Bioinks Enriched with ECM Components Obtained by Supercritical Extraction
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture and Cell Sheets Preparation
2.2. Cell Sheets Decellularization
2.2.1. Supercritical Extraction
| Variables | Pressure (MPa) | Co-Solvent | Co-Solvent Exposure Time | scCO2 Exposure Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| scCO2 only | 20 | - | - | 1 h |
| 25 | - | - | 2 h | |
| scCO2 + co-solvent | 25 | EtOH | 2 h | 2 h |
| 25 | Dehypon® | 1 h 30 | 1 h 30 | |
| 30 | ||||
| 30 | Dehypon® | 3 h 30 | 3 h 30 | |
| Dehypon® pre-treatment | 30 | - | - | 1 h |
| EtOH | 1 h | 1 h |
2.2.2. Standard Methodologies
2.3. DNA Quantification
2.4. Protein Quantification
2.5. Immunostaining
2.6. Glycosaminoglycan Quantification
2.7. ECM-Based Ink Preparation
2.8. Rheological Analysis
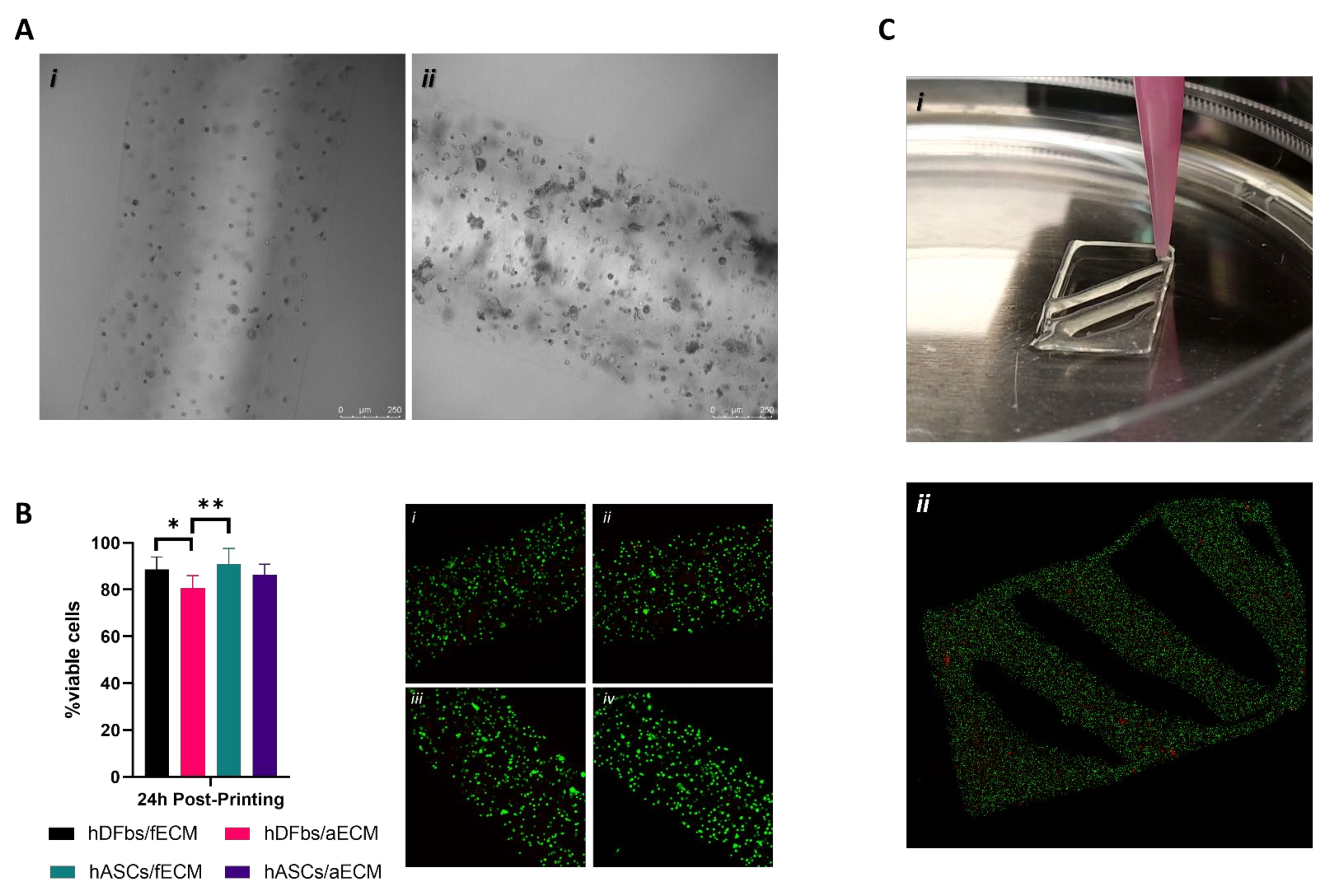
2.9. 3D Printing
2.10. Cell Viability
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Optimized Supercritical Extraction
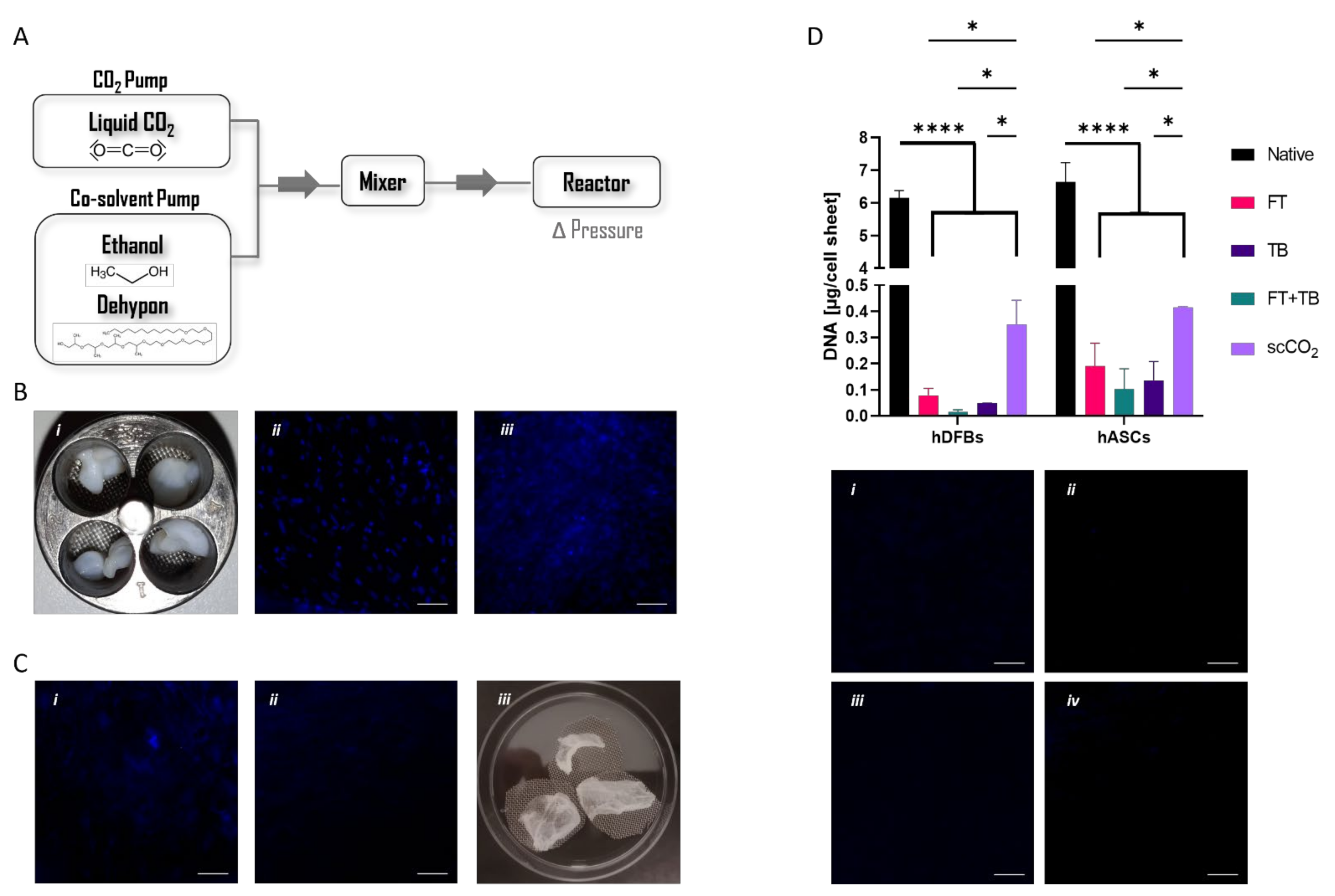
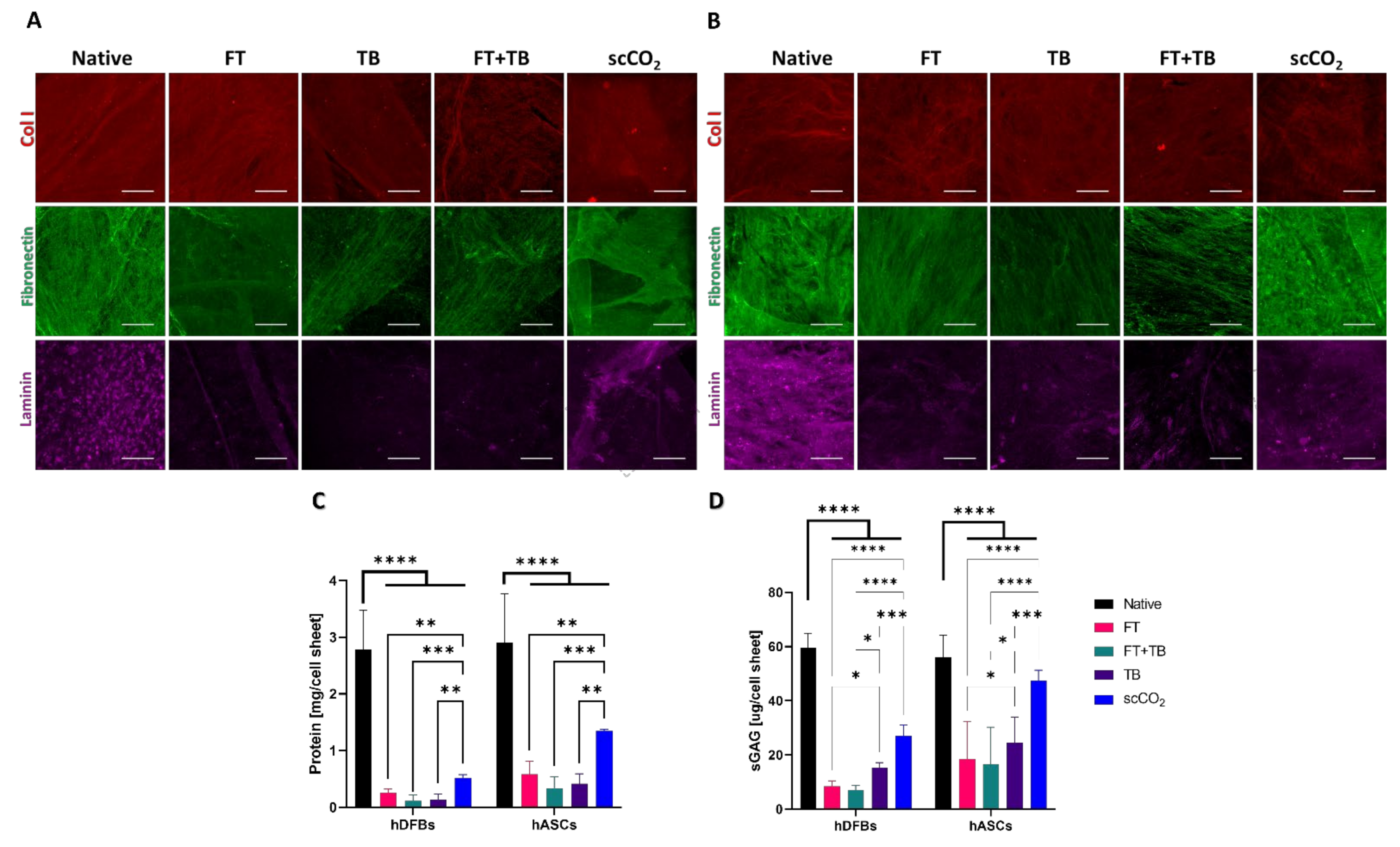
3.2. Nature of the Extracted ECM
3.3. Printability and Cytocompatibility of Alginate-ECM Formulations
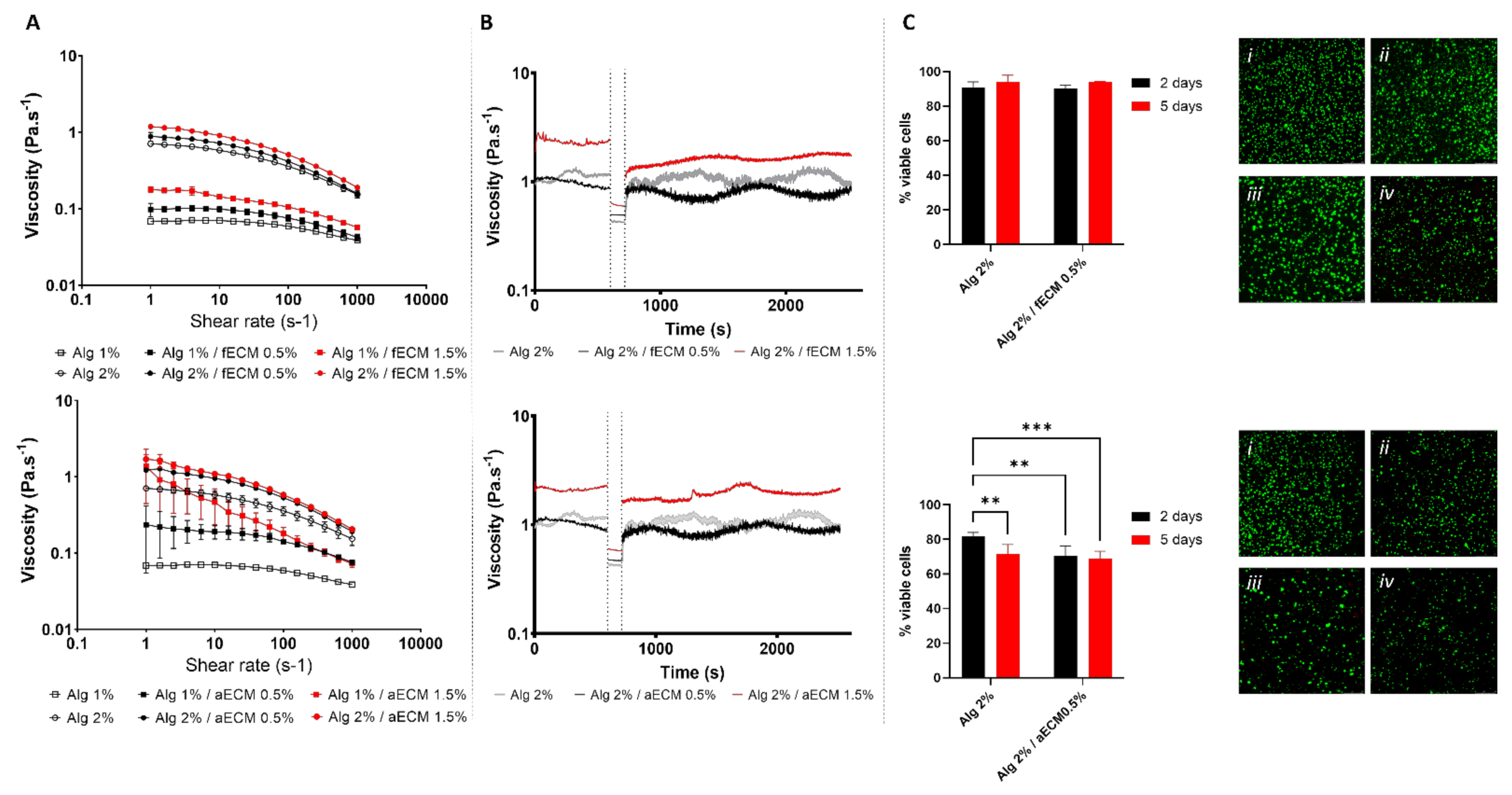
3.4. Alginate-ECM Bioprinted Constructs
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Humphrey, J.D.; Dufresne, E.R.; Schwartz, M.A. Mechanotransduction and extracellular matrix homeostasis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2014, 15, 802–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nyström, A.; Bruckner-Tuderman, L. Matrix molecules and skin biology. Semin. Cell. Dev. Biol. 2018, 89, 136–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, H.; Lee, H.; Luo, L.; Kyriakides, T.R. Extracellular matrix-derived biomaterials in engineering cell function. Biotechnol. Adv. 2019, 42, 107421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerqueira, M.T.; Pirraco, R.P.; Martins, A.R.; Santos, T.C.; Reis, R.L.; Marques, A.P. Cell sheet technology-driven re-epithelialization and neovascularization of skin wounds. Acta Biomater. 2014, 10, 3145–3155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frazão, L.P.; Vieira de Castro, J.; Nogueira-Silva, C.; Neves, N.M. Decellularized human chorion membrane as a novel biomaterial for tissue regeneration. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baltazar, T.; Merola, J.; Catarino, C.; Catherine, B.; Kirkiles-Smith, N.C.; Lee, V.; Hotta, S.; Dai, G.; Xu, X.; Ferreira, F.C.; et al. 3D bioprinting of a vascularized and perfusable skin graft using human keratinocytes, fibroblasts, pericytes and endothelial cells. Tissue Eng. Part A 2019, 26, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, K.H.; Park, K.M.; Kang, K.S.; Woo, H.M. Biocompatibility evaluation of tissue-engineered decellularized scaffolds for biomedical application. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 67, 766–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crapo, P.M.; Gilbert, T.W.; Badylak, D.V.M. An overview of tissue and whole organ decellularization processes. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 3233–3243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hölzl, K.; Lin, S.; Tytgat, L.; Van Vlierberghe, S.; Gu, L.; Ovsianikov, A. Bioink properties before, during and after 3D bioprinting. Biofabrication 2016, 8, 032002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burk, J.; Erbe, I.; Berner, D.; Kacza, J.; Kasper, C.; Pfeiffer, B.; Winter, K.; Brehm, W. Freeze-thaw cycles enhance decellularization of large tendons. Tissue Eng. Part C Methods 2014, 20, 276–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Q.; Yates, K.; Tahtinen, M.; Shearier, E.; Qian, Z.; Zhao, F. Decellularization of fibroblast cell sheets for natural extracellular matrix scaffold preparation. Tissue Eng. Part C Methods 2015, 21, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, X.; Hong, H.; Hu, R.; Liu, J.; Liu, C. Decellularized extracellular matrix scaffolds: Recent trends and emerging strategies in tissue engineering. Bioact. Mater. 2021, 10, 15–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, D.; Yee, M.; Lee, Z.; Sheng, J.; Amirul, A.; Niang, M.W. Decellularization systems and devices: State-of-the-art review. Acta Biomater. 2020, 115, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.K.; Luo, B.; Guneta, V.; Li, L.; Foo, S.E.M.; Dai, Y.; Yang Tan, T.T.; Tan, N.S.; Choong, C.; Choong Woong, M. T.Supercritical carbon dioxide extracted extracellular matrix material from adipose tissue. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 75, 349–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, Y.; Jung, Y.; Kim, S.H. Decellularized heart ECM hydrogel using supercritical carbon dioxide for improved angiogenesis. Acta Biomater. 2018, 67, 270–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halfwerk, F.R.; Rouwkema, J.; Gossen, J.A.; Grandjean, J.G. Supercritical carbon dioxide decellularised pericardium: Mechanical and structural characterisation for applications in cardio-thoracic surgery. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2018, 77, 400–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teoh, W.H.; Mammucari, R.; Foster, N.R. Solubility of organometallic complexes in supercritical carbon dioxide: A review. J. Organomet. Chem. 2013, 724, 102–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casali, D.M.; Handleton, R.M.; Shazly, T.; Matthews, M.A. A novel supercritical CO2-based decellularization method for maintaining scaffold hydration and mechanical properties. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2018, 131, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawada, K.; Terada, D.; Yamaoka, T.; Kitamura, S.; Fujisato, T. Cell removal with supercritical carbon dioxide for acellular artificial tissue. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2008, 83, 1163–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antons, J.; Marascio, M.G.M.; Aeberhard, P.; Weissenberger, G.; Hirt-Burri, N.; Applegate, L.A.; Bourban, P.E.; Pioletti, D.P. Decellularised tissues obtained by a CO2-philic detergent and supercritical CO2. Eur. Cells Mater. 2018, 36, 81–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kankala, R.K.; Zhang, Y.S.; Wang, S.; Bin Lee, C.H.; Chen, A.Z. Supercritical fluid technology: An emphasis on drug delivery and related biomedical applications. Adv. Health Mater. 2017, 6, 1700433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matthews, M.A.; Becnel, J.M. Diffusion coefficients of methyl orange in dense carbon dioxide with the micelle-forming surfactant dehypon Ls-54. J. Chem. Eng. Data. 2003, 48, 1413–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarafa, P.J.; Williams, E.; Panvelker, S.; Zhang, J.; Matthews, M.A. Removing endotoxin from metallic biomaterials with compressed carbon dioxide-based mixtures. J. Supercrit. Fluids. 2011, 55, 1052–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Mendes, L.F.; Pirraco, R.P.; Szymczyk, W.; Frias, A.M.; Santos, T.C.; Reis, R.L.; Marques, A.P. Perivascular-like cells contribute to the stability of the vascular network of osteogenic tissue formed from cell sheet-based constructs. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e41051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, M.; Cerqueira, M.T.; Santos, T.C.; Sampaio-Marques, B.; Ludovico, P.; Marques, A.P.; Pirraco, R.P.; Reis, R.L. Cell sheet engineering using the stromal vascular fraction of adipose tissue as a vascularization strategy. Acta Biomater. 2017, 55, 131–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, D.B.; Moreira, H.R.; Reis, R.L.; Marques, A.P. In vitro 3D cell sheet-based model for unraveling scar pathophysiology. Toxicol. Lett. 2017, 280, S269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerqueira, M.T.; Pirraco, R.P.; Santos, T.C.; Rodrigues, D.B.; Frias, A.M.; Martins, A.R.; Reis, R.L.; Marques, A.P. Human Adipose Stem Cells Cell Sheet Constructs Impact Epidermal Morphogenesis in Full-Thickness Excisional Wounds. Biomacromolecules 2013, 14, 3997–4008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuda, N.; Shimizu, T.; Yamato, M.; Okano, T. Tissue engineering based on cell sheet technology. Adv. Mater. 2007, 19, 3089–3099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannachi, I.E.; Yamato, M.; Okano, T. Cell sheet technology and cell patterning for biofabrication. Biofabrication 2009, 1, 022002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermida, M.A.; Kumar, J.D.; Schwarz, D.; Laverty, K.G.; Di Bartolo, A.; Ardron, M.; Bogomolnijs, M.; Clavreul, A.; Brennan, P.M.; Wiegand, U.L.; et al. Three dimensional in vitro models of cancer: Bioprinting multilineage glioblastoma models. Adv. Biol. Regul. 2020, 7, 100658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Su, X.; Xu, Y.; Kong, B.; Sun, W.; Mi, S. Bioprinting three-dimensional cell-laden tissue constructs with controllable degradation. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gasperini, L.; Maniglio, D.; Motta, A.; Migliaresi, C. An Electrohydrodynamic bioprinter for alginate hydrogels containing living cells. Tissue Eng. Part C Methods 2015, 21, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mezger, T. 8. Oscillatory Tests. In The Rheology Handbook: For Users of Rotational and Oscillatory Rheometers; Vincentz Network: Hannover, Germany, 2020; pp. 153–247. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.-H.; Hsieh, D.-J.; Periasamy, S.; Chuang, C.-T.; Tseng, F.-W.; Kuo, J.-C.; Tarng, Y.-W. Regenerative porcine dermal collagen matrix developed by supercritical carbon dioxide extraction technology: Role in accelerated wound healing. Materialia 2020, 9, 100576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernhardt, A.; Wehrl, M.; Paul, B.; Hochmuth, T.; Schumacher, M.; Schütz, K.; Gelinsky, M. Improved sterilization of sensitive biomaterials with supercritical carbon dioxide at low temperature. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0129205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guler, S.; Aslan, B.; Hosseinian, P.; Aydin, H.M. Supercritical carbon dioxide-assisted decellularization of aorta and cornea. Tissue Eng. Part C Methods 2017, 23, 540–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duarte, M.M.; Silva, I.V.; Eisenhut, A.R.; Bionda, N.; Duarte, A.R.C.; Oliveira, A.L. Contributions of supercritical fluid technology for advancing decellularization and postprocessing of viable biological materials. Mater Horizons. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Han, B.; Zhang, J.; Li, G.; Zhang, X. Formation of Water-in-CO 2 Microemulsions with Non-fluorous Surfactant. Chemistry 2002, 8, 1356–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoshiba, T.; Lu, H.; Kawazoe, N.; Chen, G. Decellularized matrices for tissue engineering. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2010, 10, 1717–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.H.; Tseng, F.W.; Chang, W.H.; Peng, I.C.; Hsieh, D.J.; Wu, S.W.; Yeh, M.L. Preparation of acellular scaffold for corneal tissue engineering by supercritical carbon dioxide extraction technology. Acta Biomater. 2017, 58, 238–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imamura, H.; Adachi, T.; Kin, T.; Ono, S.; Sakai, Y.; Adachi, T.; Soyama, A.; Hidaka, M.; Takatsuki, M.; Shapiro, A.M.J.; et al. An engineered cell sheet composed of human islets and human fibroblast, bone marrow–derived mesenchymal stem cells, or adipose–derived mesenchymal stem cells: An in vitro comparison study. Islets 2018, 10, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paganelli, A.; Benassi, L.; Rossi, E.; Magnoni, C. Extracellular matrix deposition by adipose-derived stem cells and fibroblasts: A comparative study. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2020, 312, 295–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakirci, E.; Toprakhisar, B.; Zeybek, M.C.; Ince, G.O.; Koc, B. Cell sheet based bioink for 3D bioprinting applications. Biofabrication 2017, 9, 024105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Han, W.; Kim, H.; Ha, D.H.; Jang, J.; Kim, B.S.; Cho, B.W. Development of liver decellularized extracellular matrix bioink for three-dimensional cell printing-based liver tissue engineering. Biomacromolecules 2017, 18, 1229–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rathan, S.; Dejob, L.; Schipani, R.; Haffner, B.; Möbius, M.E.; Kelly, D.J. Fiber reinforced cartilage ECM functionalized bioinks for functional cartilage tissue engineering. Adv. Health. Mater. 2019, 8, 1801501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Giuseppe, M.; Law, N.; Webb, B.; Macrae, A.R.; Liew, L.J.; Sercombe, T.B.; Dilley, R.J.; Doyle, B.J. Mechanical behaviour of alginate-gelatin hydrogels for 3D bioprinting. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2018, 79, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Hong, J.; Kim, W.J.; Kim, G.H. Bone-derived dECM/alginate bioink for fabricating a 3D cell-laden mesh structure for bone tissue engineering. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 250, 116914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Lin, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhao, B.; Zhang, J. Food hydrocolloids flow behaviour, thixotropy and dynamical viscoelasticity of sodium alginate aqueous solutions. Food Hydrocoll. 2014, 38, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorroñogoitia, I.; Urtaza, U.; Zubiarrain-laserna, A.; Alonso-varona, A.; Zaldua, A.M. A study of the printability of alginate-based bioinks by 3D bioprinting for articular cartilage tissue engineering. Polymers 2022, 14, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, H.A.; Hutton, J.F.; Walters, K. (Eds.) Chapter 2—Viscosity. In An Introduction to Rheology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1989; Volume 3, pp. 11–35. [Google Scholar]
- Curley, C.J.; Dolan, E.B.; Otten, M.; Hinderer, S.; Duffy, G.P.; Murphy, B.P. An injectable alginate/extracellular matrix hydrogel for acellular treatment of heart failure. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2016, 9, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.J.; Kim, Y.B.; Ahn, S.H.; Lee, J.; Jang, C.H.; Yoon, H.; Chun, W.; Kim, G.H. A new approach for fabricating collagen/ECM-based bioinks using preosteoblasts and human adipose stem cells. Adv. Health. Mater. 2015, 4, 1359–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorgensen, A.M.; Chou, Z.; Gillispie, G.; Lee, S.J.; Yoo, J.J.; Soker, S.; Atala, A. Decellularized skin extracellular matrix (dsECM) Improves the physical and biological properties of fibrinogen hydrogel for skin bioprinting applications. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Q.; Wang, Y.; Yang, D.; Zhang, H.; Song, Z.; Gu, Y. Optimal bioprinting parameters and experimental investigation of acellular dermal matrix scaffold. J. Renew. Mater. 2021, 9, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouser, V.H.M.; Melchels, F.P.W.; Visser, J.; Dhert, W.J.A.; Gawlitta, D.; Malda, J. Yield stress determines bioprintability of hydrogels based on gelatin-methacryloyl and gellan gum for cartilage bioprinting. Biofabrication 2016, 8, 035003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnes, H.A. Thixotropy—A review. J. Nonnewton. Fluid. Mech. 1997, 70, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boularaoui, S.; Al Hussein, G.; Khan, K.A.; Christoforou, N.; Stefanini, C. An overview of extrusion-based bioprinting with a focus on induced shear stress and its effect on cell viability. Bioprinting 2020, 20, e00093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.S.; Das, S.; Jang, J.; Cho, D.W. Decellularized extracellular matrix-based bioinks for engineering tissue- and organ-specific microenvironments. Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 10608–10661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Reis, D.P.; Domingues, B.; Fidalgo, C.; Reis, R.L.; Gasperini, L.; Marques, A.P. Bioinks Enriched with ECM Components Obtained by Supercritical Extraction. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 394. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12030394
Reis DP, Domingues B, Fidalgo C, Reis RL, Gasperini L, Marques AP. Bioinks Enriched with ECM Components Obtained by Supercritical Extraction. Biomolecules. 2022; 12(3):394. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12030394
Chicago/Turabian StyleReis, Daniel P., Beatriz Domingues, Cátia Fidalgo, Rui L. Reis, Luca Gasperini, and Alexandra P. Marques. 2022. "Bioinks Enriched with ECM Components Obtained by Supercritical Extraction" Biomolecules 12, no. 3: 394. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12030394
APA StyleReis, D. P., Domingues, B., Fidalgo, C., Reis, R. L., Gasperini, L., & Marques, A. P. (2022). Bioinks Enriched with ECM Components Obtained by Supercritical Extraction. Biomolecules, 12(3), 394. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12030394








