Chemical Fractionation Joint to In-Mixture NMR Analysis for Avoiding the Hepatotoxicity of Teucrium chamaedrys L. subsp. chamaedrys
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Extraction and Fractionation Procedures
2.3. NMR-Based Metabolic Profiling
2.4. Antioxidant Efficacy Assessment
2.4.1. DPPH• Scavenging Capacity
2.4.2. ABTS•+ Scavenging Capacity
2.4.3. Determination of oxygen radical absorbance capacity (ORAC)
2.4.4. Determination of Mo(VI) Reducing Power
2.5. Cell Culture and Cytotoxicity Evaluation
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. NMR Metabolic Profile of Teucrium Chamaedrys L. subsp. Chamaedrys Leaf MeOH Extract and Fractions Therefrom
3.2. Bioactivity of Teucrium chamaedrys L. subsp. Chamaedrys leaf MeOH Extract and Fractions Therefrom
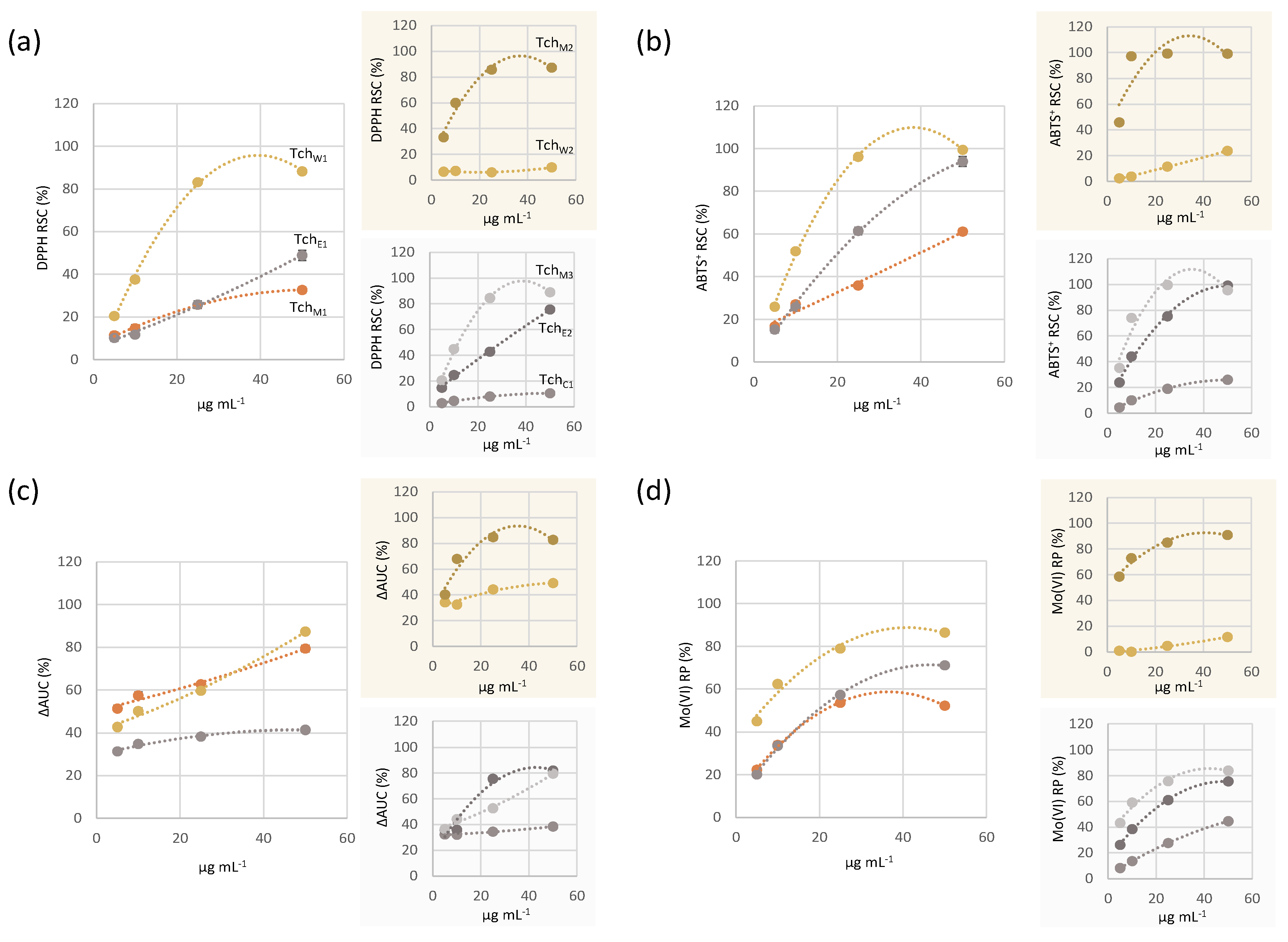
3.2.1. Antioxidant Capacity
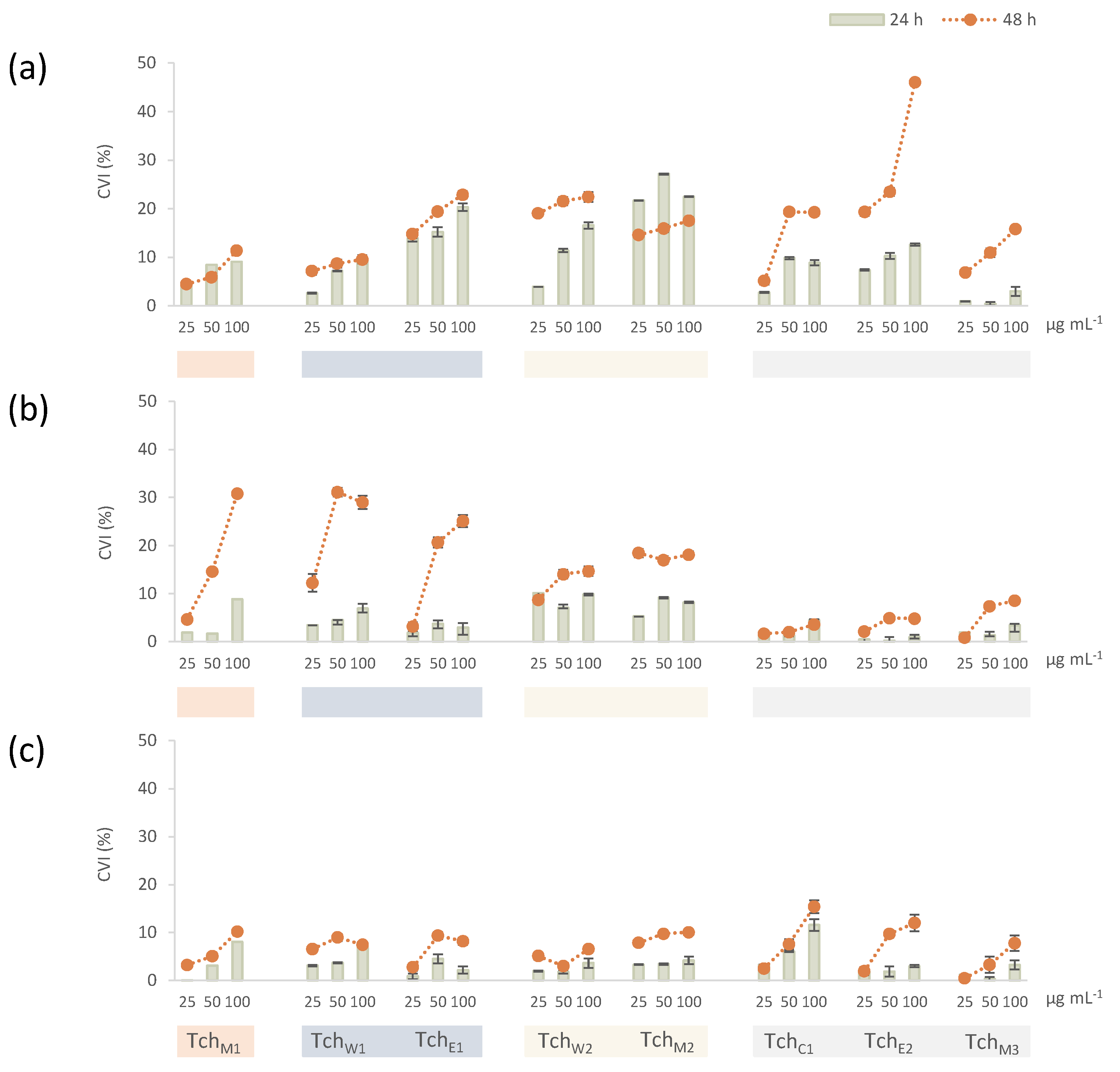
3.2.2. Cytotoxicity
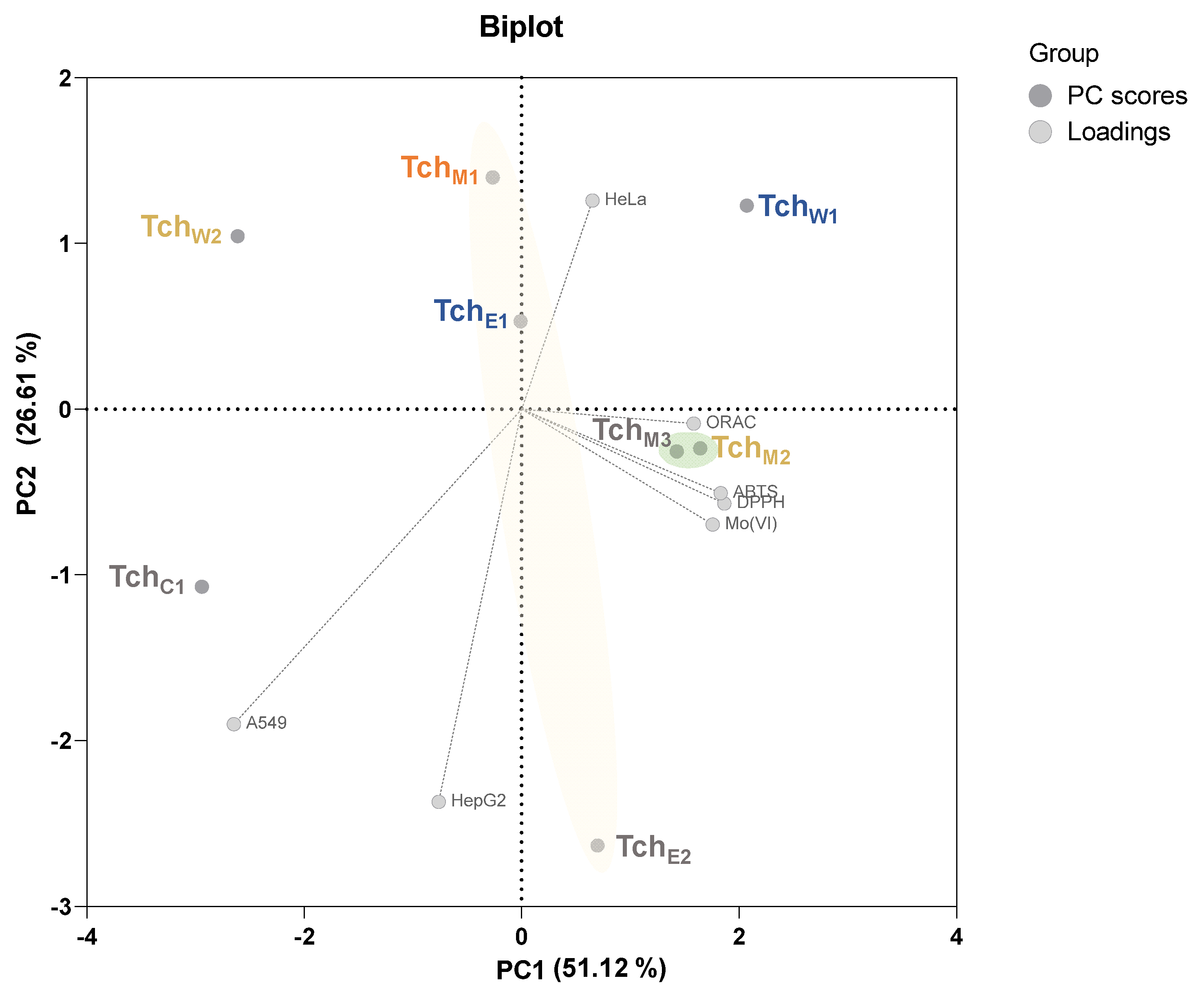
3.3. Principal Component Analysis (PCA)
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Haslan, H.; Suhaimi, F.H.; Das, S. Herbal supplements and hepatotoxicity: A short review. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2015, 10, 1779–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Boer, Y.S.; Sherker, A.H. Herbal and dietary supplement-induced liver Injury. Clin. Liver Dis. 2017, 21, 135–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cachet, X.; Langrand, J.; Riffault-Valois, L.; Bouzidi, C.; Colas, C.; Dugay, A.; Michel, S.; Boucaud-Maitre, D. Clerodane furanoditerpenoids as the probable cause of toxic hepatitis induced by Tinospora crispa. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 13520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piozzi, F.; Bruno, M.; Ciriminna, R.; Fazio, C.; Vassallo, N.; Arnold, N.A.; de la Torre, M.C.; Rodriguez, B. Putative hepatotoxic neoclerodane diterpenoids from Teucrium species. Planta Med. 1997, 63, 483–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gursoy, N.; Tepe, B. Determination of the antimicrobial and antioxidative properties and total phenolics of two “endemic” Lamiaceae species from Turkey: Ballota rotundifolia L. and Teucrium chamaedrys C. Koch. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2009, 64, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vladimir-Knežević, S.; Blažeković, B.; Kindl, M.; Vladić, J.; Lower-Nedza, A.D.; Brantner, A.H. Acetylcholinesterase inhibitory, antioxidant and phytochemical properties of selected medicinal plants of the Lamiaceae family. Molecules 2014, 19, 767–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panesar, P.S.; Kumar, N.; Marwaha, S.S.; Joshi, V.K. Vermouth production technology–an overview. Nat. Prod. Radiance 2009, 8, 334–344. [Google Scholar]
- Herrera, S.; Bruguera, M. Hepatotoxicidad inducida por el uso de hierbas y medicamentos para perder peso [Hepatotoxicity induced by herbs and medicines used to induce weight loss]. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2008, 31, 447–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gori, L.; Galluzzi, P.; Mascherini, V.; Gallo, E.; Lapi, F.; Menniti-Ippolito, F.; Raschetti, R.; Mugelli, A.; Vannacci, A.; Firenzuoli, F. Two contemporary cases of hepatitis associated with Teucrium chamaedrys L. decoction use: Case reports and review of literature. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2011, 109, 521–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nencini, C.; Galluzzi, P.; Pippi, F.; Menchiari, A.; Micheli, L. Hepatotoxicity of Teucrium chamaedrys L. decoction: Role of difference in the harvesting area and preparation method. Indian J. Pharmacol. 2014, 46, 181–184. [Google Scholar]
- Lekehal, M.; Pessayre, D.; Lereau, J.M.; Moulis, C.; Fouraste, I.; Fau, D. Hepatotoxicity of the herbal medicine germander: Metabolic activation of its furano diterpenoids by cytochrome P450 3A Depletes cytoskeleton-associated protein thiols and forms plasma membrane blebs in rat hepatocytes. Hepatology 1996, 24, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Berardinis, V.; Moulis, C.; Maurice, M.; Beaune, P.; Pessayre, D.; Pompon, D.; Loeper, J. Human microsomal epoxide hydrolase is the target of germander-induced autoantibodies on the surface of human hepatocytes. Mol. Pharmacol. 2000, 58, 542–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission Health & Consumer Protection Directorate General. Opinion of the Scientific Committee on Food on Teucrin A, Major Component of Hydroalcoholic Extracts of Teucrium Chamaedrys (Wild Germander); European Commission Health & Consumer Protection Directorate General: Ispra, Italy, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Pacifico, S.; D’Abrosca, B.; Pascarella, M.T.; Letizia, M.; Uzzo, P.; Piscopo, V.; Fiorentino, A. Antioxidant efficacy of iridoid and phenylethanoid glycosides from the medicinal plant Teucrium chamaedrys in cell-free systems. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2009, 17, 6173–6179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frezza, C.; Venditti, A.; Matrone, G.; Serafini, I.; Foddai, S.; Bianco, A.; Serafini, M. Iridoid glycosides and polyphenolic compounds from Teucrium chamaedrys L. Nat. Prod. Res. 2018, 32, 1583–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, Z.; Yang, B. Phenylethanoid glycosides: Research advances in their phytochemistry, pharmacological activity and pharmacokinetics. Molecules 2016, 21, 991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haïdara, K.; Alachkar, A.; Moustafa, A. Teucrium polium plant extract provokes significant cell death in human lung cancer cells. Health 2011, 3, 366–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacifico, S.; D’Abrosca, B.; Scognamiglio, M.; D’Angelo, G.; Gallicchio, M.; Galasso, S.; Monaco, P.; Fiorentino, A. NMR-based metabolic profiling and in vitro antioxidant and hepatotoxic assessment of partially purified fractions from Golden germander (Teucrium polium L.) methanolic extract. Food Chem. 2012, 135, 1957–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanković, M.S.; Mitrović, T.L.; Matić, I.Z.; Topuzović, M.D.; Stamenković, S.M. New values of Teucrium species: In vitro study of cytotoxic activities of secondary metabolites. Not. Bot. Horti Agrobot. Cluj Napoca 2015, 43, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özel, Ş.; Süntar, İ.; Ercan Gökay, N.; Taşkın Türkmenoğlu, T.; Demırel, M.A. The effectiveness of Teucrium chamaedrys L. extracts on endometriotic implant regression in rat endometriosis model. Vet. Res. Forum 2020, 11, 305–309. [Google Scholar]
- Croce, A.; Stinca, A.; Santangelo, A.; Esposito, A. Exploring vascular flora diversity of two protected sandy coastal areas in southern Italy. Rend. Lincei. Sci. Fis. Naturali. 2019, 30, 323–336 doiorg/101007/s122110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumner, L.W.; Amberg, A.; Barrett, D.; Beale, M.H.; Beger, R.; Daykin, C.A.; Fan, T.W.; Fiehn, O.; Goodacre, R.; Griffin, J.L.; et al. Proposed minimum reporting standards for chemical analysis Chemical Analysis Working Group (CAWG) Metabolomics Standards Initiative (MSI). Metabolomics 2007, 3, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pacifico, S.; Piccolella, S.; Marciano, S.; Galasso, S.; Nocera, P.; Piscopo, V.; Fiorentino, A.; Monaco, P. LC-MS/MS profiling of a mastic leaf phenol enriched extract and its effects on H2O2 and Aβ(25–35) oxidative injury in SK-B-NE(C)-2 cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 11957–11966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacifico, S.; Piccolella, S.; Galasso, S.; Fiorentino, A.; Kretschmer, N.; Pan, S.P.; Bauer, R.; Monaco, P. Influence of harvest season on chemical composition and bioactivity of wild rue plant hydroalcoholic extracts. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2016, 90, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorentino, A.; D’Abrosca, B.; Pacifico, S.; Mastellone, S.; Piccolella, S.; Monaco, P. Isolation, structure elucidation, and antioxidant evaluation of Cydonioside A, an unusual terpenoid from the fruits of Cydonia vulgaris. Chem. Biodivers. 2007, 4, 973–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pacifico, S.; Piccolella, S.; Lettieri, A.; Nocera, P.; Bollino, F.; Catauro, M. A metabolic profiling approach to an Italian sage leaf extract (SoA541) defines its antioxidant and anti-acetylcholinesterase properties. J. Funct. Foods 2017, 29, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antognoni, F.; Iannello, C.; Mandrone, M.; Scognamiglio, M.; Fiorentino, A.; Giovannini, P.P.; Poli, F. Elicited Teucrium chamaedrys cell cultures produce high amounts of teucrioside, but not the hepatotoxic neo-clerodane diterpenoids. Phytochemistry 2012, 81, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gross, G.-A.; Lahloub, M.F.; Anklin, C.; Schulten, H.-R.; Sticher, O. Teucrioside, a phenylpropanoid glycoside from Teucrium chamaedrys. Phytochemistry 1988, 27, 1459–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scognamiglio, M.; Fiumano, V.; D’Abrosca, B.; Esposito, A.; Choi, Y.H.; Verpoorte, R.; Fiorentino, A. Chemical interactions between plants in Mediterranean vegetation: The influence of selected plant extracts on Aegilops geniculata metabolome. Phytochemistry 2014, 106, 69–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Morris-Natschke, S.L.; Lee, K.H. Clerodane diterpenes: Sources, structures, and biological activities. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2016, 33, 1166–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorentino, A.; D’Abrosca, B.; Esposito, A.; Izzo, A.; Pascarella, M.T.; D’Angelo, G.; Monaco, P. Potential allelopathic effect of neo-clerodane diterpenes from Teucrium chamaedrys (L.) on stenomediterranean and weed cosmopolitan species. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2009, 37, 349–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorentino, A.; D’Abrosca, B.; Ricci, A.; Pacifico, S.; Piccolella, S.; Monaco, P. Structure determination of chamaedryosides A—C, three novel nor-neo-clerodane glucosides from Teucrium chamaedrys by NMR spectroscopy. Magn. Reson. Chem. 2009, 47, 1007–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prior, R.L.; Hoang, H.; Gu, L.; Wu, X.; Bacchiocca, M.; Howard, L.; Hampsch-Woodill, M.; Huang, D.; Ou, B.; Jacob, R. Assays for hydrophilic and lipophilic antioxidant capacity (Oxygen Radical Absorbance Capacity (ORACFL)) of plasma and other biological and food samples. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 3273–3279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Candela, L.; Formato, M.; Crescente, G.; Piccolella, S.; Pacifico, S. Coumaroyl flavonol glycosides and more in marketed green teas: An intrinsic value beyond much-lauded catechins. Molecules 2020, 25, 1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elizondo, G.; Medina-Diaz, L.M. Induction of CYP3A4 by 1α,25-dyhydroxyvitamin D3 in HepG2 cells. Life Sci. 2003, 73, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

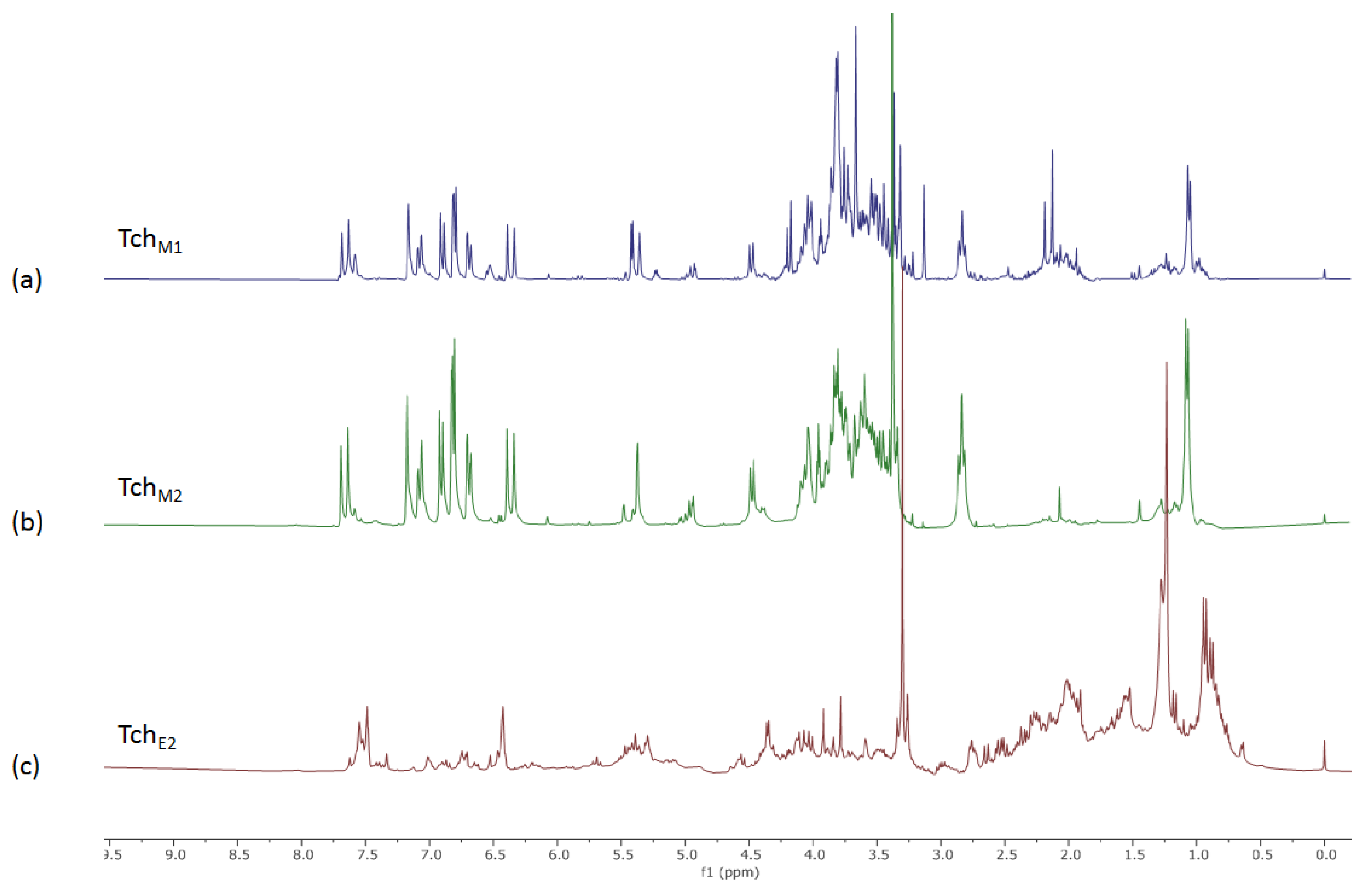
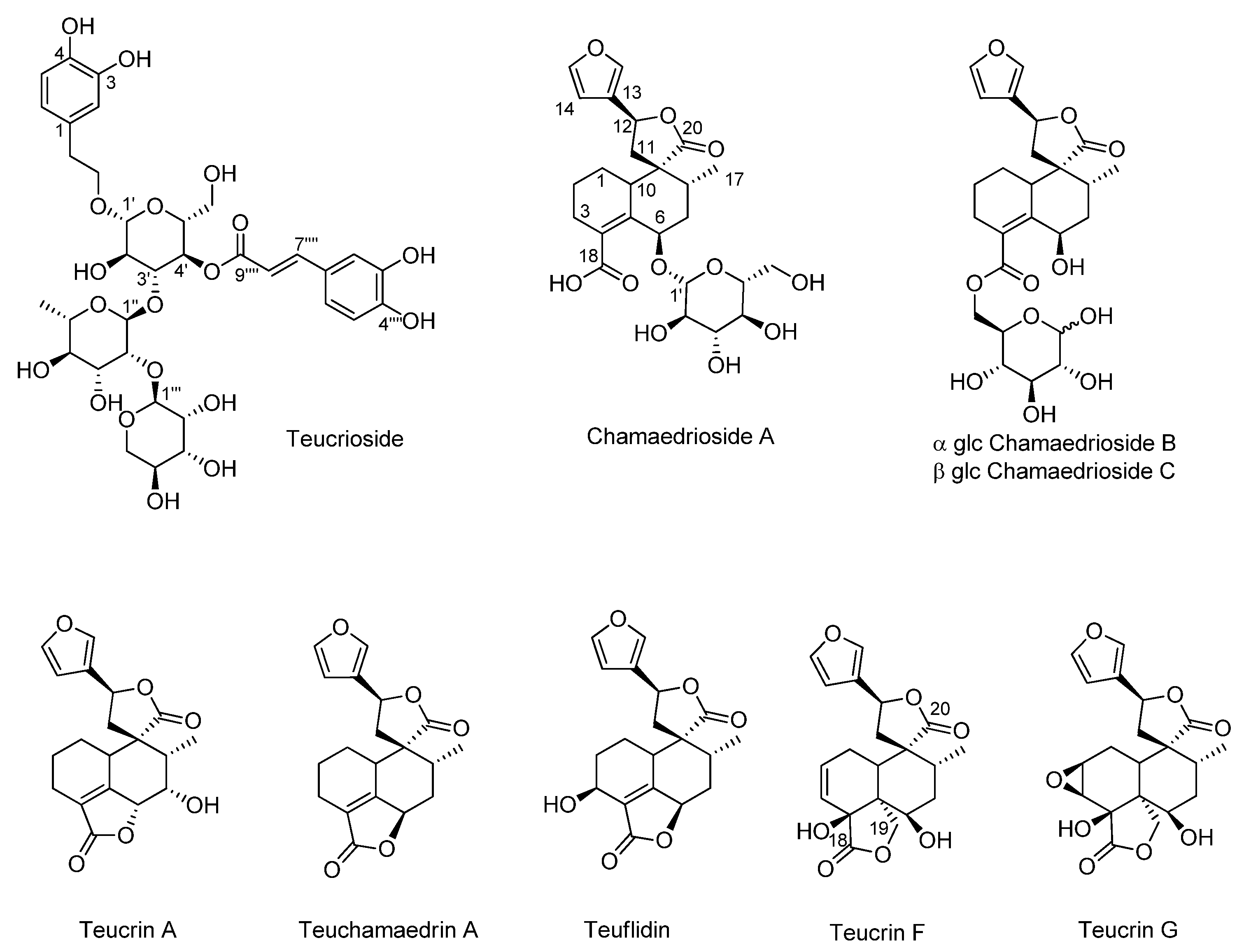
| Compounds | TchW1 | TchE1 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TchW2 | TchM2 | TchC1 | TchE2 | TchM3 | |
| Teucrioside 1 |  |  | |||
| Other phenolic compounds 4 |  | ||||
| Teucrin A 2 |  | ||||
| Teuchamaedrin A 2 |  | ||||
| Teucrin G 3 |  | ||||
| Teucrin F 3 |  | ||||
| Chamaedroxide 3 |  | ||||
| Teuflidin 3 |  | ||||
| Chamaedryosides A-C 3 |  | ||||
| Other neo-clerodane diterpenes 4 |  |  | |||
| Fatty acids 3 |  | ||||
| Alanine 2 |  | ||||
| Isoleucine 2 |  | ||||
| Threonine 2 |  | ||||
| Valine 2 |  | ||||
| Glucose 2 |  | ||||
| Sucrose 2 |  | ||||
| Acetic acid 2 |  | ||||
| Other organic acids 4 |  | ||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Piccolella, S.; Scognamiglio, M.; D’Abrosca, B.; Esposito, A.; Fiorentino, A.; Pacifico, S. Chemical Fractionation Joint to In-Mixture NMR Analysis for Avoiding the Hepatotoxicity of Teucrium chamaedrys L. subsp. chamaedrys. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 690. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11050690
Piccolella S, Scognamiglio M, D’Abrosca B, Esposito A, Fiorentino A, Pacifico S. Chemical Fractionation Joint to In-Mixture NMR Analysis for Avoiding the Hepatotoxicity of Teucrium chamaedrys L. subsp. chamaedrys. Biomolecules. 2021; 11(5):690. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11050690
Chicago/Turabian StylePiccolella, Simona, Monica Scognamiglio, Brigida D’Abrosca, Assunta Esposito, Antonio Fiorentino, and Severina Pacifico. 2021. "Chemical Fractionation Joint to In-Mixture NMR Analysis for Avoiding the Hepatotoxicity of Teucrium chamaedrys L. subsp. chamaedrys" Biomolecules 11, no. 5: 690. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11050690
APA StylePiccolella, S., Scognamiglio, M., D’Abrosca, B., Esposito, A., Fiorentino, A., & Pacifico, S. (2021). Chemical Fractionation Joint to In-Mixture NMR Analysis for Avoiding the Hepatotoxicity of Teucrium chamaedrys L. subsp. chamaedrys. Biomolecules, 11(5), 690. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11050690










