaling and cancer: New players in old arena. Curr. Drug Targets 2014, 15, 347–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashemi Goradel, N.; Najafi, M.; Salehi, E.; Farhood, B.; Mortezaee, K. Cyclooxygenase-2 in cancer: A review. J. Cell Physiol. 2019, 234, 5683–5699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinson, H.A.; Lyons, T.R.; Giles, E.D.; Borges, V.F.; Schedin, P. Developmental windows of breast cancer risk provide opportunities for targeted chemoprevention. Exp. Cell Res. 2013, 319, 1671–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyons, T.R.; Borges, V.F.; Betts, C.B.; Guo, Q.; Kapoor, P.; Martinson, H.A.; Jindal, S.; Schedin, P. Cyclooxygenase-2-dependent lymphangiogenesis promotes nodal metastasis of postpartum breast cancer. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 3901–3912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyons, T.R.; O’Brien, J.; Borges, V.F.; Conklin, M.W.; Keely, P.J.; Eliceiri, K.W.; Marusyk, A.; Tan, A.C.; Schedin, P. Postpartum mammary gland involution drives progression of ductal carcinoma in situ through collagen and COX-2. Nat. Med. 2011, 17, 1109–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyatt, G.L.; Crump, L.S.; Young, C.M.; Wessells, V.M.; McQueen, C.M.; Wall, S.W.; Gustafson, T.L.; Fan, Y.Y.; Chapkin, R.S.; Porter, W.W.; et al. Cross-talk between SIM2s and NFkappaB regulates cyclooxygenase 2 expression in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2019, 21, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slomiany, B.L.; Slomiany, A. Mechanism of Cytosolic Phospholipase A(2) Activation in Ghrelin Protection of Salivary Gland Acinar Cells against Ethanol Cytotoxicity. Adv. Pharmacol. Sci. 2010, 2010, 269274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slomiany, B.L.; Slomiany, A. Involvement of constitutive nitric oxide synthase in ghrelin-induced cytosolic phospholipase A(2) activation in gastric mucosal cell protection against ethanol cytotoxicity. Inflammopharmacology 2009, 17, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slomiany, B.L.; Slomiany, A. Ghrelin Protection against Cytotoxic Effect of Ethanol on Rat Salivary Mucin Synthesis involves Cytosolic Phospholipase A2 Activation through S-Nitrosylation. Int. J. Biomed. Sci. 2010, 6, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zeng, X.; Chen, P.; Zhao, L.; Chen, S. Acylated and unacylated ghrelin relieve cancer cachexia in mice through multiple mechanisms. Chin. J. Physiol. 2020, 63, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uysal, P.; Afsar, C.U.; Sozer, V.; Inanc, B.; Agaoglu, F.; Gural, Z.; Fazlioglu, N.Y.; Cuhadaroglu, C.; Uzun, H. Evaluation of the relationship between serum ghrelin levels and cancer cachexia in patients with locally advanced nonsmall-cell lung cancer treated with chemoradiotherapy. J. Cancer Res. Ther. 2020, 16, 855–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blum, D.; de Wolf-Linder, S.; Oberholzer, R.; Brandle, M.; Hundsberger, T.; Strasser, F. Natural ghrelin in advanced cancer patients with cachexia, a case series. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeBoer, M.D. Emergence of ghrelin as a treatment for cachexia syndromes. Nutrition 2008, 24, 806–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Currow, D.C.; Maddocks, M.; Cella, D.; Muscaritoli, M. Efficacy of Anamorelin, a Novel Non-Peptide Ghrelin Analogue, in Patients with Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) and Cachexia-Review and Expert Opinion. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temel, J.S.; Abernethy, A.P.; Currow, D.C.; Friend, J.; Duus, E.M.; Yan, Y.; Fearon, K.C. Anamorelin in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer and cachexia (ROMANA 1 and ROMANA 2): Results from two randomised, double-blind, phase 3 trials. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, 519–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katakami, N.; Uchino, J.; Yokoyama, T.; Naito, T.; Kondo, M.; Yamada, K.; Kitajima, H.; Yoshimori, K.; Sato, K.; Saito, H.; et al. Anamorelin (ONO-7643) for the treatment of patients with non-small cell lung cancer and cachexia: Results from a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter study of Japanese patients (ONO-7643-04). Cancer 2018, 124, 606–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Tsai, C.W.; Chang, W.S.; Xiong, G.Y.; Xu, Y.; Bau, D.T.; Gu, J. High circulating insulin-like growth factor-1 reduces the risk of renal cell carcinoma: A Mendelian randomization study. Carcinogenesis 2021, 42, 826–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, N.; Knuppel, A.; Papadimitriou, N.; Martin, R.M.; Tsilidis, K.K.; Smith-Byrne, K.; Fensom, G.; Perez-Cornago, A.; Travis, R.C.; Key, T.J.; et al. Insulin-like growth factor-1, insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-3, and breast cancer risk: Observational and Mendelian randomization analyses with approximately 430,000 women. Ann. Oncol. 2020, 31, 641–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Northrup, R.; Kuroda, K.; Duus, E.M.; Barnes, S.R.; Cheatham, L.; Wiley, T.; Pietra, C. Effect of ghrelin and anamorelin (ONO-7643), a selective ghrelin receptor agonist, on tumor growth in a lung cancer mouse xenograft model. Support. Care Cancer 2013, 21, 2409–2415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- le Roux, C.W.; Patterson, M.; Vincent, R.P.; Hunt, C.; Ghatei, M.A.; Bloom, S.R. Postprandial plasma ghrelin is suppressed proportional to meal calorie content in normal-weight but not obese subjects. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2005, 90, 1068–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Docanto, M.M.; Yang, F.; Callaghan, B.; Au, C.C.; Ragavan, R.; Wang, X.; Furness, J.B.; Andrews, Z.B.; Brown, K.A. Ghrelin and des-acyl ghrelin inhibit aromatase expression and activity in human adipose stromal cells: Suppression of cAMP as a possible mechanism. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2014, 147, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.; Lin, L.; Yue, J.; Wu, C.S.; Guo, C.A.; Wang, R.; Yu, K.J.; Devaraj, S.; Murano, P.; Chen, Z.; et al. Suppression of Ghrelin Exacerbates HFCS-Induced Adiposity and Insulin Resistance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Asnicar, M.; Saha, P.K.; Chan, L.; Smith, R.G. Ablation of ghrelin improves the diabetic but not obese phenotype of ob/ob mice. Cell Metab. 2006, 3, 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Au, C.C.; Docanto, M.M.; Zahid, H.; Raffaelli, F.M.; Ferrero, R.L.; Furness, J.B.; Brown, K.A. Des-acyl ghrelin inhibits the capacity of macrophages to stimulate the expression of aromatase in breast adipose stromal cells. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2017, 170, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, J.M. Leptin and the endocrine control of energy balance. Nat. Metab. 2019, 1, 754–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, X.; Yeo, G.S. Central leptin and ghrelin signalling: Comparing and contrasting their mechanisms of action in the brain. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2011, 12, 197–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monti, V.; Carlson, J.J.; Hunt, S.C.; Adams, T.D. Relationship of ghrelin and leptin hormones with body mass index and waist circumference in a random sample of adults. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 2006, 106, 822–828; quiz 829–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.C.; Hsiao, M. Leptin and Cancer: Updated Functional Roles in Carcinogenesis, Therapeutic Niches, and Developments. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabian, C.J.; Klemp, J.R.; Marchello, N.J.; Vidoni, E.D.; Sullivan, D.K.; Nydegger, J.L.; Phillips, T.A.; Kreutzjans, A.L.; Hendry, B.; Befort, C.A.; et al. Rapid Escalation of High-Volume Exercise during Caloric Restriction; Change in Visceral Adipose Tissue and Adipocytokines in Obese Sedentary Breast Cancer Survivors. Cancers 2021, 13, 4871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, Y.S.; Kwon, A.R.; Lee, Y.K.; Oh, S.W. Circulating adipokines and risk of obesity related cancers: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Obes. Res. Clin. Pract. 2019, 13, 329–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowers, L.W.; Rossi, E.L.; McDonell, S.B.; Doerstling, S.S.; Khatib, S.A.; Lineberger, C.G.; Albright, J.E.; Tang, X.; deGraffenried, L.A.; Hursting, S.D. Leptin Signaling Mediates Obesity-Associated CSC Enrichment and EMT in Preclinical TNBC Models. Mol. Cancer Res. 2018, 16, 869–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saxena, N.K.; Sharma, D.; Ding, X.; Lin, S.; Marra, F.; Merlin, D.; Anania, F.A. Concomitant activation of the JAK/STAT, PI3K/AKT, and ERK signaling is involved in leptin-mediated promotion of invasion and migration of hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 2497–2507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogunwobi, O.; Mutungi, G.; Beales, I.L. Leptin stimulates proliferation and inhibits apoptosis in Barrett’s esophageal adenocarcinoma cells by cyclooxygenase-2-dependent, prostaglandin-E2-mediated transactivation of the epidermal growth factor receptor and c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase activation. Endocrinology 2006, 147, 4505–4516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beales, I.L.; Ogunwobi, O.O. Leptin synergistically enhances the anti-apoptotic and growth-promoting effects of acid in OE33 oesophageal adenocarcinoma cells in culture. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2007, 274, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera-Vargas, A.K.; Garcia-Rodriguez, E.; Olea-Flores, M.; Mendoza-Catalan, M.A.; Flores-Alfaro, E.; Navarro-Tito, N. Pro-angiogenic activity and vasculogenic mimicry in the tumor microenvironment by leptin in cancer. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2021, 62, 23–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, J.; Prigeon, R.L.; Davis, H.W.; Bidlingmaier, M.; Kahn, S.E.; Cummings, D.E.; Tschop, M.H.; D’Alessio, D. Ghrelin suppresses glucose-stimulated insulin secretion and deteriorates glucose tolerance in healthy humans. Diabetes 2010, 59, 2145–2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauna, C.; Meyler, F.M.; Janssen, J.A.; Delhanty, P.J.; Abribat, T.; van Koetsveld, P.; Hofland, L.J.; Broglio, F.; Ghigo, E.; van der Lely, A.J. Administration of acylated ghrelin reduces insulin sensitivity, whereas the combination of acylated plus unacylated ghrelin strongly improves insulin sensitivity. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2004, 89, 5035–5042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benso, A.; St-Pierre, D.H.; Prodam, F.; Gramaglia, E.; Granata, R.; van der Lely, A.J.; Ghigo, E.; Broglio, F. Metabolic effects of overnight continuous infusion of unacylated ghrelin in humans. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2012, 166, 911–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, F.; Zhang, Q.; Dong, H.; Xiang, X.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y. Effects of Des-acyl Ghrelin on Insulin Sensitivity and Macrophage Polarization in Adipose Tissue. J. Transl. Int. Med. 2021, 9, 84–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiefari, E.; Mirabelli, M.; La Vignera, S.; Tanyolac, S.; Foti, D.P.; Aversa, A.; Brunetti, A. Insulin Resistance and Cancer: In Search for a Causal Link. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowers, L.W.; Rossi, E.L.; O’Flanagan, C.H.; deGraffenried, L.A.; Hursting, S.D. The Role of the Insulin/IGF System in Cancer: Lessons Learned from Clinical Trials and the Energy Balance-Cancer Link. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne) 2015, 6, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giles, E.D.; Wellberg, E.A.; Astling, D.P.; Anderson, S.M.; Thor, A.D.; Jindal, S.; Tan, A.C.; Schedin, P.S.; Maclean, P.S. Obesity and overfeeding affecting both tumor and systemic metabolism activates the progesterone receptor to contribute to postmenopausal breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2012, 72, 6490–6501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, A.M.Y.; Wellberg, E.A.; Kopp, J.L.; Johnson, J.D. Hyperinsulinemia in Obesity, Inflammation, and Cancer. Diabetes Metab J. 2021, 45, 285–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giles, E.D.; Jindal, S.; Wellberg, E.A.; Schedin, T.; Anderson, S.M.; Thor, A.D.; Edwards, D.P.; MacLean, P.S.; Schedin, P. Metformin inhibits stromal aromatase expression and tumor progression in a rodent model of postmenopausal breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2018, 20, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Massadi, O.; Muller, T.; Tschop, M.; Dieguez, C.; Nogueiras, R. Ghrelin and LEAP-2: Rivals in Energy Metabolism. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2018, 39, 685–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslanipour, B.; Alan, M.; Demir, I. Decreased levels of liver-expressed antimicrobial peptide-2 and ghrelin are related to insulin resistance in women with polycystic ovary syndrome. Gynecol. Endocrinol. 2020, 36, 222–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Fernandez, R.; Tena-Sempere, M.; Aguilar, E.; Pinilla, L. Ghrelin effects on gonadotropin secretion in male and female rats. Neurosci. Lett. 2004, 362, 103–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Fernandez, R.; Tena-Sempere, M.; Navarro, V.M.; Barreiro, M.L.; Castellano, J.M.; Aguilar, E.; Pinilla, L. Effects of ghrelin upon gonadotropin-releasing hormone and gonadotropin secretion in adult female rats: In vivo and in vitro studies. Neuroendocrinology 2005, 82, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grundker, C.; Emons, G. The Role of Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone in Cancer Cell Proliferation and Metastasis. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne) 2017, 8, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
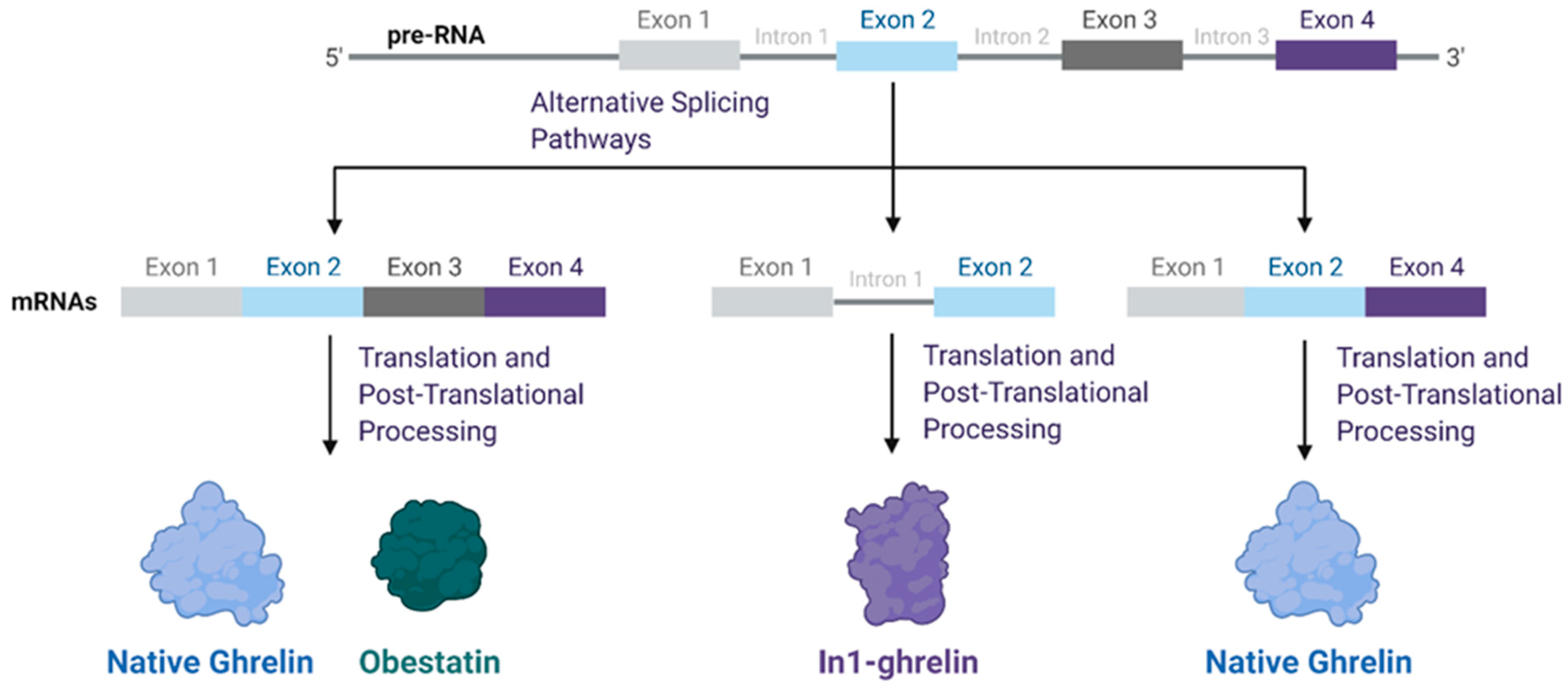
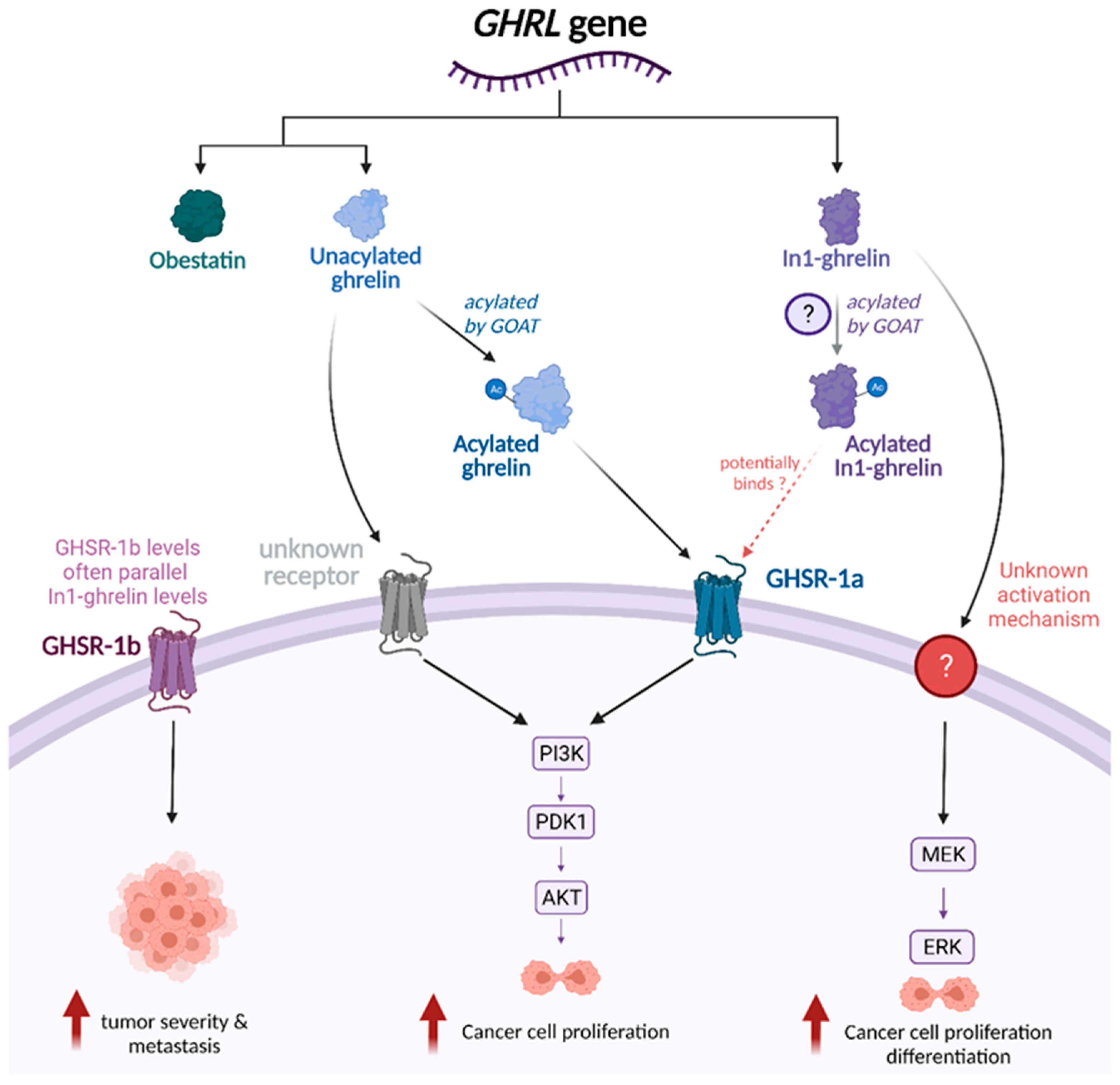

| Cancer Type | Cell Line | Ghrelin Acylation Status | Concentration | Effect | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Breast | MCF7 (ER+/PR+/HER2-) | Acylated | 0–1000 nM | No effect | [32] |
| SKBR3 (HER2+) | Unacylated | 0.1 nM | Inhibited growth | [40] | |
| MDA-MB-435 (TNBC) | Acylated | 0.1, 1, 10, 100 nM | ↑ proliferation | [32] | |
| MDA-MB-231 (TNBC) | Acylated | 10 and 100 nM | ↑ proliferation | [32] | |
| Ovarian | A2780 | Acylated | 1 nM | ↑ proliferation | [15] |
| Endometrial | HEC1B | Acylated | 10 and 100 nM | ↑ proliferation | [17] |
| KLE | Acylated | 1, 10, 100 nM | ↑ proliferation | [17] | |
| Esophageal | OE-19 | Not Specified | 20–450 nM | No effect on apoptosis | [41] |
| Prostate | PC3 | Acylated | 5 and 10 nM | ↑ proliferation | [42] |
| DU145 | Unacylated | 100 and 10,000 nM | Inhibited growth | [43] | |
| Acylated | 10–1000 nM | Inhibited growth | [43] | ||
| Gastric | AGS | Not Specified | Overexpression | ↑ apoptosis | [38] |
| Not Specified | 10 and 100 nM | ↑ proliferation | [39] | ||
| Not Specified | 10 nM | ↑ cell migration and invasion ↓ apoptosis | [44] | ||
| SGC7901 | Not Specified | 1, 10, 100 nM | ↑ proliferation | [39] | |
| Colon | HT-29 | Acylated | 0.1 and 1 nM | ↑ proliferation | [45] |
| Caco-2 | Acylated | 1 and 10 nM | ↑ proliferation | [46] | |
| Unacylated | 1 and 10 nM | ↑ proliferation | [46] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kotta, A.S.; Kelling, A.S.; Corleto, K.A.; Sun, Y.; Giles, E.D. Ghrelin and Cancer: Examining the Roles of the Ghrelin Axis in Tumor Growth and Progression. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 483. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12040483
Kotta AS, Kelling AS, Corleto KA, Sun Y, Giles ED. Ghrelin and Cancer: Examining the Roles of the Ghrelin Axis in Tumor Growth and Progression. Biomolecules. 2022; 12(4):483. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12040483
Chicago/Turabian StyleKotta, Anuhya S., Abigail S. Kelling, Karen A. Corleto, Yuxiang Sun, and Erin D. Giles. 2022. "Ghrelin and Cancer: Examining the Roles of the Ghrelin Axis in Tumor Growth and Progression" Biomolecules 12, no. 4: 483. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12040483
APA StyleKotta, A. S., Kelling, A. S., Corleto, K. A., Sun, Y., & Giles, E. D. (2022). Ghrelin and Cancer: Examining the Roles of the Ghrelin Axis in Tumor Growth and Progression. Biomolecules, 12(4), 483. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12040483








