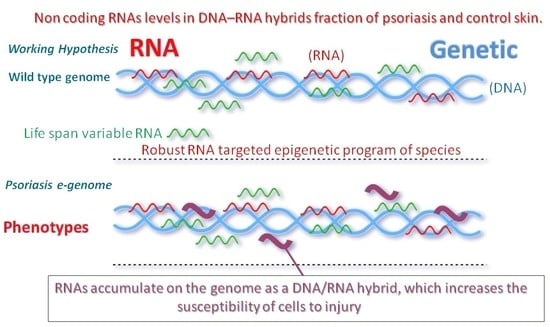
Decrease in RNase HII and Accumulation of lncRNAs/DNA Hybrids: A Causal Implication in Psoriasis?
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Selection
2.2. Taking Skin Biopsy Samples
2.3. DNA and DNA–RNA Hybrid Isolation
2.4. Determination of Telomere Length
2.5. Quantitative Real-Time PCR (RT-qPCR)
2.6. Determination of Genes Expression Levels
2.7. Statistical Analysis
2.8. RNA Library and Sequencing
2.9. Sequence Analysis
2.10. HOMER Version 4.9 Was Used for Peak Finding
2.11. Peak Finding
2.12. Statistical Analysis for Genomic Data
2.13. Data Access
3. Results
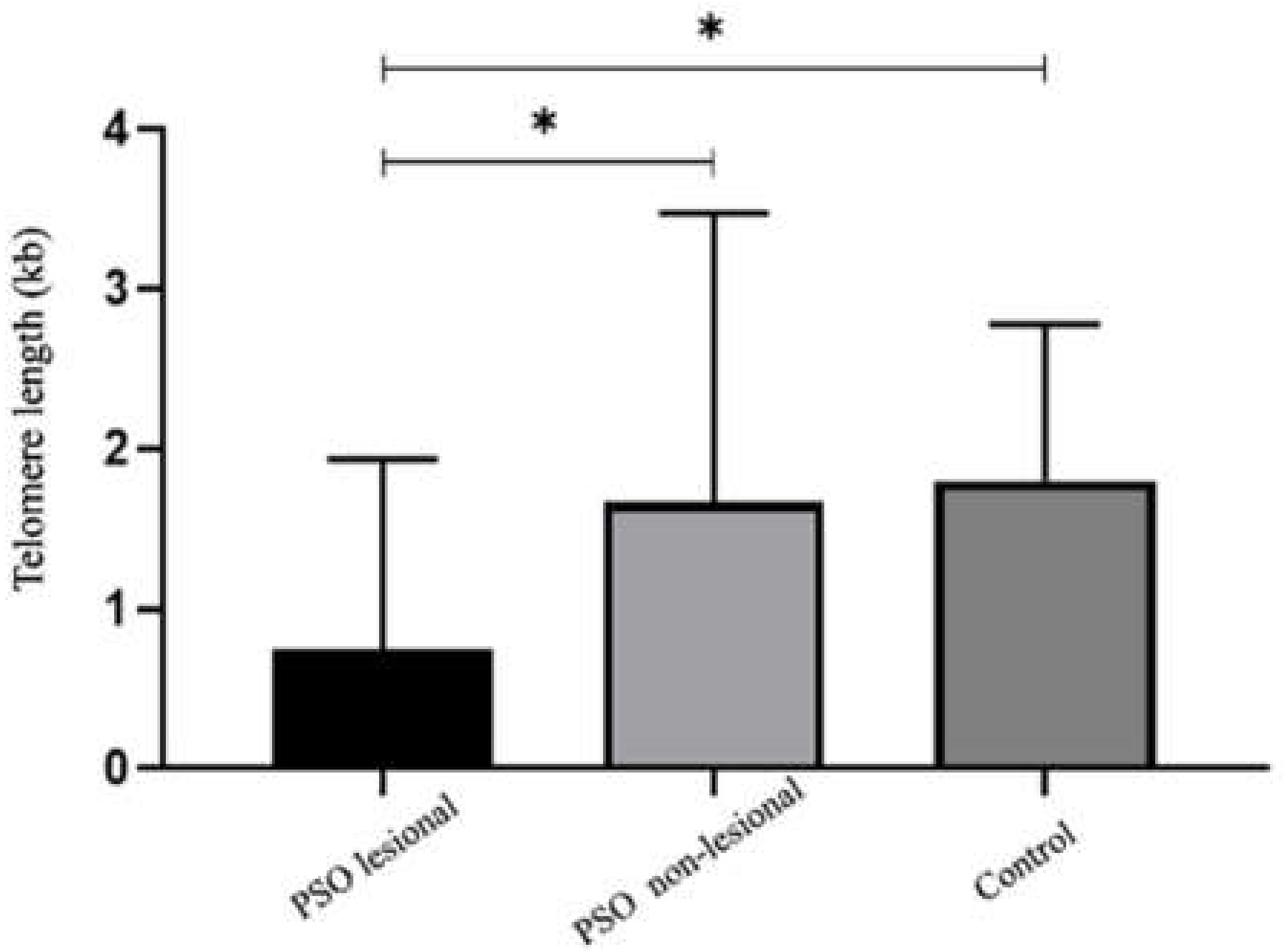
3.1. Telomere Length Is Significantly Reduced in Lesional Tissue in Patients with Psoriasis
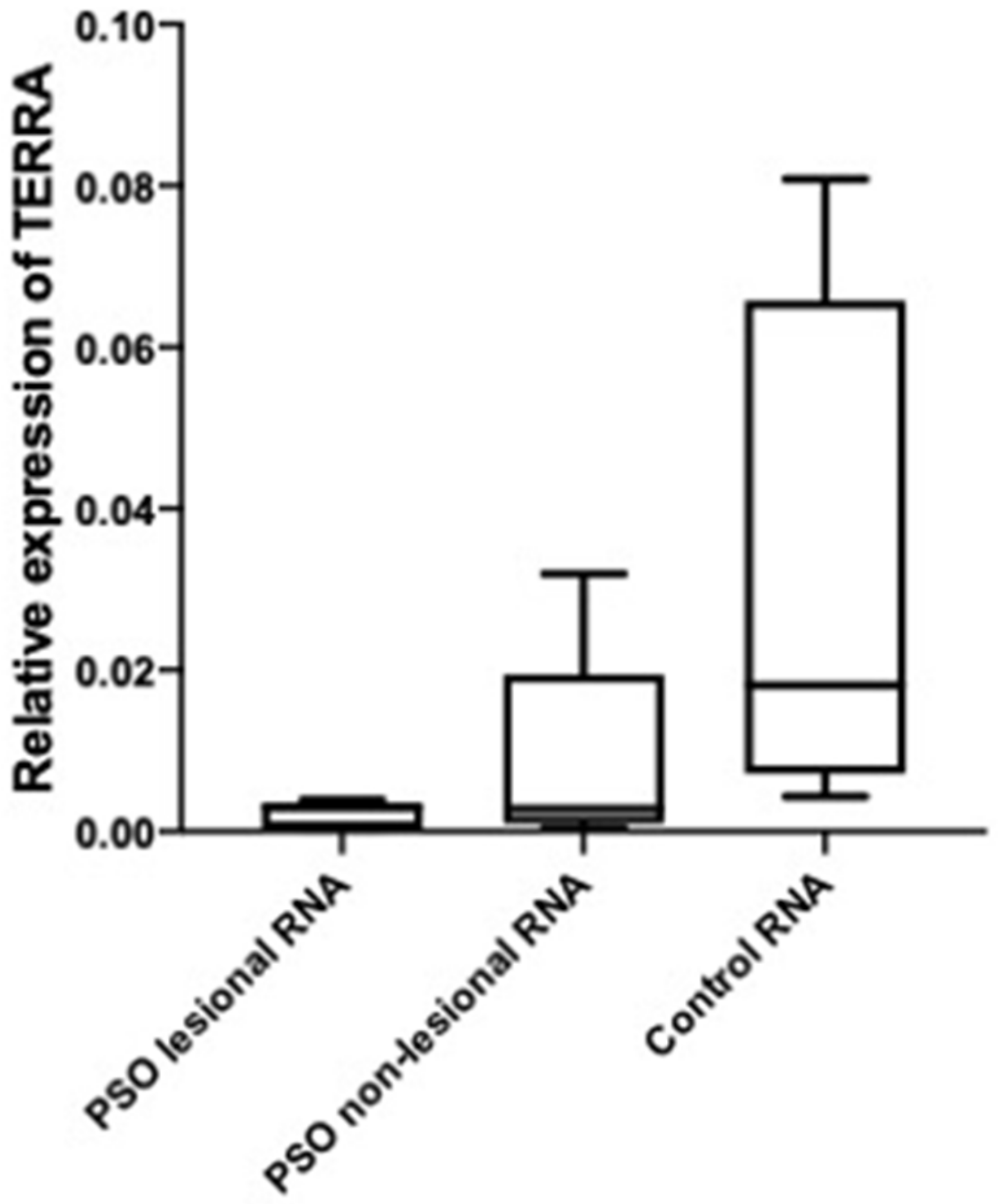
3.2. A higher Level of TERRA Is Associated with Telomeres in Psoriasis Patients
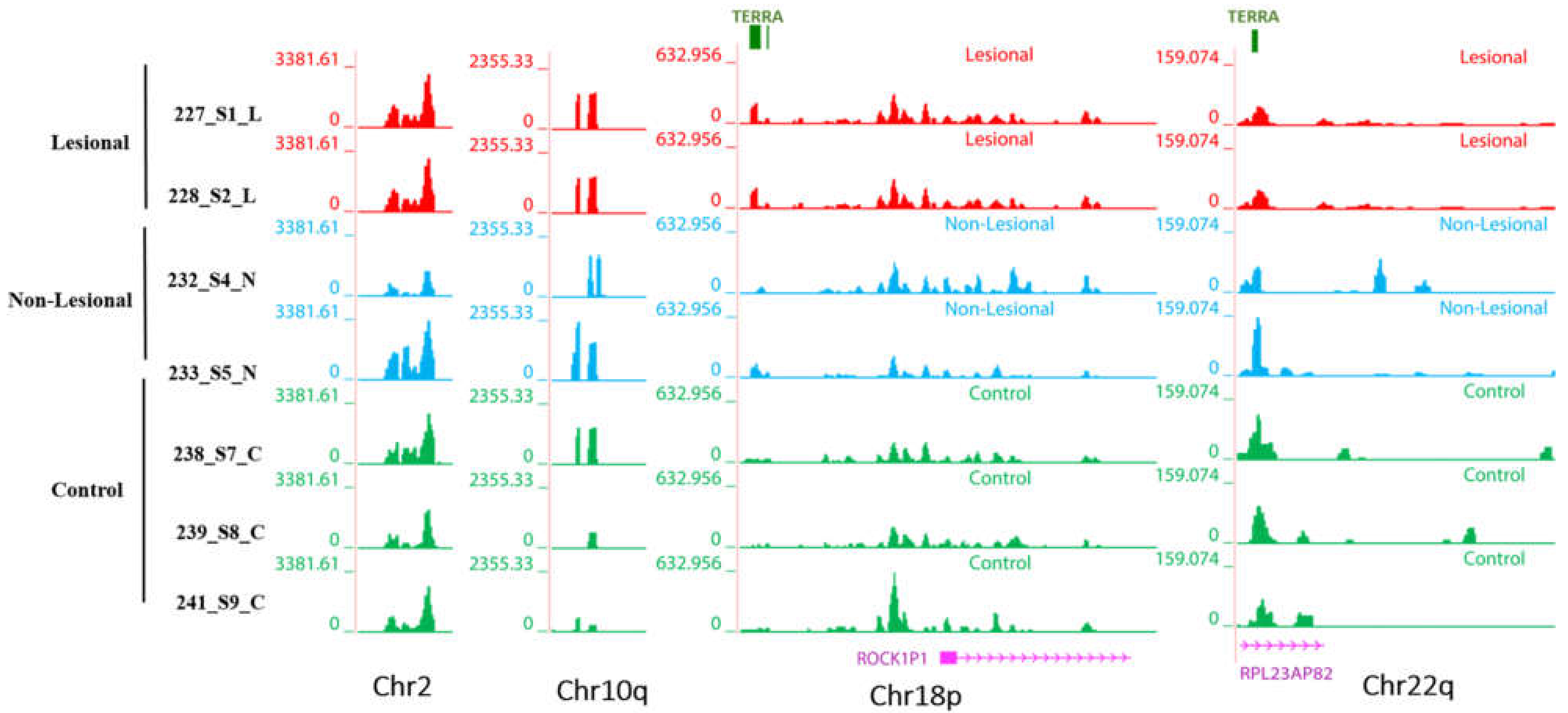
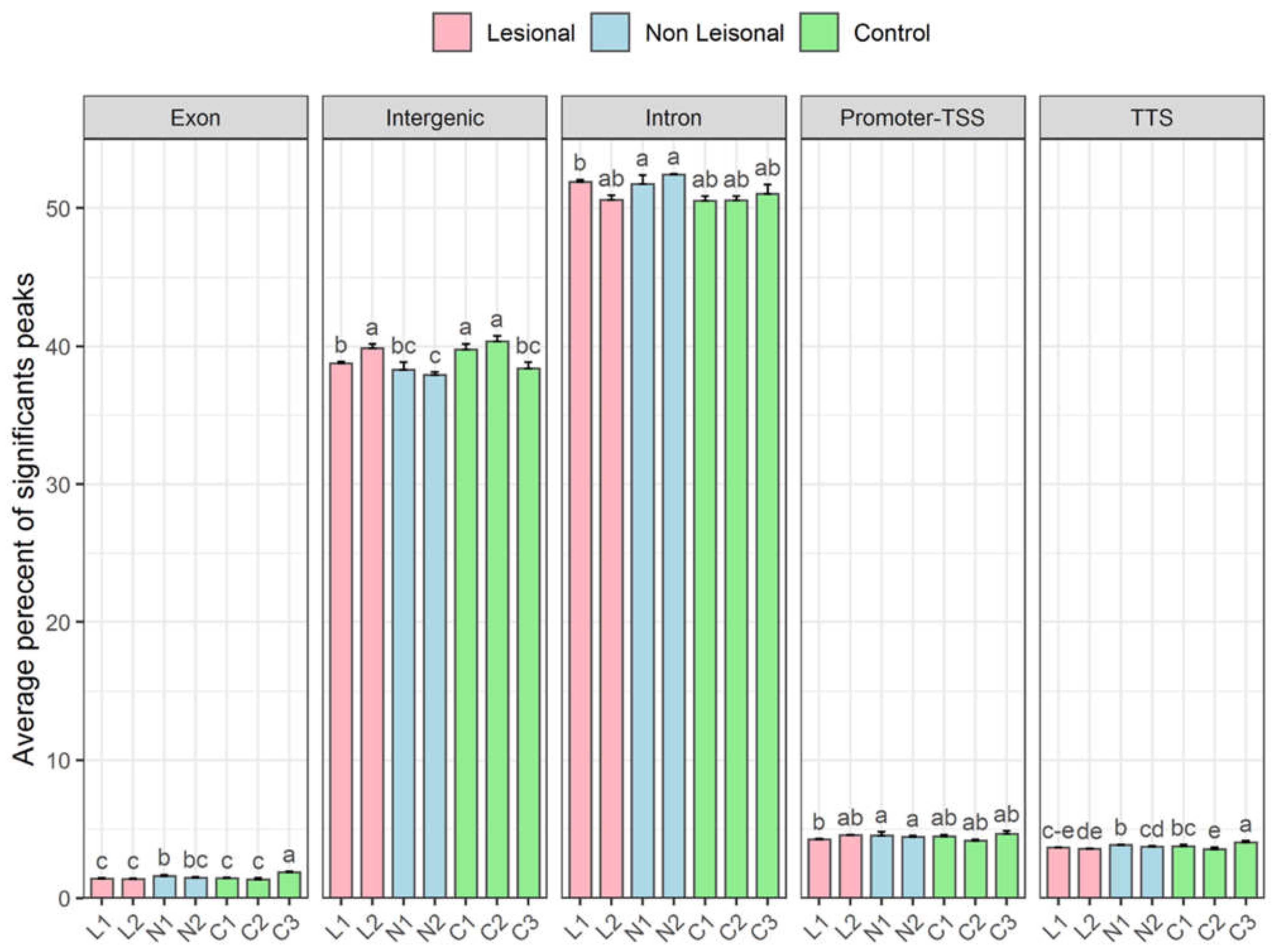
3.3. Transcription Profiles of Non-Coding RNAs in Patients with Psoriasis: DNA-Associated RNA Fraction Analysis Reveals Higher Levels of R-Loop in the Genome
3.3.1. Telomeric Regions Retain More TERRA in Patients with Psoriasis
3.3.2. Non-Telomeric TERRA Regions Retain More RNAs
3.3.3. More lncRNA Expression Signals Are Observed in Non-Telomeric Regions of the Lesional and Non-Lesional Skin of Patients with Psoriasis
3.3.4. Higher Levels of Transcripts from Centromeric Regions Are Retained on the DNA
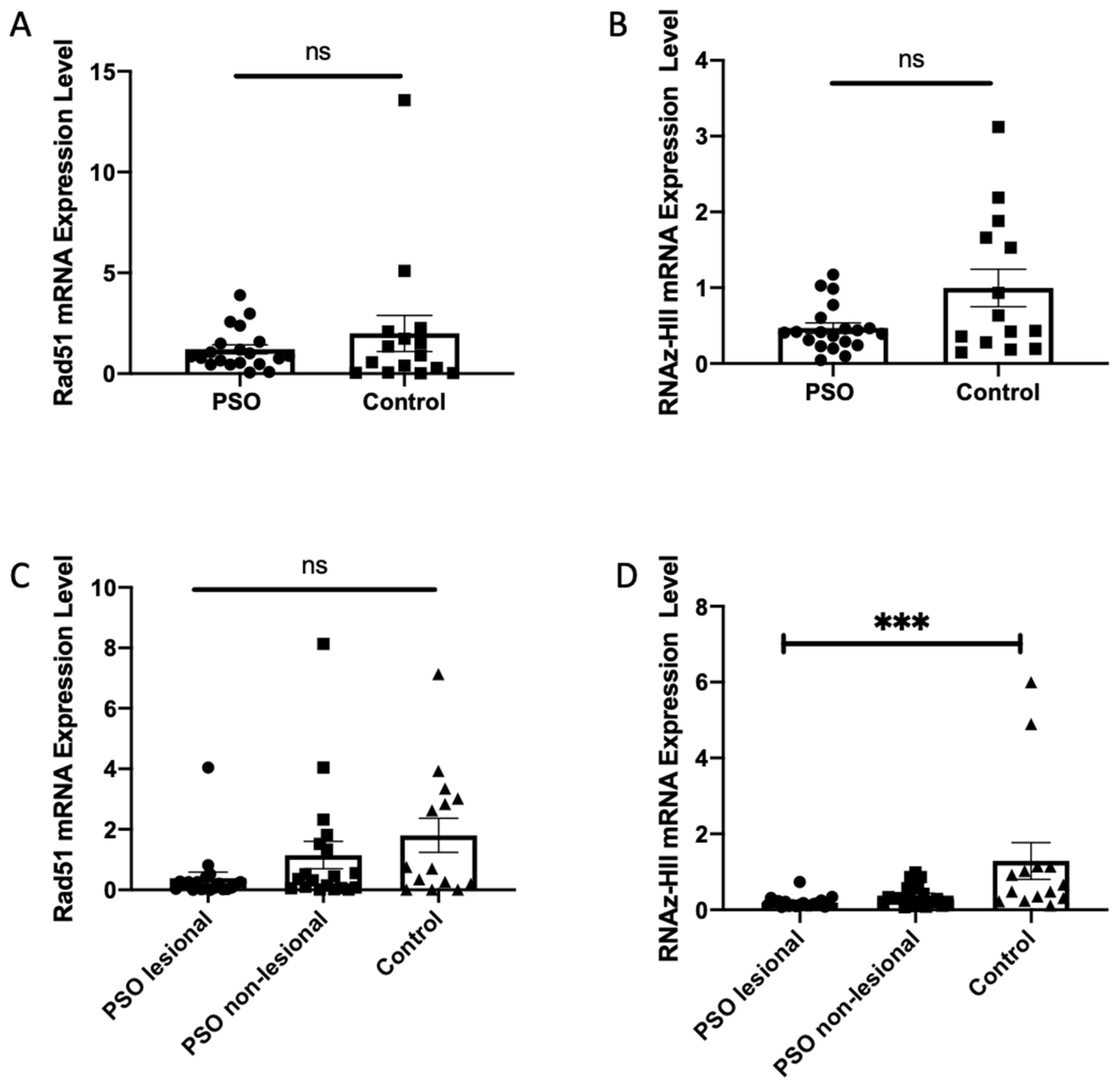
3.4. Decreased Transcription Levels of Ribonuclease HII in Patients with Psoriasis
4. Discussion
4.1. Telomere Length Is Shorter in Patients with Psoriais
4.2. TERRA Profiles Vary in Patients with Psoriasis
4.3. Dysregulation of R-Loop Structures Reveals Genome Instability
4.4. Psoriasis Patients and Cancer Risk
4.5. For Patients with Psoriasis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ogawa, E.; Sato, Y.; Minagawa, A.; Okuyama, R. Pathogenesis of psoriasis and development of treatment. J. Dermatol. 2018, 45, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Griffiths, C.E.M.; Armstrong, A.W.; Gudjonsson, J.E.; Barker, J.N.W.N. Psoriasis. Lancet. 2021, 397, 1301–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iskandar, I.Y.K.; Parisi, R.; Griffiths, C.E.M.; Ashcroft, D.M.; Global Psoriasis Atlas. Systematic review examining changes over time and variation in the incidence and prevalence of psoriasis by age and gender. Br. J. Dermatol. 2021, 184, 243–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, A.W.; Read, C. Pathophysiology, Clinical Presentation, and Treatment of Psoriasis: A Review. JAMA 2020, 323, 1945–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caiazzo, G.; Fabbrocini, G.; Di Caprio, R.; Raimondo, A.; Scala, E.; Balato, N.; Balato, A. Psoriasis, Cardiovascular Events, and Biologics: Lights and Shadows. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kunz, M.; Simon, J.C.; Saalbach, A. Psoriasis: Obesity and Fatty Acids. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCormick, T.; Ayala-Fontanez, N.; Soler, D. Current knowledge on psoriasis and autoimmune diseases. Psoriasis Targets Ther. 2016, 6, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Myers, W.; Opeola, M.; Gottlieb, A.B. Common clinical features and disease mechanisms of psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2004, 6, 306–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woo, Y.R.; Cho, D.H.; Park, H.J. Molecular Mechanisms and Management of a Cutaneous Inflammatory Disorder: Psoriasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nandakumar, P.; Tin, A.; Grove, M.L.; Ma, J.; Boerwinkle, E.; Coresh, J.; Chakravarti, A. MicroRNAs in the miR-17 and miR-15 families are downregulated in chronic kidney disease with hypertension. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0176734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fitzgerald, T.; Melsheimer, R.; Lafeuille, M.H.; Lefebvre, P.; Morrison, L.; Woodruff, K.; Lin, I.; Emond, B. Switching and discontinuation patterns among patients stable on originator infliximab who switched to an infliximab biosimilar or remained on originator infliximab. Biol. Targets Ther. 2021, 15, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, A.; Diamond, B. Autoimmune Diseases. New Engl. J. Med. 2001, 345, 340–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Non-Communicable Diseases. Available online: https://www.who.int/zh/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/noncommunicable-diseases (accessed on 24 January 2022).
- Naghavi, M.; Abajobir, A.A.; Abbafati, C.; Abbas, K.M.; Abd-Allah, F.; Abera, S.F.; Aboyans, V.; Adetokunboh, O.; Ärnlöv, J.; Afshin, A.; et al. Global, regional, and national age-sex specifc mortality for 264 causes of death, 1980–2016: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet 2017, 390, 1151–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Rane, G.; Dai, X.; Shanmugam, M.K.; Arfuso, F.; Samy, R.P.; Lai, M.K.P.; Kappei, D.; Kumar, A.P.; Sethi, G. Ageing and the telomere connection: An intimate relationship with inflammation. Ageing Res. Rev. 2016, 25, 55–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hug, N.; Lingner, J. Telomere length homeostasis. Chromosoma 2006, 115, 413–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savage, S.A.; Bertuch, A.A. The genetics and clinical manifestations of telomere biology disorders. Genet. Med. 2010, 12, 753–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heba, A.C.; Toupance, S.; Arnone, D.; Peyrin-Biroulet, L.; Benetos, A.; Ndiaye, N.C. Telomeres: New players in immune-mediated inflammatory diseases? J. Autoimmun. 2021, 123, 102699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higa, M.; Fujita, M.; Yoshida, K. DNA replication origins and fork progression at mammalian telomeres. Genes 2017, 8, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porro, A.; Feuerhahn, S.; Reichenbach, P.; Lingner, J. Molecular Dissection of Telomeric Repeat-Containing RNA Biogenesis Unveils the Presence of Distinct and Multiple Regulatory Pathways. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2010, 30, 4808–4817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Diman, A.; Decottignies, A. Genomic origin and nuclear localization of TERRA telomeric repeat-containing RNA: From Darkness to Dawn. FEBS J. 2018, 285, 1389–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sagie, S.; Toubiana, S.; Hartono, S.R.; Katzir, H.; Tzur-Gilat, A.; Havazelet, S.; Francastel, C.; Velasco, G.; Chédin, F.; Selig, S. Telomeres in ICF syndrome cells are vulnerable to DNA damage due to elevated DNA:RNA hybrids. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Griffith, J.D.; Comeau, L.; Rosenfield, S.; Stansel, R.M.; Bianchi, A.; Moss, H.; De Lange, T. Mammalian telomeres end in a large duplex loop. Cell 1999, 97, 503–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Claussin, C.; Chang, M. The many facets of homologous recombination at telomeres. Microb. Cell 2015, 2, 308–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korotkov, A.; Seluanov, A.; Gorbunova, V. Sirtuin 6: Linking longevity with genome and epigenome stability. Trends. Cell Biol. 2021, 31, 994–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Z.; Tian, X.; Van Meter, M.; Ke, Z.; Gorbunova, V.; Seluanov, A. Sirtuin 6 (SIRT6) rescues the decline of homologous recombination repair during replicative senescence. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 11800–11805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grootaert, M.O.J.; Finigan, A.; Figg, N.L.; Uryga, A.K.; Bennett, M.R. SIRT6 Protects Smooth Muscle Cells from Senescence and Reduces Atherosclerosis. Circ. Res. 2021, 128, 474–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allshire, R.C.; Madhani, H.D. Ten principles of heterochromatin formation and function. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2018, 19, 229–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Ge, J.; Zhang, L.; Ma, R.; Hou, X.; Li, B.; Moley, K.; Wang, Q. Sirt6 depletion causes spindle defects and chromosome misalignment during meiosis of mouse oocyte. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 15366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vijg, J. From DNA damage to mutations: All roads lead to aging. Ageing Res. Rev. 2021, 68, 101316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernadotte, A.; Mikhelson, V.M.; Spivak, I.M. Markers of cellular senescence. Telomere shortening as a marker of cellular senescence. Aging 2016, 8, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feretzaki, M.; Pospisilova, M.; Valador Fernandes, R.; Lunardi, T.; Krejci, L.; Lingner, J. RAD51-dependent recruitment of TERRA lncRNA to telomeres through R-loops. Nature 2020, 587, 303–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirvonen, K.; Laivuori, H.; Lahti, J.; Strandberg, T.; Eriksson, J.G.; Hackman, P. SIRT6 polymorphism rs117385980 is associated with longevity and healthy aging in Finnish men. BMC Med. Genet. 2017, 18, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, H.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, H.; Zhao, M.; Lu, Q. The pathogenic role of dysregulated epigenetic modifications in autoimmune diseases. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, K.; Volke, A.; Lund, M.; Bang, K.; Thestrup-Pedersen, K. Telomerase activity is spontaneously increased in lymphocytes from patients with atopic dermatitis and correlates with cellular proliferation. J. Dermatol. Sci. 1999, 22, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezazadeh, S.; Yang, D.; Biashad, S.A.; Firsanov, D.; Takasugi, M.; Gilbert, M.; Tombline, G.; Bhanu, N.V.; Garcia, B.A.; Seluanov, A.; et al. SIRT6 mono-ADP ribosylates KDM2A to locally increase H3K36me2 at DNA damage sites to inhibit transcription and promote repair. Aging 2020, 12, 11165–11184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rassoulzadegan, M.; Sharifi-Zarchi, A.; Kianmehr, L. DNA-RNA Hybrid (R-Loop): From a Unified Picture of the Mammalian Telomere to the Genome-Wide Profile. Cells 2021, 10, 1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moelling, K.; Broecker, F.; Russo, G.; Sunagawa, S. RNase H As gene modifier, driver of evolution and antiviral defense. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hyjek, M.; Figiel, M.; Nowotny, M. RNases H: Structure and mechanism. DNA Repair 2019, 84, 102672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crow, Y.J.; Leitch, A.; Hayward, B.E.; Garner, A.; Parmar, R.; Griffith, E.; Ali, M.; Semple, C.; Aicardi, J.; Babul-Hirji, R.; et al. Mutations in genes encoding ribonuclease H2 subunits cause Aicardi-Goutières syndrome and mimic congenital viral brain infection. Nat. Genet. 2006, 38, 910–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langley, R.G.; Ellis, C.N. Evaluating psoriasis with psoriasis area and severity index, psoriasis global assessment, and lattice system physician’s global assessment. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2004, 51, 563–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Callaghan, N.J.; Fenech, M. A quantitative PCR method for measuring absolute telomere length. Biol. Proced. Online 2011, 13, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Feretzaki, M.; Lingner, J. A practical qPCR approach to detect TERRA, the elusive telomeric repeat-containing RNA. Methods 2017, 114, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, X.; Huang, X.; Zhou, Z.; Lin, X. An improvement of the 2−ΔΔCt method for quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction data analysis. Biostat. Bioinform. Biomath. 2013, 3, 71–85. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pertea, M.; Kim, D.; Pertea, G.M.; Leek, J.T.; Salzberg, S.L. Transcript-level expression analysis of RNA-seq experiments with HISAT, StringTie and Ballgown. Nat. Protoc. 2016, 11, 1650–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kent, W.J.; Sugnet, C.W.; Furey, T.S.; Roskin, K.M.; Pringle, T.H.; Zahler, A.M.; Haussler, D. The Human Genome Browser at UCSC. Genome. Res. 2002, 12, 996–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramírez, F.; Ryan, D.P.; Grüning, B.; Bhardwaj, V.; Kilpert, F.; Richter, A.S.; Heyne, S.; Dündar, F.; Manke, T. deepTools2: A next generation web server for deep-sequencing data analysis. Nucleic. Acids Res. 2016, 44, 160–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanz, L.A.; Chédin, F. High-resolution, strand-specific R-loop mapping via S9.6-based DNA–RNA immunoprecipitation and high-throughput sequencing. Nat. Protoc. 2019, 14, 1734–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kianmehr, L.; Khazali, H.; Rajabi-Maham, H.; Sharifi-Zarchi, A.; Cuzin, F.; Rassoulzadegan, M. Rassoulzadegan Genome-Wide Distribution of Nascent Transcripts in Sperm DNA, Products of a Late Wave of General Transcription. Cells 2019, 8, 1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Costa, V.; Casamassimi, A.; Roberto, R.; Gianfrancesco, F.; Matarazzo, M.R.; D’Urso, M.; D’Esposito, M.; Rocchi, M.; Ciccodicola, A. DDX11L: A novel transcript family emerging from human subtelomeric regions. BMC Genom. 2009, 10, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kabeche, L.; Nguyen, H.D.; Buisson, R.; Zou, L. A mitosis-specific and R loop-driven ATR pathway promotes faithful chromosome segregation. Science 2018, 359, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Talbert, P.B.; Henikoff, S. Transcribing Centromeres: Noncoding RNAs and Kinetochore Assembly. Trends Genet. 2018, 34, 587–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Liu, Y.; Liu, C.; Shi, Q.; Huang, Y.; Han, F. Centromere Satellite Repeats Have Undergone Rapid Changes in Polyploid Wheat Subgenomes. Plant Cell 2019, 31, 2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leclerc, S.; Kitagawa, K. The Role of Human Centromeric RNA in Chromosome Stability. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2021, 8, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reijns, M.A.M.; Rabe, B.; Rigby, R.E.; Mill, P.; Astell, K.R.; Lettice, L.A.; Boyle, S.; Leitch, A.; Keighren, M.; Kilanowski, F.; et al. Enzymatic removal of ribonucleotides from DNA is essential for mammalian genome integrity and development. Cell 2012, 149, 1008–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, H.; Zhu, M.; Limbo, O.; Russell, P. RNase H eliminates R-loops that disrupt DNA replication but is nonessential for efficient DSB repair. EMBO Rep. 2018, 19, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lietard, J.; Damha, M.J.; Somoza, M.M. Large-Scale Photolithographic Synthesis of Chimeric DNA/RNA Hairpin Microarrays to Explore Sequence Specificity Landscapes of RNase HII Cleavage. Biochemistry 2019, 58, 4389–4397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amon, J.D.; Koshland, D. RNase H enables efficient repair of R-loop induced DNA damage. Elife. 2016, 5, e20533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crossley, M.P.; Bocek, M.; Cimprich, K.A. R-Loops as Cellular Regulators and Genomic Threats. Mol. Cell. 2019, 73, 398–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peleva, E.; Exton, L.S.; Kelley, K.; Kleyn, C.E.; Mason, K.J.; Smith, C.H. Risk of cancer in patients with psoriasis on biological therapies: A systematic review. Br. J. Dermatol. 2018, 178, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vaengebjerg, S.; Skov, L.; Egeberg, A.; Loft, N.D. Prevalence, Incidence, and Risk of Cancer in Patients with Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA Dermatol. 2020, 156, 421–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mehmetbeyoglu, E.; Kianmehr, L.; Borlu, M.; Yilmaz, Z.; Basar Kılıc, S.; Rajabi-Maham, H.; Taheri, S.; Rassoulzadegan, M. Decrease in RNase HII and Accumulation of lncRNAs/DNA Hybrids: A Causal Implication in Psoriasis? Biomolecules 2022, 12, 368. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12030368
Mehmetbeyoglu E, Kianmehr L, Borlu M, Yilmaz Z, Basar Kılıc S, Rajabi-Maham H, Taheri S, Rassoulzadegan M. Decrease in RNase HII and Accumulation of lncRNAs/DNA Hybrids: A Causal Implication in Psoriasis? Biomolecules. 2022; 12(3):368. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12030368
Chicago/Turabian StyleMehmetbeyoglu, Ecmel, Leila Kianmehr, Murat Borlu, Zeynep Yilmaz, Seyma Basar Kılıc, Hassan Rajabi-Maham, Serpil Taheri, and Minoo Rassoulzadegan. 2022. "Decrease in RNase HII and Accumulation of lncRNAs/DNA Hybrids: A Causal Implication in Psoriasis?" Biomolecules 12, no. 3: 368. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12030368
APA StyleMehmetbeyoglu, E., Kianmehr, L., Borlu, M., Yilmaz, Z., Basar Kılıc, S., Rajabi-Maham, H., Taheri, S., & Rassoulzadegan, M. (2022). Decrease in RNase HII and Accumulation of lncRNAs/DNA Hybrids: A Causal Implication in Psoriasis? Biomolecules, 12(3), 368. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12030368