Tirzepatide—Friend or Foe in Diabetic Cancer Patients?
Abstract
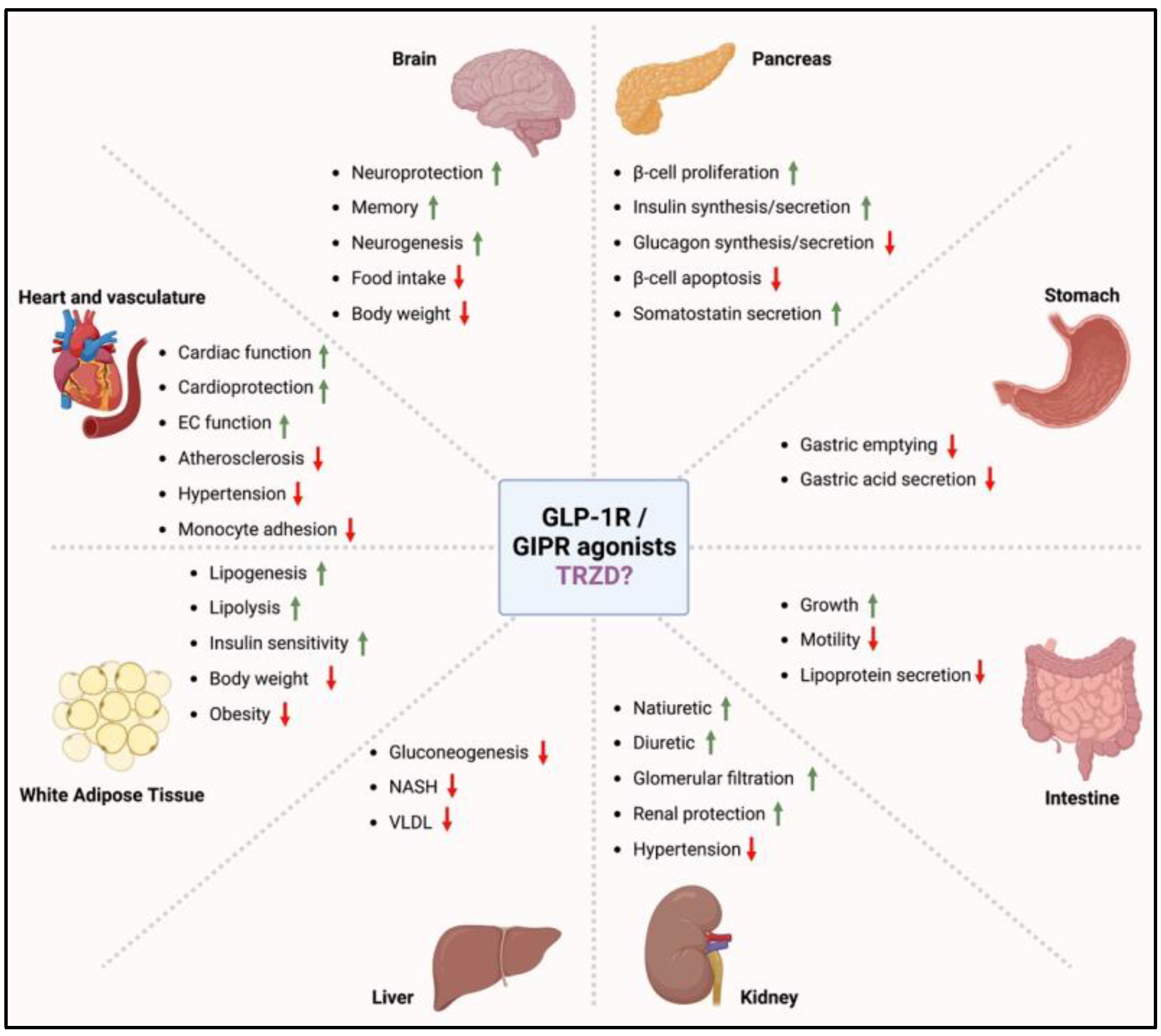
1. Incretin Mimetics for the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes
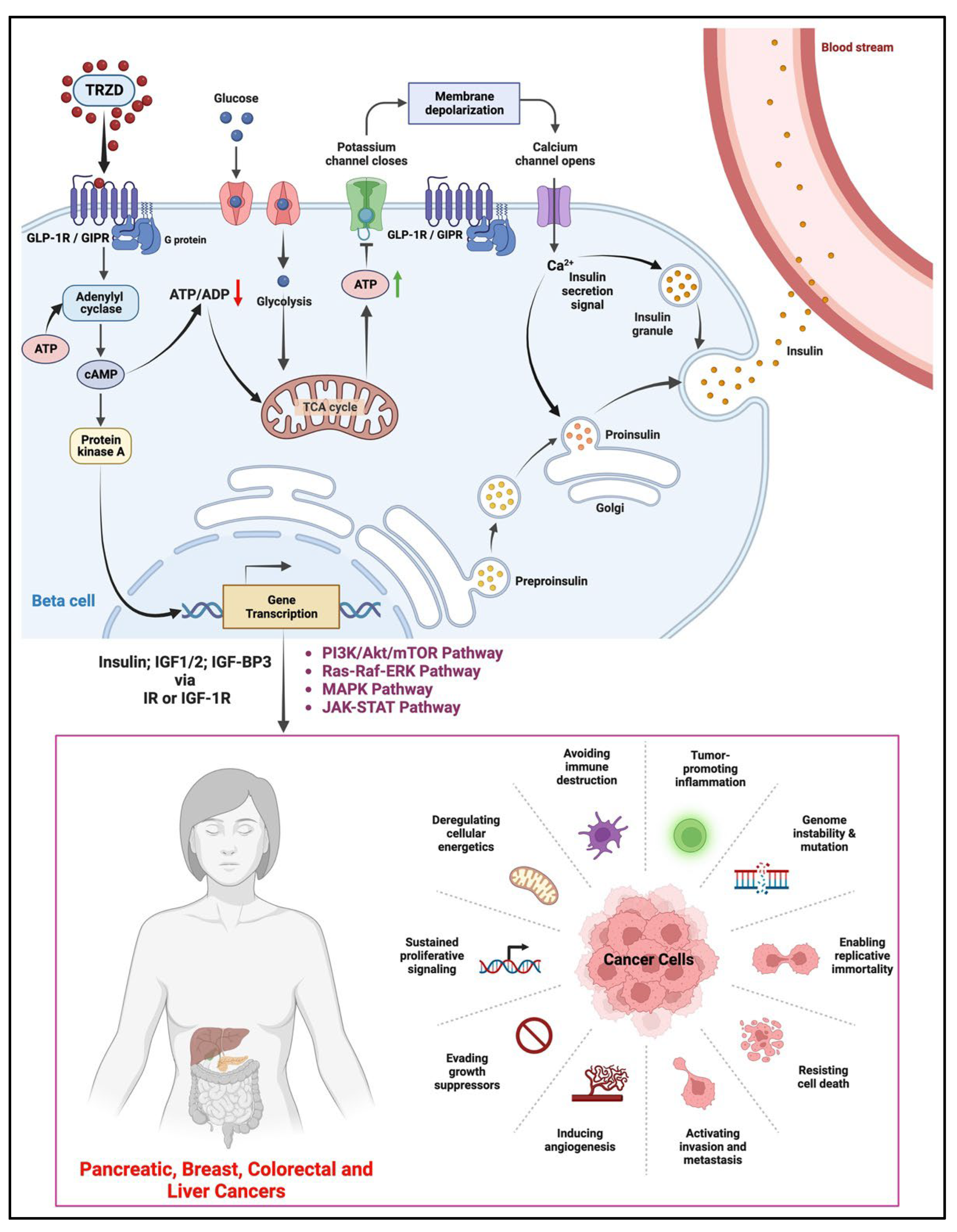
2. Possible Anti-Cancer Effects of TRZD
3. Possible Oncogenic Effects of TRZD
3.1. In the Pancreas
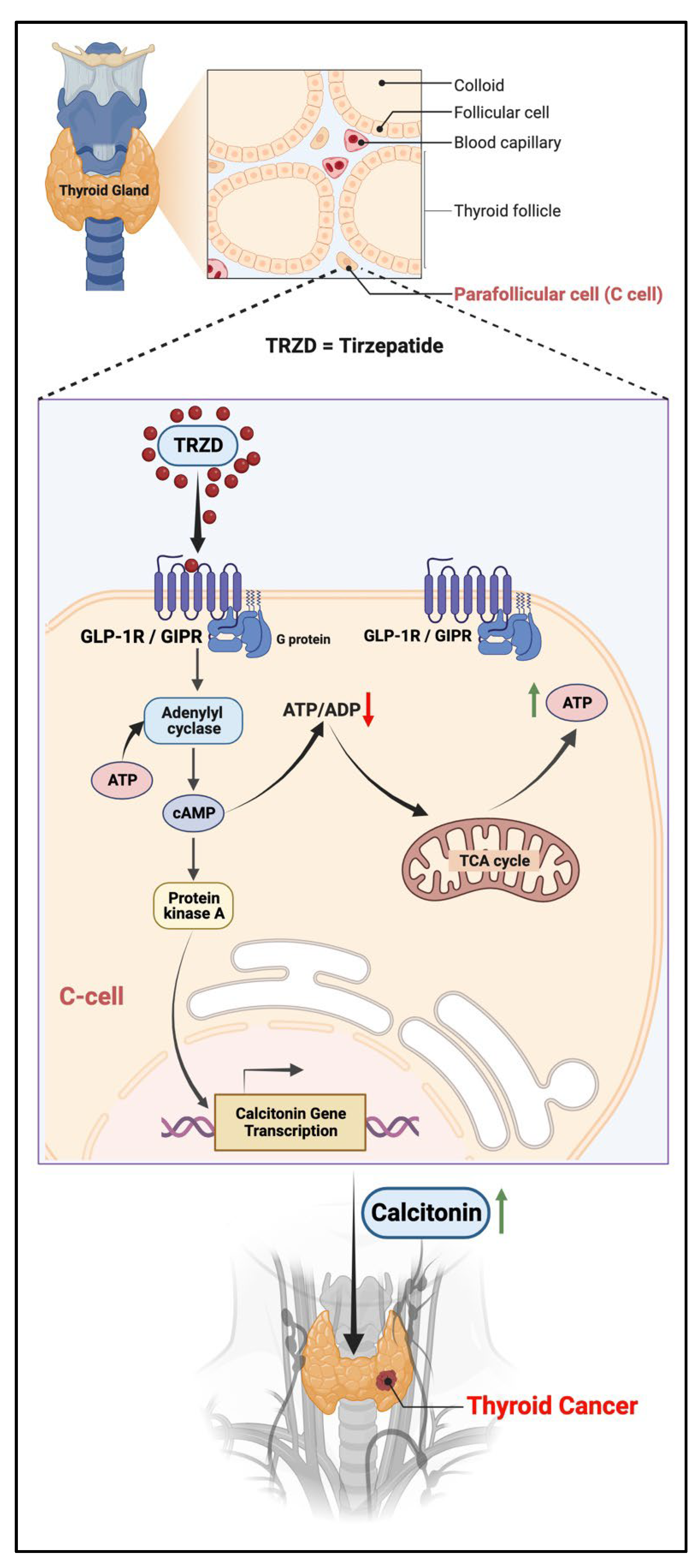
3.2. In the Thyroid
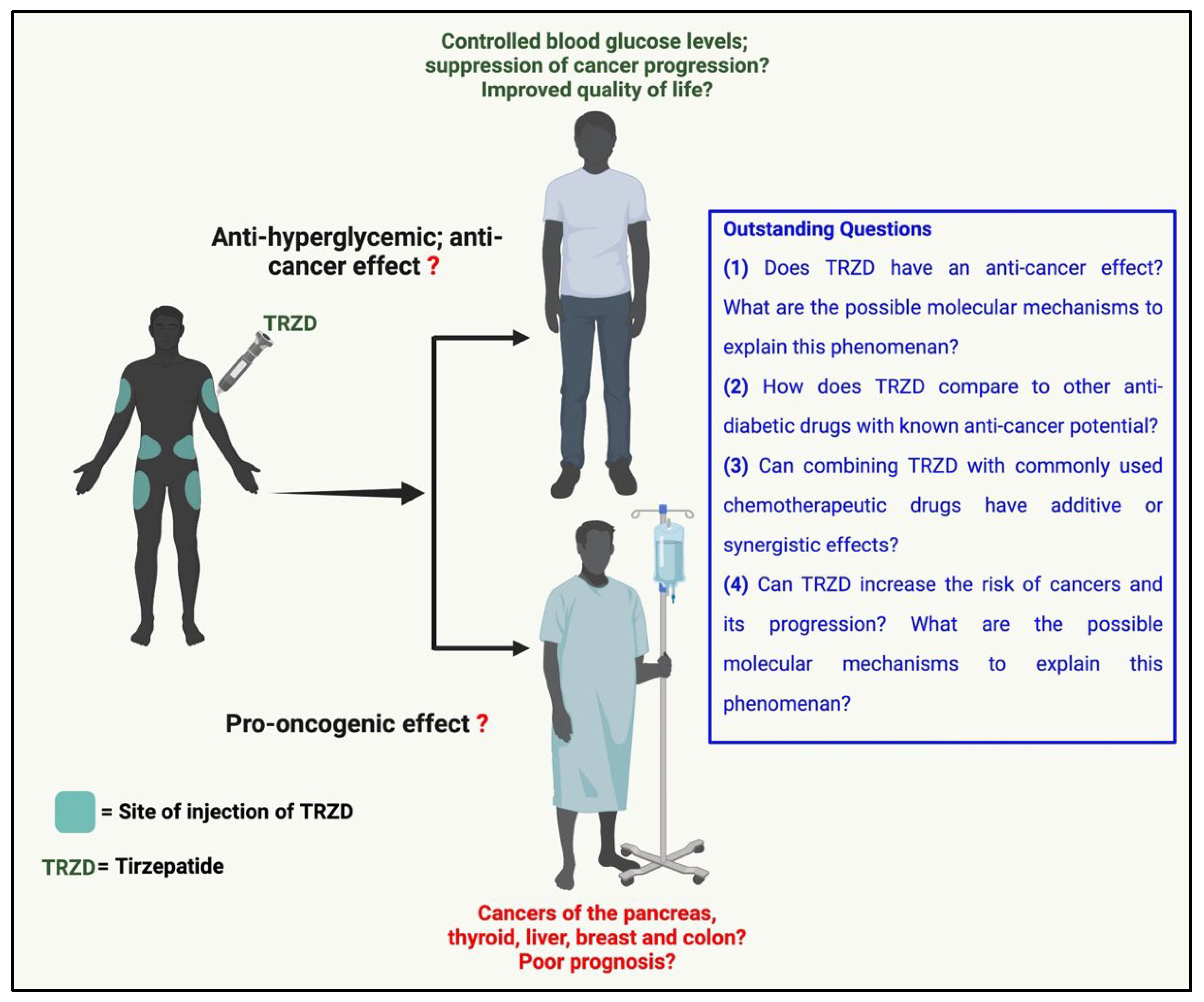
4. Clinical Data and Trials
5. Conclusions and Future Perspective
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AGEs | Advanced glycation end-products |
| Akt | Protein kinase B |
| AMP | Adenosine monophosphate |
| ATP | Adenosine triphosphate |
| cAMP | 3′,5′-cyclic AMP |
| DPP4 | Dipeptidyl peptidase 4 |
| ERK | Extracellular signal-regulated kinase |
| FAERS | FDA advance event reporting system |
| FDA | Food and drug administration |
| GIP | GIP receptor |
| GIP | Glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide/Gastric inhibitory peptide |
| GLP-1 | Glucagon-like peptide 1 |
| GLP-1R | GLP-1 receptor |
| IGF-1R | IGF-1 receptor |
| IGF-BP3 | Insulin-like growth factor binding protein 3 |
| IGF1/2 | Insulin-like growth factor 1/2 |
| JAK | Janus kinase |
| MAPK | Mitogen activated protein kinase |
| MEN2 | Multiple endocrine neoplasia syndrome type 2 |
| MTC | Medullary thyroid cancer/carcinoma |
| mTOR | mammalian target of rapamycin |
| NF-κB | Nuclear factor kappa-B |
| PARP | Poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase |
| PI3K | Phosphoinositide 3-kinase |
| PSMA2 | Proteasome alpha 2 subunit |
| RAGEs | Receptors of AGEs |
| SGLT2 | Sodium glucose co-transporter 2 |
| STAT | Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription |
| TRZD | Tirzepatide |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
References
- Bellanger, T.M.; Bray, G.A. Obesity related morbidity and mortality. J. La. State Med. Soc. 2005, 157, S42–49; quiz 49. [Google Scholar]
- Burki, T. European Commission classifies obesity as a chronic disease. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2021, 9, 418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, F.B. Globalization of diabetes: The role of diet, lifestyle, and genes. Diabetes Care 2011, 34, 1249–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rippe, J.M.; Crossley, S.; Ringer, R. Obesity as a chronic disease: Modern medical and lifestyle management. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 1998, 98, S9–S15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeedi, P.; Petersohn, I.; Salpea, P.; Malanda, B.; Karuranga, S.; Unwin, N.; Colagiuri, S.; Guariguata, L.; Motala, A.A.; Ogurtsova, K.; et al. Global and regional diabetes prevalence estimates for 2019 and projections for 2030 and 2045: Results from the International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Atlas, 9(th) edition. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2019, 157, 107843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blüher, M. Obesity: Global epidemiology and pathogenesis. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2019, 15, 288–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelaal, M.; le Roux, C.W.; Docherty, N.G. Morbidity and mortality associated with obesity. Ann. Transl. Med. 2017, 5, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuel, S.M.; Varghese, E.; Varghese, S.; Busselberg, D. Challenges and perspectives in the treatment of diabetes associated breast cancer. Cancer. Treat. Rev. 2018, 70, 98–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuel, S.M.; Varghese, E.; Kubatka, P.; Triggle, C.R.; Büsselberg, D. Metformin: The Answer to Cancer in a Flower? Current Knowledge and Future Prospects of Metformin as an Anti-Cancer Agent in Breast Cancer. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seifarth, C.; Schehler, B.; Schneider, H.J. Effectiveness of metformin on weight loss in non-diabetic individuals with obesity. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes 2013, 121, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malin, S.K.; Kashyap, S.R. Effects of metformin on weight loss: Potential mechanisms. Curr. Opin. Endocrinol. Diabetes Obes. 2014, 21, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yerevanian, A.; Soukas, A.A. Metformin: Mechanisms in Human Obesity and Weight Loss. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2019, 8, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, M.; Atif, M.A.; Tunio, A.G.; Ali, B.; Akhtar, L.; Serwar, G. Effect of Sitagliptin On Glycemic Control, Body Weight, Blood Pressure And Serum Lipid Profile In Type 2 Diabetic Hyperlipidemic Patients. J. Ayub. Med. Coll. Abbottabad. 2016, 28, 369–372. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dar, S.; Tahrani, A.A.; Piya, M.K. The role of GLP-1 receptor agonists as weight loss agents in patients with and without type 2 diabetes. Pract. Diabetes 2015, 32, 297–300b. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtis, L.; Humayun, M.A.; Walker, J.; Hampton, K.; Partridge, H. Addition of SGLT2 inhibitor to GLP-1 agonist therapy in people with type 2 diabetes and suboptimal glycaemic control. Pract. Diabetes 2016, 33, 129–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michałowska, J.; Miller-Kasprzak, E.; Bogdański, P. Incretin Hormones in Obesity and Related Cardiometabolic Disorders: The Clinical Perspective. Nutrients 2021, 13, 351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhury, A.; Duvoor, C.; Reddy Dendi, V.S.; Kraleti, S.; Chada, A.; Ravilla, R.; Marco, A.; Shekhawat, N.S.; Montales, M.T.; Kuriakose, K.; et al. Clinical Review of Antidiabetic Drugs: Implications for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Management. Front. Endocrinol. 2017, 8, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higbea, A.M.; Duval, C.; Chastain, L.M.; Chae, J. Weight effects of antidiabetic agents. Expert Rev. Endocrinol. Metab. 2017, 12, 441–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, V.; Kashyap, S.R. Weight considerations in pharmacotherapy for type 2 diabetes. J. Obes. 2011, 2011, 984245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenstock, J.; Wysham, C.; Frías, J.P.; Kaneko, S.; Lee, C.J.; Fernández Landó, L.; Mao, H.; Cui, X.; Karanikas, C.A.; Thieu, V.T. Efficacy and safety of a novel dual GIP and GLP-1 receptor agonist tirzepatide in patients with type 2 diabetes (SURPASS-1): A double-blind, randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2021, 398, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jastreboff, A.M.; Aronne, L.J.; Ahmad, N.N.; Wharton, S.; Connery, L.; Alves, B.; Kiyosue, A.; Zhang, S.; Liu, B.; Bunck, M.C.; et al. Tirzepatide Once Weekly for the Treatment of Obesity. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 387, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannan, S.; Nasr, C. Should we be concerned about thyroid cancer in patients taking glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists? Cleve. Clin. J. Med. 2015, 82, 142–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Bjerre Knudsen, L.; Madsen, L.W.; Andersen, S.; Almholt, K.; de Boer, A.S.; Drucker, D.J.; Gotfredsen, C.; Egerod, F.L.; Hegelund, A.C.; Jacobsen, H.; et al. Glucagon-like Peptide-1 receptor agonists activate rodent thyroid C-cells causing calcitonin release and C-cell proliferation. Endocrinology 2010, 151, 1473–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delfino, M.; Motola, D.; Benini, A.; Franzè, G.P.; Barotto, M.; Campi, A.; Monda, V.M. Incretin-mimetics associated pancreatitis: Evidence from the spontaneous adverse drug reactions reporting in Italy. Expert Opin. Drug Saf. 2014, 13, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FDA Approves Lilly’s Mounjaro™ (Tirzepatide) Injection, the First and Only GIP and GLP-1 Receptor Agonist for the Treatment of Adults with Type 2 Diabetes. Eli Lilly and Company. Available online: https://investor.lilly.com/news-releases/news-release-details/fda-approves-lillys-mounjarotm-tirzepatide-injection-first-and (accessed on 13 May 2022).
- Pirro, V.; Roth, K.D.; Lin, Y.; Willency, J.A.; Milligan, P.L.; Wilson, J.M.; Ruotolo, G.; Haupt, A.; Newgard, C.B.; Duffin, K.L. Effects of Tirzepatide, a Dual GIP and GLP-1 RA, on Lipid and Metabolite Profiles in Subjects with Type 2 Diabetes. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2022, 107, 363–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisman, E.Z.; Tenenbaum, A. The dual glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) and glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist tirzepatide: A novel cardiometabolic therapeutic prospect. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2021, 20, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalra, S.; Das, A.K.; Sahay, R.K.; Baruah, M.P.; Tiwaskar, M.; Das, S.; Chatterjee, S.; Saboo, B.; Bantwal, G.; Bhattacharya, S.; et al. Consensus Recommendations on GLP-1 RA Use in the Management of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: South Asian Task Force. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2019, 10, 1645–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonik, S.; Marchel, M.; Grabowski, M.; Opolski, G.; Mazurek, T. Gastrointestinal Incretins-Glucose-Dependent Insulinotropic Polypeptide (GIP) and Glucagon-like Peptide-1 (GLP-1) beyond Pleiotropic Physiological Effects Are Involved in Pathophysiology of Atherosclerosis and Coronary Artery Disease-State of the Art. Biology 2022, 11, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.J.; Jiang, X.; Hu, L.J.; Yang, L.; Deng, L.D.; Wang, Y.P.; Ren, Z.P. Activation of GLP-1 receptor enhances the chemosensitivity of pancreatic cancer cells. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2020, 64, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Wei, R.; Wang, L.; Tian, Q.; Tao, M.; Ke, J.; Liu, Y.; Hou, W.; Zhang, L.; Yang, J.; et al. Activation of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor inhibits growth and promotes apoptosis of human pancreatic cancer cells in a cAMP-dependent manner. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 306, E1431–E1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwaya, C.; Nomiyama, T.; Komatsu, S.; Kawanami, T.; Tsutsumi, Y.; Hamaguchi, Y.; Horikawa, T.; Yoshinaga, Y.; Yamashita, S.; Tanaka, T.; et al. Exendin-4, a Glucagonlike Peptide-1 Receptor Agonist, Attenuates Breast Cancer Growth by Inhibiting NF-κB Activation. Endocrinology 2017, 158, 4218–4232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fidan-Yaylalı, G.; Dodurga, Y.; Seçme, M.; Elmas, L. Antidiabetic exendin-4 activates apoptotic pathway and inhibits growth of breast cancer cells. Tumour. Biol. 2016, 37, 2647–2653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, Z.; Sun, B.; Gu, W.; Liu, J.; Zhang, H. Liraglutide inhibits the proliferation and promotes the apoptosis of MCF-7 human breast cancer cells through downregulation of microRNA-27a expression. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 17, 5202–5212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ligumsky, H.; Wolf, I.; Israeli, S.; Haimsohn, M.; Ferber, S.; Karasik, A.; Kaufman, B.; Rubinek, T. The peptide-hormone glucagon-like peptide-1 activates cAMP and inhibits growth of breast cancer cells. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2012, 132, 449–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.N.; Bu, H.M.; Ma, X.H.; Lu, S.; Zhao, S.; Cui, Y.L.; Sun, J. Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Analogues Inhibit Proliferation and Increase Apoptosis of Human Prostate Cancer Cells in vitro. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes 2017, 125, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nomiyama, T.; Kawanami, T.; Irie, S.; Hamaguchi, Y.; Terawaki, Y.; Murase, K.; Tsutsumi, Y.; Nagaishi, R.; Tanabe, M.; Morinaga, H.; et al. Exendin-4, a GLP-1 receptor agonist, attenuates prostate cancer growth. Diabetes 2014, 63, 3891–3905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsutsumi, Y.; Nomiyama, T.; Kawanami, T.; Hamaguchi, Y.; Terawaki, Y.; Tanaka, T.; Murase, K.; Motonaga, R.; Tanabe, M.; Yanase, T. Combined Treatment with Exendin-4 and Metformin Attenuates Prostate Cancer Growth. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0139709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koehler, J.A.; Kain, T.; Drucker, D.J. Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor activation inhibits growth and augments apoptosis in murine CT26 colon cancer cells. Endocrinology 2011, 152, 3362–3372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, G.; Peng, T.; Chen, Y.; Sha, L.; Dai, H.; Xiang, Y.; Zou, Z.; He, H.; Wang, S. Effects of GLP-1 Receptor Agonists on Biological Behavior of Colorectal Cancer Cells by Regulating PI3K/AKT/mTOR Signaling Pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 901559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xu, F.; Liang, H.; Cai, M.; Wen, X.; Li, X.; Weng, J. Exenatide inhibits the growth of endometrial cancer Ishikawa xenografts in nude mice. Oncol. Rep. 2016, 35, 1340–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Cheng, J.; Li, J.; He, J.; Li, X.; Xu, F. The GLP-1R Agonist Exendin-4 Attenuates Hyperglycemia-Induced Chemoresistance in Human Endometrial Cancer Cells Through ROS-Mediated Mitochondrial Pathway. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 793530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanda, R.; Hiraike, H.; Wada-Hiraike, O.; Ichinose, T.; Nagasaka, K.; Sasajima, Y.; Ryo, E.; Fujii, T.; Osuga, Y.; Ayabe, T. Expression of the glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor and its role in regulating autophagy in endometrial cancer. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosowska, A.; Gallego-Colon, E.; Garczorz, W.; Kłych-Ratuszny, A.; Aghdam, M.R.F.; Woz Niak, M.; Witek, A.; Wróblewska-Czech, A.; Cygal, A.; Wojnar, J.; et al. Exenatide modulates tumor-endothelial cell interactions in human ovarian cancer cells. Endocr. Connect. 2017, 6, 856–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, W.; Yu, S.; Wang, L.; He, M.; Cao, X.; Li, Y.; Xiao, H. Exendin-4 inhibits growth and augments apoptosis of ovarian cancer cells. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2016, 436, 240–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, D.; Cao, H.; Shi, M.; Wang, C.C.; Kwong, J.; Li, J.J.X.; Hou, Y.; Ming, X.; Lee, H.M.; Tian, X.Y.; et al. Increased co-expression of PSMA2 and GLP-1 receptor in cervical cancer models in type 2 diabetes attenuated by Exendin-4: A translational case-control study. EBioMedicine 2021, 65, 103242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palanissami, G.; Paul, S.F.D. RAGE and Its Ligands: Molecular Interplay Between Glycation, Inflammation, and Hallmarks of Cancer-a Review. Horm. Cancer 2018, 9, 295–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logsdon, C.D.; Fuentes, M.K.; Huang, E.H.; Arumugam, T. RAGE and RAGE ligands in cancer. Curr. Mol. Med. 2007, 7, 777–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Far, A.H.; Sroga, G.; Jaouni, S.K.A.; Mousa, S.A. Role and Mechanisms of RAGE-Ligand Complexes and RAGE-Inhibitors in Cancer Progression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puddu, A.; Mach, F.; Nencioni, A.; Viviani, G.L.; Montecucco, F. An emerging role of glucagon-like peptide-1 in preventing advanced-glycation-end-product-mediated damages in diabetes. Mediat. Inflamm. 2013, 2013, 591056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allam, M.M.; El Gazzar, W.B. Exendin-4, a glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist downregulates hepatic receptor for advanced glycation end products in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis rat model. Arch. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 124, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, B.; Hu, X.; Wen, Z.; Zhang, T.; Cai, Y. Exendin-4, a glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist, inhibits hyperglycemia-induced apoptosis in myocytes by suppressing receptor for advanced glycation end products expression. Exp. Ther. Med. 2014, 8, 1185–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, J.T.; Liang, Y.J.; Hsu, C.Y.; Chen, C.Y.; Chen, P.J.; Yang, Y.F.; Chen, Y.L.; Pei, D.; Chang, J.B.; Leu, J.G. Glucagon-like peptide receptor agonists attenuate advanced glycation end products-induced inflammation in rat mesangial cells. BMC Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2017, 18, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Körner, M.; Christ, E.; Wild, D.; Reubi, J.C. Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor overexpression in cancer and its impact on clinical applications. Front. Endocrinol. 2012, 3, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Körner, M.; Stöckli, M.; Waser, B.; Reubi, J.C. GLP-1 receptor expression in human tumors and human normal tissues: Potential for in vivo targeting. J. Nucl. Med. 2007, 48, 736–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gasbjerg, L.S.; Gabe, M.B.N.; Hartmann, B.; Christensen, M.B.; Knop, F.K.; Holst, J.J.; Rosenkilde, M.M. Glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) receptor antagonists as anti-diabetic agents. Peptides 2018, 100, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandarana, R.; D’Souza, J.S.; Coutinho, E.C. Glucose-Dependent Insulinotropic Polypeptide Receptor (GIPR). In Encyclopedia of Signaling Molecules; Choi, S., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 773–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, S.; He, Y.; Koya, D.; Kanasaki, K. Cancer biology in diabetes. J. Diabetes Investig. 2014, 5, 251–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prabakaran, D.; Wang, B.; Feuerstein, J.D.; Sinclair, J.A.; Bijpuria, P.; Jepeal, L.I.; Wolfe, M.M. Glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide stimulates the proliferation of colorectal cancer cells. Regul. Pept. 2010, 163, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denker, P.S.; Dimarco, P.E. Exenatide (Exendin-4)–Induced Pancreatitis: A case report. Diabetes Care 2006, 29, 471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cure, P.; Pileggi, A.; Alejandro, R. Exenatide and Rare Adverse Events. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 358, 1969–1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathy, N.R.; Basha, S.; Jain, R.; Shetty, S.; Ramachandran, A. Exenatide and acute pancreatitis. J. Assoc. Physicians India 2008, 56, 987–988. [Google Scholar]
- Dolan, R.D.; Bazarbashi, A.N.; Lo, A.; Smith, B.N. Liraglutide-Induced Hemorrhagic Pancreatitis in a Nondiabetic Patient. ACG Case Rep. J. 2020, 7, e00380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fatakhova, K.; Rahman, A.; Al-Naqeeb, G.; Al Yassin, S.; Alqaisi, S.; Ramdass, A. 1311 Acute Pancreatitis in a Patient Using Liraglutide for Weight Loss. Off. J. Am. Coll. Gastroenterol. 2019, 114, S728–S729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gameil, M.A.; Elsebaie, A.H. Mildly symptomatic liraglutide-induced acute pancreatitis in a patient with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A case report. Egypt. J. Intern. Med. 2020, 32, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vangoitsenhoven, R.; Mathieu, C.; Van der Schueren, B. GLP1 and cancer: Friend or foe? Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2012, 19, F77–F88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buse, J.B.; Bethel, M.A.; Green, J.B.; Stevens, S.R.; Lokhnygina, Y.; Aschner, P.; Grado, C.R.; Tankova, T.; Wainstein, J.; Josse, R.; et al. Pancreatic Safety of Sitagliptin in the TECOS Study. Diabetes Care 2017, 40, 164–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elashoff, M.; Matveyenko, A.V.; Gier, B.; Elashoff, R.; Butler, P.C. Pancreatitis, Pancreatic, and Thyroid Cancer with Glucagon-Like Peptide-1–Based Therapies. Gastroenterology 2011, 141, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vujasinovic, M.; Dugic, A.; Maisonneuve, P.; Aljic, A.; Berggren, R.; Panic, N.; Valente, R.; Pozzi Mucelli, R.; Waldthaler, A.; Ghorbani, P.; et al. Risk of Developing Pancreatic Cancer in Patients with Chronic Pancreatitis. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 3720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowenfels, A.B.; Maisonneuve, P.; Cavallini, G.; Ammann, R.W.; Lankisch, P.G.; Andersen, J.R.; Dimagno, E.P.; Andren-Sandberg, A.; Domellof, L. Pancreatitis and the Risk of Pancreatic Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 1993, 328, 1433–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jura, N.; Archer, H.; Bar-Sagi, D. Chronic pancreatitis, pancreatic adenocarcinoma and the black box in-between. Cell Res. 2005, 15, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebours, V.; Boutron-Ruault, M.C.; Schnee, M.; Férec, C.; Le Maréchal, C.; Hentic, O.; Maire, F.; Hammel, P.; Ruszniewski, P.; Lévy, P. The natural history of hereditary pancreatitis: A national series. Gut 2009, 58, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nauck, M.A.; Friedrich, N. Do GLP-1-based therapies increase cancer risk? Diabetes Care 2013, 36, S245–S252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boniol, M.; Franchi, M.; Bota, M.; Leclercq, A.; Guillaume, J.; van Damme, N.; Corrao, G.; Autier, P.; Boyle, P. Incretin-Based Therapies and the Short-term Risk of Pancreatic Cancer: Results from Two Retrospective Cohort Studies. Diabetes Care 2018, 41, 286–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butler, A.E.; Campbell-Thompson, M.; Gurlo, T.; Dawson, D.W.; Atkinson, M.; Butler, P.C. Marked expansion of exocrine and endocrine pancreas with incretin therapy in humans with increased exocrine pancreas dysplasia and the potential for glucagon-producing neuroendocrine tumors. Diabetes 2013, 62, 2595–2604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortazavi, M.; Moosavi, F.; Martini, M.; Giovannetti, E.; Firuzi, O. Prospects of targeting PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in pancreatic cancer. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2022, 176, 103749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furukawa, T. Impacts of activation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway in pancreatic cancer. Front. Oncol. 2015, 5, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.H.; Kim, H. Role of janus kinase/signal transducers and activators of transcription in the pathogenesis of pancreatitis and pancreatic cancer. Gut Liver 2012, 6, 417–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collisson, E.A.; Trejo, C.L.; Silva, J.M.; Gu, S.; Korkola, J.E.; Heiser, L.M.; Charles, R.P.; Rabinovich, B.A.; Hann, B.; Dankort, D.; et al. A central role for RAF→MEK→ERK signaling in the genesis of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Cancer. Discov. 2012, 2, 685–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigneri, P.G.; Tirrò, E.; Pennisi, M.S.; Massimino, M.; Stella, S.; Romano, C.; Manzella, L. The Insulin/IGF System in Colorectal Cancer Development and Resistance to Therapy. Front. Oncol. 2015, 5, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chettouh, H.; Lequoy, M.; Fartoux, L.; Vigouroux, C.; Desbois-Mouthon, C. Hyperinsulinaemia and insulin signalling in the pathogenesis and the clinical course of hepatocellular carcinoma. Liver Int. 2015, 35, 2203–2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madsen, L.W.; Knauf, J.A.; Gotfredsen, C.; Pilling, A.; Sjögren, I.; Andersen, S.; Andersen, L.; de Boer, A.S.; Manova, K.; Barlas, A.; et al. GLP-1 receptor agonists and the thyroid: C-cell effects in mice are mediated via the GLP-1 receptor and not associated with RET activation. Endocrinology 2012, 153, 1538–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosol, T.J. On-target effects of GLP-1 receptor agonists on thyroid C-cells in rats and mice. Toxicol. Pathol. 2013, 41, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Regazzo, D.; Bertazza, L.; Galletta, E.; Barollo, S.; Mondin, A.; Zovato, S.; Iacobone, M.; Zilio, E.; Scaroni, C.; Radu, C.M.; et al. The GIP/GIPR axis in medullary thyroid cancer: Clinical and molecular findings. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2022, 29, 273–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Serial No. | Condition | Total Registered Trials | Completed | Active, Not Recruiting | Active, Not Yet Recruiting | Active, Recruiting |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Diabetes | 29 | 16 | 7 | 2 | 4 |
| 2 | Obesity | 14 | 2 | 6 | 2 | 4 |
| 3 | Cancers | - | - | - | - | - |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Samuel, S.M.; Varghese, E.; Kubatka, P.; Büsselberg, D. Tirzepatide—Friend or Foe in Diabetic Cancer Patients? Biomolecules 2022, 12, 1580. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12111580
Samuel SM, Varghese E, Kubatka P, Büsselberg D. Tirzepatide—Friend or Foe in Diabetic Cancer Patients? Biomolecules. 2022; 12(11):1580. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12111580
Chicago/Turabian StyleSamuel, Samson Mathews, Elizabeth Varghese, Peter Kubatka, and Dietrich Büsselberg. 2022. "Tirzepatide—Friend or Foe in Diabetic Cancer Patients?" Biomolecules 12, no. 11: 1580. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12111580
APA StyleSamuel, S. M., Varghese, E., Kubatka, P., & Büsselberg, D. (2022). Tirzepatide—Friend or Foe in Diabetic Cancer Patients? Biomolecules, 12(11), 1580. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12111580









