Synthesis and In Vitro Evaluation of Novel Dopamine Receptor D2 3,4-dihydroquinolin-2(1H)-one Derivatives Related to Aripiprazole
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemistry
2.1.1. Preparation of 1-(3-chloropropyl)-3,4-dihydroquinolin-2(1H)-one (4a)
2.1.2. Preparation of 1-(4-chlorobutyl-3,4-dihydroquinolin-2(1H)-one (4b)
2.1.3. General Procedure for the Preparation of Final Compounds 5a-g and 6a-g
2.2. Molecular Studies
2.2.1. Docking Simulation
2.2.2. Thermodynamic Integration and Free Energy Calculations
2.3. BBB Score Prediction
2.4. Biology Evaluation
2.4.1. D2 Receptor Binding Affinity–Transfection and Membrane Preparation
2.4.2. D2R Binding Affinity–Radioligand Experiment
2.4.3. D2 Receptor Binding Affinity–Data Analysis
[3H]NMS Saturation Binding
Competition Binding
2.4.4. MTT Assay
2.4.5. PAMPA Assay
3. Results
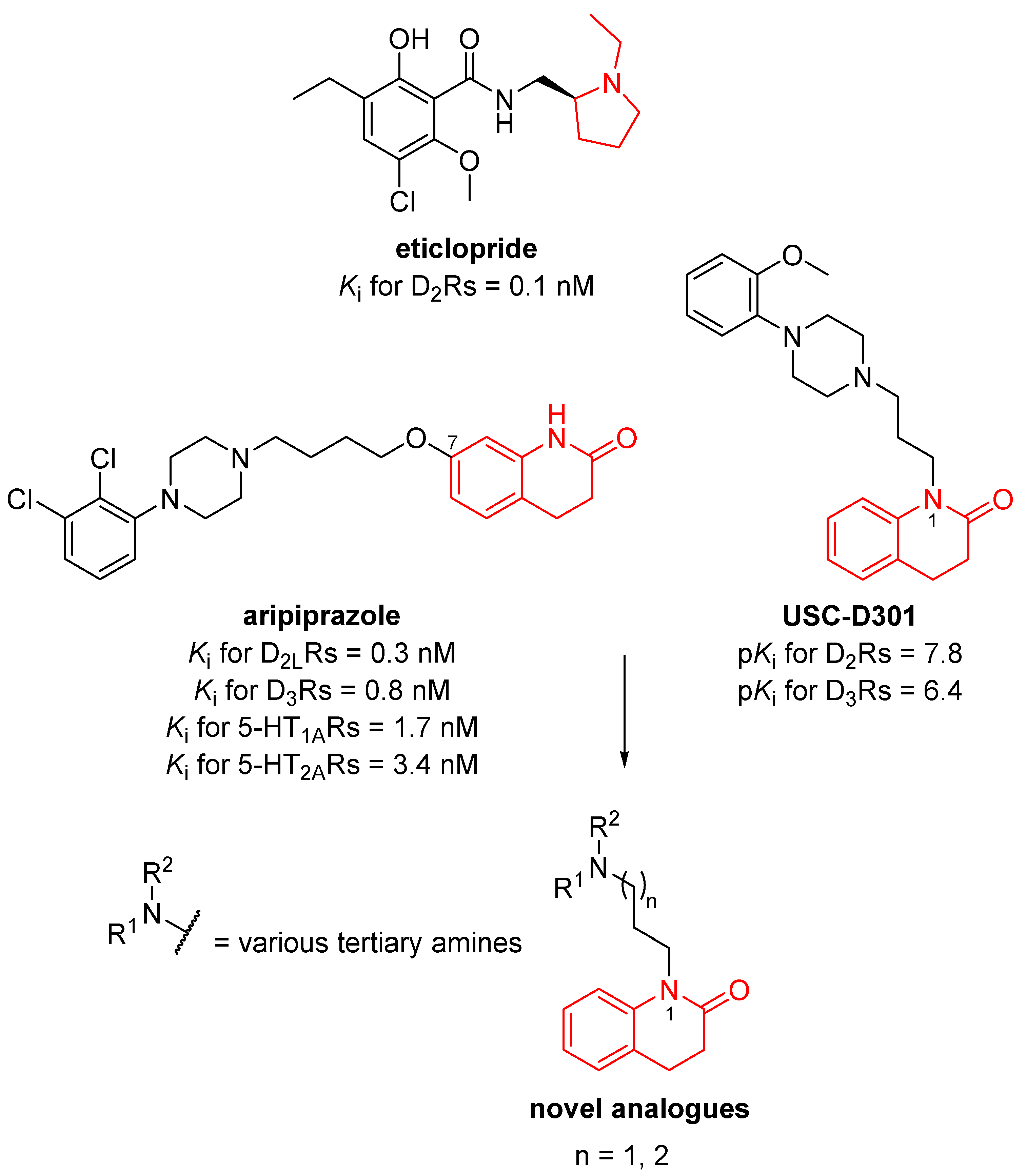
3.1. Design of Novel Compounds
3.2. The Synthesis of Novel Compounds
3.3. Binding Affinities of Novel Compounds at D2Rs and Their Cytotoxicities
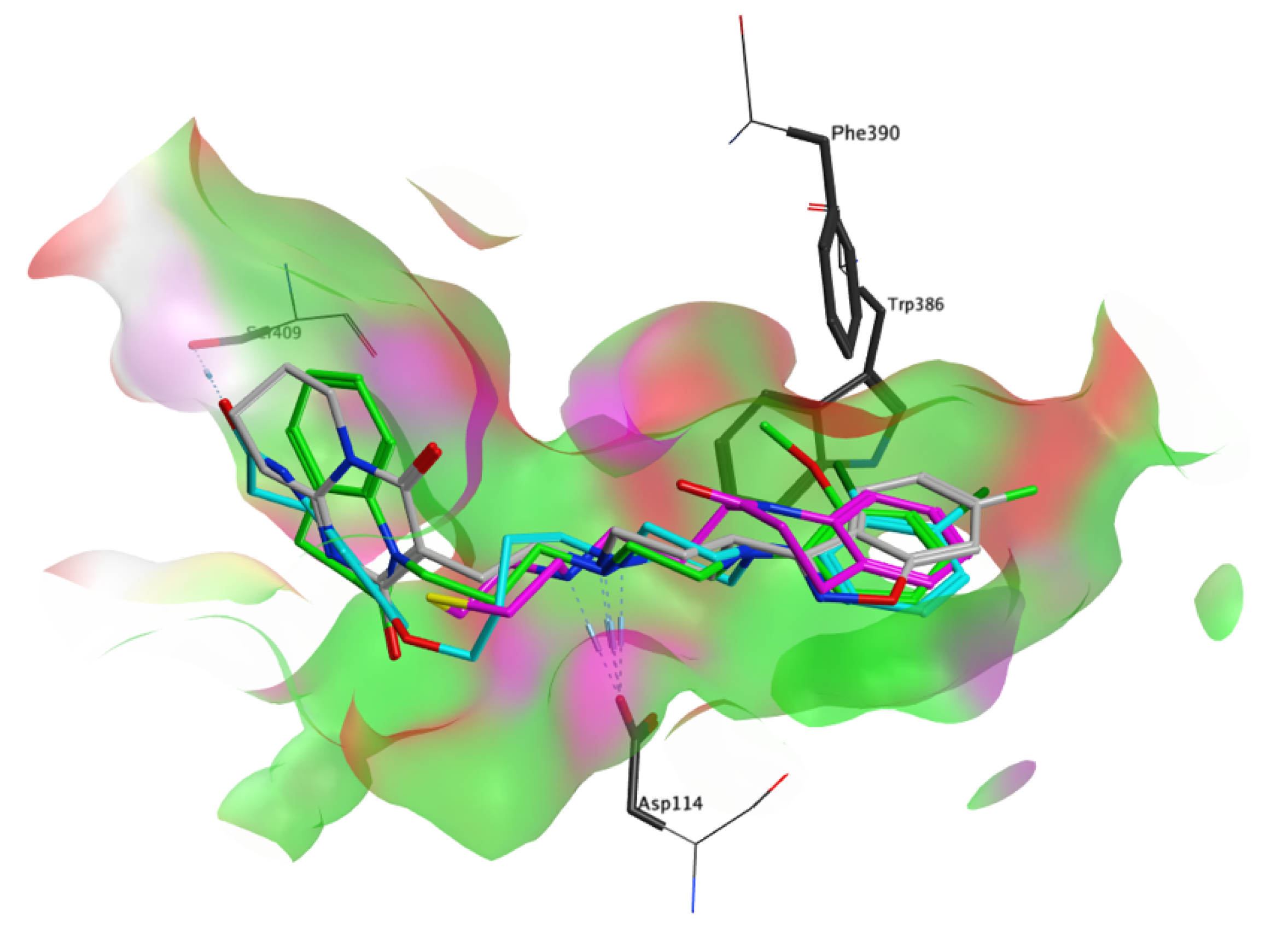
3.4. Molecular Modelling Studies
3.5. Central Nervous System Availability Prediction and Study for Novel Compounds
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Matt, S.M.; Gaskill, P.J. Where Is Dopamine and How Do Immune Cells See It? Dopamine-Mediated Immune Cell Function in Health and Disease. J. Neuroimmune Pharm. 2020, 15, 114–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayano, G. Dopamine: Receptors, Functions, Synthesis, Pathways, Locations and Mental Disorders: Review of Literatures. J. Ment. Disord. Treat. 2016, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, M.O.; Battagello, D.S.; Cardoso, A.R.; Hauser, D.N.; Bittencourt, J.C.; Correa, R.G. Dopamine: Functions, Signaling, and Association with Neurological Diseases. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2019, 39, 31–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martel, J.C.; Gatti McArthur, S. Dopamine Receptor Subtypes, Physiology and Pharmacology: New Ligands and Concepts in Schizophrenia. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pivonello, R.; Ferone, D.; Lombardi, G.; Colao, A.; Lamberts, S.W.J.; Hofland, L.J. Novel Insights in Dopamine Receptor Physiology. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2007, 156, S13–S21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Żuk, J.; Bartuzi, D.; Matosiuk, D.; Kaczor, A.A. Preferential Coupling of Dopamine D2S and D2L Receptor Isoforms with Gi1 and Gi2 Proteins—In Silico Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Usiello, A.; Baik, J.H.; Rougé-Pont, F.; Picetti, R.; Dierich, A.; LeMeur, M.; Piazza, P.V.; Borrelli, E. Distinct Functions of the Two Isoforms of Dopamine D2 Receptors. Nature 2000, 408, 199–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beaulieu, J.-M.; Gainetdinov, R.R. The Physiology, Signaling, and Pharmacology of Dopamine Receptors. Pharm. Rev. 2011, 63, 182–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stępnicki, P.; Kondej, M.; Kaczor, A.A. Current Concepts and Treatments of Schizophrenia. Molecules 2018, 23, 2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, S.-M.; Han, C.; Lee, S.-J.; Jun, T.-Y.; Patkar, A.A.; Masand, P.S.; Pae, C.-U. Second Generation Antipsychotics in the Treatment of Major Depressive Disorder: An Update. Chonnam. Med. J. 2016, 52, 159–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mulder, R.; Hamilton, A.; Irwin, L.; Boyce, P.; Morris, G.; Porter, R.J.; Malhi, G.S. Treating Depression with Adjunctive Antipsychotics. Bipolar Disord. 2018, 20, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hershenberg, R.; Gros, D.F.; Brawman-Mintzer, O. Role of Atypical Antipsychotics in the Treatment of Generalized Anxiety Disorder. CNS Drugs 2014, 28, 519–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pignon, B.; Montcel, C.T.; Carton, L.; Pelissolo, A. The Place of Antipsychotics in the Therapy of Anxiety Disorders and Obsessive-Compulsive Disorders. Curr. Psychiatry Rep. 2017, 19, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marder, S.R.; Cannon, T.D. Schizophrenia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 1753–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radhakrishnan, R.; Kaser, M.; Guloksuz, S. The Link Between the Immune System, Environment, and Psychosis. Schizophr. Bull. 2017, 43, 693–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laruelle, M. Schizophrenia: From Dopaminergic to Glutamatergic Interventions. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2014, 14, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCutcheon, R.A.; Abi-Dargham, A.; Howes, O.D. Schizophrenia, Dopamine and the Striatum: From Biology to Symptoms. Trends Neurosci. 2019, 42, 205–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kapur, S.; Zipursky, R.; Jones, C.; Remington, G.; Houle, S. Relationship Between Dopamine D2 Occupancy, Clinical Response, and Side Effects: A Double-Blind PET Study of First-Episode Schizophrenia. AJP 2000, 157, 514–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordström, A.-L.; Farde, L.; Wiesel, F.-A.; Forslund, K.; Pauli, S.; Halldin, C.; Uppfeldt, G. Central D2-Dopamine Receptor Occupancy in Relation to Antipsychotic Drug Effects: A Double-Blind PET Study of Schizophrenic Patients. Biol. Psychiatry 1993, 33, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richtand, N.M.; Welge, J.A.; Logue, A.D.; Keck, P.E.; Strakowski, S.M.; McNamara, R.K. Dopamine and Serotonin Receptor Binding and Antipsychotic Efficacy. Neuropsychopharmacology 2007, 32, 1715–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seeman, P.; Lee, T.; Chau-Wong, M.; Wong, K. Antipsychotic Drug Doses and Neuroleptic/Dopamine Receptors. Nature 1976, 261, 717–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlsson, P.; Farde, L.; Härnryd, C.; Sedvall, G.; Smith, L.; Wiesel, F.-A. Lack of Apparent Antipsychotic Effect of the D 1 -Dopamine Recepotr Antagonist SCH39166 in Acutely Ill Schizophrenic Patients. Psychopharmacology 1995, 121, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Redden, L.; Rendenbach-Mueller, B.; Abi-Saab, W.; Katz, D.; Goenjian, A.; Robieson, W.; Wang, Y.; Goss, S.; Greco, N.; Saltarelli, M. A Double-Blind, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Study of the Dopamine D-3 Receptor Antagonist ABT-925 in Patients With Acute Schizophrenia. J. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 2011, 31, 221–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bristow, L.J.; Kramer, M.S.; Kulagowski, J.; Patel, S.; Ragan, C.I.; Seabrook, G.R. Schizophrenia and L-745, 870, a Novel Dopamine D4 Receptor Antagonist. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 1997, 18, 186–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, M.S.; Molnar, C.E.; Grenesko, E.L.; Anderson, B.; Mu, Q.; Johnson, K.; Nahas, Z.; Knable, M.; Fernandes, P.; Juncos, J.; et al. A Single 20 Mg Dose of Dihydrexidine (DAR-0100), a Full Dopamine D1 Agonist, Is Safe and Tolerated in Patients with Schizophrenia. Schizophr. Res. 2007, 93, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girgis, R.R.; Van Snellenberg, J.X.; Glass, A.; Kegeles, L.S.; Thompson, J.L.; Wall, M.; Cho, R.Y.; Carter, C.S.; Slifstein, M.; Abi-Dargham, A.; et al. A Proof-of-Concept, Randomized Controlled Trial of DAR-0100A, a Dopamine-1 Receptor Agonist, for Cognitive Enhancement in Schizophrenia. J. Psychopharmacol. 2016, 30, 428–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosell, D.; Zaluda, L.; McClure, M.; Perez-Rodriguez, M.; Strike, S.; Barch, D.; Harvey, P.; Girgis, R.; Hazlett, E.; Mailman, R.; et al. Effects of the D1 Dopamine Receptor Agonist Dihydrexidine (DAR-0100A) on Working Memory in Schizotypal Personality Disorder. Neuropsychopharmacology 2015, 40, 446–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Li, X.H.; Cai, D.B.; Yang, X.H.; Ungvari, G.S.; Ng, C.H.; Ning, Y.P.; Xiang, Y.T. Adjunctive Azapirone for Schizophrenia: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trials. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2018, 28, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meltzer, H.; Huang, M. In Vivo Actions of Atypical Antipsychotic Drug on Serotonergic and Dopaminergic Systems. Prog. Brain Res. 2008, 172, 177–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaar, S.J.; Natesan, S.; McCutcheon, R.; Howes, O.D. Antipsychotics: Mechanisms Underlying Clinical Response and Side-Effects and Novel Treatment Approaches Based on Pathophysiology. Neuropharmacology 2020, 172, 107704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richelson, E.; Souder, T. Binding of Antipsychotic Drugs to Human Brain Receptors Focus on Newer Generation Compounds. Life Sci. 2000, 68, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, L.S. Pimavanserin for Patients with Alzheimer’s Disease Psychosis. Lancet Neurol. 2018, 17, 194–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bebawy, M.; Chetty, M. Differential Pharmacological Regulation of Drug Efflux and Pharmacoresistant Schizophrenia. BioEssays 2008, 30, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carbon, M.; Correll, C.U. Thinking and Acting beyond the Positive: The Role of the Cognitive and Negative Symptoms in Schizophrenia. CNS Spectr. 2014, 19, 35–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Berardis, D.; Rapini, G.; Olivieri, L.; Di Nicola, D.; Tomasetti, C.; Valchera, A.; Fornaro, M.; Di Fabio, F.; Perna, G.; Di Nicola, M.; et al. Safety of Antipsychotics for the Treatment of Schizophrenia: A Focus on the Adverse Effects of Clozapine. Adv. Drug Saf. 2018, 9, 237–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Weston-Green, K.; Huang, X.-F.; Deng, C. Second Generation Antipsychotic-Induced Type 2 Diabetes: A Role for the Muscarinic M3 Receptor. CNS Drugs 2013, 27, 1069–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osuch, E.; Marais, A. The Pharmacological Management of Depression–Update 2017. South Afr. Fam. Pract. 2017, 59, 6–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bystritsky, A.; Khalsa, S.S.; Cameron, M.E.; Schiffman, J. Current Diagnosis and Treatment of Anxiety Disorders. Pharm. Ther. 2013, 38, 30–57. [Google Scholar]
- Gustavsson, A.; Svensson, M.; Jacobi, F.; Allgulander, C.; Alonso, J.; Beghi, E.; Dodel, R.; Ekman, M.; Faravelli, C.; Fratiglioni, L.; et al. Cost of Disorders of the Brain in Europe 2010. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2011, 21, 718–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wood, M.; Reavill, C. Aripiprazole Acts as a Selective Dopamine D2 Receptor Partial Agonist. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2007, 16, 771–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, L.; Selent, J.; Ortega, R.; Masaguer, C.F.; Domínguez, E.; Areias, F.; Brea, J.; Loza, M.I.; Sanz, F.; Pastor, M. Synthesis, 3D-QSAR, and Structural Modeling of Benzolactam Derivatives with Binding Affinity for the D2 and D3 Receptors. ChemMedChem 2010, 5, 1300–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niso, M.; Pati, M.L.; Berardi, F.; Abate, C. Rigid versus Flexible Anilines or Anilides Confirm the Bicyclic Ring as the Hydrophobic Portion for Optimal Σ2 Receptor Binding and Provide Novel Tools for the Development of Future Σ2 Receptor PET Radiotracers. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 88508–88518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skjaerback, N.; Koch, K.N.; Friberg, B.L.M.; Tolf, B.-R. Tetrahydroquinoline Analogues as Muscarinic Agonists. WO2003057672A3, 13 November 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Geneste, H.; Backfisch, G.; Braje, W.; Delzer, J.; Haupt, A.; Hutchins, C.W.; King, L.L.; Lubisch, W.; Steiner, G.; Teschendorf, H.-J.; et al. Synthesis and SAR of Highly Potent and Selective Dopamine D3-Receptor Antagonists: Quinolin(Di)One and Benzazepin(Di)One Derivatives. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2006, 16, 658–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshiro, Y.; Sakurai, Y.; Sato, S.; Kurahashi, N.; Tanaka, T.; Kikuchi, T.; Tottori, K.; Uwahodo, Y.; Miwa, T.; Nishi, T. 3,4-Dihydro-2(1H)-Quinolinone as a Novel Antidepressant Drug: Synthesis and Pharmacology of 1-[3-[4-(3-Chlorophenyl)-1-Piperazinyl]Propyl]-3,4-Dihydro-5-Methoxy-2(1H)-Quinolinone and Its Derivatives. J. Med. Chem. 2000, 43, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, W.; Wang, Y.; Wu, C.; Yang, F.; Zheng, W.; Wu, S.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Z.; He, Y.; Shen, J. Synthesis and Biological Investigation of Triazolopyridinone Derivatives as Potential Multireceptor Atypical Antipsychotics. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2020, 30, 127027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chemical Computing Group ULC. Molecular Operating Environment (MOE). 2019. Available online: https://www.chemcomp.com/Research-Citing_MOE.htm (accessed on 16 June 2021).
- Wang, S.; Che, T.; Levit, A.; Shoichet, B.K.; Wacker, D.; Roth, B.L. Structure of the D2 Dopamine Receptor Bound to the Atypical Antipsychotic Drug Risperidone. Nature 2018, 555, 269–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, M.; Lee, H.J.; Barden, C.J.; Weaver, D.F. The Blood–Brain Barrier (BBB) Score. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 62, 9824–9836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Fakahany, E.E.; Jakubik, J. Radioligand Binding at Muscarinic Receptors. In Muscarinic Receptor: From Structure to Animal Models; Myslivecek, J., Jakubik, J., Eds.; Neuromethods; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 37–68. ISBN 978-1-4939-2858-3. [Google Scholar]
- Peterson, G.L. A Simplification of the Protein Assay Method of Lowry et Al. Which Is More Generally Applicable. Anal. Biochem. 1977, 83, 346–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malinak, D.; Dolezal, R.; Marek, J.; Salajkova, S.; Soukup, O.; Vejsova, M.; Korabecny, J.; Honegr, J.; Penhaker, M.; Musilek, K.; et al. 6-Hydroxyquinolinium Salts Differing in the Length of Alkyl Side-Chain: Synthesis and Antimicrobial Activity. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2014, 24, 5238–5241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di, L.; Kerns, E.H.; Fan, K.; McConnell, O.J.; Carter, G.T. High Throughput Artificial Membrane Permeability Assay for Blood–brain Barrier. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2003, 38, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, D.A.; Renock, S.; Arrington, E.; Chiodo, L.A.; Liu, L.-X.; Sibley, D.R.; Roth, B.L.; Mailman, R.; Aripiprazole, A. Novel Atypical Antipsychotic Drug with a Unique and Robust Pharmacology. Neuropsychopharmacology 2003, 28, 1400–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pae, C.-U.; Forbes, A.; Patkar, A. Aripiprazole as Adjunctive Therapy for Patients with Major Depressive Disorder. CNS Drugs 2011, 25, 109–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jauhar, S.; Young, A.H. Controversies in Bipolar Disorder; Role of Second-Generation Antipsychotic for Maintenance Therapy. Int. J. Bipolar Disord. 2019, 7, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brust, T.F.; Hayes, M.P.; Roman, D.L.; Watts, V.J. New Functional Activity of Aripiprazole Revealed: Robust Antagonism of D2 Dopamine Receptor-Stimulated Gβγ Signaling. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2015, 93, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Allen, J.A.; Yost, J.M.; Setola, V.; Chen, X.; Sassano, M.F.; Chen, M.; Peterson, S.; Yadav, P.N.; Huang, X.; Feng, B.; et al. Discovery of β-Arrestin–Biased Dopamine D2 Ligands for Probing Signal Transduction Pathways Essential for Antipsychotic Efficacy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 18488–18493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mailman, R.B.; Murthy, V. Third Generation Antipsychotic Drugs: Partial Agonism or Receptor Functional Selectivity? Curr. Pharm. Des. 2010, 16, 488–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lieberman, J.A. Dopamine Partial Agonists. CNS Drugs 2004, 18, 251–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keck, P.E., Jr.; McElroy, S.L. Aripiprazole: A Partial Dopamine D2 Receptor Agonist Antipsychotic. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2003, 12, 655–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löber, S.; Hübner, H.; Tschammer, N.; Gmeiner, P. Recent Advances in the Search for D3- and D4-Selective Drugs: Probes, Models and Candidates. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2011, 32, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bettinetti, L.; Schlotter, K.; Hübner, H.; Gmeiner, P. Interactive SAR Studies: Rational Discovery of Super-Potent and Highly Selective Dopamine D3 Receptor Antagonists and Partial Agonists. J. Med. Chem. 2002, 45, 4594–4597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrlich, K.; Götz, A.; Bollinger, S.; Tschammer, N.; Bettinetti, L.; Härterich, S.; Hübner, H.; Lanig, H.; Gmeiner, P. Dopamine D2, D3, and D4 Selective Phenylpiperazines as Molecular Probes To Explore the Origins of Subtype Specific Receptor Binding. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 52, 4923–4935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Simone, A.; Russo, D.; Ruda, G.F.; Micoli, A.; Ferraro, M.; Di Martino, R.M.C.; Ottonello, G.; Summa, M.; Armirotti, A.; Bandiera, T.; et al. Design, Synthesis, Structure–Activity Relationship Studies, and Three-Dimensional Quantitative Structure–Activity Relationship (3D-QSAR) Modeling of a Series of O-Biphenyl Carbamates as Dual Modulators of Dopamine D3 Receptor and Fatty Acid Amide Hydrolase. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 60, 2287–2304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Żmudzki, P.; Satała, G.; Bojarski, A.; Chłoń-Rzepa, G.; Popik, P.; Zajdel, P. N-(4-Arylpiperazinoalkyl)Acetamide Derivatives of 1,3- and 3,7-Dimethyl-1H-Purine-2,6(3H,7H)- Diones and Their 5-HT6, 5-HT7, and D2 Receptors Affinity. Heterocycl. Commun. 2015, 21, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banala, A.K.; Levy, B.A.; Khatri, S.S.; Furman, C.A.; Roof, R.A.; Mishra, Y.; Griffin, S.A.; Sibley, D.R.; Luedtke, R.R.; Newman, A.H. N-(3-Fluoro-4-(4-(2-Methoxy or 2,3-Dichlorophenyl) Piperazine-1-Yl)-Butyl)-Aryl Carboxamides as Selective Dopamine D3 Receptor Ligands: Critical Role of the Carboxamide Linker for D3 Receptor Selectivity. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 54, 3581–3594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, X.; Sassano, M.F.; Zheng, L.; Setola, V.; Chen, M.; Bai, X.; Frye, S.V.; Wetsel, W.C.; Roth, B.L.; Jin, J. Structure-Functional Selectivity Relationship Studies of β-Arrestin-Biased Dopamine D2 Receptor Agonists. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55, 7141–7153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, X.; McCorvy, J.D.; Fischer, M.G.; Butler, K.V.; Shen, Y.; Roth, B.L.; Jin, J. Discovery of G Protein-Biased D2 Dopamine Receptor Partial Agonists. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 10601–10618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Simone, A.D.; Ruda, G.F.; Albani, C.; Tarozzo, G.; Bandiera, T.; Piomelli, D.; Cavalli, A.; Bottegoni, G. Applying a Multitarget Rational Drug Design Strategy: The First Set of Modulators with Potent and Balanced Activity toward Dopamine D3 Receptor and Fatty Acid Amide Hydrolase. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 4904–4907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vangveravong, S.; Zhang, Z.; Taylor, M.; Bearden, M.; Xu, J.; Cui, J.; Wang, W.; Luedtke, R.R.; Mach, R.H. Synthesis and Characterization of Selective Dopamine D2 Receptor Ligands Using Aripiprazole as the Lead Compound. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2011, 19, 3502–3511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Männel, B.; Dengler, D.; Shonberg, J.; Hübner, H.; Möller, D.; Gmeiner, P. Hydroxy-Substituted Heteroarylpiperazines: Novel Scaffolds for β-Arrestin-Biased D2R Agonists. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 60, 4693–4713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Bello, F.; Bonifazi, A.; Giorgioni, G.; Cifani, C.; Micioni Di Bonaventura, M.V.; Petrelli, R.; Piergentili, A.; Fontana, S.; Mammoli, V.; Yano, H.; et al. 1-[3-(4-Butylpiperidin-1-Yl)Propyl]-1,2,3,4-Tetrahydroquinolin-2-One (77-LH-28-1) as a Model for the Rational Design of a Novel Class of Brain Penetrant Ligands with High Affinity and Selectivity for Dopamine D4 Receptor. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 3712–3725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martelle, J.L.; Nader, M.A. A Review of the Discovery, Pharmacological Characterization, and Behavioral Effects of the Dopamine D2-Like Receptor Antagonist Eticlopride. CNS Neurosci. 2008, 14, 248–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farde, L.; Wiesel, F.-A.; Halldin, C.; Sedvall, G. Central D2-Dopamine Receptor Occupancy in Schizophrenic Patients Treated With Antipsychotic Drugs. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 1988, 45, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farde, L.; Nordström, A.-L.; Wiesel, F.-A.; Pauli, S.; Halldin, C.; Sedvall, G. Positron Emission Tomographic Analysis of Central D1 and D2 Dopamine Receptor Occupancy in Patients Treated With Classical Neuroleptics and Clozapine: Relation to Extrapyramidal Side Effects. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 1992, 49, 538–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapur, S.; Zipursky, R.; Roy, P.; Jones, C.; Remington, G.; Reed, K.; Houle, S. The Relationship between D2 Receptor Occupancy and Plasma Levels on Low Dose Oral Haloperidol: A PET Study. Psychopharmacology 1997, 131, 148–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapur, S.; Zipursky, R.B.; Remington, G. Clinical and Theoretical Implications of 5-HT2 and D2 Receptor Occupancy of Clozapine, Risperidone, and Olanzapine in Schizophrenia. AJP 1999, 156, 286–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilowsky, L.S.; Costa, D.C.; Ell, P.J.; Murray, R.M.; Verhoeff, N.P.L.G.; Kerwin, R.W. Antipsychotic Medication, D2 Dopamine Receptor Blockade and Clinical Response: A 123I IBZM SPET (Single Photon Emission Tomography) Study. Psychol. Med. 1993, 23, 791–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stone, J.M.; Davis, J.M.; Leucht, S.; Pilowsky, L.S. Cortical Dopamine D2/D3 Receptors Are a Common Site of Action for Antipsychotic Drugs—An Original Patient Data Meta-Analysis of the SPECT and PET In Vivo Receptor Imaging Literature. Schizophr Bull. 2009, 35, 789–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shokrzadeh, M.; Mohammadpour, A.; Modanloo, M.; Hassani, M.; Barghi, N.G.; Niroomand, P. Cytotoxic effects of aripiprazole on mkn45 and nih3t3 cell lines and genotoxic effects on human peripheral blood lymphocytes. Arq. Gastroenterol. 2019, 56, 155–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemes, L.F.N.; Ramos, G.D.A.; Oliveira, A.; da Silva, F.M.R.; Couto, G.D.C.; Boni, M.D.S.; Guimarães, M.J.R.; Souza, I.N.D.O.; Bartolini, M.; Andrisano, V.; et al. Cardanol-derived AChE inhibitors: Towards the development of dual binding derivatives for Alzheimer’s disease. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 108, 687–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Limapichat, W.; Yu, W.Y.; Branigan, E.; Lester, H.A.; Dougherty, D.A. Key Binding Interactions for Memantine in the NMDA Receptor. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2012, 4, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Farlow, M.R.; Graham, S.M.; Alva, G. Memantine for the Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease. Drug Saf. 2008, 31, 577–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stahl, S.M. Dopamine System Stabilizers, Aripiprazole, and the Next Generation of Antipsychotics, Part 2: Illustrating Their Mechanism of Action. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2001, 62, 923–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]


| Compound | Ki (μM) ± SEM 1 | CHO-K1 IC50 (mM) ± SEM 2 |
|---|---|---|
| 5a | 24 ± 5.8 | 2.0 ± 0.8 |
| 5b | 9.7 ± 1.6 | 1.5 ± 0.3 |
| 5c | 12 ± 3.2 | 2.0 ± 1.0 |
| 5d | 20 ± 1.6 | 1.1 ± 0.3 |
| 5e | 7.6 ± 1.9 | 0.5 ± 0.1 |
| 5f | 37 ± 8.6 | 0.9 ± 0.2 |
| 5g | 26 ± 6.1 | 1.5 ± 0.5 |
| 6a | 23 ± 3.6 | 1.1 ± 0.2 |
| 6b | 14 ± 2.5 | 0.8 ± 0.2 |
| 6c | 21 ± 0.6 | 1.2 ± 0.2 |
| 6d | 41 ± 14 | 1.3 ± 0.2 |
| 6e | 9.7 ± 2.3 | 0.8 ± 0.1 |
| 6f | 27 ± 4.7 | 1.8 ± 0.3 |
| 6g | 45 ± 11 | 2.1 ± 0.8 |
| Aripiprazole | 3.3 nM 3 | 0.1 4 |
| Ligand | S (Docking Score, kcal/moL) | ddG (Relative Free Energy, kcal/moL) |
|---|---|---|
| risperidone | −9.6461 | −10.0988 |
| aripiprazole | −9.1619 | −10.2544 |
| USC-D301 | −8.4562 | −9.5903 |
| 5e | −7.0336 | −8.2686 |
| Compound | BBB Score 1 | Pe ± SEM (× 10−6 cm s−1) | CNS (+/−) 2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5a | 5.3 | 7.3 ± 0.8 | CNS + |
| 5b | 5.2 | 13 ± 0.1 | CNS + |
| 5c | 5.4 | 7.0 ± 0.4 | CNS + |
| 5d | 5.2 | 12 ± 2.0 | CNS + |
| 5e | 5.2 | 24 ± 2.1 | CNS + |
| 5f | 5.2 | 9.4 ± 0.4 | CNS + |
| 5g | 5.3 | 10 ± 1.6 | CNS + |
| 6a | 5.2 | 7.7 ± 1.8 | CNS + |
| 6b | 5.2 | 10 ± 1.4 | CNS + |
| 6c | 5.4 | 7.1 ± 1.2 | CNS + |
| 6d | 5.3 | 17 ± 2.1 | CNS + |
| 6e | 5.2 | 23 ± 3.3 | CNS + |
| 6f | 5.2 | 7.4 ± 0.9 | CNS + |
| 6g | 5.3 | 9.5 ± 1.1 | CNS + |
| Donepezil | 5.3 | 22 ± 2.1 | CNS + |
| Tacrine | 5.4 | 6.0 ± 0.6 | CNS + |
| Rivastigmine | 5.1 | 20 ± 2.1 | CNS + |
| Furosemide | - | 0.2 ± 0.1 | CNS − |
| Chlorothiazide | - | 1.2 ± 0.5 | CNS − |
| Ranitidine | - | 0.4 ± 0.3 | CNS − |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Juza, R.; Stefkova, K.; Dehaen, W.; Randakova, A.; Petrasek, T.; Vojtechova, I.; Kobrlova, T.; Pulkrabkova, L.; Muckova, L.; Mecava, M.; et al. Synthesis and In Vitro Evaluation of Novel Dopamine Receptor D2 3,4-dihydroquinolin-2(1H)-one Derivatives Related to Aripiprazole. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1262. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11091262
Juza R, Stefkova K, Dehaen W, Randakova A, Petrasek T, Vojtechova I, Kobrlova T, Pulkrabkova L, Muckova L, Mecava M, et al. Synthesis and In Vitro Evaluation of Novel Dopamine Receptor D2 3,4-dihydroquinolin-2(1H)-one Derivatives Related to Aripiprazole. Biomolecules. 2021; 11(9):1262. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11091262
Chicago/Turabian StyleJuza, Radomir, Kristyna Stefkova, Wim Dehaen, Alena Randakova, Tomas Petrasek, Iveta Vojtechova, Tereza Kobrlova, Lenka Pulkrabkova, Lubica Muckova, Marko Mecava, and et al. 2021. "Synthesis and In Vitro Evaluation of Novel Dopamine Receptor D2 3,4-dihydroquinolin-2(1H)-one Derivatives Related to Aripiprazole" Biomolecules 11, no. 9: 1262. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11091262
APA StyleJuza, R., Stefkova, K., Dehaen, W., Randakova, A., Petrasek, T., Vojtechova, I., Kobrlova, T., Pulkrabkova, L., Muckova, L., Mecava, M., Prchal, L., Mezeiova, E., Musilek, K., Soukup, O., & Korabecny, J. (2021). Synthesis and In Vitro Evaluation of Novel Dopamine Receptor D2 3,4-dihydroquinolin-2(1H)-one Derivatives Related to Aripiprazole. Biomolecules, 11(9), 1262. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11091262









