RFLMDA: A Novel Reinforcement Learning-Based Computational Model for Human MicroRNA-Disease Association Prediction
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Human miRNA-Disease Associations
2.2. MiRNA Functional Similarity
2.3. Disease Semantic Similarity
2.4. Method Models
2.4.1. Collaborative Matrix Factorization
2.4.2. Neighborhood Regularized Logistic Matrix Factorization
2.4.3. Laplacian Regularized Least Squares
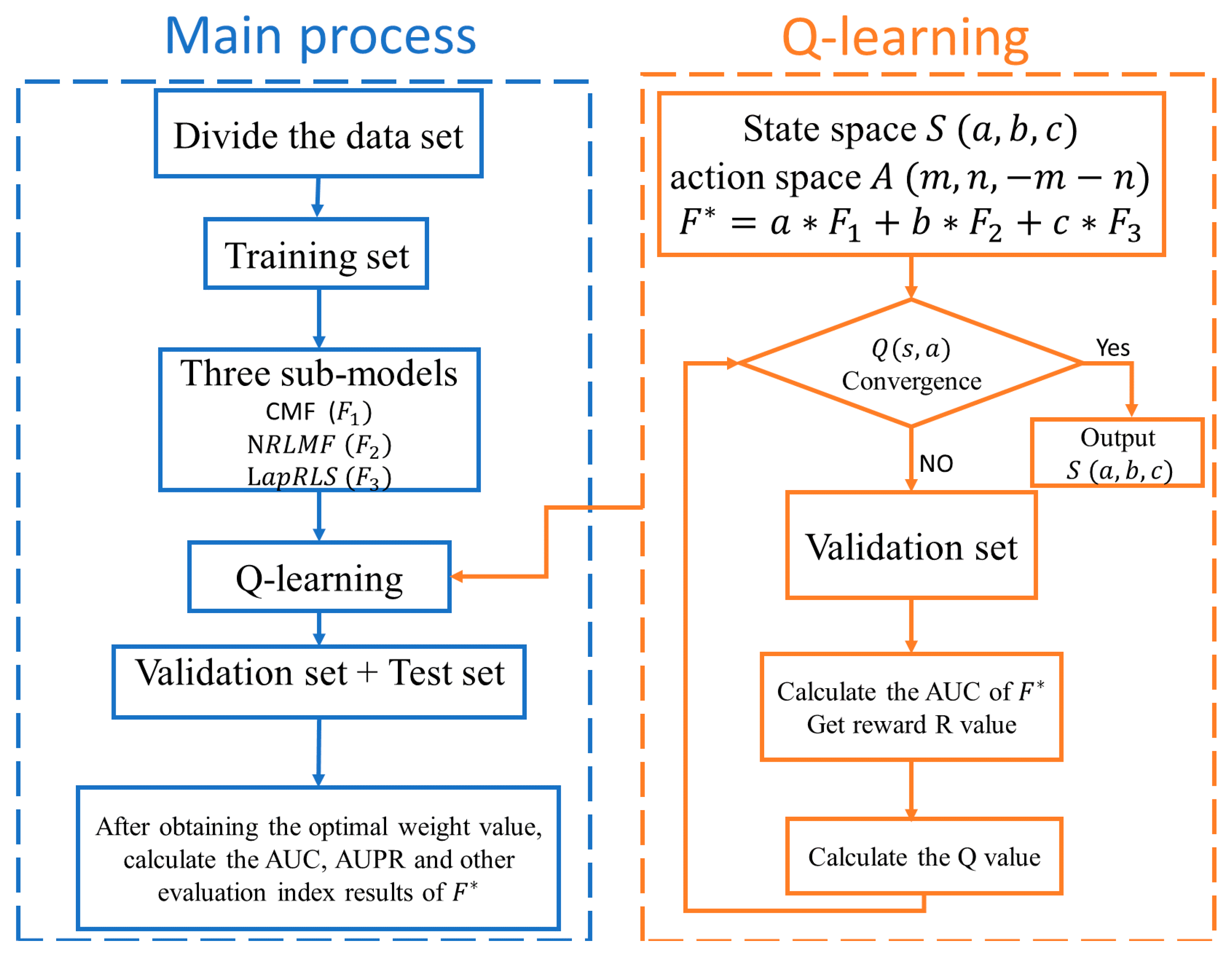
2.4.4. Reinforcement Learning
2.4.5. RFLMDA
| Algorithm1: Pseudocode for RFLMDA algorithm. |
| Require: Action space A, state space S, reward value R, sub-models CMF, NRLMF and LapRLS. Ensure: The predicted results of 1: Processing the dataset and training sub-models, namely CMF, NRLMF and LapRLS, respectively; 2: Calculation of the weights for models via Pseudocode for Q-learning algorithm, respectively; 3: Combining . |
| Algorithm2: Pseudocode for Q-learning algorithm. |
 |
3. Results
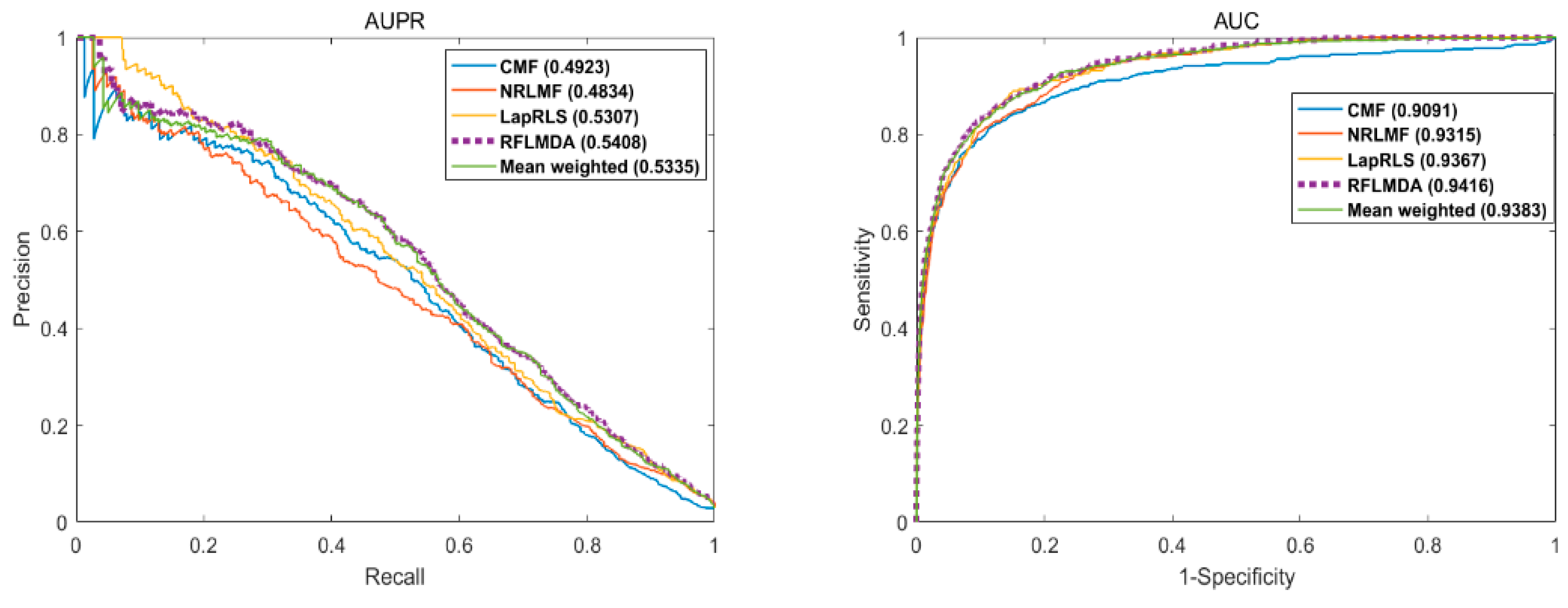
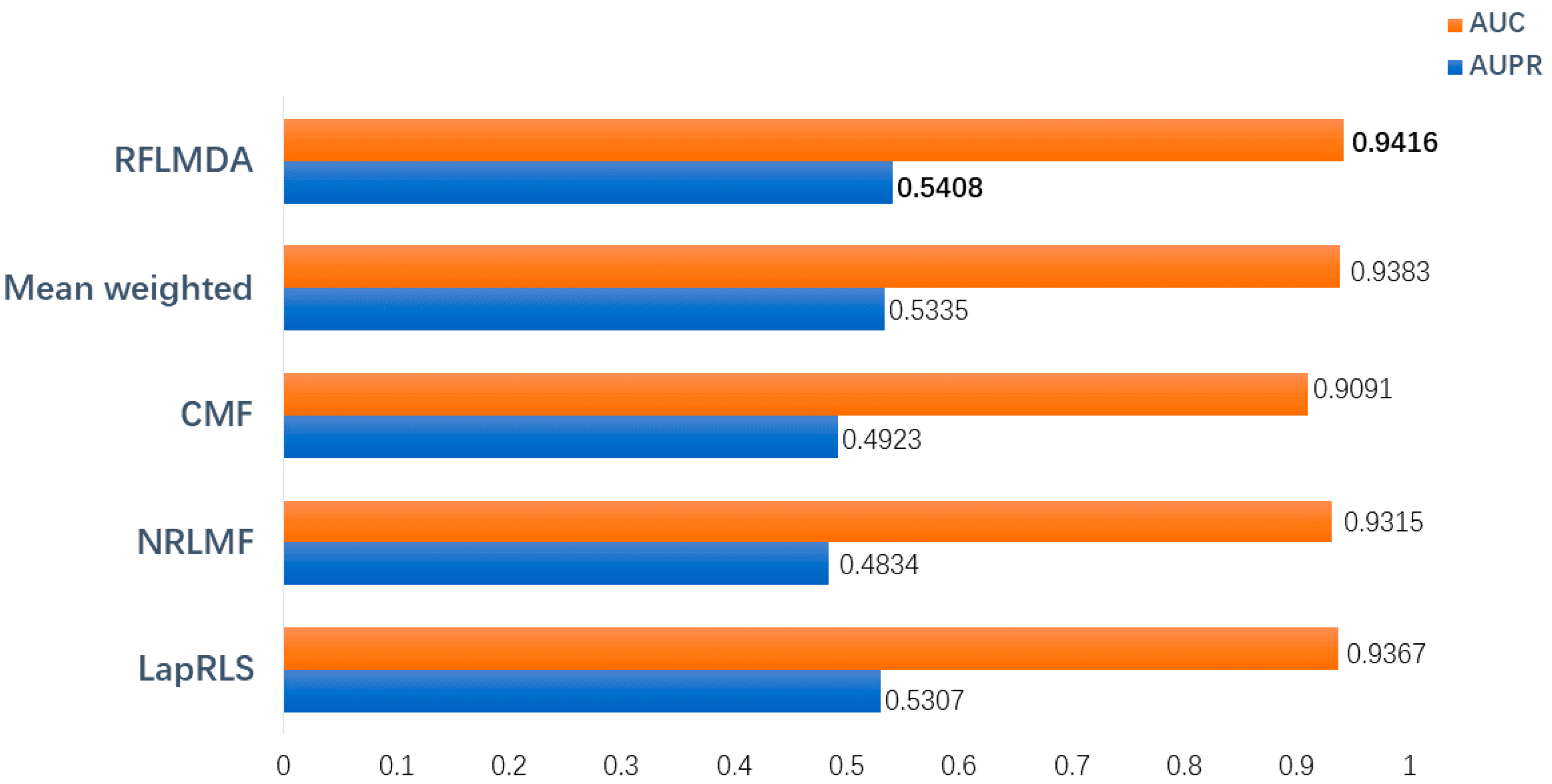
3.1. Evaluation Measurements
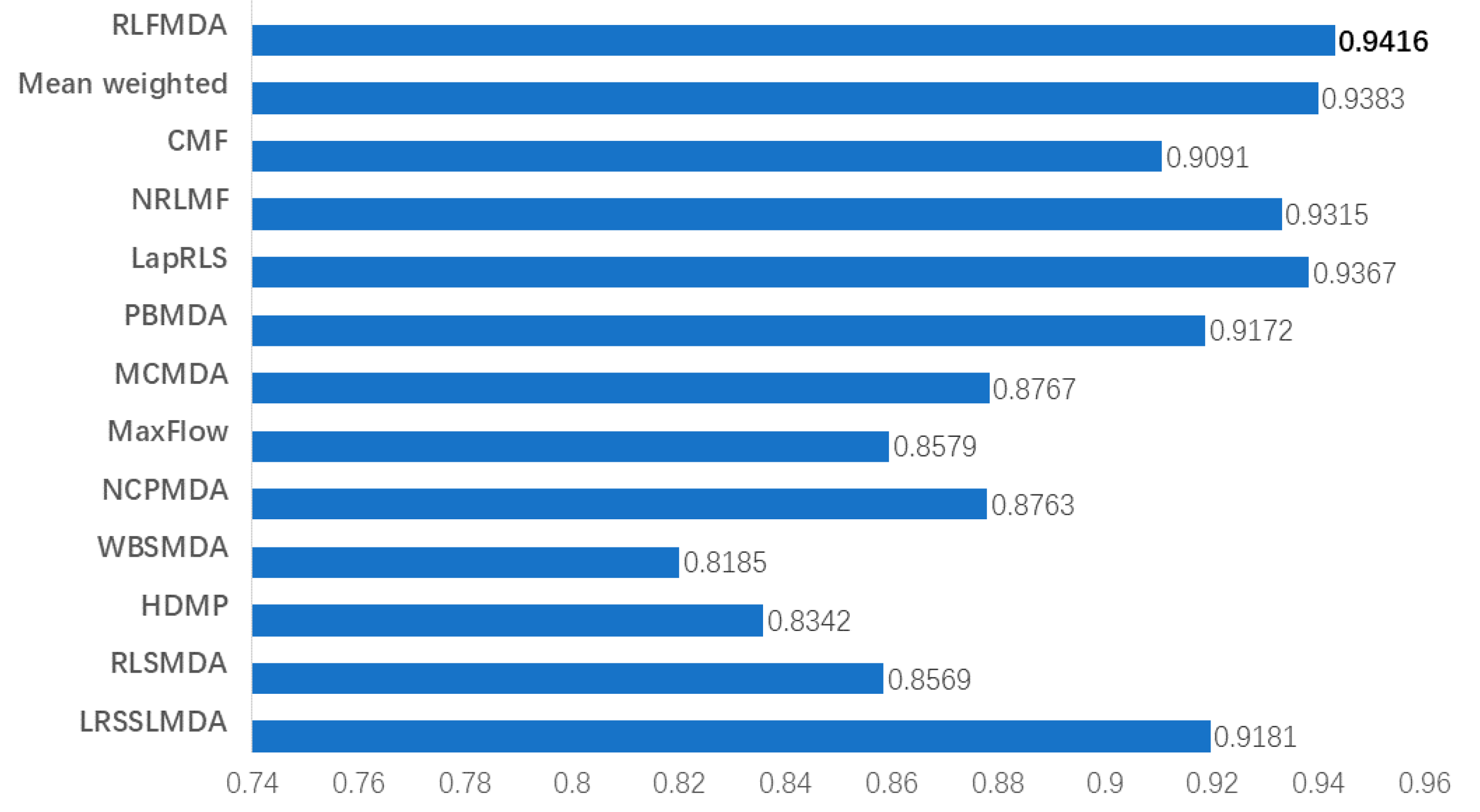
3.2. Comparison with Other Methods
4. Case Study
4.1. Colorectal Neoplasms
4.2. Breast Neoplasms
4.3. Lymphoma
5. Conclusions and Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shi, H.; Zhang, G.; Zhou, M.; Cheng, L.; Yang, H.; Wang, J.; Sun, J.; Wang, Z. Integration of Multiple Genomic and Phenotype Data to Infer Novel miRNA-Disease Associa-tions. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0148521. [Google Scholar]
- Sredni, S.T.; Huang, C.-C.; Bonaldo, M.D.F.; Tomita, T. MicroRNA expression profiling for Molecular Classification of pediatric brain tumors. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2011, 57, 183–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Claudia, B.; Fiedler, J.A.N.; Thum, T. Cardiovascular importance of the microRNA-23/27/24 family. Microcirculation 2012, 19, 208–214. [Google Scholar]
- Lumayag, S.; Haldin, C.E.; Corbett, N.J.; Wahlin, K.J.; Cowan, C.; Turturro, S.; Larsen, P.E.; Kovacs, B.; Witmer, P.D.; Valle, D.; et al. Inactivation of the microRNA-183/96/182 cluster results in syndromic retinal degeneration. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, E507–E516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- van Schooneveld, E.; Wildiers, H.; Vergote, I.; Vermeulen, P.B.; Dirix, L.Y.; Van Laere, S.J. Dysregulation of microRNAs in breast cancer and their potential role as prognostic and predictive biomarkers in patient management. Breast Cancer Res. 2015, 17, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, W.; Zhao, S.P.; Zhao, Y.H. MicroRNA-143/-145 in cardiovascular diseases. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 531740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.; Zhang, X.; Zou, Q. Integrative approaches for predicting microRNA function and prioritizing disease-related mi-croRNA using biological interaction networks. Brief Bioinform. 2016, 17, 192–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mørk, S.; Pletscher-Frankild, S.; Palleja Caro, A.; Gorodkin, J.; Jensen, L.J. Protein-driven inference of miRNA-disease associations. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 392–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, H.; Wang, H.; Ding, Y.; Tang, J. Multivariate information fusion for identifying antifungal peptides with Hilbert-Schmidt Independence Criterion. Curr. Bioinform. 2021, 16, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Wu, H.; Guo, X.; Peng, L.; Ding, Y.; Tang, J.; Guo, F. MK-FSVM-SVDD: A Multiple Kernel-based Fuzzy SVM Model for Predicting DNA-binding Proteins via Support Vector Data Description. Curr. Bioinform. 2021, 16, 274–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.; Meng, H.; Lu, W.; Liao, Z.; Ding, Y.; Wu, H. Identification of DNA-binding proteins via Hypergraph based Laplacian Support Vector Machine. Curr. Bioinform. 2021, 16, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Tang, J.; Guo, F. Identification of drug-target interactions via multi-view graph regularized link propagation model. Neurocomputing 2021, 461, 618–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; Hao, Y.; Wang, G.; Juan, L.; Zhang, T.; Teng, M.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y. Prioritization of disease microRNAs through a human phenome-microRNAome network. BMC Syst. Biol. 2010, 4 (Suppl. 1), S2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xing, C.; Liu, M.X.; Yan, G.Y. RWRMDA: Predicting novel human microRNA—Disease associations. Mol. Biosyst. 2012, 8, 2792–2798. [Google Scholar]
- Xuan, P.; Han, K.; Guo, M.; Guo, Y.; Li, J.; Ding, J.; Liu, Y.; Dai, Q.; Li, J.; Teng, Z.; et al. Prediction of microRNAs Associated with Human Diseases Based on Weighted k Most Similar Neighbors. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e70204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Xu, J.; Zhang, G.; Xu, L.; Li, C.; Wang, L.; Zhao, Z.; Jiang, W.; Guo, Z.; Li, X. Walking the interactome to identify human miRNA-disease associations through the functional link between miRNA targets and disease genes. BMC Syst. Biol. 2013, 7, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, X.; Yan, G.Y. Semi-supervised learning for potential human microRNA-disease associations inference. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 5501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Zeng, X.; He, Z.; Zou, Q. Inferring MicroRNA-Disease Associations by Random Walk on a Heterogeneous Network with Multiple Data Sources. IEEE/ACM Trans. Comput. Biol. Bioinform. 2016, 14, 905–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Yan, C.; Zhang, X.; You, Z.; Deng, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Dai, Q. WBSMDA: Within and Between Score for MiRNA-Disease Association prediction. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 21106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Yan, C.C.; Zhang, X.; You, Z.H.; Huang, Y.A.; Yan, G.Y. HGIMDA: Heterogeneous graph inference for miRNA-disease association prediction. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 65257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Luo, J.; Xiao, Q. A novel approach for predicting microRNA-disease associations by unbalanced bi-random walk on heteroge-neous network. J. Biomed. Inform. 2017, 66, 194–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, L.; Xiao, Y.; Ding, Y.; Tang, J.; Guo, F. FKL-Spa-LapRLS: An accurate method for identifying human microRNA-disease association. BMC Genom. 2018, 19, 11–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Jiang, L.; Tang, J.; Guo, F. Identification of human microRNA-disease association via hypergraph embedded bipartite local model. Comput. Biol. Chem. 2020, 89, 107369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Ding, H.; Mamitsuka, H.; Zhu, S. Collaborative matrix factorization with multiple similarities for predicting drug-target interactions. In Proceedings of the 19th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, Chicago, IL, USA, 11–14 August 2013; pp. 1025–1033. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Wu, M.; Miao, C.; Zhao, P.; Li, X.L. Neighborhood Regularized Logistic Matrix Factorization for Drug-Target Interaction Prediction. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2016, 12, e1004760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Z.; Wu, L.Y.; Zhou, X.; Wong, S.T. Semi-supervised drug-protein interaction prediction from heterogeneous biological spaces. BMC Syst. Biol. 2010, 4, S6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Qiu, C.; Tu, J.; Geng, B.; Yang, J.; Jiang, T.; Cui, Q. HMDD v2.0: A database for experimentally supported human microRNA and disease associations. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, D1070–D1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Wang, J.; Lu, M.; Song, F.; Cui, Q. Inferring the human microRNA functional similarity and functional network based on mi-croRNA-associated diseases. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 1644–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lowe, H.J.; Barnett, G.O. Understanding and using the medical subject headings (MeSH) vocabulary to perform literature searches. JAMA 1994, 271, 1103–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, Z.H.; Huang, Z.A.; Zhu, Z.; Yan, G.Y.; Li, Z.W.; Wen, Z.; Chen, X. PBMDA: A novel and effective path-based computational model for miRNA-disease asso-ciation prediction. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2017, 13, e1005455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, J.Q.; Rong, Z.H.; Chen, X.; Yan, G.Y.; You, Z.H. MCMDA: Matrix completion for MiRNA-disease association prediction. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 21187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gu, C.; Liao, B.; Li, X.; Li, K. Network Consistency Projection for Human miRNA-Disease Associations Inference. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 36054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Huang, L.; Wang, E. LRSSLMDA: Laplacian Regularized Sparse Subspace Learning for MiRNA-Disease Association prediction. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2017, 13, e1005912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Wu, L.; Wang, A.; Tang, W.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, H.; Teschendorff, A.E. dbDEMC 2.0: Updated database of differentially expressed miRNAs in human cancers. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, D812–D818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Hao, Y.; Juan, L.; Teng, M.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Y. miR2Disease: A manually curated database for microRNA deregulation in human disease. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, D98–D104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
| Type of Data | Quantity |
|---|---|
| MiRNAs | 495 |
| Diseases | 383 |
| MiRNA-Disease association | 5430 |
| Disease Name | Top-50 Prediction List |
|---|---|
| Colon Neoplasms | 47 |
| Kidney Neoplasms | 46 |
| Pancreatic Neoplasms | 49 |
| Esophageal Neoplasms | 46 |
| Breast Neoplasms | 50 |
| Gastric Neoplasms | 41 |
| Lymphoma | 48 |
| Colorectal Neoplasms | 50 |
| Disease | Rank | Name | Evidence | Rank | Name | Evidence |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Colorectal Neoplasms | 1 | mir-21 | D | 11 | mir-7 | D |
| 2 | mir-145 | D | 12 | mir-218 | D | |
| 3 | mir-210 | D | 13 | mir-148a | D | |
| 4 | mir-182 | D | 14 | mir-27a | H | |
| 5 | mir-196a | D | 15 | mir-133a | D | |
| 6 | mir-126 | D | 16 | mir-143 | D | |
| 7 | mir-30a | D | 17 | mir-31 | D | |
| 8 | mir-34a | D | 18 | mir-200c | D | |
| 9 | mir-183 | D | 19 | mir-34b | D | |
| 10 | mir-146b | H | 20 | mir-7 | D |
| Disease | Rank | Name | Evidence | Rank | Name | Evidence |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Breast Neoplasms | 1 | let-7f | D | 11 | mir-10b | D |
| 2 | mir-30c | D | 12 | mir-19a | D | |
| 3 | mir-22 | D | 13 | mir-302b | D | |
| 4 | mir-17 | D | 14 | mir-200c | D | |
| 5 | mir-34c | H | 15 | let-7g | D | |
| 6 | mir-18a | D | 16 | mir-29a | D | |
| 7 | let-7a | D | 17 | mir-191 | D | |
| 8 | mir-20a | D | 18 | mir-125a | D | |
| 9 | mir-218 | D | 19 | mir-151a | H | |
| 10 | mir-34b | H | 20 | mir-200b | D |
| Disease | Rank | Name | Evidence | Rank | Name | Evidence |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lymphoma | 1 | mir-17 | D | 11 | mir-146a | D |
| 2 | mir-20a | D | 12 | mir-34a | D | |
| 3 | mir-19b | D | 13 | mir-125b | D | |
| 4 | mir-92a | D | 14 | mir-126 | D | |
| 5 | mir-18a | D | 15 | mir-145 | D | |
| 6 | mir-21 | D | 16 | mir-181a | D | |
| 7 | mir-19a | D | 17 | mir-24 | D | |
| 8 | mir-155 | D | 18 | mir-29b | D | |
| 9 | mir-16 | D | 19 | mir-101 | D | |
| 10 | mir-15a | D | 20 | mir-150 | D |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cui, L.; Lu, Y.; Sun, J.; Fu, Q.; Xu, X.; Wu, H.; Chen, J. RFLMDA: A Novel Reinforcement Learning-Based Computational Model for Human MicroRNA-Disease Association Prediction. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1835. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11121835
Cui L, Lu Y, Sun J, Fu Q, Xu X, Wu H, Chen J. RFLMDA: A Novel Reinforcement Learning-Based Computational Model for Human MicroRNA-Disease Association Prediction. Biomolecules. 2021; 11(12):1835. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11121835
Chicago/Turabian StyleCui, Linqian, You Lu, Jiacheng Sun, Qiming Fu, Xiao Xu, Hongjie Wu, and Jianping Chen. 2021. "RFLMDA: A Novel Reinforcement Learning-Based Computational Model for Human MicroRNA-Disease Association Prediction" Biomolecules 11, no. 12: 1835. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11121835
APA StyleCui, L., Lu, Y., Sun, J., Fu, Q., Xu, X., Wu, H., & Chen, J. (2021). RFLMDA: A Novel Reinforcement Learning-Based Computational Model for Human MicroRNA-Disease Association Prediction. Biomolecules, 11(12), 1835. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11121835





