Biochemical and Clinical Effects of Vitamin E Supplementation in Hungarian Smith-Lemli-Opitz Syndrome Patients
Abstract
:1. Introduction
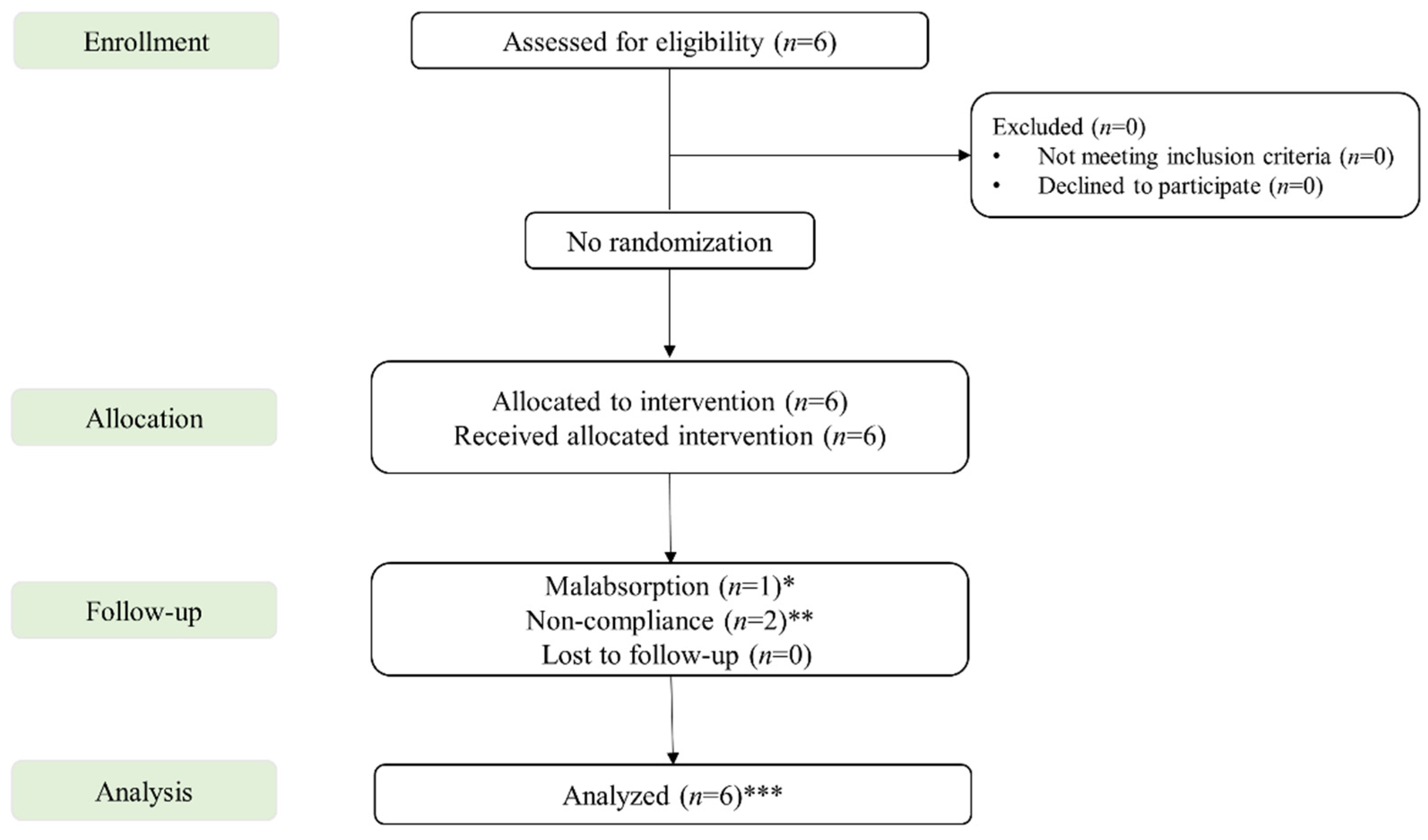
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Patients
2.3. Vitamin E Formula and Supplementation Regimen
2.4. Methods
2.4.1. Measurement of Plasma Vitamin A and E Concentrations
2.4.2. Sterol Analysis
2.4.3. Lipid Extraction
2.4.4. LC-MS/MS Conditions
2.4.5. Parental Interviews: Assessment of Clinical Effects of Vitamin E Supplementation
3. Results
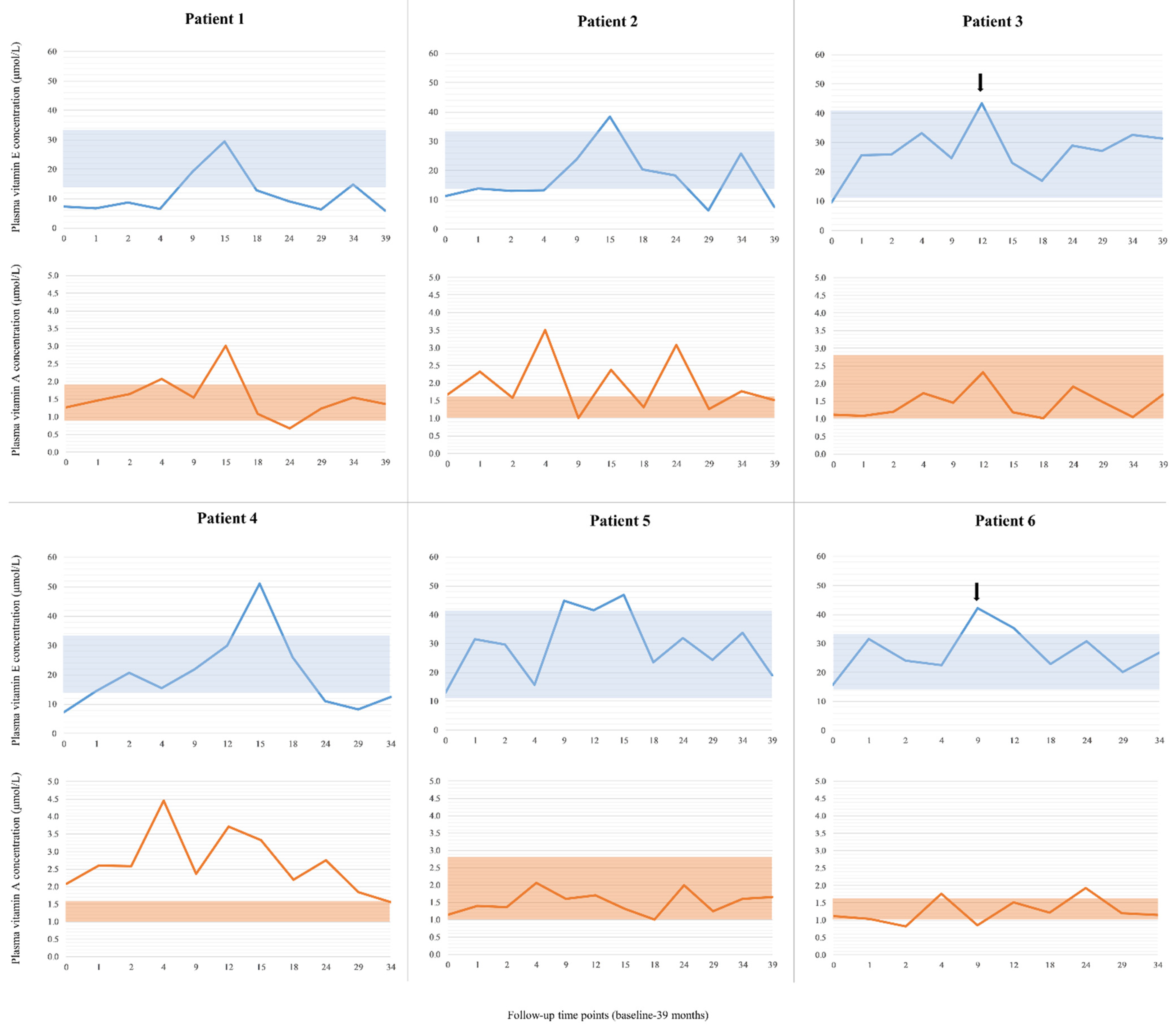
3.1. Plasma Vitamin E and Vitamin A Status in SLOS Patients—Biochemical Effects of Vitamin E Supplementation
3.2. Toxicity and Adverse Drug Reactions to Vitamin E Supplementation
3.3. Behavioral Effects of Vitamin E Supplementation
3.4. Association of Clinical Response with Baseline 7-DHC + 8-DHC/Cholesterol Ratio
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Irons, M.; Elias, E.R.; Salen, G.; Tint, G.S.; Batta, A.K. Defective Cholesterol Biosynthesis in Smith-Lemli-Opitz Syndrome. Lancet 1993, 341, 1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tint, G.S.; Irons, M.; Elias, E.R.; Batta, A.K.; Frieden, R.; Chen, T.S.; Salen, G. Defective Cholesterol Biosynthesis Associated with the Smith-Lemli-Opitz Syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 1994, 330, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waterham, H.R. Defects of Cholesterol Biosynthesis. FEBS Lett. 2006, 580, 5442–5449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Batta, A.K.; Tint, G.S.; Shefer, S.; Abuelo, D.; Salen, G. Identification of 8-Dehydrocholesterol (Cholesta-5,8-Dien-3 Beta-Ol) in Patients with Smith-Lemli-Opitz Syndrome. J. Lipid Res. 1995, 36, 705–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tint, G.S.; Seller, M.; Hµghes-Benzie, R.; Batta, A.K.; Shefer, S.; Genest, D.; Irons, M.; Elias, E.; Salen, G. Markedly Increased Tissue Concentrations of 7-Dehydrocholesterol Combined with Low Levels of Cholesterol Are Characteristic of the Smith-Lemli-Opitz Syndrome. J. Lipid Res. 1995, 36, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelley, R.I.; Hennekam, R.C. The Smith-Lemli-Opitz Syndrome. J. Med. Genet. 2000, 37, 321–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nowaczyk, M.J.M.; Irons, M.B. Smith-Lemli-Opitz Syndrome: Phenotype, Natural History, and Epidemiology. Am. J. Med. Genet. C Semin. Med. Genet. 2012, 160, 250–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tierney, E.; Nwokoro, N.A.; Kelley, R.I. Behavioral Phenotype of RSH/Smith-Lemli-Opitz Syndrome. Ment. Retard. Dev. Disabil. Res. Rev. 2000, 6, 131–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, F.D.; Herman, G.E. Malformation Syndromes Caused by Disorders of Cholesterol Synthesis. J. Lipid Res. 2011, 52, 6–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Svoboda, M.D.; Christie, J.M.; Eroglu, Y.; Freeman, K.A.; Steiner, R.D. Treatment of Smith-Lemli-Opitz Syndrome and Other Sterol Disorders. Am. J. Med. Genet. C Semin. Med. Genet. 2012, 160, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wassif, C.A.; Kratz, L.; Sparks, S.E.; Wheeler, C.; Bianconi, S.; Gropman, A.; Calis, K.A.; Kelley, R.I.; Tierney, E.; Porter, F.D. A Placebo-Controlled Trial of Simvastatin Therapy in Smith-Lemli-Opitz Syndrome. Genet. Med. 2017, 19, 297–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Korade, Z.; Xu, L.; Harrison, F.E.; Ahsen, R.; Hart, S.E.; Folkes, O.M.; Mirnics, K.; Porter, N.A. Antioxidant Supplementation Ameliorates Molecular Deficits in Smith-Lemli-Opitz Syndrome. Biol. Psychiatry 2014, 75, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xu, L.; Korade, Z.; Porter, N.A. Oxysterols from Free Radical Chain Oxidation of 7-Dehydrocholesterol: Product and Mechanistic Studies. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 2222–2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Korade, Z.; Xu, L.; Shelton, R.; Porter, N.A. Biological Activities of 7-Dehydrocholesterol-Derived Oxysterols: Implications for Smith-Lemli-Opitz Syndrome. J. Lipid Res. 2010, 51, 3259–3269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fliesler, S.J.; Peachey, N.S.; Herron, J.; Hines, K.M.; Weinstock, N.I.; Ramachandra Rao, S.; Xu, L. Prevention of Retinal Degeneration in a Rat Model of Smith-Lemli-Opitz Syndrome. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lobo, M.A.; Moeyaert, M.; Baraldi Cunha, A.; Babik, I. Single-Case Design, Analysis, and Quality Assessment for Intervention Research. J. Neurol. Phys. Ther. 2017, 41, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balogh, I.; Koczok, K.; Szabó, G.P.; Török, O.; Hadzsiev, K.; Csábi, G.; Balogh, L.; Dzsudzsák, E.; Ajzner, E.; Szabó, L.; et al. Mutational Spectrum of Smith-Lemli-Opitz Syndrome Patients in Hungary. Mol. Syndromol. 2012, 3, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szabó, G.P.; Oláh, A.V.; Kozak, L.; Balogh, E.; Nagy, A.; Blahakova, I.; Oláh, E. A Patient with Smith-Lemli-Opitz Syndrome: Novel Mutation of the DHCR7 Gene and Effects of Therapy with Simvastatin and Cholesterol Supplement. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2010, 169, 121–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Institute of Medicine (US) Panel on Dietary Antioxidants and Related Compounds. Dietary Reference Intakes for Vitamin C, Vitamin E, Selenium, and Carotenoids; National Academies Press (US): Washington, DC, USA, 2000; pp. 186–283. [Google Scholar]
- Raizman, J.E.; Cohen, A.H.; Teodoro-Morrison, T.; Wan, B.; Khun-Chen, M.; Wilkenson, C.; Bevilaqua, V.; Adeli, K. Pediatric Reference Value Distributions for Vitamins A and E in the CALIPER Cohort and Establishment of Age-Stratified Reference Intervals. Clin. Biochem. 2014, 47, 812–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burtis, C.; Ashwood, E.; Bruns, D. Tietz Textbook of Clinical Chemistry and Molecular Diagnostics, 4th ed.; Elsevier Saunders: St. Louis, MO, USA, 2006; p. 2302. [Google Scholar]
- Michel, F.; Cristol, J.P.; Vernet, M.H.; Feillet, C.; Carbonneau, M.-A.; Léger, C.L.; Castel, J.; Descomps, B. Interference of 7-Dehydrocholesterol in α-Tocopherol Determination by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography: A Possible Screening Test for the Smith-Lemli-Opitz Syndrome. J. Amer. Oil. Chem. Soc. 1998, 75, 131–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seedorf, U.; Walter, M.; Assmann, G. Diagnosis of Smith-Lemli-Opitz Syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 1994, 330, 1686–1687. [Google Scholar]
- Anastasia, M.; Fiecchi, A.; Galli, G. Synthesis of cholesta-5,8-dien-3β-beta-ol. J. Org. Chem. 1981, 46, 3421–3422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Liu, W.; Sheflin, L.G.; Fliesler, S.J.; Porter, N.A. Novel Oxysterols Observed in Tissues and Fluids of AY9944-Treated Rats: A Model for Smith-Lemli-Opitz Syndrome. J. Lipid Res. 2011, 52, 1810–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Diaz-Stransky, A.; Tierney, E. Cognitive and Behavioral Aspects of Smith-Lemli-Opitz Syndrome. Am. J. Med. Genet. C Semin. Med. Genet. 2012, 160, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zarowski, M.; Vendrame, M.; Irons, M.; Kothare, S.V. Prevalence of Sleep Problems in Smith-Lemli-Opitz Syndrome. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2011, 155, 1558–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aman, M.G.; Singh, N.N.; Stewart, A.W.; Field, C.J. The Aberrant Behavior Checklist: A Behavior Rating Scale for the Assessment of Treatment Effects. Am. J. Ment. Defic. 1985, 89, 485–491. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rizzo, C.; Dionisi-Vici, C.; D’Ippoliti, M.; Fina, F.; Sabetta, G.; Federici, G. A Simple and Rapid HPLC Method for Simultaneous Determination of Plasma 7-Dehydrocholesterol and Vitamin E: Its Application in Smith-Lemli-Opitz Patients. Clin. Chim. Acta. 2000, 291, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Davis, T.A.; Porter, N.A. Rate Constants for Peroxidation of Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids and Sterols in Solution and in Liposomes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 13037–13044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haas, D.; Niklowitz, P.; Hoffmann, G.F.; Andler, W.; Menke, T. Plasma and Thrombocyte Levels of Coenzyme Q10 in Children with Smith-Lemli-Opitz Syndrome (SLOS) and the Influence of HMG-CoA Reductase Inhibitors. Biofactors 2008, 32, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elias, E.R.; Irons, M.B.; Hurley, A.D.; Tint, G.S.; Salen, G. Clinical Effects of Cholesterol Supplementation in Six Patients with the Smith-Lemli-Opitz Syndrome (SLOS). Am. J. Med. Genet. 1997, 68, 305–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiner, R.D.; Linck, L.M.; Flavell, D.P.; Lin, D.S.; Connor, W.E. Sterol Balance in the Smith-Lemli-Opitz Syndrome. Reduction in Whole Body Cholesterol Synthesis and Normal Bile Acid Production. J. Lipid Res. 2000, 41, 1437–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, K.A.; Eagle, R.; Merkens, L.S.; Sikora, D.; Pettit-Kekel, K.; Nguyen-Driver, M.; Steiner, R.D. Challenging Behavior in Smith-Lemli-Opitz Syndrome: Initial Test of Biobehavioral Influences. Cogn. Behav. Neurol. 2013, 26, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Freeman, K.A.; Olufs, E.; Tudor, M.; Roullet, J.-B.; Steiner, R.D. A Pilot Study of the Association of Markers of Cholesterol Synthesis with Disturbed Sleep in Smith-Lemli-Opitz Syndrome. J. Dev. Behav. Pediatr. 2016, 37, 424–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valencia, A.; Rajadurai, A.; Carle, A.B.; Kochevar, I.E. 7-Dehydrocholesterol Enhances Ultraviolet A-Induced Oxidative Stress in Keratinocytes: Roles of NADPH Oxidase, Mitochondria, and Lipid Rafts. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2006, 41, 1704–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Traber, M.G.; Atkinson, J. Vitamin E, Antioxidant and Nothing More. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2007, 43, 4–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
| SLOS-Associated Behavior and Photosensitivity a | Patient 3 | Patient 5 | Patient 6 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sleep disturbance | + | + | |
| Self-injury | + | + | + |
| Aggression | + | + | |
| Repetitive body movements | + | + | + |
| Quick mood changes | + | + | + |
| Frequent sadness | + | + | |
| Inappropriate screaming | + | ||
| Temper outbursts | + | + | + |
| Attention deficit | + | + | |
| Restlessness | + | ||
| Uncontrollability | + | ||
| Skin photosensitivity or eczema | + | + |
| Patient | Age a | Gender | Genotype b | Vitamin E (%RDA) c | SS d | 7-DHC e (ng/uL) | 7- + 8-DHC/C e | Clinical Response f |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 11 years | male | c.[964-1G>C];[1190C>T] | 1882 | 50 | 70.7 | 4.9 | no |
| 2 | 5 years | male | c.[964-1G>C];[1190C>T] | 1479 | 40 | 68.1 | 4.8 | no |
| 4 | 4 years | male | c.[976G>T];[452G>A] | 1479 | 20 | 33.5 | 1.7 | no |
| 3 | 18 years | male | c.[964-1G>C];[1097G>T] | 690 | 25 | 16.8 | 0.2 | yes |
| 5 | 21 years | female | c.[452G>A];[?] | 1380 | 15 | 26.9 | 0.4 | yes |
| 6 | 5 years | male | c.[730G>A];[976G>T] | 739 | 40 | 15.6 | 0.2 | yes |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Koczok, K.; Horváth, L.; Korade, Z.; Mezei, Z.A.; Szabó, G.P.; Porter, N.A.; Kovács, E.; Mirnics, K.; Balogh, I. Biochemical and Clinical Effects of Vitamin E Supplementation in Hungarian Smith-Lemli-Opitz Syndrome Patients. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1228. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11081228
Koczok K, Horváth L, Korade Z, Mezei ZA, Szabó GP, Porter NA, Kovács E, Mirnics K, Balogh I. Biochemical and Clinical Effects of Vitamin E Supplementation in Hungarian Smith-Lemli-Opitz Syndrome Patients. Biomolecules. 2021; 11(8):1228. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11081228
Chicago/Turabian StyleKoczok, Katalin, László Horváth, Zeljka Korade, Zoltán András Mezei, Gabriella P. Szabó, Ned A. Porter, Eszter Kovács, Károly Mirnics, and István Balogh. 2021. "Biochemical and Clinical Effects of Vitamin E Supplementation in Hungarian Smith-Lemli-Opitz Syndrome Patients" Biomolecules 11, no. 8: 1228. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11081228
APA StyleKoczok, K., Horváth, L., Korade, Z., Mezei, Z. A., Szabó, G. P., Porter, N. A., Kovács, E., Mirnics, K., & Balogh, I. (2021). Biochemical and Clinical Effects of Vitamin E Supplementation in Hungarian Smith-Lemli-Opitz Syndrome Patients. Biomolecules, 11(8), 1228. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11081228







