Extremely Thermostabilizing Core Mutations in Coiled-Coil Mimetic Proteins of HIV-1 gp41 Produce Diverse Effects on Target Binding but Do Not Affect Their Inhibitory Activity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Proteins and Peptides
2.2. Circular Dichroism
2.3. Light Scattering
2.4. Differential Scanning Calorimetry
2.5. Isothermal Titration Calorimetry
2.6. HIV-1 Inhibition Assays
3. Results
3.1. Structure and Stability of the Mutant Proteins
3.2. Binding of CHR Peptides
3.3. Oligomerization State
3.4. HIV-1 Inhibition Activity
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- UNAIDS. HIV Data and Estimates. Available online: http://www.unaids.org/en/resources/documents/2020/unaids-data (accessed on 7 March 2021).
- Stephenson, K.E.; Wagh, K.; Korber, B.; Barouch, D.H. Vaccines and Broadly Neutralizing Antibodies for HIV-1 Prevention. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2020, 38, 673–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iyidogan, P.; Anderson, K.S. Current Perspectives on HIV-1 Antiretroviral Drug Resistance. Viruses 2014, 6, 4095–4139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, B.F.; Peixoto, G.M.L.; da Luz, S.R.; de Moraes, S.M.F.; Peres, S.B. Adverse effects of chronic treatment with the Main subclasses of highly active antiretroviral therapy: A systematic review. HIV Med. 2019, 20, 429–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, D.C.; Kim, P.S. HIV entry and its inhibition. Cell 1998, 93, 681–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, A.B.; Wilson, I.A. The HIV-1 envelope glycoprotein structure: Nailing down a moving target. Immunol. Rev. 2017, 275, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melikyan, G.B. Membrane Fusion Mediated by Human Immunodeficiency Virus Envelope Glycoprotein. In Membrane Fusion; Current Topics in Membranes; Chernomordik, L.V., Kozlov, M.M., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011; Volume 68, pp. 81–106. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, D.C.; Fass, D.; Berger, J.M.; Kim, P.S. Core structure of gp41 from the HIV envelope glycoprotein. Cell 1997, 89, 263–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weissenhorn, W.; Dessen, A.; Harrison, S.C.; Skehel, J.J.; Wiley, D.C. Atomic structure of the ectodomain from HIV-1 gp41. Nature 1997, 387, 426–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eckert, D.M.; Kim, P.S. Design of potent inhibitors of HIV-1 entry from the gp41 N-peptide region. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 11187–11192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, H.A.; Fochtman, B.C.; Rizzo, R.C.; Jacobs, A. Inhibition of HIV Entry by Targeting the Envelope Transmembrane Subunit gp41. Curr. HIV Res. 2016, 14, 283–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Cheng, J.; Lu, H.; Li, J.; Hu, J.; Qi, Z.; Liu, Z.; Jiang, S.; Dai, Q. Potent HIV fusion inhibitors against Enfuvirtide-resistant HIV-1 strains. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 16332–16337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welch, B.D.; VanDemark, A.P.; Heroux, A.; Hill, C.P.; Kay, M.S. Potent D-peptide inhibitors of HIV-1 entry. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 16828–16833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, W.J.; Rizzo, R.C. Computer-Aided Approaches for Targeting HIVgp41. Biology 2012, 1, 311–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Yu, F.; Cai, L.; Debnath, A.K.; Jiang, S. Development of Small-molecule HIV Entry Inhibitors Specifically Targeting gp120 or gp41. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2016, 16, 1074–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, J.; Wang, Q.; Xu, W.; Lu, L.; Jiang, S.B. Development of Protein- and Peptide-Based HIV Entry Inhibitors Targeting gp120 or gp41. Viruses 2019, 11, 705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilby, J.M.; Hopkins, S.; Venetta, T.M.; DiMassimo, B.; Cloud, G.A.; Lee, J.Y.; Alldredge, L.; Hunter, E.; Lambert, D.; Bolognesi, D.; et al. Potent suppression of HIV-1 replication in humans by T-20, a peptide inhibitor of gp41-mediated virus entry. Nat. Med. 1998, 4, 1302–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.W.; Ding, X.H.; Liu, Z.X.; Wu, X.Y.; Zhu, Y.M.; Wei, H.M.; Chong, H.H.; Cui, S.; He, Y.X. Molecular mechanism of HIV-1 resistance to sifuvirtide, a clinical trial-approved membrane fusion inhibitor. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 12703–12718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louis, J.M.; Bewley, C.A.; Clore, G.M. Design and properties of N(CCG)-gp41, a chimeric gp41 molecule with nanomolar HIV fusion inhibitory activity. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 29485–29489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Root, M.J.; Kay, M.S.; Kim, P.S. Protein design of an HIV-1 entry inhibitor. Science 2001, 291, 884–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Lu, L.; Qi, Z.; Lu, H.; Wang, J.; Yu, X.; Chen, Y.; Jiang, S. Novel Recombinant Engineered gp41 N-terminal Heptad Repeat Trimers and Their Potential as Anti-HIV-1 Therapeutics or Microbicides. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 25506–25515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crespillo, S.; Camara-Artigas, A.; Casares, S.; Morel, B.; Cobos, E.S.; Mateo, P.L.; Mouz, N.; Martin, C.E.; Roger, M.G.; El Habib, R.; et al. Single-chain protein mimetics of the N-terminal heptad-repeat region of gp41 with potential as anti-HIV-1 drugs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 18207–18212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurado, S.; Cano-Munoz, M.; Morel, B.; Standoli, S.; Santarossa, E.; Moog, C.; Schmidt, S.; Laumond, G.; Camara-Artigas, A.; Conejero-Lara, F. Structural and Thermodynamic Analysis of HIV-1 Fusion Inhibition Using Small gp41 Mimetic Proteins. J. Mol. Biol. 2019, 431, 3091–3106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jurado, S.; Cano-Munoz, M.; Polo-Megias, D.; Conejero-Lara, F.; Morel, B. Thermodynamic dissection of the interface between HIV-1 gp41 heptad repeats reveals cooperative interactions and allosteric effects. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2020, 688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, J.M.; Arndt, K.M. Coiled coil domains: Stability, specificity, and biological implications. Chembiochem 2004, 5, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Bosco, D.A.; Powers, E.T.; Kelly, J.W. Localized thermodynamic coupling between hydrogen bonding and microenvironment polarity substantially stabilizes proteins. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2009, 16, 684–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, H.; Bracken, C.; Lu, M. Buried polar interactions and conformational stability in the simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV) gp41 core. Biochemistry 2000, 39, 676–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woolfson, D.N. Coiled-Coil Design: Updated and Upgraded. In Fibrous Proteins: Structures and Mechanisms; Subcellular Biochemistry; Parry, D.A.D., Squire, J.M., Eds.; Springer International Publishing Ag: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; Volume 82, pp. 35–61. [Google Scholar]
- Gasteiger, E.; Gattiker, A.; Hoogland, C.; Ivanyi, I.; Appel, R.D.; Bairoch, A. ExPASy: The proteomics server for in-depth protein knowledge and analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003, 31, 3784–3788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lumry, R.; Eyring, H. Conformation changes of proteins. J. Phys. Chem. 1954, 58, 110–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarzotti-Kelsoe, M.; Bailer, R.T.; Turk, E.; Lin, C.L.; Bilska, M.; Greene, K.M.; Gao, H.; Todd, C.A.; Ozaki, D.A.; Seaman, M.S.; et al. Optimization and validation of the TZM-bl assay for standardized assessments of neutralizing antibodies against HIV-1. J. Immunol. Methods 2014, 409, 131–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez, L.; Woolfson, D.N.; Alber, T. Buried polar residues and structural specificity in the GCN4 leucine zipper. Nat. Struct. Biol. 1996, 3, 1011–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akey, D.L.; Malashkevich, V.N.; Kim, P.S. Buried polar residues in coiled-coil interfaces. Biochemistry 2001, 40, 6352–6360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatko, C.D.; Nanda, V.; Lear, J.D.; DeGrado, W.F. Polar networks control oligomeric assembly in membranes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 4170–4171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyken, S.E.; Chen, Z.B.; Groves, B.; Langan, R.A.; Oberdorfer, G.; Ford, A.; Gilmore, J.M.; Xu, C.F.; DiMaio, F.; Pereira, J.H.; et al. De novo design of protein homo-oligomers with modular hydrogen-bond network-mediated specificity. Science 2016, 352, 680–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jurado, S.; Moog, C.; Cano-Munoz, M.; Schmidt, S.; Laumond, G.; Ruocco, V.; Standoli, S.; Polo-Megias, D.; Conejero-Lara, F.; Morel, B. Probing Vulnerability of the gp41 C-Terminal Heptad Repeat as Target for Miniprotein HIV Inhibitors. J. Mol. Biol. 2020, 432, 5577–5592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steger, H.K.; Root, M.J. Kinetic dependence to HIV-1 entry inhibition. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 25813–25821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahle, K.M.; Steger, H.K.; Root, M.J. Asymmetric Deactivation of HIV-1 gp41 following Fusion Inhibitor Binding. PLoS Pathog. 2009, 5, e1000674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poveda, E.; Briz, V.; Soriano, V. Enfuvirtide, the first fusion inhibitor to treat HIV infection. Aids Rev. 2005, 7, 139–147. [Google Scholar]
- Martin-Carbonero, L. Discontinuation of the clinical development of fusion inhibitor T-1249. Aids Rev. 2004, 6, 61. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
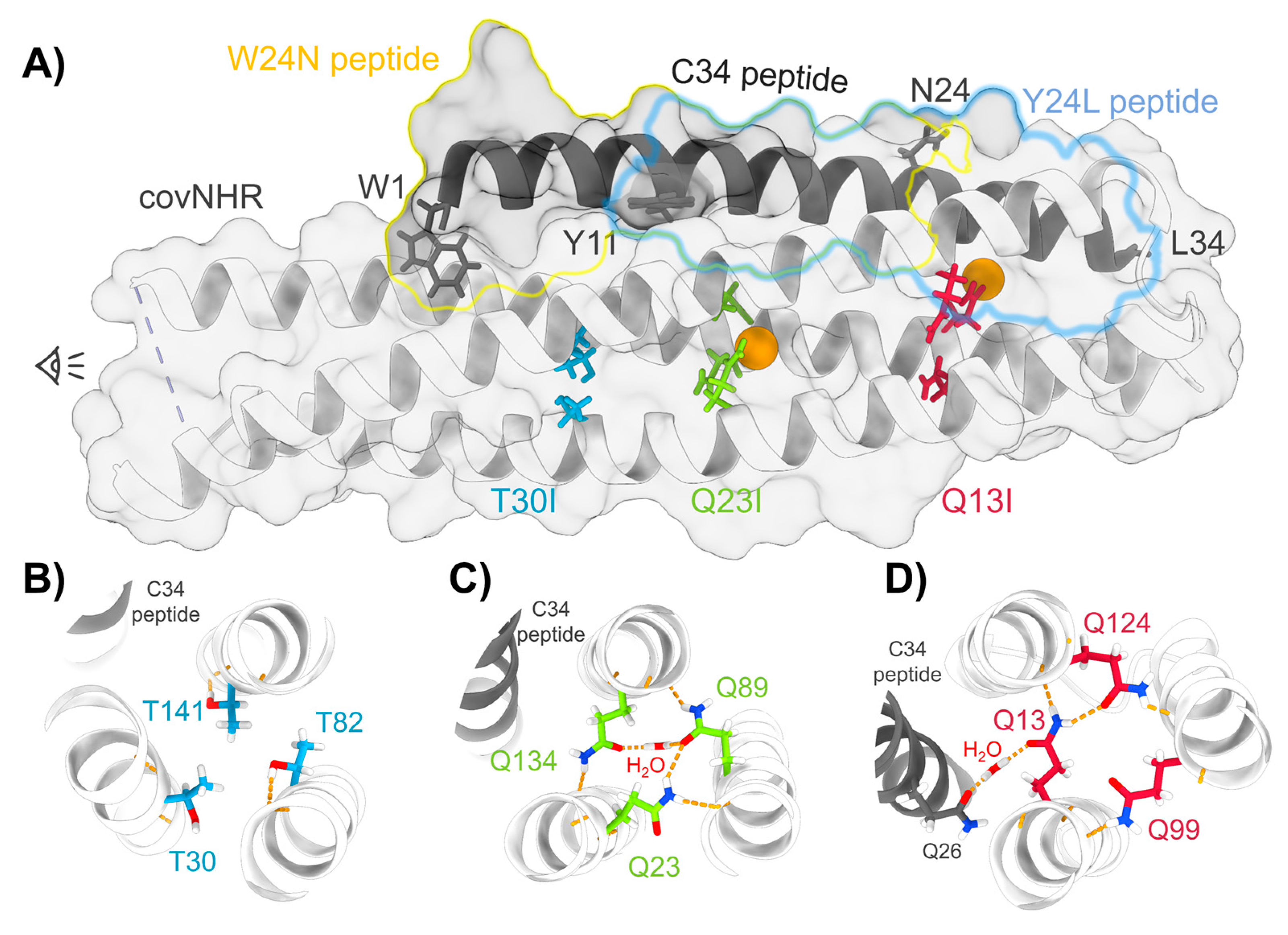
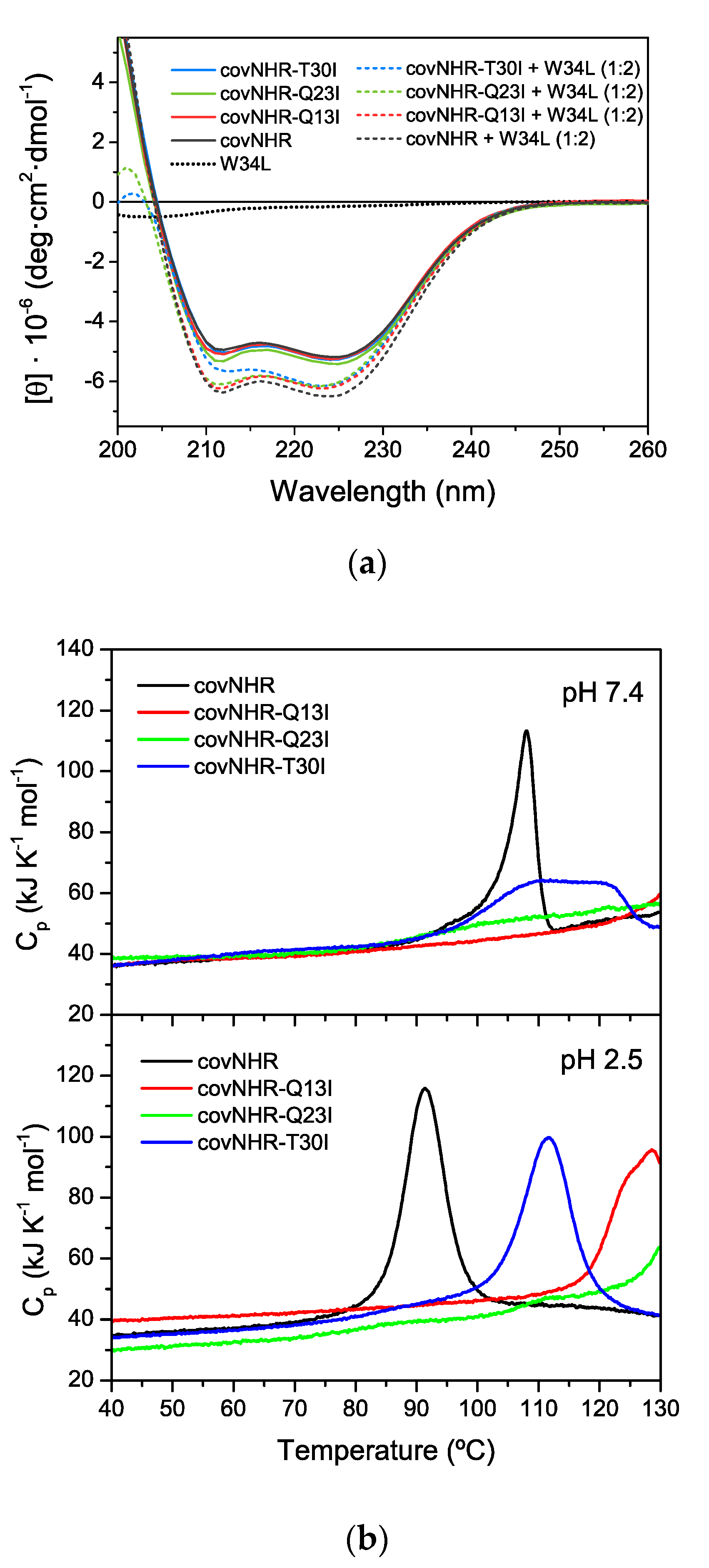
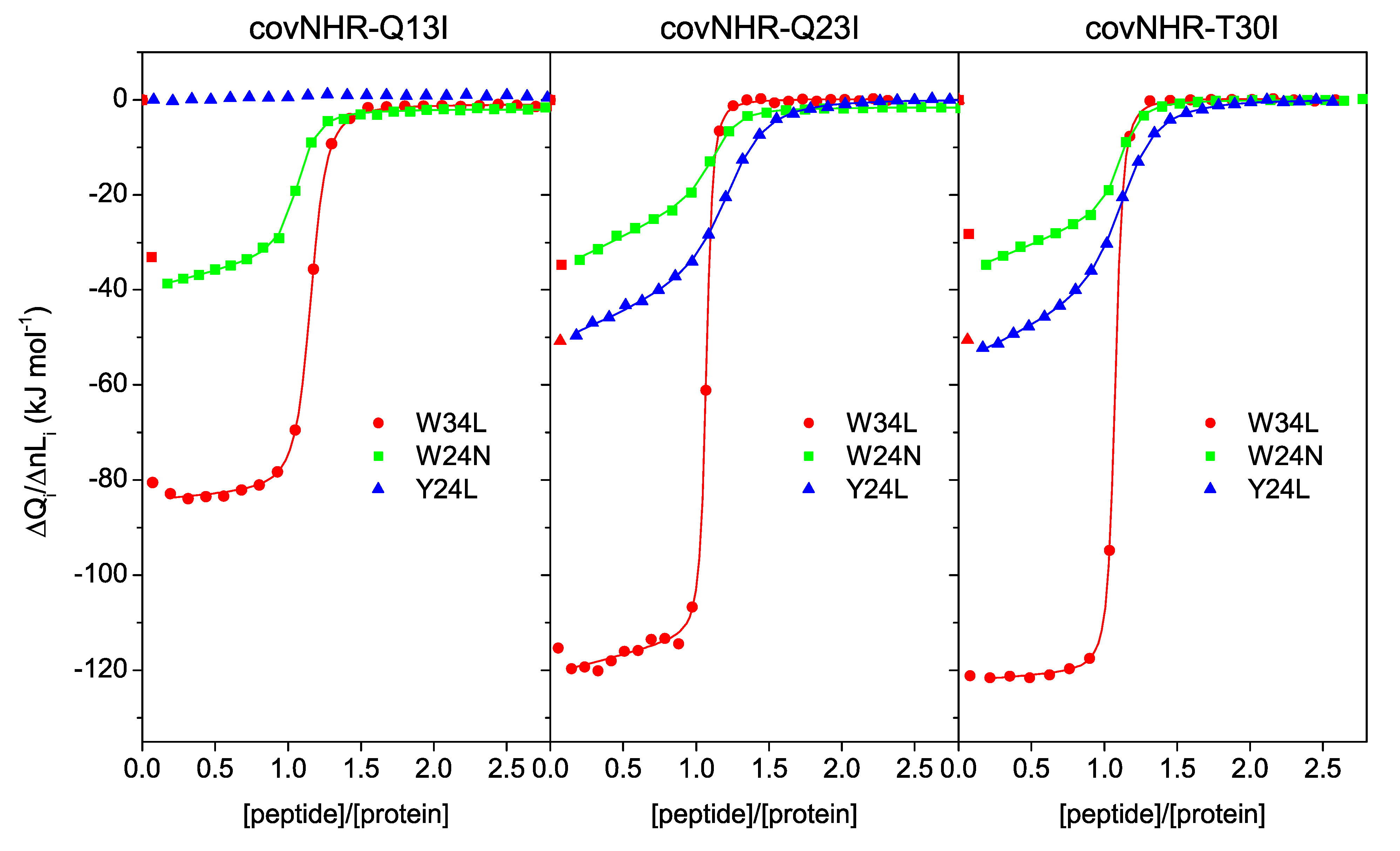
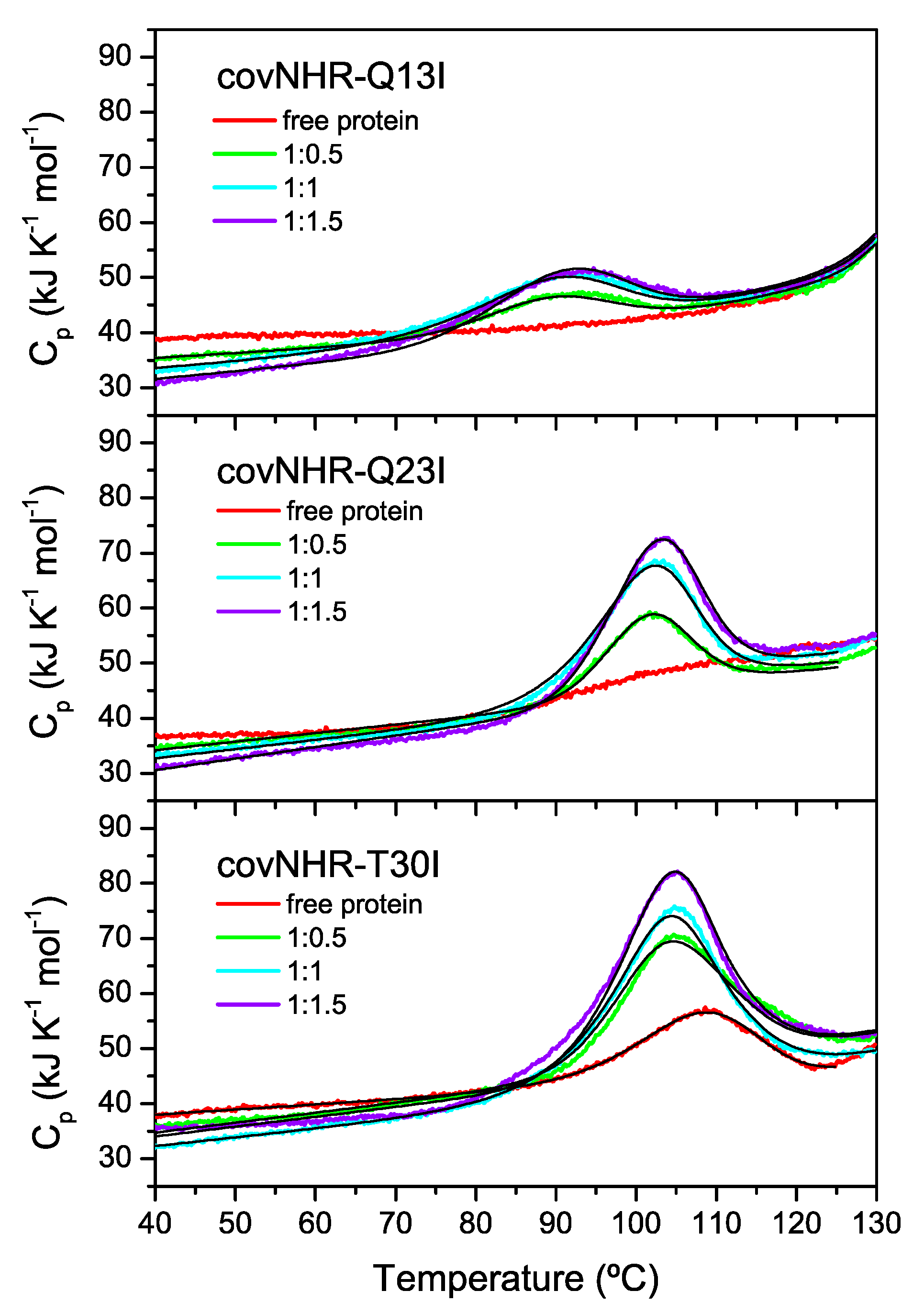

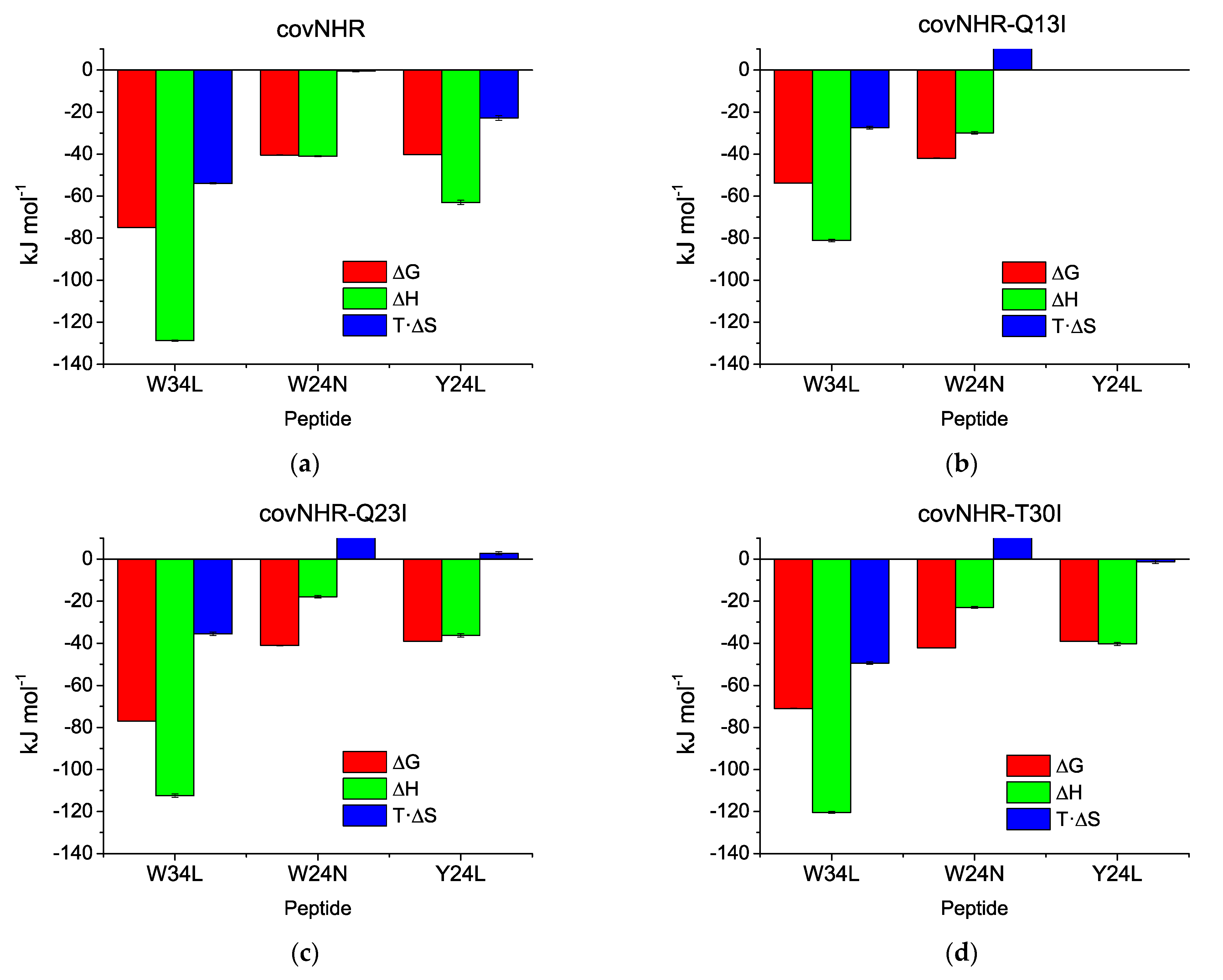
| Protein Variant | Peptide | Technique | Kb (M−1) | Kd (nM) | ΔHb (kJ·mol−1) | n |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| covNHR (1) | W34L | ITC | Not measurable | −128.8 ± 0.3 | 1.01 | |
| DSC | (1.32 ± 0.03) × 1013 | 0.000076 ± 0.000002 | ||||
| W24N | ITC | (1.25 ± 0.11) × 107 | 80 ± 7 | −41 ± 0.3 | 0.83 | |
| Y24L | ITC | (1.11 ± 0.09) × 107 | 90 ± 7 | −63 ± 1.0 | 0.83 | |
| covNHR-Q13I | W34L | ITC | (4.4 ± 0.3) × 107 | 22.7 ± 1.3 | −81.1 ± 0.6 | 1.16 |
| DSC | (2.62 ± 0.05) × 109 | 0.382 ± 0.007 | ||||
| W24N | ITC | (2.3 ± 0.3) × 107 | 44 ± 5 | −29.9 ± 0.6 | 1.07 | |
| Y24L | ITC | Undetectable binding | ||||
| covNHR-Q23I | W34L | ITC | (2.0 ± 0.3) × 108 | 5.1 ± 0.7 | −112.4 ± 0.8 | 1.07 |
| DSC | (2.96 ± 0.06) × 1013 | 0.000034 ± 0.000001 | ||||
| W24N | ITC | (1.61 ± 0.23) × 107 | 62 ± 9 | −17.9 ± 0.6 | 1.14 | |
| Y24L | ITC | (7.0 ± 0.5) × 106 | 142 ± 9 | −36.3 ± 0.8 | 1.24 | |
| covNHR-T30I | W34L | ITC | (1.58 ± 0.08) × 108 | 6.3 ± 0.3 | −120.4 ± 0.5 | 1.08 |
| DSC | (2.6 ± 0.3) × 1012 | 0.00038 ± 0.00004 | ||||
| W24N | ITC | (2.48 ± 0.24) × 107 | 40 ± 4 | −23.0 ± 0.4 | 1.12 | |
| Y24L | ITC | (7.2 ± 0.4) × 106 | 139 ± 8 | −40.4 ± 0.7 | 1.14 | |
| Protein Variant | SF162 | CE1176 |
|---|---|---|
| covNHR | 8.0 ± 1.3 | 10.8 ± 0.9 |
| covNHR-Q13I | 8.9 ± 1.3 | 10.7 ± 0.8 |
| covNHR-Q23I | 7.1 ± 0.9 | 5.3 ± 1.1 |
| covNHR-T30I | 8.6 ± 0.5 | 7.4 ± 0.05 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cano-Muñoz, M.; Cesaro, S.; Morel, B.; Lucas, J.; Moog, C.; Conejero-Lara, F. Extremely Thermostabilizing Core Mutations in Coiled-Coil Mimetic Proteins of HIV-1 gp41 Produce Diverse Effects on Target Binding but Do Not Affect Their Inhibitory Activity. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 566. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11040566
Cano-Muñoz M, Cesaro S, Morel B, Lucas J, Moog C, Conejero-Lara F. Extremely Thermostabilizing Core Mutations in Coiled-Coil Mimetic Proteins of HIV-1 gp41 Produce Diverse Effects on Target Binding but Do Not Affect Their Inhibitory Activity. Biomolecules. 2021; 11(4):566. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11040566
Chicago/Turabian StyleCano-Muñoz, Mario, Samuele Cesaro, Bertrand Morel, Julie Lucas, Christiane Moog, and Francisco Conejero-Lara. 2021. "Extremely Thermostabilizing Core Mutations in Coiled-Coil Mimetic Proteins of HIV-1 gp41 Produce Diverse Effects on Target Binding but Do Not Affect Their Inhibitory Activity" Biomolecules 11, no. 4: 566. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11040566
APA StyleCano-Muñoz, M., Cesaro, S., Morel, B., Lucas, J., Moog, C., & Conejero-Lara, F. (2021). Extremely Thermostabilizing Core Mutations in Coiled-Coil Mimetic Proteins of HIV-1 gp41 Produce Diverse Effects on Target Binding but Do Not Affect Their Inhibitory Activity. Biomolecules, 11(4), 566. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11040566







